Food GMP ssB 08-28-2008 (2)
Food GMP ssB 08-28-2008 (2).doc
Survey of Current Manufacturing Practices in the Food Industry
OMB: 0910-0628
Request for OMB Review
Supporting Statement B
SURVEY OF CURRENT MANUFACTURING PRACTICES IN THE FOOD INDUSTRY
Submitted by
Economics Staff
Office of Regulations and Policy
Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition
Food and Drug Administration
Department of Health and Human Services
August 28, 2008
B COLLECTIONS OF INFORMATION EMPLOYING STATISTICAL METHODS
B.1 Potential Respondent Universe and Sampling Frame
Universe:
The universe for this survey is all FDA-registered domestic facilities, which are those facilities registered in the 50 U.S. states, the District of Columbia, the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico and all other U.S. possessions that are engaged in manufacturing/processing of food for human consumption.1 The primary goal of this survey is to generate general purpose descriptive statistics on registered food manufacturers/processors in five (5) key areas relevant for the food CGMPs modernization effort: employee training, sanitation and personal hygiene, allergen controls, process controls, and recordkeeping. FDA plans to use the data collected in the cost-benefit and cost-effectiveness studies of its future policies related to the food CGMPs modernization effort. Additionally, FDA might also utilize the data collected to better target its outreach and promotion materials, such as “best-practices” manuals, and food safety training courses.
The FDA Food Facility Registration database collects information about the number of manufacturers that are engaged in the manufacturing or processing of food for human consumption in the U.S. (FDA, 2008). It does not, however, contain information on the 6-digit North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) code or the employment size for the registrants in the survey universe. As described below, FDA proposes obtaining this information by matching the name and location of the facilities in the universe with facility information collected and published by Dun and Bradstreet (D&B). D&B records list both the primary and secondary NAICS industry classifications as well as the employment size of each facility. The D&B data comprehensively cover virtually all active facilities in the United States. The list of 6-digit NAICS industries in-scope for this survey is shown in Table B-1.
1.2 Industry Groups
FDA has divided the universe of food manufacturers into three size classes because the nature and effectiveness of manufacturing practices may likely vary by facility size. The size classes are defined in terms of the total number of employees at each facility. The boundaries for these strata are as follows:
Size Class 1 – Less than 20 employees,
Size Class 2 – 20 to 99 employees, and
Size Class 3 – 100 or more employees.
FDA will generate estimates of the prevalence of certain types of manufacturing practices, such as employee training, allergen control procedures, etc. and other statistics for each size class that meet the precision targets as described below. Within each size class, FDA will conduct stratified random sampling using proportional sampling among ten aggregated industry groups.
Table B-1: NAICS Classifications for Facilities Manufacturing/Processing Food for Human Consumption in the U.S.
NAICS |
NAICS Title |
311211 |
Flour Milling |
311212 |
Rice Milling |
311213 |
Malt Manufacturing |
311221 |
Wet Corn Milling |
311222 |
Soybean Processing |
311223 |
Other Oilseed Processing |
311225 |
Fats and Oils Refining and Blending |
311230 |
Breakfast Cereal Manufacturing |
311311 |
Sugarcane Mills |
311312 |
Cane Sugar Refining |
311313 |
Beet Sugar Manufacturing |
311320 |
Chocolate and Confectionery Manufacturing from Cacao Beans |
311330 |
Confectionery Manufacturing from Purchased Chocolate |
311340 |
Nonchocolate Confectionery Manufacturing |
311411 |
Frozen Fruit, Juice, and Vegetable Manufacturing |
311412 |
Frozen Specialty Food Manufacturing |
311421 |
Fruit and Vegetable Canning |
311422 |
Specialty Canning |
311423 |
Dried and Dehydrated Food Manufacturing |
311511 |
Fluid Milk Manufacturing |
311512 |
Creamery Butter Manufacturing |
311513 |
Cheese Manufacturing |
311514 |
Dry, Condensed, and Evaporated Dairy Product Manufacturing |
311520 |
Ice Cream and Frozen Dessert Manufacturing |
311711 |
Seafood Canning |
311712 |
Fresh and Frozen Seafood Processing |
311811 |
Retail Bakeries |
311812 |
Commercial Bakeries |
311813 |
Frozen Cakes, Pies, and Other Pastries Manufacturing |
311821 |
Cookie and Cracker Manufacturing |
311822 |
Flour Mixes and Dough Manufacturing from Purchased Flour |
311823 |
Dry Pasta Manufacturing |
311830 |
Tortilla Manufacturing |
311911 |
Roasted Nuts and Peanut Butter Manufacturing |
311919 |
Other Snack Food Manufacturing |
311920 |
Coffee and Tea Manufacturing |
311930 |
Flavoring Syrup and Concentrate Manufacturing |
311941 |
Mayonnaise, Dressing, and Other Prepared Sauce Manufacturing |
311942 |
Spice and Extract Manufacturing |
311991 |
Perishable Prepared Food Manufacturing |
311999 |
All Other Miscellaneous Food Manufacturing |
312111 |
Soft Drink Manufacturing |
312112 |
Bottled Water Manufacturing |
312113 |
Ice Manufacturing |
The number of facilities within each industry group and size class are currently unknown, but will be determined after the facility-specific information from the FDA Facility Registration database is enhanced with facility size and industry classification information obtained from the D&B data. Table B-2 combines related categories of food manufacturers and shows abstractly the resultant distribution of the universe by size class and industry group stratum. The table entries, Pij, represent the number of facilities in size class i (e.g., with fewer than 20 employees) and industry group j (e.g., Frozen Food Manufacturing). The industry groups noted in Table B-2 are believed to have distinct processing characteristics. Thus, stratified random sampling with proportional allocation will increase the accuracy of our survey estimates.2
Table B-2: Number of Facilities Manufacturing/Processing Food for Human Consumption in the U.S. as Reported by the U.S. Census Bureau by Sampling Stratum
|
|
Facility Size (in Number of Employees) |
|
||
Sampling Stratum [a] |
NAICS Codes |
< 20 |
20 – 99 |
100 or More |
Total |
Grain & Oilseed Milling & Sugar Manufacturing |
3112 |
P11 |
P21 |
P31 |
|
31131 |
|||||
Chocolate & Nonchocolate Confectionery Manufacturing |
31132 |
P12 |
P22 |
P32 |
|
31133 |
|||||
31134 |
|||||
Frozen Food Manufacturing |
31141 |
P13 |
P23 |
P33 |
|
Fruit & Vegetable Canning |
31142 |
P14 |
P24 |
P34 |
|
Dairy Product Manufacturing |
3115 |
P15 |
P25 |
P35 |
|
Seafood Product Preparation |
3117 |
P16 |
P26 |
P36 |
|
Bakeries and Tortilla Manufacturing |
3118 |
P17 |
P27 |
P37 |
|
Other Food Manufacturing |
3119 |
P18 |
P28 |
P36 |
|
Perishable Prepared Food Manufacturing |
311991 |
P19 |
P29 |
P39 |
|
Soft Drink and Ice Manufacturing |
31211 |
P110 |
P210 |
P310 |
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
[a] The majority of sectors depicted correspond to 4-digit NAICS codes with the exception of “Grain &Oilseed Milling & Sugar Manufacturing,” “Chocolate & Nonchocolate Confectionery Manufacturing,” and “Perishable Prepared Food Manufacturing.” |
|||||
Sample Frame:
The sampling frame for the study will be based on the FDA Food Facility Registration database supplemented with information on facility size and 6-digit NAICS industry obtained from the Dun & Bradstreet (D&B) business facility database. The FDA Food Facility Registration database provides a listing of domestic food facilities, including manufacturers/processors, as well as foreign facilities that export food that will be consumed in the U.S. and is continuously updated by facilities as registration information changes. Because all domestic and foreign facilities that manufacture, process, pack, or hold food for human or animal consumption in the United States are required to register with the FDA under the Bioterrorism Act, the FDA Food Facility Registration database represents a comprehensive listing of food manufacturing facilities.
The FDA Food Facility Registration database includes contact information and general information about the type of activity conducted at the facility (e.g., “manufacturer/processor”), but it does not contain the facility size (i.e., number of employees) or NAICS code information on registered facilities. To establish a complete sampling frame, FDA will add the size and NAICS code information for those facilities registered as manufacturer/processor by purchasing the D&B database for all food manufacturers (i.e., all records for which the listed primary or secondary 6-digit NAICS code begins with either 311 or 312) and matching it to the FDA Food Facility Registration database. D&B provides information for millions of U.S. and international public and private businesses. Virtually all active businesses in the U.S. register with D&B to obtain a DUNS number, as it is required for credit reporting and other business transactions. Company records in the D&B database include company address, type of ownership, primary and secondary NAICS codes, number of employees, amount of sales and others. There is, however, no email contact information on companies in the D&B database.
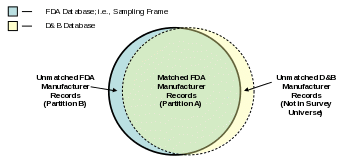
At the completion of matching D&B to the FDA Food Facility Registration database (see Figure 1), our sampling frame will be the list of facilities registered with FDA as manufacturer/processor of food for human consumption, and it will contain two categories of record types: facilities with complete information that we will call Partition A, and facilities with incomplete information that we will call Partition B. We refer to the two category types as Partitions A and B because the data will be partitioned (separated) by these two categories and sampled differently as described in section 2.2.
Facilities with Complete Information (Partition A) – The record for the facility includes name, address, 6-digit NAICS, employment size, and email address for facility contact person.
Facilities with Incomplete Information (Partition B) – The record for the facility includes name, address, and email address for facility contact person but does not contain information on the facility’s 6-digit NAICS code or employment size.
We expect that the majority of facility records in our sampling frame will fall within Partition A, as almost all active U.S. food manufacturers will have DUNS numbers. Partition B, on the other hand, will contain a likely small number of facility records that may be:
Out of business,
Out of scope – Those that have incorrectly classified themselves as a food manufacturer when registering with FDA,
In-scope, but not captured in D&B data because they have registered with D&B using a non-manufacturing NAICS code, or
In-scope, but not matchable because they registered with D&B (FDA) using a different address or name than they provided in their FDA registration (D&B).
Figure 1: Matching of D&B Database to the FDA Food Facility Registration Database
B.2 Sample Design
FDA’s primary objective in designing the survey is to develop estimates of the prevalence of certain types of food manufacturing practices with 95-percent confidence intervals defined to equal the point estimator plus or minus a confidence-interval half-width of five (5) percentage points or less for each facility size class.
2.1 Stratification
To accomplish these objectives, FDA proposes a survey in which:
Facilities with complete information (Partition A) will be sampled using a simple stratified random sample design with proportional sampling within each size class; and
Facilities with incomplete information (Partition B) will be sampled using a simple random sample design.
For Partition A, the design ensures that each facility in a given size class has an equal probability of selection. For Partition B, the design ensures that each facility has an equal probability of selection regardless of size.
2.2 Sample Allocation
Let U be the population of the survey universe (all FDA-registered facilities that manufacture food for human consumption), where
(1) ![]()
and
![]() is the population of the partition of the universe of FDA-registered
food manufacturers with complete information and
is the population of the partition of the universe of FDA-registered
food manufacturers with complete information and
![]() is the population of the partition of the universe consisting of
FDA-registered food manufacturers with incomplete information.
is the population of the partition of the universe consisting of
FDA-registered food manufacturers with incomplete information.
Similarly, let S be the size of sampled population where
(2) ![]()
and
![]() is the sample size for FDA-registered food manufacturers with
complete information and
is the sample size for FDA-registered food manufacturers with
complete information and
![]() is the sample size for FDA-registered food manufacturers with
incomplete information.
is the sample size for FDA-registered food manufacturers with
incomplete information.
Given that FDA will have employment size and
6-digit NAICS industry information for those facilities in Partition
A, the sample
![]() will be drawn based on a simple stratified random sample design with
proportional allocation, with the strata defined by employment size
and industry group. Thus,
will be drawn based on a simple stratified random sample design with
proportional allocation, with the strata defined by employment size
and industry group. Thus,
(3) ![]()
where
![]() is the sample for ith size class and the jth
industry group drawn from Partition A of the universe. Since FDA will
not have employment size and 6-digit NAICS industry information for
those facilities in Partition B, the sample
is the sample for ith size class and the jth
industry group drawn from Partition A of the universe. Since FDA will
not have employment size and 6-digit NAICS industry information for
those facilities in Partition B, the sample
![]() will
be drawn using a simple random sample design.
will
be drawn using a simple random sample design.
If r is FDA’s estimate of the overall completion rate (e.g. rate of sampling frame deficiencies and respondent nonresponse), then the overall solicited sample, SS, necessary to achieve FDA’s accuracy goals is
(4) ![]()
2.2.1 Facilities with Complete Records (Partition A)
We propose to use simple stratified random sampling with three estimation cells for those facilities with complete records where each employment size class represents an estimation cell. A five percent (5%) margin of error in population parameter estimates at the 95-percent confidence level requires an overall sample size of 384 per estimation cell (or 1,152 total given that there are 3 estimation cells). Table B-3 illustrates the disposition of the target sample for the survey of facilities with complete information that manufacture food for human consumption. The design reflects simple proportionate sampling based on population size of each stratum in the study universe. Appendix C shows the underlying mathematical relationships between the accuracy objectives and the sample targets.3
Table B-3: Target Sample for the Survey of Facilities with Complete Records (Partition A)
|
Number of Employees |
|||
Food Sector |
< 20 |
20 – 99 |
100 or More |
Total |
Grain & Oilseed Milling & Sugar Manufacturing |
TS11 |
TS21 |
TS31 |
|
Chocolate & Nonchocolate Confectionery Manufacturing |
TS12 |
TS22 |
TS32 |
|
Frozen Food Manufacturing |
TS13 |
TS23 |
TS33 |
|
Fruit & Vegetable Canning |
TS14 |
TS24 |
TS34 |
|
Dairy Product Manufacturing |
TS15 |
TS25 |
TS35 |
|
Seafood Product Preparation |
TS16 |
TS26 |
TS36 |
|
Bakeries and Tortilla Manufacturing |
TS17 |
TS27 |
TS37 |
|
Other Food Manufacturing |
TS18 |
TS28 |
TS36 |
|
Perishable Prepared Food Manufacturing |
TS19 |
TS29 |
TS39 |
|
Soft Drink and Ice Manufacturing |
TS110 |
TS210 |
TS310 |
|
Total |
384 |
384 |
384 |
1,152 |
Assuming proportional stratified random sampling, the elements of Table B-3 have the following properties:
(5) ![]() ,
and
,
and
(6) 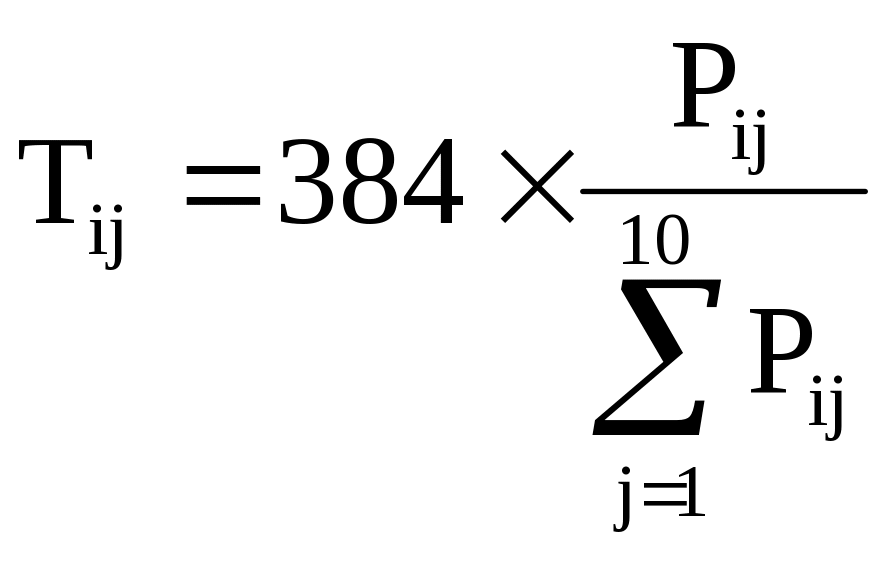 for each size class i.
for each size class i.
The overall number of solicitations required to achieve the sample targets shown in Table B-3 will depend on the incidence of invalid or out-of-scope listings in the drawn sample and on the rate of nonresponse among otherwise in-scope respondents. Reasons for nonresponse include language barriers, refusal, and other circumstances, as well as the inability to contact the respondent in a timely fashion. FDA’s experience with the FDA Food Facility Registration database indicates that approximately twenty percent (20%) of the listings might be expected to be outdated or duplicate registrations. Previous industry survey efforts also indicate that a nonresponse rate of no more than thirty percent (30%) is likely for a survey such as this one (see Table B-4).
Table B-4: Examples of Response Rates Achieved in Federal Agency Sponsored Surveys of Industry
Survey Title |
Sponsoring Agency |
Target Respondents |
Response Rate |
Single-Use Medical Device (SUD) Reuse and Reprocessing in Hospitals |
FDA |
Hospitals |
79.4% |
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) |
OSHA |
Manufacturing Facilities |
75% |
Automated External Defibrillator Use in the Workplace |
OSHA |
General industry, except for construction |
55% overall |
73% manufacturing |
|||
Conducted by Eastern Research Group, Inc. (ERG) under contract to the sponsoring Agency. |
|||
Combined, these figures suggest that the overall
completion rate (percent of completed surveys among Partition A
respondents potentially solicited) of fifty-six percent (56%) or
higher should be expected
![]() .
Thus, FDA estimates that a solicited sample of 2,058 potential
respondents is necessary to achieve the sample targets for Partition
A.
.
Thus, FDA estimates that a solicited sample of 2,058 potential
respondents is necessary to achieve the sample targets for Partition
A.
2.2.2 Facilities with Incomplete Records (Partition B)
We propose to use simple random sampling for those
facilities with incomplete records. A five percent (5%) margin of
error in population parameter estimates at the 95-percent confidence
level requires an overall sample size of 384 for this partition.
Assuming a completion rate similar to that for Partition A, FDA
estimates that a solicited sample of 686 potential respondents is
necessary to achieve the sample target for Partition B (![]() ).
).
At the completion of the survey, FDA will post-stratify the Partition B respondents into the applicable size classes based on the self-reported employment size of the respondent, mainly:4
Size Class 1 – Less than 20 employees,
Size Class 2 – 20 to 99 employees, and
Size Class 3 – 100 or more employees.
2.2.3 Supplementary Sample
Should the realized survey completion rate for either the stratified sample from Partition A or the simple random sample from Partition B be lower than estimated, FDA will draw a supplementary sample sufficiently large to ensure the stratum-specific respondent targets as derived in Table B-3 or the 384 target respondents for the Partition B sample are met. To ensure comparability, the supplementary samples, should they be necessary, will be selected from among the remaining facilities in the each size-class group using the same stratification criteria (for Partition A) or randomly selected from the remaining facilities in Partition B using the same sample selection method as used in the initial sample. FDA will use the actual completion rate obtained for the initial sample to determine the size of the supplementary sample needed to achieve the target respondent sample sizes.
B.3 Information Collection
B.3.1 Data Collection
The data collection phase of the study will be initiated with a survey invitation notice to all solicited respondents; i.e., food manufacturers with complete information and those with incomplete information (see Table B-4). According to the U.S. Census Bureau, a pre-canvas notification improves response rates in industry surveys. We believe that a survey invitation notice will have a similar effect for this effort.
The survey invitation will also enable us to confirm whether the target respondent is in-scope (i.e., food manufacturer) and determine the target respondent’s preferred mode of contact for the survey. The invitation will request the following information from the solicited respondents:
Nature of operations at the facility and what is being manufactured to confirm that the target respondent is indeed a food manufacturer and hence within the scope of the larger survey,
Number of employees at the facility,
Preferred mode of contact for the survey (electronic or U.S. Postal Service mail), and
Contact information for the person most suitable to respond to the survey.
Table B-5: Classification of Target Respondents prior to Survey Invitation
Type of Target Respondent |
With Email Address |
With Mail Address Only[a] |
With Complete Information (Partition A) |
Group A1 |
Group A2 |
With Incomplete Information (Partition B) |
Group B1 |
Group B2 |
[a] Most facilities in the FDA Food Facility Registration database are believed to have provided valid email addresses. But some, apparently, have declined to provide such contact information or have failed to update the email address they provided to FDA as information changes. |
||
FDA will utilize a mixed-mode approach via Internet and mail to administer the survey invitation notice to the sample of 2,744 (i.e., 2,744 = 2,058 + 686) target respondents. This will involve:
First contact – Survey Invitation
Solicited respondents in groups A1 and B1, an email invitation with individualized URL to the pre-canvas questions
Solicited respondents in groups A2 and B2, invitation letter sent via U.S Postal Mail with hard copy of pre-canvas questions attached
Second contact – First reminder one-week after initial invitation (sent to non-respondents only)
Solicited respondents in Partitions A1 and B1, an email reminder with individualized URL to the pre-canvas questions
Solicited respondents in groups A2 and B2, postcard reminder sent via U.S Postal Mail
Third contact – Second reminder one-week after the first reminder (sent to non-respondents only)
Solicited respondents in groups A1 and B1, a mail reminder with a hard copy of pre-canvas questions attached sent via U.S. Postal Mail
Solicited respondents in groups A2 and B2, a mail reminder with a hard copy of pre-canvas questions attached sent via U.S. Postal Mail.
We will use the information obtained from the survey invitation to divide the solicited sample according to preferred mode and point of contact as depicted in Table B-6 below. Note that those who have not responded to the survey invitation will still be solicited for the survey as described below.
Table B-6: Classification of Target Respondents after Survey Invitation
Type of Target Respondent |
Category |
||
With Complete Information |
Survey invitation respondents |
Group A1R (Preferred contact mode is email) |
Group A2R (Preferred contact mode is mail) |
Survey invitation non-respondents |
Group A1N (Email address available) |
Group A2N (Only mail address is available) |
|
With Incomplete Information |
Survey invitation respondents |
Group B1R (Preferred contact mode is email) |
Group B2R (Preferred contact mode is mail) |
Survey invitation non-respondents |
Group B1N (Email address available) |
Group B2N (Only mail address is available) |
|
The survey will use the following protocol for contacting the solicited respondents:
First contact – Survey invitation
For solicited respondents in groups A1 and B1, an introductory email with individualized URL to the survey (with a PDF version of the survey also attached)
For solicited respondents in groups A2 and B2, an introductory letter by U.S. Postal Service mail with a hard copy of the survey
Second contact: First reminder one-week after initial contact (sent to non-respondents only)
For solicited respondents in groups A1 and B1, reminder email with individualized URL to the survey (with a PDF version of the survey also attached)
For solicited respondents in groups A2 and B2, reminder letter via U.S. Postal Service with a hard copy of the survey attached
Third contact: Second reminder one-week after the first reminder (sent to non-respondents only)
For solicited respondents in groups A1 and B1, reminder postcard sent via U.S. Postal Service
For solicited respondents in groups A2 and B2, reminder postcard sent via U.S. Postal Service
Fourth contact: Final reminder one week after the second reminder (sent to non-respondents only)
For solicited respondents in groups A1 and B1, reminder phone call
For solicited respondents in groups A2 and B2, reminder phone call
B.3.2 Sample Selection Methodology
3.2.1 Facilities with Complete Information (Partition A)
The solicited sample of facilities within each
stratum will be selected using a simple random sampling procedure. To
facilitate the sampling, each facility will be assigned a random
index number, using a random number generator. The facilities in each
stratum will then be arranged in ascending order according to their
random index numbers. If
![]() is
the size of the solicited sample in the ith size class and
jth industry group in partition A, then those
is
the size of the solicited sample in the ith size class and
jth industry group in partition A, then those
![]() facilities with the smallest index numbers will be selected and
included in the sample.5
facilities with the smallest index numbers will be selected and
included in the sample.5
3.2.2 Facilities with Incomplete Information (Partition B)
Similar to the sample selection process applied to
Partition A, the solicited sample of facilities in Partition B will
also be selected using a simple random sampling procedure. To
facilitate the sampling, each facility will be assigned a random
index number, using a random number generator. The facilities in the
partition will then be arranged in ascending order according to their
random index numbers. If
![]() is
the size of the solicited sample in the partition, then those
is
the size of the solicited sample in the partition, then those
![]() facilities
with the smallest index numbers will be selected and included in the
sample.
facilities
with the smallest index numbers will be selected and included in the
sample.
B.3.3 Weighting and Estimation Procedure
3.3.1 Weighting
Facilities with Complete Information (Partition A)
Because FDA is anticipating variable nonresponse rates by stratum, weighting procedures are necessary to produce overall estimates. The weights will be the inverse of the selection probabilities of the facilities. Each stratum will have a different weight because of the different actual nonresponse rates. The sampling weights are defined as follows:
(7) 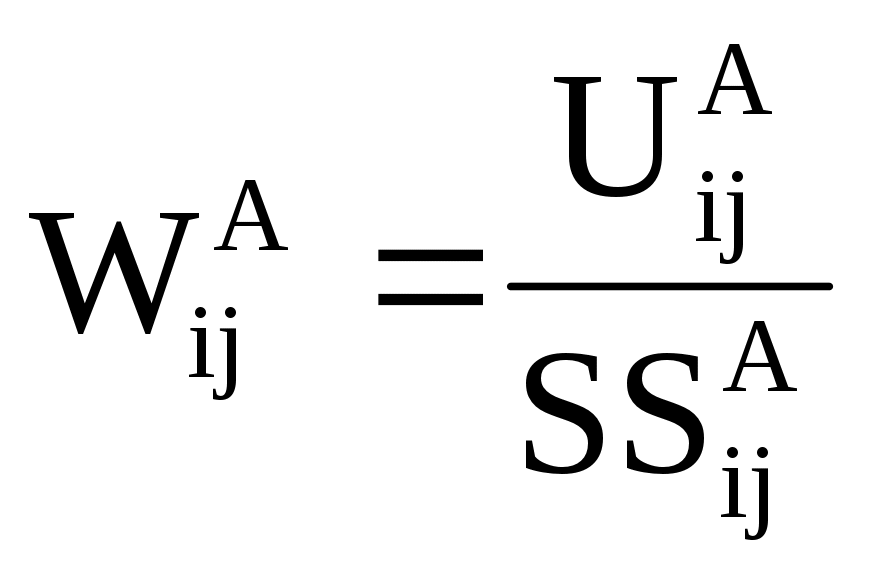
where
![]() = Sampling
weight for the ith facility size class and jth
industry group in Partition A
= Sampling
weight for the ith facility size class and jth
industry group in Partition A
![]() = Number
of elements in Partition A of the registrant universe defined by the
ith size class and jth industry group
= Number
of elements in Partition A of the registrant universe defined by the
ith size class and jth industry group
![]() = Size
of the solicited sample in the ith facility class size and
jth industry group for Partition A
= Size
of the solicited sample in the ith facility class size and
jth industry group for Partition A
Facilities with Incomplete Information (Partition B)
The sampling weight for those facilities with incomplete information will be defined as follows
(8) ![]()
where
![]() = Sample
weight for Partition B
= Sample
weight for Partition B
![]() = Number
of elements in Partition B of the registrant universe
= Number
of elements in Partition B of the registrant universe
![]() = Size
of the solicited sample for Partition B
= Size
of the solicited sample for Partition B
3.3.2 Adjustment Factor for Nonresponse
Facilities with Complete Information (Partition A)
The adjustment factor for nonresponse will be calculated by dividing the solicited sample size in each stratum by the actual number of responses from the corresponding stratum. This is written for Partition A as:
(8) 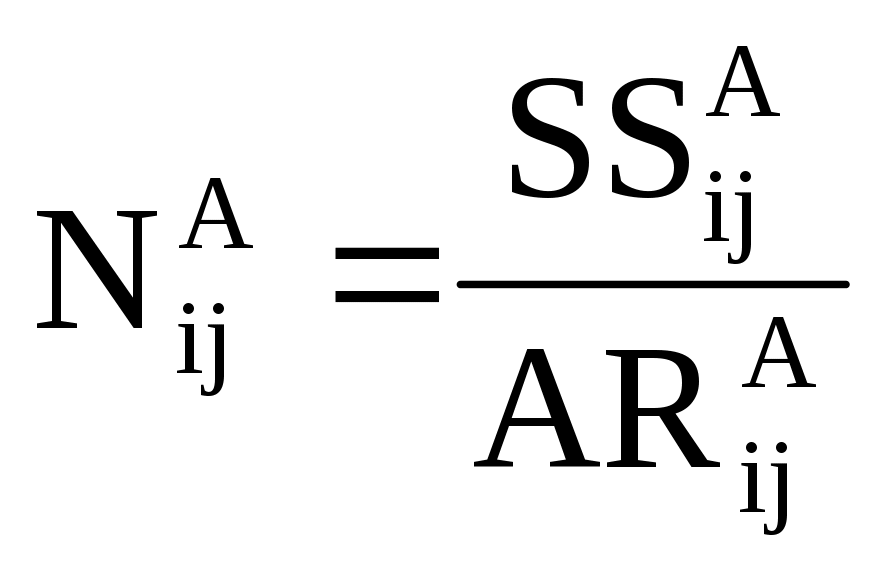
where
![]() = Size
of the solicited sample in the ith class size and jth
industry group for Partition A
= Size
of the solicited sample in the ith class size and jth
industry group for Partition A
![]() = Actual
(responded) sample in the ith class size and jth
industry group for Partition A
= Actual
(responded) sample in the ith class size and jth
industry group for Partition A
![]() = Nonresponse
factor for the ith class size and jth industry
group for Partition A
= Nonresponse
factor for the ith class size and jth industry
group for Partition A
Facilities with Incomplete Information (Partition B)
Similarly for Partition B, the adjustment factor for nonresponse will be calculated as:
(9) ![]()
where
![]() = Size
of the solicited sample for Partition B
= Size
of the solicited sample for Partition B
![]() = Actual
(responded) sample size for Partition B
= Actual
(responded) sample size for Partition B
![]() = Nonresponse
factor for Partition B
= Nonresponse
factor for Partition B
3.3.3 Point Estimation Procedures
The estimator,![]() ,
for the totals for a given survey variable will take the form:
,
for the totals for a given survey variable will take the form:
(10) ![]()
where
![]() =
Response of the kth respondent in the ith size
class and the jth industry group for Partition A sample
=
Response of the kth respondent in the ith size
class and the jth industry group for Partition A sample
![]() = Sampling
weight of the ith size class and jth industry
group for Partition A
= Sampling
weight of the ith size class and jth industry
group for Partition A
![]() = Nonresponse
adjustment of the ith size class and jth
industry group for Partition A
= Nonresponse
adjustment of the ith size class and jth
industry group for Partition A
![]() = Response
of the mth respondent in Partition B sample
= Response
of the mth respondent in Partition B sample
![]() = Sampling
weight for Partition B
= Sampling
weight for Partition B
![]() = Nonresponse
adjustment for Partition B
= Nonresponse
adjustment for Partition B
Estimates of the mean will be derived as follows:
(11) 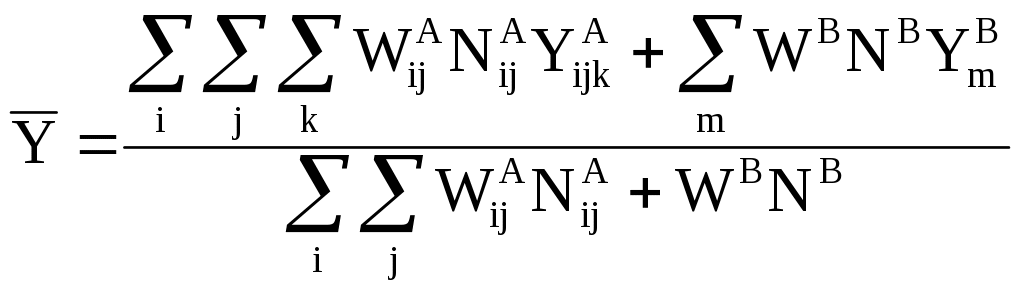
Similarly, the mean for each size class, i, will be derived as follows:
(12) 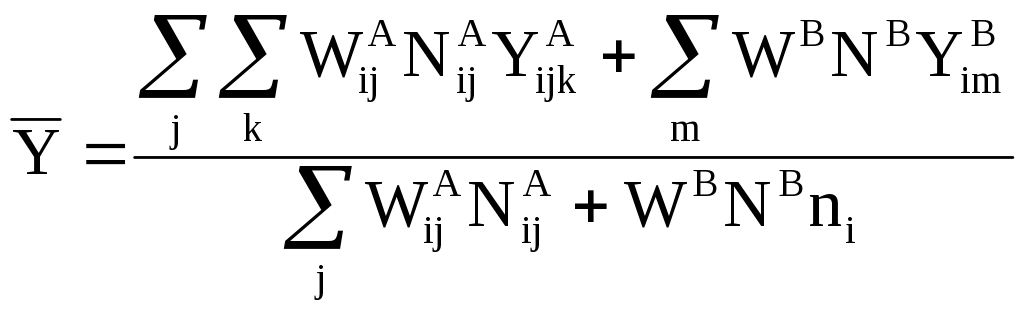
where
![]() = Response
of the mth respondent in size class i in Partition B
sample
= Response
of the mth respondent in size class i in Partition B
sample
![]() = Number
of respondents in size class i in Partition B sample
= Number
of respondents in size class i in Partition B sample
B.4 Methods To Maximize Response Rates
There is considerable research that relies on the theory of social exchange to explain why someone fills out a survey. The motivation to participate in FDA’s survey will naturally differ among respondents. There are, however, various time-tested methods for increasing participation rates in surveys. These include:
Incentives, such as pre- or post-payment of small cash prizes and drawings,
Requests for help,
Multiple contacts,
Pre-notification letters/emails, and
Multiple mode administration.
Incentives use social exchange theory by causing participants to feel obligated to respond. The use of incentives is a heavily researched area in response rate literature. Although several analyses have resulted in different conclusions, published reviews paint a very clear picture with respect to two issues: first, incentives are effective in increasing the response rates, especially for self-administered surveys (mail and Web); and second, promised incentives are not as effective as enclosed incentives. Given their cost, the use of taxpayer funds, impact on survey responses, and implications for the “social contract” between FDA and industry, we judge that monetary incentives are not appropriate for this survey effort. We will provide respondents with a copy of the final report as an incentive to participate.
Requests for help – Because most people tend to follow a norm of social responsibility, they will be more likely to comply with a survey request couched in terms of asking for help. There also is some evidence in the survey literature indicating that this is indeed the case. For example, a recent study found an eighteen percent (18%) increase in response rates by including the phrase “it would really help us out” in their communications.
Multiple contacts with members of the sample is one of the most successful techniques to increase response rates. This technique is now considered standard methodology for any survey. Studies suggest that to get full benefit from multiple contacts, surveys should use a pre-notification message followed by a copy of the survey with a cover message (a reminder sent to all respondents shortly after they receive the copy of the survey), followed finally by one or more contacts with non-respondents using combination of messages and surveys. Studies using samples of the general population have found that pre-notification letters typically increase response rates by four (4) to twenty-nine (29) percentage points. A recent example of multiple contacts with a Web survey was administered at a major university regarding student housing. After the first email notification, the response rate was leveling off at around forty-four percent (44%). After an email reminder was sent to non-respondents, the response rate increased to sixty-seven percent (67%), and a final reminder to non-respondents notifying them of the deadline for the survey resulted in a final response rate of almost seventy-two percent (72%), substantially higher than the rate after the first email notification. While they often increase costs, multiple contacts with respondents are one of the best ways to ensure a good response rate. This is one reason that Web surveys are growing in popularity as three or four contacts with respondents can be virtually costless, while three or four paper mailings can be quite expensive, especially if postage is required.
Pre-notification letters/emails that provide more information on the study increase respondent confidence in the validity and the importance of the study resulting in higher response rates.
Multiple mode administration (phone and mail, mail and Web, etc) of a survey has been shown to increase response rates (Dillman, 2000). Additionally, the use of multiple modes can also reduce nonresponse error and data collection costs.
Our proposed method of data collection (see Section 3.1) incorporates all of the above techniques. Since FDA is utilizing widely-accepted data collection techniques and is devoting substantial resources to efforts designed to minimize nonresponse, we expect the response rate to this survey to be comparable or better than that achieved for surveys of similar size and scope. Furthermore, FDA’s contractor for this survey effort has conducted a number of surveys of industrial facilities on a variety of topics that have achieved response rates comparable to, or exceeding, the response rate estimated for this survey.
B.5 Tests of Procedures or Methods
FDA plans to administer a pretest of the survey instrument. These facilities will be selected based on a random sample by employment size of the target survey population using the following simple random sample design (see Table B-7).
Pretest results will be evaluated to ensure that the survey questions are clearly understandable, terms are well defined, and the survey format is logical.
Table B-7: Survey Pretest Sample
Type of Target Respondent |
Facility Size (in Number of Employees) |
Pretest Sample Size |
With Complete Information (Partition A) |
< 20 Employees |
10 |
20 to 99 Employees |
7 |
|
100 or More Employees |
7 |
|
With Incomplete Information (Partition B) |
Not Applicable |
6 |
Total |
30 |
|
B.6 Expert Review
The statistical aspects of the survey design have been reviewed by:
Aylin Sertkaya, Ph.D.
Eastern Research Group, Inc.
110 Hartwell Ave.
Lexington, MA 02421
781-674-7227
Chester Fenton, Ph.D. (ABD)
Eastern Research Group, Inc.
110 Hartwell Ave.
Lexington, MA 02421
781-674-7326
Peter Vardon, Ph.D.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition
5100 Paint Branch Parkway
College Park, MD 20740
301-436-1830
The data will be collected and processed by:
Nyssa Ackerley
Eastern Research Group, Inc.
110 Hartwell Ave.
Lexington, MA 02421
781-674-7271
Thomas Gajnak
Eastern Research Group, Inc.
110 Hartwell Ave.
Lexington, MA 02421
781-674-7263
The summary statistics will be analyzed by:
Jordan Lin, Ph.D.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition
5100 Paint Branch Parkway
College Park, MD 20740
301-436-1831
Angela Lasher, Ph.D.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition
5100 Paint Branch Parkway
College Park, MD 20740
301-436-1763
Peter Vardon, Ph.D.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition
5100 Paint Branch Parkway
College Park, MD 20740
301-436-1830
Aylin Sertkaya, Ph.D.
Eastern Research Group, Inc.
110 Hartwell Ave.
Lexington, MA 02421
781-674-7227
Chester Fenton, Ph.D. (ABD)
Eastern Research Group, Inc.
110 Hartwell Ave.
Lexington, MA 02421
781-674-7326
References
Aly, Nael A. 1989. A Survey on the Use of Computer-Integrated Manufacturing in Food Processing Companies. Food Technology. March 1989.
Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). 2004. National Compensation Survey: Occupational wages in the United States, July 2003. U.S. Department of Labor. August.
Dillman, D. A. (2000). Mail and Internet Surveys: The Tailored Design Method (2nd Edition). New York: Wiley.
Ennen, Steve. 2002. Food Security. Food Processing. February 2002.
Ennen, Steve. 2003. Safety Tops Concerns for Coming Year. Food Processing. January 1.
Fusaro, Dave. 2004. Annual Manufacturing Trends Survey: Manufacturing Concerns for a Scary New World. Food Processing. January 12.
Ilyukhin, Sasha V., Timothy A. Haley, and Rakesh K. Singh. 2001a. A Survey of Automation Practices in the Food Industry. Food Control. Vol. 12: 285-296.
Ilyukhin, Sasha V., Timothy A. Haley, and Rakesh K. Singh. 2001b. A Survey of Control System Validation Practices in the Food Industry. Food Control. Vol. 12: 297-304.
Morris, Charles E. 2002. 3rd Annual Best Manufacturing Practices Survey. Food Engineering. February 2.
Morris, Charles E. 2000. Best Manufacturing Practices. Food Engineering. February 1.
Morris, Charles E. 2001. Best Manufacturing Practices. Food Engineering. February.
Senkel, I. Arthur, Robin A. Henderson, Beverly Jolbitado, and Jianghong Meng. 1999. Use of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point and Alternative Treatments in the Production of Apple Cider. Journal of Food Protection. Vol. 62: 778-785.
U.S. Census Bureau. 2007. 2004 County Business Patterns. http://www.census.gov/epcd/cbp/
view/cbpview.html.
Appendix A 21 USC 393
Sec. 393. Food and Drug Administration
(a) In general
There is established in the Department of Health and Human Services the Food and Drug Administration (hereinafter in this section referred to as the ''Administration'').
(b) Mission
The Administration shall -(1) promote the public health by promptly and efficiently
reviewing clinical research and taking appropriate action on the
marketing of regulated products in a timely manner;(2) with respect to such products, protect the public health by
ensuring that -(3) participate through appropriate processes with
representatives of other countries to reduce the burden of
regulation, harmonize regulatory requirements, and achieve
appropriate reciprocal arrangements; and
(4) as determined to be appropriate by the Secretary, carry out
paragraphs (1) through (3) in consultation with experts in
science, medicine, and public health, and in cooperation with
consumers, users, manufacturers, importers, packers,
distributors, and retailers of regulated products.
(c) Interagency collaboration
The Secretary shall implement programs and policies that will foster collaboration between the Administration, the National Institutes of Health, and other science-based Federal agencies, to enhance the scientific and technical expertise available to the Secretary in the conduct of the duties of the Secretary with respect to the development, clinical investigation, evaluation, and postmarket monitoring of emerging medical therapies, including complementary therapies, and advances in nutrition and food science.
-
(1) Appointment
There shall be in the Administration a Commissioner of Food and
Drugs (hereinafter in this section referred to as the
''Commissioner'') who shall be appointed by the President by and
with the advice and consent of the Senate.(2) General powers
The Secretary, through the Commissioner, shall be responsible
for executing this chapter and for -(A) providing overall direction to the Food and Drug
Administration and establishing and implementing general
policies respecting the management and operation of programs
and activities of the Food and Drug Administration;(B) coordinating and overseeing the operation of all
administrative entities within the Administration;(C) research relating to foods, drugs, cosmetics, and devices
in carrying out this chapter;(D) conducting educational and public information programs
relating to the responsibilities of the Food and Drug
Administration; and
(E) performing such other functions as the Secretary may
prescribe.
(e) Technical and scientific review groups
The Secretary through the Commissioner of Food and Drugs may, without regard to the provisions of title 5 governing appointments in the competitive service and without regard to the provisions of chapter 51 and subchapter III of chapter 53 of such title relating to classification and General Schedule pay rates, establish such technical and scientific review groups as are needed to carry out the functions of the Administration, including functions under this chapter, and appoint and pay the members of such groups, except that officers and employees of the United States shall not receive additional compensation for service as members of such groups.
(f) Agency plan for statutory compliance
(1) In general
Not later than 1 year after November 21, 1997, the Secretary,
after consultation with appropriate scientific and academic
experts, health care professionals, representatives of patient
and consumer advocacy groups, and the regulated industry, shall
develop and publish in the Federal Register a plan bringing the
Secretary into compliance with each of the obligations of the
Secretary under this chapter. The Secretary shall review the
plan biannually and shall revise the plan as necessary, in
consultation with such persons.(2) Objectives of agency plan
The plan required by paragraph (1) shall establish objectives
and mechanisms to achieve such objectives, including objectives
related to -(A) maximizing the availability and clarity of information
about the process for review of applications and submissions
(including petitions, notifications, and any other similar
forms of request) made under this chapter;(B) maximizing the availability and clarity of information
for consumers and patients concerning new products;(C) implementing inspection and postmarket monitoring
provisions of this chapter;(D) ensuring access to the scientific and technical expertise
needed by the Secretary to meet obligations described in
paragraph (1);(E) establishing mechanisms, by July 1, 1999, for meeting the
time periods specified in this chapter for the review of all
applications and submissions described in subparagraph (A) and
submitted after November 21, 1997; and
(F) eliminating backlogs in the review of applications and
submissions described in subparagraph (A), by January 1, 2000.
(g) Annual report
The Secretary shall annually prepare and publish in the Federal Register and solicit public comment on a report that -(1) provides detailed statistical information on the
performance of the Secretary under the plan described in
subsection (f) of this section;(2) compares such performance of the Secretary with the
objectives of the plan and with the statutory obligations of the
Secretary; and
(3) identifies any regulatory policy that has a significant
negative impact on compliance with any objective of the plan or
any statutory obligation and sets forth any proposed revision to
any such regulatory policy.
Appendix B Information Collection Instrument
(See a separate document)
Appendix C: Sample Size and Precision
The following discussion shows the mathematical
relationships underlying the association between FDA’s
precision objectives detailed in Section 2 and the target sample
sizes shown in Table B-3.
The basic relationships relating sample size and statistical
confidence intervals can be derived as follows: Let
![]() be
a simple random sample selected with replacement from the population
with mean and variance
be
a simple random sample selected with replacement from the population
with mean and variance![]() .
Then, the sample mean,
.
Then, the sample mean,
![]() ,
is expressed as
,
is expressed as
(A-1) ![]()
where
![]() is the value of the ith element of the sample and n is the
size of the sample. Further, the standard deviation of the sample,
is the value of the ith element of the sample and n is the
size of the sample. Further, the standard deviation of the sample,![]() ,
is defined as
,
is defined as
(A-2) ![]()
And, it can be shown that
![]() and
and
![]() are
unbiased estimators of and
are
unbiased estimators of and
![]() ,
respectively. If a series of samples is taken from the population, it
can also be shown that the resulting probability distribution of the
sample means will have an expected value of
and a variance
,
respectively. If a series of samples is taken from the population, it
can also be shown that the resulting probability distribution of the
sample means will have an expected value of
and a variance![]() ,
such that
,
such that
(A-3) ![]()
With the Central Limit Theorem, it can be shown
that as n increases, the sample mean,![]() ,
will have a distribution that approaches a normal distribution with
mean
,
will have a distribution that approaches a normal distribution with
mean![]() and
a standard deviation
and
a standard deviation
![]() .
Alternatively, the relationship
.
Alternatively, the relationship
(A-4) ![]()
is approximately normal, with mean zero and standard deviation of one for a sufficiently large sample. Further, equation (A-4) can be rewritten using (A-3) as
(A-5) 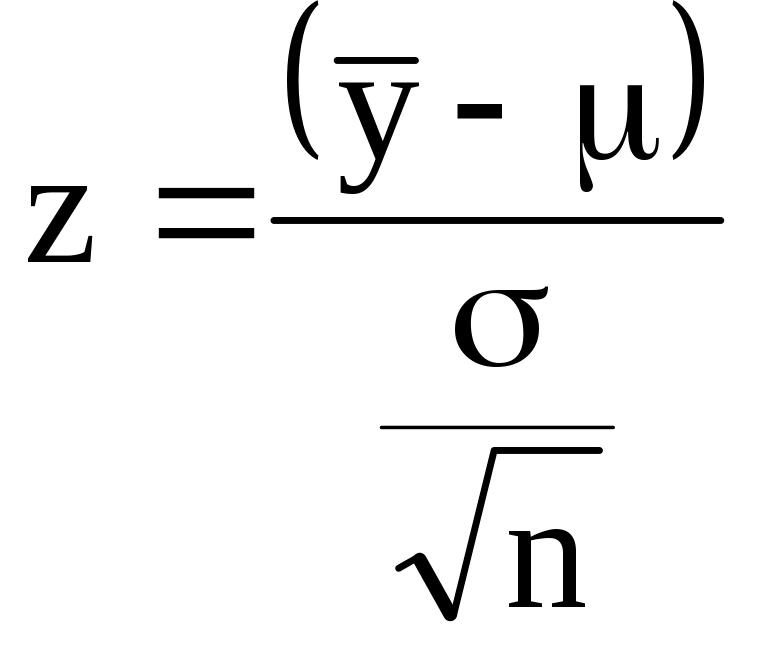
Values from the normal distribution will define
the range or confidence interval around the mean within which the
values of a normally distributed random variable may be expected to
lie with a given probability,
![]() ,
such that
,
such that
(A-6) 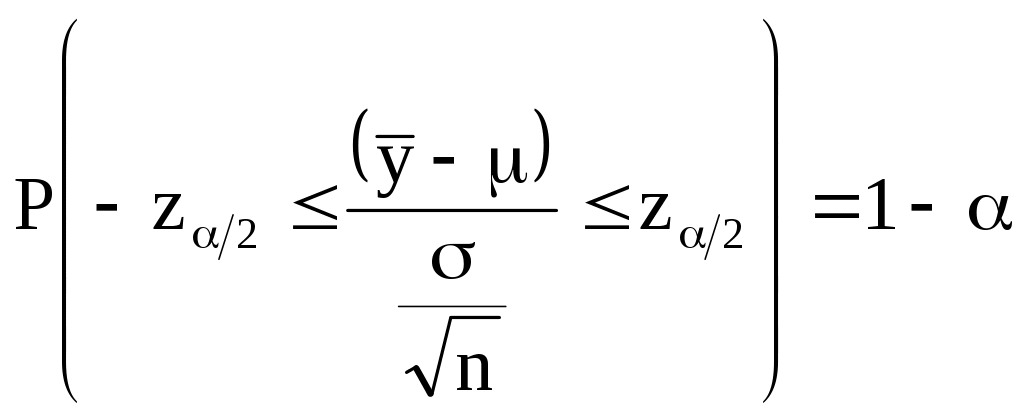
If the population standard deviation
![]() were known, the upper and the lower confidence limits (UCL and LCL)
for the population mean, ,
are then defined as follows:
were known, the upper and the lower confidence limits (UCL and LCL)
for the population mean, ,
are then defined as follows:
(A-7a) ![]()
(A-7b) ![]()
Equations (A-6) and (A-7) show the basic
relationships that relate the confidence interval, the level of
precision, and the sample size. To determine the necessary sample
size, the sample designer must, therefore, specify two parameters:
the confidence level (the value of )
and the desired precision, e (i.e., the maximum value of
![]() ).
Then, for a maximum error of
).
Then, for a maximum error of
![]() and a desired confidence level of ,
the minimum desired sample size becomes
and a desired confidence level of ,
the minimum desired sample size becomes
(A-8) 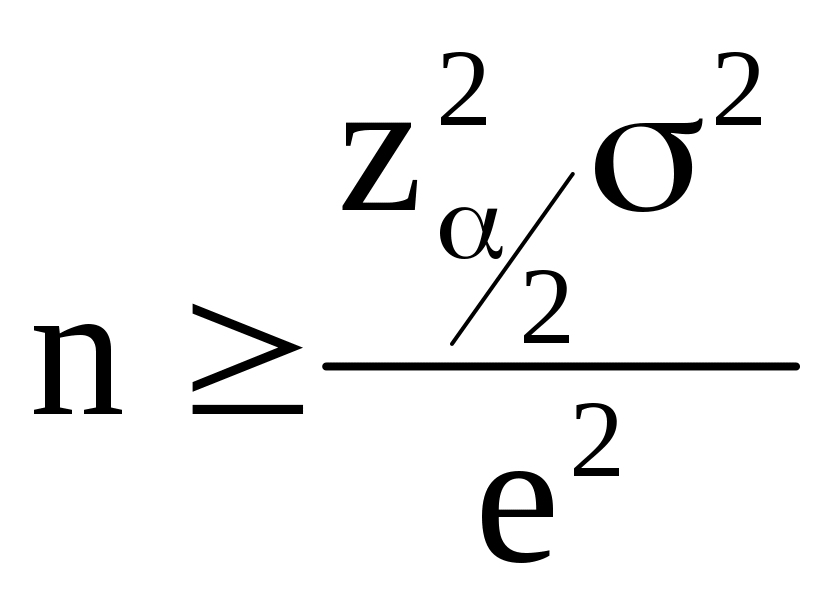
The requisite sample size, however, also depends
on
![]() ,
the population variance, which is generally not known. Thus, two
approaches are typically used to estimate the value of
,
the population variance, which is generally not known. Thus, two
approaches are typically used to estimate the value of
![]() .
First, the sample designer may have a priori information about
the population distribution that permits the approximation of
.
First, the sample designer may have a priori information about
the population distribution that permits the approximation of
![]() .
This may come from previous surveys or published studies. More
commonly, a worst case assumption about the response frequencies is
used as follows: Suppose a key survey question asks respondents about
an important attribute of their manufacturing practice. Let p be the
probability that this attribute is present for the respondents in the
survey universe. A random variable with a value of 1 if the attribute
is present and 0 if not, therefore, is binomially distributed with an
expected value of p and a variance of
.
This may come from previous surveys or published studies. More
commonly, a worst case assumption about the response frequencies is
used as follows: Suppose a key survey question asks respondents about
an important attribute of their manufacturing practice. Let p be the
probability that this attribute is present for the respondents in the
survey universe. A random variable with a value of 1 if the attribute
is present and 0 if not, therefore, is binomially distributed with an
expected value of p and a variance of![]() .
This variance is maximized where
.
This variance is maximized where
![]() .
Thus, substituting
.
Thus, substituting
![]() for
for
![]() in (A-8) will ensure that the sample size is large enough to meet the
precision and confidence level objectives.
in (A-8) will ensure that the sample size is large enough to meet the
precision and confidence level objectives.
For example, tables of the normal distribution
show than a normally distributed random variable with mean zero and
variance 1 will have values between
![]() with a 95-percent probability. Thus, a sample size of n, where
with a 95-percent probability. Thus, a sample size of n, where
(A-9) ![]()
will result in a sample sufficient to achieve a
precision of at least e at the 95-percent confidence level. That is,
![]() with
a probability of ninety-five percent (95%).
with
a probability of ninety-five percent (95%).
1 All domestic and foreign facilities that manufacture, process, pack, or hold food for human or animal consumption in the United States are required to register with the FDA by December 12, 2003, under the Public Health Security and Bioterrorism Preparedness and Response Act of 2002 (the Bioterrorism Act) or prior to beginning operations if they were established after this date.
2 It is well known in statistical theory that if a population can be subdivided into subpopulations for which the variances of the design variable are smaller than that for the overall population, then stratified random sampling can be used to obtain a more precise (smaller variance) estimate of the population mean for that variable. See, for example, William Cochran, Sampling Techniques (New York, 1977) [Third Edition], Chapter 2 and Sharon L. Lohr, Sampling: Design and Analysis (Pacific Grove, 1999), Chapter 4.
3 The sample sizes shown in Table B-3 are based on the relationship between sample size and accuracy for simple random samples. Since FDA is proposing a stratified random sample design based on proportional sampling, the accuracy levels achieved with these samples will, in general, exceed the survey’s objectives (see Appendix A).
4 The survey inquires about the number of employees at the respondent’s facility.
5 Alternatively, one could select the same number of facilities with the largest index numbers.
| File Type | application/msword |
| File Title | REQUEST FOR OMB REVIEW |
| Author | PVardon |
| Last Modified By | ATaylor |
| File Modified | 2008-08-28 |
| File Created | 2008-08-28 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy