NLSY79 Supporting Statement Part A
NLSY79 Supporting Statement Part A.doc
National Longitudinal Survey of Youth 1979
OMB: 1220-0109
Information Collection Request for
The National Longitudinal Survey of Youth 1979
OMB # 1220-0109
Submitted by the Bureau of Labor Statistics
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Summary 1
Supporting Statement 2
A. Justification 2
1. Necessity for the Data Collection 2
2. Purpose of Survey and Data-Collection Procedures 2
3. Improved Information Technology to Reduce Burden 5
4. Efforts to Identify Duplication 6
5. Involvement of Small Organizations 7
6. Consequences of Less Frequent Data Collection 7
7. Special Circumstances 9
8. Federal Register Notice and Consultations 9
9. Payment to Respondents 14
10. Confidentiality of Data 18
11. Sensitive Questions 20
12. Estimation of Information Collection Burden 24
13. Cost Burden to Respondents or Record Keepers 26
14. Estimate of Cost to the Federal Government 26
15. Change in Burden 26
16. Plans and Time Schedule for Information Collection, Tabulation, and Publication 27
17. Reasons Not to Display OMB Expiration Date 27
18. Exceptions to “Certificate for Paperwork Reduction Act Submissions” 27
B. Collections of Information Employing Statistical Methods 28
1. Respondent Universe and Respondent Selection Method 28
2. Design and Procedures for the Information Collection 29
3. Maximizing Response Rates 31
4. Testing of Questionnaire Items 32
5. Statistical Consultant 33
Attachment 1—Title 29 USC Sections 1 & 2 34
Attachment 2—Confidential Information Protection and Statistical Efficiency Act of 2002 (CIPSEA) 36
Attachment 3—BLS Commissioner's Order 1-06 45
Attachment 4—Survey Applications 53
A. Use of the NLSY79 for Diffusion of Useful Information on Labor 53
B. Use of the NLSY79 for Examination of Department of Labor Employment and Training Programs 53
C. Use of the NLSY79 in Understanding Labor Markets 54
1. Orientation toward the Labor Market 54
2. Factors in Educational Progress 54
3. Transition from School to Work 56
4. The Work Environment 57
5. Racial, Sex, and Cultural Differences in Employment and Earnings 57
6. The Relationships between Economic and Social Factors and Family Transitions and Well-Being 58
7. The Geographic Mobility of Young Baby Boomers 59
8. The Measurement and Analysis of Gross Changes in Labor Market Status 59
D. Use of the NLSY79 for Social Indicators Analysis 60
1. Delinquent Behavior, Arrest Records, and School Discipline 60
2. Drug and Alcohol Use 61
E. Use of the NLSY79 to Measure Maternal and Child Inputs and Outcomes 62
1. Research Issues Linking Employment, Income, and Child Outcomes 62
2. Other Research Issues Relating Family Structure and Child Outcomes 67
Attachment 5—Analysis of Content of Interview Schedules 70
Attachment 6—New Questions and Lines of Inquiry 77
Attachment 7—Child Assessment Measures 84
A. The Child Assessment Measures 84
B. Summary of Child Aptitude Measures To Be Used 85
1. Home Observation for Measurement of the Environment (HOME) 85
2. Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children–Revised: Digit Span Subscale 87
3. Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test–Revised (PPVT-R) 87
4. Peabody Individual Achievement Test (PIAT) 89
5. Temperament Scales 90
6. Perceived Competence Scale for Children/Self-Perception Profile 91
7. Behavior Problems Index 91
Attachment 8—Respondent Advance Letters 93
Attachment 9—Questions and Answers for NLSY79 Respondents about Uses of the Data, Confidentiality, and Burden 98
Summary
This package requests clearance for Round 24 of the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth 1979 cohort (NLSY79). The sample includes 9,964 persons who will be 45 to 52 years old on December 31, 2009. Approximately 5.3 percent of the sample members are deceased. There is no evidence of sample attrition bias at this time. The NLSY79 is a representative national sample of adults who were born in the years 1957 to 1964 and lived in the U.S. when the survey began in 1979. The sample contains an overrepresentation of black and Hispanic respondents to include a sufficient sample size to permit racial and ethnic analytical comparisons. Appropriate weights have been developed so that the sample components can be combined in a manner to aggregate to the overall U.S. population of the same ages, excluding those who have immigrated since 1978.
This package also seeks clearance for assessments and interviews of the children born to female NLSY79 respondents. The children of the NLSY79 have been assessed since 1986, when the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) began sponsoring a set of supplemental surveys to gather a large amount of information about the lives of these children. A battery of child cognitive, socio-emotional, and physiological assessments has been administered biennially since 1986 to NLSY79 mothers and their children. Starting in 1994, children who had reached age 15 by December 31 of the survey year (the Young Adults) were interviewed about their work experiences, training, schooling, health, fertility, self-esteem, and other topics. By 2010, the NLSY79 Child and Young Adult surveys will include 220 children under age 10; 600 children ages 10–14; 2,090 Young Adults ages 15–20; and 5,260 young adults age 21 and older.
The main NLSY79 is funded primarily by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). Funding for the NLSY79 Child and Young Adult surveys is provided primarily by NICHD through an interagency agreement with the BLS and through a grant awarded to researchers at the Ohio State University Center for Human Resource Research (CHRR). The BLS has overall responsibility for the project. The BLS contracts with the National Opinion Research Center (NORC) at the University of Chicago and CHRR to conduct the surveys. NORC handles the overall design and management, interviewing, initial data preparation, and weighting. Additional data cleanup and preparation, development of documentation, and preparation of data files are handled by CHRR.
The data collected in this survey are part of a larger effort that involves repeated interviews administered to a number of cohorts in the U. S. Many of the questions are identical or very similar to questions previously approved by OMB that have been asked in other cohorts of the National Longitudinal Surveys. Many of the questions in the NLSY79 also have been designed to reflect the changing nature of institutions and the different problems facing these groups of people. Those data elements of a particularly sensitive nature and those not previously collected are justified in more detail in this document.
Supporting Statement
National Longitudinal Survey of Youth 1979
A Survey of Persons who were Ages 14 to 21 on December 31, 1978
Rationale, Objectives, and Analysis of Content
A. Justification
1. Necessity for the Data Collection
This statement covers the pretest and main fielding of Round 24 of the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth 1979 (NLSY79). The NLSY79 is a nationally representative sample of persons who were born in the years 1957 to 1964 and lived in the U.S. when the survey began in 1979. The longitudinal focus of the survey requires the collection of identical information for the same individuals over the life cycle and the occasional introduction of new data elements to meet the ongoing analytical needs of policymakers and researchers. Most of the information to be collected in Round 24 has been approved by OMB in previous rounds of the NLSY79.
The mission of the Department of Labor (DOL) is, among other things, to promote the development of the U.S. labor force and the efficiency of the U.S. labor market. The BLS contributes to this mission by gathering information about the labor force and labor market and disseminating it to policymakers and to the public so that participants in those markets can make more informed and, thus, more efficient choices. The charge to the BLS to collect data related to the labor force is extremely broad, as reflected in Title 29 USC Section 1:
“The general design and duties of the Bureau of Labor Statistics shall be to acquire and diffuse among the people of the United States useful information on subjects connected with labor, in the most general and comprehensive sense of that word, and especially upon its relation to capital, the hours of labor, the earnings of laboring men and women, and the means of promoting their material, social, intellectual, and moral prosperity.”
The collection of these data contributes to the BLS mission by aiding in the understanding of labor market outcomes faced by individuals in the early stages of career and family development. See attachment 1 for Title 29 USC Sections 1 and 2.
2. Purpose of Survey and Data-Collection Procedures
Through 1984, the NLSY79 consisted of annual interviews with a national sample of 12,686 young men and women between who were ages 14 to 21 as of December 31, 1978, with overrepresentation of blacks, Hispanics, and economically disadvantaged nonblacks/non-Hispanics. The sample also included 1,280 persons serving in the military in 1978. Starting in 1985, the military sample was reduced to 201 due to a cessation of funding from the Department of Defense. Starting in 1991, interviews were discontinued with the 742 male and 901 female members of the economically disadvantaged nonblack/non-Hispanic sample. This reduced the eligible pool of respondents to 9,964. The NLSY79 was conducted annually from 1979 to 1994 and has been conducted every two years since 1994.
In addition to the regular interviews, several supplementary data-collection efforts completed during the early survey years greatly enhance the value of the survey to policymakers and researchers. The full Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) was administered to 94 percent of sample members. Also, for a large proportion of the sample, information has been collected about the characteristics of the last high school each respondent attended, as well as the courses taken, grades, and some other personal characteristics about the respondents while attending high school.
These data-collection efforts have enabled researchers to complete studies of the relationship between background environment, employment behavior, vocational aptitudes, and high school quality. The data have helped the Departments of Labor, Defense, Education, and Health and Human Services and many congressional committees to make more knowledgeable decisions when evaluating the efficacy of programs in the areas of civilian and military employment, training, and health.
The NLSY79 is a general-purpose study designed to serve a variety of policy-related research interests. Its longitudinal design and conceptual framework serve the needs of policymakers in a way that cross-sectional surveys cannot. In addition, the NLSY79 allows a broad spectrum of social scientists concerned with the labor market problems of young baby boomers to pursue their research interests. Support for the survey by other government agencies is encouraged, as the increasingly omnibus nature of the survey makes it an efficient, low-cost data set. As noted, the survey has incorporated items needed for program and policy purposes by agencies other than the Department of Labor. In this survey round, we anticipate funding from NICHD and the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
In this survey round, information once again will be collected about the biological children of the female NLSY79 respondents. For the most part, this collection of data about the children repeats surveys administered to these children biennially from 1986 to 2008. These unique data permit medical and social science researchers to consider a large number of basic research issues relating to the effects of family background, program activities, and infant and maternal health on outcomes from early childhood through adolescence and into early adulthood. While the principal focus of the survey remains the collection of data for labor force analysis, the questionnaires administered to these children and older youths include items needed by other agencies that are not always directly related to employment and training studies. As these children reach adolescence, the focus of the surveys of these young adults returns to the school-to-work transition.
Sample sizes and the expected number of Round 24 interviews for each group are listed in table 1.
Table 1. NLSY79 Sample Size and Expected Response in 2010 (Round 24)
Cohort |
Approximate sample size |
Expected number of interviews |
NLSY79 pretest |
1301 |
1001 |
NLSY79 main |
9,436 |
7,600 |
Children ages 0–9 |
220 |
180 |
Children ages 10–14 |
600 |
540 |
Young Adults ages 15–20 |
2,090 |
1,775 |
Young Adults age 21 and older |
5,260 |
4,365 |
1 These numbers include 30 remaining in-scope, living pretest respondents from the original 1979 pretest sample and 100 respondents from the pretest refresher fielding in 2007.
The specific objectives of the NLSY79 fall into several major categories that will be further explained below:
to explore the labor market activity and family formation of individuals in this age group
to explore in greater depth than previously has been possible the complex economic, social, and psychological factors responsible for variation in the labor market experience of this cohort
to explore how labor market experiences explain the evolution of careers, wealth, and the preparation of this cohort for the further education of their children and retirement
to analyze the impact of a changing socio-economic environment on the educational and labor market experiences of this cohort by comparing data from the present study with those yielded by the surveys of the earlier NLS cohorts of young men (which began in 1966 and ended in 1981) and young women (which began in 1968 and ended in 2003), as well as the more recent NLS cohort of young men and women born in the years 1980-84 and interviewed for the first time in 1997
to consider how the employment-related activities of women affect the subsequent cognitive and emotional development of their children, and how the development of the children affect the activities of the mother
to meet the data-collection and research needs of various government agencies that have been interested in the relationships between child and maternal health, drug and alcohol use, and juvenile deviant behavior and child outcomes such as education, employment, and family experiences
The NLSY79 has several characteristics that distinguish it from other data sources and make it uniquely capable of meeting the major purposes described above. The first of these is the breadth and depth of the types of information that are being collected. It has become increasingly evident in recent years that a comprehensive analysis of the dynamics of labor force activity requires an eclectic theoretical framework that draws on several disciplines, particularly economics, sociology, and psychology. For example, the exploration of the determinants and consequences of the labor force behavior and experience of this cohort requires information about (1) the individual’s family background and ongoing demographic experiences; (2) the character of all aspects of the environment with which the individual interacts; (3) human capital inputs such as formal schooling and training; (4) a complete record of the individual’s work experiences; (5) the behaviors, attitudes, and experiences of closely related family members, including spouses and children; and (6) a variety of social-psychological measures, including attitudes toward specific and general work situations, personal feelings about the future, and perceptions of how much control one has over one’s environment.
A second major advantage of the NLSY79 is its longitudinal design, which permits investigation of labor market dynamics that would not be possible with one-time surveys and allows directions of causation to be established with much greater confidence than cross-sectional analyses. Also, the considerable geographic and environmental information available for each respondent for each survey year permits a more careful examination of the impact that area employment and unemployment considerations have for altering the employment, education, and family experiences of these cohort members and their families.
Third, the oversampling of blacks and Hispanics, together with the other two advantages mentioned above, makes possible more sophisticated examinations of human capital creation programs than previously have been possible. Post-program experiences of “treatment” groups can be compared with those of groups matched not only for preprogram experience and such conventional measures as educational attainment, but also for psychological characteristics that have rarely been available in previous studies.
As has been indicated above, the study has several general research and policy-related objectives. In attachment 4, we elaborate on these basic purposes by setting forth a series of specific research themes. The detailed content of the interview schedule is then related to these themes. Attachment 5 tabulates the relationships of the recent modules of the survey to these objectives. Attachment 6 summarizes the new questions and lines of inquiry in the proposed questionnaire. A rationale for the various child assessments is contained in attachment 7. Attachment 8 provides the advance letters that will be sent to respondents prior to data collection. Attachment 9 shows the questions and answers about uses of the data, confidentiality, and burden that will appear on the back of each advance letter.
The NLSY79 is part of a broader group of surveys that are known as the BLS National Longitudinal Surveys program. In 1966, the first interviews were administered to persons representing two cohorts, Older Men ages 45-59 in 1966 and Young Men ages 14-24 in 1966. The sample of Mature Women ages 30-44 in 1967 was first interviewed in 1967. The last of the original four cohorts was the Young Women, who were ages 14-24 when first interviewed in 1968. The survey of Young Men was discontinued after the 1981 interview, and the last survey of the Older Men was conducted in 1990. The Young and Mature Women surveys were discontinued after the 2003 interviews. The most recent cohort added to the NLS program is the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth 1997 (NLSY97), which includes persons who were ages 12–16 on December 31, 1984.
The National Longitudinal Surveys are used by BLS and other government agencies to examine a wide range of labor market issues. The most recent BLS news releases that examines NLSY79 data was published on June 27, 2008, and is available online at http://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/nlsoy.pdf. In addition to BLS publications, analyses have been conducted in recent years by other agencies of the Executive Branch, the Government Accountability Office, and the Congressional Budget Office. The surveys also are used extensively by researchers in a variety of academic fields. A comprehensive bibliography of journal articles, dissertations, and other research that have examined data from all National Longitudinal Surveys cohorts is available at http://www.nlsbibliography.org/.
3. Improved Information Technology to Reduce Burden
The field staff of the National Opinion Research Center (NORC) makes every effort to ensure that the information is collected in as expeditious a manner as possible, with minimal interference in the lives of the respondents. Our success in this regard is suggested by the very high continuing response rate and low item refusal rates that have been attained. More recent efforts also have advanced technologies that lower respondent burden.
During Round 11 (1989) of the NLSY79, about 300 cases were collected using a Computer Assisted Personal Interview (CAPI). During Round 12 (1990) CAPI was again used, this time for about 2,400 cases using a longer and more complex questionnaire. The CAPI efforts in 1989 and 1990 were designed to assess the feasibility of the method and the effect of CAPI methods on data quality. Since 1993, the NLSY79 has been conducted using CAPI for all cases. Note that some cases have been completed over the telephone in each round; in recent rounds, the percentage of cases completed by phone is around 85%. The system has proved to be stable and reliable, and is well received by interviewers, respondents, and researchers.
An analysis of the Round 12 (1990) experimental data revealed that the quality of the data, as measured by missing or inconsistent responses, was greatly improved by CAPI. The effects on the pattern of responses were minor, although some answer patterns were affected because the CAPI technology in certain cases changed the way the questions were asked. Production data from rounds 15–21, based on over 80,000 completed interviews, showed these predictions of high-quality data were correct.
In 1994 we began to administer the Child Survey assessments using CAPI. CAPI simplified the administration of these assessments and reduced interview time and respondent burden. We saw the average interview time fall throughout the field period, and quality control measures revealed the data to be in excellent condition. The Young Adult survey, begun in 1994, originally had a CAPI interview with an additional paper and pencil self-report booklet. In 2000, this booklet was converted to CAPI. In 2010 fielding, the entire Young Adult questionnaire will be in a CAPI format.
CAPI surveying will continue to be used in Round 24. We estimate the average interview would be 10-15 percent longer if paper and pencil were used instead of CAPI.
In Round 24, we will continue to exploit computer interviewing to reduce the number of validation reinterviews needed to ensure that field interviewing is accurate. The survey includes a number of questions which interviewers should not be able to fabricate answers for, such as the respondent’s date of birth, height, and weight. Entries for these questions that are inconsistent with information we already have could signal that an interviewer falsified an interview. We will then conduct reinterviews only in cases where an inconsistency suggests that a check is needed. This approach, first used in Round 20, allowed us to reduce the number of validation reinterviews from about 1,250 in Round 19 to about 200 in Round 20.
In Round 24, we also plan to continue using an additional computerized check to ensure that an interview has taken place. Our laptops are equipped with an internal microphone and recording capability, and the phone system we use during the early bird phase also has a recording capability. We will record portions of the interview at points unknown to the interviewer. If we have any suspicions about a given interview, we can then listen to the sound files and ensure that an interview is taking place. In addition to identifying any interviews that are completely falsified, this can also reveal when an interviewer is taking shortcuts or not reading questions as instructed. We will use these recordings only to evaluate interviewer performance and validate suspicious interviews.
We will include in the introduction to the questionnaire a statement that “Parts of this interview may be recorded for quality control purposes. This will not compromise the strict confidentiality of your responses” (“CONSENT-1200” in the main NLSY79 questionnaire and “INTRO” in the young adult questionnaire). If the respondent does not want to be recorded, for interviews conducted during the regular field period the laptop recording capability will be immediately turned off. In the Early Bird phase of data collection (discussed in section A.9), the technology does not enable us to stop recording without breaking off the interview, ending the phone call, and calling the respondent back. If an Early Bird respondent does not consent to having the interview recorded, we will delete the recording after the interview without listening to it.
4. Efforts to Identify Duplication
A 1982 study entitled “National Social Data Series: A Compendium of Brief Descriptions” by Richard C. Taeuber and Richard C. Rockwell includes an exhaustive list with descriptions of the national data sets available at that time. A careful examination of the description of all the data sets specified in their comprehensive listing indicates that there was no other data set that would permit the comprehensive analyses of youth and young adult employment that can be conducted using the National Longitudinal Surveys. Indeed, it was the absence of alternative data sources that was the deciding factor in the Department of Labor’s determination (in 1977) to sponsor this comprehensive youth survey. The longitudinal nature of the survey and the rich background information collected mean that no survey subsequently released can provide data to replace the NLSY79. The expansion in the mid-1980s of the NLSY79 data set to incorporate the child outcome data represents a unique intergenerational data-collection effort.
Survey staff have continued to confirm that no comparable data set exists. An investigation into data sets related to wealth by F. Thomas Juster and Kathleen A. Kuester describes the data available in the wealth domain, showing the unique nature of the data available in the NLS.
The 1993 volume The Future of the Survey of Income and Program Participation points out a number of contrasts between the Survey of Income and Program Participation (SIPP) and the NLS and other major longitudinal studies (see especially pages 77, 107, and 265–7). This book was written primarily to review the SIPP but helps put the major longitudinal surveys in perspective.
As we will describe more fully below, BLS convened a conference in fall 1998 to look at the design of the NLSY79 for 2002 and beyond. In the process external reviewers assessed the coverage, quality, and duplication of the survey. In its central areas of coverage—event histories on labor supply, major demographic events, and child assessments—this conference concluded that the NLSY79 was well-designed and continued to be a unique resource, unduplicated in the national statistical inventory.
As these studies show, there is no other longitudinal data set available that can be utilized to address effectively the many research topics highlighted in attachment 4. This data set focuses specifically and in great detail on the employment, educational, demographic, and social-psychological characteristics of a national data set of young baby boomers and their families and measures changes in these characteristics over long time periods. It gathers this information for both men and women, as well as for relatively large samples of black and Hispanic adults. The repeated availability of this information permits consideration of employment, education, and family issues in ways not possible with any other available data set. The combination of (1) longitudinal data covering the time from adolescence; (2) national representation; (3) large black and Hispanic samples; and (4) detailed availability of education, employment and training, demographic, health, child outcome, and social-psychological variables make this data set, and its utility for social science policy-related research, unique.
In addition to the content of the interviews, the survey is also distinctive because of its coverage of the respondents’ lives for more than 25 years and the linkage between concurrently collected data on mothers and their children. It is these aspects that attract the thousands of users who rely on this survey for their studies of American workers, their careers, and their families.
References:
Citro, Constance C. and Kalton, Graham, eds. The Future of the Survey of Income and Program Participation. Washington, DC: National Academy Press, 1993.
Juster, F. Thomas and Kuester, Kathleen A. “Differences in the Measurement of Wealth, Wealth Inequality and Wealth Composition Obtained from Alternative U.S. Wealth Surveys.” Review of Income and Wealth Series 37, Number 1 (March 1991): 33-62.
Taeuber, Richard C. and Rockwell, Richard C. “National Social Data Series: A Compendium of Brief Descriptions.” Review of Public Data Use 10,1-2 (May 1982): 23-111.
5. Involvement of Small Organizations
The NLSY79 is a survey of individuals in household and family units and therefore does not involve small organizations.
6. Consequences of Less Frequent Data Collection
The core of the National Longitudinal Surveys is the focus on labor force behavior. It is very difficult to reconstruct labor force behavior retrospectively and still maintain sufficient precision and data quality. This is the single most important reason we strive to maintain regular interviews with these respondents, who on average have frequent transitions in employment, income and earnings, and family and household structure. Historic dates relating to these transitions are difficult to reconstruct when one focuses on events earlier than the recent past. For those who are employed, retrospective information on wages, detailed occupations, job satisfaction, or other employment-related characteristics cannot be easily recalled.
As with employment-related information, data about a respondent’s education and training history are also difficult to recall retrospectively. Completion dates of training and education programs are subject to severe memory biases. Thus, causal analyses that require a sequencing of education, training, and work experiences cannot be easily or accurately accomplished with historical data. Not only are completion dates of educational and training experiences frequently difficult to recall, but there is also evidence that misreporting of program completion is not unusual.
The precise timing and dating of demographic, socio-economic, and employment events, so crucial to most labor force analysis, is in most instances impossible to reconstruct accurately through retrospective data collection that extends very far into the past. For example, we have evidence from the NLS that dates of events of fundamental importance, such as marriage and birth histories, are subject to considerable error at the disaggregated level when collected retrospectively. Respondents have difficulty recalling when their marriages began or ended. Also, accurate information about household structure, how it changes over time, and how this relates to changes in family income and labor force dynamics is difficult to reconstruct retrospectively, as is the information on the health and related behaviors of the respondents, their spouses, and their children.
Finally, it is important to emphasize that information of a subjective nature can only be accurately reported and collected on a contemporaneous basis. Recollection of attitudes may be colored by subsequent experiences or reflect a rationalization of subsequent successes or failures. Attitudes as widely diverse as one’s ideas about women’s roles or how one perceives one’s health as of an earlier period can be recollected inaccurately, even when respondents are trying to be as honest as they can. In addition, the older the events that one tries to recall, either objective or subjective in nature, the greater the likelihood of faulty recall. The recall of events or attitudes is often biased either by a tendency to associate the event with major life-cycle changes (that may or may not be in temporal proximity to what one is trying to recall) or to move the event into the more recent past. The cognitive and socio-emotional information collected for the children of the NLSY79 respondents is, of course, sensitive to the age and life-cycle stage through which the particular children are progressing and, in many instances, changes over time. This is the reason why we need to repeat some of the assessments, in order to measure the extent to which the results are related to the age of the child as well as intervening family and non-family activities.
While more frequent interviewing is desirable, financial limitations prompted the NLSY79 to move to a biennial interview cycle beginning in 1994. The data loss due to reduced frequency is somewhat ameliorated by the fact that the cohort is more established, having negotiated the school-to-work transition with varying degrees of success. The NLSY79 uses bounded interviewing techniques and is designed so that when respondents miss an interview, information not collected in the missed interview is gathered in the next completed interview. In this way, the event history on work experience is very complete.
A study was conducted to assess the impact of the longer recall period by using an experimental design in the 1994 interview. About 10 percent of the respondents who were interviewed in 1993 were given a modified instrument that was worded as if the respondents were last interviewed in 1992. Using this experimental structure, we examined the respondents’ reports on experiences between the 1992 and 1993 interviews using information from their 1993 and 1994 reports on that same reference period. As expected, recall was degraded by a lower interview frequency. Events were misdated and some short duration jobs were not reported when the reference period was moved back in time. Based on this evidence, it is clear that less frequent data collection adversely affects longitudinal surveys.
A second potential problem caused by the move to a biennial interview is a decline in our ability to locate respondents who move. We have been able to compensate for this so far, but a change to less frequent interviewing would likely have a more negative impact.
7. Special Circumstances
None of the listed special circumstances apply.
8. Federal Register Notice and Consultations
One comment was received as a result of the Federal Register notice published in Volume 74, No. 70, on April 14, 2009. The Ewing Marion Kauffman Foundation, which promotes the understanding of entrepreneurship, endorsed the proposed NLSY79 questions on entrepreneurship and suggested future directions for research. Although it is too late in the process to test and implement these suggestions in this round of the survey, BLS will consider them for future rounds.
There have been numerous consultations regarding the NLSY79. Preceding the first round of the NLSY79, the Social Science Research Council sponsored a conference at which academic researchers from a broad spectrum within the social sciences were invited to present their views regarding (1) the value of initiating a longitudinal youth survey and (2) what the content of the surveys should be. The initial survey development drew heavily on the suggestions made at this conference, which were published in a proceeding under the auspices of the SSRC.
In 1988, the National Science Foundation sponsored a conference to consider the future of the NLS. This conference consisted of representatives from a variety of academic, government, and nonprofit research and policy organizations. There was enthusiastic support for the proposition that the NLS should be continued in the current format, and that the needs for longitudinal data would continue over the long run. The success of the NLS, which was the first general-purpose, longitudinal labor survey, has helped reorient survey work in the United States toward longitudinal data collection and away from simple cross sections.
Also, on a continuing basis, BLS and its contractors encourage NLS data users to (1) suggest ways in which the quality of the data can be improved and (2) suggest additional data elements that should be considered for inclusion in subsequent rounds. We encourage this feedback through the public information offices of each organization and through the quarterly NLS newsletter (available online at http://www.bls.gov/nls/nlsnews.htm).
Individuals from other Federal agencies who were consulted regarding the content of the 2010 survey include:
V. Jeffery Evans
Director of Intergenerational Research
National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
6100 Executive Boulevard, Room 8B07
Bethesda, MD 20892-7510
Yonette F. Thomas
Chief, Epidemiology Research Branch
Division of Epidemiology, Services, and Prevention Research
National Institute on Drug Abuse
6001 Executive Blvd. Room 5146
Suite 5153 MSC 9589
Bethesda, Maryland 20892-9589
The NLS program has a Technical Review Committee that advises BLS and its contractors on interview content and long-term objectives. The committee typically meets twice a year. Table 2 below shows the current members of the committee.
Table 2. National Longitudinal Surveys Technical Review Committee (2009)
David Autor |
Janet Currie |
Jeff Grogger |
Arie Kapteyn |
Annamaria
Lusardi |
Derek Neal |
Seth Sanders |
Chris Taber |
Bruce Western |
|
The NLS Technical Review Committee convened a conference in 1998 to review the current and future design of the NLSY79. This conference indicated that the central design of the NLSY79 remained strong, although changes in the nation’s welfare program required changes in the program recipiency section of the survey. Many of these changes were implemented in the 2000 and 2002 interviews. Some health section modifications were introduced in 2006 (cognitive functioning model), and the 2008 survey included a new health module for respondents who had reached age 50 (mirroring the age 40 module).
In addition to the Technical Review Committee, the decisions concerning which child outcome measures to include in the child assessment sections of the NLSY79 were carefully considered from a number of perspectives. NICHD has collaborated with BLS on the NLSY79 for many years, with NICHD providing funds for topical modules that are added on to the core interview. This collaboration reduces the total cost of data collection for the government. NICHD staff consult with experts outside NICHD to determine priorities for the modules it funds. NICHD staff and nationally recognized panels of experts jointly made the decisions about NICHD-sponsored survey topics from medicine and the social sciences.
The NICHD has also convened groups of outside experts to review the progress and content of the data collected for NICHD within the NLSY79 program. A brief description of outside experts consulted with respect to the child instruments and their affiliations may be found in table 3 below.
Table 3. Advisors and Experts Contributing to NLSY79 Child and Young Adult Surveys
Children of the NLSY79 |
||
Ann
L. Brown Joseph
Campione Joseph
Campos Lindsay
Chase-Lansdale William
E. Cross, Jr. Robert
Emery Rochel
Gelman Willard
H. Hartup Lois
Hoffman Jerome
Kagan |
Luis
M. Laosa Robert
Michael Marian
Radke-Yarrow Henry
Ricciuti Joseph
Rodgers Barbara
Starfield, M.D. Linda
Waite Kenneth
Wolpin Michael
Yogman, M.D. Nicholas
Zill |
|
Young Adults |
||
Kenneth
Wolpin Elizabeth
Menaghan Kristi
Williams James
R. Walker David
Blau |
Joe Rodgers Sandra
L. Hofferth Freya
L. Sonenstein Guang
Guo Wendy
Manning |
|
9. Payment to Respondents
Because this is a long-term study requiring the subjects to be reinterviewed regularly, respondents are offered financial incentives to secure their long-term cooperation. Respondent payments are appropriate given the long-term nature of the survey; 2010 will be the 24th round and the 31st year since the survey began. We conducted an experiment toward the end of the Round 19 (2000) field period to determine the effect of higher respondent incentives on reluctant sample members. During Round 20 (2002) we conducted an experiment that focused on cooperative sample members to determine whether respondent incentives can motivate these sample members to cooperate to a degree that significantly reduces our field costs. We documented the results of the first experiment in our clearance statement for the Round 20 field effort and the second (the Early Bird experiment) in our clearance statement for Round 21. We summarize those findings below:
Respondent incentives (Round 19) - Offering a higher incentive to reluctant sample members toward the end of the field period is cost-effective when the sample member refused to participate in the previous round. When the sample member had cooperated the previous round and the choice was between $40 and $80, we were able to convert a sufficiently high fraction of reluctant sample member by normal means and by a $40 incentive that the cost in respondent incentives per incremental case was about $270. When the sample member had refused in the previous round, in looking at the yield from $40 versus $80, an additional case cost about $133 in additional incentives. These costs per incremental case are calculated by dividing the change in total incentives paid by the change in cases interviewed for the $40 versus $80 treatments.
Early Bird Experiment (Round 20) - Offering our historically cooperative sample members a higher incentive if they called the interviewer rather than waiting for the interviewer to call the sample member was very effective in reducing field costs. This experiment allowed us to attain several months of production with fewer hours per case than we had observed in the best week in the past fifteen years. We tried both $60 and $80 treatments in this experiment. While the $60 incentive was more cost-effective, field costs were so low for both treatments that either incentive in return for cooperative behavior is highly favorable. This experiment was conducted in twelve replicates fielded sequentially. We were able to evaluate the experiment for each of the randomly selected replicates within a few weeks of mailing out the materials.
To provide perspective, toward the end of Round 20 in 2002, the weekly field costs per case were over $500. Respondent incentives represent only a fraction of the total field costs, and higher incentives can be a cost-effective means of increasing response while constraining the overall budget. We face a growing pool of sample members who are reluctant to cooperate. In this section we propose a set of measures to encourage cooperation that involve more than just higher respondent incentives.
Marketing - We have put a great deal of effort into respondent materials that describe the importance of the study. These materials are colorful, easy to read, and produced by experienced marketers. For example, in Round 20 one brochure used jellybeans as a visual theme illustrating the importance of each respondent. In Round 21, we extended this marketing approach to include the use of small in-kind gifts, which were tailored to the respondent’s needs or coordinated with the respondent materials. We plan to continue use of such small gifts in Round 24. For example, a flyer with the theme “You’re a Lifesaver” might be accompanied by a bag of Lifesaver candies.
Pulling these three strands together (respondent incentives, Early Bird promotion, and the marketing campaign), we request clearance for the following, integrated conversion strategy:
Main NLSY79:
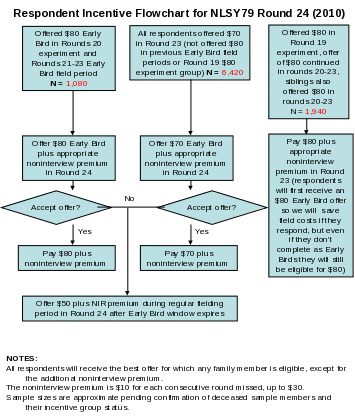
We request permission again to offer a base respondent incentive of $50, the same amount offered in Round 23 (an increase of $10 over the amount given in 2002–2006 to respondents not in one of the incentive experiment groups). Because the pretest sample is not offered the Early Bird due to the very brief field period, these respondents would receive $50 as well.
As OMB requested in past rounds, we will make an Early Bird offer to all main NLSY79 respondents. As in Round 23, we will offer an Early Bird incentive of $70 to most respondents. Some respondents have been offered an $80 Early Bird incentive in each round, since they received an $80 offer in the original 2000 experiment. Because our experience over the years indicates that respondents react negatively to decreases in incentives, we want to continue the $80 incentive for these respondents. As we have done since 2004, all main NLSY79 sample members who were in the same family in 1978 will be offered the same incentive amount.
For respondents in the $80 treatment cells in the Round 19 experiment, we request permission to continue offering $80 in the current round. Our experience indicates that offering respondents less than the previous round often results in resentment and poor cooperation, and so we continued the $80 payment for rounds 20-23.
We request permission to repeat an additional incentive payment for respondents who were not interviewed in the previous survey round(s). This is appropriate because these respondents tend to have slightly longer interviews as they catch up on previous rounds’ information. This incentive would be structured in exactly the same way as the successful noninterview premium that has been used for several rounds in the NLSY97 and in Round 23 of the NLSY79. Specifically, we would offer respondents $10 per consecutive round missed, up to $30 (3 rounds). We would be careful to inform respondents that this is a one-time additional incentive in appreciation of the additional time needed to catch up in this interview round, and that they will not receive this additional amount next round. Based on our experience in the NLSY97, we anticipate that respondents will appreciate this noninterview premium and will understand the distinction between the base amount and the additional incentive.
To avoid problems with unequal treatment within families, we will continue to offer all relatives the best deal to which any family member is entitled, except for the additional noninterview premium. Because our approach is to tie higher incentives to cooperative behavior, bringing more respondents under the Early Bird rubric will reduce our overall cost structure, hence extending higher incentives is a win-win offer for the project and respondents.
The flowchart on the following page shows the respondent incentive structure for the main NLSY79 in Round 24.
Young Adult Survey:
We request permission to offer $50 as the base incentive for young adult respondents. This is the same amount offered in Round 23.
Child Survey:
As with the main NLSY79 and Young Adult samples, we request permission to continue our 2008 payment strategy at the same amounts. Because of the three different instruments involved in the child survey and the likelihood that all instruments will not be administered at the same time, this incentive strategy involves the following payments:
We request permission to offer mothers $10 for the completion of each child interview/assessment and to give each child age 14 or younger a small toy or gift card worth not more than $10. We have found that giving a toy or gift directly to the child provides the child with encouragement and excitement to complete the survey.
We request permission to offer mothers $10 for the completion of each set of mother supplement assessments within the main NLSY79 interview. This payment would be made in conjunction with the incentive payment for the main NLSY79 interview, although we will make it clear to the respondent which portion of the money is related to the main NLSY79 interview and which is for the mother supplement(s).
We request permission to offer mothers an additional $10 for the completion of each child self-administered supplement. This is appropriate because the large additional questionnaire section represents an additional burden on children ages 10 to 14.
Cross-Sample In-Kind Incentives:
We request permission to spend no more than $5 per respondent on average, with an upper limit of $20 per case, on personalized gifts that convey the message that each respondent is special to the survey and has a unique situation that our program acknowledges and respects. For example, we may provide a small gift related to the marketing materials, or the interviewer may bring a pizza to the respondent’s house for the family dinner. Bringing dinner can be particularly effective for mothers with children in the child sample, as these interviews result in a somewhat larger time burden for the respondents. This continues our standard practice and spending limits from past rounds.
Gatekeepers:
Some “gatekeepers” are particularly helpful in tracking down reluctant sample members. For example, a parent or sibling not in the survey may provide locating information or encourage a sample member to participate. (Note that we never reveal the name of the survey to these gatekeepers; it is described simply as “a national survey.”) We often return to the same gatekeepers round after round. To maintain their goodwill, we would like to be able to offer gatekeepers who are particularly helpful a small gift worth about $5. This gift would most likely be a box of chocolates or a small plant.
In our experience, there is no such thing as a single strategy for securing respondent cooperation. The primary need is for flexibility in how we approach sample members and how we follow up with reluctant sample members. Overall, there are about 2,500 sample members who are hard to interview, either because of busy schedules or a mindset that ranges from indifference to hostility. Our Early Bird efforts attempt to reduce our total costs (incentive plus fielding costs) for cooperative sample members so that we can devote the resources necessary for difficult cases.
We reiterate that incentive payments are only part of our approach to encouraging response. An equally important part of the effort is designing an effective marketing campaign, including conversion materials that interviewers can use to respond to sample members who provide a variety of reasons for not completing the interview. This portfolio of respondent materials backs up the interviewer, providing a variety of approaches to converting refusals. We also encourage national teamwork among the interviewers and periodic calls among interviewers to share their successful “tricks of the trade” with each other that turn reluctant sample members into completed cases. Conversion materials and the ability to employ flexible respondent incentives also have important effects on interviewer morale. With a combination of a marketing campaign to “sell” the survey and the ability to personalize their approach to each respondent, interviewers will not feel they are alone and forced to deal with a difficult task of persuasion without the tools to do the job.
Locating is also a key aspect of obtaining respondent cooperation. Over the past several rounds, we have developed continuous locating strategies to keep track of sample members between interviews. For example, we monitor area code changes, which have become more frequent and play havoc with the accuracy of the phone numbers for our sample members. We review the record of calls to identify subsets of sample members for whom a particular style of advance conversion letter will respond to their particular concerns. We also will continue to include questions in the survey that solicit the views and opinions of respondents. Respondents often find such questions interesting and engaging, and the questions help to build credibility with respondents that the survey is a serious scientific and policy-related endeavor.
Our primary goal must be to continue in the good graces of the respondents. When we feel respondents are under heavy stress and suspect that additional contacts will be unproductive, we will set the case aside and try again in two years. Angering sample members is not an option in the face of their ability to screen and reject our calls. Our incentive efforts and contacting approach will continue our efforts to motivate sample members, assuage their concerns, and convey our interest in them as individuals, not numbers.
10. Confidentiality of Data
a. BLS Confidentiality Policy
The information that NLSY79 respondents provide is also protected by the Privacy Act of 1974 and the Confidential Information Protection and Statistical Efficiency Act of 2002 (CIPSEA). CIPSEA is shown in attachment 2.
The Confidential Information Protection and Statistical Efficiency Act of 2002 (CIPSEA) safeguards the confidentiality of individually identifiable information acquired under a pledge of confidentiality for exclusively statistical purposes by controlling access to, and uses made of, such information. CIPSEA includes fines and penalties for any knowing and willful disclosure of individually identifiable information by an officer, employee, or agent of the BLS.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics Commissioner's Order No. 1-06, “Confidential Nature of BLS Statistical Data,” explains the Bureau's policy on confidentiality: “In conformance with existing law and Departmental regulations, it is the policy of the BLS that respondent identifiable information collected or maintained by, or under the auspices of, the BLS for exclusively statistical purposes and under a pledge of confidentiality shall be treated in a manner that will ensure that the information will be used only for statistical purposes and will be accessible only to authorized persons.” Commissioner’s Order 1-06 is shown in attachment 3.
By signing a BLS Agent Agreement, all authorized agents employed by the BLS contractors at NORC, CHRR, and their subcontractors pledge to comply with the Privacy Act, CIPSEA, other applicable federal laws, and the BLS confidentiality policy. No interviewer or other staff member is allowed to see any case data until the BLS Agent Agreement, BLS Confidentiality Training certification, and Department of Labor Information Systems Security Awareness training certification are on file. The back of the letter that respondents receive in advance of the Round 24 interviews will show questions and answers shown about uses of the data, confidentiality, and burden.
The following confidentiality pledge is given to NLS respondents:
“We want to reassure you that your confidentiality is protected by law. In accordance with the Confidential Information Protection and Statistical Efficiency Act of 2002, the Privacy Act, and other applicable Federal laws, the Bureau of Labor Statistics, its employees and agents, will, to the full extent permitted by law, use the information you provide for statistical purposes only, will hold your responses in confidence, and will not disclose them in identifiable form without your informed consent. All the employees who work on the survey at the Bureau of Labor Statistics and its contractors must sign a document agreeing to protect the confidentiality of your information. In fact, only a few people have access to information about your identity because they need that information to carry out their job duties.
Some of your answers will be made available to researchers at the Bureau of Labor Statistics and other government agencies, universities, and private research organizations through publicly available data files. These publicly available files contain no personal identifiers, such as names, addresses, Social Security numbers, and places of work, and exclude any information about the States, counties, metropolitan areas, and other, more detailed geographic locations in which survey participants live, making it much more difficult to figure out the identities of participants. Some researchers are granted special access to data files that include geographic information, but only after those researchers go through a thorough application process at the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Those authorized researchers must sign a written agreement making them official agents of the Bureau of Labor Statistics and requiring them to protect the confidentiality of survey participants. Those researchers are never provided with the personal identities of participants. The National Archives and Records Administration and the General Services Administration may receive copies of survey data and materials because those agencies are responsible for storing the Nation’s historical documents.”
b. NORC and CHRR Confidentiality Safeguards
NORC and CHRR have safeguards to provide for the security of NLS data and the protection of the privacy of individuals in the sampled cohorts. These measures are used for the NLSY79 as well as the other NLS cohorts. Safeguards for the security of data include:
1. Storage of printed survey documents in locked space at NORC.
2. Protection of computer files at CHRR and its subcontractors against access by unauthorized individuals and groups. Procedures include using passwords, high-level “handshakes” across the network, data encryption, and fragmentation of data resources. As an example of fragmentation, should someone intercept data files over the network and defeat the encryption of these files, the meaning of the data files cannot be extracted except by referencing certain cross-walk tables that are neither transmitted nor stored on the interviewers’ laptops. Not only are questionnaire response data encrypted, but the entire contents of interviewers’ laptops are now encrypted. Interview data are periodically removed from laptops in the field so that only information that may be needed by the interviewer is retained.
3. Protection of computer files at NORC and at CHRR against access by unauthorized persons and groups. Especially sensitive files are secured through a series of passwords to restricted users. Access to files is strictly on a need-to-know basis. Passwords change every 30 days.
Protection of the privacy of individuals is accomplished through the following steps:
1. Oral permission for the interview is obtained from all respondents, after the interviewer ensures that the respondent has been provided with a copy of the appropriate BLS confidentiality information and understands that participation is voluntary.
2. Information identifying respondents is separated from the questionnaire and placed into a non-public database. Respondents are then linked to data through identification numbers.
3. After the final interview round, respondent identifier computer files will be destroyed.
4. The public-use version of the data, available on the Internet, masks data that are of sufficient specificity that individuals could theoretically be identified through some set of unique characteristics.
5. Other data files, which include variables on respondents’ State, county, metropolitan statistical area, zip code, and census tract of residence and certain other characteristics, are available only to researchers who undergo a review process established by BLS and sign an agreement with BLS that establishes specific requirements to protect respondent confidentiality. These agreements require that any results or information obtained as a result of research using the NLS data will be published only in summary or statistical form so that individuals who participated in the study cannot be identified. These confidential data are not available on the Internet.
6. Questions of a more private nature are contained in self-administered portions of the survey so the respondents’ answers are concealed both from the interviewer and anyone in the household who might overhear the interview.
7. In Round 24 we will continue several training and procedural changes to increase protection of respondent confidentiality. These include an enhanced focus on confidentiality in training materials, clearer instructions in the Field Interviewer Manual on what field interviewers may or may not do when working cases, and the introduction of formal separation procedures when interviewers complete their project assignments. Online and telephone respondent locating activities have been moved from NORC’s geographically dispersed field managers to locating staff in NORC’s central offices. Respondent social security numbers were removed from NORC and CHRR records during Round 23.
11. Sensitive Questions
Several sets of questions in the NLSY79 and Children of the NLSY79 might be considered sensitive. This section describes these questions and explains why they are a crucial part of the data collection. All of these topics have been addressed in previous rounds of the surveys, and respondents generally have been willing to answer the questions. Respondents are always free to refuse to answer any question that makes them feel uncomfortable.
NLSY79 main survey
Income and Program Participation. One major set of sensitive questions collects information about respondents’ income. The interviews record information about the sources and amounts of income received during the past calendar year by the respondent, his/her spouse or partner, or other family members. Income sources identified include the respondents’ and their spouses’ or partners’ wages and salaries, income from military service, profits from a farm or business, Social Security, pensions and annuities, and alimony/child support. These questions, or variants, have appeared in the NLSY79 since 1979. While some respondents refuse to answer these questions, our item nonresponse rate is lower than for most surveys. The survey also asks about income received by the respondent and spouse or partner from unemployment compensation, Aid to Families with Dependent Children and Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (AFDC/TANF), food stamps, Supplemental Security Income, and other public assistance programs. While questions on program participation have changed over the years, they have been in the survey for the past 20 years.
Income questions are central to the usefulness of the NLSY79 data collection. Most analyses based on the survey include some measure of the financial resources available to the respondent, either as an input variable, outcome variable, or control. It is very difficult to conceive of a replacement measure that would function in the same way in research about the returns to education, participation in the labor market, child development, and so on. The public assistance questions additionally permit research on the effects of the welfare reforms enacted in 1997, providing important information to public officials charged with overseeing the country’s public assistance programs.
In Round 24, we plan to continue the use of follow-up questions for respondents who answer “don’t know” or “refuse” to income questions. As described in a report submitted to OMB with the Round 22 clearance package, we have tested these follow-up questions to ensure that we are getting the best information possible. Based on this analysis, we implemented a hybrid approach beginning in Round 22 and plan to continue using this approach in Round 24. Briefly, respondents who answer an income question with don’t know or refuse are first asked to provide a self-generated range. Respondents who are unable to answer the self-generated intervals question then are asked unfolding bracket questions, where they are asked if the amount is more or less than a specified amount, and then more or less than a second specified amount. These unfolding brackets are a common follow-up approach in major surveys including the Health and Retirement Study. To limit any negative effects from using a hybrid follow-up, we skip potentially uncooperative respondents (for example, those giving at least one refusal in the income section) past the hybrid follow-up to subsequent refusals.
Foreclosure. Round 24 includes a series of questions on mortgage delinquencies and foreclosures. These questions were taken from the 2008 Health and Retirement Study administered by the University of Michigan Institute for Social Research. The new questions are FORECLOSURE-1_INTRO through FORECLOSURE-13. The questions cover the period since January 2007 and ask respondents whether they had been more than two months behind on mortgage payments, received a foreclosure notice, or lost property due to foreclosure.
Given the widely reported adverse conditions in the U.S. housing market in recent years, it is important from a policy standpoint to learn more about the characteristics of people who have and have not fallen behind on mortgage payments or experienced a foreclosure. The longitudinal nature of the NLSY79 makes it particularly well-suited to provide insight about the events leading up to a foreclosure, such as changes in labor force status, health, and marital status. The NLSY79 also can provide insight about what happens to households subsequent to foreclosure. The questions proposed for Round 24 also distinguish between foreclosures on owner-occupied homes and investment properties.
The NLSY79 Young Adult survey in 2010 also will include the foreclosure questions for respondents age 21 and older, thereby providing an intergenerational perspective on problems in the housing market.
Contraception. The NLSY79 includes three brief questions about contraception. Respondents are asked to report whether they have used birth control in the past month, what types they have used, and what percentage of the time they use birth control. These questions are useful in research about fertility expectations and in public health research related to unprotected sexual contact. These questions have been included in the survey for a number of years, and respondents are generally cooperative. Item nonresponse on contraception is lower than for income questions.
Cigarette and Alcohol Use. A final set of potentially sensitive survey questions is the brief series on cigarette and alcohol use. First, the Round 24 interview will include questions on smoking also asked in Round 23. These questions are whether the respondent has smoked more than 100 cigarettes in his or her life, the age the respondent began smoking daily, whether the respondent now smokes daily, the age when the respondent quit smoking, and the number of cigarettes smoked per day. These questions have been asked in several previous rounds of the survey with very low nonresponse rates.
The Round 24 survey will also include a series of four questions asking whether the respondent drank alcohol in the past 30 days, the number of days on which alcohol was consumed, the average number of drinks per day, and the number of days on which the respondent consumed 6 or more drinks (an indication of alcohol abuse). These questions are important for both economic and social research. Economists are interested in the impact that alcohol use and abuse may have on employment and earnings (for example, Dooley and Prause 1998; Kenkel and Wang 1998). Sociologists and public health researchers can use alcohol data, along with the other information collected, to examine the social and psychological impact of alcohol use and abuse.
The set of alcohol questions included in the Round 24 interviews has been asked previously in identical or similar form (the time reference period was different in the early surveys) in 1982–85, 1988, 1989, 1992, 1994, 2002, 2006, and 2008. In the earlier surveys, the questions were generally part of a longer series on alcohol use and abuse. No difficulties were encountered with these longer series in past rounds, and nonresponse is very low. For example, for the set of four questions being included this year, the largest number of respondents who refused or answered “don’t know” in 1994 was 11. No problems were experienced in Round 22 or 23 with the shorter and less intrusive set of questions, and none are expected in Round 24.
NLSY79 children/young adults
Income. Young adults (those age 15 and older) are asked a series of income questions similar to, but somewhat less detailed than, those asked of their mothers in the main interview. As described above, income data are crucial to many kinds of analysis in a variety of research fields. The young adult data additionally allow researchers to examine similarities or differences in the income sources of mothers and their children, providing information about the transmission of the ability to earn income across generations.
Foreclosure. For respondents age 21 and older, the NLSY79 Young Adult survey in 2010 will include the same questions on mortgage delinquencies and foreclosures that will be asked of their mothers in the main NLSY79. These questions were taken from the 2008 Health and Retirement Study administered by the University of Michigan Institute for Social Research. The new questions are Q15-148 through Q15-158. The questions cover the period since January 2007 and ask respondents whether they had been more than two months behind on mortgage payments, received a foreclosure notice, or lost property due to foreclosure.
Given the widely reported adverse conditions in the U.S. housing market in recent years, it is important from a policy standpoint to learn more about the characteristics of people who have and have not fallen behind on mortgage payments or experienced a foreclosure. The longitudinal nature of the NLSY79 makes it particularly well-suited to provide insight about the events leading up to a foreclosure, such as changes in labor force status, health, and marital status. The NLSY79 also can provide insight about what happens to households subsequent to foreclosure. The questions proposed for Round 24 also distinguish between foreclosures on owner-occupied homes and investment properties.
Smoking, Drug and Alcohol Use, and Criminal Activity. Children age 10 and older (including young adults) are asked about smoking, drug use, and alcohol use. These questions record whether the respondent has ever used a number of substances, including alcohol, cigarettes, marijuana, cocaine, and other drugs, and ask about the extent of the respondent’s use in the past 30 days. For young adults (age 15 and older), additional delinquent and criminal behavior questions record whether the young adult has run away from home or been convicted of criminal activities such as selling drugs, possessing drugs, theft, assault, and so on. If the respondent reports convictions, he or she is asked to describe the type of crime committed and the punishment received.
Questions about substance use and criminal behavior are crucial in understanding the education and employment outcomes of this group of young adults. To quote a report based on data from the 1990 Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services), “Patterns of tobacco, alcohol and other drug use usually are established during youth, often persist into adulthood, contribute substantially to the leading causes of mortality and morbidity, and are associated with lower educational achievement and school dropout.” One concern with long-term drug and alcohol use is the gateway effect that can occur, leading to use of heavier drugs and an increase in other risky behaviors (for example, sexual activity or criminal acts). For examples of such research, see Pacula (1997); Desimone (1998); and Parker, Harford, and Rosenstock (1994). The negative relationship between drug and alcohol use and educational attainment has been investigated by authors such as Yamada, Kendix, and Yamada (1996). Finally, as mentioned above, substance use may have a negative effect on the probability of employment and the wages and benefits received.
These sensitive questions have been asked in a nearly identical form since 1994 without difficulty. Refusals and don’t knows often have been less than 1 percent. Prior to computer-assisted administration, some respondents did not fill out the self-report booklets correctly or completely. Because these instruments are now computer-administered, starting in 2000 for the young adults and in 2002 for children under age 15, this problem has been ameliorated.
School Safety. Reflecting the growing national concern with weapons in schools, questions on this topic have been administered to adolescents in several other national surveys. Questions on whether a respondent has carried a weapon or been threatened by a weapon have been directed toward adolescents ranging in age from 12-18 in the following surveys:
The National Youth Study (Tulane, 1998)
Welfare, Children, and Families: A Three-City Study (Johns Hopkins, 2001)
NLSY97 (BLS, 1997-2004)
Youth Risk Behavior Surveys (CDC)
Other surveys have asked questions about whether young respondents carry a weapon to school for protection (Josephson Institute, 1999).
For many previous rounds, the NLSY79 Child and Young Adult surveys have included questions about the child’s attitudes and opinions regarding school, including whether the child feels safe at school. In 2002, we added two related questions that ask whether a respondent has ever seen a student with a gun, knife, or other weapon on school property and, if so, the number of times in the last year that the respondent has seen a student with a gun, knife, or other weapon on school property. These questions will continue to be asked of respondents ages 10–14 in the Child Survey and respondents attending school in the Young Adult Survey. These questions will aid researchers in investigating the presence of weapons in schools as it relates to school characteristics, neighborhood environment, child behavior, child success in school, subsequent criminal behavior, and so on.
Sexual Activity. Young adults are also asked about sexual intercourse. Because puberty and the initiation of sexual activity occur during the teenage years for many youths, and because this information may not be recalled accurately if collected retrospectively, it is important to ask these questions of respondents in this age range in each survey round. Results from a number of different surveys, including early rounds of the NLSY97, indicate that a significant proportion of adolescents report that they are sexually active. It is vital that we continue to trace the progression of sexual activity in relation to the realization of educational and occupational goals and with respect to the promotion of good health practices. The level of sexual activity and contraceptive use are important indicators of how serious young people are about reaching higher levels of educational and occupational attainment, and there should be significant congruence between anticipated life goals, sexual activity, and its associated outcomes. These questions also provide information important for analyses of programs and policies related to adolescent health and well-being.
Further, age at first intercourse is important to understanding labor market behavior because of the central role that adolescent fertility plays in the future life course of women. Early childbearing not only retards the education of the mother and hence is deleterious to her labor market opportunities but also tends to play a powerful role in the intergenerational transmission of poverty. AIDS and other sexually transmitted diseases also make sexual behavior a significant public health issue. For these reasons, this line of questioning is important to the central point of the survey.
The sensitive questions on substance use, criminal behavior, and sexual activity are only asked with the consent of a parent or guardian of a child. We inform parents about the questions we ask, and the parents and teenagers are free to refuse to answer these questions. Our experience has been that participants recognize the importance of these questions and rarely refuse to answer. To further protect respondents and encourage honest reporting, these questions are contained in a self-administered section of the interview for children ages 10–14 and for any young adults interviewed in person. Because most young adults will be interviewed on the telephone, the sensitive questions have been written in such a way that the respondent can answer the questions without revealing personal information to anyone (such as a parent) who might overhear the conversation. Although we now ask about the age of the respondent’s most recent sexual partner and his or her relationship with the respondent, no identifying information is collected about sexual partners.
Child Assessments. Attachment 7 includes a discussion of the child assessment data to be included in this survey round. For the most part these assessments are not sensitive, are well-validated, and have been asked already without difficulty or any significant respondent resistance since 1986.
Informed Consent. At OMB’s request, we conducted cognitive testing before Round 20 to determine whether children and young adults understand the informed consent statement. A report summarizing this research was submitted with the Round 20 OMB clearance package. We will continue to use the consent statement developed as a result of that research and used for the first time in Round 20.
References
Desimone, Jeffrey. “Is Marijuana a Gateway Drug?” Eastern Economic Journal 24,2 (Spring 1998): 149-163.
Dooley, David and Prause, Joann. “Underemployment and Alcohol Misuse in the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth.” Journal of Studies on Alcohol 59,6 (November 1998): 669-80.
Harford, Thomas C. and Muthen, Bengt O. “Adolescent and Young Adult Antisocial Behavior and Adult Alcohol Use Disorders: A Fourteen-Year Prospective Follow-Up in a National Survey.” Journal of Studies on Alcohol 61,4 (July 2000): 524-528.
Kenkel, Donald S. and Wang, Ping. “Are Alcoholics in Bad Jobs?” NBER Working Paper No. 6401, National Bureau of Economic Research, March 1998.
Pacula, Rosalie Liccardo. “Adolescent Alcohol and Marijuana Consumption: Is There Really a Gateway Effect?” NBER Working Paper No. 6348, National Bureau of Economic Research, January 1997.
Parker, Douglas A.; Harford, Thomas C.; and Rosenstock, Irwin M. “Alcohol, Other Drugs, and Sexual Risk-Taking among Young Adults.” Journal of Substance Abuse 6,1 (1994): 87-93.
Yamada, Tetsuji; Kendix, Michael; and Yamada, Tadashi. “The Impact of Alcohol Consumption and Marijuana Use on High School Graduation.” Health Economics 5,1 (January-February 1996): 77-92.
12. Estimation of Information Collection Burden
The NLSY79 pretest interview will be administered to approximately 100 respondents, and the average response time is about 60 minutes per respondent. The main NLSY79 interview will be administered to approximately 7,600 respondents, and the average response time also is about 60 minutes per respondent.
The time estimate for the NLSY79 Child Survey involves three components:
The Mother Supplement assessments are administered to female NLSY79 respondents who live with biological children under age 15. This section will be administered to about 635 mothers, who will be asked a series of questions about each child under age 15. On average, these women have 1.26 children under age 15, for a total number of approximately 800 children. The average response time is 20 minutes for each child or, stated alternatively, 26 minutes for each mother (20 minutes per child times 1.26 children per mother).
The Child Supplement involves testing the achievement and aptitude of about 720 children ages 4-14. The average response time for this aptitude testing is 31 minutes per child.
The Child Self-Administered Questionnaire (SAQ). The Child SAQ is administered to about 540 children ages 10–14, and the average response time is 30 minutes per child.
The Young Adult survey will be administered to approximately 6,140 respondents ages 15 to 38. These respondents will be contacted for an interview regardless of whether they reside with their mothers. The expected average response time is 45 minutes for Young Adult respondents ages 15 to 20 and 52 minutes for Young Adult respondents age 21 and older.
Reviewers should keep in mind that substantial portions of the child supplement material are only asked of small numbers of children (for example, children ages 10–14 or young adults ages 15–20). Thus, the average time in each household is not as extensive as the attached stack of survey questionnaires might suggest. We are sensitive to the fact that the interviews in households with several children can theoretically pose interviewing problems, but our experience with this material in previous rounds has clearly indicated that this is not an issue. Respondents are very interested in the child assessments and have been quite cooperative.
The projected timing for the interview is based upon data on interview length in 2008. Accurate timings are available on a section-by-section basis for each of our respondents in 1996–2008. The time required to finish an interview varies in the sample. While women with children take longer to answer the fertility and childcare questions, men are asked more questions about employment because they tend to hold more jobs. The data show the standard deviation of interview time for the main survey is around 25 minutes. The variability of the Child Survey components will be chiefly due to differences in the number and ages of children in the family.
During the field period, about 400 interviews are validated to ascertain whether the interview took place as the interviewer reported and whether the interview was done in a polite and professional manner. These reinterviews average about 6 minutes each. As mentioned earlier, we employ a number of analytical techniques in order to limit the number of validation interviews required and to target these interviews to the respondents most likely to have had a problematic experience.
Table 4 below summarizes the estimated respondent burden for Round 24 of the NLSY79.
Table 4. Number of respondents and average response time by survey questionnaire, Round 24
Instrument |
Total Respondents |
Total Responses |
Average Time per Response |
Estimated Total Burden |
NLSY79 Round 24 Pretest |
100 |
100 |
60 minutes |
100 hours |
NLSY79 Round 24 Main Survey |
7,600 |
7,600 |
60 minutes |
7,600 hours |
Round 24 Validation Interviews |
400 |
400 |
6 minutes |
40 hours |
Mother Supplement (Mothers of children under age 15) |
6351 |
800 |
20 minutes |
267 hours |
Child Supplement (Under age 15) |
720 |
720 |
31 minutes |
372 hours |
Child Self-Administered Questionnaire (Ages 10 to 14) |
540 |
540 |
30 minutes |
270 hours |
Young Adult Survey (Ages 15 to 20) |
1,775 |
1,775 |
45 minutes |
1,331 hours |
Young Adult Survey, Grant component (Age 21 and older) |
4,365 |
4,365 |
52 minutes |
3,783 hours |
TOTALS2 |
14,560 |
16,100 |
— |
13,763 hours |
1The number of respondents for the Mother Supplement (635) is less than the number of responses (800) because mothers are asked to provide separate responses for each of the biological children with whom they reside. The total number of responses for the Mother Supplement (800) is more than the number for the Child Supplement (720) because the number of children completing the Child Supplement is lower due to age restrictions and nonresponse.
2The total number of 14,560 respondents across all the survey instruments is a mutually exclusive count that does not include: (1) the 400 reinterview respondents, who were previously counted among the 7,600 main survey respondents, (2) the 635 Mother Supplement respondents, who were previously counted among the main survey respondents, and (3) the 540 Child SAQ respondents, who were previously counted among the 720 Child Supplement respondents.
13. Cost Burden to Respondents or Record Keepers
Respondents for this survey will not incur any capital and start-up costs; respondents will also not incur any operation, maintenance, or purchase-of-service costs.
14. Estimate of Cost to the Federal Government
The total estimated cost for the main NLSY79 and the associated Child and Young Adult surveys in Round 24 is $15,100,000. This cost includes survey management, questionnaire design, instrument development, pretest and main data collection including incentive payments, cleaning and preparation of data files for users, and services to users of the data files.
The BLS bears approximately $9,400,000 of this cost. The National Institute of Child Health and Human Development is expected to provide approximately $5,700,000 in funding for Round 24 through an interagency agreement with the BLS and through a grant awarded to researchers at the Ohio State University Center for Human Resource Research (CHRR). The interagency agreement funds assessments and interview with children and young adults up to age 20. The grant funds interviews of young adults age 21 and older.
15. Change in Burden
The increase in burden hours results from the reinstatement of this collection in order to conduct round 24 of the survey. The estimated total respondent burden of 13,763 hours for Round 24 is lower than the estimated burden of 14,741 hours for Round 23. The decrease can be attributed primarily to the aging of children from the longer child survey to the shorter young adult instrument, which also reduces the time needed to administer the mother supplement.
16. Plans and Time Schedule for Information Collection, Tabulation, and Publication
Following receipt of final data from NORC, approximately 9 months are then spent cleaning the data and preparing a main NLSY79 public-use data file. Subsequent to this, the child/young adult file is prepared and reports are written for the Department of Labor and the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The timing of these events is as follows:
-
Pretest Interviews
September 2009
Interviews
December 1, 2009–March 31, 2011
Data Reduction and Coding
April 1–June 30, 2011
Public-Use Data File Preparation
July 1, 2011–April 30, 2012
Release of Main NLSY79 Public-Use Data File
May 2012
Report Writing for NICHD, Release of Child/Young Adult File
Fall 2012
17. Reasons Not to Display OMB Expiration Date
The OMB number and expiration date will be provided in the advance letter.
18. Exceptions to “Certificate for Paperwork Reduction Act Submissions”
We do not have any exceptions to the “Certificate for Paperwork Reduction Act Submissions” statement.
| File Type | application/msword |
| File Title | Information Collection Request for |
| Author | Jay Meisenheimer |
| Last Modified By | rowan_c |
| File Modified | 2009-07-07 |
| File Created | 2009-06-15 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy