2310ss01
2310ss01.doc
Revisions to the RCRA Definition of Solid Waste (Final Rule)
OMB: 2050-0202
SUPPORTING STATEMENT FOR
EPA INFORMATION COLLECTION REQUEST NUMBER 2310.01
REVISIONS TO THE RCRA DEFINITION OF SOLID WASTE
(FINAL RULE)
October 28, 2008
Office of Solid Waste
United States Environmental Protection Agency
Washington, D.C. 20460
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 1
1(a) Title and Number of the Information Collection 1
2. NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION 22
2(a) Need and Authority for the Collection 22
2(b) Practical Utility and Users of the Data 30
3. NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA 35
3(d) Effects of Less Frequent Collection 39
4. THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED 40
4(a) Respondents and NAICS Codes 40
5(b) Collection Methodology and Management 90
5(c) Small Entity Flexibility 90
6. ESTIMATING THE HOUR AND COST BURDEN OF THE COLLECTION 102
6(a) Estimating Respondent Burden Hours 102
6(b) Estimating Respondent Costs 102
6(c) Estimating Agency Hour and Cost Burden 103
6(d) Estimating the Annual Respondent Universe and Total Hour and Cost Burden 103
6(e) Bottom Line Hour and Cost Burden 115
1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
1(a) Title and Number of the Information Collection
This Information Collection Request (ICR) is entitled “Revisions to the RCRA Definition of Solid Waste,” EPA ICR Number 2310.01.
1(b) Short Characterization
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has published final revisions to the definition of solid waste that exclude certain hazardous secondary materials from regulation under Subtitle C of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), as amended. Specifically, EPA has amended 40 CFR Part 261 to provide that hazardous secondary materials reclaimed under the control of the generator are not solid wastes if specified conditions are met. EPA has also amended Part 261 to provide that hazardous secondary materials that are generated and then transferred to another person for the purpose of reclamation are not solid waste, provided that specified conditions are met. In addition, EPA has established conditions for the export of excluded materials, as specified. Finally, EPA has finalized other amendments to address particular issues (e.g., it has established standards in Part 260 to enable a person to apply to EPA for a formal determination that a material is not discarded and therefore not a solid waste). The purpose of the amendments is to codify the RCRA concept of “legitimate recycling” and to respond to court decisions concerning the definition of solid waste.
In Sections 1 through 5 of this document, EPA presents a comprehensive description of the information collection requirements in the final rule. In Section 6, EPA estimates the total annual hour and cost burden to respondents associated with these new paperwork requirements. In addition, EPA estimates the total annual burden savings to generators and subsequent handlers for no longer being subject to the existing RCRA information collection requirements for the excluded materials.
In the following paragraphs, EPA describes the information collection requirements in the final rule.
CERTIFICATIONS FOR HAZARDOUS SECONDARY MATERIAL GENERATED AND RECLAIMED UNDER THE CONTROL OF THE GENERATOR
40 CFR 260.10 provides that “hazardous secondary material generated and reclaimed under the control of the generator” means: (1) that such material is generated and reclaimed at the generating facility (for purposes of this paragraph, generating facility means all contiguous property owned, leased, or otherwise controlled by the hazardous secondary material generator); or (2) that such material is generated and reclaimed at different facilities, if the reclaiming facility is controlled by the generator or if both the generating facility and the reclaiming facility are controlled by a person as defined in section 260.10, and if the generator provides one of the certifications as specified. For purposes of this paragraph, “control” means the power to direct the policies of the facility, whether by the ownership of stock, voting rights, or otherwise, except that contractors who operate facilities on behalf of a different person as defined in section 260.10 shall not be deemed to “control” such facilities; or (3) that such material is generated pursuant to a written contract between a tolling contractor and a toll manufacturer and is reclaimed by the tolling contractor, if the tolling contractor provides a certification as specified. For purposes of this paragraph, tolling contractor means a person who arranges for the production of a product or intermediate made from specified unused materials through a written contract with a toll manufacturer. Toll manufacturer means a person who produces a product or intermediate made from specified unused materials pursuant to a written contract with a tolling contractor.
NON-WASTE DETERMINATIONS
Application for Non-Waste Determination
40 CFR 260.33(a) provides that an applicant must apply to the Administrator for a variance or non-waste determination. The application must address the relevant criteria contained in section 260.31, 260.32, or 260.34, as applicable. [Note: 40 CFR 260.31 and 260.32 are existing requirements that were not affected by the final rule. Therefore, they are not addressed in this supporting statement.]
Section 260.34(a) provides that an applicant may apply to the Administrator for a formal determination that a hazardous secondary material is not discarded and therefore not a solid waste. The determinations will be based on the criteria contained in section 260.34(b) or (c), as applicable. If an application is denied, the hazardous secondary material might still be eligible for a solid waste variance or exclusion (for example, one of the solid waste variances under section 260.31). Determinations may also be granted by the State if the State is either authorized for this provision or if the specified conditions are met.
Section 260.34(b) provides that the Administrator may grant a non-waste determination for hazardous secondary material which is reclaimed in a continuous industrial process if the applicant demonstrates that the hazardous secondary material is a part of the production process and is not discarded. The determination will be based on whether the hazardous secondary material is legitimately recycled as specified in section 260.43 and on the criteria under paragraphs (b)(1)-(4).
Section 260.34(c) provides that the Administrator may grant a non-waste determination for hazardous secondary material which is indistinguishable in all relevant aspects from a product or intermediate if the applicant demonstrates that the hazardous secondary material is comparable to a product or intermediate and is not discarded. The determination will be based on whether the hazardous secondary material is legitimately recycled as specified in section 260.43 and on the criteria under paragraphs (c)(1)-(5).
Re-Application for Non-Waste Determination
40 CFR 260.33(c) applies to non-waste determinations and provides that, in the event of a change in circumstances that affects how a hazardous secondary material meets the relevant criteria contained in section 260.34 upon which a non-waste determination has been based, the applicant must re-apply to the Administrator for a formal determination that the hazardous secondary material continues to meet the relevant criteria and therefore is not a solid waste.
NOTIFICATION
40 CFR 260.42(a) provides that hazardous secondary material generators, tolling contractors, toll manufacturers, reclaimers, and intermediate facilities managing hazardous secondary materials which are excluded from regulation under section 261.2(a)(2)(ii) or section 261.4(a)(23), (24), or (25) must send a notification prior to operating under the exclusion(s) and by March 1 of each even numbered year thereafter to the Regional Administrator using EPA Form 8700-12 that includes the specified information at section 260.42(a)(1)-(10).
Section 260.42(b) provides that, if a hazardous secondary material generator, tolling contractor, toll manufacturer, reclaimer or intermediate facility has submitted a notification, but then subsequently stops managing hazardous secondary materials in accordance with the exclusion(s), the facility must notify the Regional Administrator within thirty (30) days using EPA Form 8700-12. For purposes of this section, a facility has stopped managing hazardous secondary materials if the facility no longer generates, manages and/or reclaims hazardous secondary materials under the exclusion(s) and does not expect to manage any amount of hazardous secondary materials for at least one year.
LEGITIMATE RECYCLING
40 CFR 260.43(a) provides that persons regulated under section 260.34 or claiming to be excluded from hazardous waste regulation under section 261.2(a)(2)(ii) or section 261.4(a)(23), (24), or (25) because they are engaged in reclamation must be able to demonstrate that the recycling is legitimate. Hazardous secondary material that is not legitimately recycled is discarded material and is a solid waste. In determining if their recycling is legitimate, persons must address the requirements of section 260.43(b) and must consider the requirements of section 260.43(c).
Section 260.43(b) provides that legitimate recycling must involve a hazardous secondary material that provides a useful contribution to the recycling process or to a product or intermediate of the recycling process, and the recycling process must produce a valuable product or intermediate. Section 260.43(b)(1) provides that the hazardous secondary material provides a useful contribution if it meets the specified criteria. Section 260.43(b)(2) provides that the product or intermediate is valuable if it meets the specified criteria.
Section 260.43(c) specifies the factors that must be considered in making a determination as to the overall legitimacy of a specific recycling activity.
[Note: The requirements of 40 CFR 260.43 are not information collection requirements. They are technical criteria that must be satisfied for recycling to be legitimate.]
EXCLUSIONS FROM THE DEFINITION OF SOLID WASTE
Exclusion at 40 CFR 261.2(a)(2)(ii)
40 CFR 261.2(a)(2)(ii) provides that a hazardous secondary material is not discarded if it is generated and reclaimed under the control of the generator as defined in section 260.10, it is not speculatively accumulated as defined in section 261.1(c)(8), it is handled only in non-land-based units and is contained in such units, it is generated and reclaimed within the United States and its territories, it is not otherwise subject to material-specific management conditions under section 261.4(a) when reclaimed, it is not a spent lead acid battery (see sections 266.80 and 273.2), it does not meet the listing description for K171 or K172 in section 261.32, and the reclamation of the material is legitimate, as specified under section 260.43. The notification requirements of section 260.42 also apply. For hazardous secondary materials managed in land-based units, see section 261.4(a)(23).
Exclusion at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(23)
40 CFR 261.4(a)(23) provides that hazardous secondary material generated and reclaimed within the United States or its territories and managed in land-based units as defined in section 260.10 is not a solid waste provided that: the material is contained (261.4(a)(23)(i)); the material is a hazardous secondary material generated and reclaimed under the control of the generator, as defined in section 260.10 (261.4(a)(23)(ii)); the material is not speculatively accumulated, as defined in section 261.1(c)(8) (261.4(a)(23)(iii)); the material is not otherwise subject to material-specific management conditions under section 261.4(a) when reclaimed, it is not a spent lead acid battery (see sections 266.80 and 273.2), and it does not meet the listing description for K171 or K172 in section 261.32 (261.4(a)(23)(iv)); and the reclamation of the material is legitimate, as specified under section 260.43 (261.4(a)(23)(v)). In addition, persons claiming the exclusion under section 261.4(a)(23) must provide notification as required by section 260.42 (261.4(a)(23)(vi)). For hazardous secondary materials managed in a non-land-based unit, see section 261.2(a)(2)(ii).
Exclusion at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(24)
40 CFR 261.4(a)(24) provides that hazardous secondary material that is generated and then transferred to another person for the purpose of reclamation is not a solid waste, provided that the requirements of section 261.4(a)(24)(i)-(vii) are met. Section 261.4(a)(24)(i)-(iv) sets forth technical standards applicable to the material (e.g., requirements for handling the material).
Section 261.4(a)(24)(v) provides that the hazardous secondary material generator must satisfy the conditions of section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(A)-(E). Section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(A) provides that the material must be contained. Section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(B) provides that, prior to arranging for transport of hazardous secondary materials to a reclamation facility (or facilities) where the management of the hazardous secondary materials is not addressed under a RCRA Part B permit or interim status standards, the hazardous secondary material generator must make reasonable efforts to ensure that each reclaimer intends to properly and legitimately reclaim the hazardous secondary material and not discard it, and that each reclaimer will manage the hazardous secondary material in a manner that is protective of human health and the environment. If the hazardous secondary material will be passing through an intermediate facility where the management of the hazardous secondary materials is not addressed under a RCRA Part B permit or interim status standards, the hazardous secondary material generator must make contractual arrangements with the intermediate facility to ensure that the hazardous secondary material is sent to the reclamation facility identified by the hazardous secondary material generator, and the hazardous secondary material generator must perform reasonable efforts to ensure that the intermediate facility will manage the hazardous secondary material in a manner that is protective of human health and the environment. Reasonable efforts must be repeated at a minimum of every three years for the hazardous secondary material generator to claim the exclusion and to send the hazardous secondary materials to each reclaimer and any intermediate facility. In making these reasonable efforts, the generator may use any credible evidence available, including information gathered by the hazardous secondary material generator, provided by the reclaimer or intermediate facility, and/or provided by a third party. Section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(C) provides that the hazardous secondary material generator must maintain for a minimum of three years documentation and certification that reasonable efforts were made for each reclamation facility and, if applicable, intermediate facility where the management of the hazardous secondary materials is not addressed under a RCRA Part B permit of interim status standards prior to transferring hazardous secondary material. Documentation and certification must be made available upon request by a regulatory authority within 72 hours, or within a longer period of time as specified by the regulatory authority. Section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(D) provides that the hazardous secondary material generator must maintain at the generating facility for no less than three (3) years records of all off-site shipments of hazardous secondary materials. Section 261.4(a)(v)(E) provides that the hazardous secondary material generator must maintain at the generating facility for no less than three (3) years confirmations of receipt from each reclaimer and, if applicable, each intermediate facility for all off-site shipments of hazardous secondary materials.
Section 261.4(a)(24)(vi) provides that reclaimers of hazardous secondary material excluded from regulation under this exclusion and intermediate facilities as defined in section 260.10 must satisfy the conditions of section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(A)-(F). Section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(A) provides that the reclaimer and intermediate facility must maintain at its facility for no less than three (3) years records of all shipments of hazardous secondary material that were received at the facility and, if applicable, for all shipments of hazardous secondary materials that were received and subsequently sent off-site from the facility for further reclamation. Section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(B) provides that the intermediate facility must send the hazardous secondary material to the reclaimer(s) designated by the hazardous secondary materials generator. Section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(C) provides that the reclaimer and intermediate facility must send to the hazardous secondary material generator confirmations of receipt for all off-site shipments of hazardous secondary materials. Section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(D) and (E) provides technical standards for the management of hazardous secondary material and residuals from reclamation. Section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F) provides that the reclaimer and intermediate facility must have financial assurance as required under Subpart H of 40 CFR Part 261.
Section 261.4(a)(24)(vii) provides that all persons claiming the exclusion under section 261.4(a)(24) must provide notification as required under section 260.42.
Export Requirements at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(25)
40 CFR 261.4(a)(25) provides that hazardous secondary material that is exported from the United States and reclaimed at a reclamation facility located in a foreign country is not a solid waste, provided that the hazardous secondary material generator complies with the applicable requirements of section 261.4(a)(24)(i)-(v) (excepting section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(B)(2) for foreign reclaimers and foreign intermediate facilities), and that the hazardous secondary material generator also complies with the conditions in section 261.4(a)(25).
Section 261.4(a)(25)(i) provides that the hazardous secondary material generator must notify EPA of an intended export before the hazardous secondary material is scheduled to leave the United States. A complete notification must be submitted at least sixty (60) days before the initial shipment is intended to be shipped off-site. This notification may cover export activities extending over a twelve (12) month or lesser period. Section 261.4(a)(25)(ii) sets forth addresses for submittal of notifications and provides that the following shall be prominently displayed on the front of the envelope: “Attention: Notification of Intent to Export.” Section 261.4(a)(25)(iii) provides that, except for changes to the telephone number in paragraph (i)(A) of this section and decreases in the quantity of hazardous secondary material indicated pursuant to paragraph (i)(D) of this section, when the conditions specified on the original notification change (including any exceedance of the estimate of the quantity of hazardous secondary material specified in the original notification), the hazardous secondary material generator must provide EPA with a written renotification of the change. The shipment cannot take place until consent of the receiving country to the changes (except for changes to paragraph (i)(I) of this section and in the ports of entry to and departure from transit countries pursuant to paragraph (i)(E) of this section) has been obtained and the hazardous secondary material generator receives from EPA an Acknowledgment of Consent reflecting the receiving country’s consent to the changes. Section 261.4(a)(25)(iv) provides that, upon request by EPA, the hazardous secondary material generator shall furnish to EPA any additional information which a receiving country requests in order to respond to a notification.
Section 261.4(a)(25)(v) describes procedures for EPA to notify the receiving country and any transit countries. Section 261.4(a)(25)(vi) sets forth provisions for the consent, objection, and withdrawal of prior consent of an intended export shipment by a receiving country. Section 261.4(a)(25)(vii) provides that, for exports to OECD Member countries, the receiving country may respond to the notification using tacit consent. If no objection has been lodged by any receiving country or transit countries to a notification provided pursuant to paragraph (i) of this section within thirty (30) days after the date of issuance of the acknowledgement of receipt of notification by the competent authority of the receiving country, the transboundary movement may commence. In such cases, EPA will send an Acknowledgement of Consent to inform the hazardous secondary material generator that the receiving country and any relevant transit countries have not objected to the shipment, and are thus presumed to have consented tacitly. Tacit consent expires one (1) calendar year after the close of the thirty (30) day period; renotification and renewal of all consents is required for exports after that date.
Section 261.4(a)(25)(viii) provides that a copy of the Acknowledgment of Consent must accompany the shipment. The shipment must conform to the terms of the Acknowledgment of Consent. Section 261.4(a)(25)(ix) provides that, if a shipment cannot be delivered for any reason to the reclaimer, intermediate facility or the alternate reclaimer or alternate intermediate facility, the hazardous secondary material generator must re-notify EPA of a change in the conditions of the original notification to allow shipment to a new reclaimer in accordance with paragraph (iii) of this section and obtain another Acknowledgment of Consent. Section 261.4(a)(25)(x) provides that hazardous secondary material generators must keep a copy of each notification of intent to export and each Acknowledgment of Consent for a period of three years following receipt of the Acknowledgment of Consent. Section 261.4(a)(25)(xi) provides that hazardous secondary material generators must file with the Administrator no later than March 1 of each year, a report summarizing the types, quantities, frequency and ultimate destination of all hazardous secondary materials exported during the previous calendar year. Such reports must include the information in section 261.4(a)(25)(xi)(A)-(E).
Section 261.4(a)(25)(xii) provides that all persons claiming an exclusion under section 261.4(a)(25) must provide notification as required by section 260.42.
FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS FOR MANAGEMENT OF EXCLUDED HAZARDOUS SECONDARY MATERIALS
40 CFR 261.140(a) provides that the requirements of 40 CFR Part 261 Subpart H, “Financial Requirements for Management of Excluded Hazardous Secondary Materials,” apply to owners or operators of reclamation and intermediate facilities managing hazardous secondary materials excluded under 40 CFR 261.4(a)(24), except as provided otherwise. Section 261.140(b) provides that States and the Federal government are exempt from the financial assurance requirements of the subpart.
Cost Estimate
40 CFR 261.142(a) requires owners or operators to have a detailed written estimate, in current dollars, of the cost of disposing of any hazardous secondary material as listed or characteristic hazardous waste, and the potential cost of closing the facility as a treatment, storage, and disposal facility. The cost estimate must satisfy the requirements of section 261.142(a)(1)-(4).
Section 261.142(b) requires that, during the active life of the facility, the owner or operator must adjust the cost estimate for inflation within 60 days prior to the anniversary date of the establishment of the financial instrument(s) used to comply with section 261.143. For owners or operators using the financial test or corporate guarantee, the cost estimate must be updated for inflation within 30 days after the close of the firm's fiscal year and before submission of updated information to the Regional Administrator as specified in section 261.143(e)(3).
Section 261.142(c) provides that, during the active life of the facility, the owner or operator must revise the cost estimate no later than 30 days after a change in a facility’s operating plan or design that would increase the costs of conducting the activities described in section 261.142(a) or no later than 60 days after an unexpected event which increases the cost of conducting the activities described in section 261.142(a). The revised cost estimate must be adjusted for inflation as specified in section 261.142(b).
Section 261.142(d) requires the owner or operator to keep the following at the facility during the operating life of the facility: The latest cost estimate prepared in accordance with section 261.142(a) and (c) and, when this estimate has been adjusted in accordance with section 261.142(b), the latest adjusted cost estimate.
Financial Assurance Condition
Per 40 CFR 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F), an owner or operator of a reclamation or intermediate facility must have financial assurance as a condition of the exclusion as required under section 261.4(a)(24). He must choose from the options as specified in section 261.143(a) through (e).
(1) Trust Fund
40 CFR 261.143(a)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by establishing a trust fund which conforms to the requirements of this paragraph and submitting an originally signed duplicate of the trust agreement to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(a)(2) provides that the wording of the trust agreement must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(a)(1), and the trust agreement must be accompanied by a formal certification of acknowledgment. Schedule A of the trust agreement must be updated within 60 days after a change in the amount of the current cost estimate covered by the agreement. Section 261.143(a)(3) provides that the trust fund must be funded for the full amount of the current cost estimate before it may be relied upon to satisfy the requirements of this section. Section 261.143(a)(4) provides that, whenever the current cost estimate changes, the owner or operator must compare the new estimate with the trustee's most recent annual valuation of the trust fund. If the value of the fund is less than the amount of the new estimate, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the change in the cost estimate, must either deposit an amount into the fund so that its value after this deposit at least equals the amount of the current cost estimate, or obtain other financial assurance as specified in this section to cover the difference. Section 261.143(a)(5) provides that, if the value of the trust fund is greater than the total amount of the current cost estimate, the owner or operator may submit a written request to the Regional Administrator for release of the amount in excess of the current cost estimate. Section 261.143(a)(6) provides that, if an owner or operator substitutes other financial assurance as specified in this section for all or part of the trust fund, he may submit a written request to the Regional Administrator for release of the amount in excess of the current cost estimate covered by the trust fund. Section 261.143(a)(7) provides that, within 60 days after receiving a request from the owner or operator for release of funds as specified, the Regional Administrator will instruct the trustee to release to the owner or operator such funds as the Regional Administrator specifies in writing. If the owner or operator begins final closure under Subpart G of 40 CFR Part 264 or 265, an owner or operator may request reimbursements for partial or final closure expenditures by submitting itemized bills to the Regional Administrator. The owner or operator may request reimbursements for partial closure only if sufficient funds are remaining in the trust fund to cover the maximum costs of closing the facility over its remaining operating life. Section 261.143(a)(8) describes EPA procedures for termination of the trust.
(2) Surety Bond Guaranteeing Payment into a Trust Fund
40 CFR 261.143(b)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by obtaining a surety bond which conforms to the requirements of this paragraph and submitting the bond to the Regional Administrator. The surety company issuing the bond must, at a minimum, be among those listed as acceptable sureties on Federal bonds in Circular 570 of the U.S. Department of the Treasury. Section 261.143(b)(2) requires the wording of the surety bond to be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(b). Section 261.143(b)(3) provides that the owner or operator who uses a surety bond to satisfy the requirements of this section must also establish a standby trust fund. This standby trust fund must meet the requirements specified in section 261.143(a), except as otherwise specified. Section 261.143(b)(4) provides that the bond must make specified guarantees. Section 261.143(b)(5) and (6) describe standards related to the owner or operator’s failure to perform as guaranteed and the penal sum amount. Section 261.143(b)(7) provides that, whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the penal sum, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the penal sum to be increased to an amount at least equal to the current cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Regional Administrator, or obtain other financial assurance as specified in this section to cover the increase. Whenever the current cost estimate decreases, the penal sum may be reduced to the amount of the current cost estimate following written approval by the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(b)(8) provides that, under the terms of the bond, the surety may cancel the bond by sending notice of cancellation by certified mail to the owner or operator and to the Regional Administrator. Cancellation may not occur, however, during the 120 days beginning on the date of receipt of the notice of cancellation by both the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator, as evidenced by the return receipts. Section 261.143(b)(9) provides that the owner or operator may cancel the bond if the Regional Administrator has given prior written consent based on his receipt of evidence of alternate financial assurance as specified in this section.
(3) Letter of Credit
40 CFR 261.143(c)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by obtaining an irrevocable standby letter of credit which conforms to the requirements of this paragraph and submitting the letter to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(c)(2) provides that the wording of the letter of credit must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(c). Section 261.143(c)(3) provides that an owner or operator who uses a letter of credit to satisfy the requirements of this section must also establish a standby trust fund, as specified. This standby trust fund must meet the requirements of the trust fund specified in section 261.143(a), except as otherwise specified. An originally signed duplicate of the trust agreement must be submitted to the Regional Administrator with the letter of credit. Section 261.143(c)(4) provides that the letter of credit must be accompanied by a letter from the owner or operator, referring to the letter of credit as specified. Section 261.143(c)(5) provides that the letter of credit must be irrevocable and issued for a period of at least 1 year. The letter of credit must provide that the expiration date will be automatically extended for a period of at least 1 year unless, at least 120 days before the current expiration date, the issuing institution notifies both the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator by certified mail of a decision not to extend the expiration date. Section 261.143(c)(6) specifies that the letter of credit must be issued in an amount at least equal to the current cost estimate, except as provided in section 261.143(f). Section 261.143(c)(7) provides that, whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the amount of the credit, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the amount of the credit to be increased so that it at least equals the current cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Regional Administrator, or obtain other financial assurance as specified in this section to cover the increase. Whenever the current cost estimate decreases, the amount of the credit may be reduced to the amount of the current cost estimate following written approval by the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(c)(8) provides that, following a determination by the Regional Administrator that the hazardous secondary materials do not meet the conditions of the exclusion under section 261.4(a)(24), the Regional Administrator may draw on the letter of credit. Section 261.143(c)(9) provides that, if the owner or operator does not establish alternate financial assurance as specified in this section and obtain written approval of such alternate assurance from the Regional Administrator within 90 days after receipt by both the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator of a notice from the issuing institution that it has decided not to extend the letter of credit beyond the current expiration date, the Regional Administrator will draw on the letter of credit. The Regional Administrator may delay the drawing if the issuing institution grants an extension of the term of the credit. During the last 30 days of any such extension the Regional Administrator will draw on the letter of credit if the owner or operator has failed to provide alternate financial assurance as specified in this section and obtain written approval of such assurance from the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(c)(10) addresses the return of the letter of credit by EPA to the issuing institution for termination.
(4) Insurance
40 CFR 261.143(d)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by obtaining insurance which conforms to the requirements of this paragraph and submitting a certificate of such insurance to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(d)(2) provides that the wording of the certificate of insurance must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(d). Section 261.143(d)(3) provides that the insurance policy must be issued for a face amount at least equal to the current cost estimate, except as provided in section 261.143(f). Section 261.143(d)(4) provides that the insurance policy must make specified guarantees. Section 261.143(d)(5) provides that, after beginning partial or final closure under 40 CFR Part 264 or 265, as applicable, an owner or operator or any other authorized person may request reimbursements for closure expenditures by submitting itemized bills to the Regional Administrator, in accordance with specified standards. Section 261.143(d)(6) provides that the owner or operator must maintain the policy in full force and effect until the Regional Administrator consents to termination of the policy by the owner or operator as specified in paragraph (i)(10) of this section. Failure to pay the premium, without substitution of alternate financial assurance as specified in this section, will constitute a significant violation of these regulations, warranting such remedy as the Regional Administrator deems necessary. Such violation will be deemed to begin upon receipt by the Regional Administrator of a notice of future cancellation, termination, or failure to renew due to nonpayment of the premium, rather than upon the date of expiration. Section 261.143(d)(7) provides that each policy must contain a provision allowing assignment of the policy to a successor owner or operator. Such assignment may be conditional upon consent of the insurer, provided such consent is not unreasonably refused. Section 261.143(d)(8) provides that the policy must provide that the insurer may not cancel, terminate, or fail to renew the policy except for failure to pay the premium. The automatic renewal of the policy must, at a minimum, provide the insured with the option of renewal at the face amount of the expiring policy. If there is a failure to pay the premium, the insurer may elect to cancel, terminate, or fail to renew the policy by sending notice by certified mail to the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator. Cancellation, termination, or failure to renew may not occur, however, during the 120 days beginning with the date of receipt of the notice by both the Regional Administrator and the owner or operator, as evidenced by the return receipts. Cancellation, termination, or failure to renew may not occur and the policy will remain in full force and effect as specified. Section 261.143(d)(9) provides that, whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the face amount of the policy, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the face amount to be increased to an amount at least equal to the current cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Regional Administrator, or obtain other financial assurance as specified in this section to cover the increase. Whenever the current cost estimate decreases, the face amount may be reduced to the amount of the current cost estimate following written approval by the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(d)(10) provides that the Regional Administrator will give written consent to the owner or operator that he may terminate the insurance policy as specified.
(5) Financial Test and Corporate Guarantee
40 CFR 261.143(e)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by demonstrating that he passes a financial test as specified in this paragraph. To pass this test the owner or operator must meet the criteria of either section 261.143(e)(1)(i) or (ii). Section 261.143(e)(2) defines phrases used in the regulations. Section 261.143(e)(3) provides that, to demonstrate that he meets this test, the owner or operator must submit specified items to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(e)(4) provides that the owner or operator may obtain an extension of the time allowed for submission of the documents specified in paragraph (e)(3) of this section if the fiscal year of the owner or operator ends during the 90 days prior to the effective date of these regulations and if the year-end financial statements for that fiscal year will be audited by an independent certified public accountant. The extension will end no later than 90 days after the end of the owner's or operator's fiscal year. To obtain the extension, the owner's or operator's chief financial officer must send, by the effective date of these regulations, a letter to the Regional Administrator of each Region in which the owner's or operator's facilities to be covered by the financial test are located. Section 261.143(e)(5) provides that, after the initial submission of items specified in paragraph (e)(3) of this section, the owner or operator must send updated information to the Regional Administrator within 90 days after the close of each succeeding fiscal year. This information must consist of all three items specified in paragraph (e)(3) of this section. Section 261.143(e)(6) provides that, if the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of paragraph (e)(1) of this section, he must send notice to the Regional Administrator of intent to establish alternate financial assurance as specified in this section. The notice must be sent by certified mail within 90 days after the end of the fiscal year for which the year-end financial data show that the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements. The owner or operator must provide the alternate financial assurance within 120 days after the end of such fiscal year. Section 261.143(e)(7) provides that the Regional Administrator may, based on a reasonable belief that the owner or operator may no longer meet the requirements of paragraph (e)(1) of this section, require reports of financial condition at any time from the owner or operator in addition to those specified in paragraph (e)(3) of this section. If the Regional Administrator finds, on the basis of such reports or other information, that the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of paragraph (e)(1) of this section, the owner or operator must provide alternate financial assurance as specified in this section within 30 days after notification of such a finding. Section 261.143(e)(8) provides that the Regional Administrator may disallow use of this test on the basis of qualifications in the opinion expressed by the independent certified public accountant in his report on examination of the owner's or operator's financial statements (see paragraph (e)(3)(ii) of this section). An adverse opinion or a disclaimer of opinion will be cause for disallowance. The Regional Administrator will evaluate other qualifications on an individual basis. The owner or operator must provide alternate financial assurance as specified in this section within 30 days after notification of the disallowance. Section 261.143(e)(9) describes circumstances when the owner or operator is no longer required to submit the items specified in paragraph (e)(3) of this section. Section 261.143(e)(10) provides that an owner or operator may meet the requirements of this section by obtaining a written guarantee. The guarantor must meet the requirements for owners or operators in paragraphs (e)(1) through (8) of this section and must comply with the terms of the guarantee. The wording of the guarantee must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(g)(1). A certified copy of the guarantee must accompany the items sent to the Regional Administrator as specified in paragraph (e)(3) of this section. One of these items must be the letter from the guarantor's chief financial officer, as described in section 261.143(e)(10).
Use of Financial Mechanisms for Multiple Facilities
40 CFR 261.143(g) provides for the use of a financial mechanism for multiple facilities. An owner or operator may use a financial assurance mechanism specified in this section to meet the requirements of this section for more than one facility. Evidence of financial assurance submitted to the Regional Administrator must include a list showing, for each facility, the EPA Identification Number (if any issued), name, address, and the amount of funds assured by the mechanism. If the facilities covered by the mechanism are in more than one Region, identical evidence of financial assurance must be submitted to and maintained with the Regional Administrators of all such Regions. The amount of funds available through the mechanism must be no less than the sum of funds that would be available if a separate mechanism had been established and maintained for each facility. In directing funds available through the mechanism for any of the facilities covered by the mechanism, the Regional Administrator may direct only the amount of funds designated for that facility, unless the owner or operator agrees to the use of additional funds available under the mechanism.
Removal and Decontamination Plan and Release from Financial Assurance Obligations
40 CFR 261.143(h)(1) provides that an owner or operator of a reclamation facility or an intermediate facility who wishes to be released from his financial assurance obligations under section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F) must submit a plan for removing all hazardous secondary material residues to the Regional Administrator at least 180 days prior to the date on which he expects to cease to operate under the exclusion. Section 261.143(h)(2) spells out the contents of the plan. Section 261.143(h)(3) provides that the Regional Administrator will provide the owner or operator and the public, through a newspaper notice, the opportunity to submit written comments on the plan and request modifications to the plan no later than 30 days from the date of the notice. He will also, in response to a request or at his discretion, hold a public hearing whenever such a hearing might clarify one or more issues concerning the plan. The Regional Administrator will give public notice of the hearing at least 30 days before it occurs. The Regional Administrator will approve, modify, or disapprove the plan within 90 days of its receipt. If the Regional Administrator does not approve the plan, he shall provide the owner or operator with a detailed written statement of reasons for the refusal and the owner or operator must modify the plan or submit a new plan for approval within 30 days after receiving such written statement. The Regional Administrator will approve or modify this plan in writing within 60 days. If the Regional Administrator modifies the plan, this modified plan becomes the approved plan. The Regional Administrator must assure that the approved plan is consistent with applicable requirements. A copy of the modified plan with a detailed statement of reasons for the modifications must be mailed to the owner or operator. Section 261.143(h)(4) provides that, within 60 days of completion of the activities described for each hazardous secondary materials management unit, the owner or operator must submit to the Regional Administrator, by registered mail, a certification that all hazardous secondary materials have been removed from the unit and the unit has been decontaminated in accordance with the specifications in the approved plan. The certification must be signed by the owner or operator and by a qualified Professional Engineer. Documentation supporting the Professional Engineer's certification must be furnished to the Regional Administrator, upon request, until he releases the owner or operator from the financial assurance requirements for section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F).
Section 261.143(i) provides that, within 60 days after receiving certifications from the owner or operator and a qualified Professional Engineer that all hazardous secondary materials have been removed from the facility or a unit at the facility and the facility or a unit has been decontaminated in accordance with the approved plan per paragraph (h), the Regional Administrator will notify the owner or operator in writing that he is no longer required under section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F) to maintain financial assurance for that facility or a unit at the facility, unless the Regional Administrator has reason to believe that that all hazardous secondary materials have not been removed from the facility or unit at a facility or that the facility or unit has not been decontaminated in accordance with the approved plan. The Regional Administrator will provide the owner or operator a detailed written statement of any such reason to believe that all hazardous secondary materials have not been removed from the unit or that the unit has not been decontaminated in accordance with the approved plan.
Coverage for Sudden and Non-Sudden Accidental Occurrences
40 CFR 261.147(a) provides that an owner or operator of a hazardous secondary material reclamation facility or an intermediate facility subject to financial assurance requirements under section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F), or a group of such facilities, must demonstrate financial responsibility for bodily injury and property damage to third parties caused by sudden accidental occurrences arising from operations of the facility or group of facilities. Section 261.147(b) provides that an owner or operator of a hazardous secondary material reclamation facility or intermediate facility with land-based units, as defined in section 260.10, which are used to manage hazardous secondary materials excluded under section 261.4(a)(24), or a group of such facilities, must demonstrate financial responsibility for bodily injury and property damage to third parties caused by nonsudden accidental occurrences arising from operations of the facility or group of facilities. The owner or operator must have and maintain liability coverage for sudden and nonsudden accidental occurrences in the amounts specified in the regulations. This liability coverage may be demonstrated as specified in section 261.147(a)(1), (2), (3), (4), (5), or (6) for sudden accidental occurrences and section 261.147(b)(1), (2), (3), (4), (5), or (6) for nonsudden accidental occurrences.
(1) Liability Insurance
40 CFR 261.147(a)(1) and (b)(1) provides that an owner or operator may demonstrate the required liability coverage by having liability insurance for sudden and nonsudden accidental occurrences, as specified in section 261.147(a)(1) and (b)(1), respectively. Section 261.147(a)(1)(i) and (b)(1)(i) require that each insurance policy must be amended by attachment of the Hazardous Secondary Material Facility Liability Endorsement, or evidenced by a Certificate of Liability Insurance. The wording of the endorsement must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(h). The wording of the certificate of insurance must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(i). The owner or operator must submit a signed duplicate original of the endorsement or the certificate of insurance to the Regional Administrator, or Regional Administrators if the facilities are located in more than one Region. If requested by a Regional Administrator, the owner or operator must provide a signed duplicate original of the insurance policy. Section 261.147(a)(1)(ii) and (b)(1)(ii) provide that each insurance policy must be issued by an insurer which, at a minimum, is licensed to transact the business of insurance, or eligible to provide insurance as an excess or surplus lines insurer, in one or more States.
(2) Financial Test or Guarantee
40 CFR 261.147(a)(2) and (b)(2) provide that an owner or operator may meet the requirements of this section by passing a financial test or using the guarantee for liability coverage as specified in section 261.147(f) and (g).
Section 261.147(f)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by demonstrating that he passes a financial test as specified in this paragraph. To pass this test the owner or operator must meet the criteria of paragraph (f)(1)(i) or (ii) of this section. Section 261.147(f)(2) defines phrases used in the regulations. Section 261.147(f)(3) provides that, to demonstrate that he meets this test, the owner or operator must submit the specified items to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.147(f)(4) provides that the owner or operator may obtain a one-time extension of the time allowed for submission of the documents specified in paragraph (f)(3) of this section if the fiscal year of the owner or operator ends during the 90 days prior to the effective date of these regulations and if the year-end financial statements for that fiscal year will be audited by an independent certified public accountant. The extension will end no later than 90 days after the end of the owner's or operator's fiscal year. To obtain the extension, the owner's or operator's chief financial officer must send, by the effective date of these regulations, a letter to the Regional Administrator of each Region in which the owner's or operator's facilities to be covered by the financial test are located. Section 261.147(f)(5) provides that, after the initial submission of items specified in paragraph (f)(3) of this section, the owner or operator must send updated information to the Regional Administrator within 90 days after the close of each succeeding fiscal year. This information must consist of all three items specified in paragraph (f)(3) of this section. Section 261.147(f)(6) provides that, if the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of paragraph (f)(1) of this section, he must obtain insurance, a letter of credit, a surety bond, a trust fund, or a guarantee for the entire amount of required liability coverage as specified in this section. Evidence of liability coverage must be submitted to the Regional Administrator within 90 days after the end of the fiscal year for which the year-end financial data show that the owner or operator no longer meets the test requirements. Section 261.147(f)(7) provides that the Regional Administrator may disallow use of this test on the basis of qualifications in the opinion expressed by the independent certified public accountant in his report on examination of the owner's or operator's financial statements (see paragraph (f)(3)(ii) of this section). An adverse opinion or a disclaimer of opinion will be cause for disallowance. The Regional Administrator will evaluate other qualifications on an individual basis. The owner or operator must provide evidence of insurance for the entire amount of required liability coverage as specified in this section within 30 days after notification of disallowance.
Section 261.147(g)(1) provides that, subject to paragraph (g)(2) of this section, an owner or operator may meet the requirements of this section by obtaining a written guarantee, hereinafter referred to as “guarantee.” The guarantor must be the direct or higher-tier parent corporation of the owner or operator, a firm whose parent corporation is also the parent corporation of the owner or operator, or a firm with a “substantial business relationship” with the owner or operator. The guarantor must meet the requirements for owners or operators in paragraphs (f)(1) through (f)(6) of this section. The wording of the guarantee must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(g)(2). A certified copy of the guarantee must accompany the items sent to the Regional Administrator as specified in paragraph (f)(3) of this section. One of these items must be the letter from the guarantor's chief financial officer. Section 261.147(g)(2)(i) provides that, in the case of corporations incorporated in the United States, a guarantee may be used to satisfy the requirements of this section only if the Attorneys General or Insurance Commissioners of (A) the State in which the guarantor is incorporated, and (B) each State in which a facility covered by the guarantee is located have submitted a written statement to EPA that a guarantee executed as described in this section and section 264.151(g)(2) is a legally valid and enforceable obligation in that State. Section 261.147(g)(2)(ii) provides that, in the case of corporations incorporated outside the United States, a guarantee may be used to satisfy the requirements of this section only if (A) the non-U.S. corporation has identified a registered agent for service of process in each State in which a facility covered by the guarantee is located and in the State in which it has its principal place of business, and if (B) the Attorney General or Insurance Commissioner of each State in which a facility covered by the guarantee is located and the State in which the guarantor corporation has its principal place of business, has submitted a written statement to EPA that a guarantee executed as described in this section and section 261.151(h)(2) is a legally valid and enforceable obligation in that State.
(3) Letter of Credit
40 CFR 261.147(a)(3) and (b)(3) provide that an owner or operator may meet the requirements of this section by obtaining a letter of credit for liability coverage as specified in section 261.147(h).
Section 261.147(h)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by obtaining an irrevocable standby letter of credit that conforms to the requirements of this paragraph and submitting a copy of the letter of credit to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.147(h)(2) provides that the financial institution issuing the letter of credit must be an entity that has the authority to issue letters of credit and whose letter of credit operations are regulated and examined by a Federal or State agency. Section 261.147(h)(3) provides that the wording of the letter of credit must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(j). Section 261.147(h)(4) provides that an owner or operator who uses a letter of credit to satisfy the requirements of this section may also establish a standby trust fund. Under the terms of such a letter of credit, all amounts paid pursuant to a draft by the trustee of the standby trust will be deposited by the issuing institution into the standby trust in accordance with instructions from the trustee. The trustee of the standby trust fund must be an entity which has the authority to act as a trustee and whose trust operations are regulated and examined by a Federal or State agency. Section 261.147(h)(5) provides that the wording of the standby trust fund must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(m).
(4) Surety Bond for Liability Coverage
40 CFR 261.147(a)(4) and (b)(4) provide that an owner or operator may meet the requirements of this section by obtaining a surety bond for liability coverage as specified in section 261.147(i).
Section 261.147(i)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by obtaining a surety bond that conforms to the requirements of this paragraph and submitting a copy of the bond to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.147(i)(2) provides that the surety company issuing the bond must be among those listed as acceptable sureties on Federal bonds in the most recent Circular 570 of the U.S. Department of the Treasury. Section 261.147(i)(3) provides that the wording of the surety bond must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(k). Section 261.147(i)(4) provides that a surety bond may be used to satisfy the requirements of this section only if the Attorneys General or Insurance Commissioners of (i) the State in which the surety is incorporated, and (ii) each State in which a facility covered by the surety bond is located have submitted a written statement to EPA that a surety bond executed as described in this section and section 261.151(k) is a legally valid and enforceable obligation in that State.
(5) Trust Fund
40 CFR 261.147(a)(5) and (b)(5) provide that an owner or operator may meet the requirements of this section by obtaining a trust fund for liability coverage as specified in section 261.147(j).
Section 261.147(j)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by establishing a trust fund that conforms to the requirements of this paragraph and submitting an originally signed duplicate of the trust agreement to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.147(j)(2) provides that the trustee must be an entity which has the authority to act as a trustee and whose trust operations are regulated and examined by a Federal or State agency. Section 261.147(j)(3) provides that the trust fund for liability coverage must be funded for the full amount of the liability coverage to be provided by the trust fund before it may be relied upon to satisfy the requirements of this section. If at any time after the trust fund is created the amount of funds in the trust fund is reduced below the full amount of the liability coverage to be provided, the owner or operator, by the anniversary date of the establishment of the Fund, must either add sufficient funds to the trust fund to cause its value to equal the full amount of liability coverage to be provided, or obtain other financial assurance as specified in this section to cover the difference. For purposes of this paragraph, “the full amount of the liability coverage to be provided” means the amount of coverage for sudden and/or nonsudden occurrences required to be provided by the owner or operator by this section, less the amount of financial assurance for liability coverage that is being provided by other financial assurance mechanisms being used to demonstrate financial assurance by the owner or operator. Section 261.147(j)(4) provides that the wording of the trust fund must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(l).
(6) Combination of Financial Mechanisms
40 CFR 261.147(a)(6) and (b)(6) provide that an owner or operator may demonstrate the required liability coverage through the use of combinations of insurance, financial test, guarantee, letter of credit, surety bond, and trust fund, except that the owner or operator may not combine a financial test covering part of the liability coverage requirement with a guarantee unless the financial statement of the owner or operator is not consolidated with the financial statement of the guarantor. The amounts of coverage demonstrated must total at least the minimum amounts required by this section. If the owner or operator demonstrates the required coverage through the use of a combination of financial assurances under this paragraph, the owner or operator shall specify at least one such assurance as ``primary'' coverage and shall specify other assurance as ``excess'' coverage.
Notification to EPA under 40 CFR 261.147(a)(7) and (b)(7)
40 CFR 261.147(a)(7) and (b)(7) provide that an owner or operator shall notify the Regional Administrator in writing within 30 days whenever: a claim results in a reduction in the amount of financial assurance for liability coverage provided by a financial instrument as specified (261.147(a)(7)(i) and (b)(7)(i)); or a Certification of Valid Claim for bodily injury or property damages caused by a sudden or non-sudden accidental occurrence arising from the operation of a hazardous secondary material reclamation facility or intermediate facility is entered between the owner or operator and third-party claimant for liability coverage as specified (261.147(a)(7)(ii) and (b)(7)(ii)); or a final court order establishing a judgment for bodily injury or property damage caused by a sudden or non-sudden accidental occurrence arising from the operation of a hazardous secondary material reclamation facility or intermediate facility is issued against the owner or operator or an instrument that is providing financial assurance for liability coverage as specified (261.147(a)(7)(iii) and (b)(7)(iii)).
.
Request for Variance
40 CFR 261.147(c) provides that, if an owner or operator can demonstrate to the satisfaction of the Regional Administrator that the levels of financial responsibility required by paragraph (a) or (b) of this section are not consistent with the degree and duration of risk associated with treatment and/or storage at the facility or group of facilities, the owner or operator may obtain a variance from the Regional Administrator. The request for a variance must be submitted in writing to the Regional Administrator. If granted, the variance will take the form of an adjusted level of required liability coverage, such level to be based on the Regional Administrator's assessment of the degree and duration of risk associated with the ownership or operation of the facility or group of facilities. The Regional Administrator may require an owner or operator who requests a variance to provide such technical and engineering information as is deemed necessary by the Regional Administrator to determine a level of financial responsibility other than that required by paragraph (a) or (b) of this section.
Adjustments by the Regional Administrator
40 CFR 261.147(d) provides that, if the Regional Administrator determines that the levels of financial responsibility required by paragraph (a) or (b) of this section are not consistent with the degree and duration of risk associated with treatment and/or storage at the facility or group of facilities, the Regional Administrator may adjust the level of financial responsibility required under paragraph (a) or (b) of this section as may be necessary to protect human health and the environment. This adjusted level will be based on the Regional Administrator's assessment of the degree and duration of risk associated with the ownership or operation of the facility or group of facilities. In addition, if the Regional Administrator determines that there is a significant risk to human health and the environment from nonsudden accidental occurrences resulting from the operations of a facility that is not a surface impoundment, pile, or land treatment facility, he may require that an owner or operator of the facility comply with paragraph (b) of this section. An owner or operator must furnish to the Regional Administrator, within a reasonable time, any information which the Regional Administrator requests to determine whether cause exists for such adjustments of level or type of coverage.
Incapacity of Owners or Operators, Guarantors, or Financial Institutions
40 CFR 261.148(a) provides that an owner or operator must notify the Regional Administrator by certified mail of the commencement of a voluntary or involuntary proceeding under Title 11 (Bankruptcy), U.S. Code, naming the owner or operator as debtor, within 10 days after commencement of the proceeding. A guarantor of a corporate guarantee as specified in section 261.143(e) must make such a notification if he is named as debtor, as required under the terms of the corporate guarantee. Section 261.148(b) provides that an owner or operator who fulfills the requirements of section 261.143 or section 261.147 by obtaining a trust fund, surety bond, letter of credit, or insurance policy will be deemed to be without the required financial assurance or liability coverage in the event of bankruptcy of the trustee or issuing institution, or a suspension or revocation of the authority of the trustee institution to act as trustee or of the institution issuing the surety bond, letter of credit, or insurance policy to issue such instruments. The owner or operator must establish other financial assurance or liability coverage within 60 days after such an event.
Use of State-Required Mechanisms
40 CFR 261.149(a) provides that, for a reclamation or intermediate facility located in a State where EPA is administering the requirements of Subpart H but where the State has regulations that include requirements for financial assurance of closure or liability coverage, an owner or operator may use State-required financial mechanisms to meet the requirements of section 261.143 or section 261.147 if the Regional Administrator determines that the State mechanisms are at least equivalent to the financial mechanisms specified in Subpart H. The Regional Administrator will evaluate the equivalency of the mechanisms principally in terms of (1) certainty of the availability of funds for the required closure activities or liability coverage and (2) the amount of funds that will be made available. The Regional Administrator may also consider other factors as he deems appropriate. The owner or operator must submit to the Regional Administrator evidence of the establishment of the mechanism together with a letter requesting that the State-required mechanism be considered acceptable for meeting the requirements of Subpart H. The submission must include the information specified in section 261.149(a). The Regional Administrator may require the owner or operator to submit additional information as is deemed necessary to make this determination. Pending this determination, the owner or operator will be deemed to be in compliance with the requirements of section 261.143 or section 261.147, as applicable.
Section 261.149(b) provides that, if a State-required mechanism is found acceptable as specified in paragraph (a) of this section except for the amount of funds available, the owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of Subpart H by increasing the funds available through the State-required mechanism or using additional financial mechanisms as specified in Subpart H. The amount of funds available through the State and Federal mechanisms must at least equal the amount required by Subpart H.
State Assumption of Responsibility
40 CFR 261.150(a) provides that, if a State either assumes legal responsibility for an owner's or operator's compliance with the closure or liability requirements of this part or assures that funds will be available from State sources to cover those requirements, the owner or operator will be in compliance with the requirements of section 261.143 or section 261.147 if the Regional Administrator determines that the State's assumption of responsibility is at least equivalent to the financial mechanisms specified in Subpart H. The Regional Administrator will evaluate the equivalency of State guarantees principally in terms of (1) certainty of the availability of funds for the required closure activities or liability coverage and (2) the amount of funds that will be made available. The Regional Administrator may also consider other factors as he deems appropriate. The owner or operator must submit to the Regional Administrator a letter from the State describing the nature of the State's assumption of responsibility together with a letter from the owner or operator requesting that the State's assumption of responsibility be considered acceptable for meeting the requirements of Subpart H. The letter from the State must include, or have attached to it, the information specified at section 261.150(a). The Regional Administrator may require the owner or operator to submit additional information as is deemed necessary to make this determination. Pending this determination, the owner or operator will be deemed to be in compliance with the requirements of section 265.143 or section 265.147, as applicable. Section 261.150(b) provides that, if a State's assumption of responsibility is found acceptable as specified in paragraph (a) of this section except for the amount of funds available, the owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of Subpart H by use of both the State's assurance and additional financial mechanisms as specified in Subpart H. The amount of funds available through the State and Federal mechanisms must at least equal the amount required by Subpart H.
2. NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION
2(a) Need and Authority for the Collection
The regulations are promulgated under the authority of sections 2002, 3001, 3002, 3003, 3004, 3007, 3010, and 3017 of RCRA, as amended by the Hazardous and Solid Waste Amendments of 1984 (HSWA).
CERTIFICATIONS FOR HAZARDOUS SECONDARY MATERIAL GENERATED AND RECLAIMED UNDER THE CONTROL OF THE GENERATOR
EPA has established the certification requirement for materials that are generated and reclaimed under the control of the generator because of existing complexities in corporate ownership and liability. The certification is needed to increase the company=s awareness and accountability for ensuring that the generator and reclamation facilities are in fact under its ownership. The certification also may be needed by regulators (e.g., on-site inspectors) to verify compliance.
NON-WASTE DETERMINATIONS
The intent of the non‑waste determination petition process is to provide petitioners with an administrative procedure for receiving a formal determination that their material is not a solid waste. This process is available in addition to the solid waste exclusions. Facilities may choose to continue to self‑implement the waste determination requirements of 40 CFR Part 261 and, for the vast majority of cases, self‑implementation will still be the most appropriate approach. However, for cases where there is ambiguity about whether a secondary material is a solid waste, this process may be needed to provide regulatory certainty for both the facility and Agency.
NOTIFICATION
EPA has established the notification requirements for generators, toll manufacturers, tolling contractors, intermediate facilities and reclaimers to provide basic information to regulatory agencies about who will be managing hazardous secondary materials under the exclusions and the types of materials that will be reclaimed. EPA believes its right to require such information is inherent in its authority to determine whether a material is discarded. EPA considers this to be the minimum information needed to enable credible evaluation of the status of a material under RCRA.
EXCLUSIONS FROM THE DEFINITION OF SOLID WASTE
EPA has established conditional exclusions from the definition of solid waste for hazardous secondary materials as specified. Since there is some potential for mismanagement of these materials in the absence of any regulatory controls, the exclusions specify certain conditions that must be satisfied by the generator facility and, if applicable, the intermediate and reclamation facilities to whom the materials are transferred. EPA=s assessment that conditions are needed for recycling of excluded material has been influenced by recycling studies that EPA conducted (e.g., analyses of environmental problems associated with recycling of hazardous secondary materials). These studies are described in the preamble to the final rule and contained in the administrative record.
Exclusions at 40 CFR 261.2(a)(2)(ii) and 261.4(a)(23)
This supporting statement describes the need for the information collection requirements of these exclusions under “Certifications for Hazardous Secondary Material Generated and Reclaimed under the Control of the Generator” and “Notification.”
Exclusion at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(24)
Contractual arrangements are needed between the hazardous secondary material generator and intermediate facility where the management of the hazardous secondary material is not addressed under a Part B permit or interim-status standards, as required under section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(B). This provision ensures that the hazardous secondary material is sent to the reclamation facility identified by the hazardous secondary material generator. Without these contractual arrangements, a generator may not be able to ensure that its waste is shipped to the appropriate reclaimer that is participating under the exclusion. EPA believes such contracts are a standard business practice.
In order to demonstrate that the hazardous secondary materials will not be discarded, generators who transfer their hazardous secondary materials to a third party must have a reasonable understanding of who will be reclaiming the materials and how they will be managed and reclaimed and a reasonable assurance that the recycling practice is safe and legitimate. To gain this understanding, the generator must make a reasonable effort under section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(B) to ensure that the reclaimer intends to legitimately recycle the material pursuant to section 260.43(a) and not discard it, and that the reclaimer (and any intermediate facility) will manage the material in a manner that is protective of human health and the environment.
EPA finds that the reasonable efforts provision is a critical factor in determining when hazardous secondary materials sent to another party for reclamation are not discarded. According to a study of successful recycling practices, some generators of hazardous secondary materials routinely perform audit activities and inquiries to determine whether the entity to which they are sending hazardous secondary materials is equipped to responsibly and legitimately reclaim and manage those materials without the risk of releases or other environmental damage. These recycling and waste audits of other companies’ facilities form a backbone of many of the transactions in the hazardous secondary materials markets. As noted in the 2007 supplemental proposal, EPA’s study of good practices for recycling quotes one large recycling and disposal vendor as stating that of its new customers, 60 percent of the large customers and 30–50 percent of the smaller customers now perform audits on them. Thus, although these practices are not universal, they do indicate that there are currently many generators who recognize the risk of third-party recyclers discarding their hazardous secondary materials and who take responsibility to ensure that this discard does not occur. EPA has developed a reasonable efforts provision that is objective and is based on the types of information that are typically gathered in environmental audits currently performed by generators.
EPA is requiring that generators make reasonable efforts every three years, at a minimum, in order to ensure generators adequately manage their risk and are attuned to changes at reclamation facilities and intermediate facilities with which they are partners. EPA believes that this schedule reflects an average time frame for re-evaluating facilities. By specifying periodic updates for reasonable efforts every three years at a minimum, EPA in no way intends to limit a generator to conducting evaluations only every three years. In fact, EPA expects that any generator who has concerns about an intermediate or reclamation facility, or who gains new knowledge of significant changes or extraordinary situations at such facilities, would conduct reasonable efforts regardless of the minimum required update schedule. For example, if a hazardous secondary material generator conducted reasonable efforts in the first year it took advantage of the exclusion, prior to transferring materials to an intermediate facility, and then again conducted reasonable efforts in the second year upon learning about a significant change at the intermediate facility (such as bankruptcy), the generator would be required to update reasonable efforts three years later during the generator’s fifth year of taking advantage of the exclusion.
Documentation and certification are both necessary requirements of the reasonable efforts condition. Documentation of the specified questions will support a hazardous secondary material generator’s assertion that it affirmatively answered the questions and is in compliance with the regulations. It will also facilitate any review by regulatory authorities investigating whether the conditions of the transfer-based exclusion are satisfied and help delineate liability under RCRA if the materials were discarded. Having an authorized representative certify reasonable efforts is critical for guaranteeing accountability at the generator facility for meeting the condition and for ensuring that the act of making reasonable efforts is in fact genuine. The certification is also necessary in order to allow for the “flexible” documentation requirement that does not specify a particular format. Since individual generators may use any form of documentation, EPA believes it is critical for all generators to uniformly certify that the condition is satisfied. Furthermore, EPA finds both reasonable efforts requirements (documentation and certification) to be appropriate based on its understanding that third-party auditors do not generally draw any conclusions based on their audits, but simply report the results to generators. While a generator may use any information for making reasonable efforts, the certification statement would affirm that a generator used information that is gathered and documented during the reasonable efforts inquiry, similar to how generators currently draw conclusions based on third-party audit documents.
The requirement for documentation and certification of reasonable efforts is not unlike existing forms of RCRA documentation that incorporate certifications, such as the RCRA Site ID Form, RCRA financial assurance requirements, and the Uniform Hazardous Waste Manifest.
EPA believes that certifying reasonable efforts is a necessary and minimally burdensome requirement for ensuring that the reasonable efforts condition is met prior to transferring hazardous secondary materials to a reclamation facility. EPA strongly believes that requiring the signature of an authorized representative of the generator company, who can be any appointed company representative, requires a necessary level of management oversight and is critical for ensuring accountability for satisfying the condition. In the event of an enforcement action, EPA believes that the certification will lend support to generators needing to prove that the reasonable efforts requirement was met. The certification also reflects that third parties may conduct audits on behalf of the generator. In such cases, the certification shows that the generator’s management has considered and evaluated the third-party information. Finally, EPA believes that requiring a generator to certify the reasonable efforts condition would provide them the flexibility to use audits or other information necessary in certifying that the condition of the exclusion was met.
Records retained by the generator under section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(D) and (E) of each shipment are needed so that the generator can demonstrate to regulators (e.g., in an on-site inspection) that it is in compliance with the conditions (e.g., that its excluded material is being sent to, and received by, the reclamation facility). The records enable regulators to evaluate the generator=s compliance (e.g., a regulator can use the records to track shipments from generator to reclaimer). The confirmations are also needed so that the generator is accountable for the delivery of its excluded materials to the appropriate destination.
Records retained by the intermediate and reclamation facility under section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(A) and (C) are needed to enable the effective oversight of their activities. The records enable regulators (e.g., on-site inspectors) to learn about the shipments of the excluded materials received (e.g., quantity and types). For example, the records would be important in identifying the generators of the excluded materials received by the facility.
Export Requirements at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(25)
The export requirements provide notice-and-consent procedures for the export shipments. Such procedures help ensure, for example, that the materials will not be discarded and give the receiving country an opportunity to respond to the intended shipment (e.g., request additional information).
FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS FOR MANAGEMENT OF EXCLUDED HAZARDOUS SECONDARY MATERIALS
EPA has established the financial requirements of 40 CFR Part 261 Subpart H because it has found that the financial health of a reclamation facility can be a crucial consideration in determining whether it is likely to discard a material. EPA has found that an examination of a company’s finances is an important part of many environmental audits. In addition, EPA found that bankruptcies or other types of business failures were associated with 66 percent of the damage cases in a study and a low net worth of a firm can be a strong indication of a sub-optimal outcome of recycling.
To address the issue of the correlation of financial health with the absence of discard, EPA is requiring owner/operators of intermediate and reclamation facilities to obtain financial assurance as a condition of the exclusion under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25). The financial assurance requirements will help ensure that the owner/operators who operate under the terms of this exclusion are financially sound.
In addition, by obtaining financial assurance, the owner/operator is making a direct demonstration that it will not abandon the hazardous secondary material. Discard through abandonment was a major cause of damages identified in an environmental problems study reviewed by EPA. Of the 208 damage cases, 69 (33%) involved abandoned materials. By obtaining financial assurance, a reclaimer (or intermediate facility) is demonstrating that even if events beyond his control make his operations uneconomical, the hazardous secondary material will not be abandoned.
Cost Estimate
Because hazardous secondary material that loses the exclusion may have to be disposed of as a hazardous waste and the facility may have to be closed as a hazardous waste facility in accordance with the requirements of 40 CFR Part 265, the owner or operator must have a detailed written estimate in current dollars of performing this work. The requirements are designed so that if the State or EPA must close a facility because of an owner or operator’s failure, there will be adequate funds to do so. The requirements for the cost estimate therefore are based upon the point when the extent and manner of the facility’s operation would make these activities the most expensive.
Financial Assurance Condition
EPA is specifying that an owner or operator of a reclamation or intermediate facility must establish financial assurance as a condition of the exclusion under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25). He must choose from the options as specified: trust fund, surety bond guaranteeing payment into a trust fund, letter of credit, insurance, financial test/corporate guarantee, or a combination of instruments. If the facility violates the exclusion, EPA can invoke the instruments to ensure that the hazardous materials at the facility are removed and the facility is decontaminated/cleaned up. These instruments are the same types as those allowed in Part 265 and have been found to be effective for these purposes.
Use of Financial Mechanisms for Multiple Facilities
These provisions, found at section 261.143(g), are needed because a company may own/operate multiple facilities. The company may find it beneficial to combine these facilities under a single instrument. For example, a company may be able to use the financial test to satisfy the financial assurance requirements for all of its facilities under the exclusion. This would relieve it of the need to establish separate financial instruments for each.
Removal and Decontamination Plan and Release from Financial Assurance Obligations
The provisions for releasing the reclamation or intermediate facility from the financial assurance requirements, found in 40 CFR 261.143(h) and (i), are equivalent to those under 40 CFR 265.143(h). Because 40 CFR 265.143(h) relies on receiving a certification (per 40 CFR 265.115) that the unit was closed per the approved closure plan in section 265.112, language from the closure plan requirement found in section 265.112 and from the certification requirement found in section 265.115 has been included in section 261.143(h). However, because the units are excluded, they are not subject to the RCRA Subtitle C closure requirements. Thus, instead of a “closure plan,” the regulations require submission of a plan at least 180 days prior to the date that owner or operator expects to cease operating under the exclusion in order for the owner or operator to be released from the financial assurance requirements.
The plan is needed to describe the owner/operator’s approach for removing all hazardous secondary material residues in a manner that is protective of human health and the environment. The plan goes through the same administrative review process as a 40 CFR Part 265 closure plan, because that would ensure that the reclamation or intermediate facility has arranged to appropriately manage the hazardous secondary materials and residuals and not abandon them and would also provide certainty to the facility that EPA would agree with his plan.
The certification is needed to formally notify EPA that all hazardous materials have been removed from the unit and the unit has been decontaminated in accordance with the approved plan. A signature from a qualified Professional Engineer gives EPA assurance that this has been done properly.
Coverage for Sudden and Non-Sudden Accidental Occurrences
EPA is specifying that an owner/operator of a reclamation or intermediate facility must have liability coverage for sudden and nonsudden accidental occurrences, as specified. The owner or operator must have and maintain liability coverage in the amounts specified in the regulations. This liability coverage may be demonstrated through the options as specified in the regulations: liability insurance, financial test/guarantee, letter of credit, surety bond guaranteeing payment into a trust fund, trust fund, or a combination of instruments. This coverage is needed to ensure that the facility is financially responsible and capable of addressing accidents without jeopardizing its ability to continue operating in compliance with the exclusion.
Combination of Financial Mechanisms
These provisions, found at section 261.147(a)(6) and (b)(6), are necessary because some owner/operators may not be able to fulfill their financial obligations for liability coverage through a single instrument. These provisions allow owner/operators to combine two or more instruments in order to meet their required level of coverage.
Notification to EPA under 40 CFR 261.147(a)(7) and (b)(7)
These provisions are needed to ensure that owner/operators notify EPA when a claim or court order, as specified, occurs that could result in financial responsibility for damages or injury arising from the facility. Payment of claims could decrease the facility’s ability to meet the required levels of financial assurance.
Request for Variance
The variance is needed because facility-specific factors may warrant a different level of financial responsibility than required in the regulations for sudden and/or nonsudden accidental occurrences. The variance provisions enable an owner/operator to demonstrate to EPA that the levels of financial responsibility in the regulations are not consistent with the degree and duration of risk associated with the facility’s operations. If granted, the variance will take the form of an adjusted level of required liability coverage. This level is based on the Regional Administrator's assessment of the degree and duration of risk associated with the ownership or operation of the facility or group of facilities.
Adjustment by the Regional Administrator
The adjustment procedures, found at section 261.147(d), are needed because the level of financial responsibility required in the regulations for liability coverage may not be consistent with the degree and duration of risk associated with a facility’s operation. These provisions enable EPA to adjust the level of financial responsibility based on its assessment of the degree and duration of risk associated with the facility. In addition, if EPA determines that there is a significant risk to human health and the environment from nonsudden accidental occurrences resulting from the operations of a facility that is not a surface impoundment, pile, or land treatment facility, he may require that an owner or operator of the facility comply with section 261.147(b).
Incapacity of Owners or Operators, Guarantors, or Financial Institutions
These provisions, found at section 261.148, are needed to ensure that owner/operators notify EPA in case of commencement of voluntary or involuntary bankruptcy proceedings, as specified. EPA found that bankruptcies or other types of business failures were associated with 66 percent of the damage cases in a study and a low net worth of a firm can be a strong indication of a sub-optimal outcome of recycling. This notification will inform EPA that the facility is having difficulty meeting its financial obligations.
Use of State-Required Mechanisms
These provisions, found at section 261.149, are needed to provide for owner/operators to use State-required financial mechanisms to meet the requirements of section 261.143 or 261.147 if EPA determines that the State mechanisms are at least equivalent to the financial mechanisms specified in Subpart H. These procedures may be necessary in States in which EPA is administering the financial assurance requirements, but where the State has regulations that include requirements for financial assurance of closure or liability coverage.
State Assumption of Responsibility
These provisions, found at section 261.150, are needed in cases in which a State either assumes legal responsibility for an owner/operator's compliance with the closure or liability requirements or assures that funds will be available from State sources to cover those requirements. The provisions enable EPA to determine if the State's assumption of responsibility is at least equivalent to the financial mechanisms specified in Subpart H and to grant States the assumption of responsibility.
2(b) Practical Utility and Users of the Data
CERTIFICATIONS FOR HAZARDOUS SECONDARY MATERIAL GENERATED AND RECLAIMED UNDER THE CONTROL OF THE GENERATOR
EPA is requiring the certification requirement for materials that are generated and reclaimed under the control of the generator because of existing complexities in corporate ownership and liability. The certification will be used to hold the company accountable for knowing and complying with the definition of “hazardous secondary materials generated and reclaimed under the control of the generator” and to enable regulatory authorities to determine when facilities are eligible for this exclusion.
NON-WASTE DETERMINATIONS
An applicant may apply to the Administrator for a formal determination that its material is not a solid waste. For cases where there is ambiguity about whether a secondary material is a solid waste, this process may be used to provide regulatory certainty for both the facility and Agency.
NOTIFICATION
The regulatory agencies will use the notifications from the generators, toll manufacturers, tolling contractors, intermediate facilities and reclaimers to learn basic information about who will be managing hazardous secondary materials under the exclusion and the types of materials that will be recycled. The information will help the agencies evaluate the status of the material under RCRA.
EXCLUSIONS FROM THE DEFINITION OF SOLID WASTE
Exclusions at 40 CFR 261.2(a)(2)(ii) and 261.4(a)(23)
This supporting statement addresses the utility and users of the information collection requirements of these exclusions under “Certifications for Hazardous Secondary Material Generated and Reclaimed under the Control of the Generator” and “Notification.”
Exclusion at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(24)
Contractual arrangements are used by the hazardous secondary materials generator and intermediate facility under section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(B) to ensure that the hazardous secondary material is sent to the reclamation facility identified by the generator.
The reasonable efforts required under section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(B) are used to ensure that the generator’s materials will be recycled legitimately, and otherwise managed in a manner that is protective of human health and the environment. The generator must keep documentation, including a certification, of its efforts under 261.4(a)(24)(v)(C). EPA believes the questions laid out in the regulations are normally considered by responsible generators. However, the questions will reinforce the need for generators to ask these questions. Generators must keep records of their reasonable efforts, including certifications, to demonstrate their compliance with the regulations.
The certification statement under section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(C) is used to hold the generator accountable for ensuring that the reasonable efforts condition is met prior to transferring hazardous secondary materials to a reclamation facility. Generators would provide a necessary level of management oversight for ensuring compliance with the condition. In the event of an enforcement action, generators could use the certification to prove that the reasonable efforts requirement was met. EPA would use the certification to ensure that the generators reviewed the reasonable effort documentation, including any information derived from audits conducted by third parties.
Records retained by the generator under section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(D) and (E) of each shipment are used by the generator to confirm and demonstrate that its shipments of excluded materials were received by the appropriate facilities. The records are used by regulators to confirm this.
Records retained by the intermediate and reclamation facility under section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(A) and (C) are used by regulators (e.g., on-site inspectors) to learn about the shipments of the excluded materials (e.g., to learn how much material is being received and reclaimed under the exclusion).
Export Requirements at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(25)
The requirements at section 261.4(a)(25) provide notice-and-consent procedures for export shipments. For example, the receiving country will have the opportunity to review the exporter’s notification and approve or deny the export shipment. Export of the material is prohibited unless the receiving country consents to the intended export.
FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS FOR MANAGEMENT OF EXCLUDED HAZARDOUS SECONDARY MATERIALS
Cost Estimate
The cost estimate is used to determine the level of financial assurance needed by the facility. The cost estimating requirements are designed so that if a State or EPA must close a facility because of an owner or operator’s failure, there will be adequate funds to do so.
Financial Assurance Condition
If the conditions of the exclusion are violated (including the condition to maintain financial assurance), then the hazardous secondary material is a hazardous waste and EPA can invoke the financial instruments to manage the materials and wastes and clean up/decontaminate the facility as necessary. By obtaining financial assurance, a reclaimer (or intermediate facility) is demonstrating that even if events beyond his control make his operations uneconomical, the hazardous secondary material will not be abandoned.
Use of Financial Mechanisms for Multiple Facilities
These provisions, found at section 261.143(g), may be used by companies that own/operate multiple facilities. These companies may find it advantageous to combine these facilities under a single instrument.
Removal and Decontamination Plan and Release from Financial Assurance Obligations
The plan submitted under section 261.143(h) is used by the owner or operator to remove all hazardous secondary material residues as specified. The certification from the owner or operator and a qualified Professional Engineer certifies that all hazardous secondary materials have been removed from the unit and the unit has been decontaminated in accordance with the approved plan. This information is used by EPA to ensure management of the materials in a manner that is protective of human health and the environment, prior to releasing the owner/operator from the financial assurance requirements.
Coverage for Sudden and Non-Sudden Accidental Occurrences
The requirements for liability coverage are used by facilities to prepare financially for accidental occurrences. This coverage is used to ensure that the facility is financially responsible and capable of addressing accidents (e.g., paying claims) without jeopardizing its ability to continue operating in compliance with the exclusion. These instruments are the same types as those allowed in Part 265 and have been found to be effective for these purposes.
Combination of Financial Mechanisms
These provisions, found at section 261.147(a)(6) and (b)(6), may be used by owner/operators who cannot fulfill their financial obligations for liability coverage through a single instrument. Under these provisions, they can combine two or more instruments to meet their required level of coverage, as specified.
Notification to EPA under 40 CFR 261.147(a)(7) and (b)(7)
These provisions are used by owner/operators to notify EPA whenever a claim or court order, as specified, occurs that results in liability for damages or injury arising from the facility. EPA uses the information to monitor the financial health of the facility and its ability to satisfy its financial obligations under the exclusion.
Request for Variance
The variance provisions, found at section 261.147(c), are used by owner/operators to demonstrate to EPA that the levels of financial responsibility in the regulations are not consistent with the degree and duration of risk associated with the facility’s operations. If granted, the variance will take the form of an adjusted level of required liability coverage. EPA will base the adjusted level on its assessment of the degree and duration of risk associated with the ownership or operation of the facility or group of facilities.
Adjustment by the Regional Administrator
These procedures, found at section 261.147(d), are used by EPA to adjust a facility’s level of financial responsibility based on its assessment of the degree and duration of risk associated with the facility. EPA will base the adjusted level on its assessment of the degree and duration of risk associated with the ownership or operation of the facility or group of facilities. In addition, if EPA determines that there is a significant risk to human health and the environment from nonsudden accidental occurrences resulting from the operations of a facility that is not a surface impoundment, pile, or land treatment facility, he may require that an owner or operator of the facility comply with the financial requirements for nonsudden accidental occurrences.
Incapacity of Owners or Operators, Guarantors, or Financial Institutions
These provisions, found at section 261.148, are used by owner/operators to notify EPA in case of commencement of voluntary or involuntary bankruptcy proceedings, as specified. EPA found that bankruptcies or other types of business failures were associated with 66 percent of the damage cases in a study and a low net worth of a firm can be a strong indication of a sub-optimal outcome of recycling. EPA uses this information to learn about the financial health of the facility.
Use of State-Required Mechanisms
These provisions, found at section 261.149, provide for owner/operators to use State-required financial mechanisms to meet the requirements of section 261.143 or 261.147 if EPA determines that the State mechanisms are at least equivalent to the financial mechanisms specified in Subpart H. These procedures may be used in States in which EPA is administering the financial assurance requirements, but where the State has regulations that include requirements for financial assurance of closure or liability coverage.
State Assumption of Responsibility
These provisions, found at section 261.150, are used in cases in which a State either assumes legal responsibility for an owner/operator's compliance with the closure or liability requirements or assures that funds will be available from State sources to cover those requirements. Under the provisions, EPA can determine if the State's assumption of responsibility is at least equivalent to the financial mechanisms specified in Subpart H and to grant States the assumption of responsibility.
3. NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA
3(a) Nonduplication
None of the information required by the final rule is duplicative with any information required by the existing Federal regulations.
3(b) Public Notice
EPA first proposed changes reflecting court decisions on the definition of solid waste, as well as regulatory criteria for legitimacy, on October 28, 2003 (68 FR 61558). EPA then published a supplemental proposal on March 26, 2007 (72 FR 14172). Following is a summary of the public comments received on the supplemental proposal that offered concerns or suggestions for revising the ICR. For each comment, EPA provides an Agency response describing how the comment was addressed in preparing this ICR for the final rule. [Note: Refer to the “Response to Comment Document: Revisions to the Definition of Solid Waste” for all comments and Agency responses on the supplemental proposal. It is available in the docket for this rulemaking.]
Comment: One commenter stated that the ICR’s burden estimates are based on the minimal notice and recordkeeping provisions in the supplemental proposal. The commenter stated that these estimates do not take into account EPA’s requests for public comment on more detailed notice and recordkeeping provisions. The commenter expressed concern that the final rule could differ markedly from the supplemental proposal by including more onerous recordkeeping and notice requirements, and encouraged EPA to prepare an ICR that estimates the burden of the final rule.
EPA Response: EPA thanks the commenter for its views and believes it has fulfilled the commenter’s request by preparing this ICR of the final rule. This ICR estimates the burden associated with all of the final rule’s recordkeeping and reporting requirements. Refer to Section 6 of this supporting statement for the burden estimates.
Comment: One commenter stated that the ICR supporting statement for the supplemental proposal declares that the Agency consulted with three companies, all of which are resource recovery operations using hazardous waste as their feedstocks. The commenter expressed concern that EPA consulted with organizations in one industry only (i.e., waste management). The commenter encouraged EPA to contact other industries potentially affected by the rule.
EPA Response: EPA thanks the commenter for its feedback on the Agency’s consultations. EPA agrees that its consultations were limited primarily to hazardous waste management facilities and that further consultations were warranted.
In preparing the ICR for the supplemental proposal, EPA was mindful that it could not contact more than nine organizations to collect burden estimates for the ICR. The 1995 Paperwork Reduction Act prevents a Federal agency from collecting information from more than nine organizations, unless clearance is obtained from the U.S. Office of Management and Budget. Obtaining clearance for purposes of preparing this ICR is not practicable.
Given this constraint on the number of organizations that could be contacted, the Agency consulted three large, multi-state reclamation facilities and one trade association in preparing the ICR for the supplemental proposal. EPA recognized that these organizations have a broad knowledge of the reclamation industry because they work with both small and large generators in many industries. For example, reclaimers routinely perform technical and paperwork activities on behalf of their generator customers, such as packaging their wastes and materials for shipment, preparing manifests and notices, and supporting customers in making reasonable efforts to audit the reclamation process. As a result, they were able to speak about their own activities and burdens, as well as those of their generator customers.
Notwithstanding this, EPA was persuaded by the commenter that additional consultations were warranted and contacted four additional organizations in preparing this ICR for the final rule. These organizations are hazardous secondary materials generators in the following industries: automobile manufacturing, information technology, agricultural products, and metals production. EPA believes these additional consultations address the commenter’s request to contact other industries affected by the rule. Refer to the table in Section 3(c) for the list of all organizations contacted.
Comment: One commenter stated that the ICR does not make mention of the potentially wide variation in how States might adopt the rule and which of the rule’s provisions might or might not be adopted by the States. The commenter pointed out that, to the extent that the final rule is less stringent than the current RCRA regulations, States authorized to implement their own RCRA programs will not be bound to adopt the final rule. Thus, it is conceivable that great variation may result among States on whether and how much of the final rule to adopt. The commenter stated that the rule’s requirements and resulting burden on industry will be significantly affected by States’ decisions to adopt or not adopt the final rule.
EPA Response: EPA thanks the commenter for expressing its concerns about the ICR’s burden estimates in light of State variations in rule adoption and agrees that State adoption rates will affect burden impacts under the rule. Essentially, the commenter raises two points that need an Agency response: (i) should EPA estimate burden impacts based on an assumption of full State adoption and (ii) should this assumption be made more clear in this supporting statement?
On the first point, it has been EPA’s belief that ICRs for rulemakings should be based on full State adoption. Normally, EPA cannot reliably identify States that will not adopt a final rule. Although a State may express concerns or opposition to a proposed rule (or portions of it) such as during the public comment period, modifications made in response to the public’s comments may make the State more inclined to adopt the final version. In addition, a State’s decision to adopt the final rule (as well as the timing of the adoption) may be based on factors that are not known at the time of the ICR’s preparation (e.g., the State’s regulatory needs and priorities). Therefore, EPA continues to believe that the burden impacts estimated in this ICR should be based on an assumption of full State adoption. When this ICR is renewed three years from now, EPA will be in a better position to reflect variations in States’ adoption of the final rule.
On the second point, EPA agrees that additional clarification is needed in this supporting statement on the Agency’s assumptions regarding full State adoption of the final rule. This clarification has been included in Section 6(e) of this supporting statement.
3(c) Consultations
In August 2006 and March-April 2008, EPA contacted a number of hazardous secondary materials generators and reclamation companies for the sole purpose of preparing this ICR. They provided consultative input according to four paperwork burden issues potentially affected by this rulemaking:
Use of shipping papers instead of the RCRA manifest: The representatives speculated that, in the absence of a requirement for a RCRA manifest, they would use a multi-part shipping paper to ship their excluded materials. This would enable the reclaimer to send a copy to the generator to confirm receipt of shipment.
Use of reasonable efforts to evaluate the reclaimer: The representatives believe that responsible generator customers currently make an effort to evaluate prospective reclamation facilities (e.g., to determine if the facilities have adequate equipment and procedures to reclaim their waste in a manner that is protective of human health and the environment). This may include a visit to the facility by generator employees or contracted auditor and/or a review of facility documentation.
Relief from RCRA permit: The representatives provided feedback on whether they believe their reclamation facilities could see some relief from the RCRA permitting requirements under the rule. They believe such relief would depend on a number of factors (e.g., whether a facility would manage only excluded materials under the rule or whether it would continue to receive and manage hazardous wastes in addition to excluded materials).
Types of hazardous secondary materials facilities that support the reclamation process. The representatives described facilities currently in use that store and/or aggregate secondary materials prior to transfer to reclamation. They indicated that the number of such intermediate facilities needed for reclamation operations can vary greatly depending on many factors. For example, reclaimers that receive waste predominantly from small generators may rely more heavily on intermediate aggregation facilities. Partial loads are collected and taken to aggregation facilities before shipment to the reclamation facility, enhancing economies of scale. On the other hand, reclaimers that work with larger generators may rely less on aggregation facilities.
In addition, EPA contacted a representative of CHWMEG, an organization that provides facility review services to the hazardous waste industry. The representative agreed that generators may make reasonable efforts using their own employees or a third-party auditor. The decision to use either in-house employees or a third-party auditor to perform the audit will depend on a number of considerations (e.g., trade-offs between cost and desired quality/thoroughness of the audit report).
The table below identifies the organizations contacted. Their feedback is reflected in the burden assumptions of this ICR, as appropriate.
Organizations EPA Contacted for ICR Preparation
(August 2006 and March/April 2008)
Name of Organization |
Name of Representative |
Phone Number |
Alcoa Corporation |
Gary Crouth |
412-553-4287 |
CHWMEG |
Jeff Sacre |
412-826-3056 |
Ford Motor Company |
Susan Rokosz |
313-322-3826 |
Giant Resource Recovery |
Stan Ray |
803-773-1400 |
Intel Corporation |
Cherry Moyer |
480-715-2495 |
Monsanto Company |
Mary Shaffer |
314-694-3883 |
Safety Kleen Systems, Incorporated |
Mike Fusco and Lin Longshore |
610-558-3186 |
Veolia ES Technical Solutions (formerly Onyx Environmental Services) |
Thomas Baker |
973-691-7330 |
3(d) Effects of Less Frequent Collection
EPA has carefully considered the information collection burden imposed by the final rule. EPA is confident that those activities required of respondents are necessary, and to the extent possible, the Agency has attempted to minimize the burden imposed. A number of the required activities, for example, will be performed once (e.g., one-time certifications). In addition, a number of other requirements can be satisfied by activities already being undertaken by respondents. For example, EPA has found that responsible generators currently make reasonable efforts to evaluate prospective reclaimers, as required by the rule. EPA believes strongly that, if the minimum information collection requirements of the rule are not met, EPA will not be able to ensure that the hazardous secondary materials are being properly managed and do not pose a threat to human health and the environment.
3(e) General Guidelines
This ICR adheres to the guidelines stated in the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995, OMB’s implementing regulations, EPA’s ICR Handbook, and other applicable OMB guidance.
3(f) Confidentiality
Participation under the exclusions is voluntary. EPA does not expect to deem any information collected under the rule to be CBI (Confidential Business Information). If such a claim were asserted, EPA must and will treat the information in accordance with the applicable regulations (e.g., 40 CFR Part 2, Subpart B). EPA also will assure that this information collection complies with the Privacy Act of 1974 and OMB Circular 108.
3(g) Sensitive Questions
No questions of a sensitive nature are included in the information collection requirements associated with the rule.
4. THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED
4(a) Respondents and NAICS Codes
The following is a list of North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) codes associated with industries most likely affected by the information collection requirements covered in this ICR.
NAICS Codes of Potentially Affected Industries
Industry Sector |
NAICS Codes |
Agriculture, Forestry, Fishing and Hunting |
11 |
Mining |
21 |
Utilities |
22 |
Construction |
23 |
Manufacturing |
31 |
Manufacturing |
32 |
Manufacturing |
33 |
Wholesale Trade |
42 |
Retail Trade |
44, 45 |
Transportation |
48, 49 |
Information |
51 |
Finance and Insurance |
52 |
Real Estate, Rental, Leasing |
53 |
Professional, Scientific & Technical Services |
54 |
Management of Companies and Enterprises |
55 |
Administrative Support, Waste Management & Remediation |
56 |
Educational Services |
61 |
Health Care & Social Assistance |
62 |
Arts, Entertainment, Recreation |
71 |
Accommodation and Food Services |
72 |
Other Services |
81 |
Public Administration |
92 |
Source: Exhibit 9C of EPA’s 2008 Regulatory Impact Analysis for this rulemaking. |
|
4(b) Information Requested
CERTIFICATIONS FOR HAZARDOUS SECONDARY MATERIAL GENERATED AND RECLAIMED UNDER THE CONTROL OF THE GENERATOR
40 CFR 260.10 provides that “hazardous secondary material generated and reclaimed under the control of the generator” means: (1) that such material is generated and reclaimed at the generating facility (for purposes of this paragraph, generating facility means all contiguous property owned, leased, or otherwise controlled by the hazardous secondary material generator); or (2) that such material is generated and reclaimed at different facilities, if the reclaiming facility is controlled by the generator or if both the generating facility and the reclaiming facility are controlled by a person as defined in section 260.10, and if the generator provides one of the certifications as specified. For purposes of this paragraph, “control” means the power to direct the policies of the facility, whether by the ownership of stock, voting rights, or otherwise, except that contractors who operate facilities on behalf of a different person as defined in section 260.10 shall not be deemed to “control” such facilities; or (3) that such material is generated pursuant to a written contract between a tolling contractor and a toll manufacturer and is reclaimed by the tolling contractor, if the tolling contractor provides a certification as specified. For purposes of this paragraph, tolling contractor means a person who arranges for the production of a product or intermediate made from specified unused materials through a written contract with a toll manufacturer. Toll manufacturer means a person who produces a product or intermediate made from specified unused materials pursuant to a written contract with a tolling contractor.
(i) Data items
A certification from the generator stating one of the following:
- “On behalf of [insert generator facility name], I certify that this facility will send the indicated hazardous secondary material to [insert reclaimer facility name], which is controlled by [insert generator facility name] and that [insert the name of either facility] has acknowledged full responsibility for the safe management of the hazardous secondary material;” or
- “On behalf of [insert generator facility name], I certify that this facility will send the indicated hazardous secondary material to [insert reclaimer facility name], that both facilities are under common control, and that [insert name of either facility] has acknowledged full responsibility for the safe management of the hazardous secondary material.”
A certification from the tolling contractor stating the following: “On behalf of [insert tolling contractor name], I certify that [insert tolling contractor name] has a written contract with [insert toll manufacturer name] to manufacture [insert name of product or intermediate] which is made from specified unused materials, and that [insert tolling contractor name] will reclaim the hazardous secondary materials generated during this manufacture. On behalf of [insert tolling contractor name], I also certify that [insert tolling contractor name] retains ownership of, and responsibility for, the hazardous secondary materials that are generated during the course of the manufacture, including any releases of hazardous secondary materials that occur during the manufacturing process.”
(ii) Respondent activities
The generator (including tolling contractor) must prepare the certification.
NON-WASTE DETERMINATIONS
Application for Non-Waste Determination
40 CFR 260.33(a) provides that an applicant must apply to the Administrator for a variance or non-waste determination. The application must address the relevant criteria contained in section 260.31, 260.32, or 260.34, as applicable. [Note: 40 CFR 260.31 and 260.32 are existing requirements that were not affected by the final rule. Therefore, they are not addressed in this supporting statement.]
Section 260.34(a) provides that an applicant may apply to the Administrator for a formal determination that a hazardous secondary material is not discarded and therefore not a solid waste. The determinations will be based on the criteria contained in section 260.34(b) or (c), as applicable. If an application is denied, the hazardous secondary material might still be eligible for a solid waste variance or exclusion (for example, one of the solid waste variances under section 260.31). Determinations may also be granted by the State if the State is either authorized for this provision or if the specified conditions are met.
Section 260.34(b) provides that the Administrator may grant a non-waste determination for hazardous secondary material which is reclaimed in a continuous industrial process if the applicant demonstrates that the hazardous secondary material is a part of the production process and is not discarded. The determination will be based on whether the hazardous secondary material is legitimately recycled as specified in section 260.43 and on the criteria under paragraphs (b)(1)-(4).
Section 260.34(c) provides that the Administrator may grant a non-waste determination for hazardous secondary material which is indistinguishable in all relevant aspects from a product or intermediate if the applicant demonstrates that the hazardous secondary material is comparable to a product or intermediate and is not discarded. The determination will be based on whether the hazardous secondary material is legitimately recycled as specified in section 260.43 and on the criteria under paragraphs (c)(1)-(5).
(i) Data items
Application under section 260.34(b) for a non-waste determination for hazardous secondary material which is reclaimed in a continuous industrial process. The application must demonstrate that the hazardous secondary material is a part of the production process and is not discarded and address the following criteria:
- The extent that the management of the hazardous secondary material is part of the continuous primary production process and is not waste treatment;
- Whether the capacity of the production process would use the hazardous secondary material in a reasonable time frame and ensure that the hazardous secondary material will not be abandoned (for example, based on past practices, market factors, the nature of the hazardous secondary material or any contractual arrangements);
- Whether the hazardous constituents in the hazardous secondary material are reclaimed rather than released to the air, water or land at significantly higher levels from either a statistical or from a health and environmental risk perspective than would otherwise be released by the production process; and
- Other relevant factors that demonstrate the hazardous secondary material is not discarded.
An application under section 260.34(c) for a non-waste determination for hazardous secondary material which is indistinguishable in all relevant aspects from a product or intermediate. The application must demonstrate that the hazardous secondary material is comparable to a product or intermediate and is not discarded, and address the following criteria:
- Whether market participants treat the hazardous secondary material as a product or intermediate rather than a waste (for example, based on the current positive value of the hazardous secondary material, stability of demand, or any contractual arrangements);
- Whether the chemical and physical identity of the hazardous secondary material is comparable to commercial products or intermediates;
- Whether the capacity of the market would use the hazardous secondary material in a reasonable time frame and ensure that the hazardous secondary material will not be abandoned (for example, based on past practices, market factors, the nature of the hazardous secondary material, or any contractual arrangements);
- Whether the hazardous constituents in the hazardous secondary material are reclaimed rather than released to the air, water or land at significantly higher levels from either a statistical or from a health and environmental risk perspective than would otherwise be released by the production process; and
- Other relevant factors that demonstrate the hazardous secondary material is not discarded.
(ii) Respondent activities
The applicant prepares and submits an application to EPA under section 260.34.
Re-Application for Non-Waste Determination
40 CFR 260.33(c) applies to non-waste determinations and provides that, in the event of a change in circumstances that affects how a hazardous secondary material meets the relevant criteria contained in section 260.34 upon which a non-waste determination has been based, the applicant must re-apply to the Administrator for a formal determination that the hazardous secondary material continues to meet the relevant criteria and therefore is not a solid waste.
(i) Data item
Re-application to EPA for a formal determination that the hazardous secondary material continues to meet the relevant criteria and is therefore not a solid waste.
(ii) Respondent activities
The applicant must prepare and submit a re-application to EPA for a formal determination.
NOTIFICATION
40 CFR 260.42(a) provides that hazardous secondary material generators, tolling contractors, toll manufacturers, reclaimers, and intermediate facilities managing hazardous secondary materials which are excluded from regulation under section 261.2(a)(2)(ii) or section 261.4(a)(23), (24), or (25) must send a notification prior to operating under the exclusion(s) and by March 1 of each even numbered year thereafter to the Regional Administrator using EPA Form 8700-12 that includes the specified information at section 260.42(a)(1)-(10).
Section 260.42(b) provides that, if a hazardous secondary material generator, tolling contractor, toll manufacturer, reclaimer or intermediate facility has submitted a notification, but then subsequently stops managing hazardous secondary materials in accordance with the exclusion(s), the facility must notify the Regional Administrator within thirty (30) days using EPA Form 8700-12. For purposes of this section, a facility has stopped managing hazardous secondary materials if the facility no longer generates, manages and/or reclaims hazardous secondary materials under the exclusion(s) and does not expect to manage any amount of hazardous secondary materials for at least one year
(i) Data items
Notification using EPA Form 8700-12 that includes the following information:
- The name, address, and EPA ID number (if applicable) of the facility;
- The name and telephone number of a contact person;
- The NAICS code of the facility;
- The exclusion under which the hazardous secondary materials will be managed (e.g., section 261.2(a)(2)(ii), section 261.4(a)(23), (24), and/or (25));
- For reclaimers and intermediate facilities managing hazardous secondary materials in accordance with section 261.4(a)(24) or (25), whether the reclaimer or intermediate facility has financial assurance (not applicable for persons managing hazardous secondary materials generated and reclaimed under the control of the generator);
- When the facility expects to begin managing the hazardous secondary materials in accordance with the exclusion;
- A list of hazardous secondary materials that will be managed according to the exclusion (reported as the EPA hazardous waste numbers that would apply if the hazardous secondary materials were managed as hazardous wastes);
- For each hazardous secondary material, whether the hazardous secondary material, or any portion thereof, will be managed in a land-based unit;
- The quantity of each hazardous secondary material to be managed annually; and
The certification (included in EPA Form 8700-12) signed and dated by an authorized representative of the facility.
(ii) Respondent activities
Generators, intermediate facilities, and reclamation facilities must perform the following activities:
- Prepare and submit a notification to EPA prior to operating under exclusion(s).
- Update and submit a notification to EPA by March 1 of each even numbered year thereafter.
- Update and submit a notification that the hazardous secondary materials are no longer managed in accordance with the exclusion, if applicable.
EXCLUSIONS FROM THE DEFINITION OF SOLID WASTE
Exclusion at 40 CFR 261.2(a)(2)(ii)
40 CFR 261.2(a)(2)(ii) provides that a hazardous secondary material is not discarded if it is generated and reclaimed under the control of the generator as defined in section 260.10, it is not speculatively accumulated as defined in section 261.1(c)(8), it is handled only in non-land-based units and is contained in such units, it is generated and reclaimed within the United States and its territories, it is not otherwise subject to material-specific management conditions under section 261.4(a) when reclaimed, it is not a spent lead acid battery (see sections 266.80 and 273.2), it does not meet the listing description for K171 or K172 in section 261.32, and the reclamation of the material is legitimate, as specified under section 260.43. The notification requirements of section 260.42 also apply. For hazardous secondary materials managed in land-based units, see section 261.4(a)(23). [Note: This supporting statement addresses the data items and respondent activities associated with this exclusion under “Certifications for Hazardous Secondary Material Generated and Reclaimed under the Control of the Generator” and “Notification.”]
Exclusion at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(23)
40 CFR 261.4(a)(23) provides that hazardous secondary material generated and reclaimed within the United States or its territories and managed in land-based units as defined in section 260.10 is not a solid waste provided that: the material is contained (261.4(a)(23)(i)); the material is a hazardous secondary material generated and reclaimed under the control of the generator, as defined in section 260.10 (261.4(a)(23)(ii)); the material is not speculatively accumulated, as defined in section 261.1(c)(8) (261.4(a)(23)(iii)); the material is not otherwise subject to material-specific management conditions under section 261.4(a) when reclaimed, it is not a spent lead acid battery (see sections 266.80 and 273.2), and it does not meet the listing description for K171 or K172 in section 261.32 (261.4(a)(23)(iv)); and the reclamation of the material is legitimate, as specified under section 260.43 (261.4(a)(23)(v)). In addition, persons claiming the exclusion under section 261.4(a)(23) must provide notification as required by section 260.42 (261.4(a)(23)(vi)). For hazardous secondary materials managed in a non-land-based unit, see section 261.2(a)(2)(ii). [Note: This supporting statement addresses the data items and respondent activities associated with this exclusion under “Certifications for Hazardous Secondary Material Generated and Reclaimed under the Control of the Generator” and “Notification.”]
Exclusion at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(24)
40 CFR 261.4(a)(24) provides that hazardous secondary material that is generated and then transferred to another person for the purpose of reclamation is not a solid waste, provided that the requirements of section 261.4(a)(24)(i)-(vii) are met. Section 261.4(a)(24)(i)-(iv) sets forth technical standards applicable to the material (e.g., requirements for handling the material).
Section 261.4(a)(24)(v) provides that the hazardous secondary material generator must satisfy the conditions of section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(A)-(E). Section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(A) provides that the material must be contained. Section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(B) provides that, prior to arranging for transport of hazardous secondary materials to a reclamation facility (or facilities) where the management of the hazardous secondary materials is not addressed under a RCRA Part B permit or interim status standards, the hazardous secondary material generator must make reasonable efforts to ensure that each reclaimer intends to properly and legitimately reclaim the hazardous secondary material and not discard it, and that each reclaimer will manage the hazardous secondary material in a manner that is protective of human health and the environment. If the hazardous secondary material will be passing through an intermediate facility where the management of the hazardous secondary materials is not addressed under a RCRA Part B permit or interim status standards, the hazardous secondary material generator must make contractual arrangements with the intermediate facility to ensure that the hazardous secondary material is sent to the reclamation facility identified by the hazardous secondary material generator, and the hazardous secondary material generator must perform reasonable efforts to ensure that the intermediate facility will manage the hazardous secondary material in a manner that is protective of human health and the environment. Reasonable efforts must be repeated at a minimum of every three years for the hazardous secondary material generator to claim the exclusion and to send the hazardous secondary materials to each reclaimer and any intermediate facility. In making these reasonable efforts, the generator may use any credible evidence available, including information gathered by the hazardous secondary material generator, provided by the reclaimer or intermediate facility, and/or provided by a third party. Section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(C) provides that the hazardous secondary material generator must maintain for a minimum of three years documentation and certification that reasonable efforts were made for each reclamation facility and, if applicable, intermediate facility where the management of the hazardous secondary materials is not addressed under a RCRA Part B permit or interim status standards prior to transferring hazardous secondary material. Documentation and certification must be made available upon request by a regulatory authority within 72 hours, or within a longer period of time as specified by the regulatory authority. Section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(D) provides that the hazardous secondary material generator must maintain at the generating facility for no less than three (3) years records of all off-site shipments of hazardous secondary materials. Section 261.4(a)(v)(E) provides that the hazardous secondary material generator must maintain at the generating facility for no less than three (3) years confirmations of receipt from each reclaimer and, if applicable, each intermediate facility for all off-site shipments of hazardous secondary materials.
Section 261.4(a)(24)(vi) provides that reclaimers of hazardous secondary material excluded from regulation under this exclusion and intermediate facilities as defined in section 260.10 must satisfy the conditions of section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(A)-(F). Section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(A) provides that the reclaimer and intermediate facility must maintain at its facility for no less than three (3) years records of all shipments of hazardous secondary material that were received at the facility and, if applicable, for all shipments of hazardous secondary materials that were received and subsequently sent off-site from the facility for further reclamation. Section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(B) provides that the intermediate facility must send the hazardous secondary material to the reclaimer(s) designated by the hazardous secondary materials generator. Section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(C) provides that the reclaimer and intermediate facility must send to the hazardous secondary material generator confirmations of receipt for all off-site shipments of hazardous secondary materials. Section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(D) and (E) provides technical standards for the management of hazardous secondary material and residuals from reclamation. Section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F) provides that the reclaimer and intermediate facility must have financial assurance as required under Subpart H of 40 CFR Part 261. [Note: This supporting statement addresses the data items and respondent activities associated with the financial assurance requirements under “Financial Requirements for Management of Excluded Hazardous Secondary Materials.”]
Section 261.4(a)(24)(vii) provides that all persons claiming the exclusion under section 261.4(a)(24) must provide notification as required under section 260.42. [Note: This supporting statement addresses the data items and respondent activities associated with this notification requirement under “Notification.”]
(i) Data items
Contractual arrangements between the hazardous secondary material generator and intermediate facility (or facilities) under section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(B), if needed, to ensure that the hazardous secondary material is sent to each reclamation facility identified by the hazardous secondary material generator.
Documentation under section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(C) that reasonable efforts were made for each reclamation facility and any intermediate facility, if applicable, prior to transferring hazardous secondary material. The hazardous secondary material generator must affirmatively answer all of the following questions specified under section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(B) for each reclamation facility and any intermediate facility:
- Does the available information indicate that the reclamation process is legitimate pursuant to section 260.43? In answering this question, the hazardous secondary material generator can rely on their existing knowledge of the physical and chemical properties of the hazardous secondary material, as well as information from other sources (e.g., the reclamation facility, audit reports, etc.) about the reclamation process. (By responding to this question, the hazardous secondary material generator has also satisfied its requirement in section 260.43(a) to be able to demonstrate that the recycling is legitimate).
- Does the publicly available information indicate that the reclamation facility and any intermediate facility that is used by the hazardous secondary material generator notified the appropriate authorities of hazardous secondary materials reclamation activities pursuant to section 260.42 and have they notified the appropriate authorities that the financial assurance condition is satisfied per section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F)? In answering these questions, the hazardous secondary material generator can rely on the available information documenting the reclamation facility’s and any intermediate facility’s compliance with the notification requirements per section 260.42, including the requirement in section 260.42(a)(5) to notify EPA whether the reclaimer or intermediate facility has financial assurance.
- Does publicly available information indicate that the reclamation facility or any intermediate facility that is used by the hazardous secondary material generator has not had any formal enforcement actions taken against the facility in the previous three years for violations of the RCRA hazardous waste regulations and has not been classified as a significant non-complier with RCRA Subtitle C? In answering this question, the hazardous secondary material generator can rely on the publicly available information from EPA or the state. If the reclamation facility or any intermediate facility that is used by the hazardous secondary material generator has had a formal enforcement action taken against the facility in the previous three years for violations of the RCRA hazardous waste regulations and has been classified as a significant non-complier with RCRA Subtitle C, does the hazardous secondary material generator have credible evidence that the facilities will manage the hazardous secondary materials properly? In answering this question, the hazardous secondary material generator can obtain additional information from EPA, the state, or the facility itself that the facility has addressed the violations, taken remedial steps to address the violations and prevent future violations, or that the violations are not relevant to the proper management of the hazardous secondary materials.
- Does the available information indicate that the reclamation facility and any intermediate facility that is used by the hazardous secondary material generator have the equipment and trained personnel to safely recycle the hazardous secondary material? In answering this question, the generator may rely on a description by the reclamation facility or by an independent third party of the equipment and trained personnel to be used to recycle the generator’s hazardous secondary material.
- If residuals are generated from the reclamation of the excluded hazardous secondary materials, does the reclamation facility have the permits required (if any) to manage the residuals? If not, does the reclamation facility have a contract with an appropriately permitted facility to dispose of the residuals? If not, does the hazardous secondary material generator have credible evidence that the residuals will be managed in a manner that is protective of human health and the environment? In answering these questions, the hazardous secondary material generator can rely on publicly available information from EPA or the state, or information provided by the facility itself.
A certification statement under section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(C) that must include the printed name and official title of an authorized representative of the hazardous secondary material generator company, the authorized representative’s signature, and the date signed. The certification must incorporate the following language: “I hereby certify in good faith and to the best of my knowledge that, prior to arranging for transport of excluded hazardous secondary materials to [insert name(s) of reclamation facility and any intermediate facility], reasonable efforts were made in accordance with section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(B) to ensure that the hazardous secondary materials would be recycled legitimately, and otherwise managed in a manner that is protective of human health and the environment, and that such efforts were based on current and accurate information.”
Records retained by the generator under section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(D) of each shipment, including the following information at a minimum:
- Name of the transporter and date of the shipment;
- Name and address of each reclaimer, and, if applicable, the name and address of each intermediate facility to which the hazardous secondary material was sent; and
- The type and quantity of hazardous secondary material in the shipment.
Confirmations of receipt retained under section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(E) by the generator from each intermediate and reclamation facility, including the name and address of the reclaimer (or intermediate facility), the type and quantity of the hazardous secondary materials received and the date which the hazardous secondary materials were received. This requirement may be satisfied by routine business records (e.g., financial records, bills of lading, copies of DOT shipping papers, or electronic confirmations of receipt).
Records retained by an intermediate facility or reclaimer under section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(A) of each shipment received, including the following information at a minimum:
- Name of the transporter and date of the shipment;
- Name and address of the hazardous secondary material generator and, if applicable, the name and address of the reclaimer or intermediate facility which the hazardous secondary materials were received from;
- The type and quantity of hazardous secondary material in the shipment; and
- For hazardous secondary materials that, after being received by the reclaimer or intermediate facility, were subsequently transferred off-site for further reclamation, the name and address of the (subsequent) reclaimer and, if applicable, the name and address of each intermediate facility to which the hazardous secondary material was sent.
Confirmations of receipt of shipment sent from the intermediate and reclamation facilities under section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(C) that must include the name and address of the reclaimer (or intermediate facility), the type and quantity of the hazardous secondary materials received and the date which the hazardous secondary materials were received. This requirement may be satisfied by routine business records (e.g., financial records, bills of lading, copies of DOT shipping papers, or electronic confirmations of receipt).
(ii) Respondent activities
The generator must perform the following activities:
Conduct reasonable efforts for intermediate facilities and reclaimers as specified and prepare the certification statement.
Repeat the reasonable efforts at least every three years.
Make contractual arrangements with the intermediate facility, if applicable.
- Maintain for a minimum of three years documentation and certification that reasonable efforts were made as specified.
Make documentation and certification available upon request by a regulatory authority within 72 hours, or within a longer period of time as specified by the regulatory authority.
Maintain for no less than three years records of all off-site shipments of excluded hazardous secondary materials.
Maintain for no less than three years confirmations of receipt from the intermediate and reclamation facilities.
The intermediate facility and reclaimer must perform the following activities:
- Maintain for no less than three years records of each shipment received; and
- Send confirmations of receipt of shipment to the generator.
Export Requirements at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(25)
40 CFR 261.4(a)(25) provides that hazardous secondary material that is exported from the United States and reclaimed at a reclamation facility located in a foreign country is not a solid waste, provided that the hazardous secondary material generator complies with the applicable requirements of section 261.4(a)(24)(i)-(v) (excepting section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(B)(2) for foreign reclaimers and foreign intermediate facilities), and that the hazardous secondary material generator also complies with the conditions in section 261.4(a)(25).
Section 261.4(a)(25)(i) provides that the hazardous secondary material generator must notify EPA of an intended export before the hazardous secondary material is scheduled to leave the United States. A complete notification must be submitted at least sixty (60) days before the initial shipment is intended to be shipped off-site. This notification may cover export activities extending over a twelve (12) month or lesser period. Section 261.4(a)(25)(ii) sets forth addresses for submittal of notifications and provides that the following shall be prominently displayed on the front of the envelope: “Attention: Notification of Intent to Export.” Section 261.4(a)(25)(iii) provides that, except for changes to the telephone number in paragraph (i)(A) of this section and decreases in the quantity of hazardous secondary material indicated pursuant to paragraph (i)(D) of this section, when the conditions specified on the original notification change (including any exceedance of the estimate of the quantity of hazardous secondary material specified in the original notification), the hazardous secondary material generator must provide EPA with a written renotification of the change. The shipment cannot take place until consent of the receiving country to the changes (except for changes to paragraph (i)(I) of this section and in the ports of entry to and departure from transit countries pursuant to paragraph (i)(E) of this section) has been obtained and the hazardous secondary material generator receives from EPA an Acknowledgment of Consent reflecting the receiving country’s consent to the changes. Section 261.4(a)(25)(iv) provides that, upon request by EPA, the hazardous secondary material generator shall furnish to EPA any additional information which a receiving country requests in order to respond to a notification.
Section 261.4(a)(25)(v) describes procedures for EPA to notify the receiving country and any transit countries. Section 261.4(a)(25)(vi) sets forth provisions for the consent, objection, and withdrawal of prior consent of an intended export shipment by a receiving country. Section 261.4(a)(25)(vii) provides that, for exports to OECD Member countries, the receiving country may respond to the notification using tacit consent. If no objection has been lodged by any receiving country or transit countries to a notification provided pursuant to paragraph (i) of this section within thirty (30) days after the date of issuance of the acknowledgement of receipt of notification by the competent authority of the receiving country, the transboundary movement may commence. . In such cases, EPA will send an Acknowledgment of Consent to inform the hazardous secondary material generator that the receiving country and any relevant transit countries have not objected to the shipment, and are thus presumed to have consented tacitly. Tacit consent expires one (1) calendar year after the close of the thirty (30) day period; renotification and renewal of all consents is required for exports after that date.
Section 261.4(a)(25)(viii) provides that a copy of the Acknowledgment of Consent must accompany the shipment. The shipment must conform to the terms of the Acknowledgment of Consent. Section 261.4(a)(25)(ix) provides that, if a shipment cannot be delivered for any reason to the reclaimer, intermediate facility or the alternate reclaimer or alternate intermediate facility, the hazardous secondary material generator must re-notify EPA of a change in the conditions of the original notification to allow shipment to a new reclaimer in accordance with paragraph (iii) of this section and obtain another Acknowledgment of Consent. Section 261.4(a)(25)(x) provides that hazardous secondary material generators must keep a copy of each notification of intent to export and each Acknowledgment of Consent for a period of three years following receipt of the Acknowledgment of Consent. Section 261.4(a)(25)(xi) provides that hazardous secondary material generators must file with the Administrator no later than March 1 of each year, a report summarizing the types, quantities, frequency and ultimate destination of all hazardous secondary materials exported during the previous calendar year. Such reports must include the information in section 261.4(a)(25)(xi)(A)-(E).
Section 261.4(a)(25)(xii) provides that all persons claiming an exclusion under section 261.4(a)(25) must provide notification as required by section 260.42. [Note: This supporting statement addresses the data items and respondent activities associated with this notification requirement under “Notification.”]
(i) Data items
A notification under section 261.4(a)(25)(i) that is in writing, signed by the hazardous secondary material generator, and includes the following information:
- Name, mailing address, telephone number and EPA ID number (if applicable) of the hazardous secondary material generator;
A description of the hazardous secondary material and the EPA hazardous waste number that would apply if the hazardous secondary material was managed as hazardous waste and the U.S. DOT proper shipping name, hazard class and ID number (UN/NA) for each hazardous secondary material as identified in 49 CFR parts 171 through 177;
- The estimated frequency or rate at which the hazardous secondary material is to be exported and the period of time over which the hazardous secondary material is to be exported;
- The estimated total quantity of hazardous secondary material;
- All points of entry to and departure from each foreign country through which the hazardous secondary material will pass;
- A description of the means by which each shipment of the hazardous secondary material will be transported (e.g., mode of transportation vehicle (air, highway, rail, water, etc.), type(s) of container (drums, boxes, tanks, etc.));
- A description of the manner in which the hazardous secondary material will be reclaimed in the receiving country;
- The name and address of the reclaimer, any intermediate facility and any alternate reclaimer and intermediate facilities;
The name of any transit countries through which the hazardous secondary material will be sent and a description of the approximate length of time it will remain in such countries and the nature of its handling while there (for purposes of this section, the terms “Acknowledgement of Consent”, “receiving country” and “transit country” are used as defined in 40 CFR 262.51 with the exception that the terms in this section refer to hazardous secondary materials, rather than hazardous waste); and
- The following must be prominently displayed on the front of the envelope: “Attention: Notification of Intent to Export.”
When the conditions specified on the original notification change as applicable, a written renotification of the change, as required under section 261.4(a)(25)(iii).
Any additional information which a receiving country requests in order to respond to a notification, as required under section 261.4(a)(25)(iv).
Copies of Acknowledgement of Consent.
If a shipment cannot be delivered for any reason to the reclaimer, intermediate facility or the alternate reclaimer or alternate intermediate facility, a renotification to EPA of a change in the conditions of the original notification, as required under section 261.4(a)(25)(ix).
A report under section 261.4(a)(25)(xi) summarizing the types, quantities, frequency and ultimate destination of all hazardous secondary materials exported during the previous calendar year. Such reports must include the following information:
- Name, mailing and site address, and EPA ID number (if applicable) of the hazardous secondary material generator;
- The calendar year covered by the report;
- The name and site address of each reclaimer and intermediate facility;
- By reclaimer and intermediate facility, for each hazardous secondary material exported, a description of the hazardous secondary material and the EPA hazardous waste number that would apply if the hazardous secondary material was managed as hazardous waste, DOT hazard class, the name and US EPA ID number (where applicable) for each transporter used, the total amount of hazardous secondary material shipped and the number of shipments pursuant to each notification; and
- A certification signed by the hazardous secondary material generator which states: “I certify under penalty of law that I have personally examined and am familiar with the information submitted in this and all attached documents, and that based on my inquiry of those individuals immediately responsible for obtaining the information, I believe that the submitted information is true, accurate, and complete. I am aware that there are significant penalties for submitting false information including the possibility of fine and imprisonment.”
(ii) Respondent activities
The generator must perform the following activities:
- Prepare and submit notification.
- Prepare and submit a written renotification of the change when the conditions specified on the original notification change.
Provide any additional information which a receiving country requests in order to respond to a notification, as requested by EPA.
Provide Acknowledgement of Consent to transporter.
If a shipment cannot be delivered for any reason to the reclaimer, intermediate facility or the alternate reclaimer or alternate intermediate facility, re-notify EPA of a change in the conditions of the original notification and obtain another Acknowledgment of Consent.
Keep copies of notifications and Acknowledgments of Consent for a period of three years following receipt of the Acknowledgment.
Prepare and submit annual report.
FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS FOR MANAGEMENT OF EXCLUDED HAZARDOUS SECONDARY MATERIALS
40 CFR 261.140(a) provides that the requirements of 40 CFR Part 261 Subpart H, “Financial Requirements for Management of Excluded Hazardous Secondary Materials,” apply to owners or operators of reclamation and intermediate facilities managing hazardous secondary materials excluded under 40 CFR 261.4(a)(24), except as provided otherwise. Section 261.140(b) provides that States and the Federal government are exempt from the financial assurance requirements of the subpart.
Cost Estimate
40 CFR 261.142(a) requires owners or operators to have a detailed written estimate, in current dollars, of the cost of disposing of any hazardous secondary material as listed or characteristic hazardous waste, and the potential cost of closing the facility as a treatment, storage, and disposal facility. The cost estimate must satisfy the requirements of section 261.142(a)(1)-(4).
Section 261.142(b) requires that, during the active life of the facility, the owner or operator must adjust the cost estimate for inflation within 60 days prior to the anniversary date of the establishment of the financial instrument(s) used to comply with section 261.143. For owners or operators using the financial test or corporate guarantee, the cost estimate must be updated for inflation within 30 days after the close of the firm's fiscal year and before submission of updated information to the Regional Administrator as specified in section 261.143(e)(3).
Section 261.142(c) provides that, during the active life of the facility, the owner or operator must revise the cost estimate no later than 30 days after a change in a facility’s operating plan or design that would increase the costs of conducting the activities described in section 261.142(a) or no later than 60 days after an unexpected event which increases the cost of conducting the activities described in section 261.142(a). The revised cost estimate must be adjusted for inflation as specified in section 261.142(b).
Section 261.142(d) requires the owner or operator to keep the following at the facility during the operating life of the facility: The latest cost estimate prepared in accordance with section 261.142(a) and (c) and, when this estimate has been adjusted in accordance with section 261.142(b), the latest adjusted cost estimate.
(i) Data items
A cost estimate that satisfies the requirements of section 261.142(a)(1)-(4):
- The estimate must equal the cost of conducting the activities described in paragraph (a) at the point when the extent and manner of the facility’s operation would make these activities the most expensive.
- The cost estimate must be based on the costs to the owner or operator of hiring a third party to conduct these activities. A third party is a party who is neither a parent nor a subsidiary of the owner or operator. (See definition of parent corporation in section 265.141(d).) The owner or operator may use costs for on-site disposal in accordance with applicable requirements if he can demonstrate that on-site disposal capacity will exist at all times over the life of the facility.
- The cost estimate may not incorporate any salvage value that may be realized with the sale of hazardous secondary materials, or hazardous or non-hazardous wastes if applicable under 265.113(d), facility structures or equipment, land, or other assets associated with the facility.
- The owner or operator may not incorporate a zero cost for hazardous secondary materials, or hazardous or non-hazardous wastes if applicable under 265.113(d), that might have economic value.
Adjustments to the cost estimate in accordance with section 261.142(b). The adjustment may be made by recalculating the cost estimate in current dollars, or by using an inflation factor derived from the most recent Implicit Price Deflator for Gross National Product published by the U.S. Department of Commerce in its Survey of Current Business, as specified in paragraphs (b)(1) and (2) of this section. The inflation factor is the result of dividing the latest published annual Deflator by the Deflator for the previous year. The first adjustment is made by multiplying the cost estimate by the inflation factor. The result is the adjusted cost estimate. Subsequent adjustments are made by multiplying the latest adjusted cost estimate by the latest inflation factor.
Revisions to the cost estimate in accordance with section 261.142(c).
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must perform the following activities:
- Prepare a detailed written cost estimate.
Adjust and revise the cost estimate as specified.
- Keep records of the cost estimate as specified.
Financial Assurance Condition
Per 40 CFR 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F), an owner or operator of a reclamation or intermediate facility must have financial assurance as a condition of the exclusion as required under section 261.4(a)(24). He must choose from the options as specified in section 261.143(a) through (e).
(1) Trust Fund
40 CFR 261.143(a)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by establishing a trust fund which conforms to the requirements of this paragraph and submitting an originally signed duplicate of the trust agreement to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(a)(2) provides that the wording of the trust agreement must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(a)(1), and the trust agreement must be accompanied by a formal certification of acknowledgment. Schedule A of the trust agreement must be updated within 60 days after a change in the amount of the current cost estimate covered by the agreement. Section 261.143(a)(3) provides that the trust fund must be funded for the full amount of the current cost estimate before it may be relied upon to satisfy the requirements of this section. Section 261.143(a)(4) provides that, whenever the current cost estimate changes, the owner or operator must compare the new estimate with the trustee's most recent annual valuation of the trust fund. If the value of the fund is less than the amount of the new estimate, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the change in the cost estimate, must either deposit an amount into the fund so that its value after this deposit at least equals the amount of the current cost estimate, or obtain other financial assurance as specified in this section to cover the difference. Section 261.143(a)(5) provides that, if the value of the trust fund is greater than the total amount of the current cost estimate, the owner or operator may submit a written request to the Regional Administrator for release of the amount in excess of the current cost estimate. Section 261.143(a)(6) provides that, if an owner or operator substitutes other financial assurance as specified in this section for all or part of the trust fund, he may submit a written request to the Regional Administrator for release of the amount in excess of the current cost estimate covered by the trust fund. Section 261.143(a)(7) provides that, within 60 days after receiving a request from the owner or operator for release of funds as specified, the Regional Administrator will instruct the trustee to release to the owner or operator such funds as the Regional Administrator specifies in writing. If the owner or operator begins final closure under Subpart G of 40 CFR Part 264 or 265, an owner or operator may request reimbursements for partial or final closure expenditures by submitting itemized bills to the Regional Administrator. The owner or operator may request reimbursements for partial closure only if sufficient funds are remaining in the trust fund to cover the maximum costs of closing the facility over its remaining operating life. Section 261.143(a)(8) describes EPA procedures for termination of the trust.
(i) Data items
An originally signed duplicate of a trust agreement whose wording is identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(a)(1).
A formal certification of acknowledgment, as required under section 261.143(a)(2).
Update of Schedule A of the trust agreement, as required under section 261.143(a)(2).
A written request under section 261.143(a)(5) to the Regional Administrator for release of the amount in excess of the current cost estimate, if the value of the trust fund is greater than the total amount of the current cost estimate.
A written request under section 261.143(a)(6) to the Regional Administrator for release of the amount in excess of the current cost estimate covered by the trust fund, if the owner or operator substitutes other financial assurance as specified in this section for all or part of the trust fund.
A request for reimbursements under section 261.143(a)(7) for partial or final closure expenditures, including itemized bills, to the Regional Administrator.
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must perform the following activities:
- Prepare and submit an originally signed duplicate of the trust agreement and formal certification of acknowledgement to EPA.
Update Schedule A of the trust agreement, as specified.
- Whenever the current cost estimate changes:
- Compare the new estimate with the trustee's most recent annual valuation of the trust fund; and
- If the value of the fund is less than the amount of the new estimate, obtain other financial assurance to cover the difference, unless a deposit has been made as specified.
- If the value of the trust fund is greater than the total amount of the current cost estimate, submit a written request to the Regional Administrator for release of the amount in excess of the current cost estimate.
- If the owner or operator substitutes other financial assurance as specified in this section for all or part of the trust fund, submit a written request to the Regional Administrator for release of the amount in excess of the current cost estimate covered by the trust fund.
- Submit a request for reimbursements, if applicable.
The grantor (owner/operator) and trustee must comply with the terms of the trust agreement.
(2) Surety Bond Guaranteeing Payment into a Trust Fund
40 CFR 261.143(b)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by obtaining a surety bond which conforms to the requirements of this paragraph and submitting the bond to the Regional Administrator. The surety company issuing the bond must, at a minimum, be among those listed as acceptable sureties on Federal bonds in Circular 570 of the U.S. Department of the Treasury. Section 261.143(b)(2) requires the wording of the surety bond to be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(b). Section 261.143(b)(3) provides that the owner or operator who uses a surety bond to satisfy the requirements of this section must also establish a standby trust fund. This standby trust fund must meet the requirements specified in section 261.143(a), except as otherwise specified. [Note: This supporting statement addresses the data items and respondent activities associated with the standby trust fund under “Trust Fund.”] Section 261.143(b)(4) provides that the bond must make specified guarantees. Section 261.143(b)(5) and (6) describe standards related to the owner or operator’s failure to perform as guaranteed and the penal sum amount. Section 261.143(b)(7) provides that, whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the penal sum, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the penal sum to be increased to an amount at least equal to the current cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Regional Administrator, or obtain other financial assurance as specified in this section to cover the increase. Whenever the current cost estimate decreases, the penal sum may be reduced to the amount of the current cost estimate following written approval by the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(b)(8) provides that, under the terms of the bond, the surety may cancel the bond by sending notice of cancellation by certified mail to the owner or operator and to the Regional Administrator. Cancellation may not occur, however, during the 120 days beginning on the date of receipt of the notice of cancellation by both the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator, as evidenced by the return receipts. Section 261.143(b)(9) provides that the owner or operator may cancel the bond if the Regional Administrator has given prior written consent based on his receipt of evidence of alternate financial assurance as specified in this section.
(i) Data items
A surety bond whose wording is identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(b).
Evidence of an increase in the penal sum or other financial assurance as specified to cover the increase, whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the penal sum, as provided under section 261.143(b)(7).
Notice of bond cancellation, as provided under section 261.143(b)(8).
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must perform the following activities:
- Prepare and submit the surety bond to EPA.
Whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the penal sum, submit evidence of the increase in the penal sum to the Regional Administrator or obtain other financial assurance to cover the increase.
- Obtain alternate financial assurance and obtain EPA approval if required because of cancellation of the bond.
The surety company may cancel the bond by sending notice of cancellation by certified mail to the owner or operator and to the Regional Administrator.
The owner or operator and surety company must comply with the terms of the surety bond.
(3) Letter of Credit
40 CFR 261.143(c)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by obtaining an irrevocable standby letter of credit which conforms to the requirements of this paragraph and submitting the letter to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(c)(2) provides that the wording of the letter of credit must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(c). Section 261.143(c)(3) provides that an owner or operator who uses a letter of credit to satisfy the requirements of this section must also establish a standby trust fund, as specified. This standby trust fund must meet the requirements of the trust fund specified in section 261.143(a), except as otherwise specified. An originally signed duplicate of the trust agreement must be submitted to the Regional Administrator with the letter of credit. [Note: This supporting statement addresses the data items and respondent activities associated with the standby trust fund under “Trust Fund.”] Section 261.143(c)(4) provides that the letter of credit must be accompanied by a letter from the owner or operator, referring to the letter of credit as specified. Section 261.143(c)(5) provides that the letter of credit must be irrevocable and issued for a period of at least 1 year. The letter of credit must provide that the expiration date will be automatically extended for a period of at least 1 year unless, at least 120 days before the current expiration date, the issuing institution notifies both the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator by certified mail of a decision not to extend the expiration date. Section 261.143(c)(6) specifies that the letter of credit must be issued in an amount at least equal to the current cost estimate, except as provided in section 261.143(f). Section 261.143(c)(7) provides that, whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the amount of the credit, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the amount of the credit to be increased so that it at least equals the current cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Regional Administrator, or obtain other financial assurance as specified in this section to cover the increase. Whenever the current cost estimate decreases, the amount of the credit may be reduced to the amount of the current cost estimate following written approval by the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(c)(8) provides that, following a determination by the Regional Administrator that the hazardous secondary materials do not meet the conditions of the exclusion under section 261.4(a)(24), the Regional Administrator may draw on the letter of credit. Section 261.143(c)(9) provides that, if the owner or operator does not establish alternate financial assurance as specified in this section and obtain written approval of such alternate assurance from the Regional Administrator within 90 days after receipt by both the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator of a notice from the issuing institution that it has decided not to extend the letter of credit beyond the current expiration date, the Regional Administrator will draw on the letter of credit. The Regional Administrator may delay the drawing if the issuing institution grants an extension of the term of the credit. During the last 30 days of any such extension the Regional Administrator will draw on the letter of credit if the owner or operator has failed to provide alternate financial assurance as specified in this section and obtain written approval of such assurance from the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(c)(10) addresses the return of the letter of credit by EPA to the issuing institution for termination.
(i) Data items
Irrevocable standby letter of credit whose wording is identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(c).
Letter from the owner or operator under section 261.143(c)(4), referring to the letter of credit by number, issuing institution, and date, and providing the following information: The EPA Identification Number (if any issued), name, and address of the facility, and the amount of funds assured for the facility by the letter of credit.
A letter from the issuing institution under section 261.143(c)(5), notifying both the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator by certified mail of a decision not to extend the expiration date.
Evidence of an increase in the credit or other financial assurance as specified to cover the increase, whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the amount of the credit, as provided under section 261.143(c)(7).
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must perform the following activities:
Prepare and submit letter of credit and letter referring to the letter of credit to the Regional Administrator.
Whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the amount of the credit, submit evidence to the Regional Administrator of an increase in the credit or obtain other financial assurance as specified to cover the increase.
- Obtain alternate financial assurance and obtain EPA approval if required because of termination of credit.
The issuing institution may send a notice of a decision not to extend the expiration date of the credit by certified mail to the owner or operator and to the Regional Administrator.
The owner/operator and issuing institution must comply with the terms of the letter of credit.
(4) Insurance
40 CFR 261.143(d)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by obtaining insurance which conforms to the requirements of this paragraph and submitting a certificate of such insurance to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(d)(2) provides that the wording of the certificate of insurance must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(d). Section 261.143(d)(3) provides that the insurance policy must be issued for a face amount at least equal to the current cost estimate, except as provided in section 261.143(f). Section 261.143(d)(4) provides that the insurance policy must make specified guarantees. Section 261.143(d)(5) provides that, after beginning partial or final closure under 40 CFR Part 264 or 265, as applicable, an owner or operator or any other authorized person may request reimbursements for closure expenditures by submitting itemized bills to the Regional Administrator, in accordance with specified standards. Section 261.143(d)(6) provides that the owner or operator must maintain the policy in full force and effect until the Regional Administrator consents to termination of the policy by the owner or operator as specified in paragraph (i)(10) of this section. Failure to pay the premium, without substitution of alternate financial assurance as specified in this section, will constitute a significant violation of these regulations, warranting such remedy as the Regional Administrator deems necessary. Such violation will be deemed to begin upon receipt by the Regional Administrator of a notice of future cancellation, termination, or failure to renew due to nonpayment of the premium, rather than upon the date of expiration. Section 261.143(d)(7) provides that each policy must contain a provision allowing assignment of the policy to a successor owner or operator. Such assignment may be conditional upon consent of the insurer, provided such consent is not unreasonably refused. Section 261.143(d)(8) provides that the policy must provide that the insurer may not cancel, terminate, or fail to renew the policy except for failure to pay the premium. The automatic renewal of the policy must, at a minimum, provide the insured with the option of renewal at the face amount of the expiring policy. If there is a failure to pay the premium, the insurer may elect to cancel, terminate, or fail to renew the policy by sending notice by certified mail to the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator. Cancellation, termination, or failure to renew may not occur, however, during the 120 days beginning with the date of receipt of the notice by both the Regional Administrator and the owner or operator, as evidenced by the return receipts. Cancellation, termination, or failure to renew may not occur and the policy will remain in full force and effect as specified. Section 261.143(d)(9) provides that, whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the face amount of the policy, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the face amount to be increased to an amount at least equal to the current cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Regional Administrator, or obtain other financial assurance as specified in this section to cover the increase. Whenever the current cost estimate decreases, the face amount may be reduced to the amount of the current cost estimate following written approval by the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(d)(10) provides that the Regional Administrator will give written consent to the owner or operator that he may terminate the insurance policy as specified.
(i) Data items
A certificate of insurance whose wording is identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(d).
A request for reimbursements for expenditures to EPA, including itemized bills, as specified under section 261.143(d)(5).
A notice sent by certified mail from the insurer that it has elected to cancel, terminate, or fail to renew the policy, as specified under section 261.143(d)(8).
Evidence of an increase in the credit or other financial assurance as specified to cover the increase, whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the face amount of the policy, as specified under section 261.143(d)(9).
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must perform the following activities:
- Prepare and submit a certificate of insurance to the Regional Administrator.
Request reimbursements for expenditures by submitting itemized bills to the Regional Administrator, if applicable.
Whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the face value of the policy, submit evidence to the Regional Administrator of an increase in the policy or obtain other financial assurance as specified to cover the increase.
- Obtain alternate financial assurance and obtain EPA approval if required because of cancellation, termination, or failure to renew the insurance.
The insurer may elect to cancel, terminate, or fail to renew the policy by sending notice by certified mail to the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator.
The owner/operator and insurer must comply with the terms of the certificate of insurance.
(5) Financial Test and Corporate Guarantee
40 CFR 261.143(e)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by demonstrating that he passes a financial test as specified in this paragraph. To pass this test the owner or operator must meet the criteria of either section 261.143(e)(1)(i) or (ii). Section 261.143(e)(2) defines phrases used in the regulations. Section 261.143(e)(3) provides that, to demonstrate that he meets this test, the owner or operator must submit specified items to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.143(e)(4) provides that the owner or operator may obtain an extension of the time allowed for submission of the documents specified in paragraph (e)(3) of this section if the fiscal year of the owner or operator ends during the 90 days prior to the effective date of these regulations and if the year-end financial statements for that fiscal year will be audited by an independent certified public accountant. The extension will end no later than 90 days after the end of the owner's or operator's fiscal year. To obtain the extension, the owner's or operator's chief financial officer must send, by the effective date of these regulations, a letter to the Regional Administrator of each Region in which the owner's or operator's facilities to be covered by the financial test are located. Section 261.143(e)(5) provides that, after the initial submission of items specified in paragraph (e)(3) of this section, the owner or operator must send updated information to the Regional Administrator within 90 days after the close of each succeeding fiscal year. This information must consist of all three items specified in paragraph (e)(3) of this section. Section 261.143(e)(6) provides that, if the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of paragraph (e)(1) of this section, he must send notice to the Regional Administrator of intent to establish alternate financial assurance as specified in this section. The notice must be sent by certified mail within 90 days after the end of the fiscal year for which the year-end financial data show that the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements. The owner or operator must provide the alternate financial assurance within 120 days after the end of such fiscal year. Section 261.143(e)(7) provides that the Regional Administrator may, based on a reasonable belief that the owner or operator may no longer meet the requirements of paragraph (e)(1) of this section, require reports of financial condition at any time from the owner or operator in addition to those specified in paragraph (e)(3) of this section. If the Regional Administrator finds, on the basis of such reports or other information, that the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of paragraph (e)(1) of this section, the owner or operator must provide alternate financial assurance as specified in this section within 30 days after notification of such a finding. Section 261.143(e)(8) provides that the Regional Administrator may disallow use of this test on the basis of qualifications in the opinion expressed by the independent certified public accountant in his report on examination of the owner's or operator's financial statements (see paragraph (e)(3)(ii) of this section). An adverse opinion or a disclaimer of opinion will be cause for disallowance. The Regional Administrator will evaluate other qualifications on an individual basis. The owner or operator must provide alternate financial assurance as specified in this section within 30 days after notification of the disallowance. Section 261.143(e)(9) describes circumstances when the owner or operator is no longer required to submit the items specified in paragraph (e)(3) of this section. Section 261.143(e)(10) provides that an owner or operator may meet the requirements of this section by obtaining a written guarantee. The guarantor must meet the requirements for owners or operators in paragraphs (e)(1) through (8) of this section and must comply with the terms of the guarantee. The wording of the guarantee must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(g)(1). A certified copy of the guarantee must accompany the items sent to the Regional Administrator as specified in paragraph (e)(3) of this section. One of these items must be the letter from the guarantor's chief financial officer, as described in section 261.143(e)(10).
(i) Data items
Information required under section 261.143(e)(3):
- A letter signed by the owner's or operator's chief financial officer and worded as specified in section 261.151(e).
- A copy of the independent certified public accountant's report on examination of the owner's or operator's financial statements for the latest completed fiscal year.
- A special report from the owner’s or operator’s independent certified public accountant to the owner or operator, if required. The special report shall be based upon an agreed upon procedures engagement in accordance with professional auditing standards and shall describe the procedures performed in comparing the data in the chief financial officer’s letter derived from the independently audited, year-end financial statements for the latest fiscal year with the amounts in such financial statements, the findings of the comparison, and the reasons for any differences.
A letter as required under section 261.143(e)(4) from the owner/operator’s chief financial officer that:
- Requests the extension;
- Certifies that he has grounds to believe that the owner or operator meets the criteria of the financial test;
- Specifies for each facility to be covered by the test the EPA Identification Number (if any issued), name, address, and current cost estimates to be covered by the test;
- Specifies the date ending the owner's or operator's last complete fiscal year before the effective date of these regulations;
- Specifies the date, no later than 90 days after the end of such fiscal year, when he will submit the documents specified in paragraph (e)(3) of this section; and
- Certifies that the year-end financial statements of the owner or operator for such fiscal year will be audited by an independent certified public accountant.
Annual update of information as required under section 261.143(e)(5), after the initial submission of these items.
Notice as required under section 261.143(e)(6) from the owner/operator to the Regional Administrator of intent to establish alternate financial assurance as specified in this section.
Reports as required under section 261.143(e)(7) of financial condition from the owner or operator in addition to those specified in paragraph (e)(3) of this section, if requested by the Regional Administrator.
A guarantee whose wording is identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(g)(1). A certified copy of the guarantee must accompany the items sent to the Regional Administrator. The terms of the guarantee must address the criteria specified in section 261.143(e)(10)(i)-(iii).
A letter under section 261.143(e)(10) from the guarantor's chief financial officer. If the guarantor's parent corporation is also the parent corporation of the owner or operator, the letter must describe the value received in consideration of the guarantee. If the guarantor is a firm with a ``substantial business relationship'' with the owner or operator, this letter must describe this ``substantial business relationship'' and the value received in consideration of the guarantee.
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must perform the following activities:
- Prepare and submit to EPA a signed letter, copy of the independent certified public accountant's report on examination of the owner's or operator's financial statements, a special report from the owner’s or operator’s independent certified public accountant if applicable, and a guarantee if applicable.
- To obtain an extension of the time allowed for submission of the documents specified in section 261.143(e)(3), prepare and send a letter to the Regional Administrator of each Region in which the owner's or operator's facilities to be covered by the financial test are located.
- Prepare and submit updated information to EPA under section 261.143(e)(5), at the close of each fiscal year, as specified.
- Prepare and submit a notice to EPA by certified mail of intent to establish alternate financial assurance.
- Prepare and submit reports of financial condition, if requested by the Regional Administrator.
- Obtain alternate financial assurance and obtain EPA approval if required because the financial tests are no longer met or disallowed by EPA.
- Comply with the terms in the letter from the chief financial officer and guarantee.
Use of Financial Mechanisms for Multiple Facilities
40 CFR 261.143(g) provides for the use of a financial mechanism for multiple facilities. An owner or operator may use a financial assurance mechanism specified in this section to meet the requirements of this section for more than one facility. Evidence of financial assurance submitted to the Regional Administrator must include a list showing, for each facility, the EPA Identification Number (if any issued), name, address, and the amount of funds assured by the mechanism. If the facilities covered by the mechanism are in more than one Region, identical evidence of financial assurance must be submitted to and maintained with the Regional Administrators of all such Regions. The amount of funds available through the mechanism must be no less than the sum of funds that would be available if a separate mechanism had been established and maintained for each facility. In directing funds available through the mechanism for any of the facilities covered by the mechanism, the Regional Administrator may direct only the amount of funds designated for that facility, unless the owner or operator agrees to the use of additional funds available under the mechanism.
(i) Data items
Evidence of financial assurance that must include a list showing, for each facility, the EPA Identification Number (if any issued), name, address, and the amount of funds assured by the mechanism.
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must submit identical evidence to each applicable Regional Administrator of financial assurance as specified.
Removal and Decontamination Plan and Release from Financial Assurance Obligations
40 CFR 261.143(h)(1) provides that an owner or operator of a reclamation facility or an intermediate facility who wishes to be released from his financial assurance obligations under section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F) must submit a plan for removing all hazardous secondary material residues to the Regional Administrator at least 180 days prior to the date on which he expects to cease to operate under the exclusion. Section 261.143(h)(2) spells out the contents of the plan. Section 261.143(h)(3) provides that the Regional Administrator will provide the owner or operator and the public, through a newspaper notice, the opportunity to submit written comments on the plan and request modifications to the plan no later than 30 days from the date of the notice. He will also, in response to a request or at his discretion, hold a public hearing whenever such a hearing might clarify one or more issues concerning the plan. The Regional Administrator will give public notice of the hearing at least 30 days before it occurs. The Regional Administrator will approve, modify, or disapprove the plan within 90 days of its receipt. If the Regional Administrator does not approve the plan, he shall provide the owner or operator with a detailed written statement of reasons for the refusal and the owner or operator must modify the plan or submit a new plan for approval within 30 days after receiving such written statement. The Regional Administrator will approve or modify this plan in writing within 60 days. If the Regional Administrator modifies the plan, this modified plan becomes the approved plan. The Regional Administrator must assure that the approved plan is consistent with applicable requirements. A copy of the modified plan with a detailed statement of reasons for the modifications must be mailed to the owner or operator. Section 261.143(h)(4) provides that, within 60 days of completion of the activities described for each hazardous secondary materials management unit, the owner or operator must submit to the Regional Administrator, by registered mail, a certification that all hazardous secondary materials have been removed from the unit and the unit has been decontaminated in accordance with the specifications in the approved plan. The certification must be signed by the owner or operator and by a qualified Professional Engineer. Documentation supporting the Professional Engineer's certification must be furnished to the Regional Administrator, upon request, until he releases the owner or operator from the financial assurance requirements for section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F).
Section 261.143(i) provides that, within 60 days after receiving certifications from the owner or operator and a qualified Professional Engineer that all hazardous secondary materials have been removed from the facility or a unit at the facility and the facility or a unit has been decontaminated in accordance with the approved plan per paragraph (h), the Regional Administrator will notify the owner or operator in writing that he is no longer required under section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F) to maintain financial assurance for that facility or a unit at the facility, unless the Regional Administrator has reason to believe that that all hazardous secondary materials have not been removed from the facility or unit at a facility or that the facility or unit has not been decontaminated in accordance with the approved plan. The Regional Administrator will provide the owner or operator a detailed written statement of any such reason to believe that all hazardous secondary materials have not been removed from the unit or that the unit has not been decontaminated in accordance with the approved plan.
(i) Data items
A plan under section 261.143(h)(1) and (2) for removing all hazardous secondary material residues per section 261.142(a). The plan must include, at least:
- For each hazardous secondary materials storage unit subject to financial assurance requirements under section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F), a description of how all excluded hazardous secondary materials will be recycled or sent for recycling, and how all residues, contaminated containment systems (liners, etc), contaminated soils, subsoils, structures, and equipment will be removed or decontaminated as necessary to protect human health and the environment;
- A detailed description of the steps necessary to remove or decontaminate all hazardous secondary material residues and contaminated containment system components, equipment, structures, and soils including, but not limited to, procedures for cleaning equipment and removing contaminated soils, methods for sampling and testing surrounding soils, and criteria for determining the extent of decontamination necessary to protect human health and the environment;
- A detailed description of any other activities necessary to protect human health and the environment during this timeframe, including, but not limited to, leachate collection, run-on and run-off control, etc; and
- A schedule for conducting the activities described which, at a minimum, includes the total time required to remove all excluded hazardous secondary materials for recycling and decontaminate all units subject to financial assurance under section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F) and the time required for intervening activities which will allow tracking of the progress of decontamination.
For each hazardous secondary materials management unit, a certification under section 261.143(h)(4) that all hazardous secondary materials have been removed from the unit and the unit has been decontaminated in accordance with the specifications in the approved plan. The certification must be signed by the owner or operator and by a qualified Professional Engineer.
Documentation under section 261.143(h)(4) supporting the Professional Engineer's certification.
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must perform the following activities:
Prepare and submit a plan to EPA for removing all hazardous secondary material residues.
Modify the plan or prepare a new one and submit it to EPA if a detailed written statement of reasons for EPA refusal is received.
Prepare and submit the certification to EPA by registered mail for each hazardous secondary materials management unit.
Furnish other documentation to EPA if requested supporting the Professional Engineer's certification.
Coverage for Sudden and Non-Sudden Accidental Occurrences
40 CFR 261.147(a) provides that an owner or operator of a hazardous secondary material reclamation facility or an intermediate facility subject to financial assurance requirements under section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F), or a group of such facilities, must demonstrate financial responsibility for bodily injury and property damage to third parties caused by sudden accidental occurrences arising from operations of the facility or group of facilities. Section 261.147(b) provides that an owner or operator of a hazardous secondary material reclamation facility or intermediate facility with land-based units, as defined in section 260.10, which are used to manage hazardous secondary materials excluded under section 261.4(a)(24), or a group of such facilities, must demonstrate financial responsibility for bodily injury and property damage to third parties caused by nonsudden accidental occurrences arising from operations of the facility or group of facilities. The owner or operator must have and maintain liability coverage for sudden and nonsudden accidental occurrences in the amounts specified in the regulations. This liability coverage may be demonstrated as specified in section 261.147(a)(1), (2), (3), (4), (5), or (6) for sudden accidental occurrences and section 261.147(b)(1), (2), (3), (4), (5), or (6) for nonsudden accidental occurrences.
(1) Liability Insurance
40 CFR 261.147(a)(1) and (b)(1) provides that an owner or operator may demonstrate the required liability coverage by having liability insurance for sudden and nonsudden accidental occurrences, as specified in section 261.147(a)(1) and (b)(1), respectively. Section 261.147(a)(1)(i) and (b)(1)(i) require that each insurance policy must be amended by attachment of the Hazardous Secondary Material Facility Liability Endorsement, or evidenced by a Certificate of Liability Insurance. The wording of the endorsement must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(h). The wording of the certificate of insurance must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(i). The owner or operator must submit a signed duplicate original of the endorsement or the certificate of insurance to the Regional Administrator, or Regional Administrators if the facilities are located in more than one Region. If requested by a Regional Administrator, the owner or operator must provide a signed duplicate original of the insurance policy. Section 261.147(a)(1)(ii) and (b)(1)(ii) provide that each insurance policy must be issued by an insurer which, at a minimum, is licensed to transact the business of insurance, or eligible to provide insurance as an excess or surplus lines insurer, in one or more States.
(i) Data items
An insurance policy that is amended by attachment of the Hazardous Secondary Material Facility Liability Endorsement, or evidenced by a Certificate of Liability Insurance. The wording of the endorsement must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(h). The wording of the certificate of insurance must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(i).
A signed duplicate original of the insurance policy.
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must perform the following activities:
- Prepare and submit an insurance policy that is attached to a signed duplicate original of the endorsement or the certificate of insurance to the Regional Administrator, or Regional Administrators if the facilities are located in more than one Region.
- Provide a signed duplicate original of the insurance policy, if requested by a Regional Administrator.
The owner/operator and insurer must comply with the terms of the endorsement or certificate, as applicable.
(2) Financial Test or Guarantee
40 CFR 261.147(a)(2) and (b)(2) provide that an owner or operator may meet the requirements of this section by passing a financial test or using the guarantee for liability coverage as specified in section 261.147(f) and (g).
Section 261.147(f)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by demonstrating that he passes a financial test as specified in this paragraph. To pass this test the owner or operator must meet the criteria of paragraph (f)(1)(i) or (ii) of this section. Section 261.147(f)(2) defines phrases used in the regulations. Section 261.147(f)(3) provides that, to demonstrate that he meets this test, the owner or operator must submit the specified items to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.147(f)(4) provides that the owner or operator may obtain a one-time extension of the time allowed for submission of the documents specified in paragraph (f)(3) of this section if the fiscal year of the owner or operator ends during the 90 days prior to the effective date of these regulations and if the year-end financial statements for that fiscal year will be audited by an independent certified public accountant. The extension will end no later than 90 days after the end of the owner's or operator's fiscal year. To obtain the extension, the owner's or operator's chief financial officer must send, by the effective date of these regulations, a letter to the Regional Administrator of each Region in which the owner's or operator's facilities to be covered by the financial test are located. Section 261.147(f)(5) provides that, after the initial submission of items specified in paragraph (f)(3) of this section, the owner or operator must send updated information to the Regional Administrator within 90 days after the close of each succeeding fiscal year. This information must consist of all three items specified in paragraph (f)(3) of this section. Section 261.147(f)(6) provides that, if the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of paragraph (f)(1) of this section, he must obtain insurance, a letter of credit, a surety bond, a trust fund, or a guarantee for the entire amount of required liability coverage as specified in this section. Evidence of liability coverage must be submitted to the Regional Administrator within 90 days after the end of the fiscal year for which the year-end financial data show that the owner or operator no longer meets the test requirements. Section 261.147(f)(7) provides that the Regional Administrator may disallow use of this test on the basis of qualifications in the opinion expressed by the independent certified public accountant in his report on examination of the owner's or operator's financial statements (see paragraph (f)(3)(ii) of this section). An adverse opinion or a disclaimer of opinion will be cause for disallowance. The Regional Administrator will evaluate other qualifications on an individual basis. The owner or operator must provide evidence of insurance for the entire amount of required liability coverage as specified in this section within 30 days after notification of disallowance.
Section 261.147(g)(1) provides that, subject to paragraph (g)(2) of this section, an owner or operator may meet the requirements of this section by obtaining a written guarantee, hereinafter referred to as “guarantee.” The guarantor must be the direct or higher-tier parent corporation of the owner or operator, a firm whose parent corporation is also the parent corporation of the owner or operator, or a firm with a “substantial business relationship” with the owner or operator. The guarantor must meet the requirements for owners or operators in paragraphs (f)(1) through (f)(6) of this section. The wording of the guarantee must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(g)(2). A certified copy of the guarantee must accompany the items sent to the Regional Administrator as specified in paragraph (f)(3) of this section. One of these items must be the letter from the guarantor's chief financial officer. Section 261.147(g)(2)(i) provides that, in the case of corporations incorporated in the United States, a guarantee may be used to satisfy the requirements of this section only if the Attorneys General or Insurance Commissioners of (A) the State in which the guarantor is incorporated, and (B) each State in which a facility covered by the guarantee is located have submitted a written statement to EPA that a guarantee executed as described in this section and section 264.151(g)(2) is a legally valid and enforceable obligation in that State. Section 261.147(g)(2)(ii) provides that, in the case of corporations incorporated outside the United States, a guarantee may be used to satisfy the requirements of this section only if (A) the non-U.S. corporation has identified a registered agent for service of process in each State in which a facility covered by the guarantee is located and in the State in which it has its principal place of business, and if (B) the Attorney General or Insurance Commissioner of each State in which a facility covered by the guarantee is located and the State in which the guarantor corporation has its principal place of business, has submitted a written statement to EPA that a guarantee executed as described in this section and section 261.151(h)(2) is a legally valid and enforceable obligation in that State.
(i) Data items
Information required under section 261.147(f)(3):
- A letter signed by the owner's or operator's chief financial officer and worded as specified in section 261.151(f). If an owner or operator is using the financial test to demonstrate both assurance as specified by section 261.143(e), and liability coverage, he must submit the letter specified in section 261.151(f) to cover both forms of financial responsibility; a separate letter as specified in section 261.151(e) is not required.
- A copy of the independent certified public accountant's report on examination of the owner's or operator's financial statements for the latest completed fiscal year.
- A special report from the owner’s or operator’s independent certified public accountant to the owner or operator, if the chief financial officer’s letter providing evidence of financial assurance includes financial data showing that the owner or operator satisfies paragraph (f)(1)(i) of this section that are different from the data in the audited financial statements referred to in paragraph (f)(3)(ii) of this section or any other audited financial statement or data filed with the SEC. The special report shall be based upon an agreed upon procedures engagement in accordance with professional auditing standards and shall describe the procedures performed in comparing the data in the chief financial officer’s letter derived from the independently audited, year-end financial statements for the latest fiscal year with the amounts in such financial statements, the findings of the comparison, and the reasons for any difference.
A letter under section 261.147(f)(4) from the chief financial officer that must:
- Request the extension;
- Certify that he has grounds to believe that the owner or operator meets the criteria of the financial test;
- Specify for each facility to be covered by the test the EPA Identification Number, name, address, the amount of liability coverage and, when applicable, current closure and post-closure cost estimates to be covered by the test;
- Specify the date ending the owner's or operator's last complete fiscal year before the effective date of these regulations;
- Specify the date, no later than 90 days after the end of such fiscal year, when he will submit the documents specified in paragraph (f)(3) of this section; and
- Certify that the year-end financial statements of the owner or operator for such fiscal year will be audited by an independent certified public accountant.
Annually updated information as required under section 261.147(f)(5), after the initial submission of these items.
Evidence of liability coverage under section 261.147(f)(6) if alternate financial assurance is obtained.
Evidence of insurance for the entire amount of required liability coverage as specified in this section within 30 days after notification of disallowance, as required under section 261.147(f)(7).
A guarantee whose wording is identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(g)(2). A certified copy of the guarantee must accompany the items sent to the Regional Administrator as specified in paragraph (f)(3) of this section.
A letter under section 261.147(g)(1) from the guarantor's chief financial officer. If the guarantor's parent corporation is also the parent corporation of the owner or operator, this letter must describe the value received in consideration of the guarantee. If the guarantor is a firm with a “substantial business relationship” with the owner or operator, this letter must describe this “substantial business relationship” and the value received in consideration of the guarantee.
Identification of a registered agent for service of process in each State in which a facility covered by the guarantee is located and in the State in which it has its principal place of business, for corporations incorporated outside of the U.S., as required under section 261.147(g)(2)(ii).
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must perform the following activities:
Prepare and submit to EPA a signed letter, copy of the independent certified public accountant's report on examination of the owner's or operator's financial statements, a special report from the owner’s or operator’s independent certified public accountant if applicable, and a guarantee if applicable.
Prepare and submit the information required under section 261.147(g)(2)(ii), if applicable.
- To obtain an extension of the time allowed for submission of the documents specified in section 261.147(f)(3), prepare and send a letter to the Regional Administrator of each Region in which the owner's or operator's facilities to be covered by the financial test are located.
- Prepare and submit updated information to EPA under section 261.147(f)(5), at the close of each fiscal year, as specified.
- Obtain alternate financial assurance if necessary and submit evidence of alternate financial assurance to EPA.
Obtain alternate financial assurance and submit evidence of insurance for the entire amount of required liability coverage as specified in this section within 30 days after notification of disallowance by EPA, if applicable.
- Comply with the terms in the letter from the chief financial officer and, if applicable, guarantee.
(3) Letter of Credit
40 CFR 261.147(a)(3) and (b)(3) provide that an owner or operator may meet the requirements of this section by obtaining a letter of credit for liability coverage as specified in section 261.147(h).
Section 261.147(h)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by obtaining an irrevocable standby letter of credit that conforms to the requirements of this paragraph and submitting a copy of the letter of credit to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.147(h)(2) provides that the financial institution issuing the letter of credit must be an entity that has the authority to issue letters of credit and whose letter of credit operations are regulated and examined by a Federal or State agency. Section 261.147(h)(3) provides that the wording of the letter of credit must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(j). Section 261.147(h)(4) provides that an owner or operator who uses a letter of credit to satisfy the requirements of this section may also establish a standby trust fund. Under the terms of such a letter of credit, all amounts paid pursuant to a draft by the trustee of the standby trust will be deposited by the issuing institution into the standby trust in accordance with instructions from the trustee. The trustee of the standby trust fund must be an entity which has the authority to act as a trustee and whose trust operations are regulated and examined by a Federal or State agency. Section 261.147(h)(5) provides that the wording of the standby trust fund must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(m). [Note: This supporting statement addresses the data items and respondent activities associated with the standby trust fund under “Trust Fund.”]
(i) Data items
Irrevocable standby letter of credit whose wording is identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(j).
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must prepare and submit a copy of the letter of credit to EPA.
The owner/operator and issuing institution must comply with the terms of the letter of credit.
(4) Surety Bond for Liability Coverage
40 CFR 261.147(a)(4) and (b)(4) provide that an owner or operator may meet the requirements of this section by obtaining a surety bond for liability coverage as specified in section 261.147(i).
Section 261.147(i)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by obtaining a surety bond that conforms to the requirements of this paragraph and submitting a copy of the bond to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.147(i)(2) provides that the surety company issuing the bond must be among those listed as acceptable sureties on Federal bonds in the most recent Circular 570 of the U.S. Department of the Treasury. Section 261.147(i)(3) provides that the wording of the surety bond must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(k). Section 261.147(i)(4) provides that a surety bond may be used to satisfy the requirements of this section only if the Attorneys General or Insurance Commissioners of (i) the State in which the surety is incorporated, and (ii) each State in which a facility covered by the surety bond is located have submitted a written statement to EPA that a surety bond executed as described in this section and section 261.151(k) is a legally valid and enforceable obligation in that State.
(i) Data items
A surety bond whose wording is identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(k).
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must prepare and submit a copy of the surety bond to EPA.
The owner/operator and surety company must comply with the terms of the surety bond.
(5) Trust Fund
40 CFR 261.147(a)(5) and (b)(5) provide that an owner or operator may meet the requirements of this section by obtaining a trust fund for liability coverage as specified in section 261.147(j).
Section 261.147(j)(1) provides that an owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this section by establishing a trust fund that conforms to the requirements of this paragraph and submitting an originally signed duplicate of the trust agreement to the Regional Administrator. Section 261.147(j)(2) provides that the trustee must be an entity which has the authority to act as a trustee and whose trust operations are regulated and examined by a Federal or State agency. Section 261.147(j)(3) provides that the trust fund for liability coverage must be funded for the full amount of the liability coverage to be provided by the trust fund before it may be relied upon to satisfy the requirements of this section. If at any time after the trust fund is created the amount of funds in the trust fund is reduced below the full amount of the liability coverage to be provided, the owner or operator, by the anniversary date of the establishment of the Fund, must either add sufficient funds to the trust fund to cause its value to equal the full amount of liability coverage to be provided, or obtain other financial assurance as specified in this section to cover the difference. For purposes of this paragraph, “the full amount of the liability coverage to be provided” means the amount of coverage for sudden and/or nonsudden occurrences required to be provided by the owner or operator by this section, less the amount of financial assurance for liability coverage that is being provided by other financial assurance mechanisms being used to demonstrate financial assurance by the owner or operator. Section 261.147(j)(4) provides that the wording of the trust fund must be identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(l).
(i) Data items
An originally signed duplicate of a trust agreement whose wording is identical to the wording specified in section 261.151(l).
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must perform the following activities:
- Prepare and submit a copy of the trust agreement to EPA.
- Obtain alternate financial assurance, if necessary.
The grantor (owner/operator) and trustee must comply with the terms of the trust agreement.
(6) Combination of Financial Mechanisms
40 CFR 261.147(a)(6) and (b)(6) provide that an owner or operator may demonstrate the required liability coverage through the use of combinations of insurance, financial test, guarantee, letter of credit, surety bond, and trust fund, except that the owner or operator may not combine a financial test covering part of the liability coverage requirement with a guarantee unless the financial statement of the owner or operator is not consolidated with the financial statement of the guarantor. The amounts of coverage demonstrated must total at least the minimum amounts required by this section. If the owner or operator demonstrates the required coverage through the use of a combination of financial assurances under this paragraph, the owner or operator shall specify at least one such assurance as ``primary'' coverage and shall specify other assurance as ``excess'' coverage.
(i) Data items
Specification of at least one assurance as ``primary'' coverage and specification of other assurance as ``excess'' coverage.
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must specify at least one assurance as ``primary'' coverage and shall specify other assurance as ``excess'' coverage” if applicable.
Notification to EPA under 40 CFR 261.147(a)(7) and (b)(7)
40 CFR 261.147(a)(7) and (b)(7) provide that an owner or operator shall notify the Regional Administrator in writing within 30 days whenever: a claim results in a reduction in the amount of financial assurance for liability coverage provided by a financial instrument as specified (261.147(a)(7)(i) and (b)(7)(i)); or a Certification of Valid Claim for bodily injury or property damages caused by a sudden or non-sudden accidental occurrence arising from the operation of a hazardous secondary material reclamation facility or intermediate facility is entered between the owner or operator and third-party claimant for liability coverage as specified (261.147(a)(7)(ii) and (b)(7)(ii)); or a final court order establishing a judgment for bodily injury or property damage caused by a sudden or non-sudden accidental occurrence arising from the operation of a hazardous secondary material reclamation facility or intermediate facility is issued against the owner or operator or an instrument that is providing financial assurance for liability coverage as specified (261.147(a)(7)(iii) and (b)(7)(iii)).
(i) Data items
A written notification to EPA in accordance with section 261.147(a)(7) and (b)(7).
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must prepare and submit a written notification to EPA in accordance with section 261.147(a)(7) or (b)(7), if applicable.
.
Request for Variance
40 CFR 261.147(c) provides that, if an owner or operator can demonstrate to the satisfaction of the Regional Administrator that the levels of financial responsibility required by paragraph (a) or (b) of this section are not consistent with the degree and duration of risk associated with treatment and/or storage at the facility or group of facilities, the owner or operator may obtain a variance from the Regional Administrator. The request for a variance must be submitted in writing to the Regional Administrator. If granted, the variance will take the form of an adjusted level of required liability coverage, such level to be based on the Regional Administrator's assessment of the degree and duration of risk associated with the ownership or operation of the facility or group of facilities. The Regional Administrator may require an owner or operator who requests a variance to provide such technical and engineering information as is deemed necessary by the Regional Administrator to determine a level of financial responsibility other than that required by paragraph (a) or (b) of this section.
(i) Data items
A written request for a variance, including such technical and engineering information as is deemed necessary by the Regional Administrator to determine a level of financial responsibility other than that required by paragraph (a) or (b) of this section.
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator may prepare and submit a written request for a variance.
Adjustments by the Regional Administrator
40 CFR 261.147(d) provides that, if the Regional Administrator determines that the levels of financial responsibility required by paragraph (a) or (b) of this section are not consistent with the degree and duration of risk associated with treatment and/or storage at the facility or group of facilities, the Regional Administrator may adjust the level of financial responsibility required under paragraph (a) or (b) of this section as may be necessary to protect human health and the environment. This adjusted level will be based on the Regional Administrator's assessment of the degree and duration of risk associated with the ownership or operation of the facility or group of facilities. In addition, if the Regional Administrator determines that there is a significant risk to human health and the environment from nonsudden accidental occurrences resulting from the operations of a facility that is not a surface impoundment, pile, or land treatment facility, he may require that an owner or operator of the facility comply with paragraph (b) of this section. An owner or operator must furnish to the Regional Administrator, within a reasonable time, any information which the Regional Administrator requests to determine whether cause exists for such adjustments of level or type of coverage.
(i) Data items
Any information which the Regional Administrator requests to determine whether cause exists for adjustments of level or type of coverage.
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must furnish to the Regional Administrator, within a reasonable time, any information which the Regional Administrator requests to determine whether cause exists for adjustments of level or type of coverage.
Incapacity of Owners or Operators, Guarantors, or Financial Institutions
40 CFR 261.148(a) provides that an owner or operator must notify the Regional Administrator by certified mail of the commencement of a voluntary or involuntary proceeding under Title 11 (Bankruptcy), U.S. Code, naming the owner or operator as debtor, within 10 days after commencement of the proceeding. A guarantor of a corporate guarantee as specified in section 261.143(e) must make such a notification if he is named as debtor, as required under the terms of the corporate guarantee. Section 261.148(b) provides that an owner or operator who fulfills the requirements of section 261.143 or section 261.147 by obtaining a trust fund, surety bond, letter of credit, or insurance policy will be deemed to be without the required financial assurance or liability coverage in the event of bankruptcy of the trustee or issuing institution, or a suspension or revocation of the authority of the trustee institution to act as trustee or of the institution issuing the surety bond, letter of credit, or insurance policy to issue such instruments. The owner or operator must establish other financial assurance or liability coverage within 60 days after such an event.
(i) Data items
Notification to the Regional Administrator by certified mail of the commencement of a voluntary or involuntary proceeding under Title 11 (Bankruptcy), U.S. Code.
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner/operator must perform the following activities:
- Notify the Regional Administrator by certified mail of the commencement of a voluntary or involuntary proceeding under Title 11 (Bankruptcy), U.S. Code, if applicable.
- Obtain other financial assurance of liability coverage.
Use of State-Required Mechanisms
40 CFR 261.149(a) provides that, for a reclamation or intermediate facility located in a State where EPA is administering the requirements of Subpart H but where the State has regulations that include requirements for financial assurance of closure or liability coverage, an owner or operator may use State-required financial mechanisms to meet the requirements of section 261.143 or section 261.147 if the Regional Administrator determines that the State mechanisms are at least equivalent to the financial mechanisms specified in Subpart H. The Regional Administrator will evaluate the equivalency of the mechanisms principally in terms of (1) certainty of the availability of funds for the required closure activities or liability coverage and (2) the amount of funds that will be made available. The Regional Administrator may also consider other factors as he deems appropriate. The owner or operator must submit to the Regional Administrator evidence of the establishment of the mechanism together with a letter requesting that the State-required mechanism be considered acceptable for meeting the requirements of Subpart H. The submission must include the information specified in section 261.149(a). The Regional Administrator may require the owner or operator to submit additional information as is deemed necessary to make this determination. Pending this determination, the owner or operator will be deemed to be in compliance with the requirements of section 261.143 or section 261.147, as applicable.
Section 261.149(b) provides that, if a State-required mechanism is found acceptable as specified in paragraph (a) of this section except for the amount of funds available, the owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of Subpart H by increasing the funds available through the State-required mechanism or using additional financial mechanisms as specified in Subpart H. The amount of funds available through the State and Federal mechanisms must at least equal the amount required by Subpart H.
(i) Data items
Evidence of the establishment of the State mechanism together with a letter requesting that the State-required mechanism be considered acceptable for meeting the requirements of Subpart H. The submission must include the following information: The facility's EPA Identification Number (if available), name, and address, and the amount of funds for closure or liability coverage assured by the mechanism.
Additional information as is deemed necessary by EPA to make this determination.
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner or operator must perform the following activities:
- Submit to the Regional Administrator evidence of the establishment of the mechanism together with a letter requesting that the State-required mechanism be considered acceptable for meeting the requirements of Subpart H.
Submit additional information to EPA as is deemed necessary to make this determination.
Obtain additional financial assurance if necessary.
State Assumption of Responsibility
40 CFR 261.150(a) provides that, if a State either assumes legal responsibility for an owner's or operator's compliance with the closure or liability requirements of this part or assures that funds will be available from State sources to cover those requirements, the owner or operator will be in compliance with the requirements of section 261.143 or section 261.147 if the Regional Administrator determines that the State's assumption of responsibility is at least equivalent to the financial mechanisms specified in Subpart H. The Regional Administrator will evaluate the equivalency of State guarantees principally in terms of (1) certainty of the availability of funds for the required closure activities or liability coverage and (2) the amount of funds that will be made available. The Regional Administrator may also consider other factors as he deems appropriate. The owner or operator must submit to the Regional Administrator a letter from the State describing the nature of the State's assumption of responsibility together with a letter from the owner or operator requesting that the State's assumption of responsibility be considered acceptable for meeting the requirements of Subpart H. The letter from the State must include, or have attached to it, the information specified at section 261.150(a). The Regional Administrator may require the owner or operator to submit additional information as is deemed necessary to make this determination. Pending this determination, the owner or operator will be deemed to be in compliance with the requirements of section 265.143 or section 265.147, as applicable. Section 261.150(b) provides that, if a State's assumption of responsibility is found acceptable as specified in paragraph (a) of this section except for the amount of funds available, the owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of Subpart H by use of both the State's assurance and additional financial mechanisms as specified in Subpart H. The amount of funds available through the State and Federal mechanisms must at least equal the amount required by Subpart H.
(i) Data items
A letter from the State describing the nature of the State's assumption of responsibility together with a letter from the owner or operator requesting that the State's assumption of responsibility be considered acceptable for meeting the requirements of Subpart H. The letter from the State must include, or have attached to it, the following information: The facility's EPA Identification Number (if available), name, and address, and the amount of funds for closure or liability coverage that are guaranteed by the State.
Additional information as is deemed necessary by EPA to make its determination.
(ii) Respondent activities
The owner or operator must perform the following activities:
- Submit to the Regional Administrator a letter from the State describing the nature of the State's assumption of responsibility together with a letter from the owner or operator requesting that the State's assumption of responsibility be considered acceptable for meeting the requirements of Subpart H.
Submit additional information as is deemed necessary by EPA to make its determination
Obtain additional financial assurance if necessary.
5. THE INFORMATION COLLECTED: AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
5(a) Agency Activities
CERTIFICATIONS FOR HAZARDOUS SECONDARY MATERIAL GENERATED AND RECLAIMED UNDER THE CONTROL OF THE GENERATOR
There is no Agency activity.
NON-WASTE DETERMINATIONS
Application for Non-Waste Determination
Evaluate and either approve or deny the application.
Re-Application for Non-Waste Determination
Evaluate and either approve or deny the re-application.
NOTIFICATION
Receive, review, and file the notifications.
EXCLUSIONS FROM THE DEFINITION OF SOLID WASTE
Exclusion at 40 CFR 261.2(a)(2)(ii)
Refer to “Notification” for Agency activities.
Exclusion at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(23)
Refer to “Notification” for Agency activities.
Exclusion at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(24)
Request documentation and certification of reasonable efforts, if applicable.
Export Requirements at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(25)
Receive, review, file, and transmit notifications as necessary.
Receive, file, and transmit any additional information which a receiving country requests in order to respond to a notification, as requested by EPA.
Transmit information to the generator in connection with its notification to export (e.g., Acknowledgement of Consent), as applicable.
Receive, review, and file annual report.
FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS FOR MANAGEMENT OF EXCLUDED HAZARDOUS SECONDARY MATERIALS
Cost Estimate
There is no Agency activity.
Financial Assurance Condition
(1) Trust Fund
Receive and evaluate originally signed duplicate of the trust agreement and formal certification of acknowledgement.
Receive and evaluate other financial assurance, if provided.
Receive, review, and respond to request for release of the amount in excess of the current cost estimate.
Receive, review, and respond to request for release of the amount in excess of current cost estimate covered by trust fund.
Instruct the trustee to release to the owner/operator such funds as EPA specifies in writing.
Take other action as needed.
(2) Surety Bond Guaranteeing Payment into a Trust Fund
Receive and evaluate surety bond.
Receive, review, and file evidence of the increase in the penal sum or other financial assurance to cover the increase.
Receive and evaluate alternate financial assurance if required because of cancellation of the bond.
Receive, review, and file notice of cancellation from surety company.
Take other action as needed.
(3) Letter of Credit
Receive and evaluate letter of credit and letter referring to the letter of credit.
Receive, review, and file evidence of an increase in the credit or other financial assurance as specified to cover the increase.
Receive and evaluate alternate financial assurance if required because of termination of credit.
Receive, review, and file a notice of a decision not to extend the expiration date of the credit from the issuing institution.
Take other action as needed.
(4) Insurance
Receive and evaluate certificate of insurance.
Receive, review, and approve reimbursements for expenditures, if applicable.
Receive, review, and file evidence of an increase in the policy or approve other financial assurance as specified to cover the increase.
Receive and evaluate alternate financial assurance if required because of cancellation, termination, or failure to renew the insurance.
Receive, review, and file notice of cancellation.
Take other action as needed.
(5) Financial Test and Corporate Guarantee
Receive and evaluate a signed letter and accompanying material.
Receive, review, and approve an extension of the time allowed for submission of the documents specified in section 261.143(e)(3).
Receive, review, and file updated information at the close of each fiscal year, as specified.
Receive, review, and file a notice of intent to establish alternate financial assurance.
Request, receive, review, and file reports of financial condition, if applicable.
Receive and evaluate alternate financial assurance, if required.
Prepare and transmit notice of disallowance.
Take other action as needed.
Use of Financial Mechanisms for Multiple Facilities
Receive, review, and file evidence of financial assurance that must include specified information.
Removal and Decontamination Plan and Release from Financial Assurance Obligations
Receive plan, issue public notice and, if applicable, hold a hearing.
Review, modify, and approve/disapprove plan.
Issue written statement for refusal, if applicable.
Review, modify, and approve resubmittal of plan in response to detailed written statement of reasons for EPA refusal.
Receive and review certification for each hazardous secondary materials management unit.
Request and review other documentation if needed to support the Professional Engineer's certification.
Notify owner/operator of release from financial assurance obligations, or reasons why it believes hazardous secondary materials have not been removed from the unit.
Coverage for Sudden and Non-Sudden Accidental Occurrences
(1) Liability Insurance
Receive and evaluate insurance policy as specified.
Request and review signed duplicate original of the insurance policy, if applicable.
Take other action as needed (e.g., notifying an owner/operator that he is no longer required to maintain liability coverage, if a certification of closure completion has been received).
(2) Financial Test or Guarantee
Receive and evaluate a signed letter and accompanying material.
Receive, review, and approve an extension, if applicable.
Receive, review, and file updated information at the close of each fiscal year, as specified.
Receive and evaluate alternate financial assurance, if necessary.
Issue notice of disallowance and receive and evaluate alternate financial assurance, if applicable.
Take other action as needed.
(3) Letter of Credit
Receive and evaluate a copy of the letter of credit.
Take other action as needed.
(4) Surety Bond for Liability Coverage
Receive and evaluate a copy of the surety bond.
Take other action as needed.
(5) Trust Fund
Receive and evaluate trust agreement.
Receive and evaluate alternate financial assurance, if necessary.
Take other action as needed.
(6) Combination of Financial Mechanisms
Receive, review, and file specification of at least one assurance as ``primary'' coverage and specification of other assurance as ``excess'' coverage, if applicable.
Notification to EPA under 40 CFR 261.147(a)(7) and (b)(7)
Receive, review, and file a written notification in accordance with section 261.147(a)(7) or (b)(7), if applicable.
.
Request for Variance
Receive, process, and approve written request for a variance.
Request and review any technical or engineering documentation necessary to establish level of financial responsibility.
Hold a public hearing, if necessary.
Adjustments by the Regional Administrator
Request information deemed necessary to assess the need for adjustments to an owner/operator’s level of financial responsibility as specified.
Hold a public hearing, if necessary, and process the adjustment.
Incapacity of Owners or Operators, Guarantors, or Financial Institutions
Receive, review, and file notification of commencement of a voluntary or involuntary proceeding under Title 11 (Bankruptcy), U.S. Code, if applicable.
Receive and evaluate other financial assurance of liability coverage.
Use of State-Required Mechanisms
Receive and evaluate evidence of the establishment of the mechanism together with a letter requesting that the State-required mechanism be considered acceptable for meeting the requirements of Subpart H.
Request and review additional information as is deemed necessary to make this determination.
Notify owner/operator of EPA’s decision.
Receive and evaluate additional financial assurance, if necessary.
State Assumption of Responsibility
Receive and evaluate a letter from the State and accompanying information requesting that the State's assumption of responsibility be considered acceptable for meeting the requirements of Subpart H.
Receive and review additional information as is deemed necessary by EPA to make its determination.
Notify owner/operator of EPA’s decision.
Receive and evaluate additional financial assurance, if necessary.
5(b) Collection Methodology and Management
In collecting and analyzing the information associated with this ICR, EPA and authorized States may use a telephone system, personal computers, and applicable database software. They will ensure the accuracy and completeness of collected information by reviewing the submittals. They will keep records of this information in file cabinets and/or computer systems.
5(c) Small Entity Flexibility
The exclusions in the final rule are voluntary and deregulatory. As such, there is no adverse burden impact to large or small entities.
5(d) Collection Schedule
CERTIFICATIONS FOR HAZARDOUS SECONDARY MATERIAL GENERATED AND RECLAIMED UNDER THE CONTROL OF THE GENERATOR
The one-time certification under 40 CFR 260.10 must be prepared by the generator for the material to be excluded.
NON-WASTE DETERMINATIONS
Application for Non-Waste Determination
There is no schedule for collecting applications.
Re-Application for Non-Waste Determination
The applicant must re-apply for non-waste determinations, in the event of a change in circumstances that affects how a hazardous secondary material meets the relevant criteria contained in section 260.34 upon which a non-waste determination has been based.
NOTIFICATION
A claimant must prepare and submit a notification to EPA prior to operating under the exclusion(s).
A claimant must update and submit notification to EPA by March 1 of each even numbered year thereafter.
A claimant that submitted a notification but then subsequently stops managing hazardous secondary materials in accordance with the exclusion(s) must submit notification to EPA within 30 days.
EXCLUSIONS FROM THE DEFINITION OF SOLID WASTE
Exclusions at 40 CFR 261.2(a)(2)(ii) and 261.4(a)(23)
Refer to “Certifications for Hazardous Secondary Material Generated and Reclaimed under the Control of the Generator” and “Notification” for collection schedules under these exclusions.
Exclusion at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(24)
A generator must conduct reasonable efforts and prepare the certification statement for any intermediate facilities and reclaimers as specified prior to arranging for transport of the materials.
A generator must repeat the reasonable efforts at least every three years.
Generators that send their hazardous secondary material to an intermediate facility where the management of the hazardous secondary material is not addressed under a Part B permit or interim-status standards must make contractual arrangements to ensure the facility sends the material to the reclamation facility identified by the generator prior to the shipment.
A generator must maintain for a minimum of three years documentation and certification that reasonable efforts were made as specified.
A generator must make documentation and certification available upon request by a regulatory authority within 72 hours, or within a longer period of time as specified by the regulatory authority.
A generator must maintain for no less than three years records of all off-site shipments of excluded hazardous secondary materials.
A generator must maintain for no less than three years confirmations of receipt from the intermediate and reclamation facilities.
An intermediate or reclamation facility must maintain for no less than three years records of each shipment received.
An intermediate or reclamation facility must send confirmations of receipt of shipment to the generator.
Export Requirements at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(25)
A generator must submit a complete notification at least sixty days before the initial shipment is intended to be shipped offsite. This notification may cover export activities extending over a twelve month or lesser period.
A generator must submit a renotification when specified conditions on the notification change as applicable.
A generator must re-notify EPA if a shipment cannot be delivered for any reason to the reclaimer, intermediate facility or the alternate reclaimer or alternate intermediate facility.
A generator must keep copies of notifications and Acknowledgments of Consent to Export for a period of three years following receipt of the Acknowledgment.
A generator must prepare and submit annual report no later than March 1 of each year.
FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS FOR MANAGEMENT OF EXCLUDED HAZARDOUS SECONDARY MATERIALS
Cost Estimate
An owner/operator must adjust the cost estimate for inflation within 60 days prior to the anniversary date of the establishment of the financial instrument(s) used to comply with section 261.143. For owners or operators using the financial test or corporate guarantee, the cost estimate must be updated for inflation within 30 days after the close of the firm's fiscal year and before submission of updated information to the Regional Administrator as specified in section 261.143(e)(3).
An owner/operator must revise the cost estimate no later than 30 days after a change in a facility’s operating plan or design that would increase the costs of conducting the activities described in section 261.142(a) or no later that 60 days after an unexpected event which increases the cost of conducting the activities described in section 261.142(a).
An owner/operator must retain the cost estimate on site during the operating life of the facility.
Financial Assurance Condition
An owner/operator of a hazardous secondary material reclamation facility or an intermediate facility must establish financial assurance as a condition of the exclusion under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25).
(1) Trust Fund
An owner/operator may establish a trust fund as a condition of the exclusions under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25).
An owner/operator must update Schedule A of the trust agreement within 60 days after a change in the amount of the current cost estimate covered by the agreement.
An owner/operator must, whenever the current cost estimate changes, compare the new estimate with the trustee's most recent annual valuation of the trust fund. If the value of the fund is less than the amount of the new estimate, it must, within 60 days after the change in the cost estimate, either make a deposit or obtain other financial assurance to cover the difference, as specified.
(2) Surety Bond Guaranteeing Payment into a Trust Fund
An owner/operator may establish a surety bond as a condition of the exclusions under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25).
An owner/operator must provide alternate financial assurance as specified, and obtain the Regional Administrator's written approval of the assurance provided, within 90 days after receipt by both the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator of a notice of cancellation of the bond from the surety.
Whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the penal sum, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the penal sum to be increased to an amount at least equal to the current cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Regional Administrator, or obtain other financial assurance as specified to cover the increase.
Whenever the current cost estimate decreases, the penal sum may be reduced to the amount of the current cost estimate following written approval by the Regional Administrator.
Under the terms of the bond, the surety may cancel the bond by sending notice of cancellation by certified mail to the owner or operator and to the Regional Administrator. Cancellation may not occur, however, during the 120 days beginning on the date of receipt of the notice of cancellation by both the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator, as evidenced by the return receipts.
An owner/operator must obtain alternate financial assurance within 90 days of receipt of notice of cancellation of bond.
(3) Letter of Credit
An owner/operator may establish a letter of credit as a condition of the exclusions under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25).
The letter of credit must provide that the expiration date will be automatically extended for a period of at least 1 year unless, at least 120 days before the current expiration date, the issuing institution notifies both the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator by certified mail of a decision not to extend the expiration date.
Whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the amount of the credit, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the amount of the credit to be increased so that it at least equals the current cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Regional Administrator, or obtain other financial assurance as specified to cover the increase.
Whenever the current cost estimate decreases, the amount of the credit may be reduced to the amount of the current cost estimate following written approval by the Regional Administrator.
If the owner or operator does not establish alternate financial assurance as specified and obtain written approval of such alternate assurance from the Regional Administrator within 90 days after receipt by both the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator of a notice from the issuing institution that it has decided not to extend the letter of credit beyond the current expiration date, the owner or operator will lose the conditional exclusion, and the Regional Administrator will draw on the letter of credit. The Regional Administrator may delay the drawing if the issuing institution grants an extension of the term of the credit. During the last 30 days of any such extension the owner or operator will lose the conditional exclusion and the Regional Administrator will draw on the letter of credit if the owner or operator has failed to provide alternate financial assurance as specified and obtain written approval of such assurance from the Regional Administrator.
(4) Insurance
An owner/operator may establish insurance as a condition of the exclusions under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25).
After beginning partial or final closure under 40 CFR Parts 264 or 265, as applicable, an owner or operator or any other authorized person may request reimbursements for closure expenditures by submitting itemized bills to the Regional Administrator.
Cancellation, termination, or failure to renew the insurance policy may not occur, however, during the 120 days beginning with the date of receipt of the notice by both the Regional Administrator and the owner or operator, as evidenced by the return receipts.
Whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the face amount of the policy, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the face amount to be increased to an amount at least equal to the current cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Regional Administrator, or obtain other financial assurance as specified to cover the increase.
Whenever the current cost estimate decreases, the face amount may be reduced to the amount of the current cost estimate following written approval by the Regional Administrator.
(5) Financial Test and Corporate Guarantee
An owner/operator may establish a financial test or guarantee as a condition of the exclusions under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25).
To obtain an extension under section 261.143(e)(4), the owner's or operator's chief financial officer must send, by the effective date of these regulations, a letter to the Regional Administrator of each Region in which the owner's or operator's facilities to be covered by the financial test are located.
After the initial submission of items specified in section 261.143(e)(3), the owner or operator must send updated information to the Regional Administrator within 90 days after the close of each succeeding fiscal year.
If the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of section 261.143(e)(1), he must send notice to the Regional Administrator of intent to establish alternate financial assurance. The notice must be sent by certified mail within 90 days after the end of the fiscal year for which the year-end financial data show that the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements. The owner or operator must provide the alternate financial assurance within 120 days after the end of such fiscal year.
The Regional Administrator may, based on a reasonable belief that the owner or operator may no longer meet the applicable requirements, require reports of financial condition at any time from the owner or operator in addition to those specified in section 261.143(e)(3). If the Regional Administrator finds, on the basis of such reports or other information, that the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of 261.143(e)(1), the owner or operator must provide alternate financial assurance as specified within 30 days after notification of such a finding.
If the Regional Administrator disallows use of the tests as specified, the owner or operator must provide alternate financial assurance as specified within 30 days after notification of the disallowance.
If the Regional Administrator determines that the hazardous secondary materials at the owner or operator’s facility covered by the guarantee do not meet the conditions of the exclusion, the guarantor must establish a trust fund as specified, unless it disposes of any hazardous secondary material as hazardous waste and closes the facility as specified.
Cancellation of the guarantee may not occur during the 120 days beginning on the date of receipt of the notice of cancellation by both the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator, as evidenced by the return receipts.
If the owner or operator fails to provide alternate financial assurance as specified and obtain EPA approval within 90 days after receipt by both the owner or operator and the Regional Administrator of a notice of cancellation of the corporate guarantee from the guarantor, the guarantor will provide such alternate financial assurance in the name of the owner or operator.
Use of Financial Mechanisms for Multiple Facilities
An owner/operator may establish financial mechanisms for multiple facilities as a condition of the exclusions under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25). The owner/operator must submit the evidence of financial assurance for each facility as specified.
Removal and Decontamination Plan and Release from Financial Assurance Obligations
An owner or operator of a reclamation facility or an intermediate facility who wishes to be released from his financial assurance obligations must submit a plan for removing all hazardous secondary material residues to the Regional Administrator at least 180 days prior to the date on which he expects to cease to operate under the exclusion.
The Regional Administrator will provide the owner or operator and the public, through a newspaper notice, the opportunity to submit written comments on the plan and request modifications to the plan no later than 30 days from the date of the notice.
If the Regional Administrator does not approve the plan, he shall provide the owner or operator with a detailed written statement of reasons for the refusal and the owner or operator must modify the plan or submit a new plan for approval within 30 days after receiving such written statement.
Within 60 days of completion of the activities as specified for each hazardous secondary materials management unit, the owner or operator must submit to the Regional Administrator, by registered mail, a certification that all hazardous secondary materials have been removed from the unit and the unit has been decontaminated in accordance with the specifications in the approved plan.
Documentation supporting the Professional Engineer's certification must be furnished to the Regional Administrator, upon request, until he releases the owner or operator from the financial assurance requirements for section 261.4(a)(24)(vi)(F).
Coverage for Sudden and Non-Sudden Accidental Occurrences
An owner or operator of a hazardous secondary material reclamation facility or an intermediate facility must demonstrate financial assurance for sudden and nonsudden accidental occurrences as a condition of the exclusion under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25).
(1) Liability Insurance
An owner/operator may establish liability insurance as a condition of the exclusions under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25) for sudden and/or nonsudden accidental occurrences.
If requested by a Regional Administrator, the owner or operator must provide a signed duplicate original of the insurance policy.
(2) Financial Test or Guarantee
An owner/operator may establish a financial test or guarantee as a condition of the exclusions under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25) for sudden and/or nonsudden accidental occurrences.
The owner or operator may obtain a one-time extension of the time allowed for submission of the documents as specified if the fiscal year of the owner or operator ends during the 90 days prior to the effective date of these regulations and if the year-end financial statements for that fiscal year will be audited by an independent certified public accountant. To obtain the extension, the owner's or operator's chief financial officer must send, by the effective date of these regulations, a letter to the Regional Administrator of each Region in which the owner's or operator's facilities to be covered by the financial test are located.
After the initial submission of items specified in section 261.147(f)(3), the owner or operator must send updated information to the Regional Administrator within 90 days after the close of each succeeding fiscal year.
If the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of section 261.147(f)(1), he must obtain insurance, a letter of credit, a surety bond, a trust fund, or a guarantee for the entire amount of required liability coverage as specified. Evidence of liability coverage must be submitted to the Regional Administrator within 90 days after the end of the fiscal year for which the year-end financial data show that the owner or operator no longer meets the test requirements.
The owner or operator must provide evidence of insurance for the entire amount of required liability coverage, as specified, within 30 days after notification of disallowance from EPA.
(3) Letter of Credit
An owner/operator may establish a letter of credit as a condition of the exclusions under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25) for sudden and/or nonsudden accidental occurrences.
(4) Surety Bond for Liability Coverage
An owner/operator may establish a surety bond as a condition of the exclusions under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25) for sudden and/or nonsudden accidental occurrences.
(5) Trust Fund
An owner/operator may establish a trust fund as a condition of the exclusions under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25) for sudden and/or nonsudden accidental occurrences.
If at any time after the trust fund is created the amount of funds in the trust fund is reduced below the full amount of the liability coverage to be provided, the owner or operator, by the anniversary date of the establishment of the fund, must either add sufficient funds to the trust fund to cause its value to equal the full amount of liability coverage to be provided, or obtain other financial assurance as specified to cover the difference.
(6) Combination of Financial Mechanisms
An owner/operator may establish multiple financial assurance mechanisms, as a condition of the exclusions under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25) for sudden and/or nonsudden accidental occurrences. The owner/operator must specify at least one such assurance as “primary” coverage and specify other assurance as “excess” coverage.
Notification to EPA under 40 CFR 261.147(a)(7) and (b)(7)
An owner or operator shall notify the Regional Administrator in writing within 30 days whenever: (i) A claim results in a reduction in the amount of financial assurance for liability coverage provided by a financial instrument as specified; or a Certification of Valid Claim for bodily injury or property damages caused by a sudden or non-sudden accidental occurrence arising from the operation of a hazardous secondary material reclamation facility or intermediate facility is entered between the owner or operator and third-party claimant for liability coverage as specified; or a final court order establishing a judgment for bodily injury or property damage caused by a sudden or non-sudden accidental occurrence arising from the operation of a hazardous secondary material reclamation facility or intermediate facility is issued against the owner or operator or an instrument that is providing financial assurance for liability coverage as specified.
Request for Variance
There is no schedule for collecting applications for variance. An owner/operator may be required to submit technical and engineering information to EPA if deemed necessary to establish the level of financial responsibility.
Adjustments by the Regional Administrator
The owner/operator must furnish to the Regional Administrator, within a reasonable time, any information which the Regional Administrator requests to determine whether cause exists for adjustments of level or type of coverage.
Incapacity of Owners or Operators, Guarantors, or Financial Institutions
An owner or operator must notify the Regional Administrator by certified mail of the commencement of a voluntary or involuntary proceeding under Title 11 (Bankruptcy), U.S. Code, naming the owner or operator as debtor, within 10 days after commencement of the proceeding.
An owner or operator who fulfills the requirements of section 261.143 or 261.147 by obtaining a trust fund, surety bond, letter of credit, or insurance policy will be deemed to be without the required financial assurance or liability coverage in the event of bankruptcy of the trustee or issuing institution, or a suspension or revocation of the authority of the trustee institution to act as trustee or of the institution issuing the surety bond, letter of credit, or insurance policy to issue such instruments. The owner or operator must establish other financial assurance or liability coverage within 60 days after such an event.
Use of State-Required Mechanisms
An owner/operator may establish State-required mechanisms as a condition of the exclusions under section 261.4(a)(24) and (25), as specified, provided that he submits specified information to EPA.
The Regional Administrator may require the owner or operator to submit additional information as is deemed necessary to make this determination.
State Assumption of Responsibility
A State may assume legal responsibility for an owner's or operator's compliance with the closure or liability requirements or assure that funds will be available from State sources to cover those requirements, as specified, so long as specified information is submitted to EPA.
The Regional Administrator may require the owner or operator to submit additional information as is deemed necessary to make this determination.
6. ESTIMATING THE HOUR AND COST BURDEN OF THE COLLECTION
6(a) Estimating Respondent Burden Hours
Exhibit 1 provides estimates of the respondent hourly burden associated with the rule’s paperwork requirements. Exhibit 1 includes burden hours (total and by labor type) per respondent, as well as the overall burden hours for all respondents.
6(b) Estimating Respondent Costs
Exhibit 1 provides estimates of the annual respondent costs associated with the rule’s paperwork requirements. These costs are based on the cost of labor, capital, and operation and maintenance (O&M).
(1) Labor Costs
The labor wage rates used to estimate costs to respondents were obtained from EPA’s 2008 Regulatory Impact Analysis (RIA) developed for this rulemaking.1 EPA estimates an average loaded respondent hourly labor rate of $116.58 for legal staff, $68.91 for managerial staff, $51.34 for technical staff, and $30.88 for clerical staff.
Using the total burden hours discussed in Section 6(a) and the hourly wage rates outlined in this section, Exhibit 1 estimates the labor costs associated with the information collection requirements covered in this ICR.
(2) Capital Costs
Capital costs usually include any produced physical good needed to provide the needed information, such as machinery, computers, and other equipment. EPA does not anticipate that respondents will incur capital costs in carrying out the information collection requirements covered in this ICR.
(3) Operation & Maintenance Costs
O&M costs are those costs associated with a paperwork requirement incurred continually over the life of the ICR. They are defined by the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995 as “the recurring dollar amount of costs associated with O&M or purchasing services.” This ICR includes O&M costs for postage (i.e., $0.42 for regular mail, $2.81 for certified mail, and $8.50 for registered mail). The ICR includes $22 for respondents in preparing their petition (e.g., copying and communications) under Part 260. The ICR includes $600 for a respondent to purchase a roundtrip airline ticket to send an employee to perform an audit under section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(B). It includes $3,000 for a respondent to purchase an audit report of a facility under section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(B).2
6(c) Estimating Agency Hour and Cost Burden
The final rule will be administered by RCRA-authorized State government regulatory programs. Unloaded hourly labor wage rates for States’ activities were taken from “Table 2-3. State and Local Government: Mean Hourly Earnings and Weekly Hours by Full-time and Part-time Workers for Selected Occupations, National Compensation Survey, June 2005.” The table is found in the “National Compensation Survey: Occupational Wages in the United States, June 2005,” U.S. Department of Labor, Bureau of Labor Statistics, August 2006, Bulletin 8521. EPA updated these rates to 2008 levels based on the Employment Cost Index, then multiplied the rates by the fringe benefits and overhead factor of 1.45.3 Based on this, EPA estimated the following average loaded hourly wage rates for government labor: $54.41 per hour for legal staff, $47.75 per hour for managerial staff, $35.80 per hour for technical staff, and $23.04 per hour for clerical staff. Hour and cost burden to regulators is estimated in Exhibit 3.
6(d) Estimating the Annual Respondent Universe and Total Hour and Cost Burden
In this section, EPA first describes the estimated respondent universe under the rule. EPA then estimates the annual burden to respondents under the rule’s paperwork requirements. Finally, EPA estimates the burden impacts to respondents under the existing RCRA paperwork requirements in handling excluded materials.
(1) Respondent Universe
EPA obtained most of the respondent universe estimates for this ICR from EPA’s 2008 Regulatory Impact Analysis (RIA) for this rulemaking. The RIA estimates the number of affected industries and entities based on analysis of EPA’s 2005 RCRA Hazardous Waste Report data.
Following are the primary respondent universe estimates that are used in this ICR:
7 petitioners will submit an application under section 260.34 to EPA each year. This is based on Exhibit 1B of the RIA.
290 generators will generate and reclaim their hazardous secondary materials under the control of the generator under section 261.2(a)(2)(ii) or 261.4(a)(23). This is based on data from Exhibit 9G of the RIA.4 Of these generators, EPA estimates that 106 will generate and reclaim on site, 88 will reclaim offsite within the same company, and 96 will reclaim under a tolling arrangement. This is based on Exhibit 9B of the RIA.5
4,448 generators will participate in the conditional exclusion at section 261.4(a)(24). This is based on Exhibit 9G of the RIA.6
159 reclaimers will participate in the conditional exclusion at section 261.4(a)(24). This is based on Exhibit 4A of the RIA.
240 intermediate facilities will participate in the conditional exclusion at section 261.4(a)(24). The RIA does not estimate the number of intermediate facilities separately from other potentially affected entities. To estimate their number for this ICR, EPA considered the following:
359 facilities reported to the 2005 Hazardous Waste Report as being storage/transfer facilities during the year. EPA expects that a number of these facilities might claim the exclusion. For example, some of them are likely owned by, or have working arrangements with, reclaimers that will operate under the exclusion.
Facilities previously unreported to the Hazardous Waste Report also could claim the exclusion (e.g., new entrants to the industry).
One of the reclaimers contacted by EPA predicted that, for each reclamation facility under the exclusion, there will be fewer than four facilities that store/aggregate the materials prior to shipment for reclamation.7 The reclaimer stated that some reclamation facilities rely on aggregation facilities, while others do not. It depends on several factors (e.g., type and size of reclamation operations).
Another reclaimer estimated there would be at least one intermediate facility for each reclaimer under the exclusion, and believed that 1.5 intermediate facilities for each reclaimer on average is a reasonable estimate.8
Based on the above, EPA estimates that, for each reclamation facility under the exclusion, there will be 1.5 intermediate facilities on average. This equates to 240 intermediate facilities (i.e., 159 reclaimers x 1.5 ≈ 240).
36 generators will export excluded material under section 261.4(a)(25) each year. EPA obtained this estimate from Exhibit 8 of EPA’s Hazardous Waste Generator Standards ICR (EPA ICR Number 820), which estimates that 36 generators export their hazardous waste for reclamation to member countries of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) each year.
These estimates are summarized in the table.
Annual Number of Respondents under Final Rule
Type of Respondent |
Annual Number of Respondents |
Petitioners under 260.34 |
7 |
Generators |
|
Generators, tolling contractors and toll manufacturers under 261.2(a)(2)(ii) and 261.4(a)(23) |
290 |
Generators under 261.4(a)(24) |
4,448 |
Total generators |
4,738 |
Reclamation facilities under 261.4(a)(24) |
159 |
Intermediate facilities under 261.4(a)(24) |
240 |
Exporters under 261.4(a)(25) |
36 |
(2) Annual Respondent Burden under Final Rule
CERTIFICATIONS FOR HAZARDOUS SECONDARY MATERIAL GENERATED AND RECLAIMED UNDER THE CONTROL OF THE GENERATOR (EXHIBIT 1)
EPA estimates that 184 generators and tolling contractors must prepare a certification under section 260.10 for hazardous secondary materials that are generated and reclaimed under the control of the generator. This includes 88 generators that reclaim offsite within the same company and 96 tolling contractors that reclaim under a tolling arrangement. Because each site will perform this activity once during the three-year life of this ICR, EPA has annualized the number of sites by dividing them by three, to estimate that 61 will prepare the certification annually (i.e., 184 sites/3 years = 61). This is reflected in Exhibit 1.
NON-WASTE DETERMINATIONS (EXHIBIT 1)
Application for Non-Waste Determination
EPA estimates that seven applicants will submit a petition to EPA under section 260.34 each year. This is reflected in Exhibit 1.
Re-Application for Non-Waste Determination
EPA estimates that no petitioners will submit a re-application to EPA under section 260.34 during the three-year life of this ICR. This is reflected in Exhibit 1.
NOTIFICATION (EXHIBIT 1)
EPA estimates that 5,137 entities will notify EPA under section 260.42 prior to operating under the exclusion and be required to complete the information laid out at section 260.42(a). This includes 4,738 hazardous secondary materials generators, tolling contractors and toll manufacturers; 240 intermediate facilities; and 159 reclaimers. Because each of these entities will perform this activity once during the three-year life of this ICR, EPA has annualized the number of entities by dividing them by three, to estimate that 1,712 will prepare and submit the notification annually.
Entities must re-notify EPA by March 1 of each even numbered year thereafter. Note that the existing regulations already require the submittal of the notification by March 1 of each even numbered year by large quantity generators (40 CFR Part 262) and treatment, storage and disposal facilities (40 CFR Part 264 and 265). Hence, this ICR estimates burden for small quantity generators (SQGs) only. Specifically, Exhibit 9G of the RIA estimates that 1,385 SQGs will operate under the exclusions. For purposes of this ICR, EPA estimates that one-third will notify EPA in the first year of this ICR (462) and another one-third will notify in the second year (462). EPA estimates that these 924 SQGs must re-notify in the third year. Because each of these entities will perform this re-notification activity once during the three-year life of this ICR, EPA has annualized the number of entities by dividing them by three (i.e., 308 SQGs annually).9
EPA estimates that, each year, five percent of entities (86) will re-notify because they stopped operating under the exclusion.
These assumptions are reflected in Exhibit 1.
EXCLUSIONS FROM THE DEFINITION OF SOLID WASTE (EXHIBIT 1)
Exclusions at 40 CFR 261.2(a)(2)(ii) and 261.4(a)(23)
Refer to “Certifications for Hazardous Secondary Material Generated and Reclaimed under the Control of the Generator” and “Notification” for the respondent burden estimated under these exclusions.
Exclusion at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(24)
Generators
EPA estimates that 4,448 generators will ship to reclaimers under the exclusion at section 261.4(a)(24). Through the industry consultations described in Section 3(c), EPA estimates that 40 percent of generators make reasonable efforts to evaluate a prospective intermediate and/or reclamation facility as a customary industry practice. Industry representatives indicated such generators may send their own employees or contract with a vendor to audit the facility and/or review available company information.
The reasonable efforts condition applies when hazardous secondary materials are transferred to intermediate facilities and reclamation facilities where the management of the hazardous secondary materials is not addressed under a RCRA Part B permit or interim status standards. If the permit or interim status standards address the management of the hazardous secondary materials, the rule does not require generators to conduct reasonable efforts, i.e., because EPA believes that a Part B permit or interim status standards provide assurance to generators that the facility has a measure of financial stability and that the hazardous secondary materials will be managed in a protective manner.
Given the above, EPA estimates that 60 percent of the 4,448 generators (2,669) do not conduct reasonable efforts as a standard business practice (i.e., 4,448 x 60% = 2,669). Of these, EPA estimates that 50 percent will send their excluded materials to an intermediate and/or reclamation facility whose permit or interim-status standards do not address the management of the excluded materials. Hence, EPA estimates that 1,335 generators will make reasonable efforts as a result of the final rule (i.e., 2,669 x 50% = 1,335).
Because these reasonable efforts must be conducted once during the three-year life of this ICR, EPA annualized the number of generators over three years, to estimate that 445 will make these efforts each year (i.e., 1,335/3 = 445). Further, EPA estimates that one-third (i.e., 148) will send an employee to conduct an audit and another one-third will buy an audit report from a vendor. EPA estimates that the remaining one-third will find alternate methods to get the information, such as from a trade association. These 445 generators must keep records that reasonable efforts were made, including a certification.
Generators that send their excluded materials to an intermediate facility where the management of the hazardous secondary material is not addressed under a Part B permit or interim-status standards must make contractual arrangements to ensure the facility sends the material to the reclamation facility identified by the generator. EPA believes this is a standard business practice already taken by generators and therefore has not burdened them in this ICR for this activity.
EPA estimates that 50 percent of generators will send their excluded materials to an intermediate and/or reclamation facility whose permit or interim-status standards do not address the management of the excluded materials, and will need to conduct reasonable efforts (i.e., 4,448 x 50% = 2,224). These generators may be asked to submit documentation, including a certification, of their reasonable efforts to regulatory authorities. EPA has used its best judgment to estimate that 30 percent will be asked to mail documentation and certification on their reasonable efforts to regulatory authorities each year (i.e., 2,224 x 30% = 667).
Generators under the exclusion must maintain records of all off-site shipments of excluded hazardous secondary materials as required by section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(D), and confirmation of receipt from the intermediate and reclamation facilities as required by section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(E). Based on data in the RIA, EPA estimates that 50,555 shipments of excluded materials will be made each year under the exclusion.10
Note that the recordkeeping required at section 261.4(a)(24)(v)(D) is already required by the Department of Transportation (DOT) for hazardous materials, or otherwise undertaken as a customary industry practice. For example, the DOT regulations require shippers to prepare, transmit, and maintain shipping papers for their hazardous materials shipments. Therefore, EPA does not expect generators to incur incremental burden for this requirement.
Industry representatives indicated that, upon receipt of a shipping paper under the exclusion, the intermediate or reclamation facility will mail a copy to the generator as confirmation of receipt. Shipping papers are often multi-part forms to make this easy to do. EPA estimates that generators will receive and keep confirmations for 50,555 shipments of excluded materials each year.
These assumptions are reflected in Exhibit 1.
Intermediate and Reclamation Facilities
EPA estimates that 50,555 shipments of excluded materials will be received by intermediate or reclamation facilities each year under the exclusion.11 Facilities must keep records of, and transmit confirmations of receipt for, each of these shipments. EPA expects that the facilities will automate the process of preparing confirmations of receipt (e.g., computer-generated labels, etc.) and see minimal burden for sending a confirmation to the generator. These assumptions are reflected in Exhibit 1.
Export Requirements at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(25)
EPA estimates that 36 generators will export excluded material under section 261.4(a)(25) each year. This is reflected in Exhibit 1.
FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS FOR MANAGEMENT OF EXCLUDED HAZARDOUS SECONDARY MATERIALS (EXHIBIT 1)
EPA estimates that 240 intermediate facilities and 159 reclamation facilities (399 in total) will claim an exclusion under section 261.4(a)(24) and therefore be subject to the financial assurance requirements.
Cost Estimate
Each facility must prepare a cost estimate under section 261.142. Because this is a one-time activity, EPA has annualized the number of facilities by dividing them by three, to estimate that 133 will prepare a cost estimate annually during the three-year life of this ICR. In addition, each facility must update the cost estimate annually, revise it as required, and maintain records of the most up-to-date version (399). These assumptions are reflected in Exhibit 1.
Financial Assurance Condition
Each facility must establish financial assurance as required under section 261.143. Facilities must establish coverage by using one or more of the following: trust fund, surety bond guaranteeing payment into a trust fund, letter of credit, insurance, and financial test or guarantee.
(1) Trust Fund
EPA estimates that 20 percent of the facilities will establish a trust fund (399 x 20% = 80). These facilities must submit the required information to establish the instrument. Because this is a one-time activity, EPA has annualized the number of facilities over the three-year life of this ICR, to estimate that 27 will submit the information annually.
Facilities must compare their trust funds to their cost estimate whenever the estimate changes, to ensure an appropriate level of assurance. EPA estimates that facilities will perform the comparison annually (i.e., after the cost estimate is updated for inflation). EPA estimates that 10 percent of the facilities using this instrument will submit other paperwork as specified each year (e.g., written request for release of the amount in excess of the current cost estimate).
Both the facilities and their trustees must comply with the terms of the trust agreement each year (e.g., transmittal of information specified in the agreement).
These assumptions are reflected in Exhibit 1.
(2) Surety Bond Guaranteeing Payment into a Trust Fund
EPA estimates that 20 percent of the facilities will establish a surety bond (399 x 20% = 80). These facilities must submit the required information to establish the instrument. Because this is a one-time activity, EPA has annualized the number of facilities over the three-year life of this ICR, to estimate that 27 will submit the information annually. EPA estimates that 10 percent of the facilities using this instrument will submit other paperwork as specified each year (e.g., evidence of increase in penal sum).
Both the facilities and surety companies must comply with the terms of the bond each year.
These assumptions are reflected in Exhibit 1.
(3) Letter of Credit
EPA estimates that 20 percent of the facilities will establish a letter of credit (399 x 20% = 80). These facilities must submit the required information to establish the instrument. Because this is a one-time activity, EPA has annualized the number of facilities over the three-year life of this ICR, to estimate that 27 will submit the information annually. EPA estimates that 10 percent of the facilities using this instrument will submit other paperwork as specified each year (e.g., evidence of increase in credit).
Both the facilities and issuing institutions must comply with the terms of the letter of credit each year.
These assumptions are reflected in Exhibit 1.
(4) Insurance
EPA estimates that 20 percent of the facilities will establish insurance (399 x 20% = 80). These facilities must submit the required information to establish the instrument. Because this is a one-time activity, EPA has annualized the number of facilities over the three-year life of this ICR, to estimate that 27 will submit the information annually. EPA estimates that 10 percent of the facilities using this instrument will submit other paperwork as specified each year (e.g., evidence of increase in the policy).
Both the facilities and insurer must comply with the terms of the insurance each year.
These assumptions are reflected in Exhibit 1.
(5) Financial Test or Guarantee
EPA estimates that 20 percent of the facilities will establish the financial test or guarantee (399 x 20% = 80). These facilities must submit the required information to establish the instruments. Because this is a one-time activity, EPA has annualized the number of facilities over the three-year life of this ICR, to estimate that 27 will submit the information annually.
Facilities must submit annual updates of their originally submitted information. In addition, facilities must comply with the terms of the letter from the chief financial officer and, if applicable, guarantee, each year.
These assumptions are reflected in Exhibit 1.
Use of Financial Mechanisms for Multiple Facilities
EPA estimates that ten percent of facilities will submit information under section 261.143(g) to establish financial mechanisms for multiple facilities. Because this is a one-time activity, EPA has annualized the number of facilities over the three-year life of this ICR, to estimate that 13 will submit the information annually (i.e., 399/3 = 133 x 10% = 13). This is reflected in Exhibit 1.
Removal and Decontamination Plan and Release from Financial Assurance Obligations
Because the exclusions are newly established, EPA estimates that no facilities will seek release from their financial assurance obligations during the three-year life of this ICR. This is reflected in Exhibit 1.
Coverage for Sudden and Nonsudden Accidental Occurrences
Each facility must obtain liability coverage for sudden accidental occurrences under section 261.147(a) and, if applicable, nonsudden accidental occurrences under section 261.147(b). Facilities must establish coverage using one or more of the following: liability insurance, financial test or guarantee, letter of credit, surety bond, or trust fund.
(1) Liability Insurance
EPA estimates that 20 percent of the facilities will establish liability insurance for sudden accidental occurrences and, if applicable, nonsudden accidental occurrences (399 x 20% = 80). These facilities must submit the required information to establish the instruments. Because this is a one-time activity, EPA has annualized the number of facilities over the three-year life of this ICR, to estimate that 27 will submit the information annually. EPA estimates that 10 percent of the facilities using this instrument will submit a signed duplicate original of the insurance policy.
Both the facilities and insurer must comply with the terms of the insurance each year.
These assumptions are reflected in Exhibit 1.
(2) Financial Test or Guarantee
EPA estimates that 20 percent of the facilities will establish the financial test or guarantee for sudden accidental occurrences and, if applicable, nonsudden accidental occurrences (399 x 20% = 80). These facilities must submit the required information to establish the instruments. Because this is a one-time activity, EPA has annualized the number of facilities over the three-year life of this ICR, to estimate that 27 will submit the information annually.
Facilities must submit annual updates of their originally submitted information. In addition, facilities must comply with the terms of the letter from the chief financial officer and, if applicable, guarantee, each year.
These assumptions are reflected in Exhibit 1.
(3) Letter of Credit
EPA estimates that 20 percent of the facilities will establish a letter of credit for sudden accidental occurrences and, if applicable, nonsudden accidental occurrences (399 x 20% = 80). These facilities must submit the required information to establish the instrument. Because this is a one-time activity, EPA has annualized the number of facilities over the three-year life of this ICR, to estimate that 27 will submit the information annually.
Both the facilities and issuing institutions must comply with the terms of the letter of credit each year.
These assumptions are reflected in Exhibit 1.
(4) Surety Bond Guaranteeing Payment into a Trust Fund
EPA estimates that 20 percent of the facilities will establish a surety bond for sudden accidental occurrences and, if applicable, nonsudden accidental occurrences (399 x 20% = 80). These facilities must submit the required information to establish the instrument. Because this is a one-time activity, EPA has annualized the number of facilities over the three-year life of this ICR, to estimate that 27 will submit the information annually.
Both the facilities and surety companies must comply with the terms of the bond each year.
These assumptions are reflected in Exhibit 1.
(5) Trust Fund
EPA estimates that 20 percent of the facilities will establish a trust fund for sudden accidental occurrences and, if applicable, nonsudden accidental occurrences (399 x 20% = 80). These facilities must submit the required information to establish the instrument. Because this is a one-time activity, EPA has annualized the number of facilities over the three-year life of this ICR, to estimate that 27 will submit the information annually.
Both the facilities and their trustees must comply with the terms of the trust agreement each year.
These assumptions are reflected in Exhibit 1.
Combination of Financial Mechanisms
EPA estimates that ten percent of facilities will submit information under section 261.147(a)(6) and (b)(6) to use a combination of financial mechanisms for sudden accidental occurrences and, if applicable, nonsudden accidental occurrences. Because this is a one-time activity, EPA has annualized the number of facilities over the three-year life of this ICR, to estimate that 13 will submit the information annually (i.e., 399/3 = 133 x 10% = 13). This is reflected in Exhibit 1.
Notification to EPA under 40 CFR 261.147(a)(7) and (b)(7)
EPA estimates that, each year, a very small number of facilities will need to submit a notification. EPA estimates that 0.5 percent of facilities (2) will submit a notification to EPA each year (i.e., 0.5% x 399 = 2). This is reflected in Exhibit 1.
Request for Variance
EPA does not expect any facilities to submit a variance request during the three-year life of this ICR. This is reflected in Exhibit 1.
Adjustments by the Regional Administrator
EPA does not expect EPA to make adjustments to the financial assurance levels of any facilities during the three-year life of this ICR. This is reflected in Exhibit 1.
Incapacity of Owners or Operators, Guarantors, or Financial Institutions
EPA does not expect any facilities to notify EPA of bankruptcy proceedings under Title 11 during the three-year life of this ICR. This is reflected in Exhibit 1.
Use of State-Required Mechanisms
EPA does not expect any facilities to use State-required mechanisms to satisfy the financial assurance requirements during the three-year life of this ICR. This is reflected in Exhibit 1.
State Assumption of Responsibility
EPA does not expect any States to assume responsibility for an owner/operator’s compliance or assure that funds will be available from State sources to cover the requirements during the three-year life of this ICR. This is reflected in Exhibit 1.
(3) Annual Respondent Hour and Cost Impacts under Existing Paperwork Requirements
Generators, transporters, intermediate facilities, and reclaimers of excluded material are not subject to existing RCRA information collection requirements in handling the material. As a result, these entities will see some burden impacts under the existing paperwork requirements.
Exhibit 2 presents the total annual burden under the final rule’s paperwork requirements, as well as the annual burden impacts (i.e., savings) under the existing paperwork requirements. The savings under the existing requirements are presented according to the approved ICR in which the requirements are addressed. Below is a brief discussion of these ICRs, along with a description of relevant capital and O&M costs affected:
Requirements for Generators, Transporters, and Waste Management Facilities under the RCRA Hazardous Waste Manifest System (EPA ICR Number 801). EPA estimates that generators will see savings for no longer manifesting their shipments of hazardous secondary materials that are excluded under the rule. There are annual savings in capital costs of $9,999. These savings are associated with the use of fewer file cabinets to store manifests. There are annual savings in O&M costs of $54,652. These savings are associated with the photocopying and transmittal of fewer manifests.
Hazardous Waste Generator Standards (EPA ICR Number 820). EPA estimates that generators that drop in generator status (e.g., change from large quantity generator to small quantity generator) under the exclusions will see savings from reduced generator requirements. There are no capital cost savings. There are annual savings in O&M costs of $353. These savings are associated with the photocopying and transmittal of fewer records.
The 2005 Hazardous Waste Report (EPA ICR Number 976). EPA estimates that large quantity generators that drop in generator status (e.g., change to small quantity generator) under the exclusions will see savings for no longer preparing/submitting a Hazardous Waste Report. In addition, large quantity generators under the rule will see a savings for no longer preparing/submitting Form GMs for the excluded material. Offsite facilities will see a savings for no longer preparing Form WRs for the excluded material. There are no capital cost savings. There are annual savings in O&M costs of $1,108. These savings are associated with the transmittal and recordkeeping of fewer forms.
Land Disposal Restrictions ICR (EPA ICR Number 1442). EPA estimates that generators that drop in generator status (e.g., change from small quantity generator to conditionally exempt small quantity generator) under the exclusions will see savings from reduced land disposal requirements. There are annual savings in capital costs of $267. These savings are associated with the use of fewer file cabinets to store records. There are annual savings in O&M costs of $952,321. These savings are associated with the photocopying and transmittal of fewer records and fewer generators paying for hazardous waste determinations.
6(e) Bottom Line Hour and Cost Burden
(1) Respondent Tally
As shown in Exhibit 2, EPA estimates the total annual burden to respondents under the new paperwork requirements to be 20,403 hours and $1,508,239. The total annual savings to respondents under the new and existing paperwork requirements is estimated to be 105,990 hours and $4,892,506. The bottom-line savings over three years is estimated to be 317,970 hours and $14,677,518.
Note: The burden estimates in Exhibits 1 and 2 are based on an assumption that all States will adopt the final rule. EPA notes, however, that authorized States are not required to adopt the final rule. Because of this, some States may not adopt it and others may adopt only parts of it. This could reduce the burden savings expected under the rule.
(2) Agency Tally
As shown in Exhibit 3, EPA estimates the total annual burden to the government under the new paperwork requirements to be 3,597 hours and $126,739. The bottom-line burden over three years is estimated to be 10,791 hours and $380,217.
6(f) Reasons for Change In Burden
The final rule places necessary conditions on generators, intermediate facilities and reclaimers in managing the excluded hazardous materials. At the same time, the rule relieves these entities of existing RCRA paperwork requirements in handling the excluded material, resulting in savings to them. As shown in Exhibit 2, EPA estimates that these savings more than offset the burden of the rule’s paperwork requirements.
6(g) Public Burden Statement
The average annual public reporting burden under the petition procedures at 40 CFR 260.34 is estimated to be 146 hours per applicant. This includes time to prepare and submit the petition. There is no recordkeeping burden.
The average annual public reporting burden under the exclusions at 40 CFR 261.2(a)(2)(ii) and 261.4(a)(23) is estimated to be ten minutes for a hazardous secondary material generator, toll manufacturer, or tolling contractor. This includes time to notify EPA under section 260.42. The average annual recordkeeping burden is estimated to be less than five minutes. This includes time to prepare a certification under section 260.10.
The average annual public reporting burden under the exclusion at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(24) is estimated to be about ten minutes for a hazardous secondary material generator. This includes time to notify EPA under section 260.42 and submit documentation of reasonable efforts, if requested. The average annual recordkeeping burden is estimated to be about one hour and 30 minutes. This includes time to make reasonable efforts to evaluate the intermediate and reclamation facilities and to keep records of these efforts as well as confirmations of receipt of excluded materials sent from the intermediate and reclamation facilities.
The average annual public reporting burden under the exclusion at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(24) is estimated to be about nine hours and 30 minutes for a hazardous secondary material intermediate or reclamation facility. This includes time to notify EPA under section 260.42, send confirmations of receipt of shipments to the hazardous secondary material generator, and submit the necessary paperwork for financial assurance under Subpart H of Part 261. The average annual recordkeeping burden is estimated to be about 18 hours and 15 minutes. This includes time to keep records of offsite shipments of excluded materials and to prepare/update the cost estimate under Subpart H.
The average annual public reporting burden under the export conditions at 40 CFR 261.4(a)(25) is estimated to be four hours per exporter. This includes time to submit to EPA a notification of intent to export, additional information if requested, and an annual report. The average annual recordkeeping burden is estimated to be less than five minutes. This includes time to keep records of notices and Acknowledgments of Consent.
To comment on the Agency's need for this information, the accuracy of the provided burden estimates, and any suggested methods for minimizing respondent burden, including the use of automated collection techniques, EPA has established a public docket for this ICR under Docket ID Number EPA‑HQ-RCRA-2002-0031, which is available for online viewing at www.regulations.gov, or in person viewing at the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) Docket in the EPA Docket Center (EPA/DC), EPA West, Room 3334, 1301 Constitution Avenue, NW, Washington, D.C. The EPA Docket Center Public Reading Room is open from 8:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m., Monday through Friday, excluding legal holidays. The telephone number for the Reading Room is (202) 566‑1744, and the telephone number for the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) Docket is 202-566-0270. An electronic version of the public docket is available at http://www.regulations.gov. This site can be used to submit or view public comments, access the index listing of the contents of the public docket, and to access those documents in the public docket that are available electronically. When in the system, select "search," then key in the Docket ID Number identified above. Also, you can send comments to the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs, Office of Management and Budget, 725 17th Street, NW, Washington, D.C. 20503, Attention: Desk Officer for EPA. Please include the EPA Docket ID Number EPA‑HQ-RCRA-2002-0031, and OMB Control Number 2050-NEW in any correspondence.
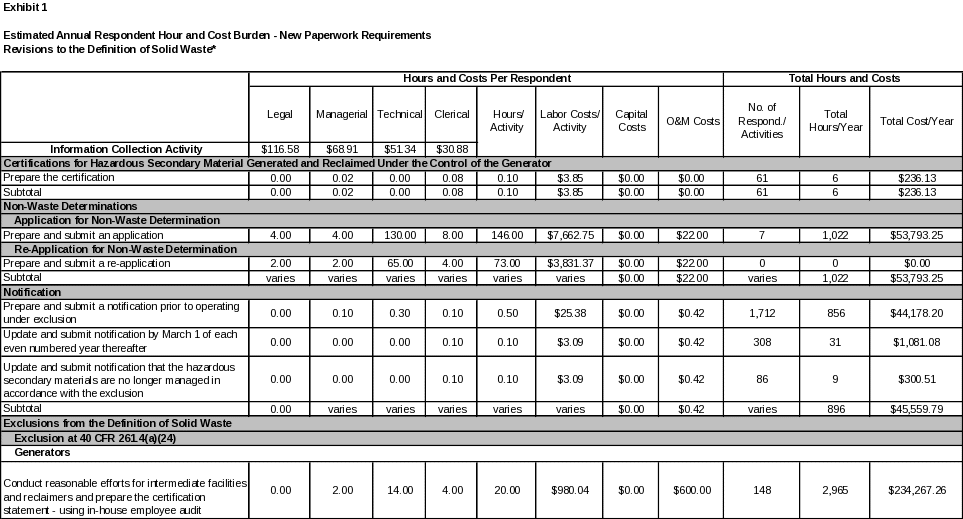
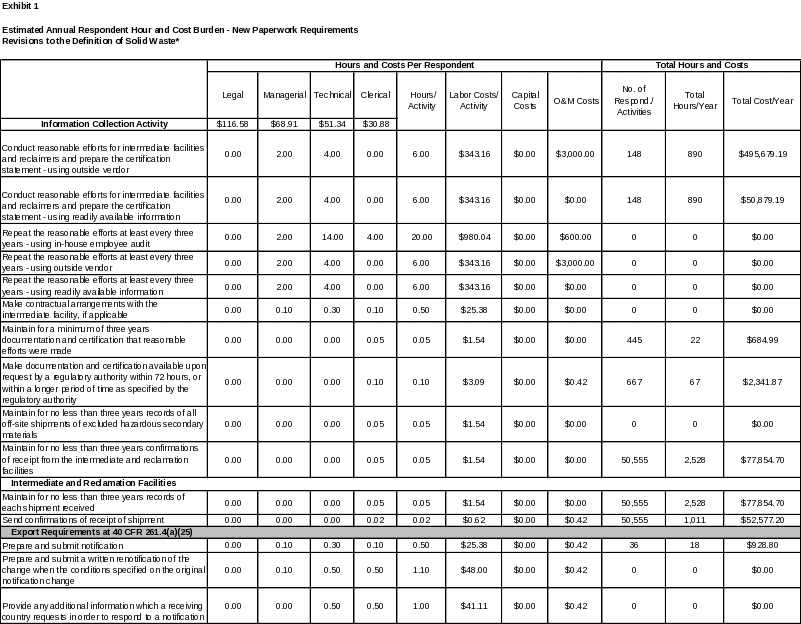
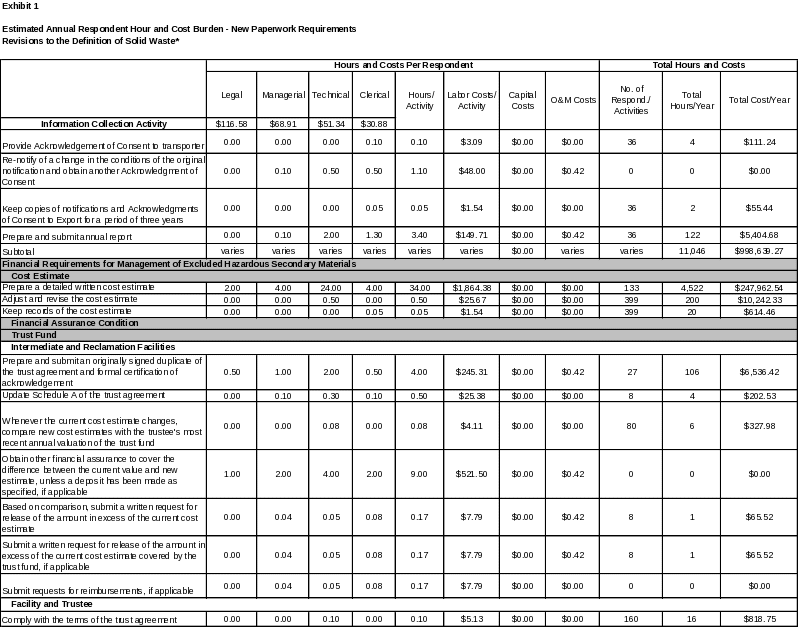
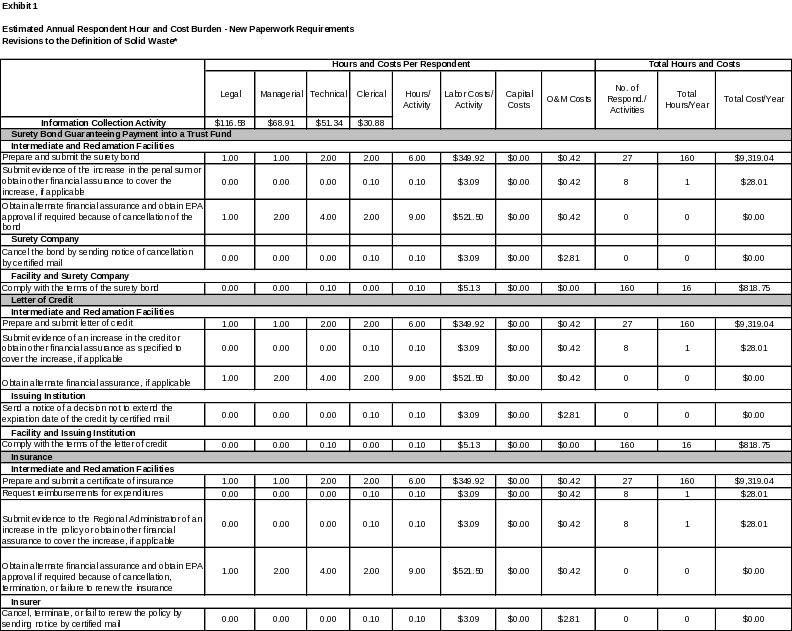
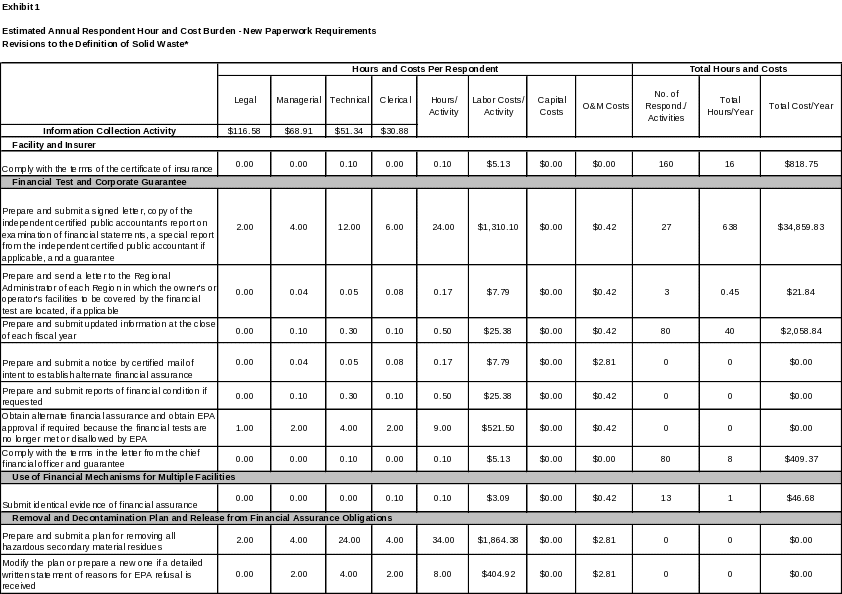
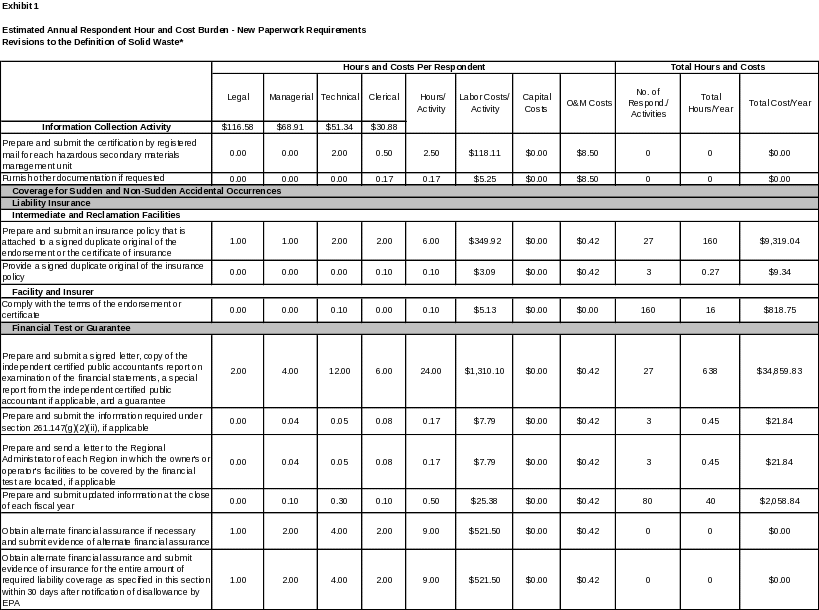
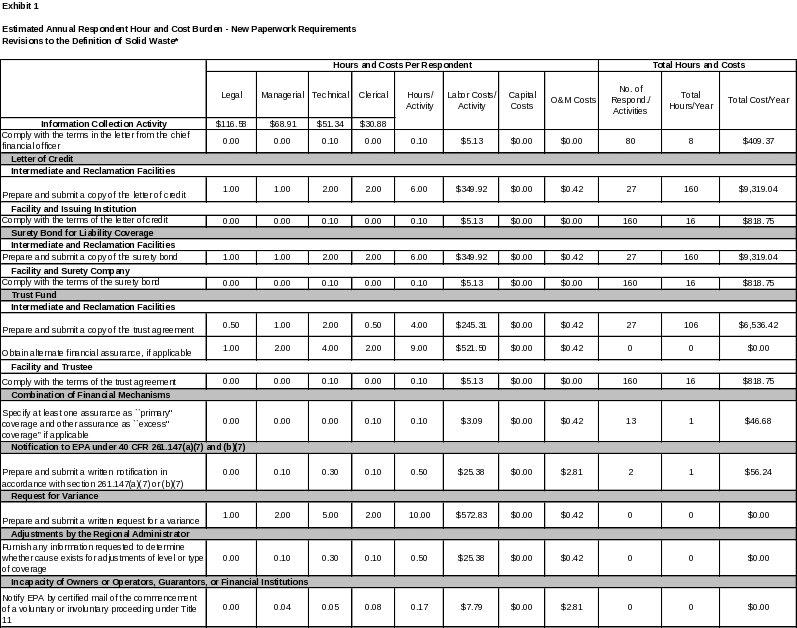

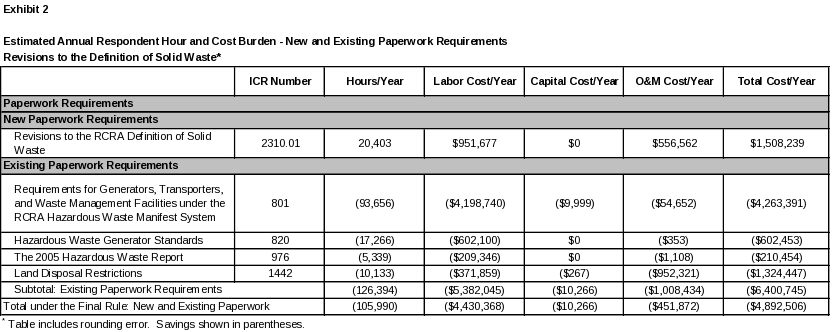
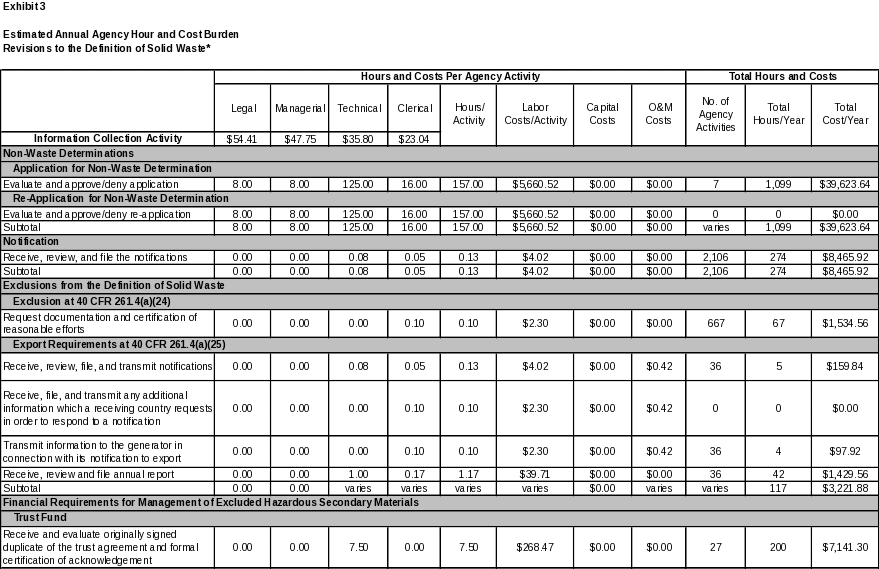
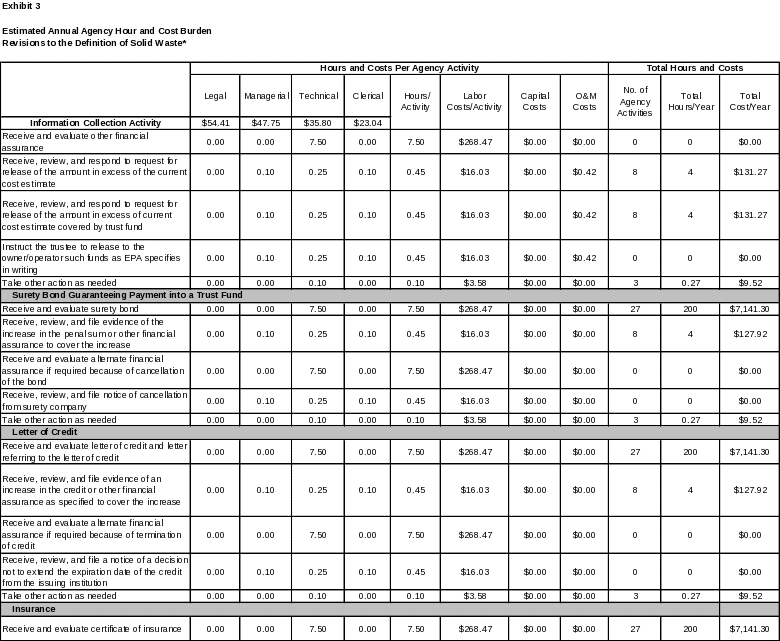
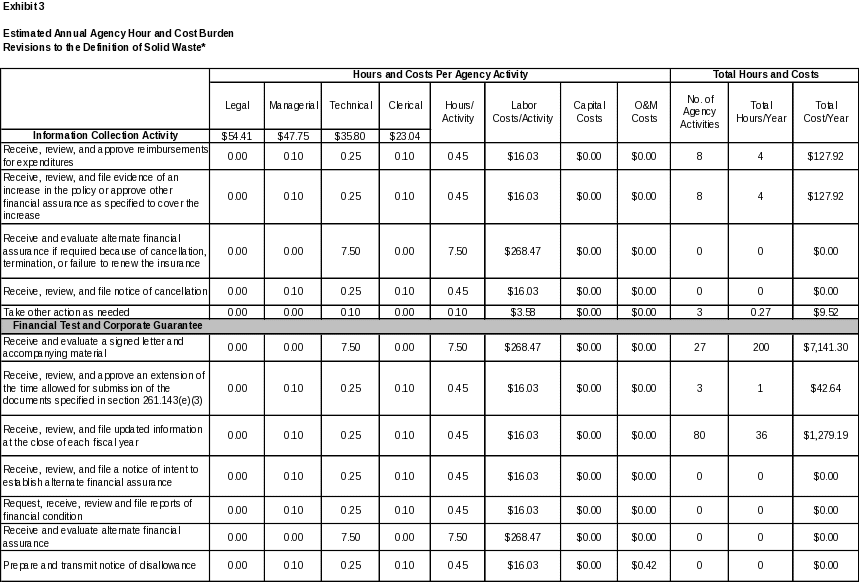
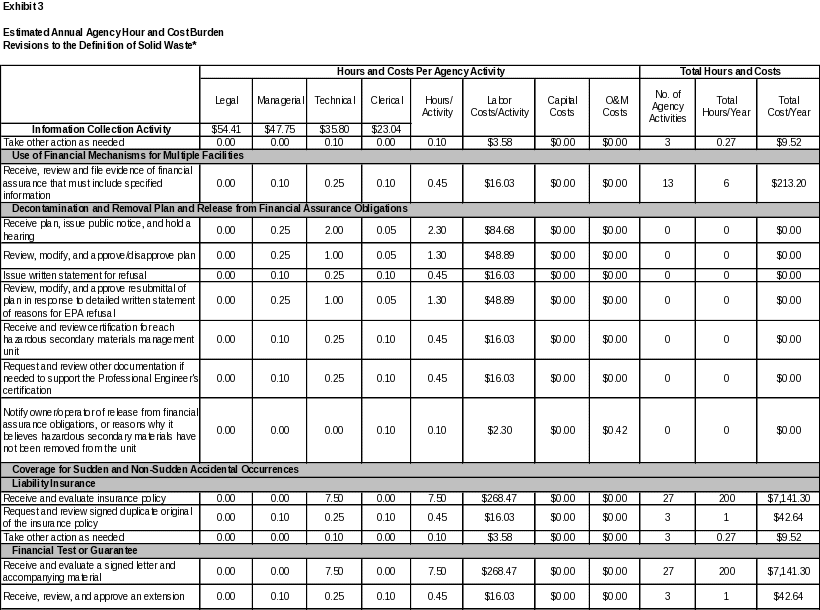
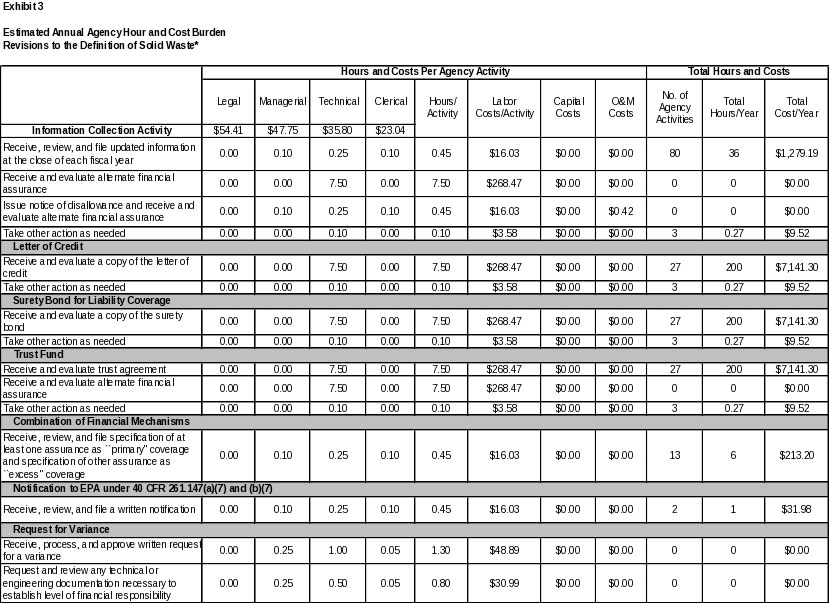
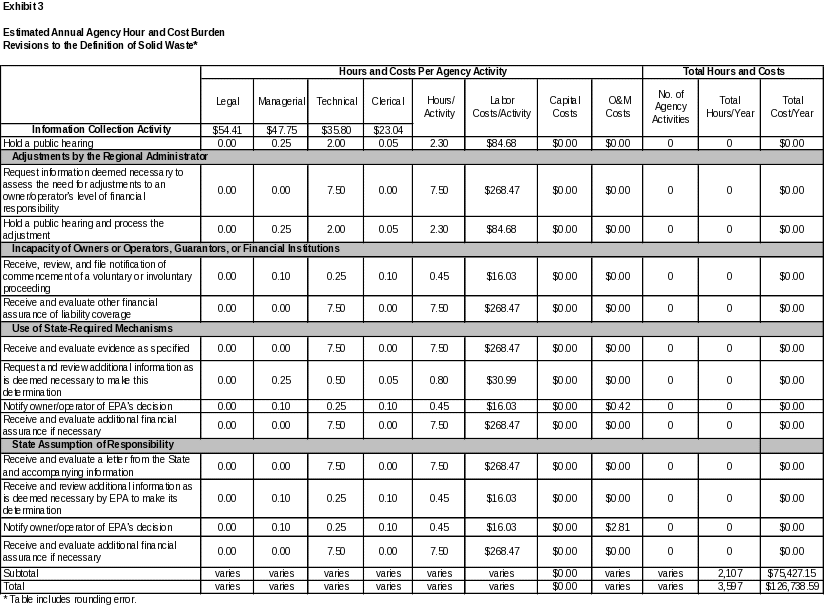
1 “Regulatory Impact Analysis, USEPA’s 2008 Final Rule Amendments to the Industrial Recycling Exclusions of the RCRA Definition of Solid Waste,” September 25, 2008.
2 EPA’s research indicates that an airline fare of $600 is representative of a roundtrip flight within the U.S. EPA also found that respondents can purchase an audit report of a reclaimer for about $3,000.
3 Source: The 1.45 fringe and overhead multiplier factor represents 32.85% full fringe benefits factor plus 12% overhead cost factor. See OMB Circular No. A-76, Attachment C, May 29, 2003: Calculating Public-Private Competition Costs, Figure C1 Table of Standard A-76 Costing Factors. The document can be found at: http://www.whitehouse.gov/omb/circulars/a076/a76_incl_tech_correction.pdf.
4 EPA subtracted conditionally exempt small quantity generators (i.e., 18) from the total estimated number of generators in Exhibit 9G (i.e., 308), to estimate solely the number of large and small quantity generators subject to the exclusions. In general, conditionally exempt small quantity generators are not subject to the requirements of the Federal RCRA program.
5 EPA subtracted conditionally exempt small quantity generators (i.e., 18) from the estimated number of generators in Exhibit 9B (i.e., 308 in columns A-C), to estimate solely the number of large and small quantity generators subject to the exclusions. The estimate of 18 conditionally exempt small quantity generators is from Exhibit 9G. In general, conditionally exempt small quantity generators are not subject to the requirements of the Federal RCRA program.
6 EPA subtracted conditionally exempt small quantity generators (i.e., 734) from the total estimated number of generators in Exhibit 9G (i.e., 5,182), to estimate solely the number of large and small quantity generators subject to the exclusion. In general, conditionally exempt small quantity generators are not subject to the requirements of the Federal RCRA program.
7 Phone call with Safety Kleen Systems Incorporated on March 23, 2008.
8 Phone call with Veolia ES Technical Solutions on April 2, 2008.
9 Even though these 924 SQGs are expected to re-notify in the third year of this ICR, EPA has annualized them over three years to estimate the average annual burden of the requirements. Note that this approach is taken with other one-time activities in this ICR as applicable.
10 The RIA calculates the number of shipments per year under the exclusion by dividing the total annual generation quantity by the assumed maximum truckload size of 18 tons (p. 183). The RIA estimates that, under the exclusion, 909,990 tons of excluded material will be generated/shipped each year (Exhibit 9D). Hence, 909,990 tons/18 tons per shipment = 50,555 shipments.
? Ibid.
| File Type | application/msword |
| File Title | 4(b) |
| Author | ICF |
| Last Modified By | Spencer W. Clark |
| File Modified | 2008-10-29 |
| File Created | 2008-10-29 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy