0261ss16
0261ss16.doc
Notification of Regulated Waste Activity (Renewal)
OMB: 2050-0028
SUPPORTING STATEMENT FOR
EPA INFORMATION COLLECTION REQUEST NUMBER 261.16
"NOTIFICATION OF REGULATED WASTE ACTIVITY"
May, 2009
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
1(a) TITLE AND NUMBER OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 1
1(b) CHARACTERIZATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 1
1(c) ESTIMATED BURDEN HOURS AND COST OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 5
2. NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION
2(a) NEED AND AUTHORITY FOR THE COLLECTION 5
2(b) USE AND USERS OF THE DATA 6
3. NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA
3(a) NONDUPLICATION 6
3(b) PUBLIC NOTICE 6
3(c) CONSULTATIONS 6
3(d) EFFECTS OF LESS FREQUENT COLLECTION 7
3(e) GENERAL GUIDELINES 7
3(f) CONFIDENTIALITY 7
3(g) SENSITIVE QUESTIONS 8
4. RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED
4(a) RESPONDENTS AND NAICS CODES 8
4(b) INFORMATION REQUESTED 9
5. THE INFORMATION COLLECTED -- AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
5(a) AGENCY ACTIVITIES 11
5(b) COLLECTION METHODOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT 11
5(c) SMALL ENTITY FLEXIBILITY 11
5(d) COLLECTION SCHEDULE 11
6. ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF COLLECTION
6(a) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT BURDEN 13
6(b) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT COSTS 13
6(c) ESTIMATING AGENCY BURDEN AND COST 14
6(d) ESTIMATING THE RESPONDENT UNIVERSE AND TOTAL BURDEN AND COSTS 14
6(e) BOTTOM LINE BURDEN HOURS AND COSTS 15
6(f) REASONS FOR CHANGE IN BURDEN 15
6(g) BURDEN STATEMENT 15
Exhibit 1 -4 17-20
1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
1(a) TITLE AND NUMBER OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
This ICR is titled "Notification of Regulated Waste Activity," EPA ICR number 261.16, OMB Control No. 2050-0028. This ICR will eventually be merged with the ICR for the Hazardous Waste Report (EPA ICR No. 0976.14, OMB Control No. 2050-0024), since this form (EPA Form No. 8700-12) is part of the Hazardous Waste Report (EPA Form No. 8700-13 A/B).
1(b) CHARACTERIZATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) of 1976, as amended by the Hazardous and Solid Waste Amendments (HSWA) of 1984, requires EPA to establish a national regulatory program to ensure that regulated wastes are managed in a manner protective of human health and the environment. Section 3010 of Subtitle C of RCRA, as amended, requires any person who generates, transports, or recycles regulated waste or who owns or operates a facility for the treatment, storage, or disposal of regulated waste to notify EPA of their waste activities, including the location and general description of the activities and the regulated wastes handled.
In 1980, EPA created a standard form (EPA Form 8700‑12) to be used by the general public to notify EPA of their regulated waste activities and satisfy the statutory requirements of Section 3010. EPA revised EPA Form 8700-12 (also known as the Notification Form) in 1986 to make it compatible for use with the RCRA Information System (RCRIS) and has revised it periodically thereafter to incorporate new or revised notification requirements. In1999, EPA revised the Notification Form based on new notification requirements for universal waste handlers and destination facilities.
The Notification Form is the vehicle by which most generators, handlers, and managers of regulated waste notify EPA of their regulated waste activities. It also is used by them to acquire an EPA Identification Number. However, as discussed below and throughout this ICR, large quantity handlers of universal waste and used oil handlers have the option of using a letter in lieu of submitting the Notification Form.
This ICR provides a discussion of all of the notification requirements for facilities generating, handling, or managing regulated wastes. These regulated wastes include hazardous wastes as defined by 40 CFR Part 261, universal wastes as defined by 40 CFR Part 273, and used oil as defined by 40 CFR Part 279. Because there are different notification requirements and data items for each of these regulated wastes, the notification requirements for each type of regulated waste are described separately in sections 1 and 4 of this ICR. However, the Agency activities that are described in section 5 and the burden estimates that are presented in section 6 of this ICR are not broken out by type of regulated waste.
Hazardous Waste Activity
Facilities that generate, transport, recycle, treat, store, or dispose of hazardous waste as defined by 40 CFR Part 261 must notify EPA of their hazardous waste activities and obtain an EPA Identification Number. All of these facilities are required to use the Notification Form (EPA Form 8700-12) to notify EPA of their hazardous waste activities. These notification requirements are codified at 40 CFR Parts 262, 263, 264, 265, 266, 270, and 273. The specific notification requirements for each of these parts are described below and listed in Table 1.
40 CFR Parts 262, 263, 264, and 265 include the notification requirements for generators, transporters, and owners or operators of permitted and interim status treatment, storage and disposal facilities (TSDFs), respectively. Sections 262.12, 263.11, 264.11, and 265.11 list the specific notification requirements. Persons regulated under these sections must obtain an EPA Identification Number before treating, storing, transporting, offering for transport, or disposing of hazardous waste.
40 CFR Part 266, Subpart D includes notification requirements for generators and transporters; storers; and users of recyclable materials that are used in a manner that constitutes disposal. Specifically, sections 266.21, 266.22, and 266.23 subject generators and transporters of these materials; storers who are not the ultimate users; and users, respectively, to the notification requirement under section 3010 of RCRA. In addition, these sections also subject these same generators and transporters; storers; and users to all of the applicable requirements of 40 CFR Parts 262 and 263; Parts 264 and 265, Subparts A through L; and Parts 264 and 265, respectively, that include the specific mechanics for implementing the notification requirements as described in sections 262.12, 263.11, 264.11, and 265.11.
40 CFR Part 266, Subpart F includes notification requirements for generators, transporters, and storers of recyclable materials that are utilized for precious metal recovery. Specifically, section 266.70(b)(1) subjects these facilities to the RCRA section 3010 notification requirements.
40 CFR Part 266, Subpart G includes notification requirements for owners or operators of interim status and permitted TSDFs that store spent lead-acid batteries (other than spent lead-acid batteries that are regenerated) before reclaiming them. Specifically, section 266.80(b)(1)(i) requires interim status TSDFs that store these batteries before reclaiming them meet the notification requirements of section 3010 of RCRA. In addition, section 266.80(b)(2)(i) requires permitted TSDFs that store these batteries before reclaiming them meet the notification requirements of section 3010 of RCRA.
40 CFR Part 266, Subpart H includes notification requirements for facilities that burn or process hazardous waste in a boiler or industrial furnace (BIF). Subpart H also subjects generators, transporters, and storers (including processors, blenders, and distributors of hazardous waste fuel) of hazardous waste that is burned or processed in a BIF to the notification requirements of 40 CFR Parts 262, 263, and 264 and 265, respectively. Specifically, sections 266.100(c)(1)(i) and 266.100(f)(1) require that owners or operators of smelting, melting, and refining furnaces that processes hazardous waste either solely for metals recovery or for recovery of economically significant amounts of certain precious metals, respectively, to provide a written, one-time notification of their hazardous waste activities. In addition, sections 266.101(a), 266.101(b), and 266.101(c) require that generators, transporters, and storers of hazardous waste that is burned or processed in a BIF follow specific notification requirements and procedures of sections 262.12, 263.11, and 264.11 and 265.11, respectively. Further, sections 266.102(a)(2)(ii) and 266.103(a)(4)(ii) subject owners or operators of permitted and interim status BIFs that burn or process hazardous waste, respectively, to 40 CFR Parts 264 and 265, Subpart B, which includes the section 264.11 and 265.11 notification requirements. Finally, section 266.108(d) requires that facilities that qualify for the small quantity on-site burner exemption to provide a written, one-time notification of their hazardous waste activities.
40 CFR Part 270 prescribes the timing for notification of hazardous waste activities due to the listing of a hazardous waste in 40 CFR Part 261. Specifically, section 270.1(b) requires that "not later than 90 days after the promulgation or revision of regulations in Part 261 (identifying and listing hazardous wastes), generators and transporters of hazardous waste, and owners or operators of hazardous waste treatment, storage, or disposal facilities may be required to file a notification of that activity under Section 3010."
40 CFR Part 273, Subpart D describes certain conditions under which a transporter of universal waste may be subject to the section 3010 notification requirements of RCRA. Specifically, section 273.54 makes transporters who determine that any material resulting from a release of universal waste is a hazardous waste subject to 40 CFR Part 262. As a result, section 273.54 may also make them, in certain circumstances, subject to the section 262.12 notification requirements and procedures.
40 CFR Part 273, Subpart E includes notification requirements for destination facilities of universal waste. Specifically, section 273.60(a) subjects owners or operators of destination facilities to the notification requirement under section 3010 of RCRA. Section 273.60(a) also subjects destination facilities to all applicable requirements of 40 CFR Parts 264, 265, 266, 268, and 270, which include the section 264.11 and 265.11 notification requirements and procedures.
Table 1
Hazardous Waste Notification Requirements
40 CFR Regulatory Citation |
Regulated Entity |
§262.12 |
Hazardous Waste Generators |
§263.11 |
Hazardous Waste Transporters |
§264.11 |
Permitted Hazardous Waste Treatment, Storage, and Disposal Facilities |
§265.11 |
Interim Status Hazardous Waste Treatment, Storage, and Disposal Facilities |
§266.21 |
Generators and Transporters of Recyclable Materials Used in a Manner Constituting Disposal |
§266.22 |
Storers of Recyclable Materials Used in a Manner Constituting Disposal |
§266.23 |
Users of Recyclable Materials in a Manner Constituting Disposal |
§266.70(b)(1) |
Generators, Transporters, and Storers of Recyclable Materials Utilized for Precious Metal Recovery |
§266.80(b)(1)(i) |
Interim Status TSDFs Storing Spent Lead-Acid Batteries (other than Spent Batteries that are to be Regenerated) before Reclamation |
§266.80(b)(2)(i) |
Permitted TSDFs Storing Spent Lead-Acid Batteries (other than Spent Batteries that are to be Regenerated) before Reclamation |
§266.100(c)(1)(i) |
Smelting, Melting, and Refining Furnaces Processing Hazardous Waste Solely for Metal Recovery |
§266.100(f)(1) |
Smelting, Melting, and Refining Furnaces Processing Hazardous Waste for Recovery of Significant Amounts of Certain Precious Metals |
§266.101(a) |
Generators of Hazardous Waste Burned in Boilers or Industrial Furnaces |
§266.101(b) |
Transporters of Hazardous Waste Burned in Boilers or Industrial Furnaces |
§266.101(c) |
Storers of Hazardous Waste Burned in Boilers or Industrial Furnaces |
§266.102(a)(2)(ii) |
Permitted Boilers and Industrial Furnaces |
§266.103(a)(4)(ii) |
Interim Status Boilers and Industrial Furnaces |
§266.108(d) |
Burners of Small Quantities of Hazardous Waste in On-Site Boilers or Industrial Furnaces |
§270.1(b) |
Generators and Transporters of, and TSDFs Managing Newly Listed Hazardous Wastes |
§273.54 |
Transporters of Universal Waste That is Released and Determined to be Hazardous Waste |
§273.60(a) |
Universal Waste Destination Facilities |
Universal Waste Activity
Large quantity handlers of universal waste must notify EPA of their universal waste activities and obtain an EPA Identification Number. These notification requirements are codified at 40 CFR Part 273, Subpart C. Specifically, section 273.32(a) requires large quantity handlers of universal waste to have notified EPA of their universal waste handling activities and received an EPA Identification Number prior to meeting or exceeding the 5,000 kilogram storage limit, unless they already have notified EPA, as provided by section 273.32(a)(2) or 273.32(a)(3). Section 273.32(b) prescribes the contents of the notification. Large quantity handlers of universal waste have the option of using a letter in lieu of submitting the Notification Form.
Used Oil Management Activity
Used oil handlers must notify EPA of their used oil management activities and obtain an EPA Identification Number. These notification requirements are codified at 40 CFR Part 279. Specifically, sections 279.42, 279.51, 279.62, and 279.73 require used oil transporters and transfer facilities, used oil processors and re‑refiners, burners of off‑specification used oil, and used oil fuel marketers, respectively, who have not previously complied with RCRA Section 3010 requirements (under 40 CFR Part 266, Subpart E) to comply with these requirements and obtain an EPA Identification Number. These used oil handlers have the option of using a letter in lieu of submitting the Notification Form.
Table 2
Used Oil Notification Requirements
40 CFR Regulatory Citation |
Regulated Entity |
§279.42 |
Used Oil Transporters and Transfer Facilities |
§279.51 |
Used Oil Processors and Re-Refiners |
§279.62 |
Burners of Off-Specification Used Oil |
§279.73 |
Used Oil Fuel Marketers |
1(c) ESTIMATED BURDEN HOURS AND COST OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
Section 6 of this supporting statement provides detailed information on the Agency’s estimate of the annual burden on the regulated community for complying with the information collection requirements. EPA estimates that 13,487 regulated waste generators, handlers, and managers will submit initial notifications and 42,428 regulated waste generators, handlers, and managers will submit subsequent notifications to EPA each year during the three years covered by this ICR. The total annual estimated burden is 139,656 hours, at annual cost of $9,081,569.
2. NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION
2(a) NEED AND AUTHORITY FOR THE COLLECTION
Section 3010 of Subtitle C of RCRA, as amended, requires any person who generates, transports, or recycles regulated wastes or who owns or operates a facility for the treatment, storage, or disposal of regulated wastes to notify EPA of their activities, including the location and general description of the activities and the regulated wastes handled. As required by statute, EPA promulgated regulations to implement these notification requirements at 40 CFR Parts 262, 263, 264, 265, 266, 270, 273, and 279. (See Section 1(b) above for a detailed listing of notification requirements by type of regulated waste and regulated entity). EPA needs this information to determine the universe of persons who generate, handle, and manage these regulated wastes; assign EPA Identification Numbers; and ensure that these regulated wastes are managed in a way that protects human health and the environment, as required by RCRA, as amended.
2(b) PRACTICAL UTILITY/USERS OF DATA
EPA enters notification information submitted by respondents into the EPA National data base and assigns EPA Identification Numbers. EPA uses the information primarily for tracking purposes, and secondarily for a variety of enforcement and inspection purposes. In addition, EPA uses this information to identify the universe of regulated waste generators, handlers, and managers and their specific regulated waste activities. Finally, EPA uses this information to ensure that regulated waste is managed properly, that statutory provisions are upheld, and that regulations are adhered to by facility owners or operators.
3. NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA
3(a) NONDUPLICATION
RCRA is the primary Federal statutory vehicle for prescribing regulated waste management practices that are necessary to protect human health and the environment. There are no other Federal statutes or regulations that require information regarding the operation of regulated waste generation, handling, and management practices.
3(b) PUBLIC NOTICE
EPA issued a public notice in the Federal Register on March 13, 2009 (74 FR 10909). The comment period ended on May 12, 2009. No comments were received in response to the notice.
3(c) CONSULTATIONS
Form 8700-12 will be revised to implement the requirements of two final rules: the Revisions to the Definition of Solid Waste, promulgated on October 30, 2008 (73 FR 64668); and the Standards Applicable to Generators of Hazardous Waste; Alternative Requirements for Hazardous Waste Determination and Accumulation of Unwanted Material at Laboratories Owned by Colleges and Universities and Other Eligible Academic Entities Formally Affiliated With Colleges and Universities, promulgated on December 1, 2008 (73 FR 72912). These form revisions are currently undergoing a national review process. As part of this process, we have asked for comments on the burden estimates. Once the revisions to Form 8700-12 are finalized, this ICR will be amended and consolidated with ICR No. 0976.14 (OMB Control No. 2050-0024), which is the ICR for EPA Form #8700-13 A/B. The reason for the consolidation is that Form 8700-12 and Form 8700-13 A/B are both part of the Hazardous Waste Report form.
3(d) EFFECTS OF LESS FREQUENT COLLECTION
New hazardous waste generators, transporters, or TSDFs must submit a Notification Form and obtain an EPA Identification Number prior to treating (including recycling), storing, transporting, offering for transport, or disposing of hazardous waste. Existing hazardous waste generators, transporters, or TSDFs are required to notify the Agency of their hazardous waste activity(ies) not later than 90 days after the promulgation or revision of regulations in 40 CFR Part 261 (identification and listing of hazardous wastes). Owners or operators of smelting, melting, and refining furnaces that process hazardous waste either solely for metals recovery or for recovery of economically significant amounts of certain precious metals under sections 266.100(c)(1)(i) and 266.100(f)(1), respectively, and facilities that qualify for the small quantity on-site burner exemption under section 266.108(d) must provide a written, one-time notification of their hazardous waste activities. Under Section 273.32(a), large quantity handlers of universal waste must submit a written, one-time notification of universal waste management to the Regional Administrator and obtain an EPA Identification Number before meeting or exceeding the 5,000 kg storage limit, unless they already have notified EPA, as provided by section 273.32(a)(2) or 273.32(a)(3). Under sections 279.42, 279.51, 279.62 and 279.73, used oil handlers who have not previously complied with the notification requirement (under 40 CFR Part 266, Subpart E) must submit a written, one-time notification of used oil management activities and obtain an EPA Identification Number. Any reduction in the frequency of this information collection would prevent the Agency from meeting the statutory requirements of Section 3010 of RCRA.
3(e) GENERAL GUIDELINES
This ICR adheres to the guidelines stated in the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995, OMB's implementing regulations, EPA's Information Collection Review Handbook, and other applicable OMB guidance.
3(f) CONFIDENTIALITY
Section 3007(b) of RCRA and 40 CFR Part 2, Subpart B, which defines EPA's general policy on public disclosure of information, both contain provisions for confidentiality. However, the Agency does not anticipate that businesses will assert a claim of confidentiality covering all or part of the Notification of Regulated Waste Activity. If such a claim were asserted, EPA must and will treat the information in accordance with the regulations cited above. EPA also will assure that this information collection complies with the Privacy Act of 1974 and OMB Circular 108.
3(g) SENSITIVE QUESTIONS
No questions of a sensitive nature are included in these information collection requirements.
4. THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED
4(a) RESPONDENTS AND NAICS CODES
The following is a list of NAICS codes associated with the facilities most likely to be affected by the notification requirements discussed in this ICR:
NAICS Code
221121 Electric Bulk Power Transmission and Control
221122 Electric Power Distribution
22132 Sewage Treatment Facilities
311942 Spice and Extract Manufacturing
323114 Quick Printing
32411 Petroleum Refineries
325131 Inorganic Dye and Pigment Manufacturing
325199 All Other Basic Organic Chemical Manufacturing
325211 Plastics Material and Resin Manufacturing
32551 Paint and Coating Manufacturing
325998 All Other Miscellaneous Chemical Product Manufacturing
331311 Alumina Refining
33271 Machine Shops
332813 Electroplating, Plating, Polishing, Anodizing, and Coloring
332999 All Other Miscellaneous Fabricated Metal Product Manufacturing
333319 Other Commercial and Service Industry Machinery Manufacturing
333999 All Other General Purpose Machinery Manufacturing
33422 Radio and Television Broadcasting and Wireless Communications Equipment Manufacturing
334418 Printed Circuit/Electronics Assembly Manufacturing
334419 Other Electronic Component Manufacturing
336211 Motor Vehicle Body Manufacturing
336312 Gasoline Engine and Engine Parts Manufacturing
336322 Other Motor Vehicle Electrical and Electronic Equipment Manufacturing
33633 Motor Vehicle Steering and Suspension Components (except Spring)
Manufacturing
33634 Motor Vehicle Brake System Manufacturing
33635 Motor Vehicle Transmission and Power Train Parts Manufacturing
336399 All Other Motor Vehicle Part Manufacturing
44111 New Car Dealers
44711 Gasoline Stations with Convenience Store
44719 Other Gasoline Stations
454312 Liquefied Petroleum Gas (Bottled Gas) Dealers
48411 General Freight Trucking, Local
48421 Used Household and Office Goods Moving
48422 Specialized Freight (except Used Goods) Trucking, Local
562112 Hazardous Waste Collection
562119 Other Waste Collection
562211 Hazardous Waste Treatment and Disposal
562219 Other Nonhazardous Waste Treatment and Disposal
56292 Materials Recovery Facilities
811111 General Automotive Repair
4(b) INFORMATION REQUESTED
This section describes the data items and respondent activities for notification requirements for facilities generating, handling, or managing regulated wastes. These regulated wastes include hazardous wastes as defined by 40 CFR Part 261, universal wastes as defined by 40 CFR Part 273, and used oil as defined by 40 CFR Part 279. Since there are different notification requirements and data items for each of these regulated wastes, the data items for each type of regulated waste are described separately. (See Section 1(b) above for a detailed listing of notification requirements by type of regulated waste activity and regulated entity). However, the respondent activities for each type of regulated waste are largely the same and are not described separately.
(i) Data Items
Hazardous Waste Activity
Hazardous waste generators; transporters; recyclers; and treatment, storage, and disposal facilities must notify of their hazardous waste activities, including the location and general description of the activities and the hazardous wastes handled. They also must obtain an EPA Identification Number. To do so, they must complete a Notification Form (EPA Form 8700‑12), including the following data items:
‑‑ Name of the facility;
‑‑ Facility mailing address;
‑‑ Facility location;
‑‑ Name, title, and business telephone number of the person who should be contacted regarding information on the form;
‑‑ Ownership information, including the legal status of the current owner of the facility;
‑‑ Information on the type of hazardous waste activity;
‑‑ Information on whether this is the initial notification or a subsequent notification;
‑‑ A description of the hazardous wastes handled at the facility; and
‑‑ A certification signed by the facility owner, operator, or authorized representative
Universal Waste Activity
Large quantity handlers of universal waste must notify EPA of their universal waste activities and obtain an EPA Identification Number by completing and submitting EPA Form 8700‑12, as described above, or completing and submitting a letter to EPA requesting an EPA Identification Number. The letter must include the following data items:
-- The universal waste handler’s name and mailing address;
-- Name and business telephone number of the person who should be contacted regarding the universal waste management activities;
-- Address or physical location of the universal waste management activities;
-- A list of all of the types of universal waste managed by the handler; and
-- A statement indicating that the handler is accumulating more than 5,000 kg of universal waste at one time and the types of universal waste (e.g., batteries, pesticides, thermostats) the handler is accumulating above this quantity.
Used Oil Management Activity
Used oil handlers must notify EPA of their used oil management activities and obtain an EPA Identification Number by completing and submitting EPA Form 8700‑12, as described above, or completing and submitting a letter to EPA requesting an EPA Identification Number. The letter must include the following data items:
‑‑ Company name;
‑‑ Owner of company;
‑‑ Mailing address of company;
‑‑ Name and telephone number of company contact;
‑‑ Type of used oil management activity(ies);
‑‑ Location of facility(ies) (except for used oil fuel marketers); and
‑‑ Name and telephone number of each contact at each transfer facility, if applicable (for used oil transporters and transfer facilities only).
(ii) Respondent Activities
To provide EPA with the required information, facilities generating, handling, or managing regulated wastes, including hazardous wastes as defined by 40 CFR Part 261, universal wastes as defined by 40 CFR Part 273, and used oil as defined by 40 CFR Part 279 must perform the following activities for both initial and subsequent notifications:
-- Read the regulations and instructions; and
-- Complete and submit EPA Form 8700‑12, or (for large quantity handlers of universal waste or used oil handlers only) a letter requesting an EPA Identification Number.
5. THE INFORMATION COLLECTED ‑‑ AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
5(a) AGENCY ACTIVITIES
Activities of authorized State agencies and EPA Regional offices associated with the requirement for regulated waste generators, handlers, and managers to obtain an EPA Identification Number include reviewing the completed Notification Form, entering information into the EPA national data base, generating an EPA Identification Number and sending that number to the regulated waste generator, handler, or management facility.
5(b) COLLECTION METHODOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
EPA keeps records of and reviews all of the information submitted. Authorized States and EPA Regions enter the information on the Notification Forms into electronic data base systems. States coordinate with the EPA Regions and OSW Headquarters to supply EPA with the data reported for inclusion in the RCRAInfo national database.
5(c) SMALL ENTITY FLEXIBILITY
Some respondents will be individuals or small organizations. However, EPA believes that the information to be collected is the minimum amount necessary to fulfill the statutory requirements of RCRA.
5(d) COLLECTION SCHEDULE
Hazardous Waste Activity
Under sections 262.12, 263.11, 264.11 and 265.11, all new hazardous waste generators, transporters, and TSDFs must notify EPA of their hazardous waste activities and obtain an EPA Identification Number before treating, storing, transporting, offering for transport, or disposing of hazardous waste. Under section 270.1(b), these hazardous waste generators, transporters, and TSDFs, are also subject to newly promulgated or revised regulations at 40 CFR Part 261 (identification and listing of hazardous wastes) and must notify EPA of new or revised hazardous waste activities no later than 90 days after promulgation or revision. In addition, other generators; transporters; recyclers; and treatment, storage and disposal facilities that are subject to notification requirements under sections 266.21, 266.22, 266.23, 266.70(b)(1), 266.80(b)(1)(i), 266.80(b)(2)(i), 266.101(a), 266.101(b), 266.101(c), 266.102(a)(2)(ii), 266.103(a)(4)(ii), and 273.60(a) must notify EPA of their hazardous waste activities within the same time frame. Under section 273.54, universal waste transporters who determine that any material resulting from a release of universal waste is a hazardous waste are subject to 40 CFR Part 262. As a result, these transporters may also be subject to, under these circumstances, the section 262.12 notification requirements and procedures. As such, these transporters must, at that time, notify EPA of their hazardous waste activities and obtain an EPA Identification Number before treating, storing, transporting, offering for transport, or disposing of hazardous waste. Finally, owners or operators of smelting, melting, and refining furnaces that process hazardous waste either solely for metals recovery or for recovery of economically significant amounts of certain precious metals under sections 266.100(c)(1)(i) and 266.100(f)(1), respectively, and facilities that qualify for the small quantity on-site burner exemption under section 266.108(d) must provide a written, one-time notification of their hazardous waste activities.
Universal Waste Activity
Under Section 273.32(a)(1), large quantity handlers of universal waste must submit a written, one-time notification of universal waste activity to the Regional Administrator and obtain an EPA Identification Number before meeting or exceeding the 5,000 kg storage limit, unless they already have notified EPA, as provided by section 273.32(a)(2) or 273.32(a)(3).
Used Oil Management Activity
Under sections 279.42, 279.51, 279.62 and 279.73, used oil handlers who were not previously required to comply with the notification requirements (under 40 CFR Part 266, Subpart E) must submit a written, one-time notification of their used oil management activities and obtain an EPA Identification Number.
6. ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF THE COLLECTION
6(a) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT BURDEN
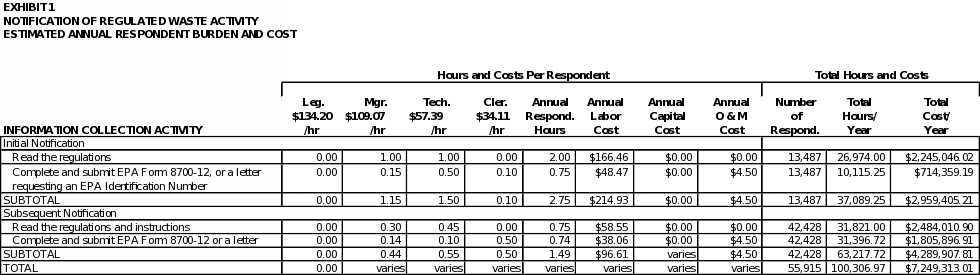
EPA estimated respondent burden hours associated with all of the requirements covered in this ICR in Exhibit 1. The exhibit includes the number of hours required to conduct the information collection activity and the cost associated with each requirement. Some totals may not add up due to rounding errors. In developing burden estimates for each information collection requirement in this ICR, EPA consulted with members of the regulated community.
Based on consultations with members of the regulated community, EPA split the respondent activities into initial and subsequent notifications. In doing so, EPA estimates that the average time for an initial notification to be 2 hours. In contrast, the average time for a subsequent notification is estimated to be 1 hour.
However, EPA did not split the respondent activities for large quantity handlers of universal waste or used oil handlers into two activities: completing the Notification Form or writing a letter. While the amount of time for using a letter in lieu of the Notification Form might be less, EPA assumed that all large quantity handlers of universal waste and used oil handlers will use the Notification Form to comply with their respective notification requirements. In using this approach, EPA has likely overstated the burden associated with these two types of handlers.
6(b) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT COSTS
In Exhibit 1, EPA also estimates respondent costs associated with this ICR. In the following paragraphs, EPA describes the data and assumptions used in the exhibit.
(i) Estimating Labor Costs
For purposes of this analysis, EPA estimates an average hourly respondent labor cost (including fringe and overhead) of $134.20 for legal staff, $109.07 for managerial staff, $57.39 for technical staff, and $34.11 for clerical staff, which includes an average overhead factor of 1.4845. These respondent labor costs were generated from data obtained from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Occupational Employment Statistics (OES) for May 2007 National Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates (averages across all NAICS codes): http://www.bls.gov/oes/current/oes_nat.htm.
Loaded wage rates estimated by multiplying the BLS unloaded wage rates by 1.4845, which represents addition of two cost factors (i.e., Federal government civilian wage full fringe benefit cost factor of 36.45%, plus 12% overhead cost factors) from Figure C1 of the 29 May 2003 OMB Circular A-76: Performance of Commercial Activities: http://www.whitehouse.gov/omb/circulars/a076/a76_incl_tech_correction.html.
(ii) Estimating Capital and Operations and Maintenance (O&M) Costs
EPA estimates that facilities may incur annual capital and operations and maintenance costs associated with specific activities. There are no capital costs associated with completing and submitting the Part A Permit Application. For submittal of information or notices, EPA estimates that facilities will incur $4.50 in costs each year for the three-year period of the ICR. This estimate is based on the mailing cost of $4.50 for a two-pound package. There are no costs associated with the purchase of a service included in the O&M costs.
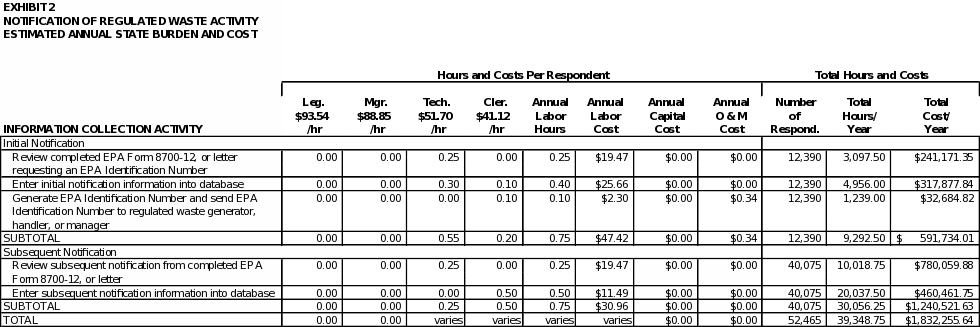
6(c) ESTIMATING AGENCY BURDEN AND COSTS
EPA estimates the Agency hour and cost burden associated with all the requirements covered in this ICR in Exhibit 2. As shown in the exhibit, EPA estimates an average hourly labor cost of $113.57 for legal staff (GS‑15, Step 1), $106.19 for managerial staff (GS‑14, Step 4), $77.86 for technical staff (GS‑12, Step 5), and $22.98 for clerical staff (GS‑5, Step 1). To derive these hourly estimates, EPA referred to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Occupational Employment Statistics (OES) for May 2007 at: http://www.bls.gov/oes/current/naics4_999100.htm
The loaded wage rates above were calculated by multiplying the BLS unloaded wage rates by 1.4845, which represents addition of two cost factors (i.e., civilian position full fringe benefit cost factor of 36.45%, plus 12% overhead cost factor) from Figure C1 of OMB Circular A-76 to be used to reflect the full cost of government employees: http://www.whitehouse.gov/omb/circulars/a076/a76_incl_tech_correction.html.
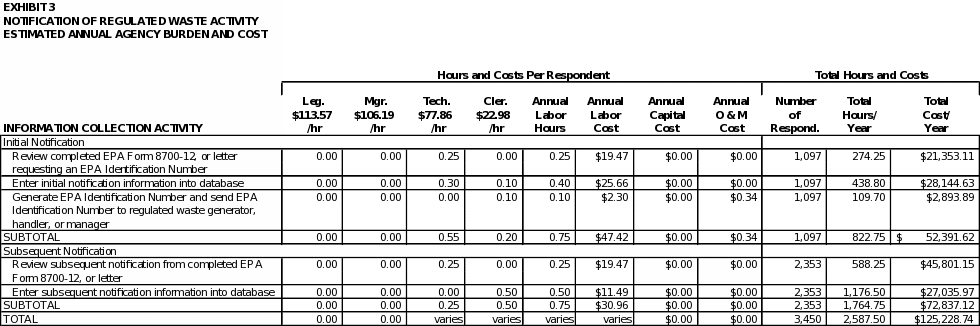
6(d) ESTIMATING STATE AGENCY BURDEN AND COSTS
EPA estimates the State Agency hour and cost burden associated with all information collection requirements covered in this ICR in Exhibit 3. As shown in the exhibit, EPA estimates an average hourly labor cost of $93.54 for legal staff, $88.85 for managerial staff, $51.70 for technical staff, and $41.12 for clerical staff.
These State government employee unloaded average (mean) wage rates were generated from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Occupational Employment Statistics (OES) for May 2007 at: http://www.bls.gov/oes/current/naics4_999200.htm.
OMB does not publish a state government wage rate loading cost factor; thus the same OMB cost factor for Federal government labor is applied in this table above. The loaded wage rates above were calculated by multiplying the BLS unloaded wage rates by 1.4845, which represents addition of two cost factors (i.e., civilian position full fringe benefit cost factor of 36.45%, plus 12% overhead cost factor) from Figure C1 of OMB Circular A-76 to be used to reflect the full cost of government employees: http://www.whitehouse.gov/omb/circulars/a076/a76_incl_tech_correction.html.
6(e) ESTIMATING THE RESPONDENT UNIVERSE AND TOTAL BURDEN AND COSTS
Respondent Universe
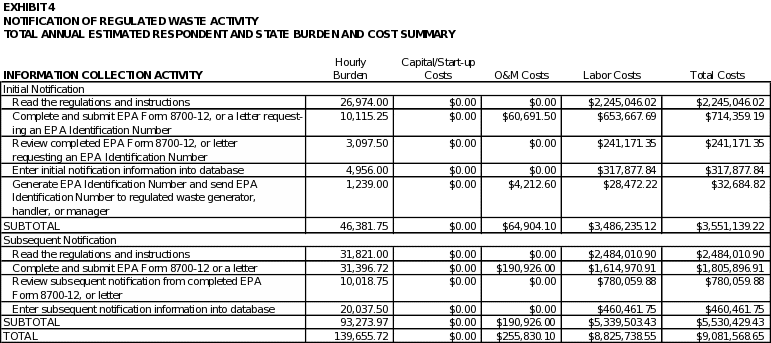
Based on the RCRAInfo database, EPA estimates that approximately 13,487 regulated waste generators, handlers, and managers will submit initial notifications and 42,428 regulated waste generators, handlers, and managers will submit subsequent notifications to EPA annually over the three years covered by this ICR. The universe numbers are used to calculate the total respondent burden and costs per information collection activity shown in Exhibit 4 of this ICR.
Total Burden and Cost
Exhibit 4 illustrates the respondent costs associated with all of the information collection activities covered in this ICR. As shown in Exhibit 3, EPA estimates that the total annual respondent burden for all activities covered in this ICR is approximately 139,656 hours, at an annual cost of $9,081,569.
6(e) BOTTOM LINE BURDEN HOURS AND COSTS
Exhibit 4 shows the aggregate annual hour and cost burden to respondents. As shown in the exhibit, EPA estimates the annual respondent burden to be 139,656 hours and $9,081,569.
6(f) REASONS FOR CHANGE IN BURDEN
There is an increase of 39,349 hours in the total estimated burden compared to what is currently identified in the OMB Inventory of Approved ICR Burdens (from 100,307 total hours to 139,656 total hours). This increase is due to the inclusion of State burden hours that were not previously counted.
6(g) BURDEN STATEMENT
EPA believes this ICR is an accurate and complete portrait of the burden for both initial and subsequent notifications, total respondent burden, and number of respondents to be affected by the notification requirements.
The reporting burden for information collection requirements associated with initial notification requirements is estimated to be approximately 2 hours. The burden estimate includes time for reading the regulations and preparing and submitting the initial notification. There are no recordkeeping requirements associated with the initial notifications, and as such, there is no recordkeeping burden.
The reporting burden for information collection requirements associated with subsequent notification is estimated to be approximately 1hour. The burden estimate includes time for reading the regulations, preparing and submitting a subsequent notification. There are no recordkeeping requirements associated with subsequent notifications, and as such, there is no recordkeeping burden.
Burden means the total time, effort, or financial resources expended by persons to generate, maintain, retain, or disclose or provide information to or for a Federal agency. This includes the time needed to review instructions; develop, acquire, install, and utilize technology and systems for the purposes of collecting, validating, and verifying information, processing and maintaining information, and disclosing and providing information; adjust the existing ways to comply with any previously applicable instructions and requirements; train personnel to be able to respond to a collection of information; search data sources; complete and review the collection of information; and transmit or otherwise disclose the information. An agency may not conduct or sponsor, and a person is not required to respond to, a collection of information unless it displays a currently valid OMB control number. The OMB control numbers for EPA’s regulations are listed in 40 CFR Part 9 and 48 CFR Chapter 15.
To comment on EPA 's need for this information, the accuracy of the provided burden estimates, and any suggested methods for minimizing respondent burden, including the use of automated collection techniques, EPA has established a public docket for this ICR under Docket ID Number EPA-HQ-RCRA-2008-0911, which is available for online viewing at www.regulations.gov, or in person viewing at the RCRA Docket in the EPA Docket Center (EPA/DC), EPA West, Room 3334, 1301 Constitution Avenue, NW, Washington, D.C. The EPA Docket Center Public Reading Room is open from 8:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m., Monday through Friday, excluding legal holidays. The telephone number for the Reading Room is (202) 566-1744, and the telephone number for the RCRA Docket is (202) 566-0270. An electronic version of the public docket is available at www.regulations.gov. This site can be used to submit or view public comments, access the index listing of the contents of the public docket, and to access those documents in the public docket that are available electronically. When in the system, select “search,” then key in the Docket ID Number identified above. Also, you can send comments to the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs, Office of Management and Budget, 725 17th Street, NW, Washington, D.C. 20503, Attention: Desk Officer for EPA. Please include the EPA Docket ID Number EPA-HQ-RCRA-2008-0911 and OMB Control Number 2050-0028 in any correspondence.
| File Type | application/msword |
| File Title | SUPPORTING STATEMENT FOR |
| Author | ctsuser |
| Last Modified By | Spencer W. Clark |
| File Modified | 2009-06-11 |
| File Created | 2009-06-04 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy