Supporting Statement OMB 2009 B (2)
Supporting Statement OMB 2009 B (2).docx
National Youth Gang Survey
OMB: 1121-0224
Paperwork Reduction Act Submission
Supporting Statement - B
Agency: Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP)
Title: National Youth Gang Survey (NYGC)
Form: N/A
OMB No.: 1121-0224
B. COLLECTION OF INFORMATION EMPLOYING STATISTICAL METHODS
1. Potential Respondent Universe—There are 28,291 cities, towns/townships, and counties in the United States. Many of these towns and townships, although incorporated, have no active, local governing bodies and, of those that do only 13,617 have law enforcement agencies. Since law enforcement agencies could be expected to be the most authoritative sources for information about gang activity, the universe from which the sample was selected was reduced to those cities, towns, and counties that had local police or sheriffs’ departments. Further, to retain comparative analysis potential, departments selected as survey respondents had to be contributors to the FBI Uniform Crime Report. Finally, based on previous survey experience showing little gang activity in very small communities, towns with populations below 2,500 were excluded.
The resulting sample consists of 2,549 cities, towns, and counties. It is divided into four parts or area types.
All police departments serving cities above 50,000 in population (large cities) (n = 624).
All suburban county sheriffs’ and police departments as defined in the FBI’s annual report Crime in the United States (suburban counties) (n = 739).
A representative sample, selected at random, of rural county sheriffs’ departments, as defined in the FBI’s annual report Crime in the United States (rural counties) (n = 492).
A representative sample of police departments, selected at random, serving cities between 2,500 and 49,999 in population (small cities)
(n = 694).
Table 1 depicts the survey sample, stratified by population served.
-
Table 1. Survey Sample by Population and Counties Served
Population
No. of Agencies
250,000 and Above
70
100,000–249,999
164
50,000–99,999
390
25,000–49,999
234
10,000–24,999
138
2,500–9,999
322
Rural Counties
492
Suburban Counties
739
Total
2,549
Table 2 shows the survey sample by area type.
-
Table 2. Survey Sample by Area Type
Area Type
No. of Agencies
Rural Counties
492
Suburban Counties
739
Smaller Cities
694
Larger Cities
624
Total
2,549
Expected Response Rates—The response rates to the National Youth Gang Survey conducted from 1996–2007 have exceeded 80 percent.
2. Statistical Methodology of Stratification and Sample Selection
Municipalities
were stratified by population size by the late
Professor Walter
Miller based on his prior surveys (Miller, 1975, 1982) and his
analysis of surveys conducted by others (Miller, 1997). Professor
Miller believed this breakdown by size to be a minimal one to yield
the most needed information about the current spread and nature of
youth gang problems as identified by law enforcement agencies.
Estimation Procedure—The estimated required sample size n was derived using the formula:
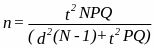
Where—
t is the abscissa of the normal curve that cuts off an area of at the tails.
N is the true population size.
P is the true proportion of the population with a specific characteristic.
Q is (1-P) or the true proportion of the population without a specific characteristic.
d is an acceptable error of size that can be incurred at probability
This computing formula is
derived from the formula provided by
William Cochran's Sampling
Techniques (Wiley &
Sons, 1977, p. 75) for sample size n
required for producing an error of size d
at a specific probability .
Cochran uses t,
the abscissa of the normal curve that cuts off an area of
at the tails, to produce the formula:
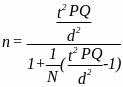
All the terms in the computing formula are presented in a form equivalent to that in Cochran's formula.
Degree of Accuracy Needed for the Purpose Described in the Justification—An error rate d was computed as 5 percent. The probability of an estimated error being greater than d used in the computations above is .05. All computations are based on an estimated true population of P=.5 and Q=.5, since this results in the most conservative and largest estimates for required samples for each stratum.
Unusual Problems Requiring Specialized Sampling Procedures—None.
Use of Periodic (Less Frequent Than Annual) Data Collection Cycles to Reduce Burden—Less frequent than annual collection is not proposed.
3. Methods to Maximize Response Rates and to Deal With Issues of Nonresponse
NYGC
maintains a database containing the names, addresses, and telephone
numbers of representatives of law enforcement agencies who have
furnished information on gang activity in previous National Youth
Gang Surveys. The survey will be sent directly to these contacts.
Respondents will be encouraged to return the completed survey
instrument by fax or Internet. Follow-up telephone calls will be
initiated to all nonrespondents
30 days after the initial
mailing of the survey instruments. These nonrespondents will be
encouraged to complete the form and return it by fax, complete it on
the Internet, or answer the survey questions during the telephone
interview. Based on the computations above, the proposed data
collection and sampling strategies should produce reliable data that
can be generalized to the universe studied.
4. Tests of Procedures
The survey will be tested locally by NYGC. Fewer than ten test respondents will be used.
5a. Statistical Consultants
Arlen Egley, Jr., Ph.D., National Youth Gang Center, (850) 385-0600
G. David Curry, Ph.D., University of Missouri at St. Louis,
(314) 516-5042Cheryl L. Maxson, Ph.D., University of California,
(949) 824-5150James C. Howell, Ph.D., National Youth Gang Center, (910) 235-3708
Malcolm W. Klein, Ph.D., University of Southern California,
(213) 740-4255Dennis Mondoro, Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention, (202) 514-3913
Terrance J. Taylor, Ph.D., University of Missouri at St. Louis,
(314) 516-4387Charles M. Katz, Ph.D., Arizona State University, (602) 543-6618
b. Agency Contact:
Dennis Mondoro
Strategic Community Development Office
Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention
U.S. Department of Justice
810 Seventh Street, NW
Washington, DC 20531
(202) 514-3913
c. Contractor Contact:
Mr. John P. Moore
National Youth Gang Center
Institute for Intergovernmental Research
Post Office Box 12729
Tallahassee, FL 32317
(850) 385-0600
OMB Submission—2009 National Youth Gang Survey Page
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | Paperwork Reduction Act Submission |
| Author | Christina O'Donnell |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-02-03 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy