9610--18 Supporting Statements 20091001 (2)_Sec B
9610--18 Supporting Statements 20091001 (2)_Sec B.docx
2008 National Survey on Reported and Unreported Motor Vehicle Crashes
OMB: 2127-0663
Survey of Reported and Unreported Motor Vehicle Crashes
Supporting Statement for Information Collection Request
Prepared for:
Jonathan Walker
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
Prepared By:
Morris Davis and Company
1520
Locust Street, 3rd Floor
Philadelphia, PA 19102
Abt SRBI
8403 Colesville Road, Ste 820
Silver Spring, MD 20910
January 29, 2009
Changes By:
Jonathan Walker
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
September 30, 2009
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SUPPORTING STATEMENT
B. COLLECTION OF INFORMATION EMPLOYING STATISTICAL METHODS
1. Describe the potential respondent universe and any sampling or other respondent
selection method to be used................................................................................................ 9
2. Describe the procedures for the collection of information............................................... 10
3. Describe methods to maximize response rates and to deal with issues of
non-response..................................................................................................................... 14
4. Describe any tests of procedures or methods to be undertaken........................................ 15
5. Provide the name and telephone number of individuals consulted on statistical
aspects of the design......................................................................................................... 16
B. Collections of Information Employing Statistical Methods
The proposed study will employ statistical methods to analyze the information collected from respondents. The following sections describe the procedures for respondent sampling and data tabulation.
B.1. Describe the potential respondent universe and any sampling or other respondent selection method to be used.
The potential respondent universe for this survey consists of all non-institutionalized persons residing in the United States who are 16 years and older. This population age-eligible to drive motor vehicles. Reported and unreported crashes will include both drivers and passengers of these crashes.
A total of 2,000 interviews are planned for this universe of more than 200 million persons. A single questionnaire will be administered to all respondents. We will conduct 1,800 of these interviews by contacting the respondent on a landline telephone. We will conduct the remaining 200 of these interviews by contacting the respondent on a cell phone. These respondents will be screened to ensure that they live in a cell phone-only household. This will enable us to obtain a reasonably representative sample of the target population that will require only a limited degree of post-stratification weighting.
Random Digit Dialing (RDD) will be used to select and screen the landline sample. The cell phone sample will be randomly generated from 1,000 series blocks that are dedicated to providing cellular service and dialed manually. Given that an automobile crash is a relatively rare event, we expect the screening effort necessary to identify individuals who have experienced crashes in the last 12 months to be considerable.
There are no up-to-date statistics regarding the breakdown of who is involved in unreported crashes (hence the impetus for the survey). However, from Traffic Safety Facts 2006, there were 202,810,428 registered drivers and 10,584,000 police-reported crashes in that year. If we assume a 1:1 ratio of unreported crashes to reported crashes, as was found in a study by Greenblatt et al. in 1981,1 we need to add another 10,584,000 crashes to the reported crashes. The total yearly crashes for both reported and unreported crashes therefore is 21,168,000 crashes. Dividing the total crashes by the number of registered drivers (21,168,000/202,810,428) we find that approximately 10% of the drivers experienced a crash in 2006. A study by Dingus in 20062 suggests unreported crashes may have increased from an equal number of crashes to reported crashes (1:1 ratio), to as much as four times the level of reported crashes (4:1 ratio). If this is correct, then our estimate of 10% of drivers having an accident in a year is a conservatively low estimate. The result is that a sample size of 20,000 drivers should be more than adequate to produce 2,000 completed interviews. Table 2 presents this summary.
Table 2. Sample Size Estimate Assuming a 1:1 Ratio of Reported to Unreported Crashes |
|||
Category |
Population |
Percentage |
Sample |
Drivers |
202,810,428 |
100% |
20,000 |
Reported Crash in past year |
10,584,000 |
5% |
1,000 |
Unreported Crash in past year |
10,584,000 |
5% |
1,000 |
Total Crashes in past year |
21,168,000 |
10% |
2,000 |
We intend to determine estimates of underreporting by comparing the number of reported crashes to unreported crashes. This ratio then will be compared to the ratios found in the Greenblatt (1:1) and Dingus (4:1) studies.
In Table 3 we show the Census Bureau Expected Population and Sample Distribution by age for the 2,000 respondent sample. Although we expect our final sample to include a higher proportion of younger drivers relative to the US population, we are unable to make an educated guess about the age proportions of the final sample.
TABLE 3
EXPECTED POPULATION AND SAMPLE DISTRIBUTION BY AGE
BASED ON June 1, 2008 CENSUS BUREAU ESTIMATES
|
Population |
Sample |
|
Age Category |
Target Population (in thousands) |
Percentage of Target Population |
Population-Based Distribution of Sample |
Total (16+) |
233,627 |
|
2,000 |
16-24 |
37,476 |
16.04% |
321 |
25-34 |
39,960 |
17.10% |
342 |
35-44 |
41,735 |
17.86% |
357 |
45-64 |
77,397 |
33.13% |
663 |
65+ |
37,060 |
15.86% |
317 |
U.S. Bureau of the Census, Population Estimates, Age Category Estimates, 6/01/2008 |
|||
The response rate target for this survey will be 50% based on the subject matter, interview length, callback procedures and government sponsorship. In order to maximize response rates the strategy will focus on more limited sample release to reduce cases in callback status. The methods proposed to maximize response rates on this survey are described in Section B.3.
Cell phones are a growing problem for telephone surveys. The coverage error that can result from excluding cell phones from the sample will introduce bias into the estimates. In 2008 more than 1 out of 6 American households (17.5%) were cell phone only, did not have a landline, and could not be reached via traditional RDD survey methods. An additional 13.3% of American households were cell phone mostly meaning the residents received all or almost all of their calls on their cell phone, despite the fact that there is a landline in the household (Blumberg, 20083). Many studies have started to include cell phones in their sample in order to account for the cell only households and cell mostly households. However, the expense to include cell phone only/mostly households in the sample is as much as 2.5 times greater per case, than those of traditional landline households (Keeter, 20074).
The bias that results from not including cell phone only households in RDD studies is related to the differences between the households with landlines and those that are cell phone only. Cell phone only households are much more likely to be younger, renters, minority, and lower income.
Another concern for the current data collection is the social desirability effect. Simply stated, the social desirability effect warns that when asking about circumstances that could potentially be incriminating or unethical in nature the respondent may not report past behavior truthfully in order to conform to social expectations. This could be an issue for those who were in a crash and did not report it to the police even though they are supposed to do so. We do expect respondents to underreport such behavior – such as leaving the scene of an accident without notifying the police. However, benchmark data exist which will help us determine the extent to which underreporting has taken place. The initial Unreported Crashes Survey conducted by NHTSA (Greenblatt, 1981), gives us an indication that people are willing to report such behavior, although this tells us nothing regarding the rate of underreporting. More importantly, NHTSA conducted an in-vehicle study (Dingus, 2006) which provides recent, and accurate, estimates of unreported crashes. The estimates from the survey will be compared to both studies in order to generate a data-based estimate of the social desirability effect.
B.2. Describe the procedures for the collection of information.
The most important elements of the study design of the Survey of Reported and Unreported Motor Vehicle Crashes are:
Survey population is defined as total non-institutionalized population, age 16 and older, of the United States residing in households having telephones.
Survey will be conducted by telephone, using computer-assisted telephone interviewing.
There will be one questionnaire delivered to every respondent. This questionnaire will take approximately 15 minutes to complete.
One eligible adult (16 years or older) will be selected in each sampled household, using the “most recent/next birthday” for systematic selection within household.
A total sample size of 2,000 persons ages 16 and older will be interviewed (1,800 on a landline telephone and 200 on a cell phone) using the questionnaire. The questionnaire focuses on whether or not the respondent was ever involved in an unreported crash, and the details of the incident.
The survey will include a Spanish language version of the questionnaires used by bilingual interviewers to minimize language barriers.
Professional interviewers who are experienced in conducting interviews will carry out the interviews, using computer assisted telephone interviewing.
The completed data sets will be weighted to correct for disproportionate sampling and non-response bias.
B.2.a. Sampling Frame
The purpose of this study is to generate accurate population estimates of the non-institutionalized population age 16 and older currently living in the United States and the District of Columbia. Traditionally this would require the use of a sample of randomly generated landline telephone numbers (RDD). However, increasing numbers of households have been dropping their landline in favor of exclusively using their cell phone. The result is the lowering of covering in the RDD sample. Because of this, we will now incorporate randomly generated cell phone numbers in the study.
An efficient method of constructing a national area probability landline survey involves multi-stage geographic sampling. The sample is first stratified by geographic region, with sample allocation proportionate to population distribution. The second stage involves random selection of residential telephone exchanges within the geographic strata. The third stage involves random digit dialing (RDD) selection of a telephone number within selected exchanges for household contact. The fourth stage requires the random selection of one age-eligible respondent within each household as the designated respondent.
Cellular samples are generated randomly within 1,000 series blocks that are dedicated to providing cellular service (these blocks are excluded from the RDD sample frames). Unlike landline RDD sample, cellular RDD sample is generated with the absence of working bank information. This is because there is no white page listings of cell phones as there is for listed landlines. Given this fact and the extreme mobility of cellular telephone numbers, it is necessary to limit cellular sample generation to area code and state geographies.
The specific steps that will be used to construct the sample are outlined in detail below.
B.2.b. National Population Sample Design
National samples of assigned telephone banks will be randomly selected from the active landline and cell phone telephone exchanges within the United States. Phone numbers in the United States are 10 digits long - where the first three numbers are the area code, the next three are the exchange, and the last four numbers are the number within the exchange. The first two digits of the four-digit number define a cluster, with each cluster containing 100 numbers or a “100-bank” (the last two digits). Selection will be made from those 100-banks containing residential listings for the landline survey and from the 1,000 series blocks for the cell phone survey.
In the second sampling stage, a two-digit number is randomly generated for each 100-bank with one or more listed residential number (landline survey) or 1,000 series block (cell phone survey) selected in the first stage. This second stage sampling technique is known as random digit dialing (RDD). Every telephone number within the 100-block has an equal probability of selection, regardless of whether it is listed or unlisted. The use of RDD sampling eliminates the otherwise serious problem of unlisted telephone numbers. The use of cell phone sampling eliminates the undercoverage in the landline frame due to the cell phone only households.
Landline RDD sample is typically put through a purging process to eliminate non-working and business numbers. These purging processes typically utilize an automated dialer. Cell phone samples will not be purged of non-working or business numbers. There are two reasons for this: there is no database of business cell phone numbers for purging and it is illegal to use an automated dialer to call cell phone numbers. The cell phone sample will be manually dialed during the fielding period of the study due to this law.
B.2.c. Selection of Respondent Within Households (Landline Survey)
The sample construction described above yields a population-based, random digit dialing sample of telephone numbers. The systematic dialing of those numbers to obtain a residential contact should yield a random sample of telephone households. Next, a random selection procedure will be used to select one designated respondent for each household sampled. The “most recent/next birthday method” will be used for within household selection among multiple eligible respondents. Salmon and Nichols (19835) proposed the birthday selection method as a less obtrusive method of selection than the traditional grid selections of Kish, et al. In theory, birthday selection methods represent true random selection (Lavrakas, 19876). Empirical studies indicate that the birthday method produces shorter interviews with higher response rates than grid selection (Tarnai, Rosa and Scott, 19877).
Upon contacting the household, interviewers will briefly state the purpose of their call (including noting the respondents will remain anonymous), and then request to speak to the person in the household within the eligible age range who has had the most recent birthday, or will have the next birthday. The CATI system will randomly select whether the interviewer asks for the most recent or next birthday. If the person who answered the phone is the selected respondent, then the interviewer will proceed with the interview. If the selected respondent is someone else who then comes to the phone, then the interviewer will again introduce the survey and proceed with the interview. If the selected respondent is not available, then the interviewer will arrange a callback.
B.2.d. Precision of Sample Estimates
The objective of the sampling procedures described above is to produce a random sample of the target population. A random sample shares the same properties and characteristics of the total population from which it is drawn, subject to a certain level of sampling error. This means that with a properly drawn sample one can make statements about the properties and characteristics of the total population within certain specified limits of certainty and sampling variability.
The 95% confidence interval for a sample estimate of a population proportion, using simple random sampling without replacement, is calculated by the following formulas:
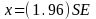
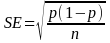
Where:
x = half-width of the confidence interval
SE = the standard error of the sample estimate for a population proportion
p = the proportion of the sample displaying a certain characteristic or attribute
n = the size of the sample
Using this formula, the maximum expected sampling error at the 95% confidence level (i.e., in 95 out of 100 repeated samples) for a total sample of 2,000 is + 2.2 percentage points. It should be noted that the maximum sampling error is based upon the conservative estimate that
p = 0.5.
The total sample size for the survey is large enough to permit robust estimates for sub-samples of particular interest to this study, such as reported vs unreported crashes, injury severity, age, gender and income. Subsamples will consist of at least 384 respondents to allow for a + 5 sampling error. Respondents will be grouped into categories based on these characteristics and cell size. The analysis will ensure that cell size is large enough for these subsamples to produce reliable estimates.
B.2.e Data Collection
Data collection for the National Telephone Survey of Reported and Unreported Motor Vehicle Crashes will be conducted from the telephone call centers of organizations experienced in conducting large-scale national surveys. The contractor will administer the survey using computer-assisted telephone interviewing (CATI), and will have sufficient numbers of CATI stations to conduct large numbers of interviews in short periods of time.
All interviewers on the project will have been previously trained in effective interviewing techniques as a condition of their employment. The contractor will develop an interview manual for this survey, and conduct a training session specific to this study with all interviewers prior to their conducting any interviews.
Interviewing will be conducted on a schedule designed to facilitate successful contact with targeted households (concentrating on weekends and weekday evenings). Interviewers will make up to fifteen call attempts to ring no answer numbers before the number is classified as a permanent no answer. These call attempts shall be made at different times, on different days over a number of weeks, according to a standard call attempt strategy. However, the fifteen-call attempt protocol shall only apply to telephone numbers where nobody picks up the telephone. If someone picks up the phone but terminates the contact before in-house selection of a subject can be made, then the Contractor shall apply an alternative protocol of five additional contact attempts designed not to repeatedly call and annoy the prospective household participant.
The Contractor will implement a plan for gaining participation from persons in households where telephone contact is made with an answering machine. The Contractor will leave a message on the machine encouraging survey participation and providing information that the household member can use to verify the legitimacy of the survey and contact the Contractor. The Contractor will set up a toll free number that the prospective survey participant can call. In addition, NHTSA shall place a statement on its Web site that the prospective survey participant can access by computer to verify the legitimacy of the survey. The Contractor may also note these sources of verification to persons directly contacted on the phone if that would be deemed helpful in getting their participation.
For landline respondents when the household is reached, the interviewer will use a systematic procedure to randomly select one respondent from the household. If the respondent is reached but an interview at that time is inconvenient or inappropriate, the interviewer will set up an appointment with the respondent. If contact is made with the household, but not the designated respondent, the interviewer will probe for an appropriate callback time to set up an appointment. Once a household is reached, a minimum of five additional contact attempts will be made to identify and interview the designated respondents. A total of 15 contact attempts represent a tradeoff between the agency goals of achieving a high response rate and minimizing public complaints about harassment. If contact is made with the eligible respondent, but the respondent refuses to participate, then the interviewer will record information for use in refusal conversion to be conducted at a later time (see Section B.3.).
For cell phone respondents the interviewer will follow a special protocol. This protocol includes:
Hand dialing the number. Due to most state regulations, auto-dialers are not permitted for the conduct of the cell phone sample.
Using a cell phone screener which asks the respondent if they are in a safe place to conduct the interview (i.e. not driving while holding the phone, out to dinner, or socializing in bar, etc).
Offering to schedule a time to callback later, if they are not in a safe place to conduct the interview.
Offering a toll-free number which the respondent can call to complete the interview.
Asking for a landline number they can be reached at, if they would prefer not to use their cell phone to speak with our interviewers. If the respondent does use their cell phone to complete the screener questions, we will pay the respondent a five dollar incentive.
The cell phone procedures are necessary to ensure that the respondent is comfortable speaking with us on his/her cell phone and to follow the regulations regarding calling cell phones for research purposes.
If the interviewer encounters a language barrier, either with the person answering the phone or with the designated respondent, the interviewer will thank the person and terminate the call. If the case is designated as Spanish language, it will be turned over to a Spanish-speaking interviewer.
All interviewers on the study will be supervised in a manner designed to maintain high quality control. One component of this supervision will entail periodic monitoring of interviewers while they are working. Through computer and phone technology, supervisors can silently monitor an interviewer’s work without the awareness of either the interviewer or respondent. Second, supervisors will check interviewers’ completed work for accuracy and completeness.
B.2.f. Sample Weighting
The Contractor will carry out a multi-stage sequential process of weighting. The first stage weight will correct for known selection biases in the sampling procedures. Since random digit dialing gives households with more than one telephone number an unequal likelihood of selection in the landline sample, the first stage weight will be equal to the inverse of the number of different telephone numbers in the household. The second stage weight will correct for unequal probability of selection within sampled households in the landline sample. Since a respondent’s probability for selection within a household is inverse to the number of eligible adults in the household, the second stage weight equals the number of eligible respondents within the household. No such weights are required within the cell phone only sample. The next step corrects the study design for disproportionate selection of population subsets in the sample design. The third stage weight corrects the achieved sample for disproportionate sampling by dividing the expected population distribution, based on Census projections or estimates, by the (weighted) achieved sample distribution on the stratification variables. Finally, we must weight the landline and cell phone only respondents to their estimated population sizes based on the most recent National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) estimates. These steps correct the achieved sample for known biases in sample selection.
B.2.g. Statistical Analysis
The sample estimates from which population projections are derived initially involve univariate frequencies of survey responses. The frequency of all responses to each question will be tallied. Where appropriate, measures of central tendency will be calculated, such as means and medians. NHTSA personnel will use SAS© to test for significant differences between the previous telephone survey and the present one, and to test for significant differences among the demographic variables listed below. Given that many such tests will be made, differences will not be considered significant unless they exceed the 99% confidence level.
It is important for NHTSA’s strategic planning needs that the status of awareness, knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors related to traffic safety be determined for identifiable subgroups of the total respondent sample. Thus, questionnaire items will be cross-tabulated with key demographic variables including:
o Age;
o Sex;
o Race/Ethnicity;
o Education;
These cross-tabulations will be scanned to determine the most important bivariate relationships. This data will be extracted, and tables suitable for survey reports and research notes will be constructed. These tables will present response distributions for respondents as a whole (total) and within specific subgroups of interest.
Where appropriate, multivariate analyses will be conducted to assess the predictors of key dependent measures within the survey.
B.3. Describe methods to maximize response rates and to deal with issues of non-response.
In order to attain the highest possible response rate, an interviewing strategy with the following major components will be followed. The initial contact script has been carefully developed and refined to be persuasive and appealing to the sample. Only thoroughly trained and experienced interviewers, highly motivated and carefully monitored, will conduct the interviewing. Interviewers will be trained on how to overcome initial reluctance, lack of interest or hostility during the contact phase of the interview. The interviewing corps will include Spanish-speaking interviewers to ensure that Spanish language is not a barrier to survey participation. The Contractor will make fifteen call attempts to ring-no-answer numbers, and shall leave an approved message on answering machines according to study protocol (see Section B.2.f.).
The CATI program will record all refusals and interview terminations in a permanent file, including the nature, reason, time, and the interviewer. This information will be reviewed on an ongoing basis to identify any problems with the contact script, interviewing procedures, questionnaire items, etc. Also, the refusal rate by interviewer will be closely monitored. Using these analyses, a “Conversion Script” will be developed. This script will provide interviewers with responses to the more common reasons given by persons for not wanting to participate in the survey. The responses are designed to allay concerns or problems expressed by the telephone contacts.
The contractor will implement a refusal conversion plan in which each person selected for the sample who refuses to participate will be re-contacted by the contractor approximately one-to-two weeks following the refusal. The contractor will use the Conversion Script in an attempt to convince the individual to reconsider and participate in the survey. Only the most experienced and skilled interviewers will conduct the refusal conversions. Exceptions to refusal conversion will be allowed on an individual basis if for some reason the refusal conversion effort is deemed inappropriate.
There will be maintenance and regular review of field outcome data in the sample reporting file, derived from both the sample control and CATI files, so that patterns and problems in both response rate and production rates can be detected and analyzed. Meetings will be held with the interviewing and field supervisory staff and the study management staff to discuss problems with contact and interviewing procedures and to share methods of successful persuasion and conversion.
The procedures described above resulted in a response rate for the cross-sectional sample of between 45% and 50% for past NHTSA surveys. The contractor will release less sample initially for the current survey and apply the 15 contact and callback strategy to improve response rates for this survey. The sampling methods described above will yield reliable data that can be generalized to the universe studied.
Non-Response Analysis
A comparison of the characteristics of the completed and non-completed cases from the random digit dialing sample will be conducted to determine whether there is any evidence of significant non-response bias in the completed sample. There are three points at which sample characteristics are collected in the course of the telephone survey: prior to household contact; at respondent selection for the survey; and after beginning the interview. Analysis will be conducted with the data available for respondents and non-respondents at each of these points.
The drawn sample of random digit dialing numbers that are released to telephone interviewers for contact attempts can be coded for certain contextual characteristics. The “hundreds bank” from which the RDD number is drawn (e.g., 301-608-38xx) is classified geographically according to the unit from which the majority of listed numbers in that bank are located. This permits us to classify all of the numbers drawn by Census region, Census district and urbanicity (central city, metro remainder, and non-metropolitan area). It also permits us to classify those numbers by percent African-American and Hispanic based on Census data. A comparison of the characteristics of all dialed numbers in which an interview had not been completed with those that had been completed can be done with these variables.
Once contact is achieved with a household, one adult is selected in each household as the designated respondent. If there is more than one eligible respondent per household, then the individual with the most recent/next birthday is selected. The age and gender of this individual is obtained so that they can be identified if callbacks are necessary. This information permits additional comparisons of any differences in the age and gender of respondents in the completed sample and those in the non-completed sample after household contact and respondent selection had been made.
Finally, we expect there will be a small percentage (~2.5%) of terminated interviews based on a past survey we conducted for NHTSA (MVOSS 20038) throughout the course of data collection. A terminated interview is one in which the designated respondent begins the interview (answers the first question) but refuses to complete the interview at some point after the first question. Some key motor vehicle and driving characteristics are collected at the very beginning of the interview, including frequency of driving, type of vehicle and seat belt use. Difference in driver characteristics can be analyzed at this third stage between those who terminate the interview and those who complete the interview.
This three-step process of analyzing the characteristics of respondents and non-respondents to the survey should identify whether there is any evidence of significant non-response bias in the most likely areas: region, size of place, minority communities, age, gender, and driving characteristics. This analysis will suggest whether any weighting or other statistical adjustment needs to be made to correct for non-response bias in the completed sample.
B.4. Describe any tests of procedures or methods to be undertaken.
A pretest will be conducted among 10 people, to ensure the CATI script is functioning properly and the data is being collected accurately. The pretest will consist of the entire survey process, from sample management to tabulation of results. Any problems encountered during the pretest of the questionnaire will be resolved before the survey is put into the field.
B.5. Provide the name and telephone number of individuals consulted on statistical aspects of the design.
The following individuals have reviewed technical and statistical aspects of procedures that will be used to conduct the Unreported Crashes Survey:
John Boyle, Ph.D.
Executive Vice President
Abt SRBI, Inc.
8403 Colesville Road, Suite 820
Silver Spring, MD 20910
(301) 608-3883
Paul Schroeder
Senior Analyst
Abt SRBI, Inc.
8403 Colesville Road, Suite 820
Silver Spring, MD 20910
(301) 608-3883
Thomas Sexton, Ph.D.
Statistician,
M. Davis & Co. Inc.,
Stony Brook University
317 Harriman Hall
College of Business
Stony Brook, NY 11794
(631) 632-7181 (office)
1 Greenblatt, J, Merrin, M.B., Morganstein, D., Schwartz, S. National Accident Sampling System Nonreported Accident Survey. NHTSA, November 1981, Report No. DOT HS-806 198.
2 Dingus, T.A., Klauer, S.G., Neale, V.L., Petersen, A., Lee, S.E., Sudweeks, J., Perez, M.A., Hankey, J., Ramsey, D., Gupta, S., Bucher, C., Doerzaph, Z.R., Jermeland, J., and Knipling, R.R. The 100-Car Naturalistic Driving Study, Phase II – Results of the 100-Car Field Experiment. NHTSA, April 2006, Report No. DOT HS 810593.
3 Blumberg SJ, Luke JV. Wireless substi-tution: Early release of estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, January-June 2008. National Center for Health Statistics. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis.htm. December 17, 2008.
4 Keeter, S. (2006, May 15). The cell phone challenge to survey research. Retrieved from http://people-press.org/reports/display.php3?ReportID=276
5 Salmon, C. and Nichols, J. The Next-Birthday Method of Respondent Selection. Public Opinion Quarterly, 1983, Vol. 47, pp. 270-276.
6 Lavrakas, P. Telephone Survey Methods: Sampling, Selection and Supervision. Beverly Hills: Sage Publications, 1987.
7 Tarnai, J., Rosa, E. and Scott, L. An Empirical Comparison of the Kish and the Most Recent Birthday Method for Selecting a Random Household Respondent in Telephone Surveys. Presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Association for Public Opinion Research. Hershey, PA, 1987.
8 Boyle, John and Patricia Vanderwolf. 2003 Motor Vehicle Occupant Safety Survey. September, 2003.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | OMB Package |
| Subject | OMB Package |
| Author | MDavis and Co (ABlock??) |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-02-02 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy