SPF-SIGOMBSupportingStatement A-5.2.11
SPF-SIGOMBSupportingStatement A-5.2.11.doc
Strategic Prevention Framework State Incentive Grant (SPF SIG) Program
OMB: 0930-0279
Strategic Prevention Framework State Incentive Grant (SPF SIG) Program
Supporting Statement
Part A. Justification
A1. Circumstances Necessitating Data Collection
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration’s (SAMHSA) Center for Substance Abuse Prevention (CSAP) requests OMB approval for revision to the protocol for the ongoing cross-site evaluation for the Strategic Prevention Framework State Incentive Grant (SPF SIG) (OMB No. 0930-0279) which expires on 11/30/2012. This revision includes three parts:
Continuation of the use of the previously approved two-part Community Level Instrument (CLI Parts I and II) for Cohorts I and II and the use of an instrument to assess sustainability of Cohort 1 and 2 grantee infrastructure and implementation accomplishments which is a modification of instruments used in an earlier phase of the evaluation
Addition of a new Cohort of SPF SIG grantees (Cohort V) to the SPF SIG cross-site evaluation. All instruments that will be used with Cohort V have already received OMB approval for use with Cohorts III and IV (OMB No. 0930-0279).
Recalculation of burden numbers for Cohort IV to replace estimates based on 20 grantees to reflect the 25 grantees actually funded.
CSAP is funding two cross-site evaluations of the Strategic Prevention Framework State Incentive Grant (SPF SIG), one focusing on Cohorts I and II and the other focusing on Cohorts III, IV, and V. Collectively, these evaluations of the SPF SIG program provide an important opportunity for the field of prevention.
Every attempt has been made to make the evaluation for Cohorts III, IV, and V comparable to Cohorts I and II. However, resource constraints for the Cohorts III, IV, and V evaluation have necessitated some streamlining of the original evaluation design. In addition, because the ultimate goal is to fund all eligible jurisdictions, there are no control groups at the grantee level for Cohorts III, IV, and V. The primary evaluation objective is to determine the impact of SPF SIG on the reduction of substance abuse related problems, on building state prevention capacity and infrastructure, and preventing the onset and reducing the progression of substance abuse, as measured by the SAMHSA National Outcomes Measures (NOMs). Data collected at the grantee, community, and participant levels will provide information about process and system outcomes at the grantee and community levels as well as context for analyzing population-level and participant-level outcome measures. The Community-Level Part I and Part II Instrument used by Cohorts I and II (previously approved), the Sustainability Interview for use with grantees during Phase II of the Cohort 1 and 2 evaluation, and the addition of an additional Cohort (Cohort V) in the previously OMB approved design for Cohorts III and IV are included in this OMB review package and are the main focus of this request.
A1a. The SPF SIG Program
The SPF SIG is a major SAMHSA Infrastructure Grant program that supports an array of activities to help states and communities build a solid foundation for delivering and sustaining effective substance abuse prevention services. The SPF SIG is implemented by CSAP and is designed to: (1) prevent the onset and reduce the progression of substance abuse, including childhood and underage drinking; (2) reduce substance abuse-related problems in communities; and (3) build prevention capacity and infrastructure at the state/territory and community levels. CSAP provides funding to states, Pacific jurisdictions, and tribal entities to implement the five steps of the strategic prevention framework (SPF), which are:
Step 1: Profile population needs, resources, and readiness to address the problems and gaps in service delivery;
Step 2: Mobilize and/or build capacity to address needs;
Step 3: Develop a comprehensive strategic plan;
Step 4: Implement evidence-based prevention programs, policies, practices and infrastructure development activities; and
Step 5: Monitor process, evaluate effectiveness, sustain effective programs/activities, and improve or replace those that fail.
In FY 2004, CSAP funded Cohort I, which consisted of 21 states and territories, for up to five years to implement the SPF SIG program. Cohort II was funded in FY 2005 and includes five additional states and territories. Cohort III, which was funded by CSAP in FY 2006, includes 10 states, 1 Pacific jurisdiction, and five tribal entities. Cohort IV, which includes 25 grantees, was funded in 2009. An additional 10 grantees (Cohort V) were funded in 2010. For the purposes of this document the word grantee will refer to all funded states, Pacific jurisdictions, and tribal territories.
A1b. The Cross-site Evaluations
CSAP has funded two cross-site evaluations of SPF SIG, one focused on Cohorts I and II and the other focused on Cohorts III, IV, and V. The SPF SIG is the first broad-based, data-driven effort that simultaneously attempts to influence both strategic planning and prevention systems at the jurisdiction and community levels, as well as implement evidence-based prevention interventions in communities. These evaluations will help determine whether the SPF SIG has met these expectations and, if so, under what conditions.
A1b1. Cohorts I and II Cross-site Evaluation
The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) is providing support to CSAP to evaluate the impact of the SPF SIG project for Cohorts I and II. Since funding for the evaluation began in September 2004 and OMB clearance was received in 2006, this evaluation is already in process. Information on the overall evaluation is presented below as context for understanding SAMHSA’s request to apply the existing approved timeline of 11/30/12 to the follow-up grantee-level data collection.
The Cohorts I and II cross-site evaluation team is currently implementing a multi-method quasi-experimental evaluation of the SPF SIG project at national, state, and community levels. A major objective of the SPF SIG evaluation is to determine the impact of SPF SIG on the SAMHSA National Outcome Measures (NOMs), and to assess the impact of the program as a whole. The data from the CLI (Parts I and II) will be used to interpret the impact of the SPF SIG on all of the NOMs domains related to prevention (i.e., Abstinence, Education/Employment, Crime and Criminal Justice, Access/Capacity, Retention, Cost Efficiency and Use of Evidence-based Practices). The evaluation is also measuring: the effect of establishing and sustaining infrastructure at the state and community-levels to allow for data-based decision-making; the implementation of the SPF; and environmental factors that affect substance abuse.
Both quantitative and qualitative data are being gathered as a part of the SPF SIG cross-site evaluation for Cohorts I and II. Specifically, data are being collected from the 26 states and territories receiving grants in 2004 (Cohort I sites) and 2005 (Cohort II sites) and as many as 32 non-Cohort I and II grantee states and territories that will serve as a comparison group. Data sources include: (1) grantee Epidemiology and Outcome Workgroups (EOW) and communities, (2) state-level evaluations, (3) existing national- and state-level population-based indicators, (4) standardized data collected by the evaluators on the implementation of the SPF, and (5) archival sources such as grant applications and State Prevention Advancement and Support Program (SPAS) reports.
The timing of the Cohort I and II evaluation, which began concurrently with the funding of the program, allowed the team to gather meaningful baseline data. However, since the majority of the Cohort I grantees are expected to receive one year no cost extensions and the Cohort II grantees will not complete their original period of performance until FY 2010, a continuation of CLI and grantee data collection through FY 2012 will be required to allow the team to observe community-level accomplishments within SPF SIG states throughout the full life-cycle of the program and the degree to which grantee accomplishments are sustained following expiration of the funding period.
A1b2. Cohorts III, IV, and V Cross-site Evaluation
The Cohort III, IV, and V cross-site evaluation team is implementing a multi-level evaluation design encompassing data collection at the grantee, community and participant levels. Data will be gathered from the 16 states, Pacific jurisdictions, and tribal territories receiving grants in FY 2006, 25 Cohort IV grantees funded in FY 2009, and 10 Cohort V grantees funded in FY2010.
In accordance with CSAP’s program goals to assess the impact of the SPF on measurable quantifiable outcomes, a major focus of the evaluation is on impact. However, the collection of process data at the grantee and community level is necessary for describing and documenting the activities undertaken as part of the SPF SIGs and supporting the results of project outcomes.
The evaluation design will rely heavily on the use of standardized self-report data collection instruments specifically designed to collect information on known mediators, moderators, and outcomes of interest to the evaluation plan. The data from the two revised grantee-level instruments and the revised community-level instrument will specifically measure: the effect of establishing and sustaining infrastructure at the grantee and community-levels to allow for data-based decision-making; the implementation of the Strategic Prevention Framework; and environmental factors that affect substance abuse. Recognizing that all grantees have prevention activities already underway, the collection of baseline data using these instruments will account for pre-SPF SIG activities in estimating the effects of SPF SIG-initiated activities. In addition, these data will be used to assess whether the steps of the framework were fully implemented as intended, thereby avoiding the attribution that any lack of effect is due to the SPF itself rather than failure to implement steps of the framework or implementing them improperly or incompletely. The process components of the SPF SIG evaluation will allow the evaluators to disentangle the effects of various project-related activities and help identify which program and policy elements are effective, under what conditions, and with which target populations.
A2. Purpose and Use of Information
The SPF SIG is a major investment by the Federal Government to improve state substance abuse prevention systems, and enhance the quality of prevention programs, primarily through the implementation of the SPF. The goal of this initiative is to provide states, Pacific jurisdictions, tribal entities and communities within them with the tools necessary to develop an effective prevention system with attention to the processes, directions, goals, expectations, and accountabilities necessary for functionality. SAMHSA/CSAP needs to collect information over the course of the grant period to monitor the progress of the SPF SIG initiative, particularly the implementation of evidence-based practices by communities. CSAP will use the findings from the cross-site evaluations to assess the implementation of the SPF, infrastructure development at the grantee and community level, and the outcomes achieved by this initiative. Without these data the impact of the SPF SIG will be unknown. Additionally, findings from these evaluations may assist CSAP policymakers and program developers as they design and implement future initiatives.
A2a. Cohorts I and II Cross-site Evaluation
The primary sources of data for the Cohorts I and II cross-site evaluation consist of instruments implemented at the grantee and community-levels.
A2a1. Grantee-Level Instruments
Phase I data collection, using the State Implementation and State Infrastructure Interview protocols, was completed within the initial period of OMB approval for Cohorts I and II. The Sustainability Interview Guide (Attachment A1a) will be conducted during Phase II of the evaluation in 2011 (Cohort I) and 2012 (Cohort II). The interview guide is adapted from the Phase I instruments and focuses on state-level prevention capacity and infrastructure in relation to the five steps of the SPF process: needs assessment, capacity building, strategic planning, implementation of evidence-based programs, policies, and practices (EBPPPs), and evaluation/monitoring. The interviews will be aimed at understanding the status of the prevention infrastructure at the time of the interview, whether the status has changed since the previous rounds of interviews (conducted in 2007 and 2009), and whether the SPF SIG had any influence on changes that might have occurred. The interview protocol includes a combination of open- and closed-ended questions, allowing us to quantify data on prevention capacity and infrastructure, and capture rich contextual information from the expert respondents. We will conduct one sustainability interview per State. The interviews will be conducted after each State’s SPF SIG funding period has expired to ensure that conditions assessed truly reflect the infrastructure of the State prevention system rather than operational features of the SPF SIG projects. Results will indicate the extent to which Phase I accomplishments related to the third goal of the SPF SIG project—to build prevention capacity and infrastructure at the state level—were sustained.
A2a2. Community-Level Instrument (CLI)
The CLI is a two part, web-based survey for capturing information about SPF SIG implementation at the community level (originally submitted as an addendum to OMB No. 0930-0279). Part I (Attachment A1b) of this instrument was developed to assess the progress of communities as they implement the Strategic Prevention Framework (SPF), and Part II (Attachment A1c) was developed to gather descriptive information about the specific interventions being implemented at the community level and the populations being served including the gender, age, race, ethnicity, and number of individuals in target populations. Each SPF SIG funded community will complete a separate Part II form for each intervention they implement.
The Community-level Instrument (Parts I and II) was designed to be administered two times a year (every six months) over the course of the SPF SIG initiative. The Cohorts I and II cross-site evaluation team plans to collect data for two more years once this request for a revision is approved. Data from this instrument will allow CSAP to assess the progress of the communities in their implementation of both the SPF and prevention-related interventions funded under the initiative. The data may also be used to assess obstacles to the implementation of the SPF and prevention-related interventions and facilitate mid-course corrections for communities experiencing implementation difficulties.
In keeping with the objectives of the Cohorts I and II cross-site evaluation, data from the CLI (Parts I and II) will also be used to assess the relationship between SPF implementation and changes in the NOMs. Additionally, data from this instrument will be used to assess the types of interventions being implemented in communities that receive SPF funds and changes in prevention infrastructure at the community level. Prevention infrastructure refers to the organizational characteristics of the system that delivers prevention services, including all procedures related to planning, data management systems, workforce development, intervention implementation, evaluation and monitoring, financial management, and sustainability. All of the data from this instrument will be used to determine what accounts for any variation in the NOMs. Without these data, it would be impossible to determine how the SPF SIG initiative had an impact on changes in the NOMs or which components of the SPF process were responsible for the observed changes.
A2b. Cohorts III, IV, and V Cross-site Evaluation
The primary sources of data for the Cohorts III, IV, and V cross-site evaluation include instruments implemented at the grantee- community- and participant-level. These instruments have been approved for Cohorts III and IV (OMB No. 0930-0279). The same instruments will be used for Cohort V.
A2b1. Grantee-Level Instruments (GLI)
Two web-based surveys, GLI Infrastructure Instrument and GLI Implementation Instrument, were developed for assessing grantee-level efforts and progress (Attachments B1a and B1b). Both instruments are modified versions of the face-to-face interviews used in the SPF SIG Cohort I and II Cross-Site Evaluation and have been approved already for use with Cohorts III and IV.
The original Cohort I and II interview protocols were developed to assess the implementation of the SPF process at the grantee-level and measure the development of jurisdiction-wide systems to manage prevention services. The interview protocols were developed by the Cohorts I and II cross-site evaluators using an iterative approach combining findings from the empirical literature, CSAP documents, lessons learned from the State Infrastructure Grant (SIG) program, and input from SPF-SIG grantee stakeholders solicited during interviews and via feedback on drafts. The Infrastructure protocol was used to assess Alcohol, Tobacco and other Drug (ATOD) prevention capacity within various domains at the grantee system level. It captured infrastructure development activities that occurred as a consequence of SPF but also those that resulted from other causes. The SPF Implementation protocol was more normative in character and directly assessed each grantee’s implementation of the 5 SPF steps and was limited to actions that have occurred as a direct result of the SPF including the implementation of the EOW. Both protocols were implemented via a telephone survey of key informants in each jurisdiction, conducted annually.
Because of resource constraints, the evaluation team modified the original instruments to eliminate evaluation staff involvement in the data collection effort and reduce the amount of time required to contextualize narrative data into categorized data. Every attempt was made to preserve the content areas to allow for the collection of comparable information across all cohorts. The original interview protocols were adapted into a survey format by replacing the majority of open-ended questions with forced-choice-response questions using data collected from the Cohort I and II grantees to indentify common themes and using the existing descriptive anchors developed by the Cohort I and II evaluation team when available. The original protocol was also shortened by eliminating questions that did not produce discriminating information.
Both the Grantee Infrastructure Instrument and the Grantee SPF Implementation Instrument will be completed by the grantees’ evaluators twice over the life of the SPF SIG award. The grantee’s evaluator is strongly encouraged to obtain input from others involved with the SPF SIG funded project. As part of this process, we encourage the local evaluator to complete and review responses with key individuals, such as the project coordinator, members of the EOW and SPF SIG Advisory Council, prevention agency staff, and others, as appropriate. Detailed administration Question by Question Guides have been developed to help improve the reliability and validity of the data collected thereby ensuring quality data with which to evaluate grantee-level progress.
GLI Infrastructure Instrument
The Infrastructure Instrument collects information with regard to the operations of the overall prevention system in the jurisdiction (i.e., the entire set of agencies, organizations, and persons that contribute to efforts to prevent substance abuse and related problems within the jurisdiction), not just the SPF SIG project. The GLI Infrastructure Instrument is designed to collect information about a specific snapshot in time. The purpose of the baseline data collection of the GLI Infrastructure Instrument is to gather information about how the overall prevention system was structured and functioned at the time the grant was awarded. A second collection of the GLI Infrastructure Instrument (follow-up data collection) will occur near the completion of the grant. The purpose of the follow-up data collection of the GLI Infrastructure Instrument is to gather information about how the overall prevention system was structured and functioned 5 years after the grant was awarded.
GLI Implementation Instrument
The GLI Implementation Instrument collects information specific to the execution of the 5 steps of the Strategic Prevention Framework in the jurisdiction. Data collected from the instrument will be used to evaluate the effectiveness of the Strategic Prevention Framework. Baseline data collection is designed to provide a retrospective picture of the period of time during the development and approval process of the strategic plan and is expected to be completed near the date of the approval of the strategic plan. A second collection of the GLI Implementation Instrument (follow-up data collection) will occur approximately 36 months after the approval of the strategic plan. The purpose of the follow-up data collection of the GLI Implementation Instrument is to gather information about ongoing activities related to the SPF planning steps.
A2b2. Community-Level Instrument (CLI)
The Community-Level Instrument is a two part, web-based instrument for capturing information about SPF SIG implementation at the community sub-recipient level (communities that receive SPF SIG funds from the Cohort III, IV, and V grantees) (Attachments B1c and B1d). The instrument is a modified version of the one in use in the SPF SIG Cohorts I and II Cross-Site Evaluation (OMB No. 0930-0279). Slight modifications were made to clarify question intent or refine response items to help improve data quality. Content areas were preserved to allow for the collection of comparable information across all 5 cohorts. Overall reductions in burden were accomplished by reorganizing the format of the original instrument, optimizing the use of skip patterns, and replacing the majority of open-ended questions with multiple-choice-response questions.
Part 1 of the instrument will gather information on the communities’ progress implementing the five SPF SIG steps and efforts taken to ensure cultural competency throughout the SPF SIG process. Sub-recipient communities receiving SPF SIG awards will be required to complete Part I of the instrument annually. Part II will capture data on the specific prevention intervention(s) implemented at the community level. A single prevention intervention may be comprised of a single strategy or a set of multiple strategies. A Part II instrument will be completed for each prevention intervention strategy implemented during the specified reporting period. Specific questions will be tailored to match the type of prevention intervention strategy implemented (e.g., Prevention Education, Community-based Processes, and Environmental). Information collected on each strategy will include date of implementation, numbers of groups and participants served, frequency of activities, and gender, age, race, and ethnicity of the population served/affected. Sub-recipient communities’ partners receiving SPF SIG awards will be required to update Part II of the instrument a minimum of every six months.
Data from this instrument will allow CSAP to assess the progress of the communities in their implementation of both the SPF and prevention-related interventions funded under the initiative. The data may also be used to assess obstacles to the implementation of the SPF and prevention-related interventions and facilitate mid-course corrections for communities experiencing implementation difficulties. Without these data, it would be impossible to determine how the SPF SIG initiative had an effect on changes in community- and participant-level NOMs or which components of the SPF process were responsible for the observed changes.
A2b3. Participant-Level Instrument
Participant-level change will be measured using CSAP NOMs Adult (participants aged 18 or older) and Youth (participants aged 12-17) Programs Instrument. Sub-recipient communities will have the opportunity to select relevant measures from the CSAP NOMs Adult and Youth Programs Instrument Forms based on site-specific targeted program outcomes and may voluntarily select additional outcome measures that are relevant to their own initiatives. Participant-level data will be collected from all participants in direct-service programs lasting 30 days or longer. The participant-level instruments will be administered to each participant at program entry, program exit, and six months after program exit to examine the effect of direct service evidence-based strategies on participant-level NOMS outcomes. Cohort III, IV, and V SPF SIG grantees have been included in the currently OMB approved umbrella NOMs application (OMB No. 0930-0230) covering the collection of participant-level NOMs by all SAMHSA/CSAP grantees. Therefore no additional burden for this evaluation activity is being imposed and clearance to conduct the activities is not being requested.
A3. Use of Information Technology
Both of the cross-site evaluations for Cohorts I and II and Cohorts III, IV, and V use information technology to minimize respondent burden.
A3a. Cohorts I and II Cross-site Evaluation
The CLI is a web-based survey and both Part I and Part II will continue to be completed online. The Cohorts I and II cross-site evaluation team has found that web-based administration of this instrument increases the efficiency of data submission and improves data quality. Additionally, completion of this instrument online reduces the burden on communities as some items are pre-filled based on information from the initial submission, and some items in Part II are pre-filled with information from Part I of the instrument.
Technology is also being used to facilitate communication and provide updates to SPF SIG personnel for Cohorts I and II. Through the SPF SIG web board, State evaluators, project directors, coordinators and other key staff have the opportunity to exchange valuable advice and receive announcements and clarifications from CSAP, other SPF SIG States, and the cross-site evaluation team. In addition to the web board, the cross-site evaluation team also sends electronic copies of the guidance and resource materials via e-mail and CD to SPF SIG States upon request. Data from the CLI (Parts I and II) are made available to State grantees and funded communities via the web for online analysis or by downloading for offline analysis. Sustainability Interview results will be shared with Cohort I and II grantees via the web board. Individual grantees will receive their results, along with averages for all grantees, upon request.
A3b. Cohorts III, IV, and V Cross-site Evaluation
The Grantee-Level Instruments (the SPF Implementation Instrument and the Infrastructure Instrument) and the Community-Level Instrument (Parts I and II) are web-based surveys and will be completed online through SAMHSA/CSAP’s Prevention Management and Reporting System (PMRTS). Web-based administration of the instruments will increase the efficiency of data submission and improve data quality. Additionally, completion of the instruments online will reduce the burden on grantees and communities, as some items will be pre-filled based on information from the initial submission. In the Community-Level Instrument, some items in Part II will be pre-filled with information from Part I of the instrument.
The Participant-Level Instrument will also be submitted via a web-based data entry tool. The data entry tool will also be available through SAMHSA/CSAP’s PMRTS. The NOMs-based data entry tools in PMRTS are designed to reflect the structure of the questionnaires. The system allows for the entry of data from completed questionnaires directly into the system. Grantees preferring to create their own data files have the option of uploading complete data files to PMRTS.
PMRTS is maintained by CSAP’s Data Information Technology Infrastructure Center (DITIC). Data entered online by grantees are periodically extracted by DITIC and transmitted in encrypted form to CSAP’s Data Analysis Coordination and Consolidation Center (DACCC). Grantees have two options for accessing the data they enter online. In the first option, grantees can download, in spreadsheet form, the raw data they have entered online as soon as it is submitted. Grantees can also access their data from the cleaned analysis files prepared by DACCC through the Cohort III, IV, and V SPF SIG web board.
Finally, technology will be used to facilitate communication and provide updates to SPF SIG personnel. Through a SPF SIG web board, grantee evaluators, project directors, coordinators and other key staff will have the opportunity to exchange valuable advice; find guidance and resource materials; and receive announcements and clarifications from CSAP, other SPF SIG grantees, and the cross-site evaluation team. In addition to the web board, the cross-site evaluation team will also send electronic copies of guidance and resource materials via email and CD to SPF SIG grantees upon request.
A4. Efforts to Identify Duplication
The information being collected by the cross-site evaluations for SPF SIG Cohorts I and II and Cohorts III, IV, and V is specific to the program and is not available elsewhere.
A5. Involvement of Small Entities
The primary entities for the Cohort I and II and the Cohort III, IV, and V studies are states, jurisdictions, and tribal territories and the communities funded within these entities. Community is broadly defined as the politically or geographically defined area or culturally or epidemiologically defined target population that the grantee chooses for any given prevention intervention. Because grantees and funded communities involve government or tribal agencies, universities, hospitals, or other large organizations, the evaluation will have no significant economic impact on small entities or small businesses.
A6. Consequences If Information Collected Less Frequently
The cross-site evaluation of the SPF SIG program provides an important opportunity for the field of prevention. Not conducting this data collection would significantly impede SAMHSA’s ability to assess the implementation of the SPF SIG process and measure improvements in: strategic planning; capacity and infrastructure development; data-driven decision making; and implementation of evidence-based prevention programs. Less frequent data collection would also impede CSAP’s ability to track changes in substance use and substance use related problems.
A6a. Cohorts I and II Cross-site Evaluation
The CLI instrument is currently being administered twice per year to each State and community that receives SPF funding over the course of three years. A continuation will ensure that comparable data are collected for the remainder of the SPF SIG program for Cohorts I and II.
Experience from the State Incentive Grant (SIG) project, the precursor to the SPF SIG program, as well as discussions with state-level evaluators, indicate that it is necessary to gather this information at least twice per year. Community-level activities change frequently within a year, and staff turnover at the community-level is common. Thus, to ensure the collection of valid and reliable data, data collection needs to occur twice per year. In addition, data from multiple time periods within a year is essential for monitoring the progress of states and communities as they implement the SPF, and for identifying communities that are experiencing obstacles to implementing the SPF. Without data from multiple time periods during the program, it will be impossible to determine whether implementation progress is related to changes in NOMs.
CSAP will conduct sustainability interviews with Cohort I grantees in 2011 and Cohort II grantees in 2012 to determine whether the accomplishments reported during Phase I endure after SPF SIG funding is no longer available.
A6b. Cohorts III, IV, and V Cross-site Evaluation
Information will be gathered retrospectively and prospectively to allow the team to gather meaningful baseline data and observation of the SPF SIG grantees and funded communities throughout the life-cycle of the program. The specific schedule of data collection is dependent upon the data being collected: The Grantee-Level Infrastructure and Implementation Instruments are completed twice over the grant period; the Community-Level Instrument (Part 1) is collected annually, the Community-Level Instrument (Part 2) is collected a minimum of every 6-months; and the Participant-Level Instrument will be collected as necessary dependent on how often participant level programs are run. Data from multiple time periods are essential for monitoring the progress of states and communities as they implement the SPF and deliver evidence-based strategies and for identifying communities that are experiencing obstacles and may need technical assistance.
A7. Consistency With Guidelines in 5 CFR 1320.5(d) (2)
The proposed data collection for the Cohorts I and II and Cohorts III, IV, and V cross-site evaluations fully complies with all guidelines of 5 CFR 1320.5.
A8. Consultation Outside the Agency
A8a. Federal Registry Announcement
The notice required in 5 CFR 1320.8(d) was published in the Federal Register on February 1, 2011 (Vol. 76, Page 5598). No comments were received.
A8b. Consultations Outside the Agency
A8b1. Cohorts I and II Cross-site Evaluation
The Cohorts I and II cross-site evaluation design, data analysis plan, the Sustainability Interview Guide and CLI (Parts I and II) received several rounds of review prior to the original OMB submission. These reviews were the result of ongoing collaboration with two SPF SIG advisory groups, State level evaluators, and program directors.
Consultation with Internal and External Advisory Groups. Members of the SPF SIG External Technical Advisory Group (ETAG) reviewed the cross-site evaluation design, analysis plan, the grantee-level instruments and CLI (Parts I and II). The ETAG includes a group of SPF SIG project directors and evaluators; evaluation and prevention experts; a representative from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA); and three SAMHSA staff not directly involved in the evaluation. Each ETAG member was carefully selected to ensure representation from the following: Federal and State government staff; local providers; representatives of the national prevention network system (CADCA); and members versed in specialized areas such as cultural competence, environmental strategies, fidelity and adaptation, evaluation design, and data analysis. Their feedback was incorporated into working and final drafts of the evaluation design, data analysis plan, the Sustainability Interview Guide, and CLI (Parts I and II). These reviewers’ names, titles, organizational affiliations, and current telephone numbers are provided in Attachment A2.
The Cohorts I and II cross-site evaluation team also seeks regular consultation with the SPF SIG Internal Workgroup. This group meets on a monthly basis at CSAP and consists primarily of CSAP and NIDA staff but also includes two SAMHSA staff outside of CSAP. As with the External Technical Advisory Group, the Internal Work Group provided feedback on the evaluation design and data analysis plan which was incorporated in working and final drafts. These reviewers’ names, titles, organizational affiliations, and current telephone numbers are also provided in Attachment A2.
Consultation with Respondents. The SPF SIG Cohorts I and II cross-site evaluation team was responsible for the development and pilot testing of the CLI (Parts I and II) and the Sustainability Interview Guide. This team frequently sought consultation with respondents in the development and refinement of this Instrument, as well as the pilot testing of this Instrument.
In the development of the CLI (Parts I and II) and the Sustainability Interview Guide, key prevention stakeholders, including State SPF SIG project directors and evaluators and other key SPF SIG staff, were consulted. They provided feedback on the content and format of the instrument’s domains, indicators, and measures to ensure that they had face validity and were not too burdensome for respondents to answer. In addition, all SPF SIG States were given the opportunity to review the instruments and provide comments and questions on their content and format.
The CLI (Parts I and II) was pilot tested in four States in January 2006. The individuals that participated in the pilot test represented the following types of organizations: mental health services, juvenile justice program services, substance abuse prevention services, youth-focused community organizations, and coalitions. Minor changes were made to the instrument as a result of the pilot testing; these are discussed in section B4a. Participants in the pilot test were also consulted on their estimate of the amount of time required to complete this instrument, and the burden associated with this instrument; these are discussed in section A12a.
The cross-site evaluation team engaged in extensive consultation during the Phase I development of the Infrastructure and Implementation Interview guides from which the Sustainability Interview Guide was derived. Key prevention stakeholders, including state SPF SIG project directors and evaluators and other key SPF SIG staff, were consulted provided feedback on the content and format of the instruments to ensure that they were not too burdensome for respondents to answer. All Cohort I SPF SIG States were given the opportunity to review these instruments and provide comments and questions on their content and format. Finally, the original instruments were pilot tested in six states in October and November 2005. Project Directors; State Epidemiology Work Group Chairs; State Advisory Committee members; SPF SIG evaluators; and SSA staff were interviewed for the pilot test. Because the Phase II Sustainability Interview Guide incorporated items from the Phase I interview guides, the interview guide was pilot tested in May 2010 with a state evaluator familiar with the SPF SIG initiative to ensure that item wording was clear and that the total interview time did not exceed 90 minutes.
A8b2. Cohorts III, IV, and V Cross-site Evaluation
This submission is drawn from the one originally submitted by SAMHSA for the cross-site evaluation of SPF-SIG Cohort I and II grantees. The current evaluation design, data analysis plan, and revised instruments received several rounds of review. These reviews were the result of ongoing collaboration with the CSAP SPF SIG project officer, the SAMHSA/CSAP Data Analysis Coordination and Consolidation Center (DACCC) project officer and team members, the DACCC External Steering Committee (ESC), and a grantee-level workgroup consisting of evaluators and project directors. All SPF SIG grantees were given the opportunity to review instruments and provide comments and questions on their content and format. The purpose of such consultations is to ensure the technical soundness of the evaluation, and to verify the importance, relevance, and accessibility of the information sought in the evaluation and to insure that this type of monitoring will continue to take place throughout the evaluation.
Members of the DACCC, the ESC, and other outside expert participants including researchers, evaluators, state representatives, and grantees who participated in these processes may be found in Attachment B2.
A9. Payment to Respondents
There is no payment to any respondents.
A10. Assurance of Confidentiality
A10a. Cohorts I and II Cross-site Evaluation
All information gathered through the administration of the CLI (Parts I and II) and the Sustainability Interview Guide focuses on organizational activities undertaken as part of the SPF SIG program rather than information about individuals. However, all respondents to the CLI (Parts I and II) will be required to register with the online survey site where the instrument will be completed. As part of this registration, it will be necessary to obtain identifying information about these individuals (i.e., name, e-mail address, organizational affiliation, and title/position). This information will be used for the creation of a user profile and every attempt will be made to keep this information private. After participants have registered with the Web site they will be provided with a User ID and temporary password to ensure that all of their survey responses remain private. Additionally, no survey responses will be attributed to a specific individual in any reports prepared from this data.
CLI (Parts I and II) participants will also be provided with the following information prior to completing the instrument: the purpose of the instrument; how the results will be used; the fact that participation is voluntary; that they may refuse to answer any question at any time or end the instrument at any time; that responses will be kept private to the extent possible; that individual names and positions will not be connected with any responses in any reports prepared from the data; and that all individual responses will be combined with the responses of others in all reports prepared from the data.
Also, because individuals who participate in the Sustainability Interview will be identified by the state project director as respondents, identifying information (phone number, email address) will be necessary to schedule these interviews. Every attempt will be made to keep this information confidential, and it will not be released or used for any purpose other than for follow-up clarification of responses. No statements gathered during these interviews will be attributed to a specific individual in any reports prepared from this data.
A10b. Cohorts III, IV, and V Cross-site Evaluation
A10b1. Grantee- and Community-Level Instruments
All information gathered through the administration of the Grantee-Level Instruments (Infrastructure and Implementation) and Community-level Instruments (Parts I and II) focus on organizational activities undertaken as part of the SPF SIG program, rather than information about individuals. However, all respondents to the Grantee- and Community-Level Instruments) will be required to register with the online survey site where the instrument will be completed. As part of this registration, it will be necessary to obtain identifying information about these individuals (i.e., name, email address, organizational affiliation, and title/position). This information will be used for the creation of a user profile and every attempt will be made to keep this information private. After participants have registered with the website they will be provided with a UserID and temporary password to ensure that all of their survey responses remain private. Additionally, no survey responses will be attributed to a specific individual in any reports prepared from this data.
Grantee- and Community-Level Instrument respondents will also be provided with the following information prior to completing the instrument: the purpose of the instrument; how the results will be used; that responses will be kept private to the extent possible; that individual names and positions will not be connected with any responses in any reports prepared from the data; and that all individual responses will be combined with the responses of others in all reports prepared from the data.
A10b2. Participant-Level Instruments
Individual level data will be collected using the Participant-Level Instrument (OMB No. 0930-0230). As part of its grant application process, SAMHSA/CSAP requires that Cohort III, IV, and V grantees describe the procedures they will use to ensure the privacy of participant data. These include by whom and how data will be collected, how data collection instruments will be administered, where data will be stored, who will/will not have access to information, and how the identity of participants will be safeguarded. Data files provided by the grantees to the DITIC do not contain client identifiers. The DACCC reviews these data files to ensure identifiers are removed before creating analysis files.
A11. Questions of a Sensitive Nature
No information of a sensitive nature will be directly collected on the Grantee- or Community-Level Instruments.
A12. Estimates of Annualized Hour Burden
The estimated annualized hour burden of conducting the cross-site evaluations of SPF SIG cohorts I and II and III, IV, and V is 5,971 hours. The calculation procedure is described in the sections below.
Table 1. Estimates of Annualized Hour and Cost Burden to Respondents (Table includes new estimates for the CLI and Sustainability Instrument for Cohorts I and II, revised estimates for Cohort IV, and the addition of Cohort V for grantee and community level instruments.)
Instrument Type |
Respondent |
Burden per Response (Hrs.) |
No. of Respon-dents |
No. of Responses per Respondent |
Total Burden (Hrs.) |
Hourly Wage Cost |
Total Hour Cost |
|
Cohorts 1 and 2 Grantee-Level Burden |
||||||||
CLI Grantee Level Input |
Grantee |
1 |
26 |
2 |
52.0 |
$42.00 |
$2,184 |
|
Sustainability Interview |
Grantee |
1.3 |
26 |
1 |
33.8 |
$42.00 |
$1,420 |
|
Total Burden |
Grantee |
2.3 |
26 |
3 |
85.8 |
$42.00 |
$3,604 |
|
Average Annual Burden Over 4 Reporting Periods |
Grantee |
0.6 |
26 |
0.8 |
21.5 |
$42.00 |
$901 |
|
Cohorts 1 and 2 Community-Level Burden |
||||||||
CLI Part I |
Community |
2.35 |
443 |
2 |
2,082.1 |
$32.00 |
$66,627 |
|
CLI Part II |
Community |
2.35 |
443 |
8 |
8,328.4 |
$32.00 |
$266,509 |
|
Review of Past Responses |
Community |
2.5 |
443 |
2 |
2,215.0 |
$32.00 |
$70,880 |
|
Total Burden |
Community |
7.2 |
443 |
12 |
12,625.5 |
$32.00 |
$404,016 |
|
Average Annual Burden Over 4 Reporting Periods |
Community |
1.8 |
443 |
3 |
3,156.4 |
$32.00 |
$101,004 |
|
Grantee-Level Burden Cohort 3 |
||||||||
GLI Infrastructure Instrument |
Grantee |
2. 50 |
16 |
1 |
40.0 |
$42.00 |
$1,680 |
|
GLI Implementation Instrument |
Grantee |
2.25 |
16 |
1 |
36.0 |
$42.00 |
$1,512 |
|
CLI Part I, 1—20: Community Contact Information—Updates |
Grantee |
0.25 |
16 |
1 |
4.0 |
$42.00 |
$168 |
|
Total Burden |
Grantee |
5 |
16 |
3 |
80.0 |
$42.00 |
$3,360 |
|
Average Annual Burden Over 4 Reporting Periods |
Grantee |
1.3 |
16 |
0.8 |
20.0 |
$42.00 |
$840 |
|
Community-Level Burden Cohort 3 |
|
|||||||
CLI Part I, 21–172: Community SPF Activities —Updates |
Community |
0.75 |
240 |
1 |
180 |
$32.00 |
$5,760 |
|
CLI Part II —Updates |
Community |
0.5 |
240 |
6 |
720 |
$32.00 |
$23,040 |
|
Total burden |
Community |
1.25 |
240 |
7 |
900 |
$32.00 |
$28,800 |
|
Average Annual Burden Over 4 Reporting Periods |
Community |
0.3 |
240 |
1.8 |
225 |
$32.00 |
$7,200 |
|
Grantee-Level Burden Cohort 4 |
||||||||
GLI Infrastructure Instruments |
Grantee |
2. 50 |
25 |
1 |
62.5 |
$42.00 |
$2,625 |
|
GLI Implementation Instruments |
Grantee |
2.25 |
25 |
2 |
112.5 |
$42.00 |
$4,725 |
|
CLI Part I, 1—20: Community Contact Information -Initialization |
Grantee |
1.5 |
25 |
1 |
37.5 |
$42.00 |
$1,575 |
|
CLI Part I, 1—20: Community Contact Information —Updates |
Grantee |
0.25 |
25 |
3 |
18.8 |
$42.00 |
$788 |
|
Total Burden |
Grantee |
6.5 |
25 |
7 |
231.3 |
$42.00 |
$9,713 |
|
Average Annual Burden Over 4 Reporting Periods |
Grantee |
1.6 |
25 |
1.8 |
57.8 |
$42.00 |
$2,428 |
|
Community-Level Burden Cohort 4 |
||||||||
CLI Part I, 21–172: Community SPF Activities —Initialization |
Community |
3 |
375 |
1 |
1,125 |
$32.00 |
$36,000 |
|
CLI Part II —Initialization |
Community |
0.75 |
375 |
6 |
1,687.5 |
$32.00 |
$54,000 |
|
CLI Part I, 21–172: Community SPF Activities -Updates |
Community |
0.75 |
375 |
3 |
843.8 |
$32.00 |
$27,000 |
|
CLI Part II —Updates |
Community |
0.5 |
375 |
18 |
3,375 |
$32.00 |
$108,000 |
|
Total burden |
Community |
5 |
375 |
28 |
7031.3 |
$32.00 |
$225,000 |
|
Average Annual Burden Over 4 Reporting Periods |
Community |
1.3 |
375 |
7.0 |
1,757.8 |
$32.00 |
$56,250 |
|
Grantee-Level Burden Cohort 5 |
||||||||
GLI Infrastructure Instruments |
Grantee |
2. 5 |
10 |
2 |
50 |
$42.00 |
$2,100 |
|
GLI Implementation Instruments |
Grantee |
2.25 |
10 |
2 |
45 |
$42.00 |
$1,890 |
|
CLI Part I, 1—20: Community Contact Information —Initialization |
Grantee |
1.5 |
10 |
1 |
15.0 |
$42.00 |
$630 |
|
CLI Part I, 1—20: Community Contact Information —Updates |
Grantee |
0.25 |
10 |
3 |
7.5 |
$42.00 |
$315 |
|
Total Burden |
Grantee |
6.5 |
10 |
8 |
117.5 |
$42.00 |
$4,935 |
|
Average Annual Burden Over 4 Reporting Periods |
Grantee |
1.6 |
10 |
2.0 |
29.4 |
$42.00 |
$1,234 |
|
Community-Level Burden Cohort 5 |
||||||||
CLI Part I, 21–172: Community SPF Activities —Initialization |
Community |
3 |
150 |
1 |
450 |
$32.00 |
$14,400 |
|
CLI Part II —Initialization |
Community |
0.75 |
150 |
6 |
675 |
$32.00 |
$21,600 |
|
CLI Part I, 21–172: Community SPF Activities -Updates |
Community |
0.75 |
150 |
3 |
337.5 |
$32.00 |
$10,800 |
|
CLI Part II —Updates |
Community |
0.5 |
150 |
18 |
1,350 |
$32.00 |
$43,200 |
|
Total burden |
Community |
5 |
150 |
28 |
2,812.5 |
$32.00 |
$90,000 |
|
Average Annual Burden Over 4 Reporting Periods |
Community |
1.3 |
150 |
7.0 |
703.1 |
$32.00 |
$22,500 |
|
Table 2. Annualized Summary Table
|
Respondent |
Burden per Response (Hrs.) |
No. of Respon-dents |
No. of Responses |
Total Burden (Hrs.) |
Hourly Wage Cost |
Total Hour Cost |
Total Burden All Cohorts |
|||||||
Average Annual Burden |
Grantee |
1.35 |
77 |
95.25 |
128.6 |
$42.00 |
$5,402.8 |
|
Community |
1.08 |
1,208 |
5,424 |
5,842 |
$32.00 |
$186,954 |
|
Overall |
1.08 |
1,285 |
5,519 |
5,971 |
|
$192,357 |
A12a. Cohorts I and II Cross-site Evaluation
The estimated average annual burden for Cohort I and II grantee-level and community-level personnel is based on the completion of the Community Level-Instrument (CLI Parts I and II) and the response to the Sustainability Interview. Annualized reporting burden for 2 additional years of data collection for Cohorts I and II for both the CLI (Parts I and II) and the Sustainability Interview is shown in Table 1. The continuation of CLI data collection expects that Cohort I communities be required to complete the CLI for 1 additional year and Cohort II communities be required to complete the CLI for 2 additional years. The Sustainability Interview will occur once for each Cohort I and Cohort II grantee. Cohort 1 grantees will respond during FY 2011. Cohort II grantees will respond during FY 2012. Burden estimates are based on pilot respondents’ feedback as well as the experience of the instrument developers. Additionally, individual community burdens may be lower than the burdens displayed in Table 1 because all sections of the Community-level Instrument (parts I and II) may not apply for each reporting period as community partners work through the SPF steps and only report on the step-related activities addressed. Note also that some questions will be addressed only once and the responses will be used to pre-fill subsequent instruments. To date, 357 communities have received SPF funds from their respective Cohort I States and 86 communities have received SPF funds from their respective Cohort II States. All of the directors of the community-based organizations that receive SPF funds are required to complete both parts of this instrument.
Moreover, because the Sustainability Interview Guide is based upon the Infrastructure Interview Guide and Implementation Interview Guide used during Phase I of the evaluation, and the respondents will be familiar with the SPF SIG implementation, the interviews should proceed smoothly.
A12b. Cohorts III, IV, and V Cross-site Evaluation
Estimates of total (across four years) and annualized reporting for Cohort III, IV, and V grantee-level and community-level personnel are based on the completion of the Grantee-Level Instrument (GLI) and the Community-Level Instrument (CLI). Total and annualized burden estimates for grantee- and community-level personnel are displayed separately in Table 1. Clearance to collect Participant-level NOMs outcomes is not being requested because no new burden associated with these evaluation components is being imposed. Specifically, the burden associated with the Participant-Level Instrument has already been approved by OMB for SPF SIG grantees (OMB No. 0930-0230).
The burden estimates for the GLI and CLI are based on the experience in the Cohort I and II SPF SIG evaluation, less the considerable reduction in length of these instruments implemented by the Cohort III, IV, and V evaluation team. Burden estimates are provided by respondent group for specific instrument segments, by reporting year. In some cases, the burden estimates vary by year because all sections of the instruments may not apply for each reporting period as grantees and community partners work through the SPF steps and only report on the step-related activities addressed. In addition, some questions will be addressed only once and the responses will be used to pre-fill subsequent instruments.
Estimated burden of the grantee-level instruments is based on the current 16 grantees funded in Cohort III, 25 funded in Cohort IV and 10 funded in Cohort V, all of whom will be asked to complete the GLI Infrastructure and Implementation instruments twice each during the four year reporting period, with the exception of Cohort III who have already completed both surveys once. Estimated burden of the community-level instruments assumes an estimated 765 communities (an average of 15 communities per grantee), annual completion of the CLI Part I, a minimum of two instrument updates per year for the CLI Part II, and an average of three distinct prevention intervention strategies implemented by each community during a 6-month period.
A13. Estimates of Annualized Cost Burden to Respondents
There are no capital/startup costs or operational/maintenance of services costs associated with this project.
A14. Estimates of Annualized Cost to the Government
The estimated annual cost to the Federal government of conducting the cross-site evaluations of SPF SIG cohorts I and II and III, IV, and V is $1,601,831. Procedures for calculating the costs are described below.
A14a. Cohorts I and II Cross-site Evaluation
The estimated cost to the Federal government of conducting the evaluation of SPF SIG Cohort I and II is based on the government’s contracted cost of the data collection and related evaluation activities along with the personnel cost of government employees involved in oversight and/or analysis. The National Institute on Drug Abuse is funding all of the proposed activities.
The total contractor cost, over the four-year OMB approval period, for the extended Cohort 1 and Cohort 2 data collection is $371,736. The estimated annual cost is $92, 934. The total cost for Cohorts I and II CLI data collection is $209,940. The total cost for the sustainability Interview data collection is $161, 796. The average annual cost for the Sustainability Interview data collection over the four-year approval period is $40,449. Data collection will begin in Year 2 of the four-year OMB approval period. Year 2 costs are $96,378 and include costs associated with interview guide development. Year 3 costs of $54,354 reflect interviews with 21 Cohort 1 grantees. Costs for Year 4 of $11,064 are lower than costs for the other years because of the reduction in number of grantees (from 26 to 5).
When 25 percent of a GS-14 CSAP project officer’s salary ($116,419 per year) of $29,104 is included with the annual cost of $92,934, the total annual cost over the four-year OMB approval period for the extended CLI data collection and the Sustainability Interview is $122,038.
A14b. Cohorts III, IV, and V Cross-site Evaluation
The estimated cost to the Federal government of conducting the evaluation of SPF SIG Cohort III, IV, and V is based on the government contracted cost of the data collection and related evaluation activities along with the personnel cost of government employees involved in oversight and/or analysis. The DACCC is currently subcontracting with RMC for the Cross-site evaluation for which OMB approval is currently being requested, the annual cost to the government of this subcontract is $1,057,715. In addition, DataCorp has a subcontract for all the data management and data cleaning activities related to the Cross-site. The annual cost to the government of this subcontract is $409,727. Additional costs include: 25 percent cost for a GS-14 CSAP project officer ($29,104), and 10 percent cost for the DACCC Project Manager ($12,351). Thus, the total annual cost to the government for this Cross-site evaluation is $1,508,897.
A15. Changes in Burden
Currently, there are 5,621 annualized burden hours in the OMB inventory for SPF SIG Cohorts I, II, III, and IV (OMB No. 0930-0279). CSAP is requesting 5,971 annualized burden hours for this revision. Burden changes are the result of several factors: The addition of Cohort V, the addition of 5 Cohort IV grantees (bringing the total to 25 grantees, replacing the original estimate of 20 grantees), the addition of a new Sustainability Interview for Cohorts I and II, reduction of the number of CLI completions for Cohort II from 4 to 2, and reduction of the number of responses to the GLI Implementation instrument from 2 to 1 for Cohort III grantees.
For the continuation of data collection for Cohorts I and II, CSAP is requesting an average annual estimate of 3,178 hours for 26 grantees and 443 communities to complete the CLI instrument and the Sustainability Interview. The burden specific to the continuation of CLI data collection in Cohorts I and II is based on estimates of the number of interventions each community is likely to implement (approximately 4) and thus need to report on. For the additional 51 grantees and 765 sub-recipient communities included in the Cohort III, IV, and V cross-site evaluation CSAP is requesting an average annual total burden of 2,793 hours to complete three survey efforts (Note that 245 of these hours are included in the existing OMB approval). The total annualized burden for the Cohort III, IV, and V grantees and sub-recipient communities was reduced by changing the format of the grantee-level instruments from interview protocols to survey instruments, reducing the grantee-level data collection effort from annually to twice over the course of the funding period, and optimizing the use of skip patterns and replacing the majority of open-ended questions with multiple-choice-response questions in both the grantee- and community-level instruments.
A16. Time Schedule, Analysis and Publication Plans
This section describes the analysis, tabulation, and publication of results for the Cohorts I and II and Cohorts III, IV, and V cross-site evaluations. The evaluation design for both sets of cohorts is similar except for the inclusion of a non-Cohort grantee comparison group in the Cohort I and II evaluation design and the addition of participant level data collection in the Cohort III, IV, and V evaluation design. The following discussion pertaining to the evaluation schedule, analysis, and publication plans for Cohorts I and II and Cohorts III, IV, and V will therefore be combined.
Research Questions
Eight outcome questions are guiding the SPF SIG outcome evaluation. Questions 4a and 4b referring to participant-level improvements are specific to Cohorts III, IV, and V. These eight questions assess whether observed conditions/events can be attributed to SPF SIG programmatic interventions. The eight questions are:
1a. Did SPF funding improve grantee-wide performance on NOMs and other outcomes?
1b. What accounted for variation in NOMs and other outcomes performance across SPF grantees?
2a. Within grantees, did SPF funding lead to community-level improvement on NOMs and other outcomes?
2b. Within grantees, what accounted for variation in NOMs and other outcomes performance across funded communities?
3a. Across grantees, did SPF funding lead to community-level improvement on NOMs and other outcomes?
3b. Across grantees, what accounted for variation in NOMs and other outcomes performance across funded communities?
4a. Did SPF funding lead to participant-level improvement on NOMs and other outcomes?
4b. What accounted for variation in participant-level NOMs and other outcomes performance across funded grantees and communities?
In addition to these eight outcome research questions which are the central focus of the SPF SIG evaluation, the evaluation design also includes process-related research questions. These provide information necessary for interpreting the outcomes found in the evaluation, and focus on: interpreting the effects of project-related activities; identifying effective program and policy elements (e.g., conditions necessary for effective programs, populations for whom programs are effective); and assessing contextual factors related to SPF SIG outcomes. Some examples of process-related research questions included in the design are: What changes in allocation of funds and other resources for substance abuse prevention programs and other activities occurred at the grantee and community-levels; what grantee and community level mobilization and capacity building activities have been implemented; has cultural competence been integrated into prevention programs, policies, and practices in states, jurisdictions, and tribal entities; to what extent has the prevention infrastructure improved; to what extent are selected programs evidence-based; and to what extent are selected programs implemented with fidelity?
Logic Model of SPF SIG Impact
A logic model of SPF SIG impact has been developed to help guide the evaluation design and requirements. This logic model depicts the flow of grantee- and community-level activities that lead to systems change, and participant-level outcomes where evidence-based prevention-intervention programs are implemented. The model is depicted in Figure 1 below.
Grantee activities are represented in the logic model as rectangles, community activities are represented as ovals, and participant-level activities are represented as hexagons. The stacked ovals and hexagons represent the multiple communities and participants involved. The logic model is operationalized with SPF funding being received by funded jurisdictions and tribal entities. After receipt of funds, jurisdictions and tribal entities begin the planning and implementation of the SPF. The implementation of the SPF is expected to lead to both grantee-level systems change and funding of selected sub-recipient communities. Funding of selected communities is expected to lead to planning and implementation of the SPF also resulting in community-level system change. Systems change at both the state and community levels is expected to lead to changes in grantee- and community-level outcomes and participant-level outcomes.
The arrow connecting planning and implementation (both at the grantee and community levels) to systems change is bidirectional, indicating that both influence each other. The SPF model suggests that planning and implementation lead to systems change, and systems change leads to further refinement and efficiency of planning and implementation.
Figure 1: SPF SIG Logic Model
Grantee-Level
Epi Outcomes
Planning
& Implementation
SPF
$ in Selected Jurisdictions and Tribal Entities
Baseline
Status
Grantee-Level
State-Level
Systems Change
Contextual
Change & Unmeasured Factors
LEGEND: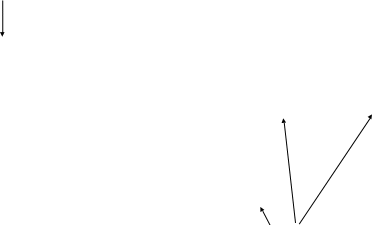
















To examine the impact of SPF SIG funding on systems change and outcomes, the logic model includes variations in baseline status, contextual change and unmeasured factors for grantees and communities. Baseline status refers to pre-SPF SIG activities and achievements related to SPF SIG-initiated activities. Contextual change and unmeasured factors refer to anything that occurs in grantees and communities unrelated to the SPF SIG project that may potentially have an impact on systems change and outcomes.
Evaluation Timeline
Table 2 shows the time schedule for the cross-site evaluation of the SPF SIG initiative. The table is broken out to display two separate timelines specific to the Cohorts I and II and Cohorts III, IV, and V evaluation schedules.
As indicated in Table 2, Cohorts I and II grantees began data collection of the CLI (Parts I and II) in January 2008, following OMB approval. Both parts of this instrument will be administered twice per year (every six months). The Sustainability Interview will be administered to Cohort I grantees between September and December 2011. The Interview will be administered to Cohort II grantees between September and December of 2012. Evaluation reports which include results of preliminary analyses conducted, using data from these instruments, have been produced every year in December. The first report was delivered in December 2005. A comprehensive final report for the SPF SIG will be delivered in September 2012.
As also indicated in Table 2, all data collection and reporting requirements for Cohort III and IV began following OMB approval which was received in November 2009 and are scheduled to end in September 2012. Pending OMB approval of this amendment, data collection for Cohort V is expected to begin in the summer 2011 and will be completed by August 2015.
Table 2: SPF SIG Evaluation Time Schedule
Data Collection, Analysis, and Reporting Timeline |
|
Evaluation Activity |
Date |
Cohorts I and II |
|
Obtain OMB revision for CLI (Parts I and II) |
November 2009 |
Obtain OMB clearance for the Sustainability Interview |
TBD |
Collect community sub-recipient survey data (semi-annually) |
Through July 2011 |
Collect grantee sustainability interview data |
September 2011 through December 2012 |
Analyze evaluation data to assess relationship between interview/survey data and outcomes |
Annual interim analyses (2006-2011); comprehensive final analyses (2012) |
Create data files for secondary analysis |
December 2006 – December 2012 |
Produce bi-monthly reports |
November 2004 – September 2012 |
Produce annual evaluation reports |
December 2005 – December 2011 |
Produce final evaluation report |
September 2012 |
Cohorts III and IV |
|
Database Design |
October 2008 –June 2009 |
Instrument Manual Development |
November 2008- June 2009 |
OMB Package Under Review |
May 2009- November 2009 |
Database Beta Testing |
May –September 2009 |
Data Collection/Instrument Training |
September 2009 |
Database Training |
September 2009 |
OMB Package Approved |
November 2009 |
PLI Reporting (bi-annually) |
November 2009 (Cohort III) May 2010; November 2010 (Cohort III) May 2011 (Cohort III); August 2011 (Cohort III) November 2011 (Cohort IV) May 2012; November 2012 (Cohort IV) May 2013; November 2013 (Cohort IV) May 2014; August 2014 (Cohort IV) |
GLI Infrastructure Data Collection |
November 2009 (Cohort III/IV) August 2011 (Cohort III) August 2014 (Cohort IV) |
GLI SPF Implementation Data Collection |
November 2009 (Cohort III) August 2011 (Cohort III) November 2010-July 2011 (Cohort IV) November 2013-July 2014 (Cohort IV) |
CLI (Part 1)Data Collection |
November 2009 (Cohort III) November 2010 (Cohort III) August 2011 (Cohort III) November 2011(Cohort IV) November 2012 (Cohort IV) November 2013 (Cohort IV) August 2014 (Cohort IV) |
CLI (Part 2)Data Collection |
November 2009 (Cohort III) May 2010; November 2010 (Cohort III) May 2011 (Cohort III); August 2011 (Cohort III) November 2011(Cohort IV) May 2012; November 2012 (Cohort IV) May 2013; November 2013 (Cohort IV) May 2014; August 2014 (Cohort IV) |
Analyze evaluation data to assess relationship between survey data and outcomes |
Annual interim analyses (2009-2011) Comprehensive final analyses (2012) |
Annual Evaluation Reports |
March 2011 March 2012 March 2013 March 2014 |
Special Topic Reports |
August 2011 |
Cohort V |
|
OMB Package Under Review |
Dec 2010-March 2011 |
MRT Database Training |
Dec 2010 |
Data Entry/Instrument Training |
February 2011 (GLI) April 2011 (Community Outcome) September 2011 (CLI) |
OMB Package Approved |
Summer 2011 |
PLI Reporting (bi-annually) |
May 2012; November 2012 May 2013; November 2013 May 2014; November 2014 May 2015; August 2015 |
GLI Infrastructure Data Collection |
Summer 2011 August 2015 |
GLI SPF Implementation Data Collection |
September 2011-March 2012 February 2015-August 2015
|
CLI (Part 1)Data Collection |
November 2011 November 2012 November 2013 November 2014 August 2015 |
CLI (Part 2)Data Collection |
November 2011 May 2012; November 2012 May 2013; November 2013 May 2014; November 2014 May 2015; August 2015 |
Analyze evaluation data to assess relationship between survey data and outcomes |
Annual interim analyses (2011-2014) Comprehensive final analyses (2015) |
Annual Evaluation Reports |
March 2012 March 2013 March 2014 March 2015 March 2016 (Comprehensive Final Report) |
Special Topic Reports |
August 2013 August 2015 |
Plans for Tabulation and Analysis
Plans for tabulation and analysis will include qualitative and quantitative analyses of data collected and graphic and tabular displays of the key findings. The community-level epidemiological data and participant-level NOMs will be used to answer questions 1a, 2a, 3a, and 4a listed in section A16. The grantee-level instrument (Sustainability Interview) and Community-level Instrument (Parts I and II) will be used to gather data related to research questions 1b, 2b, 3b, and 4b listed in section A16, each of which addresses the effect of the SPF SIG initiative on grantee- and community-level system outcomes and community- and participant-level NOMs outcomes. Specifically, the four questions address the moderators and mediators of outcome variation across SPF-funded grantees and communities across funded grantees. The Sustainability Interview asks a series of open-ended questions within each of the SPF steps regarding the extent to which State’s prevention infrastructure has developed and the extent to which key elements of the SPF have been, or will be, sustained by the State. Data from the Community-level Instrument (Parts I and II) in particular will be used to identify similarities and differences in the way SPF SIG is being implemented across communities and grantees including the specific prevention-intervention programs and strategy-types being implemented. This information will be linked to the participant-level NOMs for examining relationships between different types of community approaches for selecting and implementing evidence-based practices and corresponding outcomes.
Data reduction, scoring and scaling. Our use of data from the Sustainability Interview in outcome and process analyses will focus more on the scales and indexes that will be constructed within each SPF step (also known as a prevention domain), rather than on a state’s responses to any individual item. The first phase of the analysis of data will consist of review, coding, scoring and scaling of responses within each domain with the goal of reducing the data to a set of reliable scales that will be used in subsequent analyses. For each domain, a summary score or index will be developed. Although some revision and winnowing of questions within domains has already taken place based on our pilot interview, it is expected that some items in each domain will yield more useful information for coding and some may show insufficient variation to be retained in final versions of the summary scores. Attention will be given to developing reliable and valid measures of the constructs in each domain, including assessment of inter-coder reliabilities and relationships among both the items within potential summary scores and between the domains. In addition to our scoring (or quantifying) the responses, we will use the open-ended responses to provide contextual qualitative data to support and enrich the quantitative scores. The qualitative information will be included as narrative in our reports to help explain the scores and to provide concrete illustrations of how the scores regarding prevention infrastructure and sustainability manifest themselves within each state.
The grantee-level Implementation and Infrastructure instruments and the CLI (Parts I and II) were developed using input from program staff in Cohort I and II states who are implementing the SPF initiative and policymakers who designed it. For Cohort III, IV, and V grantees the grantee-level interviews were reformatted to be implemented in a survey format and the CLI (Parts I and II) were slightly modified. The original intent to include questions representing key aspects of prevention infrastructure and steps in the SPF initiative as outlined in the SPF-SIG RFA and GFA were maintained for all four instruments. Use of data from these instruments in outcome and process analyses will focus more on the scales and indexes that will be derived from each of the sections in the instrument than on a community’s or grantee’s responses to any individual item.
The first phase of the analysis of data from the grantee- and community-level instruments will consist of review, coding, scoring and scaling of responses within each instrument section with the goal of reducing the data to a set of reliable scales that will be used in subsequent analyses. For each section, summary scores or indexes will be developed that go beyond the limited response codes contained in the instrument to encompass the range of responses. Further development of empirically-based anchors for scales and the development of additional summary scores for sections will be based on analysis of the first wave of surveys using standard scale development procedures. Although considerable revision and winnowing of questions within sections has already taken place based on the pilot test, it is expected that some items in each section will yield more useful information for coding and some may show insufficient variation to be retained in final versions of the summary scores. Attention will be given to developing reliable and valid measures of the constructs in each instrument section, including relationships among both the items within potential summary scores and between the sections.
The collection of participant-level data was added to the Cohort III, IV, and V evaluation to assess the impact of the SPF SIG on substance use and substance use related consequences. Responses to individual items collected from participants in direct-service programs lasting 30 days or longer will be used in combination with the grantee- and community-level instruments to examine the relationship between the SPF SIG process and participant-level outcomes.
Descriptive/normative analyses. Although the primary focus of the cross-site evaluation is on assessing impact, many descriptive and normative analyses will occur. The scales and indexes from the Grantee-level instruments, including the Sustainability Interview, and CLI (Parts I and II) will support these analyses, in tandem with coded data from archival sources such as grant applications, quarterly reports, and strategic plans. We will use standard techniques for analyzing, displaying, and reporting descriptive and normative results as they become available throughout the evaluation period. These will include summary statistics (means, medians, ranges, and standard deviations) and univariate and multivariate statistics (including cross-classification displays), as well as appropriate charts and graphs. Subsequently, the scales and indexes developed in the initial phases of analysis will also support the impact questions as key predictors of systems-, population-, and participant-level outcomes.
The nature of the analyses of Sustainability Interview data will be to determine how prevention infrastructure has changed since our last Infrastructure Interview (2009) and to what extent States are sustaining elements of the SPF. To address the former, we will compare the data we obtain during Phase II of the project with data we obtained during Phase I to see if there is change over time. We will not be able to make direct comparisons for all our data because we are using a much-reduced interview protocol for this Phase; we will, however, make comparisons where possible. For example, we can adjust the Phase I data to take into account the reduction in items and then make direct comparisons on those items. Subsequently, the scales and indexes developed in these analyses will also support the impact questions as key predictors of systems- and population-level outcomes.
Outcome analyses. The data gathered will be used to conduct a variety of quantitative and qualitative analyses related to the eight outcome evaluation questions and also the process-related research questions. As part of these analyses, the distributional characteristics of the data as well as the baseline differences among the groups being compared will be assessed. Then, within-grantee and cross-grantee outcome analyses will be conducted using multilevel statistical modeling methods that account for the “nested” nature of the data (i.e., the data are not independent, they are nested within the communities and within the states). To estimate the effects of SPF, trends in repeated cross-sectional measurements of population (all cohorts) and participant-level (Cohorts III, IV, and V) outcomes at the grantee and community-level will be evaluated in these analyses. Additionally, propensity scores will be used to reduce potential bias from group nonequivalence between funded and non-funded communities in Cohorts I & II.
Statistical modeling methods will be performed using Hierarchical Linear Modeling (HLM) Version 6 (Raudenbush et al., 2002)1. The coefficients estimated by the HLM model are applicable to a hierarchical data structure with up to three levels of random variation. In our case, the three levels will be: 1) State, 2) community, and 3) time. HLM also accommodates sampling weights in both linear and nonlinear models. This is relevant to our analysis because 1) most of the NOMs and other outcomes will not meet normality assumptions and therefore require nonlinear models, and 2) states will contribute unequal numbers of communities and population sizes to the cross-site database. Therefore, inverse weighting by these inequalities at the appropriate level will increase the generalizability of the findings. Note that the Grantee-level instruments will support analyses of variation at level 3, the CLI will support analyses of variation at level 2, and both will support analyses of variation at level 1 through repeated administrations over time.
One system-level outcome of interest will be changes in prevention infrastructure over time. Data from the grantee-level instruments and CLI (Part I) will be used to measure state systems infrastructure. This includes changes in planning capacity, training capacity, and support for the implementation of evidence-based practices. Thus, data from these instruments will serve as outcome data for grantee systems change and as mediators of changes in population- and participant-level consumption and consequence outcomes. To support analyses that explain outcome variation among the SPF SIG grantees, a global index of grantee prevention infrastructure will be developed using data from the grantee instruments and CLI (Part I). This index will enable us to categorize the prevention infrastructure of grantees as “highly developed,” “moderately developed,” or “less well developed” over the course of SPF implementation. The grantee prevention infrastructure index will also be used in analyses to measure changes from year to year among the SPF SIG grantees.
The construct of prevention infrastructure is, however, too complex to be captured by a single summary statistic. In addition to the global index, therefore, indexes will also be developed based on specific infrastructure domains (planning, workforce development, etc.). Analyses of these indexes will help show whether some domains appear more critical to outcomes than others. Other analyses will focus on the relationship between SPF implementation and observed variation in outcomes across grantees.
Community-level analyses conducted with the data gathered from CLI (Parts I and II) will aim to identify characteristics of community-level interventions that are most effective in producing desired population and participant-level outcomes. These analyses will focus on: 1) comparisons of community-level outcomes from funded communities across multiple states with outcomes from unfunded communities where comparable data are available (Cohorts I & II only) or with state and national data; and 2) comparisons of systems-level outcomes across the funded communities, exploring the relationships between different types of community approaches, target populations, levels of implementation and fidelity, mix of strategy types, and aggregated community-and participant-level outcomes. Systems-level outcomes to be included in these analyses include changes in the number and operation of coalitions as assessed by CLI (Parts I and II). Population outcomes will focus on changes in consumption and consequences NOMs and other outcomes over time. Participant-level outcomes will focus on changes in risk perceptions and alcohol and drug consumption.
Public Use Data and Publication Plans
The cross-site team will provide CSAP with the reports necessary to determine, in consultation with the relevant federal staff, if the overall quality and quantity of the evaluation data are adequate for public release. Once it is determined that the data will be released, the cross-site team will perform a disclosure analysis of the data to detect both direct and indirect identifiers within the data, as well as the most likely sources for a possible breach of privacy. Based on the standards published by the Standing Review Committee for Disclosure Analysis at the Inter-University Consortium for Political and Social Research (ICPSR) the cross-site team will recommend a plan for each detected identifier. Once the disclosure plan is approved by CSAP, the cross-site team will produce a public use data file in compliance with ICPSR recommendations for public use data. Data will also be made available to the prevention community through the DITIC.
A17. Display of Expiration Date
The expiration date for OMB approval will be displayed on all approved instruments.
A18. Exceptions to Certification Statement
This collection of information involves no exceptions to the Certification for Paperwork Reduction Act Submissions.
1 Raudenbush, S. W., & Bryk, A. S. (2002). Hierarchical linear models: Applications and data analysis methods, Second Edition. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
SPF
SIG Supporting Statement
| File Type | application/msword |
| File Title | RMC Basic Report & Proposal Template |
| Author | RMC Research Corporation |
| Last Modified By | summer.king |
| File Modified | 2011-05-02 |
| File Created | 2011-05-02 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy