LTC UTI Protocol
LTC UTI Protocol.docx
The National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN)
LTC UTI Protocol
OMB: 0920-0666
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Event for LTCF
Introduction: The urinary tract is one of the most common sites of healthcare-associated infections, accounting for 20-30% of infections reported by long-term care facilities (LTCFs). In the LTC resident, risk factors for developing bacteriuria and UTI include age-related physiologic changes to the genitor-urinary tract, comorbid conditions resulting in neurogenic bladder, and instrumentation required to manage bladder voiding. The incidence of asymptomatic bacteriuria in the LTC resident can range from 25-50%. Although the incidence of symptomatic UTI is lower, it still comprises a significant proportion of infections manifesting in LTCFs and results in a large amount of antibiotic use.
Though prevalence of indwelling urinary catheter use in LTCFs is lower than in the acute care setting, catheter-associated UTI (CA-UTI)can lead to such complications as cystitis, pyelonephritis, gram-negative bacteremia, and septic shock. These complications associated with CA-UTI can result in decline in resident function and mobility, acute care hospitalizations, and increased mortality. Prevention of CA-UTIs is discussed in the CDC/HICPAC document, Guideline for Prevention of Catheter-associated Urinary Tract Infections.
Settings: UTI event reporting is currently available for certified skilled nursing facilities/nursing homes (LTC:SNF) and intermediate/chronic care facilities for the developmentally disabled (LTC:DevDis). Infection surveillance should be performed facility-wide.
NOTE: If a resident is transferred to an acute care facility for suspected UTI, it is important to report this into NHSN. No additional indwelling catheter days are reported after the day of transfer.
NOTE: If a resident is transferred from an acute care facility and develops signs/symptoms of a UTI within the first 3 calendar days of admission to the LTCF, it would be considered present at the time of transfer and not attributed to the LTCF. It should be reported back to the transferring facility.
Requirements: Surveillance for UTI is performed facility-wide for at least six consecutive calendar months as indicated in the Monthly Reporting Plan for LTCF (CDC 57.141).
Definitions:
Urinary tract infections (UTI) are defined using Symptomatic urinary tract infection (SUTI) criteria or Asymptomatic Bacteremic UTI (ABUTI) criteria (Table 1 and Figure 1). All symptomatic UTIs can be reported, regardless of whether a catheter is in place. Catheter-associated UTIs (CA-UTI) are captured if the resident had an indwelling urinary catheter at the time of or within 48 hours before onset of the event. NOTE: There is no minimum period of time that the catheter must be in place in order for the UTI to be considered catheter-associated.
Indwelling catheter: a drainage tube that is inserted into the urinary bladder through the urethra, is left in place, and is connected to a closed collection system; also called a Foley catheter. Catheter days among residents with indwelling urethral catheters will be captured as a separate denominator.
Permanent catheters placed through the skin in the suprapubic region are a type of indwelling catheter but may have a different risk for symptomatic UTI compared to temporary indwelling urethral catheters. Therefore, UTIs in residents with suprapubic catheters will be captured as symptomatic UTI (SUTI), not CA-UTI. Similar to suprapubic catheters, straight in-and-out catheters will not contribute to catheter days.
Numerator Data: The Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) for LTCF Form (CDC 57.140) is used to collect and report each SUTI or CA-UTI that is identified during the month selected for surveillance. The Instructions for Completion of Urinary Tract Infection for LTCF Form (Tables of Instructions, Tables XX) includes brief instructions for collection and entry of each data element on the form. The UTI form includes resident demographic information and information on whether or not an indwelling urinary catheter was present. Additional data include the specific criteria met for identifying the UTI, whether the resident developed a secondary bloodstream infection, whether the resident was transferred to an acute care facility for any reason or died from any cause within 30 days of the UTI event, and the organisms isolated from cultures and their antimicrobial susceptibilities.
Denominator data: Device days and resident days are used for denominators (See Chapter 16 Key Terms). Urinary catheter days, which are the number of residents with an indwelling urethral urinary catheter device, are collected daily, at the same time each day, for all residents in the facility using the Denominators for LTCF Locations form (CDC 57.142). These daily counts are summed and only the total for the month is entered into NHSN. Indwelling urinary catheter days and resident days are collected every month for the entire facility. Neither suprapubic catheters nor in/out catheters or condom catheters should be included when counting catheter days.
Data Analyses:
The SUTI incidence rate per 1000 resident days is calculated by dividing the number of SUTIs by the number of resident days and multiplying by 1000. Only SUTIs which are NOT catheter associated will be included in the SUTI incidence rate.
CA-UTI incidence rate per 1000 urinary catheter days is calculated by dividing the number of CA-UTIs by the number of catheter days and multiplying the result by 1000. Only UTIs which develop at the time an indwelling urethral catheter is in place or <48 hours from catheter removal will contribute to the CA-UTI rate. The Urinary Catheter Utilization Ratio is calculated by dividing the number of urinary catheter days by the number of resident days.
J Am Geriatr Soc. 2007 Jul;55(7):1072-7.
J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009 Jun;57(6):963-70.
J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008 May;56(5):871-4. Epub 2008 Mar 5.
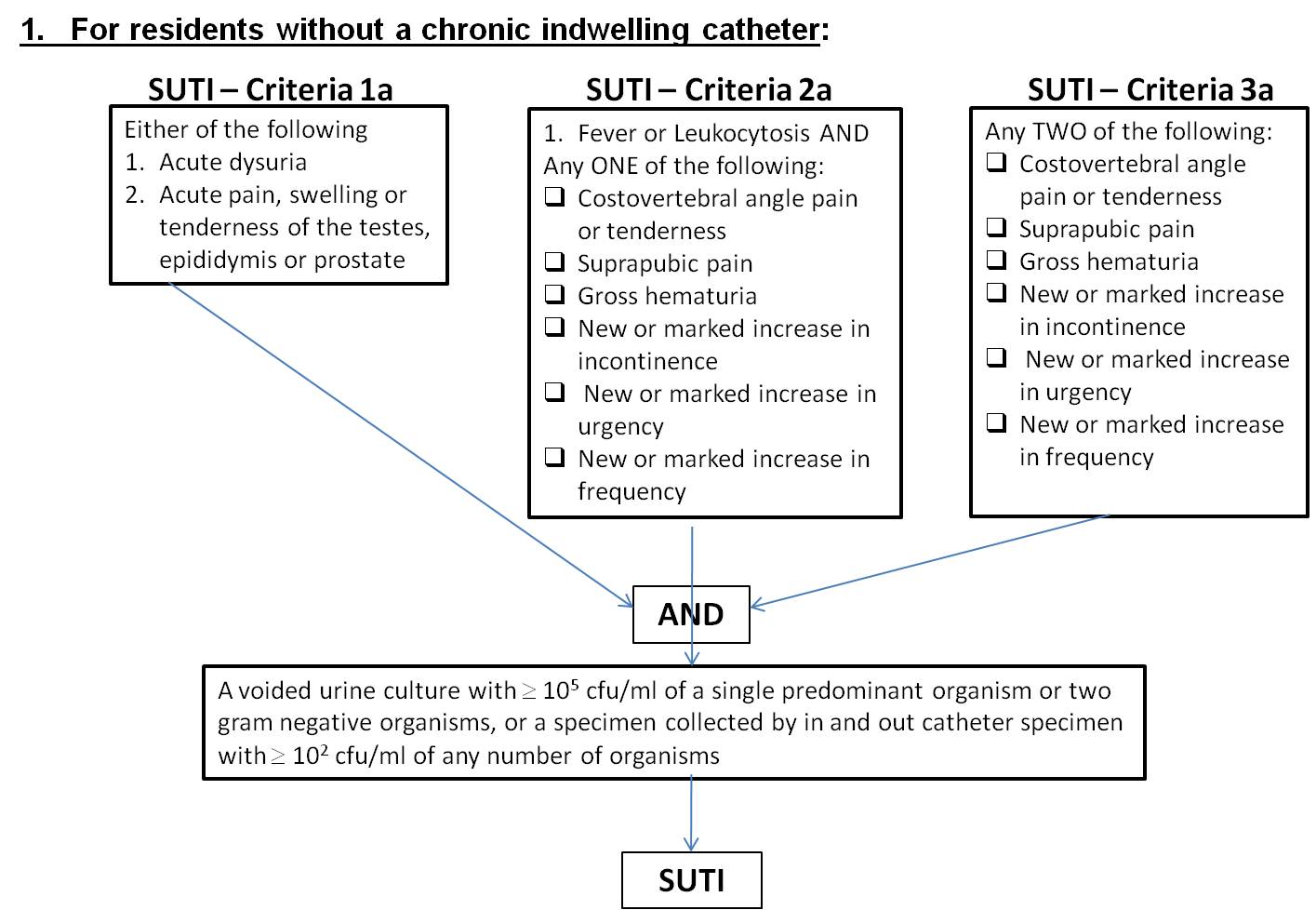
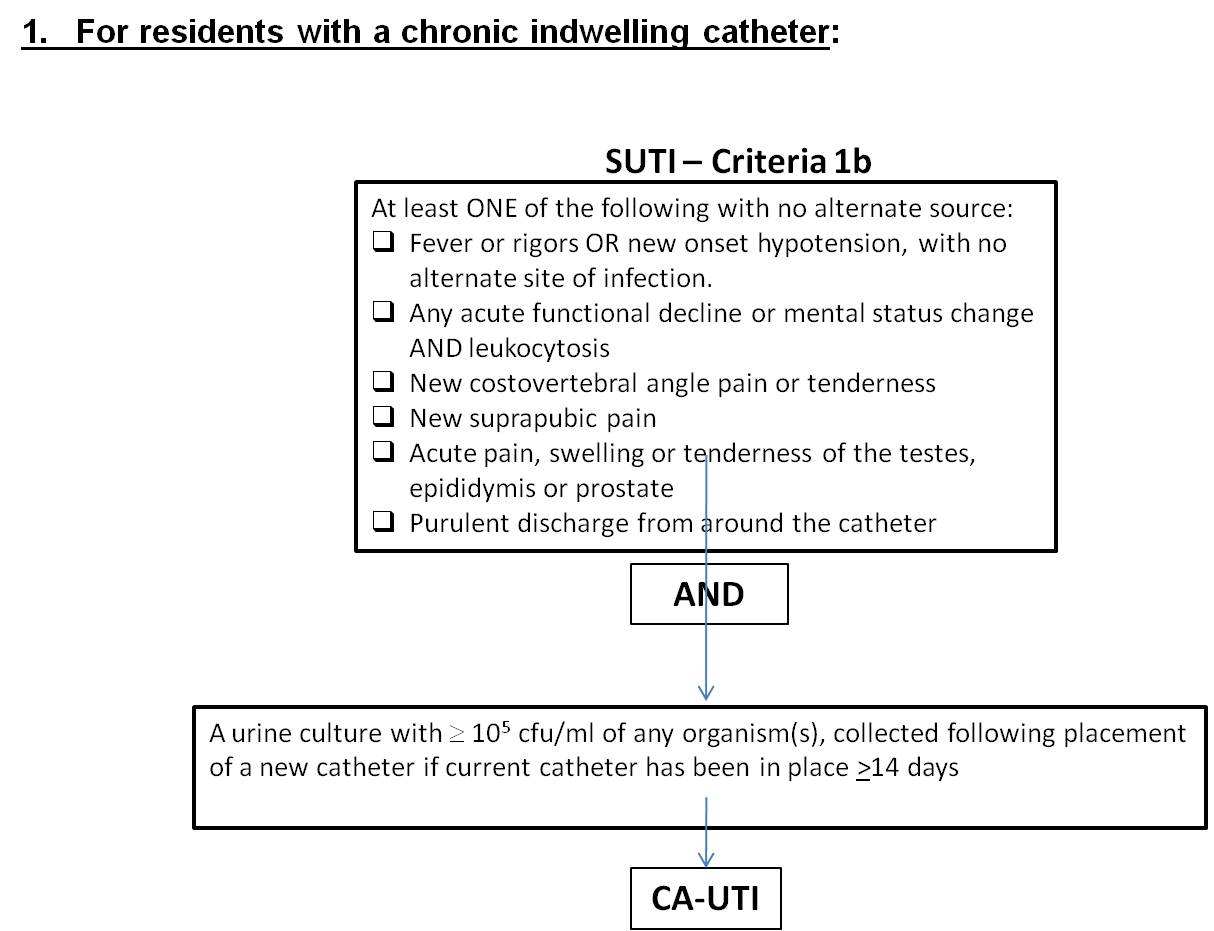
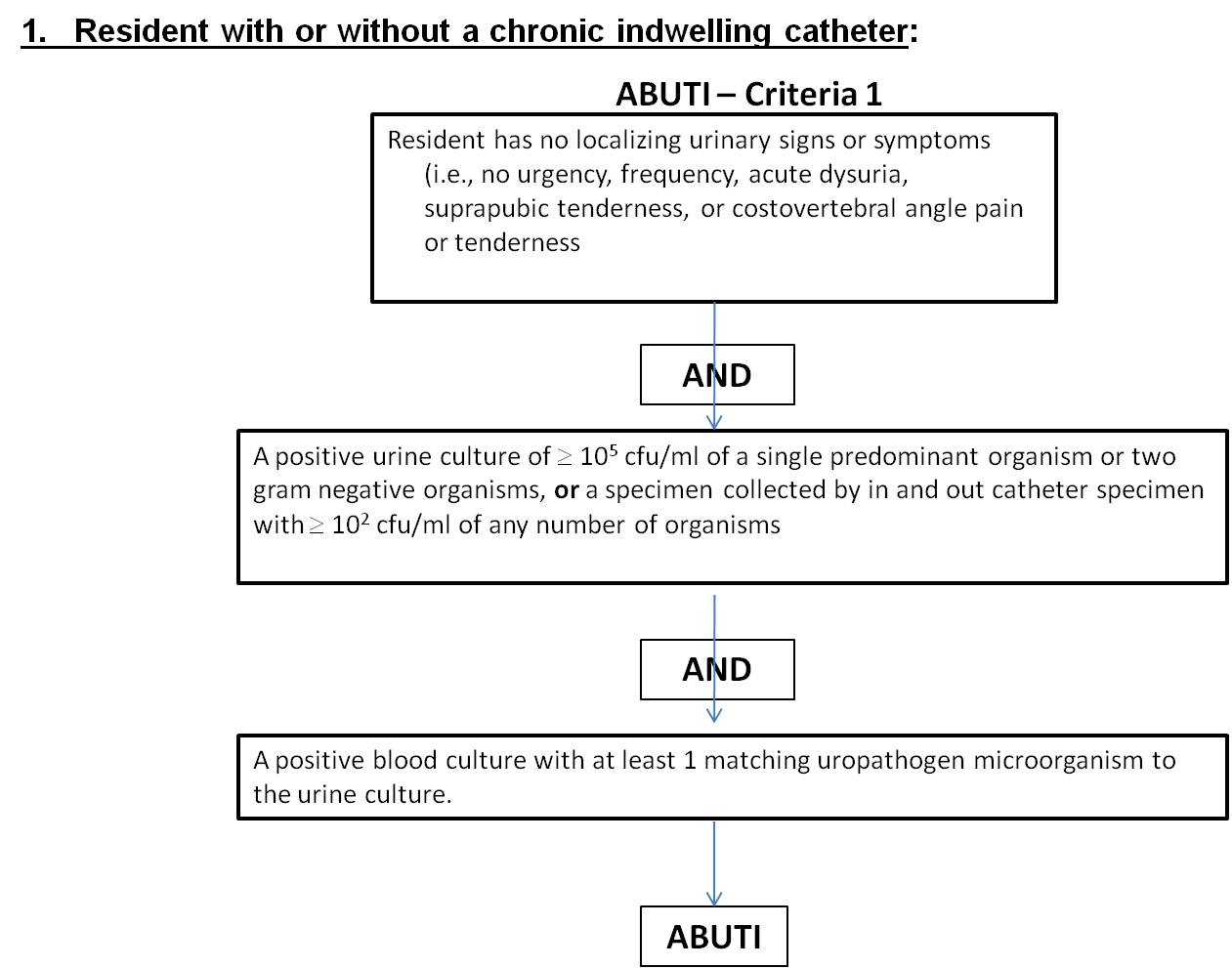
Table 1
Criterion |
Symptomatic Urinary Tract Infection (SUTI) For residents without a chronic indwelling catheter: |
1a |
Acute dysuria or acute pain, swelling, or tenderness of the testes, epididymis, or prostate
AND A voided urine culture with 105 cfu/ml of a single predominant organism or two gram negative organisms, or a specimen collected by in and out catheter specimen with 102 cfu/ml of any number of organisms. |
2a |
Fever or leukocytosis and at least one of the following: Acute costovertebral angle pain or tenderness, suprapubic pain, or gross hematuria, new or marked increase in incontinence, urgency, or frequency AND A voided urine culture with 105 cfu/ml of a single predominant organism or two gram negative organisms, or a specimen collected by in and out catheter specimen with 102 cfu/ml of any number of organisms. |
3a |
Two or more of the following: Costovertebral angle pain or tenderness, new or marked increase in incontinence, urgency, frequency, suprapubic pain, or new gross hematuria
AND A voided urine culture with 105 cfu/ml of a single predominant organism or two gram negative organisms, or a specimen collected by in and out catheter specimen with 102 cfu/ml of any number of organisms. |
Criterion |
Symptomatic Urinary Tract Infection (SUTI) – CA-SUTI For residents with a chronic indwelling catheter (or removed within 48 hrs): |
1b. |
Any one of the following:
AND Urine specimen 105 cfu/ml of any organism(s) collected following placement of a new catheter (if current catheter has been in place >14 days) |
Criterion |
Asymptomatic Bacteremic Urinary Tract Infection (ABUTI) |
1 |
Resident with or without an indwelling urinary catheter has no signs or symptoms (i.e., no urgency, frequency, acute dysuria, suprapubic tenderness, or costovertebral angle pain or tenderness) AND A positive urine culture of 105 cfu/ml of a single predominant organism or two gram negative organisms, or a specimen collected by in and out catheter specimen with 102 cfu/ml of any number of organisms AND
A positive blood culture with at least 1 matching uropathogen microorganism to the urine culture.
**Uropathogen microorganisms are: Gram-negative bacilli, Staphylococcus spp., yeasts, beta-hemolytic Streptococcus spp., Enterococcus spp., G. vaginalis, Aerococcus urinae, and Corynebacterium (urease positive). |
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | Nimalie Stone |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-31 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy