NHANES_2013-14_Sup_Stat_A_091912_Clean_Copy_rev_100412[1] Special studies edits only
NHANES_2013-14_Sup_Stat_A_091912_Clean_Copy_rev_100412[1] Special studies edits only.doc
National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
OMB: 0920-0950
Supporting Statement A for Request for Clearance
National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey
OMB No. 0920-NEW
Contact Information:
Vicki Burt
National Center for Health Statistics (CDC)
Chief, Planning Branch
National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
3311 Toledo Road, Room 4211
Hyattsville, MD 20782
Email: [email protected]
Phone: 301 458-4127
FAX: 301-458-4028
September 19, 2012
Section A TABLE OF CONTENTS
Sections |
pages |
A. Justification.................................................................................................................................................. |
5 |
1. Circumstances Making The Collection Of Information Necessary............................................................... |
5 |
2. Purpose And Use Of The Information Collection......................................................................................... |
9 |
NHANES Examination.................................................................................................................................. |
9 |
a. Chronic Conditions…............................................................................................................................. |
10 |
b. Dietary Assessment............................................................................................................................... |
10 |
c. Osteoporosis, Vertebral Fractures and Aortic Calcification................................................................... |
10 |
d. Oral Health............................................................................................................................................ |
10 |
e. Taste and Smell..................................................................................................................................... |
11 |
f. Physical Activity Monitor (PAM)............................................................................................................. |
11 |
g. Upper Body Muscle Strength................................................................................................................. |
11 |
h. HPV Penile Swab in Males……………………………………………………………………………………. |
11 |
NHANES Laboratory Assessments.............................................................................................................. |
11 |
a. Urine Assessments............................................................................................................................... |
12 |
Urine Flow Rate......................................................................................................................................... |
12 |
b. Environmental Chemical Exposures..................................................................................................... |
12 |
c. Infectious Disease and Immunization Status Assessments................................................................. |
14 |
d. Nutritional Biochemistries, Hematologies And Other Nutrition Related Laboratory Measures.............. |
15 |
e. Biologic Specimen Banking................................................................................................................... |
16 |
f. Other laboratory...................................................................................................................................... |
16 |
The NHANES Interviews............................................................................................................................... |
17 |
a. Food Security And Nutrition Program Participation............................................................................... |
20 |
b. Dietary Supplement (DS) Use.............................................................................................................. |
20 |
c. Prescription Drug Use............................................................................................................................ |
20 |
d. Mental Health (Depression)................................................................................................................... e. Cognitive Functioning …….................................................................................................................... |
20 21 |
f. Weight History, Weight Self Image and Weight Related Behavior......................................................... |
21 |
g. Oral Health............................................................................................................................................ h. Muscles Pain and Injury........................................................................................................................ i. Urologic Health....................................................................................................................................... |
21 21 21 |
j. Pubertal Maturation............................................................................................................................... |
22 |
k. Other Interview Information.................................................................................................................... |
22 |
Responding to Emerging Public Health Issues, New Technology and Future Survey Options.................... Privacy Impact Assessment Information...................................................................................................... |
23 25 |
3. Use Of Information Technology And Burden Reduction............................................................................. |
25 |
4. Efforts To Identify Duplication And Use Of Similar Information................................................................... |
25 |
5. Impact On Small Businesses Or Other Small Entities................................................................................ |
26 |
6. Consequences Of Collecting The Information Less Frequently ................................................................. |
26 |
7. Special Circumstances Relating To The Guidelines For 5CFR1320.5........................................................ |
26 |
8. Comments In Response To The Federal Register Notice And Efforts To Consult Outside The Agency.... |
26 |
a. Federal Register Notice............................................................................................................................... |
26 |
b. Outside Consultation.................................................................................................................................... |
26 |
9. Explanation Of Any Payment Or Gifts To Respondents............................................................................. |
27 |
10. Assurance Of Confidentiality Provided To Respondents.......................................................................... |
29 |
11. Justifications For Sensitive Questions...................................................................................................... |
31 |
a. Social Security Number............................................................................................................................ |
31 |
b. CMS Health Insurance Claim Number..................................................................................................... |
32 |
c. Residency Status..................................................................................................................................... |
32 |
d. Other Content........................................................................................................................................... |
32 |
12. Estimates of Annualized Burden Hours and Costs.................................................................................... |
34 |
a. Time Estimates......................................................................................................................................... |
34 |
b. Cost to Respondents................................................................................................................................ |
35 |
13. Estimate Of Other Total Annual Cost Burden To Respondents Or Record Keepers............................... |
35 |
14. Annualized Cost To The Federal Government........................................................................................... |
35 |
15. Explanation For Program Changes Or Adjustments.................................................................................. |
36 |
16. Plans For Tabulation And Publication And Project Time Schedule.......................................................... |
36 |
17. Reason(S) Display Of OMB Expiration Date Is Inappropriate.................................................................. |
36 |
18. Exceptions to Certification for Paperwork Reduction Act Submissions.................................................... |
36 |
|
|
NCHS National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
This is a new request for data collection for three years for the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) and to modify selected sections of the NHANES (formerly OMB # 0920-0237 Expires November 30, 2012). The NHANES is a major ongoing source of information on the health and nutritional status of the civilian, non-institutionalized population of the United States. It is conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The NHANES has, to date, been authorized as a generic clearance; however, a change in accounting practice requires a shift to a newly-assigned clearance number for future full cycles of the survey. This request is for a new approval specifically to:
collect data for 2013-2014,
conduct activities related to data collection/processing through 2015,
conduct special studies to support data collection for 2015 and beyond,
conduct non-response studies if needed,
and to conduct other nutrition and health special projects (like the National Youth Fitness Survey (NYFS) for example)
A three year clearance is requested.
Brief summary of planned changes for the 2013-2014 NHANES
This request includes obtaining clearance to conduct NHANES Sample Person Household and Family Interviews; Mobile Examination Center (MEC) interviews and dietary interviews; the NHANES examination; Laboratory assessments; and Telephone follow-up interviews and other follow-up activities for 2013-14.
New for 2013-14
Adding laboratory assessments on chemicals related to tobacco use (7 categories of chemicals), plasma fluoride, water fluoride, serum estradiol, serum sex hormone-binding globulin, formaldehyde adducts, human papilloma virus swabs for men, and urinary Trichomonas vaginalis.
Adding new questions on environmental tobacco exposure, disability, spoken English proficiency, hepatitis, jaundice, and oral fluorosis. Added back from previous cycles are osteoporosis questions and 8 questions on menu labeling in restaurants.
Additionally, a few questions on assorted topics have been added as noted in the Changes in Questionnaire for 2013-14 table in section 2, the NHANES Interviews.
Adding a second home urine collection in addition to first morning void (provided that funding is available)
Modified for 2013-14
Cycling back from previous cycles are ethylene oxide, acrylamide and glycidamide laboratory assessments. Twelve new blood volatile organic compounds (VOCs) will be added and ten will cycle out. Two urinary VOCs will be added. The only halogenated phenolic compound to continue in 2013-14 will be serum pentachlorophenol.
Whole blood mercury, cadmium and lead will change from full sample to ½ sample of participants 12 and older.
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) will be modified to cycle back in scans of the hip and spine to estimate the prevalence of osteoporosis. Additionally, a lateral scan will be included to assess vertebral fracture risk and calcification of the aorta.
Oral health exam will include digital photos to assess fluorosis.
Questions on race, Hispanic origin, health, VOC exposure, reproductive health and supplemental nutrition assistance program.
Additionally, a few questions on assorted topics have been modified as noted in the Changes in Questionnaire for 2013-14 table in section 2, the NHANES Interviews.
Cycling Out for 2013-14
Tuberculin skin testing, respiratory health and hearing examination components and the hepatitis C follow-up questionnaire.
Laboratory assessments on cytomegalovirus, thyroid profile, osmolality, QuantiFERON-TB, and organochlorine pesticides will be cycled out.
The NHANES National Youth Fitness Survey will completed.
Collection of a genetic specimen for future testing.
Household questionnaire sections on tuberculosis, respiratory health, and hearing and occupational health questions related to respiratory health
Additionally, a few questions on assorted topics have been cycled out as noted in the Changes in Questionnaire for 2013-14 table in section 2, the NHANES Interviews.
Request for continued permission to conduct pilot or methodological testing for future NHANES will be submitted through a non-substantive change request. Special studies would be submitted for approval using a full revision or through a separate clearance request under a different OMB number.
Justification
1. Circumstances Making the Collection of Information Necessary
The National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), Division of Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (DHANES), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is seeking a three-year approval to conduct the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) (formerly OMB # 0920-0237 Expires November 30, 2012)), and specifically to collect data for 2013-2014; to conduct activities related to data collection/processing for 2015; to conduct special studies to support data collection for 2015 and beyond, and to conduct other health and nutrition studies.
Background
NCHS has conducted a series of health and nutrition surveys since the early 1960s. The surveys are unique in that physical examination data are obtained from national samples of the U.S. population. The NHANES examination is conducted in mobile examination centers (MECs) that travel to fifteen survey locations per year. NHANES data have been the cornerstone for numerous national health and nutrition policy and surveillance activities.
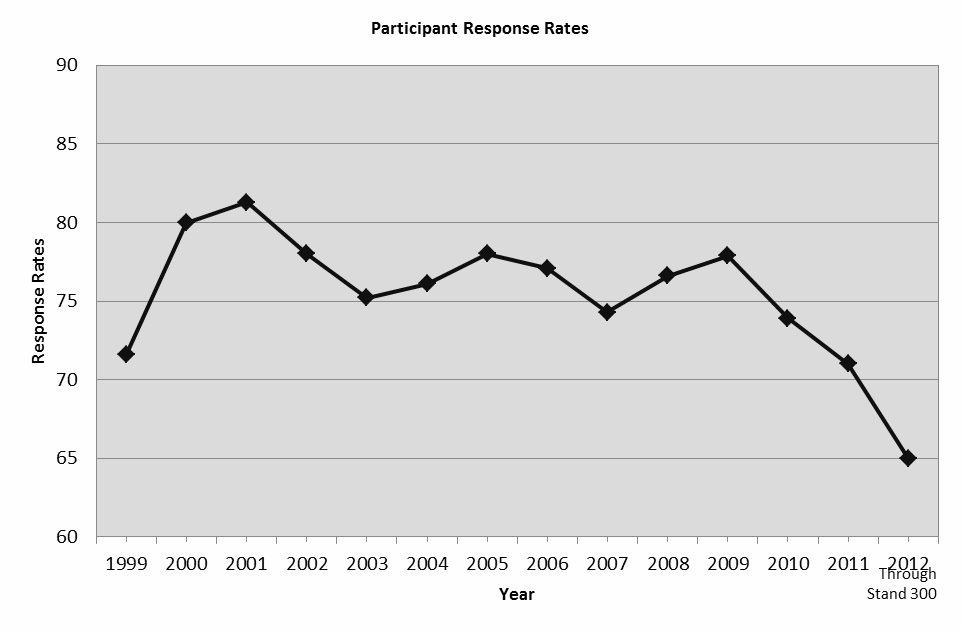
The NHANES were conducted on a periodic basis from 1971 to 1994. NHANES became a continuous, annual survey program in 1999. Each year, a nationally representative sample of the civilian, non-institutionalized U.S. population, all ages, is interviewed and examined. The response rates, for participants both interviewed and examined, for 2011 and 2012 to date are 71% and 65% respectively. Innovative recruitment methods and remuneration have contributed to the high response rates over the years. However, it is increasingly difficult to maintain high response rates.
NHANES data are released in two-year cycles. One-year estimates may be produced if there is a compelling public health need and if one year of data can provide a reliable estimate. Data from NHANES are posted on the NCHS website at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes.htm.
The continuous data collection requires that pilot tests of new or revised survey material be conducted during the ongoing data collection. NHANES will continue to request permission to conduct pilot and and other methodologic studies through the use of the OMB nonsubstantive change procedures.
A major advantage of continuous NHANES data collection is the ability to address emerging public health issues and provide objective data on additional health conditions and issues.
NHANES continues to report on major public health topics in a timely and efficient manner. Examples of contributions from NHANES data may be found on the NCHS/NHANES website.
The continuous survey design also makes earlier availability of the data possible. The first release of NHANES 2009-2010 data occurred in September 2011. In planning for 2013-2014 we have tried to take maximum advantage of the abilities of all software used in data collection to reduce data review and editing required after data collection. We hope to continue to meet our NCHS/NHANES data release date goals and have the greatest proportion possible of NHANES data released within a year of ending the data collection.
Authorization
Four public laws authorize or necessitate the collection of information about the health of the American people. Excerpts of these laws are in Attachment 1.
a) Section 306 of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 242k) directs the National Center for Health Statistics to collect statistics on subjects such as: the extent and nature of illness and disability of the population; environmental, social and other health hazards; and determinants of health.
b) Section 4403 (Joint Nutrition Monitoring And Related Research Activities) of the Food, Conservation, and Energy Act of 2008 (P.L. 110-234) specifies that the Secretary and the Secretary of Health and Human Services shall continue to provide jointly for national nutrition monitoring and related research activities carried out as of the date of enactment of this Act.
c) The Food Quality Protection Act of 1996 (P.L. 104-170) requires the implementation of surveys to collect data on food consumption patterns of infants and children and data on dietary exposure to pesticides among infants and children.
d) Title 21 – Food and Drugs, Chapter 9 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act
(21 USC 393) authorizes the collection of information to support the Food and Drug Administration’s objective to obtain current, timely, and policy-relevant consumer information to carry out its statutory functions.
The NHANES program, within NCHS, contributes to the mission of CDC by collecting objective data that are used to promote health by preventing and controlling disease and disability. CDC works with partners throughout the nation and the world to monitor public health, formulate and implement prevention strategies, develop health policies, promote healthy behaviors, and foster safe and healthful environments. In addition to the groups within the CDC, NCHS collaborates with over two dozen federal agencies to plan and fund the NHANES. The survey partners include numerous institutes of the National Institutes of Health, several programs within the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the Food and Drug Administration, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. NHANES data are used to assess environmental exposures; evaluate nutrition program and policy impacts; and estimate prevalences of health risk factors, chronic conditions, and infectious diseases.
Privacy Impact Assessment
A Privacy Impact Assessment was submitted on September 8, 2011.
Overview of the Data Collection System
For the 2013-14 NHANES a contractor will carry out the data collection. The Contractor’s responsibilities include all aspects of sample design and participant selection. This includes the following activities.
makes advance arrangements for each location
provides input on NCHS’s publicity/outreach methods and materials
sets up and maintains field offices and examination centers
translates all questionnaires as required
hires field staff
creates procedure manuals and training programs (including training in NCHS confidentiality guidelines and regulations)
trains the field staff
conducts all interviews in the households
performs all interview and examination procedures in the examination centers
designs and carries out quality control procedures and
transmits interview, examination and laboratory data to NCHS
Extensive details on the data collection procedures are included in Supporting Statement section “B. 2. Procedures for the Collection of Information” and in multiple attachments referenced there.
The following is a summary of the attachments related to the data collection procedures.
A pre-Advance Letter postcard and an Advance Letter (Attachment 4)
Household Screener Questionnaire (Attachment 9),
Household Relationship Questionnaire (Attachment 9),
Household/Family Questionnaire (Attachment 9)
Household Sample Person Questionnaire (Attachment 9)
MEC Data Collection Forms (Attachment 9)
Interview Informed Consent (Attachment 5)
Examination informed Consent (Attachment 5)
Stored Specimen Consent (Attachment 5)
Items of Information to be Collected
NHANES consists of the examination, conducted in the Mobile Examination Center (MEC), laboratory analytes, the household interview and follow-up activities, which take place after the MEC exam. Additional information about the information collected in the examination, laboratory assessments and interviews is shown below.
NHANES Examination
Cardiovascular Health
Diabetes Mellitus
Dietary Assessment
Oral Health
Sensory Performance
Physical Activity
Muscle Strength
Body composition
Osteoporosis
NHANES Laboratory Assessments
Renal and hepatic function
Environmental Chemical Exposures
Infectious Disease and Immunization Status Assessments
Nutritional Status
Biologic Specimen Banking
The NHANES Interviews
Demographic Information
Food Security And Nutrition Program Participation
Dietary Supplement (DS) Use
Prescription Drug Use
Mental Health
Cognitive Functioning
Weight History, Weight Self Image and Weight Related Behavior
Muscle Pain and Injury
Urologic Health
Alcohol Use
Cigarette and Tobacco Use
Reproductive Health and History
Pubertal Maturation
Information in Identifiable Form (IIF)
Information in identifiable form (IIF) is collected for linkage with other federal sources of data, to allow future recontact of participants and to notify participants of health test results. The identifiable information includes:
Name
Date of Birth
Social Security Number (SSN)
Medicare Beneficiary Number
Biometric Identifiers
Mother’s Maiden Name
Name of mother on birth certificate (including maiden name)
Name of father on birth certificate
Parent’s relationship to child
Child’s date of birth
Child’s sex
Child’s place of birth (hospital, city, county/township, state)
Mailing Address
Phone Numbers
Medical Information and Notes
Biological Specimens
Employment Status
Contact information for two people close to the respondent
More details on some of this information are found in “A.11 Justifications for Sensitive Questions”.
Identification of Website(s) and Website Content Directed at Children Under 13 Years of Age
There is no website content directed at children less than 13 years of age.
2. Purpose and Use of the Information Collection
The major objectives of NHANES are:
To estimate the number and percentage of persons in the U.S. population and designated subgroups with selected diseases and risk factors,
To monitor trends in the prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of
selected diseases,
To monitor trends in risk behaviors and environmental exposures,
To analyze risk factors for selected diseases,
To study the relationship between diet, nutrition and health,
To explore emerging public health issues and new technologies,
To establish a national probability sample of genetic material for future genetic research, and
To establish and maintain a national probability sample of baseline information
on health and nutritional status.
The NHANES consists of three primary methods of data collection: the NHANES examination, NHANES laboratory assessments and the NHANES interviews. Headings for components that are new or modified include the word “new” or “modified” in parentheses. The purposes and uses survey content are detailed below.
NHANES Examination
NHANES Examination changes for 2013-14 include:
Adding MEC examination components for self-collection of penile swab on males 14-59 For Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)
Modifying MEC examination components for oral health and dual x-ray absorptiometry
Cycling out the MEC examination components on hearing, respiratory health and tuberculin skin testing.
The following summarizes the NHANES examination for 2013-14. (See Attachment 9 for list of examination data collection forms.)
a. Chronic Conditions (Modified)
NHANES continues to monitor trends in the prevalence and treatment of many common chronic conditions with content included on the examination, laboratory and questionnaires.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD). The main elements of the CVD content on NHANES are measurements of blood pressure and blood total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, Triglyceride, and Apo (B) levels. A measure of aortic calcification will be obtained on participants ages 40 and older for the first time. This information will be collected during the dual X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) lateral scan.
Diabetes Mellitus (DM). NHANES continues to monitor DM via fasting and two-hour blood glucose assessments, fasting insulin and measurement of glycohemoglobin (HbA1c). The household interview will include questions about diabetes awareness and treatment.
Obesity. NHANES will continue to collect body measures of height, weight, circumferences and skinfold thicknesses (anthropometry) and Sagittal Abdominal Diameter. Body composition (lean and fat mass), will be measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) for those ages 8-59.
b. Dietary Assessment
All NHANES examinees are eligible for two dietary recall (DR) interviews. The first DR will be conducted in-person in the MEC and the second will be conducted by trained telephone dietary interviewers, during a follow-up phone interview. Additionally, a 24-hour intake of dietary supplements will be asked during both DRs.
c. Osteoporosis, Vertebral Fractures and Aortic Calcification (modified/new)
The hip and spine dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans last conducted in NHANES 2009-10 will resume for participants ages 40 and older. The scans will provide estimates of the prevalence of low bone mass and osteoporosis. Vertebral fracture risk and aortic calcification will be estimated through DXA scans of the lateral spine for the first time in NHANES. Fractures of the spine are the typical osteoporotic fracture and are prognostic of future fracture risk. In one study, only 1.5% of patients with vertebral spine fractures identified through lateral spine scans were aware they had these fractures.
d. Oral Health (Modified)
The target age group for the Oral Health component is participants ages 2 and older. The specific assessment a participant receives is dependent on their age. NHANES will collect information on tooth retention and loss, tooth decay, dental restorations, dental fluorosis, dental sealants, and periodontal health status. A rinsed specimen to test for oral Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) infection will continue. New for 2013-14 is Dental Fluorosis Imaging (DFI) which consists of digital photos for participants ages 6-19 to assess dental fluorosis. This is a more standardized method with multiple readers of the same images. This will assist CDC in exploring and developing cost effective surveillance measures for dental fluorosis. Such efforts are part of an overall strategy to balance continual caries reduction measures using fluoride in other delivery vehicles, such as school rinse programs, fluoridated toothpaste, etc. and the recommended levels of fluoride additive to U.S. public drinking water systems, while minimizing the prevalence of dental fluorosis in the US population.
e. Taste and Smell
Smell testing will be performed using the Brief Smell Identification Test (BSIT- also known as the CC-SIT) which is a well standardized "scratch and sniff" smell identification test. Taste testing will be performed by having the examinee taste a small amount of a test substance (bitter, salty) to determine if they can correctly identify the taste. This component continues for participants 40 and older.
f. Physical Activity Monitor
In addition to monitoring physical activity, the physical activity monitor (PAM) collects data on patterns of sleep. This component continues for participants 3 years and older.
g. Upper Body Muscle Strength
Upper body muscle strength testing (grip test) continues for participants ages 6 and older.
h. HPV penile swab in males (New)
Human papilloma virus (HPV) infection is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections in the U.S. Estimates of the prevalence of HPV infection in females via vaginal swabs have been part of the NHANES content since 2002. Recently a method to assess prevalence in males has become available. In October, 2009 quadrivalent HPV vaccine was licensed for males 9 through 26 years, although not included in the routine immunization schedule. Information on the prevalence of HPV infection in a representative sample of the male U.S. population is useful to describe characteristics of those with HPV infection, and provide estimates to measure impact of prophylactic vaccines.
NHANES Laboratory Assessments
Laboratory Assessment changes for 2013-2014 include:
Adding laboratory assessments on chemicals related to tobacco use, plasma fluoride, water fluoride, serum estradiol, serum sex hormone-binding globulin, formaldehyde adducts, human papilloma virus swabs for men and urine Trichomonas vaginalis.
Modifying laboratory assessments on whole blood mercury, and cadmium in lead from full sample to ½ sample of participants 12 and older.
Twelve new blood volatile organic compounds (VOCs) will be added and ten will cycle out. Two urinary VOCs will be added. The only halogenated phenolic compound to continue in 2013-14 will be serum pentachlorophenol.
Cycling out laboratory assessments on QuantiFERON-TB, cytomegalovirus, thyroid profile, urine osmolality, and organochlorine pesticides.
Cycling out collection of genetic specimens for future testing.
Cycling back from previous cycles are ethylene oxide, acrylamide and glycidamide.
Adding a second home urine collection in addition to first morning void (if funding is available)
The following summarizes NHANES laboratory assessments for 2013-14. (See Attachment 8 for detailed list of planned laboratory tests.)
Urine assessments (Modified)
Urine osmolality will be cycled out.
Urine Flow Rate
The urine excretion rate of an analyte is a more accurate measure of the exposure to environmental chemicals. The urine excretion rate (mg/min) is the product of the urine flow rate (mL/min) and the urine analyte concentration (mg/mL). Participants ages 6 and older will be asked to record their time of last void before coming to the MEC and then asked to void in the MEC where the time of collection and volume of the urine will be recorded and a urine flow rate will be calculated.
b. Environmental Chemical Exposures (Modified)
The NHANES environmental health laboratory assessments were expanded in 1999 in collaboration with the Division of Laboratory Sciences (DLS), National Center for Environmental Health (NCEH). It now includes more than 250 measures of environmental chemicals or metabolites in blood and urine specimens collected from survey participants. These NHANES data are the cornerstone of the CDC publication, The Fourth National Report on Human Exposure to Environmental Chemicals (URL: http://www.cdc.gov/exposurereport/). The most recent report, published in February, 2012 includes 246 chemicals.
In general, within classes of chemicals, analytes new in 2013-14 were added to the protocol because either a method became available to measure the analyte and/or an analyte was added to a panel that was already on the protocol.
Note that selected categories of environmental chemicals are analyzed using pooled specimens (See Attachment 8). This is done because of the expense of measuring the compounds in hundreds of subjects and because a high proportion of results are below the limit of detection (LOD) for some chemicals.
The environmental analytes include the following chemical categories (unless noted there are no changes in the chemicals within a category for 2013-14):
• Tobacco biomarkers (See changes below)
• Metals (See changes below)
• Phthalates and phthalate alternatives
• Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)
• Non-persistent pesticides (organophosphate insecticides, pyrethroid pesticides)
• Other pesticides/herbicides (See changes below)
• Perfluorinated compounds
• Environmental phenols
• Antiseptics
• Polychlorinated and polybrominated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans
• Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
• Polybrominated diphenyl ether
• Polychlorinated naphthalenes
• Volatile organic compounds (See changes below)
• Other (See changes below)
The uses of the NHANES environmental exposure information by the public health community include the following:
to determine the types of chemicals and concentration levels to which Americans are exposed
for chemicals with a known toxicity level, to determine the prevalence of persons above that toxicity level (e.g., blood lead > 10 µg/dL)
to establish reference ranges that may be used by state and local public health physicians and scientists to determine whether an individual or group has an unusually high exposure
to assess the effectiveness of efforts to reduce exposure to specific chemicals
to determine whether exposure levels are higher among minorities, children, women of childbearing age, and other vulnerable groups
to observe time trends in the levels of exposure within the population
to set priorities for human health effects research
Additional information on classes of environmental chemicals with changes in 2013-14 follows:
Tobacco biomarkers (Modified)
Cotinine: Cotinine, a metabolite of nicotine, has been measured in the blood as a biochemical marker to substantiate self-report of smoking and to define exposure to environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) on NHANES since NHANES III (1988-94).
NNAL: NNAL is a tobacco-specific nitrosamine which has been detected in the urine of smokers, and in many cases, in nonsmokers exposed to Second Hand Smoke (SHS). Total NNAL in urine samples will continue to be analyzed from NHANES 2013-14; measurement began in 2007-8.
Other tobacco biomarkers: (Modified) On June 22, 2009, the Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act, which gave the Food and Drug Administration regulatory authority over tobacco products, was signed into law. Significant parts of the legislation are focused on setting product standards. To successfully evaluate the impact that product standards might have on the exposure of smokers a system needs to be in place to monitor the exposure of smokers. The tobacco biomarkers, unless otherwise stated, are measured in a 1/3 NHANES subsample. In 2011 only about 15 percent of the adult NHANES participants were cigarette smokers. To increase the sample size of smokers for these chemicals all self-reported cigarette smokers within the other two 1/3 subsamples will be included in the laboratory analysis.
The categories of tobacco biomarkers included are:
Cotinine and Nicotine Analogs (New except serum cotinine)
Aldehydes (New)
Aromatic amines (New)
Heterocyclic amines (New)
Tobacco-specific nitrosamines (New except NNAL)
N-nitrosamines (New)
Heterocyclic amine hemoglobin adducts (New)
Metals (Modified)
Numerous metals are measured in the urine, whole blood and serum of NHANES participants. In 2013-2014 the only change will be to have a one-half sample of participants ages 12 and older, rather than a full sample, have the whole blood metals panel for Lead (Pb), Cadmium (Cd), Mercury (Hg) (total, inorganic, ethyl, methyl), Manganese (Mn) and Selenium (Se).
Organochlorine pesticides (Modified)
All are cycling out in 2013-2014.
Other pesticides/herbicides (Modified)
Only serum pentachlorophenol among halogenated phenolic compounds will continue in 2013-2014.
Volatile organic compounds (VOC) (blood and urine) (Modified):
Twelve whole blood VOCs are being added in 2013-2014. The current laboratory method has been expanded to measure 12 additional compounds without additional specimen being required. Ten of the additional (ethyl acetate, propyl bromide, methylcyclopentane, cyclohexane, benzonitrile, α,α,α-trifluorotoluene, chloroethane, methyl isobutyl ketone, tetrahydrofuran, vinyl bromide) are considered toxic, as are the continuing VOCs. Two, heptane and octane, are included as source specific biomarkers that are intended to help distinguish exposure from such sources as fuel, solvents and edible oil. Having heptane and octane is useful in distinguishing exposure sources and are important in interpreting VOC biomonitoring data. Ten whole blood VOCs are being cycled out in 2013-2014.
Additionally, in 2013-14 two urinary VOCs are being added to the protocol.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other chemicals (Modified)
We are cycling back in ethylene oxide, acrylamide and glycidamide which were last on the survey in 2009-2010. These all require packed red cell collection that had been discontinued while the QuantiFERON-TB was in the protocol. With the cycling out of QuantaFERON-TB we now have staff resources to again process packed red cells in the MEC.
Additionally, we are adding formaldehyde adducts to the NHANES protocol. Inclusion in NHANES will allow determination of national population estimates for hemoglobin adducts of formaldehyde. This will be the first assessment of formaldehyde adducts in a representative set of the US population and will establish baseline data and reference values, allowing assessment of trends over time. These baseline reference values will provide data on total exposure from formaldehyde (endogenous and exogenous) in the US population, which will be useful in studies to distinguish exogenous from endogenous sources and to assess unusual exposures.
c. Infectious Disease and Immunization Status Assessments (Modified)
New laboratory assessments added in 2013-14 are: Penile swab for human papilloma virus (HPV) in males ages 14-59 and urine trichomonas in participants 14-59. The cytomegalovirus in 1-5 year olds is cycling out.
HPV Prevalence Among U.S. Men (New)
The prevalence of current infection with HPV in US males is unknown. Assessment of the prevalence of current infection of HPV via DNA detection will contribute to measuring the impact of prophylactic vaccines introduced in 2009. NHANES has collected information on HPV DNA among females using a vaginal swab component since 2002. The specimen will be self-collected by male survey participants, 14-59 years old. See pilot study summary in B.4. Pilot Tests for 2013-14 NHANES.
Trichomonas vaginalis (New)
Trichomonas vaginalis infection is the most common curable sexually transmitted infection among women in the United States; it can cause inflammation that has been associated with an increased risk of HIV transmission and acquisition, and low birth weight. Prevalence in adult men has never been measured in a nationally representative sample. Recently a highly sensitive diagnostic test was FDA-approved for clinical use. And due to the widespread availability of a simple treatment (metronidazole in a single dose), including T. vaginalis testing in NHANES would give the first national data about the prevalence of the infection in men and updated data in women ages 14-59. This will also provide important information about demographic, behavioral, and health-related risk factors associated with the infection.
Laboratory tests for the following infectious diseases remain unchanged from 2011-12:
Chlamydia trachomatis
Hepatitis profile
Herpes simplex 1 and 2
Human immunodeficiency virus
HPV (Oral rinse and vaginal swab)
d. Nutritional Biochemistries, Hematologies and other nutrition related analytes (Modified)
One new laboratory analyte added in 2013-14 will be plasma fluoride, for participants ages 6-19, to accompany the enhanced Oral Health fluorosis examination component. Water fluoride levels will be measured in the tap water of homes for participants ages 0-19 as described below in f. Other laboratory.
Laboratory tests for the following nutrition biomarkers remain unchanged from 2011-12:
Complete blood counts
Serum and red blood cell folate
Standard biochemical profile
Serum lipids
Urinary iodine
Vitamins D and B-12
Methylmalonic acid
Caffeine
Omega-3 fatty acids continue in 2013-14
e. Biologic Specimen Banking (Modified)
In 2013-14 a genetic specimen will not be collected for future use.
Serum, plasma and urine continue to be stored for future research. The availability of stored biologic specimens from a representative sample of the U.S. population provides the scientific research community with a potential resource for the measurement of new and evolving laboratory tests for emerging diseases, risk factors, and environmental exposures. NCHS solicits proposals for use of the stored specimens. A technical panel will review and approve all proposals. All uses of stored specimens are subject to review and approval by the NCHS Ethics Review Board and the NCHS Confidentiality Officer. All unused serum from laboratories will be stored for potential additional analyses.
f. Other laboratory (Modified)
Three new tests in 2013-14 will be the assessment of fluoride levels in tap water, serum estradiol, and sex hormone binding globulin.
Water fluoride level (New)
Community water fluoridation has been identified as one of the 10 most significant public health achievements in the U.S. in the past century and is a key disease prevention activity for CDC. Dental fluorosis occurs when an individual has been exposed to higher levels of fluoride during tooth development. Fluorosis is a condition that affects the dental enamel, resulting in mild, white striations in its mildest form, through to brown pitting or even complete loss of the enamel in its most severe forms. It has been shown that there is a relationship between water fluoride concentration and the extent of fluorosis. Tap water samples will be collected in the home of participants ages 0-19.
Serum estradiol (New)
Serum estradiol will be measured in NHANES participants ages 6 and older. Inclusion in NHANES will provide important reference ranges for people of all ages and both genders, as well as varying race-ethnicities. The Division of Laboratory Sciences (DLS) at CDC convened a workshop on March 17-18, 2008 to discuss current needs and problems in steroid hormone testing, with special focus on testosterone and estradiol, and to discuss CDC's activities to improve and standardize measurements obtained with steroid hormone tests. More than 60 experts from the research and clinical community, industry, assay manufacturers, and government attended the workshop. The Endocrine Society, American Society of Clinical Endocrinologists, American Association of Clinical Chemistry, and American Society for Reproductive Medicine were represented. The presenters and workshop participants emphasized that measurement of estradiol is highly valuable in assessing disease risk, diagnosing disease, and monitoring treatment. However, lack of generally accepted reference ranges limits progress in disease research and translating valuable research findings into information useful for patient care and disease management, as stated in several editorials and research publications.
Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) (New)
Serum SHBG will be measured on all participants ages 6 and older. SHBG is a glycoprotein that binds to testosterone (T) as well as other androgens and estrogens. It is essential in the investigation of hormone status and monitoring of stimulatory, suppressive or replacement therapy in children, adults and older adults of both sexes. Since 2011-12 NHANES has measured total testosterone. Addition of the SHBG will permit calculation of the free testosterone levels. The Endocrine Society recommends the calculation of free testosterone using SHBG and total testosterone values, because of the unreliability of current homogenous, free testosterone assays. No information is available about total and free testosterone levels in the U.S. population, especially in children and women. Knowledge about these levels in the U.S. population would allow for the verification of proposed normal ranges.
Laboratory tests for the following biomarkers remain unchanged from 2011-12:
Standard biochemical profile (kidney, liver function)
Serologic testing for celiac disease
Serum total testosterone levels
The NHANES Interviews
The topics presented in this section are questionnaire data, collected as stand-alone questionnaire sections or to complement NHANES examination or laboratory content. The questions are asked in the home or the MEC. Household interview changes are summarized in the following table. Details about select sections follow. The complete questionnaires are found in Attachment 9 where the table of contents within the attachment lists each questionnaire section by section name with a corresponding 3 letter abbreviation.
Most sections of the NHANES questionnaire remain unchanged from 2011-12. The tables below summarize changes for 2013-14 with a brief description of the change and rationale for it. Below the table is some discussion of specific sections.
The following table summarizes the NHANES questionnaire changes for 2013-14. (See Attachment 9 for all NHANES questionnaire sections and items.)
Screener Questionnaire
Section Name and (3 Letter ID) |
Descriptions |
Screener Module 1 (SCQ) |
|
Sample Person Questionnaire
Section Name and (3 Letter ID) |
Descriptions |
Respondent Information (RIQ) |
|
Health care utilization (HUQ) |
|
Tuberculosis (TBQ) |
|
Medical condition (MCQ) |
|
Hepatitis |
|
Disability |
|
Blood pressure (BPQ) |
|
Osteoporosis (OSQ) |
|
Respiratory health (RDQ) |
|
Audiometry (AUQ) |
|
Chemosenses (CSQ) |
|
Oral Health (OHQ) |
|
Diet behavior and Nutrition (DBQ) |
|
Weight history (WHQ) |
|
Smoking (SMQ) |
|
Occupation (OCQ) |
|
Demographics (DMQ) |
|
Dietary supplements and antacids (DSQ) |
|
Prescription Drugs (RXQ) |
|
Family Questionnaire
Section Name and (3 Letter ID) |
Descriptions |
Smoking (SMQ) |
|
Income (INQ) |
|
Food Security (FSQ) |
|
MEC Questionnaire - CAPI
Section Name and (3 Letter ID) |
Descriptions |
Volatile Toxicant (VTQ) |
|
Smoking (SMQ) |
|
Reproductive health (RHQ) |
|
Weight history (WHQ) |
|
MEC Questionnaire - ACASI
Section Name and (3 Letter ID) |
Descriptions |
Smoking and tobacco use (SMQ) |
|
Sexual behavior (SXQ) |
|
Follow-up Questionnaire - Telephone
Section Name and (3 Letter ID) |
Descriptions |
Hepatitis C- Follow-up (HCQ) |
|
Food Security and Nutrition Program Participation (Modified)
The 2013-14 NHANES continues to include a food security section (FSQ) that contains the 18-item U.S. Household Food Security Survey Module (US FSSM) and individually-referenced food security questions for respondents 12 and older. Questions on participation in the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), formerly known as the Food Stamp Program are also included in the FSQ section. SNAP and Household and Child Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants and Children (WIC) data are collected, for infants and children, in the Family and Sample Person interviews. WIC data for women of childbearing age are collected in the reproductive health section of the MEC interview. Based on a project linking NHANES data to administrative data in Texas, during periods that included the last two versions of the SNAP questions, this section was changed to include elements of both previous versions to more fully capture recipients of the SNAP program.
b. Dietary Supplement Use
NHANES continues to collect dietary supplement (DS) use information on all respondents during the household interview. The information collected on DS and antacid use pertains to all DSs and antacids taken in the past 30 days. This includes the name of the specific supplement, duration and frequency of use, and the amount taken. Since 2007-2008 NHANES has collected a 24 hour supplement intake recall after both of the dietary recalls.
c. Prescription Drug and Aspirin Use
NHANES continues to collect information on all prescription medications (RXQ) used by participants during the past month. The duration of drug use and reason for use are also collected. Prevention of cardiovascular disease is the most critical public health issue in the U.S. Taking low-dose aspirin regularly has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke. In addition, numerous studies have suggested that aspirin may hold promise in helping to prevent cancer. Since 2011-12, eleven questions have been asked about the prophylactic use of aspirin.
d. Mental Health (Depression)
NHANES continues to administer a depression screener questionnaire (DPQ) to all respondents 12 years and older. Depression is being assessed using the Patient Health Questionnaire (“PHQ-9”). This screening instrument has been validated against independent structured diagnostic interviews in both clinical and general population studies. It serves both as a depression severity measure as well as a diagnostic instrument for the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edition (DSM-IV) depressive disorders. The PHQ-9 refers to the previous 2-week interval and consists of 9 items of depression symptoms and question on functional impairment
e. Cognitive Functioning
The Cognitive Functioning evaluation continues unchanged from 2011-12. Cognitive functioning was assessed in NHANES 1999-2002 during the household interview portion of the survey, and as an examination component in NHANES III (1988-94). Its inclusion in NHANES provides the ability to investigate prevalence and co-morbidities of declining cognitive functioning with other self-reported and objective physical measures.
Participants ages 60 and older are administered three tests:
The Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease (CERAD) Word List Learning Test assesses recall and memory. The examinee is asked to read aloud 10 words, one at a time, displayed on the computer screen. There are three trials that are administered identically, except for the order of the words. Ten words are presented at a rate of 2 seconds between each word. After the words are presented, the examinee is asked to recall as many of the words as possible within 90 seconds. A fourth recall occurs after the other two tests are administered.
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) digit symbol subtest evaluates attention and processing speed. It involves substituting a symbol for a random succession of numbers ranging between 1 and 9. This was previously used in NHANES III and the 1999-2002 NHANES.
The Animal fluency Test is designed to assess categorical verbal fluency, a component of executive function. The participant is asked to name as many animals as they can in 60 seconds.
f. Weight History, Weight Self Image and Weight Related Behavior (Modified)
NHANES continues to collect data for participants 8 and older on weight history and weight self-image. The information on 8-15 year olds will be used with socio-demographic and related nutrition and health information to develop programs to prevent and manage overweight among children and adolescents. The weight history questions, for participants 16 years and older, is designed to permit evaluation of height loss with aging and weight status (stable or cyclical) over time. Added 1 new question about “yo-yo” dieting, cycled out 7 questions about rarely reported behaviors and modified 1 question by adding a response category.
g. Oral Health (Modified)
Ten new questions primarily related to dental fluorosis have been added in 2013-14.
h. Muscle Pain and Injury
Since 2011-12, a short series of questions have been administered during the MEC interview on recent muscle injury or strenuous exercise. These questions make the Creatinine Phosphokinase (CPK) laboratory data more useful.
i. Urologic Health
Self-reported information on urinary incontinence and nocturia will continue to be collected. These data are collected during the MEC CAPI interview. NHANES will provide national estimates on the prevalence of urinary incontinence and quality of life issues for those affected.
j. Pubertal Maturation Self-assessment
The pubertal maturation self-assessment questions are administered during the MEC Audio Computer-Assisted Self-Interview (ACASI) interview, for participants 8 to 19 years old. They continue from 2011-12. These data will improve the utility of NHANES clinical, biomarker, and questionnaire data. Information on pubertal maturation status is useful to include in NHANES since the endocrine changes manifested in secondary sexual characteristics underlie many physiological changes during puberty. Sexual development correlates more closely with physical changes such as height, weight, bone density and certain biochemical markers than chronological age, thus facilitating assessment of body composition in pre-adolescence and adolescence. Furthermore, early sexual maturity has been found to closely correlate with self-image and sexual behaviors, which are also assessed in the MEC interview.
k. Other Interview Information
The NHANES interviews include questions that are also asked in other population surveys. Typically, these questions are used as covariates in data analyses rather than to compute national prevalence estimates. Some examples in NHANES are the Demographic (DMQ), Income (INQ), Health Insurance (HIQ), Housing Characteristics (HUQ), Health Care Utilization (HCQ), and Occupation (OCQ) sections.
Additional questions are included in the survey to assess such topics as reproductive health, risk behavior, and diet behavior in the U.S. population. Brief descriptions of the major NHANES supporting interview sections are provided.
Alcohol Use: Questions on alcohol use are included for all participants 12 years and older. The questions are designed to ascertain quantity and frequency of use for quantifying alcohol intake; to identify nondrinkers, light drinkers, and former heavy drinkers; and to determine the frequency of heavy drinking occasions among current drinkers. Data on alcohol intake during the previous day will also be obtained as part of the 24-hour dietary recall.
Cigarette and Tobacco Use (Modified): Participants ages 12 and older will be asked questions about their history of cigarette and tobacco use. Questions about tobacco use in the last 5 days will be asked to aid the interpretation of the serum cotinine data. Eight questions about second hand smoke exposure have been added and are asked of all ages. Some new smokeless tobacco products have been added to the questionnaire in 2013-14. Questions on rarely reported items, for which the sample size of NHANES was inadequate, were removed.
Reproductive Health and History (Modified): Information about women’s reproductive health is essential for evaluating their health status and the relationship of menopausal status to chronic disease. A personal private interview is conducted with females 12 years and older. Information is obtained on age at menarche, pregnancy history, history of breast feeding, history of hysterectomy and oophorectomy, menopausal status and symptoms of menopause, and use of exogenous hormones (oral contraceptives, hormone replacement therapy). To decrease the burden of this section and to make the data more relevant to current NHANES content, six questions were removed and 14 were simplified. Three new questions related to fertility were added.
Sexual Behavior (Modified): The information on sexual behavior is key to reducing the risk of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Participants 14 -59 years are asked about age of first intercourse, number of sexual partners, use of condoms, and history of sexually-transmitted diseases. The questions on sexual behavior are included to provide for targeting risk reduction efforts; assessing the results of such efforts; and improving current understanding of the epidemiology of STDs. One new question, about age of first onset, was added as a follow-up to those reporting genital warts. Participants 60-69 are asked a selected subset of these questions including, types of sexual behavior they have engaged in, age of first intercourse, and number of sexual partners in their lifetime.
Drug Use: Questions on drug use are included for participants 14-59 years. The questions focus on lifetime use of street drugs or recreational drugs and the intravenous use of these drugs. Additional questions on age of initiation of drug injection, duration of injection drug use, and lifetime history of drug treatment are included in this section. The use of drugs has been demonstrated to be a risk factor for sexually transmitted diseases. Injection drug use is also a risk for blood borne pathogens such as HIV, HBV and HCV. Information on drug use is necessary along with sexual behavior questions to develop a profile of risk-taking behavior. Participants ages 60-69 will be asked a selected subset of these questions.
Responding to Emerging Public Health Issues, New Technology and Future Survey Options
One objective of the continuous NHANES is to provide a mechanism to respond to emerging and re‑emerging public health topics. The content of the survey is modified biannually to accomplish this objective. Survey modifications may include removing or “cycling out” survey content that has been in the survey for multiple years, modifying existing survey content to include new target age groups, modified data collection methods, the use of updated technology, and the addition of new interview, laboratory, and examination components and topics. The NHANES Program utilizes a public proposal solicitation process to develop recommendations for survey content. The process and proposal guidelines are posted on the NHANES website (http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/about/major/nhanes/research_proposal_guidelines.htm). NCHS disseminates this information to survey collaborators, federal agencies, and NHANES data users.
The Division of Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (DHANES) anticipates that new technology will be adopted during future data collection activities. NCHS staff design, plan, implement and evaluate numerous methodology projects to evaluate new technology proposed for use in NHANES. For example, new questionnaire items or sections and examination component protocols are often pre-tested in-house and in the field prior to full survey implementation. This process may include cognitive testing of questions as well as pilot testing of content in the actual NHANES environment. Past experience has shown that one to three years of preparatory work may be required to fully test and prepare a new NHANES examination component for the survey. New equipment must be installed, calibrated, and tested; software must be installed and tested; database variables and data processing procedures must be developed and documented; data security provisions must be developed, tested, and approved; and training manuals, staff training, and quality control procedures must be developed.
Pilot Tests for the 2013-14 NHANES
Several protocols included in the 2013-2014 NHANES were tested under OMB No. 0920-0237. As such, the burden for these tests is not requested in this current package. The pilot test for HPV has been completed and the pilot study for Fluorosis will be completed before the end of February, when OMB No. 0920-0237 expires.
NHANES Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Prevalence Among U.S. Men Pilot Study (ages 14-59). This component was pilot tested in July-August 2012. Ninety-six percent of 14-59 year old males who were asked agreed to collect a specimen.
NHANES Dental Fluorosis Imaging Project Feasibility Study (ages 6-19)
If the pilots are successful they will be included in the NHANES 2013-14. A report of each test is produced after completion of the pilot test.
Methodological Studies to be conducted during the approval period for the NHANES 2013-14
NHANES expects to conduct several methodological studies during 2013-14. Possibilities include tests of :
24 hour dietary recall and/or MEC interview via web-conferencing technology.
Collection of blood spot specimens on NHANES participants.
Food Assistance Program Linkage Studies.
A 24 hour urine collection on a sample of NHANES participants to evaluate feasibility.
For these projects and any currently unforeseen methodological studies, a non-substantive change package would be submitted to OMB before undertaking the study.
Pilot Tests to be conducted in 2013-14 for the 2015-16 NHANES
The survey expects to continue conducting pilot studies for future cycles of continuous NHANES. During 2013-2014, pilot studies will be conducted to prepare for implementation during NHANES 2015-2016. A non-substantive change package would be submitted to OMB before undertaking any pilot study.
Special Studies and Additional Health and Nutrition Examination Studies
This request permits NCHS the option to plan and test additional Health and Nutrition Examination Studies yet to be proposed. Such a project would be an additional data collection effort focused on a specific age group and/or topic. The interview and/or examination content would be all, or a subset, of the concurrent NHANES content with minor differences. An example might be to sample children such as was done for the NHANES National Youth Fitness Survey. Another example might be a sample of adults that receive an abbreviated examination plus a 24-hour urine in an independent sample from the current NHANES (e.g., a possibility under consideration is a separate national sample of as many as 1500 participants who receive a 24 hour urine, dietary recall, venipuncture, blood pressure, height, and weight).
CDC is including burden hours to accommodate such special studies (Attachment 11) involving up to 2,500 participants (Section A12, Table 1, line 2), however, CDC understands that such special studies would require submission of a full revision to OMB for clearance.
Nonresponse Investigation
Nonresponse investigations under DHHS task order contracts or other contract mechanisms may be necessary should nonresponse rates make that advisable. Details of any such investigations that involve public participation will be described under a non-substantive change package using burden from pilot of methodological studies.
Privacy Impact Assessment Information
A Privacy Impact Assessment was submitted September 8, 2011. The NHANES continues to collect personal identifying information, on a confidential basis, needed to re-contact respondents and to match respondents to administrative records such as the National Death Index. The ability to track respondents and match to other records greatly expands the usefulness of the data at very low cost.
Only those NCHS employees, specially designated agents, and our full research partners, who must use the personal information for a specific purpose, can use such data.
The collection of information in identifiable form requires strong measures to ensure that private information is not disclosed in a breach of confidentiality. All NCHS employees as well as all contract staff receive appropriate training and sign a “Nondisclosure Statement.” Staffs of collaborating agencies are also required to sign this statement and outside agencies are required to enter into a more formal agreement with NCHS. The transmission and storage of confidential data are protected through procedures such as encryption and carefully restricted access.
3. Use of lnformation Technology and Burden Reduction
The majority of NHANES data are collected from respondents electronically. NHANES uses survey information technology architecture (SITA) that supports fully automated and integrated information technology. SITA provides increased capabilities that allow processing of complex data with significantly less editing than in previous NHANES surveys.
SITA provides NHANES with access to all data that are collected, much of which is available in real-time. The nature of the survey requires that data be accessible at multiple sites including contractor facilities, MECs, field offices, laboratories, and NCHS headquarters. SITA supports: 1) survey planning and design, 2) data collection, 3) data receipt, control and quality assurance, 4) reporting of survey results to survey participants, 5) data review, editing and analysis, 6) generation and documentation of public use data products, 7) tracking of survey respondents and 8) generation of status reports on all aspects of the survey.
There are no legal obstacles to reducing the burden.
4. Efforts to Identify Duplication and Use of Similar Information
NHANES is a unique source of health information on the U.S. population. Each year health interview and examination data are obtained. There are no other studies that collect the detailed health, dietary, laboratory and examination data that NHANES does. Duplication of effort is avoided through contacts and discussions with numerous Federal Government agencies during the content development and planning stage of NHANES. The organizations contacted are listed in Attachment 3 of this clearance request.
5. Impact on Small Businesses or Other Small Entities
Only individuals will be asked to participate. No small businesses will be involved in this data collection.
6. Consequences of Collecting the Information Less Frequently
The continuous nature of the NHANES is necessary for several reasons. First, many of the data items collected in the NHANES are used for annual tracking of health events and circumstances, including tracking of the National Objectives for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention. Second, the continuous design makes it possible to aggregate data over longer periods of time to include enough cases to study rare events and small populations. Third, nutrition monitoring legislation explicitly calls for continuous coverage to monitor nutrition changes as they occur (see Attachment 1). Fourth, a continuous survey is more cost effective because it makes possible a stable field staff, which increases the quality of the data and avoids start-up and shut-down costs. Reducing the frequency of data collection would undermine all of these desirable features of the NHANES.
Respondents are asked to respond to the NHANES only one time.
7. Special Circumstances Relating to the Guidelines for 5CFR1320.5
This data collection fully complies with regulation 5CFR1320.5.
8. Comments in Response to the Federal Register Notice and Efforts to Consult Outside the Agency
a. Federal Register Notice
In compliance with 5 CFR 1320.8(d), a notice soliciting comments on the collection for NHANES was published in the Federal Register on May 15, 2012, volume 77, number 94, pp. 28599 - 28600. See Attachment 2a for a copy of the notice. Public comments were received. See Attachment 2b for further details.
b. Outside Consultation
The content of NHANES is developed with input from numerous DHHS agencies (including NIH, FDA, and CDC), several USDA entities (ARS, ERS, and FNS), other Federal agencies, non-government organizations, and individuals. The DHHS Data Council has been kept informed of the future NHANES plans. The DHHS Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation has been briefed about the NHANES. Additionally, NCHS’s Board of Scientific Counselors has been informed of future planning.
NHANES is a collaborative undertaking. Broad input is sought from data users and interested parties to maximize the utility of the survey data. Extensive consultations occur in meetings with NHANES collaborators and interested agencies. A formal research proposal solicitation process occurs prior to content planning and development.
The major efforts taken to support collaboration processes are described below. New content proposals were solicited for the 2013-2014 data collection cycle by publishing the proposal guidelines on the NHANES website. Members of the NHANES user community received letters inviting them to submit research proposals. Correspondence was sent to dozens of persons who have expressed interest in being kept informed of NHANES activities. Over 20 proposals were received in response to this solicitation.
NCHS staff made numerous presentations throughout the year at major medical and public health professional meetings as well as internal meetings organized by Federal agency research staff. The meetings provide an excellent forum for updating stakeholders on survey research activities and data products.
In August 2011, USDA’s Agricultural Research Service (ARS) and DHANES organized a meeting of stakeholders who would be interested in the two days of dietary recall collected on NHANES, referred to as What We Eat in America (WWEIA) by ARS. The joint budgets of ARS and DHANES could not support two days of dietary data in 2012 and beyond. Options such as reducing the sample size of participants providing the second day of dietary recall were discussed. As an outcome of that stakeholders meeting the Food and Nutrition Service, USDA provided funding in 2012 to support two days of dietary recall and are expected to continue for 2013.
9. Explanation of any Payment or Gifts to Respondents
To maximize response rates for the examination, NHANES participants have been remunerated for their examination participation since the 1970s. Remuneration began after a study was conducted to test the effect of remunerating sample persons who participated in NHANES I. The response rate for those who were told they would receive remuneration was 82%. The response rate for those who were not told they would receive remuneration was 70%. Results of the study were published as "A Study of the Effect of Remuneration Upon Response in the Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, United States," Vital and Health Statistics, Series 2-No.67. During NHANES II another study was conducted, this time on the effect of increasing remuneration. It showed that those who were told they would receive $20 after their examination had an examination rate of 79% while those who were told they would receive $10 had an examination rate of 74%.
In NHANES III (1988‑94) differential remuneration was successfully used to get participants to come to the examination session (morning, afternoon, or evening session) they were randomly assigned to. In prior NHANES, much data were lost due to failure of the participants to attend the randomly assigned session.
Continuous NHANES began in 1999 and the response rate was only 72%, therefore a remuneration study was undertaken in 2000. The basic comparison groups were the current level of remuneration plus a level approximately 50 percent higher. After 5,900 observations the overall response rate was the same in both groups. Interviewers were not blinded to the remuneration and their primary objective is to get the participant to the examination center. Comments made during the debriefing suggested that interviewers spent more time convincing the lower remuneration group to be examined.
The response rates for participants examined for 2011 and 2012 to date are 71% and 65% respectively. The response rates to the examination from 1999-2012 are presented in the graph
below.
 Below
are the 2013-4 NHANES remuneration rates. They are the same as those
in 2011-12.
Below
are the 2013-4 NHANES remuneration rates. They are the same as those
in 2011-12.
Examination incentive
Subgroup |
2013-14 Incentive |
16 and older assigned session |
$125 |
16 and older not assigned session |
$90 |
12-15 assigned session |
$75 |
12-15 not assigned session |
$60 |
Under 12 |
$40 |
Post-primary examination incentive
Dietary Phone Follow Up $30
Urine collection in the home $40
Physical Activity Monitor $40
If a family has one or more children under the age of 16 and no parent/guardian has been selected into the sample, a $20 incentive is provided to accompany the child(ren) to the MEC. If participants must hire a sitter to care for children, elderly, or handicapped persons so that the participant can leave their home to be examined in the MEC, they are reimbursed at $5.25 an hour up to 6 hours for a sitter. Participants also receive a transportation allowance for driving to the MEC, or for when a taxi is provided.
Participant transportation allowance
TRANSPORTATION ALLOWANCE 2007–2012 |
||
SP Transportation Allowance Mileages to MEC |
Cities |
Rural Areas |
<16 miles |
$30 |
$25 |
16–30 miles |
$45 |
$40 |
31–59 miles |
$55 |
$50 |
>60 miles |
$70 |
$65 |
Other efforts are made to maintain and increase response rates on a day-to-day basis (See Section B. 3. Methods to Maximize Response Rates and Deal with Nonresponse).
Potential remuneration changes may be requested during the 2013-14 NHANES. In the future, it may be necessary to test methods to encourage more participants to accept weekday MEC appointments, to avoid overly crowded exam sessions. Currently, weekend appointments are frequently filled within the first two weeks at an exam site. As more participants are scheduled for exams, the already full weekend exam sessions may become overbooked with participants who are only available on weekends. Overbooking can result in incomplete data due to not having enough time to get all participants through their schedule of exams. Finding incentives to encourage participants to accept a weekday examination will ease the strain on the weekend sessions and increase the likelihood of having complete data on everyone who is MEC examined. NCHS is instituting and considering other non-monetary mechanisms to shift more appointments to weekdays. For example, modifying exam sessions hours on select days of the week to avoid participants having to travel during rush hours or changing exam schedules so that some sessions include the lunch hour to reduce the amount of leave participants might have to take off from work. If NCHS is unsuccessful in shifting more appointment to weekdays we may return to OMB with a change request for differential remuneration based on the day of the week. That is, offering higher remuneration for weekday MEC visits than for weekend appointments to make a weekday appointment more attractive to participants with schedules flexible enough to attend either a weekend or weekday MEC session.
10. Assurance of Confidentiality Provided to Respondents
The Privacy Act of 1974 (5 U.S.C. 552a) “requires the safeguarding of individuals”, and Section 308(d) of the Public Health Service Act (42 U.S.C. 242m) requires the safeguarding of both individuals and establishments against invasion of privacy. Contractors who collect information identifying individuals and/or establishments must stipulate the appropriate safeguards to be taken regarding such information. The Privacy Act also provides for the confidential treatment of records of individuals, which are maintained by a Federal agency according to either individual’s name or some other identifier. This law also requires that such records in NCHS are to be protected from “uses other than those purposes for which they were collected.”
The confidentiality of individuals participating in NHANES is protected by section 308(d) of the Public Health Service Act (42 USC 242m), which states:
"No information, if an establishment or person supplying the information or described in it is identifiable, obtained in the course of activities undertaken or supported under section...306,...may be used for any purpose other than the purpose for which it was supplied unless such establishment or person has consented (as determined under regulations of the Secretary) to its use for such other purpose and (1) in the case of information obtained in the course of health statistical or epidemiological activities under section...306, such information may not be published or released in other form if the particular establishment or person supplying the information or described in it is identifiable unless such establishment or person has consented (as determined under regulations of the Secretary) to its publication or release in other form..."
In addition, legislation covering confidentiality is provided according to section 513 of the Confidential Information Protection and Statistical Efficiency Act of 2002 (CIPSEA) (PL-107-347), which states:
“Whoever, being an officer, employee, or agent of an agency acquiring information for exclusively statistical purposes, having taken and subscribed the oath of office, or having sworn to observe the limitations imposed by section 512, comes into possession of such information by reason of his or her being an officer, employee, or agent and, knowing that the disclosure of the specific information is prohibited under the provisions of this title, willfully discloses the information in any manner to a person or agency not entitled to receive it, shall be guilty of a class E felony and imprisoned for not more than 5 years, or fined not more than $250,000, or both.”
Consequently, all information collected in NHANES will be kept confidential, with an exception for suspected child abuse.
Privacy Impact Assessment Information
The NCHS Privacy Act Coordinator and the NCHS Confidentiality Officer have reviewed this package and have determined that the Privacy Act is applicable. This study is covered under Privacy Act System of Records Notice 09-20-0164 (“Health and Demographic Surveys Conducted in Probability Samples of the U.S. Population”).
An Advance Letter (Attachment 4) is mailed to each household in the sample segments announcing the impending arrival of an NHANES interviewer and explaining the confidential treatment of their responses. The informed consent documents for the interview, the
examination and the stored specimens each repeat the confidentiality assurance (Attachment 5).
It is the responsibility of all employees of NCHS, including NCHS contract staff, to protect and preserve all NHANES data (this includes all oral or recorded information in any form or medium) from unauthorized persons and uses. All NCHS employees as well as all contract staff have received appropriate training and made a commitment to assure confidentiality and have signed a “Nondisclosure Affidavit”. Staffs of collaborating agencies are also required to sign this statement and agencies are required to enter into a formal Designated Agent Agreement with NCHS before access to non-public data is permitted. It is understood that protection of the confidentiality of records is a vital and essential element of the operation of NCHS, and that Federal law demands that NCHS provide full protection at all times of the confidential data in its custody. Only authorized personnel are allowed access to confidential records and only when their work requires it. When confidential materials are moved between locations, records are maintained to insure that there is no loss in transit and when confidential information is not in use, it is stored in secure conditions.
NCHS policy requires physical protection of records in the field, and has delineated these requirements for the data collection contractor. The contractor also has its own policy and procedures regarding assurance of confidentiality and a pledge that all employees involved in NHANES must sign. The contractor provides all safeguards mandated by Privacy Act and confidentiality legislation to protect the confidentiality of the data. The contractor’s data security procedures comply fully with security requirements delineated by the Information Resources Management Office of CDC.
It is NCHS policy to make NHANES data available via public use data files to the scientific community. Confidential data will never be released to the public. For example, all personal information that could be potentially identifiable (including participant name, address, survey location number, sample person number), are removed from the public release files. The NCHS Disclosure Review Board reviews all files that will be released, to assure that directly or indirectly identifiable data are not included.
11. Justification for Sensitive Questions
Self-reported and objective data of a sensitive nature are described in this section.
a. Social Security Number
Social Security Number (SSN) of all participants, children through adults, is requested in the household interview as a key item. The information is used to link administrative and vital records, such as the National Death Index (NDI), to the survey information. Additionally, in 2013-2014 NHANES will continue to use the SSN to link with Food Stamp Program and Women, Infants and Children (WIC) Program administrative records from the USDA.
Permission to link is obtained from respondents as follows: “The National Center for Health Statistics will conduct statistical research by combining {your/his/her} survey data with vital, health, nutrition and other related records. {Your/SP’s} social security number is used only for these purposes and the Center will not release it to anyone, including any government agency, for any other reason. Providing this information is voluntary and is collected under the authority of Section 306 of the Public Health Service Act. There will be no effect on {your/his/her} benefits if you do not provide it.”
ONLY READ IF ASKED. [Public Health Service Act is title 42, United States Code, section 242k.]
b. CMS Health Insurance Claim Number
Participants covered by Medicare will be asked to provide the CMS Health Insurance Claim Number. This will be used to link to Medicare records for further health research and also to link with other records for possible recontact of NHANES participants.
Permission to link is obtained from respondents as follows: “May I please see {your/SP's} Medicare card to record the Health Insurance Claim Number? This number is needed to allow Medicare records of the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services to be easily and accurately located and identified for statistical or research purposes. We may also need to link it with other records in order to re-contact {you/SP}. Except for these purposes, the Department of Health and Human Services will not release {your/his/her} Health Insurance Claim Number to anyone, including any other government agency. Providing the Health Insurance Claim Number is voluntary and collected under the authority of the Public Health Service Act. Whether the number is given or not, there will be no effect on {your/his/her} benefits. This number will be held in strict confidence. [The Public Health Service Act is Title 42, United States Code, Section 242K.]”
c. Residency Status
Information about country of birth and length of residency in the U.S. is requested and may be sensitive for recent immigrants. This information is important in analyzing health and nutrition data because acculturation may be related to use of the health care system, diet, and health practices. Additionally, recent immigrants may not have access to health, nutrition, and income assistance programs that affect access to health care and health and nutrition status. Interviewers will be trained to reassure participants that the information is confidential and will be used for statistical reporting only.
d. Other Content
Some of the NHANES research topics include potentially sensitive questions or examinations. In the informed consent procedure, all sample persons are advised of the voluntary nature of their participation in the survey or in any of its content. Again during the physical examination, each sample person is reminded that he or she can refuse to answer questions or to undergo any parts of the examination they find objectionable.
All questions and procedures have been reviewed by the NCHS Ethics Review Board (formerly called the NCHS Institutional Review Board) (see Attachment 6). The potential sensitivity of questions and procedures is an evaluation criterion in determining content of the survey. The multipurpose nature of NHANES makes it necessary to exclude topics so sensitive that they may interfere with participation.
Questions and procedures thought to be of a sensitive nature are listed below. Most of these are questions commonly asked in health care settings. Within the Mobile Examination Center, answers to sensitive questions are obtained privately.
i. Sexual behavior and sexually transmitted diseases: Several sexually transmitted diseases are part of the NHANES—herpes simplex I and II, HIV, hepatitis B and C, chlamydia and human papilloma virus (HPV). Information is obtained through questionnaires, exams, and lab tests. It is essential to clarify risk factors and identify at-risk population subgroups associated with infection in order to plan and evaluate prevention programs. This requires self-reported information on sexual behavior combined with objective data on infection.
Questions on sexual activity are asked of males and females 14 years and older. The results of tests for sexually transmitted diseases will not be mailed to examinees for reasons of confidentiality. Examinees will be given a toll-free number they can call, with the use of a self-selected password, to obtain their results. These questions will be administered using ACASI methods in a private room.
ii. Drugs, alcohol, and tobacco: Drug, alcohol, and tobacco use are risk factors for many of the health conditions studied in NHANES. Questions are asked in the MEC of persons 14 years of age and older concerning the use of alcohol, marijuana, and cocaine; participants 12 and older will be asked about alcohol consumption and tobacco use. Illicit drug use, tobacco, and alcohol questions are administered to youth 12-19 years of age using ACASI methods in a private room.
iii. Reproductive health and menstruation: Questions on reproductive health history asked of females 12 years and older may be considered sensitive by some respondents. The interviews will be conducted in a private room in the mobile examination center by specially trained interviewers.
Age of first menstruation will be obtained for females 8 years and older. This question will be asked of parents of girls 8 to 11 years of age. Information on menarche for 8-11 years of age is necessary for interpretation of biochemical and hematological assessments. As a safety screen for the dual X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), a pregnancy test will be performed on menstruating females ages 8-11 and all females 12 through 59 years.
iv. Mental health: Adolescents and adults of all ages will be asked a short depression screening module called the Patient Health Questionnaire or the "PHQ-9." The questions are taken from the depression module of the PRIME-MD, a self-administered questionnaire that was first used in clinical setting. The interviews will be conducted in a private room in the mobile examination center by specially trained interviewers.
v. Male and female urologic health: Conditions such as urinary incontinence and gynecologic infections affect millions of Americans. The information collected in NHANES is critical to understanding the magnitude of these problems and their impact on health and quality of life. The interviews will be conducted in a private room in the mobile examination center by specially trained interviewers.
vi. Pubertal Maturation: The pubertal maturation module, conducted among participants ages 8-19, may be considered sensitive by some respondents. These questions will be administered using ACASI methods in a private room.
In addition to standard informed consent procedures, designated staff at the MEC will meet with parents or proxies of children aged 8-17 years and participants aged 18 and 19 years regarding the Pubertal Assessment module. Parents and participants will be asked to read the appropriate Pubertal Maturation Assessment Informational Flyer (Attachment 12b). The MEC physicians will be trained to share age and gender appropriate drawings with parents and participants as requested and to answer general questions regarding puberty. The designated MEC staff will record that the parents or participants were given the flyers and the opportunity to read the flyers, see the drawings, and ask questions. Participants will be blocked from the MEC Interview until this has been completed.
vii. Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) Swabs: Women ages 14-59 years will be requested to collect a self-obtained vaginal swab. Men ages 14-59 will be requested to collect a self-obtained penile swab. The swabs will be used to test for HPV infection. Survey participants will perform the swab collection in a private bathroom after being instructed on how to collect by the physician.
In addition to standard informed consent procedures, designated staff at the MEC will meet with parents or proxies of children aged 14-17 years regarding the HPV swab collection. Parents will have the opportunity to review gender specific materials related to the self-collection (Attachment 12b). Participants ages 14-17 will be blocked from the Physician’s examination until this has been completed.
viii. Future content: As discussed in the Responding to Emerging Public Health Issues, New Technology and Future Survey Options portion of section A.2., during NHANES, new content may be pilot-tested or added, as new diagnostic procedures become available or as new conditions emerge. This content will be handled in similar fashion to that discussed above in the introduction to this section (A. 11d Other Content). Information will be explicitly discussed in the informed consent document if the content is considered sensitive, and appropriate privacy and confidentiality safeguards included.
12. Estimates of Annualized Burden Hours and Costs
a. Time Estimates
This submission requests OMB approval for three years of data collection, specifically for the 2013-2014 NHANES and for data processing efforts through 2015. These data collections will occur within the context of ongoing NHANES data collection activities. The burden for each survey component of one complete survey cycle is shown in the table below. The estimated total burden for one year is 38,528 hours, including screening, household interview, examination and follow-up interviews.
Annually, approximately 15,411 respondents participate in some aspect of the full survey (Attachment 9). About 10,000 complete the screener for the survey. About 142 complete the household interview only. About 5,269 complete both the household interview and the MEC examination. The majority of people completing both the interview and examination also participate in a second dietary recall interview. Averaging the burden across all respondents, at these varying levels of participation, results in an average burden of 2.5 hours. (The respondents who participate in all aspects of the survey can expect an estimated burden of 6.7 hours as documented in the signed informed consent documents [attachment 5].)
Up to 2,500 additional persons (non-NHANES respondents) might participate in tests of procedures, special studies, or for methodological studies, if budgeted. The average burden for these special study/pretest respondents is 3 hours (Attachment 11).
TABLE 1 – ANNUALIZED BURDEN HOURS AND COSTS
Type of Respondent |
Form |
Number of Respondents |
Number of Responses per respondent |
Average Burden per Response (in hours) |
Total Burden Hours |
1. Individuals in households |
NHANES Questionnaire |
15,411 |
1 |
2.5 |
38,528 |
2. Individuals in households |
Special Studies |
2,500 |
1 |
3 |
7,500 |
Total |
|
|
|
|
46,028 |
b. Cost to Respondents
The hourly wage rate of $21.74 per person is based on income from wages and salary from the Bureau of Labor Statistics: http://www.bls.gov/oes/current/oes_nat.htm#00-0000. This wage rate for all persons was used since respondents do not fall into a single economic or occupational category. The total cost was $1,064,956 or $54.86 per respondent. (NOTE: There are no out-of-pocket costs to survey participants. Participants are remunerated for their time as well as for child care and transportation expenses.)
13. Estimate of Other Total Annual Cost Burden to Respondents or Record Keepers
None.
14. Annualized Cost to the Federal Government
This project is a multi-year, continuous survey, with survey planning, data processing and analysis, and data collection occurring simultaneously. These figures are broad estimates based on past NHANES data collection budget estimates. Staff costs were primarily based on Division of Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys personnel costs, which were obtained from the NCHS Financial Management Office. A proportion of these costs are paid by funds transferred to the CDC budget from collaborating agencies. It is estimated that about 30 percent of survey costs will be covered through this support from agencies outside of NCHS.
Table 1. Estimated survey cost per year
Category |
Annualized Cost |
Equipment, exam centers, data collection and processing, contracts, labs/readings |
$35,000,000
|
NCHS staff costs for survey planning, data analysis and overhead |
$6,000,000 |
NCHS printing, travel, supplies, etc. for NHANES staff |
$200,000 |
Total |
$41,200,000 |
15. Explanation for Program Changes or Adjustments
The requested burden is 46,028. This is a new request.
16. Plans for Tabulation and Publication and Project Time Schedule
The following are key activities and projected completion dates for the 2013-2014 NHANES:
Activity Projected Completion Date
Planning survey content February 2011-November 2012
2013-14 data collection November 2012 – February 2015
First public release of data September 2015
First publication of
summary statistics September 2015
17. Reason(s) Display of OMB Expiration Date is Inappropriate
We have several forms that are triplicate, NCR-type pages pasted into glossy, multi-page brochures, which require considerable advance time for printing. To save substantial printing costs, since 1999 OMB has granted an exception from printing the expiration date on these forms for data collection. We request that exemption be continued through the term of this clearance.
18. Exceptions to Certification for Paperwork Reduction Act Submissions.
There are no exceptions to the certification.
| File Type | application/msword |
| Author | Vicki Burt |
| Last Modified By | CTAC |
| File Modified | 2012-11-27 |
| File Created | 2012-11-27 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy