SS Part B ERUS 2014 May 28 2014
SS Part B ERUS 2014 May 28 2014.docx
Electricity Data Program
OMB: 1905-0129
OMB NUMBER 1905-0129 SUPPORTING STATEMENT, PART B



Assistant Administrator for Energy Statistics | Office of Electricity, Renewables & Uranium Statistics
Supporting
Statement for Survey Clearance: Electric Power and Renewable Surveys
Part
B: Collection of Information Employing Statistical Methods
OMB
Number 1905-0129
May
28, 2014
FORM
EIA-861,
Annual Electric Power Industry Report FORM
EIA-861S,
Annual Electric Power Industry Report (Short Form) FORM
EIA-923,
Power Plant Operations Report FORM
EIA-930,
Hourly and Daily Balancing Authority Operations Report
FORM
EIA-63B,
Annual Photovoltaic Cell/Module Shipments Report FORM
EIA-411,
Coordinated Bulk Power Supply Program Report FORM
EIA-826,
Monthly Electric Utility Sales and Revenue Report with State
Distributions FORM
EIA-860,
Annual Electric Generator Report FORM
EIA-860M,
Monthly Update to the Annual Electric Generator Report
U.S.
Department of Energy Washington,
DC 20585
Independent
Statistics & Analysis www.eia.gov







TABLE OF CONTENTS
B STATISTICAL METHODS 1
B.2.1 Cutoff Sampling Methods 4
B.2.2 Relative Standard Error as a Measure of Sample Accuracy 5
B.2.3 Electric Power Surveys Sampling and Estimation 5
B.3 Maximizing Response Rates 9
B.4 Test Procedures and Forms Consultations 11
B.5 Statistical Consultations 11
Form EIA-63B, “Annual Photovoltaic Cell/Module Shipments Report”
The Form EIA-63B is a mandatory annual census survey of companies engaged in photovoltaic cell/module manufacturing, shipping, importing, or exporting within the United States, its territories, and possessions. The information collected includes volume of shipments, value of shipments, technical characteristics of the photovoltaic cells/modules shipped, and employment data. The survey frame for the Form EIA-63B contains approximately 177 respondents. Potential respondents are identified from Department of Energy (DOE) and U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) databases; industry/manufacturer directories; and trade publications.
Form EIA-411, “Coordinated Bulk Power Supply Program Report”
The Form EIA-411 survey collects a subset of the electric power system reliability information collected by the by the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) in the execution of its responsibilities as the Electric Reliability Organization for the United States.1 The data collected by the Form EIA-411 includes information about regional electricity supply and demand projections for a ten-year advance period and information on the characteristics and reliability of the transmission system and supporting facilities.
The Form EIA-411 is mandatory for those entities required to report. With the exception of Schedules 7 and 8, the form is completed by each of the eight Regional Entities of NERC. Each Regional Entity compiles the responses from data furnished by utilities and other members within their Region and provided to NERC headquarters. NERC then compiles and edits these data and provides an extract to EIA. Schedule 7 and 8 data for each Regional Entity are provided by NERC from, respectively, its Transmission Availability Data System and Generating Availability Data System databases.
There are nine respondents to this survey, the eight NERC Regional Entities and NERC headquarters.
Form EIA-861, "Annual Electric Power Industry Report"
Form EIA-861S, "Annual Electric Power Industry Report (Short Form)"
Form EIA-826, “Monthly Electric Utility Sales and Revenue Report with State Distributions”
The approximately 3,300 entities that constitute the universe for these three mandatory surveys are all participants in the electric power industry who are involved in the generation, transmission, or distribution of electricity in the United States and its territories. Target population members include electric utilities, wholesale power marketers (registered with the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission), energy service providers (registered with the states), and electric power producers.
The Form EIA-861 annual survey collects a range of information related to electricity sales, customers, and demand response and energy efficiency activities. The Form EIA-861 is administered as a cutoff sample, where the largest approximately 2,200 of the 3,300 entities in the survey universe are sampled, based on a threshold of annual retail sales and other factors explained below. The remaining smaller entities, about 1,100 of the potential respondents, account for only about 1 percent of total U.S. electricity sales and rarely perform any activities outside of basic electricity sales and distribution. Consequently, these smaller entities are required to complete only the short form version of the Form EIA-861 (the Form EIA-861S) every four calendar years and the longer Form EIA-861 every fifth year.
The Form EIA-861S is completed by all electric utilities with annual retail sales in the prior year of 100,000 megawatt hours (MWh) or less, except when of any one of the following conditions hold:
The respondent has retail sales of unbundled service
The full set of data is required from the respondent to ensure that statistical estimates for a state or business sector are of acceptable quality
The respondent instead reports in aggregate under the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) or WPPI Energy2
The company is part of the sample for the Form EIA-826, "Monthly Electric Utility Sales and Revenue Report with State Distributions.”
Utilities for which any of these exceptions apply must complete the regular (long) version of the Form EIA–861 survey. Note that respondents can only complete one type of Form EIA-861 in a given reporting period: either the Form EIA-861 or the Form EIA-861S, but not both.
The monthly Form EIA-826 survey collects data from a sample of the universe of entities that report on the Form EIA-861 and Form EIA-861S surveys. Cutoff sampling is used to select the survey frame for the Form EIA-826 of approximately 533 entities. The survey respondents are generally identified though information submitted on the Form EIA-861. New respondents to the monthly Form EIA-826 survey frame update the annual mandatory Form EIA-861 census survey (all respondents to the monthly Form EIA-826 also report on the annual Form EIA-861/861S).
Form EIA-860, “Annual Electric Generator Report” and Form EIA-860M, “Monthly Update to the Annual Electric Generator Report”
The mandatory Form EIA-860 annual survey collects data on the status of electric generating plants and associated equipment (such as environmental control systems) that are connected to the U.S. power transmission grids. The target population comprises existing and proposed electric power plants, including the following:
A. All existing plants that have a total generator nameplate capacity (sum for generators at a single site) of 1 Megawatt (MW) or greater; and where the generator(s), or the facility in which the generator(s) resides, is connected to the local or regional electric power grid and has the ability to draw power from the grid or deliver power to the grid; and
B. All proposed plants that: 1) have an expected total generator(s) nameplate capacity of 1 MW or greater; 2) expect the generator(s), or the facility in which the generator(s) resides, to be connected to the local or regional electric power grid and is expected to be able to draw power from the grid or deliver power to the grid; and 3) expect to commence commercial operation within 10 years in the case of coal, petroleum coke, nuclear and hydroelectric (both conventional and pumped storage) units, or within 5 years for all other units.
Companies complete the form for all the plants they operate. Approximately 3,500 entities operate and/or propose to operate about 6,800 facilities, containing over 19,000 generators, who are required to file the Form EIA-860. The respondents to this survey form the basis of the EIA electric power entity frame, from which samples for other surveys are drawn. Respondents are either self-identified or identified through industry publications and data services to which EIA subscribes.
The Form EIA-860M monthly surveys collects data from the Form EIA-860 population when a respondent has any of the following:
A new generator scheduled to begin commercial operations within the next 12 months
An existing generator scheduled for retirement within the next 12 months
An existing generator undergoing modifications resulting in changes in capacity or other major modifications that are scheduled to be completed within 1 month
The survey respondents are generally identified though information submitted on the EIA-860 survey, but in some cases information from other sources, such as industry publications, is also used.
Respondents are the operators of the power plants where these new generators and existing generators are located. Based on recent experience, EIA estimates that Form EIA-860M will collect data from approximately 190 respondent entities each month.
Form EIA-923, “Power Plant Operations Report”
The target population for this mandatory annual and monthly survey comprises all electric plants in the United States that are connected to the electric power grid and have a generating capacity of 1 megawatt or greater. The survey frame is established by the Form EIA-860 survey and is identical to the set of operational and standby power plants in the frame of that survey.
There are over 6,400 power plants for which data are collected through Form EIA-923. The data collected for plants includes electric power generation, fuel consumption, fossil fuel stocks, delivered fossil fuel cost, combustion byproducts, operational cooling water data, and operational data for NOx, SO2, particulate matter mercury and acid gas control equipment. Not all respondents answer all questions on the survey instrument; for example, questions on fuel consumption are inapplicable to hydroelectric, wind, and certain other types of power plants.
A survey form is completed for each power plant in the survey. If a single entity operates several power plants, it will complete a separate form for each plant and each form is treated as a unique response for estimation and burden calculation purposes.
A cutoff sample of approximately 2,108 plants report monthly data on electricity generation, fuel consumption, and, in some cases, the cost and quality of certain fossil fuel deliveries.3 At the end of the year, most of the monthly respondents (1,632 plants) also file a supplemental form that provides annual information on non-utility power sales and the operation of environmental control equipment.4
The 4,351 plants not in the monthly sample file data annually only. This includes data on generation and fuel consumption and, where applicable, data on fuel cost and quality and environmental equipment performance.
Form EIA-930, “Hourly and Daily Balancing Authority Operating Report”
The proposed new mandatory Form EIA–930 is a census survey of hourly electric power operating data from Balancing Authorities in the contiguous United States. The data collected include:
Hourly demand,
Hourly next-day demand forecast,
Hourly net generation,
Hourly actual interchange with each interconnected Balancing Authority.
Balancing Authorities are generally either Regional Transmission Organizations or electric utilities that have transmission grid management responsibilities. The 77 Balancing Authorities in the contiguous United States constitute the census frame for this survey.
Four of the surveys addressed in this supporting statement make use of sampling:
The three surveys of electric power sales and related data: the annual Form EIA-861, Form EIA-861S (Short Form), and the monthly Form EIA-826 survey.
The Form EIA-923 monthly and annual survey of power plant operations.
These surveys are discussed below.
To reduce reporting burden for respondents and the agency’s own workload, EIA utilizes cutoff samples for the survey frames of four of its electric power surveys: the monthly Forms EIA-826 and EIA-923, and the annual Forms EIA-861 and EIA-861S. These cutoff samples are comprised of all units with measures of size capacity and/or production variables larger than predefined thresholds, taking into account the need for data on multiple variables of interest within survey instruments.
Cutoff sampling eliminates the monthly reporting burden for smaller industry participants. Because smaller units have been responsible for a high percentage of reporting errors at EIA, cutoff sampling may also reduce the levels of non-sampling error affecting the published estimates. Sections B.2.2 and B.2.3, respectively, provide details about the sampling and estimation methods used for the electric power surveys that employ samples.
EIA uses the relative standard error (RSE) measure to evaluate the reliability of an estimated statistic. Relative standard error is based on the standard deviation about the mean of a statistic in a sample. Standard deviation is a measure of the spread of data values in relation to the mean value. Standard error normalizes this measure in terms of sample size or the number of samples, and relative standard error expresses this result as a percentage of the mean. Sampling plans that yield lower RSEs for estimated electric power survey statistics are considered to have greater accuracy.
Form EIA-826
Note: This clearance does not involve any revisions to the sampling or estimation methodology of the Form EIA-826 survey.
The EIA-826 is a monthly survey of a sample of electric power utilities and marketers that sell or deliver electric power to end users. Included in the survey is a sample of electric power entities providing bundled electric service and a census of power marketers.5 The survey collects information that includes retail electric sales and revenue by operating company, end-use sector (residential, commercial, industrial, transportation, total), and state. These data are the monthly equivalent to the corresponding annual data reported on the EIA-861.
The EIA-826 uses the annual EIA-861 as its sampling frame and estimates for the nonsampled members of the universe. The sample is basically a cutoff sample composed of those companies that typically sell most of the electricity in each customer class in each state. Respondents include:
• All investor-owned utilities (IOUs), except for a few small IOUs in Alaska
• All retail power marketers
• All Federal Utilities
• All entities selling in the public transportation sector
• A sample of the municipal and cooperative utilities.
The EIA-826 sample design and estimation procedures employ a weighted linear regression model to represent the relationship between a respondent’s past annual data and current monthly data. For example, the model used for estimating sales of company i in January 2014 would be:
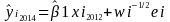
where 1 represents January, and x represents 2012 sales. (Additional details on the models are in “On Model-Failure When Estimating from Cutoff Samples” at http://interstat.statjournals.net/YEAR/2010/articles/1007005.pdf).
This model is fit for all respondents having valid data for both the current month on the Form EIA-826 and the most recent annual Form EIA-861 data. The model is not used when prior annual data are unavailable, as is the case for respondents that are new to the target population (although this is uncommon). For a new respondent, the respondent’s monthly data are used in estimating totals.
The models are fit separately each month for three variables (sales volume, revenues, and number of customers) by end-use sector and geographic region. The models are then applied to estimate data for entities not in the Form EIA-826 monthly sample but with valid annual Form EIA-861 data. The same model is used to impute for non-respondents and cases where submitted data fails EIA’s data review. Data for which EIA has a complete census each month – that is, retail power marketers and the electric utilities that provide distribution services for the marketers6 -- is added to the sampled and estimated values to obtain monthly estimates for the entire universe.
In past years, EIA had Form EIA-861 data for the universe of respondents that were one or two years old. However, with the 2013 change in the Form EIA-861 from a survey of the respondent universe to a sample, EIA will have data for the respondent universe that are one-to-six years old. As noted in section B.2.1 of the EIA clearance package submitted in October 2012, EIA research indicates that this will not adversely impact the accuracy of the estimates.
The monthly cutoff sample thresholds for the Form EIA-826 are selected based on the criterion of having estimated relative standard error (RSE) values less than 1 percent for all data published at the state level by end-use sector. The RSE is a percentage measure of the precision of a survey statistic and is used in part as one way to measure error introduced by using model-based predicted monthly values in place of missing and non-sampled data for the quantities of interest (revenues, sales, and number of customers). Threshold values for the cutoff sampling have been adjusted over time to maintain low RSEs for the published estimates.
For a general description of cutoff sampling as applied at EIA, see “Using Prediction-Oriented Software for Survey Estimation” at http://interstat.statjournals.net/YEAR/1999/articles/9908001.pdf, or “Model-Based Sampling, Inference and Imputation” at http://www.eia.gov/electricity/data/methodology/eiawebme.pdf.
Form EIA-923
Note: This clearance does not involve any revisions to the sampling or estimation methodology of the Form EIA-923 survey.
The Form EIA-923 is a monthly and annual survey of electric power plants. The survey collects information that includes electric power generation, energy source consumption, end of reporting period fossil fuel stocks, as well as the quality and cost of fossil fuel receipts.
A cutoff sampling methodology is used for the Form EIA-923. EIA utilizes cutoff sampling to reduce the burden on smaller capacity plants and EIA’s own workload. EIA collects monthly data on the Form EIA-923 from respondents (i.e., plants) with a large energy capacity and collects annual totals at the end of the reporting year on the Form EIA-923 from plants with a small energy capacity. The monthly sample is selected from the Form EIA-860 sampling frame of electric power plants. With the combination of monthly and annual respondents, the Form EIA-923 achieves a full census of operational and standby power plants with generation capacity of at least 1MW.
Since a cutoff sample is used, EIA predicts values for the smaller plants using weighted linear regression models depending on the module estimated. EIA can estimate values for out-of-sample plants in current time, because there is a census of the previous year’s data; i.e., regressor data. For example, the model used for estimating generation in January 2014 for plant i would be:
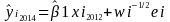
where 1 represents January, and x represents 2012 generation for plant i. (Additional details on the models are in “On Model-Failure When Estimating from Cutoff Samples” at http://interstat.statjournals.net/YEAR/2010/articles/1007005.pdf).
Nameplate capacity was used as the measure of size in the original sample selection process and its high correlation with other data elements on the Form EIA-923 ensured good coverage results for other reported values. Since then, sample validation studies were conducted on fuel consumption, receipts, costs and stocks, and the sampling methodology was adjusted accordingly.
The sampling strata are defined by facility type, energy source, and geographic region. For instance, one stratum is identified as electric utilities burning coal in the South Atlantic Census Division. There are four facility types: electric utilities, independent power producers, commercial facilities, and industrial facilities; 14 energy source categories, which correspond to the energy source classifications used in the Electric Power Monthly (EPM); and 10 geographic groups, which correspond to the 10 modified Census divisions published in the EPM.
The original Form EIA-923 monthly sample was selected with the 2008 data collection cycle. By the inception of the 2014 collection cycle, EIA estimates that over 200 plants will have been added to the monthly sample to maintain the targeted sample coverage ratios. These sample additions are necessary as new large plants become operational. EIA intends to conduct future sample validation studies as the universe of power plants changes to reassess sample size.
Form EIA-923 Sample Selection Criteria
The Form EIA-923 sampling methodology provides accurate results while minimizing the burden on the industry and the Federal Government. The following five steps are used in selecting plants for the monthly sample:
1. Select preliminary cutoff samples based on nameplate capacity values
2. Add sample units, where necessary, based on generation, consumption and stocks
3. Add sample units, where necessary, to provide adequate sample counts for estimation groups
4. Add sample units, where necessary, to reduce relative standard errors (RSEs) of key estimates to acceptable levels
5. Add other facilities, based on special-case criteria
The first three steps were designed to ensure adequate coverage of the target population by including all of the largest contributors to key data elements. The fourth step helps ensure that the published estimates meet reasonable reliability standards, which is the key goal, given acceptable resource expenditure. The final criterion covers special cases, as described below.
Facilities in the target population that meet any one of the sample selection criteria applied at any of the five steps are included in the final sample. Further, any additional prime movers and energy sources used by a sample facility are also included in the sample, even if they individually did not meet any of the sample selection criteria.
Each sample facility reports data each month for all combinations of prime mover and fuel source. All nuclear and pumped storage facilities are included in the monthly sample. The remainder of this section provides further detail on the sampling steps.
Step 1: Select Cutoff Samples Based on Nameplate Capacity.
Pre-determined capacity coverage percentages are tested to ensure a certain proportion of operational Form EIA-860 capacity is covered within each stratum. Stand-by generators are not included in the operational capacity totals when data are aggregated to the level of prime mover, and only the largest consumed fuel source for each generator is used in identifying the stratum.
Different target coverage percentages are selected for each facility classification using plants with nameplate capacity over 25 megawatts and are applied to all regions and energy sources within each facility classification. Otherwise, the percentages of capacity included in the sample are, as follows:
1. Electric utilities – 70 percent
2. Independent power producers – 70 percent
3. Commercial facilities – 50 percent
4. Industrial facilities – 50 percent
Step 2: Add Units Based on Generation, Consumption, and Stocks.
Facilities accounting for large percentages of actual past reported gross generation, fuel consumption, or fuel stocks, are added to the sample, even if their nameplate capacities fall below the percentage cutoff for capacity coverage.
Step 3: Add Units to Ensure Adequate Sample in Estimation Groups.
Instead of fitting models separately for each sampling stratum, the cases are collapsed to form “estimation groups” that have data as homogenous as possible while also having the largest number of observations. This will provide better fitting models than if the models were fit separately on each sampling stratum. These groups are re-formed over time as changes in the data occur. Units below the threshold value were added to any estimation group with fewer than 10 usable observations, until the usable count was brought up to 10.
Step 4: Add Sample to Meet Reliability Standards.
Weighted linear regression equations, identical to those currently employed in the Form EIA-923 imputation system, are run, and relative standard error (RSE or Coefficient of Variation) estimates are calculated for each publication group by month. An additional diagnostic measure, the relative standard error for a super population (RSESP), is calculated to indicate the adequacy of the regression model fit. Limits for both measures (RSE and RSESP) are set individually for each facility classification and applied to all energy sources for the U.S. total for each classification.
If one or both of the error measures fall outside of the limits, the next largest facilities, ranked by gross generation, are included until the estimated RSE/RSESP values are brought into the desired range. If only the RSESP estimate (and not the RSE estimate) is out of range, then it is difficult to lower the estimate of RSESP based on sampling, alone. In these cases, a change in modeling may be necessary. The RSE/RSESP data quality limits are outlined, as follows:
Electric utilities – RSE less than 5 percent and RSESP less than 20 percent
Independent power producers – RSE less than 5 percent and RSESP less than 20 percent
Commercial facilities – RSE less than 10 percent and RSESP less than 30 percent
Industrial facilities – RSE less than 10 percent and RSESP less than 30 percent
Step 5: Add Special Cases.
Lastly, additional facilities are added to the sample, as necessary. These include storage-only facilities (used in estimating stocks); new facilities for which the EIA has no prior-year’s annual data for use in regression imputation; and any new large facilities that the survey staff identifies for inclusion in the sample.
The response rates for the EIA electric power and renewable surveys have historically been at or near 100 percent. Recent response rates are shown below in Table 1.
Table 1. Recent Survey Response Rates
Frequency of Survey |
Survey |
Survey Frame |
Number of Responses |
Response Percentage |
Non-Responses |
Non-Response Percentage |
Annual Surveys Collection of 2011 Data (See Notes) |
EIA-63B |
171 |
171 |
100% |
0 |
0% |
EIA-411 |
9 |
9 |
100% |
0 |
0% |
|
EIA-860 |
3160 |
3154 |
99.8% |
6 |
0.2% |
|
EIA-861 |
3287 |
3287 |
100% |
0 |
0% |
|
EIA-861S |
See Notes |
|
|
|
|
|
EIA-923 |
5600 |
5593 |
99.9% |
7 |
0.1% |
|
Monthly Surveys: Collection for June 2013 |
EIA-826 |
533 |
533 |
100% |
0 |
0% |
EIA-860M |
188 |
187 |
99.5% |
1 |
0.5% |
|
EIA-923 |
2108 |
2108 |
100% |
0 |
0% |
|
Notes: Monthly collections in June 2013 are for April 2013 data. The Annual Surveys Collection of 2011 data (completed in 2012) are the most current, complete annual surveys collection. The current annual surveys collection of 2012 data (conducted in calendar year 2013) is still on-going. The Form EIA-861S did not exist in calendar year 2012 when 2011 data was collected. The survey was introduced in calendar year 2013 for the collection of 2012 data. At the end of June 2013, with data collection still underway, the Form EIA-861S had a frame of 1115 respondents of whom 1108 had submitted data (99%). |
||||||
To maximize response rates, EIA surveys and instructions are designed and written for clarity and conciseness. Data that are not expected to change from year-to-year or month-to-month are pre-populated on the forms. Notifications are emailed early to maximize the time that respondents have to complete the surveys.
As noted in Part A, EIA’s Internet data collection system makes forms available on-line as soon as respondents obtain a secure ID and password. Given the high Internet use rate among respondents to these surveys (approximately 95 percent), most online respondents will log on in the next data collection period and access their required forms. Form due dates are the same each period so that respondents can schedule their completion activities.
Any non-respondents are contacted by email, telephone, and letter to request data submission, until an insignificant or zero non-response rate is obtained. Follow-up email messages citing failure to file the required form are sent to all non-respondents. If the follow-up email messages do not result in a response, additional correspondence requesting immediate submission is sent to the supervisor of the primary contact and, if necessary, to higher-level management officials at the non-responding entity. These letters are sent from the EIA Office Director or (rarely) from the Assistant Administrator or EIA Administrator.
Respondents who file via the Internet system are given the opportunity to either correct or explain unusual data during their submission. These explanations are reviewed by EIA staff. Respondents are contacted if further clarification is needed. For those respondents that do not file via the Internet, but rather on a hard copy of the form, email messages are sent and/or telephone calls are made to confirm corrections or clarifications of any data suspected to be in error.
Changes in plant ownership and/or contacts have contributed in the past to non-response. To address this issue, EIA developed an improved centralized frame system for the electric power surveys. This system affords all survey staff almost immediate knowledge of changes in entity ownership and/or contacts. This frame system is integrated with the EIA’s Internet Data Collection system so that access can quickly be given to new owners and/or contacts.
The survey designs were reviewed by EIA cognitive specialists and modified as necessary to improve clarity and reduce burden. Draft surveys are also made available for review as part of the 60-day and 30-day Federal Register Notice (FRN) comment periods. When the FRNs were published, emails were sent to in excess of 5,000 monthly and annual survey contacts, 77 Balancing Authorities, and a list of about 226 stakeholders concerning the survey changes with links to the proposed forms. In addition, the draft forms and instructions are posted on EIA’s website for the general public. When comments are received on form design and content the comments are evaluated and changes made as necessary.
For additional information on forms review, please see Part A, section A.8., “Summary of Consultations Outside of the Agency.” For a summary of the comments received and EIA’s responses, see the Supporting Statement, Part A, Appendix A-1.
For additional information concerning this proposed information collection, please contact Rebecca A. Peterson at 202-586-4509, or at [email protected].
For information concerning this request for OMB approval, please contact the agency Forms Clearance Officer, Alethea Jennings, at 202-586-5879, or [email protected].
1 NERC was designated as the official Electric Reliability Organization by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission pursuant to the power system reliability provisions of the Energy Policy Act of 2005. EIA has had a long-standing relationship with NERC and its predecessor for the collection of the Form EIA-411 data.
2 TVA and WPPI Energy (the latter a consortium of public power utilities in the Midwest) consolidate responses for their wholesale customers and deliver the information to EIA. Extracting a subset of utilities from the joint filings of TVA and WPPI would be administratively cumbersome and would defeat the purpose of the proposed change to the Form EIA-861 frame, which is to reduce the cost of managing the survey for both EIA and respondents.
3 Plants report fuel cost and quality data only if they meet the following criteria: 200 MW or greater nameplate capacity for plants fueled by natural gas, petroleum coke, distillate fuel oil, and residual fuel oil, and/or have coal-fueled capacity of 50 megawatts or greater.
4 Plants file data on environmental control system performance only if the plant has a minimum of 10 MW of nameplate capacity using combustible fuels.
5 Bundled service, which includes the supply of energy and delivery, is typically provided by traditional electric utility companies. In states where retail choice for electric power service is available, the energy may be supplied by a power marketer (also referred to as an energy service provider) and the utility provides delivery service only.
6 If imputation is necessary due to nonresponse of either census group, the most recent census monthly data would be used to impute for the missing data.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | Draft ERUS 2014 OMB Supporting Statement, Part B |
| Subject | ERUS 2014 OMB Clearance Supporting Statement, Part B |
| Author | Elizabeth E. Panarelli |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-28 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy