1363ss23 rev 11.17.2014
1363ss23 rev 11.17.2014.docx
Toxic Chemical Release Reporting (Change)
OMB: 2025-0009
TOXICS RELEASE INVENTORY
TRI FORM R AND FORM A
TOXIC CHEMICAL RELEASE REPORTING
INFORMATION COLLECTION
REQUEST
SUPPORTING STATEMENT
OMB
CONTROL NO. 2025-0009
EPA ICR #1363.23
June 2014
IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 3
Title of the Information Collection 3
Short Characterization/Abstract 3
NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION 5
Need/Authority for the Collection 5
Practical Utility/Users of the Data 7
NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA 8
3(a) Nonduplication 8
3(b) Public Notice Required Prior to ICR Submission to OMB 13
3(c) Consultations 13
3(d) Effects of Less Frequent Collection 13
3(e) General Guidelines 14
3(f) Confidentiality 15
3(g) Sensitive Questions 15
THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED 15
4(a) Respondents/NAICS Codes 15
4(b) Information Requested 16
THE INFORMATION COLLECTED—AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION
METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT 22
5(a) Agency Activities 22
5(b) Collection Methodology and Management 25
5(c) Small Entity Flexibility 25
5(d) Collection Schedule 26
ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF THE COLLECTION 26
Estimating Respondent Burden 28
Estimating Respondent Costs 35
Estimating Agency Burden and Cost 37
Estimating the Respondent Universe and Total Burden and Costs 38
Bottom Line Burden Hours and Cost Tables 40
Reasons for Change in Burden 41
Burden Statement 45
APPENDICES
Appendix A: Blank Form A, Form R, and Form R Schedule 1
Appendix B: Reporting Form R and Form A Changes and Associated Instruction Revisions
Appendix C: Information Sources Containing Data Subsets, but not Comprehensively Comparable Alternatives to TRI
Appendix D: TRI Consultation Meetings
Appendix E: Facilities Required to Report to TRI (NAICS)
IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
Title of the Information Collection
TITLE: Toxic Chemical Release Reporting (Renewal)
EPA ICR No.: 1363.23
OMB Control No.: 2025-0009
Short Characterization/Abstract
This Information Collection Request (ICR) is for the information collection requirements associated with EPA’s Toxics Release Inventory (TRI) Program. Pursuant to section 313 of The Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (EPCRA), certain facilities that manufacture, process, or otherwise use specified toxic chemicals in amounts above reporting threshold levels as provided in 40 CFR 372.25 must submit annually to EPA and to their designated State or Indian Country officials toxic chemical release forms containing information specified by EPA, 42 U.S.C. 11023. In addition, pursuant to section 6607 of the Pollution Prevention Act (PPA), facilities reporting under section 313 of EPCRA must also report pollution prevention and waste management data, including recycling information, for such chemicals. 42 U.S.C. 13106. EPA compiles and stores these reports in a publicly accessible database known as the Toxics Release Inventory (TRI).1
Currently, facilities subject to the TRI reporting requirements may use either the EPA Toxics Release Inventory Form R (EPA Form #9350-1), or, if they meet alternate threshold requirements, the EPA Toxics Release Inventory Form A Certification Statement2 (simply referred to as “Form A” - EPA Form #9350-2). With Form R, a facility reports one chemical per form; with Form A, a facility may report multiple chemicals per form.3
In the last ICR Renewal, EPA transitioned from issuing two separate ICRs to issuing a single ICR—EPA ICR No. 1363.21, OMB Control No. 2025-0009 that encompasses both Form R and Form A. In this Renewal, EPA proposes revisions to the Form R and Form A to clarify data elements and enhance data utility. Specifically, EPA proposes to make the following changes to the forms:4
Add an optional extension to all phone numbers to allow facility representatives to provide the extension needed for a direct connection.
Add an optional field to allow facilities to indicate the section of the water body that received the surface water discharges reported in Section 5.3. Specifically, facilities will be able to provide “reach codes,” which are unique codes that identify a continuous piece of surface water with similar hydrologic characteristics.
Move the header “5.5 Disposal to land on-site” to precede Sections 5.4 and 5.5 on Form R so that it covers both 5.4 and 5.5. Re-word 5.4.1 and 5.4.2 to fit under the new header as follows: Section 5.4-5.5: Disposal to land on-site, Section 5.4.1: Class 1 Underground Injection Wells, Section 5.4.2 Class II-V Underground Injection Wells. The remaining sections of Section 5.5 are unchanged.
Provide the heading, “Production-related waste managed” for Sections 8.1-8.7 and re-label Section 8.8 “Non-production-related waste managed.”
Add checkboxes to indicate whether facilities have provided a “Production Ratio” or “Activity Ratio” in Section 8.9.
Add a new column (d) in Section 8.10 where facilities have the option to provide a percentage range indicating the estimated annual reduction in chemical waste generation associated with a given source reduction activity.
Provide optional barrier codes in Section 8.11 that facilities have the option to use to indicate why they could not implement any source reduction activities during the reporting year.
Allow facilities to categorize optional free-text information entered in Sections 8.11 and 9.1 by selecting from a list of topics provided in TRI-MEweb.
Pursuant to EPCRA §313 (and PPA §6607 because of its linkage to EPCRA), EPA's Office of Environmental Information (OEI) collects, processes, and makes available to the public all of the information collected. EPA stores the information gathered under these authorities in a database available through the Internet. EPA, other federal, state, and local government agencies; industry; and the public use TRI extensively. Program offices within EPA and other government agencies have used TRI, along with other sources of data, to establish priorities, evaluate potential exposure scenarios, and conduct enforcement activities. Industries use TRI data to identify pollution prevention opportunities and set goals for emissions reductions. Environmental and public interest groups use TRI data to make the public more aware of releases of chemicals in their communities, as well as to initiate direct negotiation and risk reduction with facilities.
EPA developed EPA Information Quality Guidelines to ensure the utility, objectivity, and integrity of information that the Agency disseminates. The information supporting this ICR aligns with all appropriate EPA policies, including EPA's Information Quality Guidelines. In particular, the EPA Agency-wide quality system helps ensure that EPA organizations maximize the quality of information disseminated by the Agency. The quality system is documented in EPA Order 5360.1 A2, Policy and Program Requirements for the Mandatory Agency-wide Quality System and the EPA CIO Policy 2106.0 US Environmental Policy: Quality Policy Oct 2008.
An updated Procedure for Quality Policy was published in October 2008.5 The information supporting this action is also consistent with EPA's Guide to Writing Information Collection Requests Under the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995, revised November 2005. It is EPA's intention that collection of information under this ICR will result in information that will be collected, maintained, and used in ways consistent with both EPA's Information Quality Guidelines and the OMB Information Quality Guidelines.6
The TRI data are unique in providing a multi-media (air, water, and land) picture of toxic chemical releases, transfers, and other waste management activities by covered facilities on a yearly basis. With a centralized database and electronic data access tools, TRI provides a wide range of capabilities for a variety of users. Communities and governments can access the identities and quantities of listed toxic chemicals that many industrial facilities in their area release, transfer, or otherwise manage as waste. In addition, industries can use TRI as a tool for evaluating progress on their pollution prevention goals.
OMB last approved a combined Form R/Form A ICR on October 14, 2011, with an expiration date of October 31, 2014. The ICR approved at that time reflected a total program reporting burden projection of 73,727 responses, 3.52 million hours and $174.5 million for Form R and Form A respondents. For this ICR Renewal, EPA projects total responses, burden, and cost of Form R and Form A reporting at 74,869 responses, 3.56 million hours and $183.4 million. This slight increase is due to rulemakings since the last OMB approval (see Figure 2 on p. 40 for TRI Rulemaking and ICR Chronology). Further, the TRI program proposes to revise data elements for the reporting forms, though these proposed revisions should have a negligible impact on form burden.
This ICR estimates an average of 35.71 hours per Form R (including all proposed form changes) to complete all activities associated with Form R completion (rule familiarization, reporter compliance determination, calculations, form completion, and recordkeeping). By comparison, EPA estimates an average 21.96 hours for facilities submitting a Form A for a single listed chemical (all estimates incorporate proposed changes).7 Thus, for a facility filing a Form A instead of Form R for a single listed chemical, according to EPA’s TRI burden methodology, the alternate threshold yields an average savings of 13.7 hours per chemical.
2 NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION
2(a) Need/Authority for the Collection
This information collection activity is a statutory requirement pursuant to EPCRA §313 (42 U.S.C. 11001 et seq.) and PPA §6607 (42 U.S.C. 11071 to 11079). According to EPCRA §313(h), the purpose of the data collected by the forms is to "inform persons about releases of toxic chemicals to the environment; to assist governmental agencies, researchers, and other persons in the conduct of research and data gathering; to aid in the development of appropriate regulations, guidelines, and standards; and for other similar purposes."
Section 6602 of the PPA establishes a national policy to prevent or reduce pollution at the source whenever feasible. To further this goal, EPA collects and disseminates information intended to fulfill that responsibility in part and to provide a basis for measuring progress in pollution prevention.
EPA’s regulations implementing TRI reporting are codified at 40 CFR part 372. Each covered facility must report on each listed chemical manufactured, processed or otherwise used in excess of the reporting thresholds established in EPCRA §313(f)(1).
EPA established an alternate threshold8 under EPCRA §313(f)(2) for a category of facilities with low amounts of a listed toxic chemical in wastes. A facility with such lower amounts of listed chemicals in wastes may submit an EPA Toxics Release Inventory Form A for the reportable chemicals instead of a Form R for each reportable chemical. Note that a Form A may contain multiple chemicals. Form A submissions foster continued attention to chemical management practices and provide important facility identification information. With a Form A, EPA and the general public receive a specific indication annually that a facility has a certain chemical; however, facilities provide less extensive reporting on chemicals when using the alternate threshold.
The information collected on the Form R, or alternatively on the shorter Form A, fulfills EPA’s responsibilities under EPCRA §313(f)(2), addressing the statutory mandates and the public's right-to-know. Table 1 summarizes the information reported by facilities on the two types of TRI reporting forms.
Table 1
Form R and Form A Information Collection
Information Collected |
Form R |
Form A |
Location of facilities manufacturing, processing or otherwise using these chemicals |
√ |
√ |
Indication that the chemicals are being manufactured, processed or otherwise used at current reporting thresholds |
√ |
√ |
Certification that the sum of amounts of the chemical in releases and waste did not exceed the appropriate Non-PBT or PBT (lead in stainless steel, brass, or bronze alloy) release and waste annual reportable amounts for that reporting year |
|
√ |
Accounting of quantities of chemicals entering environmental mediums on site |
√ |
|
Disclosure of chemical transfers to off site locations |
√ |
|
Description of on-site waste treatment, energy recovery, and recycling processes |
√ |
|
Accounting of other disposal, source reduction and recycling activities |
√ |
|
Additional optional information on source reduction, recycling and pollution control activities |
√ |
|
2(b) Practical Utility/Users of the Data
The overall goal of the Toxics Release Inventory Program is to provide communities with information about toxic chemical releases and other waste management activities and to support informed decision making by industry, government, non-governmental organizations, and the public.9 The Program’s success is due, in large part, to the right-to-know provisions contained in the legislation. By requiring that the resulting data be made publicly available "by electronic and other means," Congress ensured that the general public, the media, environmental advocates, researchers, the business community, and others could evaluate and influence industry's efforts to manage toxic emissions. Consequently, EPA makes available data collected under EPCRA §313 and PPA §6607 through access tools such as EPA's Envirofacts, TRI Explorer, TRI.NET, and the web-enabled mobile application myRTK.
The TRI Program now provides the TRI Preliminary Dataset within weeks after the annual July 1st TRI reporting deadline. The release consists of downloadable files on the TRI website (also accessible through Data.gov), as well as updated online data access tools (Envirofacts and TRI Explorer).
The EPA generally makes available the annual TRI National Analysis and the final dataset used for that analysis within eight months after the reporting deadline. In addition to providing information to the public via electronic means, EPA also conducts outreach activities to make key groups and the public aware of TRI. Libraries in communities all across the United States (in particular, members of the Federal Depository Library Program) provide public access to TRI data. Environmental agencies, industry, and the public use TRI data. EPA program offices use TRI data, along with other data, to help establish programmatic priorities, evaluate potential hazards to human health and the natural environment, and undertake appropriate regulatory and/or enforcement activities. Environmental and public interest groups use the data to better understand toxic chemical releases at the community level and to work with industry, government agencies, and others to promote reductions in toxic chemical releases. Industrial facilities use the TRI data to evaluate the efficiency of their production processes and to help track and communicate their progress in achieving pollution prevention goals. States use the TRI data to compare toxic chemical releases and other waste management approaches within specific industries and to set environmental priorities at the state level. See EPA’s The Toxics Release Inventory in Action: Media, Government, Business, Community and Academic Uses of TRI Data for more detailed descriptions of how these organizations use TRI data.10 EPA encourages TRI data users to provide feedback on ways to improve TRI products and services.
3 NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA
3(a) Nonduplication
The basic information requested on Form R/Form A is required to be reported by law. Other statutes, however, also necessitate the reporting of information about releases of chemicals to the environment, as well as transfers, treatment, and source reduction and recycling activities, creating the possibility of overlap or duplication of reporting requirements. EPA anticipates some overlap and notes that section 313(g)(2) of EPCRA specifies that respondents may use readily available data collected pursuant to other provisions of law to complete the EPCRA §313 reports. Information required by these other statutes may not provide readily accessible multi-media release and transfer, inventory, or pollution prevention data with the same scope, level of detail, chemical coverage, and frequency of collection as data currently included in TRI.
Several existing data sources contain media-specific data on releases and transfers, chemical inventory data, or pollution prevention information. In theory, information from these databases could be combined to form an analog of release and transfer data contained in TRI. However, given the currently available data sources (see Table 2 and Appendix C), this substitution is extremely unlikely. For example, differences exist across the databases in chemical coverage and facility coverage, as well as differences in the level of public access, reporting frequency, and the integration of data from various sources at the facility level. TRI contains information on releases, transfers, and other waste management activities for 594 individually listed chemicals and 30 chemical categories—with total number of chemicals and chemical categories at 683. The following sections describe other sources of chemical releases and transfers, chemical inventory, and pollution prevention data and compare these sources with TRI.
Chemical Release and Transfer Data
TRI contains information on toxic chemicals handled by facilities, including details on quantities of chemicals managed through disposal or other release, recycling, energy recovery or treatment. These data include: 1) on-site releases with details on releases by environmental media (e.g., stack or point air emissions, discharges to receiving streams or water bodies, etc.), and 2) off-site transfer data with details on the off-site locations that receive transfers and the disposal, treatment, energy recovery, or recycling methods used to manage the chemicals at the off-site locations. Waste management data include quantities that are treated, used for energy recovery, or recycled and are discussed in the section on pollution prevention below.
Table 2 presents a summary of major databases containing release and transfer data that are discussed in this section. Appendix C provides a comprehensive list of relevant data sources.
Table 2
Major Federal Databases with Air Release, Water Discharge, and Waste Disposal Data
Data Source |
Media and Chemical Coverage |
Relevant Release Statistics Available |
Ease of Database Substitution for TRI Dataa |
National Emissions Inventory (NEI) |
Contains annual emissions of 8 criteria air pollutants (CAPs) and 187 hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) for facilities above reporting thresholds. |
Total annual releases. |
Includes air releases only. Data are updated only every 3 years. Coverage of TRI chemicals is limited. |
Integrated Compliance Information System–National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (ICIS-NPDES) |
Contains monthly discharge monitoring data for selected water pollutants and flow rates for major sources. |
Concentration data; total annual releases (can be estimated); average daily releases, maximum “moment” if continuous monitoring. |
Includes only chemicals for which a discharge limit has been set. Many discharge parameters are not specific to an individual Chemical Abstract Service (CAS) number. Very limited monitoring data for minor dischargers. |
Biennial Reporting System (BRS) |
Contains waste volumes by Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) waste code reported biennially. |
Total annual off-site transfers of hazardous waste for land disposal; total annual releases to publicly owned treatment works (POTWs). |
Many RCRA waste codes are not specific to an individual CAS number. Quantities of chemicals in waste cannot be determined. Portion of waste stream matching each waste code cannot be determined. |
a “Ease of substitution” refers only to the potential of the information in the database to substitute for TRI reporting. It does not imply that the database is not adequate for the purposes for which it was designed. |
|||
Air Releases
The 1990 amendments to the Clean Air Act require EPA to monitor and regulate the emissions of criteria air pollutants (CAPs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs), requiring EPA to identify the sources of these pollutants, quantify the sources by category, develop regulations, and then assess public health and environmental impacts. To facilitate this process, the Agency created two emissions inventories: the National Toxics Inventory (NTI) for HAPs and the National Emission Trends (NET) for CAPs. In 1999, the EPA combined these two databases to form the National Emissions Inventory (NEI) database.
NEI is EPA's compilation of estimates of air pollutants discharged on an annual basis and their sources. Five main categories organize NEI data: point sources (stationary), nonpoint sources (stationary), on-road sources (mobile), non-road sources (mobile), and events (fires). The compilation includes emissions estimates submitted by state, local and tribal air pollution control agencies, emissions estimates calculated by EPA, and emissions obtained from other sources. EPA uses the NEI to track emissions trends over time, develop regional pollutant reduction strategies, set and analyze regulations, perform air toxics risk assessments including inhalation risks and multi-pathway exposure, model air pollutant dispersion and deposition, and measure environmental performance as required by the Government Performance and Results Act.
Since 1996, EPA has compiled the NEI every three years. For 2008, the Agency reengineered the NEI business process to shorten the period between collecting data for a given inventory year and publication of that data. The most recent inventory is the 2011 NEI, which EPA published in 2013.
NEI and TRI data have many differences, including the type and number of pollutants measured, the industrial sectors included in the inventory, and the type of information collected (e.g., which environmental media releases are measured and what other release or management-specific information is collected). TRI includes 594 chemicals and 30 chemical categories known or reasonably anticipated to cause acute or chronic health effects or significant adverse environmental effects. NEI covers 8 Criteria Air Pollutants (CAPs) (i.e., carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds, oxides of nitrogen, sulfur dioxide, particulate matter ≤ 2.5 microns, particulate matter ≤ 10 microns, ammonia, and lead) and 187 Hazardous Air Pollutants (HAPs). TRI covers two of the CAPs (ammonia and lead) and 181 of the HAPs covered by NEI. NEI covers all sources of CAP and HAP emissions, including a number of sectors that are not included in TRI (e.g., agriculture, oil extraction and construction). In addition, NEI includes county-level emissions estimates for area, mobile and other sources not found in TRI.
Various reporting thresholds also differ between TRI and NEI. For example, a facility must report to TRI only if it has 10 or more full-time employee equivalents and manufactures, processes or otherwise uses any TRI-listed chemical in quantities greater than the established threshold (typically 25,000 pounds for manufacturing and processing and 10,000 pounds for otherwise use). PBT chemicals have lower thresholds for reporting to TRI. For HAPs, under NEI, a facility must participate in the point source inventory if it has the potential to emit ten or more tons per year of one HAP or 25 tons per year or more of any combination of HAPs.
Information captured by TRI differs from that captured by NEI on a number of counts. TRI includes multimedia data on chemical releases, including air emissions and other types of releases (e.g., surface water discharges, underground injection, and landfill disposal of toxic chemicals). TRI also includes source reduction and waste management data, which can be used to assess pollution prevention trends on a facility basis. NEI focuses entirely on air emissions, but provides much more detailed emission source-specific data about releases, such as process descriptions, throughput and stack height. The different information captured by the data systems largely reflects the different goals behind the development of the inventories. TRI’s main purpose is to provide the public with information about potential chemical hazards, whereas NEI, among other purposes, seeks to produce data that would support modeling and risk assessment needs.
Water Discharges
The Integrated Compliance Information System–National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (ICIS-NPDES)11 tracks the permit compliance and enforcement status of facilities that discharge to surface waters (www.epa.gov/enviro/facts/pcs-icis/search.html). For entities permitted to discharge wastewater into navigable waters, ICIS-NPDES contains information on permit issuance and expiration dates, quantities facilities are permitted to discharge, and monitoring data measuring facilities’ discharges. ICIS-NPDES data are not directly comparable to TRI; permit compliance data in ICIS-NPDES typically include monthly monitoring measures of pollutant concentrations in effluent discharges while TRI includes estimates of the total amount (in pounds) of a pollutant discharged to water. Monitoring required by the National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) covers only selected chemicals in the wastewater and does not comprehensively cover all TRI chemicals discharged to surface water at specific facilities.
Waste Disposal
Under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), large quantity generators and treatment, storage, and disposal facilities submit information on the generation, management, and final disposition of RCRA-defined hazardous wastes. Every two years, filers must report the following information about each waste generated or managed in the preceding year: constituent waste codes; amounts generated; on- and off-site treatment, storage, and management; wastes received; and off-site shipment recipients. Facilities submit these biennial Hazardous Waste Reports to the state or EPA Regional office. The biennial reports (BR) include one year’s data (e.g., 2009 Biennial Report reflects data on waste management during 2009) and are stored centrally in EPA’s RCRAInfo. Biennial Reporting System (BRS) data do not duplicate the information contained within TRI, as: (1) hazardous waste codes do not necessarily map to unique chemicals; (2) quantities of specific chemicals in the waste stream cannot be determined; and (3) reporting occurs every other year, as opposed to annually for TRI.
Chemical Inventory Data
In addition to data pertaining to on-site management and transfers, a single element of the TRI form R requires reporting of the maximum amount of a chemical on site at any one time. Under EPCRA §312, the Emergency Response Program requires regulated facilities to submit annual inventory reports of hazardous chemicals stored on site to the state. Tier I requires reporting on broad categories of physical hazards, while Tier II requires chemical-specific information by CAS number. The information contained in the Tier I and Tier II reports surpasses the chemical inventory data requested on TRI Form R in terms of the chemicals covered and level of detail. However, there is limited public access of Tier I and Tier II data because of restrictions due to security concerns.
Under §112(r) of the Clean Air Act, facilities with processes that use or store more than a specified amount of certain flammable and toxic substances must develop and implement a risk management program and submit to EPA a summary of their program—called a Risk Management Plan (RMP). These plans include the amounts (in pounds) of each substance that are processed or used, hazard assessments of the potential effects of hypothetical accident scenarios, a five-year history of accidental releases involving regulated substances at the facility, and information about the facility’s accident prevention and emergency response programs. Facilities with processes that use or store more than a threshold amount (500–20,000 pounds) of a listed chemical must file an RMP and update their filing at specified times, including following a significant accidental release. TRI data do not duplicate RMP data as: (1) RMP covers only 54 of the 683 TRI chemical and chemical compound categories;12 (2) some RMP data are considered to be confidential business information (CBI) and are therefore not publically available; and (3) RMP reporting occurs every five years, as opposed to annually for TRI.13
Under Section 8(a) of the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), chemical manufacturers (including importers) must report to EPA’s Chemical Data Reporting (CDR) every four years. Facilities must report manufacturing-related information for sites that manufactured (including imported) 25,000 pounds or more of a reportable chemical substance during any one calendar year between submission periods. Facilities must also report industrial processing and use information as well as commercial and consumer use information. CDR contains more detailed inventory information than TRI; for example, CDR includes chemical concentration and physical form data not found in TRI. CDR also contains a broader range of chemicals than TRI; in a typical CDR reporting cycle, EPA collects information for about 7,000 to 8,000 chemicals. However, CDR’s base for information collection is much narrower than that for TRI. CDR reporting requirements only apply to chemical manufacturers (including importers). CDR reporting requirement do not apply to industrial facilities in other sectors that process or otherwise use chemicals.
Pollution Prevention Data
TRI also collects pollution prevention data from reporting facilities. These data include quantities of chemicals managed as waste by waste management practice (e.g., recycling, energy recovery, etc.) and source reduction activities implemented at the facility.
Under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), facilities must report pollution prevention data in their Biennial Hazardous Waste Reports (described above). While BR data provide qualitative and quantitative pollution prevention information, facility and chemical coverage is not directly comparable to data required for TRI reporting. BR contains data on generation, transfer, and management of hazardous wastes; TRI reporting requires data on toxic chemicals in waste streams or process by-products (all production phases and media).
Under various state regulations, at least fourteen states14 implement mandatory pollution prevention programs for TRI filers, facilities that use toxic chemicals, or generators of hazardous waste. Pollution prevention data are collected under these programs and stored in databases administered by state environmental agencies. The types of pollution prevention data collected vary by state, and may include both data similar to that collected by TRI (e.g., quantities of waste managed, source reduction activities) and details not found in TRI (e.g., pollution prevention plans, costs associated with waste management, etc.). However, no federal or state program collects all of the pollution prevention data currently required by TRI.
3(b) Public Notice Required Prior to ICR Submission to OMB
This Supporting Statement is part of EPA’s request to renew the existing approved Form R/A ICR which is scheduled to expire on October 31, 2014. The notice of plans to renew the ICR was published in the federal register on March 3, 2014 under 79 FR 11783.
EPA received four comments on this ICR. The comments and responses are listed in the attached supplementary document, “1363.23 Response to Comments.”
3(c) Consultations
EPA has consulted with a large number of individuals and organizations throughout all segments of the public in the development and continued implementation of the TRI Program. EPA has received feedback from environmental and public interest groups, trade associations, educational institutions, individual representatives, and others through its outreach efforts in venues such as:
meetings with stakeholders to provide TRI program updates and obtain input on rulemakings;
on-line dialogues to discuss issues and obtain input on potential rulemakings;
webinars to provide training on various topics, including expanding the use of TRI for environmental justice; and
the TRI National Training Conference, held every 18-24 months.
For more specific information on meetings and organizations consulted, see Appendix D. EPA continually seeks this feedback and incorporates it into the ongoing evolution of the TRI Program.
3(d) Effects of Less Frequent Collection
Section 313 requires annual reporting. Section 313(i) permits EPA to modify the reporting frequency by rulemaking; however, EPA must first notify Congress and then delay the initiation of such a rulemaking for at least 12 months, but no more than 24 months, from the date of the notification. In addition, EPA must find: that the modification is consistent with the provisions of subsection (h) of §313 based on:
(i) experience from previously submitted toxic chemical release forms; and
(ii) determinations made under paragraph (3).
Paragraph (3), in turn, provides that EPA must determine:
The extent to which information relating to the proposed modification provided on the toxic chemical release forms has been used by the Administrator or other agencies of the federal government, states, local governments, health professionals and the public.
The extent to which information is (i) readily available to potential users from other sources, such as state reporting programs, and (ii) provided to the Administrator under another federal law or through a state program.
The extent to which the modification would impose additional and unreasonable burdens on facilities subject to the reporting requirements under this section.
Since TRI represents the best available multi-media database for tracking toxic chemical releases in the United States, a change in the reporting frequency to less than once a year could have a significant impact on the availability of timely toxic chemical data and affect data users, particularly at the community level. Additionally, public access to the most current toxic chemical release data and other waste management information would become more difficult.
3(e) General Guidelines
This ICR adheres to the 1995 Paperwork Reduction Act, as amended, OMB's implementing regulations, and all applicable OMB guidance.
Although reporting facilities must identify the chemical for which they submit reports, they can claim the chemical identity as a trade secret. In such circumstances, facilities provide a generic name as part of the information made available to the public. EPA securely stores and maintains the true identity of the chemical (see also Section 3(f) below).
Effective January 21, 2014, EPA requires the electronic submission of TRI Form R/Form A through the Internet via EPA’s Central Data Exchange (CDX) by using the Toxics Release Inventory Made Easy Web (TRI-MEweb) reporting software. TRI-MEweb helps facilities prepare high-quality reports more easily than they could using paper reporting forms due to a number of technology advances, including built-in data quality checks.
Small facilities (with fewer than 10 full-time employees or the equivalent) are exempt from reporting under EPCRA §313. Two particular provisions that apply to TRI reporters universally: 1) the optional range reporting provision 15 and 2) an alternate threshold allowing Form A eligibility, are particularly beneficial to non-exempt smaller facilities with small releases and wastes.
3(f) Confidentiality
Respondents may designate the specific chemical identity of a substance as a trade secret according to EPCRA §322. Procedures for submission and review of trade secret claims under EPCRA §313 are set forth in 40 CFR 350. When a facility claims the chemical identity to be a trade secret and properly substantiates the claim, EPA will not disclose the identity of the chemical to the public. EPA securely stores forms with trade secret information and allows access to those documents only to persons with Trade Secret clearance. Data made available to the public through any means do not include trade secret information.
3(g) Sensitive Questions
This collection does not request any sensitive information.
4 THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED
4(a) Respondents/NAICS Codes
The reporting requirements found in EPCRA §313 apply to owners and operators of facilities that have 10 or more full-time employee equivalents (i.e., a total of 20,000 hours worked per year or greater; see 40 CFR 372.3); are included in a North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) Code listed at 40 CFR 372.23 or under Executive Order 13148, federal facilities regardless of their industry classification; and manufacture (defined to include importing), process, or otherwise use any EPCRA section 313 (TRI) chemical in quantities greater than the established thresholds for the specific chemical in the course of a calendar year. Historically the TRI-covered industrial sectors were identified by their Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) codes. Beginning with Reporting Year (RY) 2006, the TRI Program converted from SIC codes to North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) codes (71 FR 32464, June 6, 2006). The full list of NAICS codes for facilities that must report to TRI (including exemptions and/or limitations), if all other threshold determinations are met, can be found in Appendix E.
4(b) Information Requested
Data Items, Including Recordkeeping Requirements
Appendix A provides a copy of the proposed Form R, Form R Schedule 1 and Form A. For instruction revisions associated with the proposed form revisions, see Appendix B. To access existing TRI Reporting Forms and Instructions, see http://www.epa.gov/tri/report/#forms.
Form R
Facilities reporting to TRI report releases and other waste management of listed chemicals on Form R. The required data items, summarized below, are specified in 40 CFR §372.85. Form R consists of two sections. In Part I, respondents report facility identification information including: facility identification number; facility name and address; NAICS code; facility Dun and Bradstreet (D&B) number; parent company name; parent company D&B number; name, email address, and phone of the technical contact; and name, email address, and phone of the public contact. In Part II, respondents report:
Toxic chemical identity,
Mixture component identity,
Activities and uses of the toxic chemical at the facility,
Maximum amount of the toxic chemical on site at any time during the calendar year,
Quantity of the toxic chemical entering each environmental medium on site,
Transfers of the toxic chemical in wastes to off-site locations,
On-site waste treatment methods and efficiency, and
Source reduction and recycling activities.
On Form R Schedule 1, facilities reporting on dioxin and dioxin-like compounds report the individual grams data for each member of the dioxin and dioxin-like compounds category present. Form R Schedule 1 is a four-page form that mirrors the data elements from Form R Part II Chemical-Specific Information sections 5, 6, and 8 (current year only).
Form A
Form A also consists of two sections. Part I solicits the same information as Part I of Form R (see list above) but requires a different certification statement which represents a signed statement by a facility owner/operator or senior management official. In contrast to Form R where reduced threshold eligibility is not an issue, the Form A’s signed statement certifies that the annual reportable amount as defined by 40 CFR 372.27(a) did not exceed 500 pounds for the reporting year, and that the amounts manufactured, or processed, or otherwise used did not exceed 1 million pounds for that year. In most instances, PBT chemicals may not be reported using Form A.16 In Part II, a facility may report multiple chemicals on a single Form A. Specifically Form A solicits:
Toxic chemical identity, and
Mixture component identity.
In addition to annual reporting requirements, facilities must maintain records used to provide the information required on the form according to 40 CFR §372.10. Those records may include estimation methodology and calculations; engineering reports; inventory, incident, and operating logs; and other supporting materials. Facilities must keep a copy of each report filed for at least three years.
Proposed Form Revisions
As mentioned above, EPA is proposing revisions to the Form R and Form A that clarify data elements and enhance data utility. Specifically, the revisions to the forms and rationale for the revisions are presented in Table 3.
Table 3
Proposed Form Revisions
|
Form Revision |
Rationale |
Form |
1 |
Add an optional extension to all phone numbers to allow facility representatives to provide the extension needed for a direct connection. (Part I: Section 4) |
The phone number provided is often the main company line. Many companies have extensions for direct connection with employees. Addition of the optional phone extension would allow facilities to ensure that incoming calls are directed to the appropriate person. |
R/A |
2 |
Add an optional field for the reach code corresponding with the receiving water body for each surface water discharge. (Part II: Section 5.3)
|
40 CFR §372.85(b)(7) requires facilities to include on their form Rs “the name(s) of receiving stream(s) or water body to which the chemical is released.” Water body name is not a unique identifier, however, and a single water body can cover a large and disparate geographic area. Therefore, in order to model the potential impact of chemical discharges on downstream and intermediate receiving water bodies, EPA and other regulatory agencies, researchers, and analysts use the 14-digit reach code assigned in the USGS’s National Hydrography Dataset (NHD).
These reach codes identify a continuous piece of surface water with similar hydrologic characteristics. Once linked to the NHD by their reach code, the upstream/downstream relationships of water-related entities such as drinking water supplies, fish habitat areas, or wild and scenic rivers can be analyzed using software tools ranging from spreadsheets to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and the potential cumulative environmental impacts of TRI chemical can be assessed.
When using TRI-MEweb, respondents would be able to compete this field even if they did not know their reach code. Instead, TRI-MEweb would populate the code automatically when a user selects their receiving water body on the map provided in the TRI-MEweb interface for this section. Thus, in the process of completing the required field for stream or water body name, respondents will be able to concurrently complete the new optional field without any additional steps.
|
R |
3 |
Move the header “5.5 Disposal to land on-site” to precede Sections 5.4 and 5.5 on Form R so that it covers both 5.4 and 5.5. Re-word 5.4.1 and 5.4.2 to fit under the new header as follows: Section 5.4-5.5: Disposal to land on-site, Section 5.4.1: Class 1 Underground Injection Wells, Section 5.4.2 Class II-V Underground Injection Wells. (Part II: Section 5.4-5.5) |
This change would clarify that releases to underground injection wells are considered releases to land.
|
R |
4 |
Provide the heading, “Production-related waste managed” for Sections 8.1-8.7 and re-label Section 8.8 “Non-production-related waste managed,” with a footnote indicating that this Section “includes quantities released to the environment or transferred off-site as a result of remedial actions, catastrophic events, or other one-time events not associated with production processes” (Part II: Section 8.1-8.8). |
Form R does not currently indicate that quantities reported in Sections 8.1 through 8.7 are exclusive of the amounts reported in Section 8.8. Adding the labels “Production-related” and “Non-production-related” waste managed would mirror the terminology used to describe these data elements in TRI tools and the TRI National Analysis and clearly delineate which releases and transfers to report in which Sections. |
R |
5 |
Add checkboxes to indicate whether the facility has provided a “Production Ratio” or an “Activity Ratio” (Part II: Section 8.9). |
Section 6607(b)(5) of the PPA requires facilities to submit a ratio of production in the reporting year to production in the previous year. Where some variable other than production is the primary influence on waste characteristics or volumes, facilities may base this ratio on the primary influencing variable. The existing form does not specify which type of ratio was used and thus limits the utility of this metric. Additionally, “production or activity ratio” is a more precise description of this Section than “production ratio or activity index” since the metric reported is a ratio regardless of whether production or some other activity variable is used. |
R |
6 |
Add a new column where the facility can provide an optional percentage range indicating the estimated annual reduction in chemical waste generation associated with a given source reduction activity (Part II: Section 8.10). |
This change would make it easier to report and assess the effectiveness of different types of source reduction activities and thus promote the adoption and recognition of successful pollution prevention practices. To simplify reporting, facilities would report their estimates using one of six percentage ranges (just as treatment efficiencies are reported in ranges in Section 7). While optional, completion of this Section would be a simple way for a facility to highlight positive steps it has taken to reduce releases of toxic chemicals to the environment. |
R |
7 |
Provide optional barrier codes in Section 8.11 that facilities can use to indicate why they could not implement any source reduction activities during the reporting year (Part II: Section 8.xx)..
|
Currently, facilities are required to pick a source reduction activity code if they performed a new source reduction activity. However, there is currently no way for a facility to indicate why they did not implement a source reduction activity. While the new codes provided for this purpose would be optional, it would allow EPA to assist facilities in overcoming barriers to implementing source reduction activities. |
R |
8 |
Allow facilities to categorize optional free-text information entered in Sections 8.11 and 9.1 by selecting from a list of topics provided in TRI-MEweb (Part II: Section 8.11 and Section 9.1).
|
Letting facilities provide free-text entries for specific commonly-used topics would improve TRI tools that display free-text information, data quality efforts, and overall analytical utility of the dataset. This option would be provided by having TRI-MEweb present a checklist of commonly used topics in Section 8.11 (seven topics) and Section 9.1 (eight topics) for which a user may provide topic-specific optional information via a text box. |
R |
Proposed Revision to TRI-MEweb
Additionally, the EPA proposes modifying TRI-MEweb to collect, as optional, information that some facilities have historically provided, unsolicited, to EPA on matters related to TRI (collectively called miscellaneous TRI documents). Examples of these miscellaneous TRI documents include updates to contact and location information for the facility and reasons for non-reporting. Some of this information is useful to the Agency and could be useful to the public. Currently, the EPA receives this unsolicited information on paper.
This proposed modification would allow for an online means for the EPA to receive miscellaneous documents, therefore reducing the cost of processing their submission and aligning how EPA processes such documents with the recent requirement to submit TRI reporting forms electronically. In other words, with this change, facilities could use TRI-MEweb to provide details on specific categories of information that they have been providing on a voluntary basis to the EPA throughout the existence of the program (e.g., supplemental information on updates to the facility’s name, status, location, and/or parent company; supplemental information on updates on whom to contact for technical and/or public matters; and reasons for not reporting (indicating the facility did not meet thresholds or did not report for any other appropriate reason)). Receipt and processing of this information would not affect any reporting forms certified and submitted to the agency, but rather would allow facilities to provide an electronic means to submit contextual information concerning their facilities that can enhance the context of TRI data for the EPA as well as for the public.
(ii) Respondent Activities
Facilities engage in a number of activities to comply with the EPCRA §313 reporting requirements. These activities fall into two distinct groups: Form Activities, consisting of rule familiarization, compliance determination, calculations and form completion, and recordkeeping and submission; and Non-Form Activities, consisting of supplier notification, non-reporter compliance determination, and petitions.
Form Activities
Rule Familiarization: Staff of a facility that is reporting under EPCRA §313 for the first time must read the reporting package and become familiar with the reporting requirements. This includes the time needed to review instructions, and the time needed to train personnel to respond to a collection of information.
Reporter Compliance Determination: At reporting facilities staff must make the determination that the facility meets the criteria for EPCRA §313 reporting. This activity includes the time required to become familiar with the definitions, exemptions, and threshold requirements under the TRI Program, to review the list of TRI chemicals, and to conduct preliminary threshold determinations to determine if the facility is required to report.
Calculations and Form Completion: Facility staff must gather data and perform calculations to provide the information required on the form. This activity includes the time required to search data sources and the time to complete and review the information.
Recordkeeping and Submission: Facility staff must maintain recordkeeping systems and submit the report to EPA and the state in which the facility is located. This activity includes the time required to transmit or otherwise disclose the information.
Non-Form Activities
Supplier Notification: Certain suppliers of mixtures or trade name products containing reportable substances must annually notify their customers of the product's composition, if the customer is subject to EPCRA §313 reporting. This activity includes the time required to inform customers, either by letter or through the materials safety data sheet (MSDS) for the product.
Non-Reporter Compliance Determination: In any given reporting year, a group of eligible facilities will complete compliance determination but will not file a Form R or Form A. The process for determining whether reporting is required is the same as described above under Form Activities; however, given that compliance determination applies to all other facilities in NAICS-code-eligible sectors (with ten or more employees)—including those that ultimately do not report to TRI—this separate activity accounts for the latter category.
Petitions: Any person may petition the EPA to add or delete a chemical from the TRI toxic chemical list. EPA evaluates the toxicity of the chemical against the listing criteria established by Congress and makes a determination whether to grant or deny the petition request. If the petition is granted, EPA will propose a rule to either add or delete the chemical and after reviewing the public comments will issue a final rule. If the petition is not granted, EPA issues a notice explaining why the petition was denied. The activities required to prepare and file a petition include the following:
Read EPA policy and guidance documents and consult with EPA;
Plan activities;
Prepare literature search;
Conduct literature search;
Process, review, and focus information;
Write petition;
Review and edit petition; and
Submit petition to EPA and file.
EPA provides the reporting community with instructions, guidance documents, training materials, and toll-free hotlines to assist them in completing and submitting their reporting forms to EPA.
5 THE INFORMATION COLLECTED—AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
5(a) Agency Activities
EPA engages in many activities to fulfill the purpose and requirements of EPCRA. These activities fall into the following categories that cover what the Agency does to assist the regulated community with compliance, to process the data, to maintain the database, and to make the data available:
Assistance to Reporters;
Electronic Reporting;
Paper-Based Reporting (limited to trade secret reporting forms);
Data Processing and Quality Control;
Database Organization;
Links to State Reporting;
Making Data Available;
List Revisions and Petition Reviews;
Trade Secrecy Reviews.
Assistance to Reporters. The Agency operates an outreach program to assist reporters with activities related to Form R (including Schedule 1)/Form A completion. EPA provides TRI reporting assistance with a variety of online tools and guidance, including TRI Reporting Forms and Instructions and TRI-MEweb (TRI Made Easy) reporting software. TRI-MEweb is a Web-based software application that TRI facilities can use for entering, validating and submitting their data. The TRI Program also provides both basic and advanced downloadable TRI training slides plus online audio training modules on the TRI website.
EPA operates two toll-free hotlines to answer general questions and questions pertaining to electronic reporting and data certification over the internet. In addition, the Agency maintains a website with current program-specific information and guidance (http://www.epa.gov/tri). General guidance has been prepared for estimating releases, including 14 industry-specific guidance documents. Additionally, EPA provides guidance and assistance for persons or organizations regarding petitions to add or delete chemicals from the TRI list.
Electronic Reporting. As observed in 2013 for reporting year (RY) 2012, close to ninety-eight percent of all TRI Form Rs and Form As were prepared and submitted electronically using TRI-MEweb. 17,18 Capabilities in TRI-MEweb include:
Easy Upload and Validation Checks. Facilities can key, preload from a prior year submission or upload their data into TRI-MEweb. TRI-MEweb also provides facilities with extensive data validation checking through point-of-entry edit checks as well as a cumulative, mandatory validation checks prior to submission.
Submittal to the Central Data Exchange (CDX). After facilities enter and validate their data, certifying officials must electronically sign (i.e., certify) forms within TRI-MEweb.
Automatic Data Transmittal. Once a facility’s certifying official has certified its TRI submission, CDX automatically forwards it to the TRI EPCRA Data Processing Center (DPC), which loads it into the TRI Processing System (TRIPS) database. The TRIPS database is located at EPA’s National Computer Center in Research Triangle Park, NC.
TRI Submission shared with States. Through the TRI Data Exchange, facilities can submit the data via CDX, which transmits the data to both EPA and the participating state government. This reporting option allows facilities to fulfill their legal obligation to report to both EPA and the appropriate State through a single transmission of data to CDX.
Preloaded Forms and Central Data Storage. The TRI-MEweb application allows users to preload their forms with prior year data stored in an EPA-maintained database. This database is separate from the TRIPS database, which stores certified TRI submissions.
Quick Lists. TRI-MEweb provides “quick lists” that allow users to narrow their data entry to only the pertinent areas.
Data Quality Checks. TRI-MEweb contains a number of data quality checks including internal consistency and semantic checks that compare a facility’s data to prior year submissions.
On-Line Revisions and Withdrawals. The application allows online revision and withdrawal of data by facilities. Through this feature, facilities can access previously submitted forms, and revise or withdraw as needed.
Automated Section 8 Calculator. TRI-MEweb automatically calculates Section 8 Column B (current year) estimates based on data entered in other form sections. Users may tailor the calculation's inputs, but cannot enter their own calculated values. This approach aims to reduce the frequent mathematical errors in Section 8 and simplify the reporting process.
TRI Assistance Library. An online TRI Assistance Library (TRIAL) is available to help facility reporters complete their TRI submissions.
Paper-Based Reporting. As of January 21, 2014, only facilities submitting trade secret reporting forms are allowed to submit data to TRI on paper forms. Facilities submitting trade secret forms must submit two forms, one that is trade secret and one that is sanitized. The trade secret form goes into a separate database, and EPA keys the sanitized information into the TRIPS database. Automated data quality checks begin at data entry. At this point, the emphasis is on identifying forms that are not completed correctly and cannot be processed further because of fundamental errors (e.g. no chemical specified).
Data Processing and Quality Control. EPA no longer processes paper forms as of RY 2013. EPA only performs additional validation checks of electronic data that have been certified by TRI-MEweb and sent for processing into TRIPS through CDX. The validation checks look for duplicate records and determine if a facility reconciliation is required before the data are released. EPA also conducts a set of data quality checks that compare the incoming data with prior years’ data and various data threshold checks.
Upon passing the data validation and quality checks in TRIPS, EPA generates an electronic Facility Data Profile (eFDP) report and makes it available for facility review through TRI-ME web. The report contains an echoing back of the data and confirms that all validation checks have passed and that the facility’s data have been processed into the TRIPS database. However, as of RY 2013, the eFDP report can no longer be used by facilities to manually correct data submitted to EPA.
Database Organization. EPCRA §313(j) requires EPA to make TRI data available to the public through computer telecommunications and other means. EPA ensures that each facility has a unique identifier—the TRI facility ID (TRIFID). EPA generates a TRIFID for newly reporting facilities at the time of data entry. The identification number allows easy retrieval of cross-year data, even when a facility is sold or changes its name. Facilities receive notification of their TRIFID and must use it consistently over time.
Links to State and Indian Country Reporting. EPCRA §313 requires facilities to submit forms to both EPA and the state or Indian country agency in which they operate. For coordination, tracking, and quality assurance purposes, EPA, state, and Indian country agencies reconcile their submissions at the end of the reporting cycle.
In 2004, EPA implemented the TRI State Data Exchange (now referred to as the TRI Data Exchange (TDX)), which enables facilities to simultaneously submit their data to EPA and the State or Indian country in which they are located. There are currently 48 TDX participants. This reporting option allows facilities to fulfill their legal obligation to report to EPA as well as the State or Indian country through the sole submission of data through CDX.
Making TRI Data Available. There are many options available for accessing TRI data - ranging from data files to refined analyses. The annual TRI National Analysis is an overview of the most recently reported TRI data. It includes key findings, in-depth analyses, and information on trends. Two on-line data access tools, TRI Explorer and Envirofacts, make TRI data available to the public for further analysis. In addition, the public can download a desktop application, TRI.NET, from the TRI website. TRI.NET allows users to build custom reports of TRI data, to view and analyze TRI data using geospatial capabilities, and to combine TRI data with other related data for further analysis. Envirofacts provides Web services that allow developers to include dynamic TRI data queries in their applications.
The TRI Program historically did not release the latest year of TRI reported data until the release of the TRI National Analysis. However, starting in 2009, EPA began releasing the most recent year of TRI data within weeks after the July 1st reporting deadline. EPA provides the TRI preliminary dataset in downloadable data files, as well as via TRI Explorer, Envirofacts and Web services. Note, however, that these data have not undergone the manual data quality checks and verifications that EPA conducts prior to the TRI National Analysis release.
List Revisions and Petition Reviews. The list of toxic chemicals subject to reporting under EPCRA §313 may undergo changes. EPA can initiate regulatory additions or subtractions of chemicals from the list of TRI-covered chemicals, either independently or in response to a petition.
Trade Secrecy Reviews. Facilities claiming a chemical identity as a trade secret must substantiate the claim by completing the Trade Secret Substantiation Form available from the TRI website (www.epa.gov/tri) under "TRI Reporting Materials." For more information on trade secrecy reviews, including the costs to EPA, see the ICR for the Trade Secrecy Rule for EPCRA (EPA #1428, OMB #2050-0078).
5(b) Collection Methodology and Management
As of January 21, 2014, EPA requires electronic submission of all non-trade secret reporting forms through the Internet via EPA’s CDX and the TRI-MEweb application. Note that for RY 2012, filers prepared close to ninety-eight percent of all TRI submissions using TRI-MEweb and submitted electronically to EPA via CDX.
5(c) Small Entity Flexibility
Under EPCRA §313 (b)(1)(A), facilities with fewer than 10 full-time employees (or the equivalent) do not have to report. In addition, EPA has taken several steps to minimize the burden for covered small businesses. EPA added a range reporting option to the Final Rule (53 FR 4500, February 16, 1988), which codified the EPCRA §313 reporting requirements. Range reporting was the preferred option from the Regulatory Flexibility Act analysis to provide burden reduction for small businesses. Range reporting provides an option for releases of less than 1,000 pounds to be recorded as a code representing one of three ranges (1 to 10 pounds, 11 to 499 pounds, or 500 to 999 pounds) rather than as a specific estimate of the release amount. The benefit is not, however, limited to small businesses. Note that facilities may not use range reporting on Form Rs for PBT chemicals.
In response to a petition from the Small Business Administration, EPA promulgated the alternate threshold (59 FR 61488, November 30, 1994), manifested in Form A reporting, as discussed in Section 1(b). Although any reporting facility meeting the criteria may use the alternate threshold, this alternate threshold may be particularly advantageous to small entities.
5(d) Collection Schedule
Facilities must report their information on a calendar-year basis, and submit Form Rs or Form As to EPA by July 1 of the following year. In response to public requests to shorten the time frame for release of TRI information, TRI began a modernization effort in 2007 that included transition to TRI-MEweb from desktop software, and a number of streamlining initiatives. One of the resultant improvements was the Preliminary Data Release which provides TRI database information as quickly as possible after the reporting deadline. Since 2010, EPA has released data less than one month after the reporting deadline in the TRI preliminary dataset with downloadable data files and access via TRI Explorer and Envirofacts.
ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF THE COLLECTION
This information collection activity imposes burden and cost on certain facilities affected by EPCRA §313 reporting requirements. It also imposes costs on EPA to process and make available the data collected and stored in the Toxics Release Inventory. The following sections present the derivation of Form R and Form A respondent burden and cost as well as Agency burden and cost. For TRI reporters, the following sections present estimates of average Form R and Form A reporting burden per respondent. EPA develops unit costs by combining these form-level unit burden estimates with an appropriate wage rate. Combining the universe of reporting forms with estimates of unit burden and cost provides an estimate of Total Form R and Form A respondent burden and costs. This universe of reporting forms consists of reporting in RY 2012 plus updates to reflect changes during the year of the ICR project—in this case, the modeled number of chemicals and facilities estimated to report under the Addition of ortho-Nitrotoluene rule, published on November 7, 2013, and the Electronic Reporting of TRI Data rule, published on August 27, 2013. The combined total number of forms and facilities (i.e., respondents) is hereafter referred to as the ICR Universe.
The methodology used to estimate reporting burden in this ICR Renewal—Ratio-Based Burden Methodology (RBBM)19 —is a restructured and simplified formulation of the previously employed methodology; OMB approved this new methodology published on April 28, 2011.20 When estimating reporter burden using RBBM, the Nominal Form R unit burden (35.70516 hours) is the base number and Form A unit burden is set at 61.5% of that value. These unit burdens reflect burden associated with form activities including rule familiarization, reporter compliance determination, calculations and form completion, and recordkeeping. In addition to Form R and Form A burden, total TRI program burden is captured by adding non-form burden associated with supplier notification, non-reporter compliance determination, and petitions to form burden.
In accordance with the EPA’s RBBM methodology, certain types of modifications to forms are employed for the purpose of clarifying data elements and/or enhancing data utility and are considered to not accrue burden (See Docket #: EPA-HQ-OEI-2010-0835, “Revising TRI Burden to Ratio-based Burden Methodology,” Table C-5, Appendix C). Such changes can be so minuscule that EPA estimates them to have a negligible impact on form-related burden. The scope of these types of minuscule changes includes situations where burden associated with the data gathering and recording is negligible (and the frequency of reporting the data element is low), if a response is already implied in an existing data element (e.g., addition of an NA box), and where clarification on the reporting form is made but no new information is required. Additionally, the EPA associates no burden by convention for certain optional elements on TRI reporting forms.
OMB approved a combined Form R/Form A ICR on October 14, 2011, with an expiration date of October 31, 2014. The OMB approved burden estimate at that time was a total of 3.52 million hours. Several changes in the reporting requirements have occurred since OMB’s approval of the ICR on October 14, 2011.21 Specifically:
On October 17, 2011, EPA lifted the Administrative Stay of the Toxics Release Inventory reporting requirements for hydrogen sulfide. EPA received the first submissions for hydrogen sulfide for reporting year 2012; the total number of form submissions used to calculate the overall program burden therefore includes these hydrogen sulfide submissions.
On April 19, 2012, EPA published a rule requiring facilities located in Indian country to report to tribal governments beginning with TRI reporting year 2012 (TRI reports due by July 1, 2013). On December 10, 2012, OMB approved a change in the program burden hours (due to rule familiarization only) for Form R and Form A to reflect passage of the TRI Reporting for Facilities located in Indian Country rule, increasing burden by 6,985 hours. Concurrent with the TRI program’s decision to begin estimating burden due to rule familiarization and compliance determination separately, the program has estimated that the burden associated with staff at a facility learning and understanding new reporting requirements only occurs in the first year that a facility is subject to reporting. In subsequent years, EPA assumes that facility staff are familiar with the requirement that apply to their facility, and the facility does not incur this burden again. Accordingly, this burden applies in the first year of the rule only, and is prior to this ICR renewal period. Therefore, this rule adds no ongoing steady state burden to the TRI program.
On July 18, 2013, EPA published a rule updating the list of North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) codes subject to reporting under the Toxics Release Inventory (TRI) to reflect the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) 2012 NAICS revision. Facilities would be required to use 2012 NAICS codes when reporting to TRI beginning with TRI reporting forms that are due on July 1, 2014, covering releases and other waste management quantities for the 2013 calendar year. EPA estimated no additional reporting burden due to this rule as it adds no new reporting requirements.
On August 27, 2013, EPA published a rule requiring facilities to report non-trade secret Toxics Release Inventory (TRI) forms to EPA using electronic software provided by the Agency. EPA estimated burden under three possible scenarios for this transition. Expected ongoing steady state burden equals approximately $1,000 in capital costs (i.e., total ongoing Internet costs for facilities who do not already have Internet access).
Lastly, on November 7, 2013, EPA added ortho-Nitrotoluene (o-Nitrotoluene) to the list of toxic chemicals subject to reporting under section 313 of the Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (EPCRA) of 1986 and section 6607 of the Pollution Prevention Act (PPA) of 1990. EPA estimates that this rule will increase the number of newly reporting facilities by 1 and the total number of Form Rs and Form As submitted by 17 and 5 respectively, with an associated ongoing steady state burden increase of 717 hours.
Based on the latest data for RY 2012 with
updates to reflect the estimated additional reporting resulting from
the Addition of the o-Nitrotoluene rule,
EPA now estimates the total number of combined Form R and Form A
responses to be 74,869, the associated total annual burden hours to
be 3.56 million and the annual cost to be $183.4 million (see
Section 6(b) for breakdown by Form R, Form A, and non-Form
contributions). These estimates
incorporate the proposed revisions to Form R and Form A which have
been estimated to have a negligible impact on form burden.
Agency burden and cost associated with the TRI Program includes RFI and Compliance Assistance; TRI Reporting Software and Related Data Collection/Exchange IT Infrastructure, and Data Processing. Section 6(b) presents the Agency’s burden and cost of these activities.
6(a) Estimating Respondent Burden
This section presents the burden of this information collection activity to Form R and Form A respondents in terms of the time required for facility personnel to perform the activities outlined in Section 3 of this document. As was done in the previous ICR, this ICR Renewal uses EPA’s new Ratio-Based Burden Methodology (RBBM), to estimate TRI respondent burden for both Form R and Form A reporting.22
Ratio-Based Burden Methodology simplifies calculations, supports internal consistency, and sharpens transparency while retaining the components of the previous methodology and maintaining its overall total burden estimate as a starting point.23 For activities associated with filing TRI chemical reports, RBBM burden estimates include rule familiarization, reporter compliance determination, calculations and form completion, and recordkeeping. Similarly, for activities unrelated to form reporting (non-form burden) RBBM estimates include supplier notification, non-reporter compliance determination, and preparation and submission of petitions.
Figure 1 presents the equations of RBBM’s primary method: Steady State Total Burden Calculation. With RBBM’s calculation of form burden, the only variables/inputs required are total counts for Form R Chemicals and Form A Chemicals. The factors/constants of the equations include: 1) Nominal Form R unit burden, in units of burden hours per Form R Chemical and 2) A/R,24 a model for the ratio of Form A (single-chemical)25 to Form R burden.
As shown in Figure 1, multiplying the Nominal Form R unit burden by the number of Form R Chemicals provides an estimate of the total Form R burden. Similarly, multiplying the Form A unit burden (formulated as the product of A/R and Nominal Form R unit burden) by the number of Form A Chemicals provides an estimate of the total Form A burden.

EPA considers the burden estimates it uses to be average values for the reporting community overall. As with any average, some facilities will be above the average, and others will be below it. Large, complex facilities may require more than the average time to comply; however, many other facilities subject to the rule are not large or complex. Overall, EPA considers the TRI Program burden estimates to be reasonably representative of the reporting community overall, on average.
Form R and Form A Respondent Requirements
Facilities engage in a number of activities to comply with the EPCRA §313 reporting requirements. These activities can be divided into two distinct groups: Form Activities, consisting of rule familiarization, reporter compliance determination, calculations and form completion, and recordkeeping and submission; and Non-Form Activities consisting of supplier notification, non-reporter compliance determination, and petitions. Section 4(b)(ii) presents a detailed description of these activities.
Form Activities
Rule Familiarization
Reporter Compliance Determination
Calculations and Form Completion
Recordkeeping and Submission
Non-Form Activities
Supplier Notification
Non-Reporter Compliance Determination
Petitions
Note that for burden unrelated to reporting on a Form R or Form A (Non-Form Activities), the RBBM simplifies calculations by holding all of these values at a constant level, as estimated in the 2008 ICR Renewal.26
Updating Nominal Form R and Form A Unit Burdens
As discussed above, since the last ICR Renewal, five changes to the reporting requirements have occurred via rulemakings. Two of these rulemakings, tribal reporting and NAICS code updates, create no additional steady state programmatic burden. Due to the electronic reporting rule, a small number of facilities currently filing non-trade secret reports via paper will have to switch to electronic submission. The economic analysis supporting the rulemaking presents estimates of burden under a range of possible scenarios for this transition. Given the very small number of facilities potentially experiencing burden and the minor compliance costs, distributing this burden/cost across the full reporting universe results in negligible incremental per facility burden/cost. Therefore, at the margin, the electronic reporting rule does not constitute enough change to estimate additional burden. The lifting of the stay on hydrogen sulfide resulted in the reporting of 487 hydrogen sulfide reports (464 Form Rs and 23 Form As) by 484 facilities in RY 2012. The baseline for this ICR Renewal captures these reports. EPA estimates that the o-Nitrotoluene rule will increase the number of first time reporting facilities by 1 and the total number of Form Rs and Form As submitted by 17 and 5, respectively. The unit burdens associated with filling out Form R and Form A, however, remain unchanged. Section 6(d) discusses the anticipated change in the number of Form Rs and Form As filed.
Additionally, EPA is proposing to revise data elements for Form Rs and Form As that would improve the consistency and utility of TRI data. However, EPA estimates that the revision of data elements will have no measurable impact on Form R and Form A burden.
The following discussion explains how changes from rulemakings since the last ICR affect form unit burdens and how these changes will negligibly affect form unit burdens if EPA finalizes the proposed form revisions (analysis is based on RY 2012 data with updates to reflect the estimated additional reporting resulting from the Addition of o-Nitrotoluene rule).
Addition of o-Nitrotoluene
On November 7, 2013, EPA added o-Nitrotoluene to the list of toxic chemicals subject to reporting under section 313 of the Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (EPCRA) of 1986 and section 6607 of the Pollution Prevention Act (PPA) of 1990. EPA determined it meets the criteria for listing under EPCRA section 313(d)(2)(B) because the National Toxicology Program reasonably anticipates it to be a human carcinogen. Further, EPA estimates that facilities currently manufacture, process or otherwise use this chemical above TRI thresholds and therefore would file TRI reports. EPA expects facilities to file Form Rs and Form As on o-Nitrotoluene. The total number of additional TRI reports expected due to the rule is 17 Form Rs and 5 Form As, and the number of new facilities reporting to TRI is one. Note that this rule does not affect the value of the Nominal Form R unit burden.
Revised Data Elements
EPA is proposing several revisions to Form R and Form A. As mentioned above, these revisions will contribute to the standardization of responses and enhancement of data utility. Specifically, EPA is proposing:
to add an optional extension to all phone numbers to allow facility representatives to provide the extension needed for a direct connection. Because this is an optional question, by convention, no regulatory burden is imposed on facilities with its addition.
to add an optional field to allow facilities to indicate of the section of the water body that received the surface water discharges reported in Section 5.3. Specifically, facilities will be able to provide “reach codes,” which are unique codes that identify a continuous piece of surface water with similar hydrologic characteristics. Because this is an optional question, by convention, no regulatory burden is imposed on facilities with its addition.
to move the header “5.5 Disposal to land on-site” to precede Sections 5.4 and 5.5 on Form R so that it covers both 5.4 and 5.5. Re-word 5.4.1 and 5.4.2 to fit under the new header as follows: Section 5.4-5.5: Disposal to land on-site, Section 5.4.1: Class 1 Underground Injection Wells, Section 5.4.2 Class II-V Underground Injection Wells. These changes serve only to clarify what is already being reported in these sections and thus do not impose any additional regulatory burden.
to provide the heading, “Production-related waste managed” for Sections 8.1-8.7 and re-label Section 8.8 “Non-production-related waste managed.” These changes serve only to clarify what is already being reported in these sections and thus do not impose any additional regulatory burden.
to add checkboxes to indicate whether a facility has provided a “Production Ratio” or “Activity Ratio” in Section 8.9. The existing form already includes a field to submit one of these two ratios, so facilities must already decide which type of ratio to report and then report the calculated value. The only change is that facilities must now also indicate which type of ratio they selected. No additional regulatory burden is imposed as facilities already possess this information and are just identifying which ratio they are reporting.
to add a new column (d) in Section 8.10 where facilities can provide a percentage range indicating the estimated annual reduction in chemical waste generation associated with a given source reduction activity. Because this is an optional question, by convention, it imposes no regulatory burden on facilities with its addition. Note that while this change may create additional burden for facilities choosing to report the information, requesting range reporting, rather than the development of a point estimate, minimizes the burden on facilities.
to provide optional barrier codes in Section 8.11 that facilities can use to indicate why they could not implement any source reduction activities during the reporting year.
to allow a facility to categorize optional free-text information entered in Sections 8.11 and 9.1 by selecting from a list of topics provided in TRI-MEweb. Because this is an optional question, by convention, it imposes no regulatory burden on facilities with its addition. Note that while this change may create additional burden for facilities choosing to report the information, facilities need only read from a short list of topics and select one.
The changes proposed, along with their contributions to the forms and estimated additional burden are presented in Table 4.
Table 4
Additional Unit Reporting Burden Associated with New Data Elements
Section Number |
Form Change |
Estimated Burden (minutes) |
Form R, Form A – Part I: Section 4 |
Add optional extension to all phone numbers |
0.00 |
Form R – Part II: Section 5.3 |
Add an optional field for the code corresponding with the receiving water body for each surface water discharge in Section 5.3 |
0.00 |
Form R – Part II: Section 5.4 – 5.5 |
Move the header “5.5 Disposal to land on-site” to precede Sections 5.4 and 5.5 on Form R so that it covers both 5.4 and 5.5. Re-word 5.4.1 and 5.4.2 to fit under the new header as follows: Section 5.4-5.5: Disposal to land on-site, Section 5.4.1: Class 1 Underground Injection Wells, Section 5.4.2 Class II-V Underground Injection Wells. |
0.00 |
Form R – Part II: Section 8.1-8.8 |
Provide the heading, “Production-related waste managed” for Sections 8.1-8.7 and re-label Section 8.8 “Non-production-related waste managed.” |
0.00 |
Form R – Part II: Section 8.9 |
Add checkboxes to indicate whether facility has provided a “Production Ratio” or “Activity Ratio” |
0.00 |
Form R – Part II: Section 8.10 |
Add a new column (d) in Section 8.10 where facilities can provide a percentage range indicating the estimated annual reduction in chemical waste generation associated with a given source reduction activity |
0.00 |
Form R – Part II: Section 8.11 |
Provide optional barrier codes in Section 8.11 that facilities can use to indicate why they could not implement any source reduction activities during the reporting year |
0.00 |
Form R – Part II: Section 8.11 and 9.1 |
Allow facility to categorize optional free-text information entered in Sections 8.11 and 9.1 by selecting from a list of topics provided in TRI-MEweb |
0.00 |
Table 5 presents the average annual burden hour estimates by form type.
Table 5 |
|
Form Type |
Unit Burden Hours per Form |
Form R |
35.70516 |
Form A |
21.95867 |
Notes: |
|
Any given facility may file only Form Rs, only Form As, or a combination of Form Rs and Form As. Table 6 provides more details on the distribution of reporting by form type among facilities. Note also that for a given Form A filing (where multiple chemicals can be reported on a single form), the average number of chemicals reported is 2.29. Overall, each facility reports an average of 3.80 chemicals (Rs and As), with 11.3% of all chemicals filed via Form As.
Table 6 Form
per Facility Distribution |
|||||||
Form per Facility Distribution (RY 2012) |
Unique Facilities |
Chemicals |
Average Chemicals per Facility |
||||
Form R |
Form A |
Total |
Form R |
Form A |
Total |
||
Form A Only |
1,840 |
0 |
3,836 |
3,836 |
0.00 |
2.08 |
2.08 |
Form R Only |
17,094 |
62,196 |
0 |
62,196 |
3.64 |
0.00 |
3.64 |
Both Form R & Form A |
2,091 |
8,742 |
5,164 |
13,906 |
4.18 |
2.47 |
6.65 |
Total |
21,025 |
70,938 |
9,000 |
79,938 |
3.37 |
0.43 |
3.80 |
Notes: 4) The average number of Form A chemicals per Form A is 2.29. 5)
The total average number of chemicals per facility across all
types of facilities filing the form (Form A only, Form R only,
Both Form R and Form A) is calculated by dividing the total number
of chemicals by the total number of unique facilities. |
|||||||
Table 7 presents the annual estimated burden hours for the overall average conditions. These estimates represent the burden on a "typical" facility as defined by the facility filing the average number of chemicals (as represented by overall averages). As shown in Table 6, there are a variety of patterns for Form R and Form A Chemical filings by facility. Section 6(d) discusses the total annual burden to all facilities.
Table 7 |
|
Form Type |
Annual Average Facility Burden Hours |
Form R Contribution [35.70516 hrs per chemical × 3.37 chemicals per facility] |
120.469 |
Form A Contribution [21.95867 hrs per chemical × 0.43 chemicals per facility] |
9.4 |
Overall Average |
129.869 |
6(b) Estimating Respondent Costs
EPA calculates the steady state total cost to respondents based on the time needed to complete the activities listed in Section 6(a) and the weighted average wage rate (WAWR) which is the average loaded cost for a mix of managerial, technical, and clerical labor (in proportions of .03, .89, and .08, respectively) per hour of TRI reporter burden.27 There are no specific capital and operation and maintenance costs associated directly with this information collection activity. There may be some small additional costs for mailing and supplies, although with the recent promulgation of the electronic reporting rule, these costs are minimized. Section 6(d) discusses total annual costs for all facilities.
(i) Estimating Labor Costs
EPA estimates labor burden for three separate labor categories (management, technical, and clerical) across multiple activities; it is necessary to obtain wage rates for each labor category in order to estimate labor costs and compute WAWR, as shown in Table 8.
Table 8 |
||||
Wage Type (Burden Proportion) |
Managerial (0.03) |
Technical (0.89) |
Clerical (0.08) |
WAWR Composite |
Occupational Type |
Management, business, and financial |
Professional and related |
Office and administrative support |
Weighted hourly wage rate |
Wages and Salaries |
$41.35 |
$33.66 |
$16.49 |
|
Total benefits |
$18.28 |
$13.91 |
$7.31 |
|
Overhead |
$7.03 |
$5.72 |
$2.80 |
|
Total Loaded Rate |
$66.66 |
$53.29 |
$26.60 |
|
WAWR Contribution |
$2.06 |
$47.40 |
$2.12 |
$51.58 |
Table 9 summarizes average respondent costs for Form R and Form A.
Table 9 |
|
Form Type |
Annual Average Facility Cost |
Form R Contribution [35.70516 hrs per chemical × 3.37 chemicals per facility × $51.58] |
$6,213.77 |
Form R Contribution [21.95867 hrs per chemical × 0.43 chemicals per facility × $51.58] |
$484.83 |
Overall Average |
$6,698.60 |
Note that these estimates assume non-form burden to be a constant at 825,517 hours with an associated cost of $42,580,167. The components of this burden are:
Petitions – 925 hours
Supplier Notification – 89,616 hours
Non Reporters’ Compliance Determination – 734,976 hours
EPA estimates the total cost associated with non-form burden by multiplying this constant by the WAWR (see Section 6(d) for total respondent cost associated with the TRI Program).
6(c) Estimating Agency Burden and Cost
This section estimates the burden and costs to EPA to process Form R and Form A reports based on information characterizing the resources used in previous years. EPA incurs burden and costs for three categories of activities: RFI and Compliance Assistance; TRI Reporting Software and Related Data Collection and Exchange; and Data Processing. Table 10 outlines these activities in detail.
Table 10
EPA Activities for Collecting, Processing, and
Managing TRI Data
Category |
Description |
Reporting Forms and Instructions (RFI) and Compliance Assistance |
|
TRI Reporting Software and Related Data Collection and Exchange |
|
Data Processing |
|
Table 11 presents the estimate of EPA burden specific to RFI and Compliance Assistance, TRI Reporting Software and Related Data Collection and Exchange, and Data Processing, in terms of Agency costs and number of FTEs.
Table 11
Agency Costs and FTEs to Support the Collection, Processing, and
Management of TRI Form Submissionsa
Description |
Non-FTE Cost |
FTEb |
RFI and Compliance Assistance |
$ 320,000 |
1.1 |
TRI Reporting Software and Related Data Collection/Exchange IT Infrastructure |
$ 1,279,803 |
2.1 |
Data Processing |
$ 3,030,968 |
2.0 |
Total |
$ 4,630,771 |
5.2 |
a E-mail communication with TRI Data Processing Center, January 10, 2014. |
||
b Based on actual headcounts for RY2012. |
||
The estimated Data Processing costs include fixed costs (overhead) and variable costs, which depend on the number and type of form submissions. The cost of processing TRI forms is approximately $27.86 per chemical for paper submissions and $6.05 per chemical for TRI-MEweb submissions.28 Based on reporting year 2012, the total annual Agency cost for items, as shown in Table 11, is $4,630,771. Note that, due to the Electronic Reporting Rule, EPA expects that data processing costs will decrease, however, the magnitude of this decrease is unclear at this time. While it will no longer be necessary for EPA to key the data from paper forms, TRI-MEweb submissions sometimes require other manual steps (i.e., facility reconciliation). In addition, in the first year of mandatory electronic reporting, EPA has developed a process to reject (return) any paper forms submitted.
6(d) Estimating the Respondent Universe and Total Burden and Costs
Estimated Total Annual Burden for All Respondents
This section presents the total annual burden hours for all respondents, incorporating both form and non-form burden (see detailed bases in Section 6(a)). EPA uses the Steady State Total Burden method to estimate the total burden hours for all respondents under this ICR, as depicted in Figure 1. EPA calculates Form R burden and Form A burden using unit burdens and single-chemical form counts; non-Form burden is a constant. These three burden components sum to calculate the Steady State Total Burden. Table 12 shows the assumed universe of TRI facilities and forms for both Form Rs and Form As for this ICR Renewal.
Table 12 |
||
|
Form R |
Form A |
RY 2012 Universe |
Number
of Chemicals |
Number
of Chemicals |
Number of Facilities |
19,185 |
3,931 |
Number of PBT Chemicals |
13,927 |
25 |
Number of Non-PBT Chemicals |
57,011 |
8,975 |
Number of Total Chemicals |
70,938 |
9,000 |
Notes: |
||
Table 13 presents the total annual burden hours estimates for both Form R and Form A.
Table 13
Total Annual Burden Hour Estimate
Form Type |
Unit Burden Hours Per Form |
Number of Responses |
Number of Form R or A Chemicals |
Steady State Total Burden |
Form R (Including Form R Schedule 1) |
35.70516 |
70,938 |
70,938 |
2,532,853 |
Form A |
21.95867 |
3,931 |
9,000 |
197,628 |
Non-Form (constant) |
|
|
|
825,517 |
Total |
|
|
|
3,555,998 |
Estimated Total Annual Cost for All Respondents
EPA determined the total annual reporting cost for all respondent facilities by multiplying the WAWR by the steady state total burden. Table 14 presents the total annual reporting cost for Form R and Form A.
Table 14 |
|||
Form Type |
WAWR |
Steady State Total Burden |
Steady State Total Cost |
Form R |
$51.58 |
2,532,853 |
$130,644,558 |
Form A |
$51.58 |
197,628 |
$10,193,652 |
Non-Form (Constant) |
$51.58 |
825,517 |
$42,580,167 |
Total |
|
3,555,998 |
$183,418,377 |
Note: WAWR is based on September 2013 BLS wage data from Table 9 of the Employer Costs for Employee Compensation news release (http://www.bls.gov/news.release/ecec.t09.htm). |
|||
6(e) Bottom-Line Burden Hours and Cost Tables
This section presents the total burden and cost to the regulated industry to comply with the information collection requirements under EPCRA §313 and under PPA §6607, as well as the cost to EPA to process Form R and Form As annually.
(i) Respondent Tally
Table 15 presents the total burden and cost for complying with EPCRA §313 for current and new reporting requirements.
Table 15 |
||||
Activity |
Number of Facilities |
Number of Responses |
Annual Burden Hours |
Annual Costs |
Existing Form Rs |
19,185 |
70,938 |
2,532,853 |
$130,644,558 |
Existing Form As |
3,931 |
3,931 |
197,628 |
$10,193,652 |
Non-Form (Constant) |
|
|
825,517 |
$42,580,167 |
Subtotal |
21,025 a |
74,869 b |
3,555,998 |
$183,418,377 |
New Form R Data Elements c |
19,185 |
70,938 |
0 |
$0 |
New Form A Data Elements c |
3,931 |
3,931 |
0 |
$0 |
Total |
21,025 |
74,869 |
3,555,998 |
$183,418,377 |
a The
total number of facilities reporting (21,025) is not equal to the
sum of Form R and Form A respondents as some facilities may file
both Form Rs and Form As. |
||||
The Agency Tally
EPA estimates the total annual program burden to the Agency to be $4.63 million, and 5.2 FTEs. These costs reflect the burden to conduct the EPA activities described above.
Variations in the Annual Bottom Line
EPA does not expect significant variation in the annual respondent reporting/recordkeeping burden and cost over the course of the ICR approval period.
6(f) Reasons for Change in Burden
Change in burden estimates since OMB approved of the combined Form R/A ICR on October 14, 2011 include:29
the lifting of the Administrative Stay of the Toxics Release Inventory reporting requirements for hydrogen sulfide on October 17, 2011. EPA received the first submissions for hydrogen sulfide for reporting year 2012; the total number of form submissions used to calculate the overall program burden therefore includes these hydrogen sulfide submissions.
the Addition of o-Nitrotoluene Rule, which the Federal Register included in its publication on November 7, 2013. EPA estimates this rule will increase the number of reporting facilities by 1 and the number of Form Rs and Form As submitted by 17 and 5 respectively, with an associated ongoing steady state burden increase of 717 hours.
Over the last few years, there has been a slight increase in the number of facilities reporting to TRI. Based on the latest data for RY 2012 with updates to reflect the estimated burden due to the addition of o-Nitrotoluene, EPA now estimates the total number of combined Form R and Form A responses to be 74,869, the associated total annual burden hours to be 3,555,998, and the annual cost to be $183,418,361. Further, the TRI program is proposing to revise data elements for the reporting forms. EPA estimates that the revised data elements will have a negligible impact on form burden.
Since the ICR approval on October 14, 2011, the increase in the estimate of total burden of 39,530 hours (exclusive of o-Nitrotoluene reports which have not yet been received) primarily resulted from the filing of approximately 1,124 more forms in RY 2012 than was projected in the 2011 ICR Renewal (based on RY 2009 data). Refer to Figure 2 and Table 17 for background information on the chronology of both TRI rulemakings and ICR renewals which outlines changes that have occurred due to rulemaking.
Figure 2
TRI Rulemaking and ICR Chronology
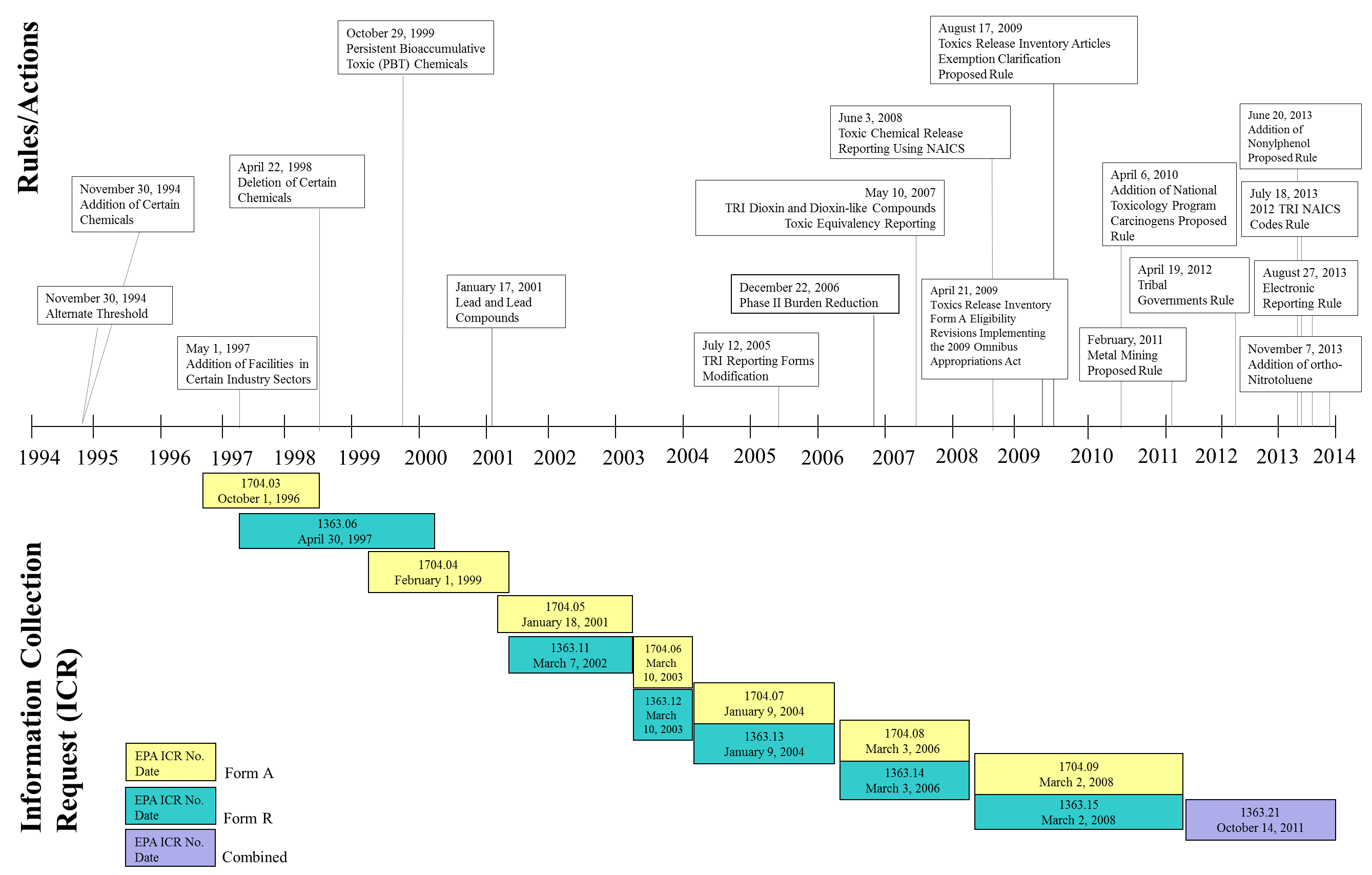
Table 16
Recent Changes in TRI Form R Burden
Activity – Explanation |
TRI Form R ICR (EPA # 1363.23, OMB #2025-0009) |
|||
Change |
Total |
|||
# Responses |
Burden Hours |
Total Responses |
Total Burden Hours |
|
1997 Baseline |
— |
— |
90,362 |
5,538,727 |
RY 1997 Program Change – Industry Expansion Rule: This rule added 7 new industries to the list of industries subject to TRI reporting beginning in RY1998. |
39,033 |
2,467,463 |
129,395 |
8,006,190 |
1999 Adjustment – Form R Correction Worksheet: This adjustment revised the number of responses to be more consistent with actual reporting levels. However, it did not correct for overestimation of expected reporting from the Industry Expansion Rule. |
(13,226) |
(665,666) |
116,169 |
7,340,524 |
RY 1999 Program Change – PBT Rule: This rule lowered reporting thresholds for certain PBT Chemicals, and added other PBT Chemicals at lower thresholds beginning in RY 2000. |
19,990 |
1,485,411 |
136,159 |
8,825,935 |
RY 2000 Program Change – Lead Rule: This rule lowered reporting thresholds for lead and lead compounds beginning in RY 2001. |
9,813 |
786,169 |
145,972 |
9,612,104 |
January 2003 Form R ICR Renewal: This request incorporated accounting adjustments to reflect actual number of responses. |
(57,855) |
(4,045,540) |
88,117 |
5,566,564 |
October 2003 Form R ICR Renewal: This request reflected actual number of responses and accounted for a lower subsequent year reporting burden for non-PBT Chemicals. |
(4,117) |
(1,677,812) |
84,000 |
3,888,752 |
May 2005 Form R ICR Renewal: This request reflected actual number of responses. |
(2,000) |
(91,413) |
82,000 |
3,797,339 |
RY 2005 Program Change – TRI Reporting Forms Modification Rule: This rule eliminated certain data elements and simplified others beginning in RY 2005. |
— |
(50,749) |
82,000 |
3,746,590 |
RY 2006 Program Change – TRI Burden Reduction Rule: This rule expanded non-PBT Chemical eligibility for Form A and, for the first time, allowed limited use of Form A for PBT Chemicals. |
(15,100) |
(505,117) |
66,900 |
3,241,473 |
RY 2008 New Data Elements: The proposed additions and revisions improve and enhance the data as well as standardize the information collected. |
(149) |
(24,193) |
66,751 |
3,217,280 |
RY 2008 Form R ICR Renewal |
— |
— |
66,751 |
3,217,280 |
RY 2010 New Data Element |
— |
— |
69,876 |
2,494,934 |
RY 2011 Form R ICR Renewal |
3,125 |
(722,346) |
69,876 |
2,494,934 |
RY 2014 Form R ICR Universe Projection |
1,062 |
37,919 |
70,938 |
2,532,853 |
6(g) Burden Statement (To appear on Collection Instrument)
EPA estimates the annual public burden for form calculations such as rule familiarization, compliance determination, calculations and form completion, and recordkeeping, which is approved under OMB Control No. 2025-0009, to average 47 hours per response for a facility filing a Form R and 50 hours for a facility filing a Form A for one chemical. There is additional non-form burden associated with non-reporter compliance determination, petitions and supplier notification.
Burden is defined as the total time, effort, or financial resources expended by persons to generate, maintain, retain, or disclose or provide information to or for a federal agency. This includes the time needed to review instructions; develop, acquire, install, and utilize technology and systems for the purposes of collecting, validating, and verifying information, processing and maintaining information, and disclosing and providing information; adjust the existing ways to comply with any previously applicable instructions and requirements; train personnel to be able to respond to a collection of information; search data sources; complete and review the collection of information; and transmit or otherwise disclose the information.
An agency may not conduct or sponsor, and a person does not have to respond to, a collection of information unless it displays a currently valid OMB control number. The OMB control numbers for EPA's regulations are listed in 40 CFR Part 9 and 48 CFR Chapter 15.
To comment on the Agency's need for this information, the accuracy of the provided burden estimates, and any suggested methods for minimizing respondent burden, including the use of automated collection techniques, EPA has established a public docket for this ICR under Docket ID No. EPA-HQ-OEI-2013-0803 which is available for online viewing at www.regulations.gov, or in-person viewing at the Office of Environmental Information Docket in the EPA Docket Center (EPA/DC), EPA West, Room 3334, 1301 Constitution Avenue, NW., Washington, D.C. The EPA Docket Center Public Reading Room is open from 8:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m., Monday through Friday, excluding legal holidays. The telephone number for the Reading Room is (202) 566-1744, and the telephone number for the Office of Environmental Information Docket is (202) 566-1752. The www.regulations.gov site enables visitors to submit or view public comments, access the index listing of the contents of the public docket, and access those documents in the public docket that are available electronically. When in the system, select “search,” then key in the Docket ID Number identified above. Also, you can send comments to the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs, Office of Management and Budget, 725 17th Street, NW., Washington, D.C. 20503, Attention: Desk Officer for EPA. Please include the EPA Docket ID No. EPA-HQ-OEI-2013-0803 and OMB Control No. 2025-0009 in any correspondence.
The completed form should be submitted in accordance with the instructions accompanying the form.
REFERENCES
Arbuckle, J. Gordon, et al., 1993. Environmental Law Handbook, Twelfth Edition. Government Institutes, Inc., Rockland MD.
U.S. Department of Labor, Bureau of Labor Statistics. Employer Costs for Employee Compensation. U.S. Department of Labor, Washington, D.C. December 2013.
U.S. EPA, 1986. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act of 1986, §313 (42 U.S.C.A. §1023. http://www.epa.gov/tri/lawsandregs/index.htm.
U.S. EPA, 1990. Pollution Prevention Act (42 U.S.C.A. §13101-13109. U.S. EPA http://www.epa.gov/tri/lawsandregs/index.htm.
U.S. EPA, 2007. Analysis of the Estimated Burden and Cost of Form R Schedule 1 for Dioxin and Dioxin-like Compounds; Toxic Equivalency Reporting; Community Right to Know Toxic Chemical Release Reporting (May 10, 2007).
U.S. EPA, 2008. Procedure for Quality Policy. CIO 2106-P-0.10. October 20, 2008.
U.S. EPA, 2011. Revising TRI Burden to Ratio-Based Methodology; TRI Regulatory Development Branch, TRI Program Division, Office of Information Analysis and Access, Office of Environmental Information (February 1, 2011).
U.S. EPA. 40 CFR Part 372 Toxic Chemical Release Reporting: Community Right-to-Know. http://www.epa.gov/tri/lawsandregs/index.htm#cfr
Hydrogen Sulfide; Community Right-to-Know Toxic Chemical Release Reporting. 40 CFR Part 372. EPA Docket ID Number EPA-HQ-TRI-2009-0844. Federal Register Vol. 76 No. 200. October 167, 2011.
Toxics Release Inventory (TRI) Reporting for Facilities Located in Indian Country and Clarification of Additional Opportunities Available to Tribal Governments Under the TRI Program. 40 CFR Part 372. EPA Docket ID Number EPA–HQ–OEI–2011–0196. Federal Register Vol. 77 No. 76. April 19, 2012.
Addition of ortho-Nitrotoluene; Community Right-to-Know Toxic Chemical Release Reporting. 40 CFR Part 372. EPA Docket ID Number EPA-HQ-TRI-2012-0111. Federal Register Vol. 78 No. 49. March 13, 2013.
Addition of Nonylphenol Category; Community Right-to-Know Toxic Chemical Release Reporting. 40 CFR Part 372. EPA Docket ID Number EPA-HQ-TRI-2011-0979. Federal Register Vol. 78 No. 138. July 18, 2013.
Community Right-to-Know; Adoption of 2012 North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) Codes for Toxics Release Inventory (TRI) Reporting. 40 CFR Part 372. EPA Docket ID Number EPA-HQ-OEI-2012-0110. Federal Register Vol. 78 No. 119. June 20, 2013.
Electronic Reporting of Toxics Release Inventory Data. 40 CFR Part 372. EPA Docket ID Number EPA–HQ–TRI–2011–0174. Federal Register Vol. 78 No. 166. August 27, 2013.
APPENDIX A
PROPOSED FORMS
FORM A
FORM R
FORM R SCHEDULE 1
1 Certain sectors are subject to TRI reporting. For a complete listing of the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) codes subject to TRI reporting see Appendix E of this ICR Supporting Statement.
2 The Form A submission requires a Certification Statement confirming that the sum of amounts of the chemical in releases and waste does not exceed the appropriate release and waste annual reportable amounts for that reporting year (see Form A in Appendix A for Certification Statement details).
3 Refer to Appendix A of this Supporting Statement for a blank Form R and Form A. For the full set of instructions and Forms, refer to http://www.epa.gov/tri/report/#forms.
4 For additional details, refer to Appendix A: Blank Form R, Form R Schedule 1, and Form A, and Appendix B: Reporting Form Instructions Associated with Form Changes.
5 US Environmental Protection Agency. Procedure for Quality Policy. CIO 2106-P-0.10. October 20, 2008.
6 The Office of Management and Budget publishes these guidelines in accordance with the Guidelines for Ensuring and Maximizing the Quality, Objectivity, Utility, and Integrity of Information Disseminated by Federal Agencies (Government-wide Guidelines) published in interim final form by OMB in the Federal Register in Volume 66, No. 189 at 49718 on September 28, 2001, and updated in final form in Volume 2, No. 67 at 8452 on February 22, 2002.
7 Actual Form R burden is estimated at 35.70516, which reflects the nominal Form R burden as developed in EPA’s Ratio Based Burden Methodology (RBBM, see Section 6 for a discussion of this methodology), with updates for subsequent rulemakings (dioxin) affecting unit reporting burden. Similarly, actual Form A burden is estimated at 21.95867.
8 EPA has authority to revise the threshold amounts pursuant to EPCRA §313(f)(2) provided that revised threshold amounts still result in reporting on a substantial majority of total releases of the chemical at all facilities subject to EPCRA §313. A revised threshold may be based on classes of chemicals or categories of facilities.
9 U.S. EPA Toxics Release Inventory Program. http://www.epa.gov/tri/
10 http://www2.epa.gov/sites/production/files/documents/tri_in_action_final_report_july_2013.pdf
11 Note that ICIS-NPDES recently replaced the former Permit Compliance System (PCS).
12 wwwww.epa.gov/osweroe1/docs/chem/list_of_lists_05_07_10.xls
13 wwwww.epa.gov/oem/docs/chem/Chap-09-final.pdf
14 Arizona, California, Georgia, Maine, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Mississippi, New Jersey, New York, Oregon, Tennessee, Texas, Vermont, and Washington.
15 Range reporting provides an option for releases of less than 1,000 pounds to be recorded as a code representing one of three ranges (1 to 10 pounds, 11 to 499 pounds, or 500 to 999 pounds) rather than as a specific estimate of the release amount. Range reporting is not permitted on Form Rs for PBT chemicals. For further discussion, see Section 5(c).
16 The exception is lead in stainless steel, brass, or bronze alloys, which are not excluded from Form A eligibility.
17 Based on TRI 2012 baseline dataset from EPA 11/08/2013.
18 Prior to TRI-MEweb, TRI reporting software had been desktop-based, distributed via the TRI Web site and mailed directly to facilities (via CD-ROM) each year. In RY 2007, TRI-MEweb, the new Web version of TRI-ME, was fully launched. The TRI-ME desktop software was retired from service in RY 2009.
19 Revising TRI Burden to Ratio-Based Methodology, TRI Regulatory Development Branch, TRI Program Division, Office of Information Analysis and Access, Office of Environmental Information, January 2011, EPA Docket ID Number EPA-HQ-OEI-2010-0835; hereafter referred to as RBBM Reference Document (Docket #EPA-HQ-OEI-2010-0835), EPA, 2011.
20 As opposed to a system several large matrices containing mixed scales, this structure is four ratio models plus a base number for Nominal Form R unit burden. For mathematical derivations, see Ibid.
21 For a complete chronology of rule changes and ICR renewals along with resultant impact on Form R reporting burden, see Figure 2 and Table 18.
22 For references on methodology development, see RBBM Reference Document (Docket #EPA-HQ-OEI-2010-0835), EPA, 2011.
23At the time of transition (the start of the 2008 ICR) the comparison between totals is exact. Later, in an interim spot-check (April 2010), totals were within 2%.
24 In A/R, Form A unit burden is derived using the activities associated with the subset of elements from Form R that a reporter would complete in order to determine TRI reporting eligibility and file a Form A, ensuring internal consistency. For further details, see RBBM Reference Document (Docket #EPA-HQ-OEI-2010-0835), EPA, 2011.
25 Although Form A permits multiple chemical reports on the same form (on average 2.29 Chemicals per Form A), for purposes of methods development and modeling, EPA works with chemical counts, referring to “Form R Chemicals” and “Form A Chemicals.”
26 RBBM Reference Document (Docket #EPA-HQ-OEI-2010-0835), EPA, 2011.
27 For the derivation and justification of the WAWR, see RBBM Reference Document (Docket #EPA-HQ-OEI-2010-0835), EPA, 2011.
28 E-mail communication with TRI Data Processing Center, January 10, 2014.
29 As noted in Section 6(a) given the very small number of facilities potentially experiencing burden and the minor compliance costs due to the electronic reporting rule, distributing this burden/cost across the full reporting universe results in negligible incremental per facility burden/cost. Therefore, at the margin, the electronic reporting rule does not constitute enough change to estimate additional burden.
6/11/14
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | TOXICS RELEASE INVENTORY |
| Author | Juan Parra |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-24 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy