1896ss10
1896ss10.docx
Disinfectants/Disinfection Byproducts, Chemical and Radionuclides (Renewal)
OMB: 2040-0204

Information Collection Request for the Disinfectants/Disinfection Byproducts, Chemical, and Radionuclides Rules
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 1
1(a) Title and Number of the Information Collection 1
2 NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION 3
2(a) Need/Authority for the Collection 3
3 NON-DUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA 11
3(b) Public Notice Required Prior to ICR Submission to OMB 11
3(d) Effects of Less Frequent Collection 11
4 RESPONDENTS AND INFORMATION REQUESTED 13
4(a) Respondents/NAICS Codes 13
4(b)(ii) Respondent Activities 28
5 INFORMATION COLLECTED — AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT 41
5(b) Collection Methodology and Management 42
5(c) Small Entity Flexibility 43
6 ESTIMATING BURDEN AND COST OF COLLECTION 46
6(a)(i) Burden to Public Water Systems 47
6(a)(ii) Burden to Primacy Agencies 50
6(b)(i) Cost to Public Water Systems 52
6(b)(ii) Cost to Primacy Agencies 52
6(c) Agency Burden and Costs 54
6(d) Estimating Respondent Universe and Total Burden and Costs 54
6(e) Bottom Line Burden Hours and Costs 55
6(f) Reasons for Change in Burden 56
6(f)(i) Restructuring Adjustments 57
LIST OF EXHIBITS
Exhibit 1: Structure of OGWDW ICRs 5
Exhibit 2: PWS Recordkeeping and Reporting Requirements 14
Exhibit 3: Primacy Agency Recordkeeping and Reporting Requirements 19
Exhibit 4: Regulated Organic Compounds and Inorganic Chemicals 35
Exhibit 5: EPA Requirements 42
Exhibit 6: Collection Schedule 45
Exhibit 7: Annual PWS Burden and Cost January 1, 2016 – December 31, 2018 53
Exhibit 8: Annual Primacy Agency Burden and Cost January 1, 2016 – December 31, 2018 54
Exhibit 9: Bottom Line Annual Burden and Cost January 1, 2016 – December 31, 2018 56
Exhibit 10: Summary of Changes in Annual Burden (Includes both PWS and Primacy Agency Burden) 57
Exhibit 12: Adjustments to PWS Burden from Previous ICR Estimates 59
Exhibit 13: Adjustments to Primacy Agency Burden from Previous ICR Estimates 59
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1: Structure of OGWDW ICRs…………………………………………………………….5
APPENDICES
Appendix A. Federal Register Notices Soliciting Comment on Information Collection Requests
Appendix B. Stage 1 Disinfectants/Disinfection Byproducts Rule Spreadsheets
Appendix C. Stage 2 Disinfectants/Disinfection Byproducts Rule Spreadsheets
Appendix D. Chemical Phase Regulation Spreadsheets
Appendix E. Radionuclides Rule Spreadsheets
Appendix F. Disinfectant Residual Monitoring and Associated Activities under the Surface
Water Treatment Rule Spreadsheets
Appendix G. Arsenic Rule Spreadsheets
Appendix H. Lead and Copper Rule Spreadsheets
ACRONYMS
AMWA Association of Metropolitan Water Agencies
ASDWA Association of State Drinking Water Administrators
AWWA American Water Works Association
BATs Best Available Technologies
BLS Bureau of Labor Statistics
CCR Consumer Confidence Report
CCT Corrosion Control Treatment
CDC Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
CFR Code of Federal Regulations
CT Contact Time
CWS Community Water System
CWSS Community Water System Survey
DBP Disinfection Byproduct
DBPR Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule
DDBP/Chem/Rads Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts, Chemical, and Radionuclides Rules
DWSRF Drinking Water State Revolving Fund
EA Economic Analysis
EPA Environmental Protection Agency
ERP Enforcement Response Policy
ETT Enforcement Targeting Tool
FACA Federal Advisory Committee Act
FR Federal Register
GWR Ground Water Rule
HAA5 Haloacetic Acids
ICR Information Collection Request
IDSE Initial Distribution System Evaluation
IESWTR Interim Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule
IOCs Inorganic Compounds
LCR Lead and Copper Rule
LCRMR Lead and Copper Rule Minor Revisions
LSL Lead Service Line
LSLR Lead Service Line Replacement
LT1ESWTR Long Term 1 Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule
LT2ESWTR Long Term 2 Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule
MCL Maximum Contaminant Level
MCLG Maximum Contaminant Level Goal
MDL Method Detection Limit
MRDL Maximum Residual Disinfection Level
mrem Millirem
NAICS North American Industry Classification System
NAWC National Association of Water Companies
NDWAC National Drinking Water Advisory Council
NPDWRs National Primary Drinking Water Regulations
NRWA National Rural Water Association
NTNCWS Nontransient Noncommunity Water System
OECA Office of Enforcement and Compliance Assurance
OGWDW Office of Ground Water and Drinking Water
O&M Operation and Maintenance
OMB Office of Management and Budget
pCi/L PicoCuries per liter
PN Public Notification
PRA Paperwork Reduction Act
PWS Public Water System
PWSS Public Water System Supervision
RegNeg Regulatory Negotiation
RFA Regulatory Flexibility Act
SBREFA Small Business Regulatory Enforcement Fairness Act
SDWA Safe Drinking Water Act
SDWIS Safe Drinking Water Information System
SMF Standardized Monitoring Framework
SOCs Synthetic Organic Compounds
SWAP Source Water Assessment Program
SWTR Surface Water Treatment Rule
TCR Total Coliform Rule
TNCWS Transient Noncommunity Water System
TOC Total Organic Carbon
TTHM Total Trihalomethane
UCMR Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule
UIC Underground Injection Program
VOCs Volatile Organic Compounds
WQP Water Quality Parameter
1 IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
1(a) Title and Number of the Information Collection
Title: Disinfectants/Disinfection Byproducts, Chemical, and Radionuclides Rules
OMB Control Number: 2040-0204
EPA Tracking Number: 1896.10
The Office of Ground Water and Drinking Water (OGWDW) in the Office of Water at the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is responsible for managing the Public Water System Supervision (PWSS) Program, a national program mandated by the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA). Section 1412 of the SDWA requires EPA to establish National Primary Drinking Water Regulations (NPDWRs) for contaminants that may adversely impact human health. The Act requires EPA to monitor and enforce these regulations to ensure that the nation’s drinking water dependably complies with the maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) or maximum residual disinfectant levels (MRDLs), as stipulated in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), 40 CFR Part 141, Subpart B.
Section 1445 of the SDWA states that public water systems shall conduct monitoring, maintain records, and provide such information as is needed for EPA to implement its monitoring and enforcement responsibilities with respect to the Act. Primacy agencies, state governments that have assumed primary enforcement responsibility under SDWA section 1413, ensure that PWSs are complying with these monitoring requirements.
As part of the PWSS Program, OGWDW uses the Safe Drinking Water Information System (SDWIS) to record some of the data collected as a result of NPDWR requirements. These data assist EPA in fulfilling its SDWA obligations. SDWIS is a database management system that assists EPA in tracking and interpreting violations data and other program-related data. Revisions are currently being made to SDWIS. EPA expects primacy agencies to fully transition to the revised system, a centralized, cloud-based system called SDWIS Prime, in the subsequent ICR period.
This ICR was prepared in accordance with the October 2009 version of EPA’s Guide to Writing Information Collection Requests Under the Paperwork Reduction Act (PRA) of 1995 (or “ICR Handbook”) prepared by EPA’s Office of Environmental Information, Office of Information Collection, Collection Strategies Division. The ICR Handbook provides the most current instructions for ICR preparation to ensure compliance with the 1995 PRA amendments and the Office of Management and Budget’s (OMB’s) implementing guidelines.
Many information collection requirements associated with SDWA and its implementing regulations are associated with rulemakings that address specific contaminants or groups of contaminants. This ICR examines PWS, primacy agency, and EPA burden and cost for chemical and disinfection byproduct regulations only. Microbial contaminants, such as those regulated under the Total Coliform Rule (TCR), are addressed in the Microbial Rules ICR (OMB No. 2040-0205). Cross-cutting recordkeeping and reporting requirements—are addressed in the PWSS Program ICR (OMB No. 2040-0090).
The specific chemical regulations addressed in this ICR include the following:
Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule (Stage 1 DBPR)
Stage 2 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule (Stage 2 DBPR)
Chemical Phase Rules (Phases II/IIB/V)
Radionuclides Rule
Disinfectant Residual Monitoring and Associated Activities under the
Surface Water Treatment Rule (SWTR)1
Arsenic Rule
Lead and Copper Rule (LCR)
This ICR estimates burden and costs for January 1, 2016 – December 31, 2018.
The total annual burden associated with this ICR is estimated to be 5.3 million hours per year. The total annual cost associated with this ICR is estimated to be approximately $464.9 million. The distribution of annual burden between PWSs and primacy agencies is approximately 3.3 million hours and 2.0 million hours, respectively (numbers may not add due to rounding). The distribution of annual costs between PWSs and primacy agencies is approximately $374 million and $90 million, respectively. There is no Agency burden or cost. Section 6 and Appendices B through H provide details of all burden and cost estimates.
The approximate annual operation and maintenance (O&M) and capital costs are $259 million, with $253 million attributed for O&M and $5.5 million for capital. This represents the “cost burden” as reported in the OMB inventory.
The total annual number of respondents for this ICR is 149,822. Fifty-seven of these respondents are primacy agencies and the remaining 149,765 respondents are existing PWSs. The total annual number of responses for these respondents is 12.9 million; 11.9 million for PWSs and 1.0 million for primacy agencies.
2 NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION
2(a) Need/Authority for the Collection
This section identifies the regulatory or statutory authority for the information collection activities covered in this ICR and explains EPA’s need for the information. A summary of the major types of recordkeeping and reporting requirements for the contaminants covered by this ICR is provided in Section 4 of this ICR.
To allow the public to better understand the impact of the recordkeeping and reporting requirements stemming from the SDWA and 40 CFR Parts 141 and 142, OGWDW has organized its ICRs so that related activities are addressed in the same ICR. Specifically, there are three primary ICRs —the Microbial Rules ICR, the Disinfectants/Disinfection Byproducts, Chemical and Radionuclides Rules (DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules) ICR, and the Public Water Systems Supervision Program (PWSS Program) ICR. The Microbial Rules ICR includes rules addressing microbial contaminants, such as the TCR, Surface Water Treatment Rule (SWTR), and the Ground Water Rule (GWR). The PWSS Program ICR includes public notification and rules and programs addressing cross-cutting requirements that are not contaminant-specific. The DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR includes rules addressing chemical contaminants. The specific chemical regulations addressed in this ICR are:
Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule (Stage 1 DBPR)
Stage 2 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule (Stage 2 DBPR)
Chemical Phase Rules (Phases II/IIB/V)
Radionuclides Rule
Disinfectant Residual Monitoring and Associated Activities under the Surface
Water Treatment Rule (SWTR)2
Arsenic Rule
Lead and Copper Rule (LCR), including the Lead and Copper Rule Short Term Revisions
For a graphical depiction of the structure of the OGWDW ICRs, see Figure 1. A complete itemization of the activities included in the three primary ICRs, as well as other drinking water program ICRs, is included as Exhibit 1.
The 1986 Amendments to SDWA required the Agency to publish maximum contaminant level goals (MCLGs) and promulgate NPDWRs for 83 specific contaminants. Promulgation of the chemical-related rules contained in this ICR complies with the statutory requirements for some of these contaminants. Promulgation of the Stage 1 and Stage 2 DBPRs and the Arsenic Rule complies with the 1996 amended statutory requirements for these contaminants.
The 1986 SDWA Amendments required the EPA to propose and promulgate a NPDWR specifying criteria under which filtration would be required as a treatment technique for PWSs supplied by surface water sources (section 1412 (b)(7)(C)(i)). Promulgation of the SWTR satisfied this SDWA requirement. The SWTR includes disinfection residual monitoring requirements that are addressed in this ICR.
The information collected under this ICR is required by EPA to carry out its monitoring and enforcement responsibilities as specified under SDWA and its amendments. Without comprehensive, up-to-date information on these contaminants, the Agency would not be able to meet these statutory requirements.
Section 1412(b) authorizes EPA to establish NPDWRs to protect public health. Section 1445 of the SDWA requires that “every person who is a supplier of water shall establish and maintain such records, make such reports, conduct such monitoring, and provide such information as the Administrator may reasonably require by regulation to assist him in establishing regulations, in determining whether such person has acted or is in compliance with this title...”
In addition, section 1401(1)(d) of the SDWA 1986 Amendments defines NPDWRs to include “criteria and procedures to assure a supply of drinking water which dependably complies with such maximum contaminant levels; including accepted methods for quality control and testing procedures...” This section authorizes EPA to require systems and laboratories to use Agency-approved methods and quality assurance criteria for collecting and analyzing water samples.
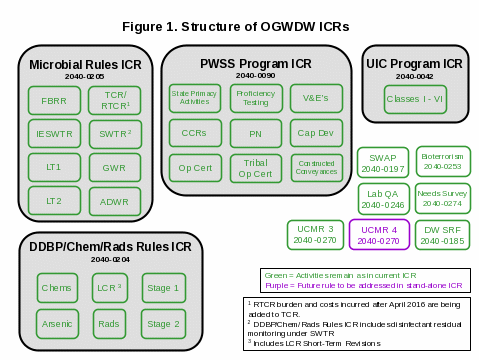
Exhibit 1: Structure of OGWDW ICRs
Currently covered |
To be covered in the future |
PWSS Program ICR (2040-0090)
|
|
Consumer Confidence Reports (CCRs) |
|
Variances & Exemptions |
|
Capacity Development Program |
|
General State Primacy Activities |
|
Public Notification (PN) |
|
Operator Certification Program |
|
Tribal Operator Certification |
|
Constructed Conveyances |
|
Proficiency Testing |
|
Microbial Rules ICR (2040-0205)
|
|
Surface Water Treatment Rule, except disinfectant residual monitoring and associated activities3 |
|
Total Coliform Rule/ Revised Total Coliform Rule |
|
Interim Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule (IESWTR) |
|
Filter Backwash Recycling Rule |
|
Long Term 1 Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule (LT1ESWTR) |
|
Long Term 2 Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule (LT2ESWTR) |
|
Ground Water Rule |
|
Aircraft Drinking Water Rule |
|
Disinfectants/Disinfection Byproducts, Chemical, and Radionuclides Rules ICR (2040-0204)
|
|
Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule |
Lead and Copper Rule Long Term Revisions |
Disinfectant Residual Monitoring and associated activities under the SWTR |
|
Stage 2 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule |
|
Chemical Phase Rules |
|
Radionuclides Rule |
|
Arsenic Rule |
|
Lead and Copper Rule |
|
Source Water Assessment Program (SWAP) ICR (2040-0197)
|
|
SWAP |
|
Underground Injection Control (UIC) Program ICR (2040-0042)
|
|
UIC Base Program Activities |
|
Classes I-VI Rules |
|
Florida Class I Rule |
|
Drinking Water State Revolving Fund (DWSRF) Program ICR (2040-0185)
|
|
Drinking Water State Revolving Fund Program |
|
Drinking Water Infrastructure Needs Survey ICR (2040-0274)
|
|
Drinking Water Infrastructure Needs Survey |
|
Title VI of the Public Health Security and Bioterrorism Preparedness and Response Act of 2002: Drinking Water Security and Safety ICR (2040-0253) |
|
Vulnerability Assessments and Emergency Response Plans for community water systems (CWSs). |
|
Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule ICR (2040-0270)
|
|
Monitoring of Unregulated Contaminants (UCMR 3) |
UCMR 4 |
Laboratory Quality Assurance Evaluation Program for Analysis of Cryptosporidium ICR (2040-0246)
|
|
Proficiency Testing Program for Laboratories Analyzing Cryptosporidium Samples |
|
To implement its compliance oversight and enforcement responsibilities under the SDWA, EPA requires PWSs to monitor for various drinking water contaminants. The results of this monitoring must be reported to primacy agencies, which in turn report a specified subset of this information in SDWIS. Additionally, both PWSs and primacy agencies must maintain records of analytic results and other related activities (e.g., sanitary survey results). Without comprehensive, up-to-date information on drinking water contaminants (as provided by SDWIS), EPA would not be able to implement the national drinking water program. . If these monitoring requirements were voluntary, EPA would not receive timely, comprehensive data on contaminant levels and associated acute and long-term public health risks. Specifically, voluntary monitoring would not:
Reliably occur with sufficient frequency.
Follow uniform national standards on quality of sampling, collection, and analysis.
Ensure that monitoring addresses all contaminants listed in the regulations.
Additionally, EPA uses SDWIS data to estimate the costs of new regulations and to conduct economic and policy analyses that promote cost-effective regulatory approaches. These uses are discussed in more detail in section 2(b) below.
Section 4 of the ICR contains a summary of the major types of chemical contaminant recordkeeping and reporting requirements, as mandated by 40 CFR Parts 141 and 142. Specifically, most reporting required by PWSs can be found in 40 CFR 141.31, 141.34, and 141.35.
Most recordkeeping requirements for PWSs are codified in 40 CFR 141.33, which requires that the results of chemical analyses be kept for a period of at least 10 years. Reporting and recordkeeping required by states can be found in 40 CFR 142.15 and 142.14, respectively.
Primary users of the data collected under this ICR are EPA, PWS managers, and primacy agencies, which include state regulators and Indian Tribes. This section contains more information about how chemical-related data are used specifically for analytical monitoring, regulatory enforcement, oversight of state programs, implementation assistance, economic and policy analyses, and other Agency and public data evaluations. Each of these functions is discussed in greater detail below.
Analytical Monitoring
PWSs maintain records on the analytical results of monitoring and use these data to:
Evaluate the quality of water delivered to customers.
Examine treatment efficacy.
Determine compliance with national standards.
Modify monitoring frequencies, schedules, and variances to address potential health risks.
Alert the public, when the system is not in compliance with federal and state regulations so that they may take actions to minimize exposure to potentially harmful drinking water contaminants.4
Quarterly and annual reports that primacy agencies must submit to EPA include PWS information, enforcement information and analytical results for certain violations of the NPDWRs. This reporting is required to establish primacy and maintain eligibility for grants. All of this information is stored in SDWIS, which supports overall maintenance and retrieval of information.
Regulatory Enforcement
Using SDWIS, system-level compliance data may be compared from year to year and trends in compliance data can be evaluated at the system, state, and national program levels. Primacy agencies are responsible for enforcement activities and can use SDWIS data to track compliance progress in their jurisdictions, to identify enforcement targets and remedial actions, and to monitor progress of capacity development strategies. The primacy agency must also track enforcement actions issued against each PWS not in compliance with drinking water standards and evaluate the system’s status in meeting schedules designed to return the PWS to compliance.
On a quarterly basis, EPA uses the Enforcement Tracking Tool (ETT) to generate a list of PWSs that are considered “priority systems” for enforcement. The Enforcement Response Policy (ERP) and ETT prioritize and direct enforcement response to systems with the most systemic noncompliance by considering all violations incurred by a system in a comprehensive way. If a state has failed to take timely and appropriate action, EPA may become directly involved in enforcement by issuing an administrative order. If the system does not comply with the order, EPA may seek an administrative penalty or court action.
Oversight of State Programs
State reporting is a condition for maintaining primacy. Primacy agencies play a crucial role in implementing the SDWA, and EPA is charged with overseeing the performance of these states. EPA uses SDWIS data to develop summary statistics on individual state performance.
Implementation Assistance
EPA and primacy agencies also use the data collected to assist small systems in implementing SDWA requirements, including developing variances and exemptions and evaluating PWS capacity. If a PWS is unable to meet standard requirements due to source water quality or affordability concerns, a variance or exemption may be issued to allow the system to comply with slightly different drinking water standards or implementation schedules that are still protective of public health. Capacity development is a state program designed to help all drinking water systems, particularly small systems, enhance their technical, managerial and /or financial capacity to achieve or maintain their compliance with drinking water regulations.
Economic and Policy Analyses
SDWIS data are used in the development of economic analyses for proposed regulations or revisions of existing regulations. The data help to determine a system’s susceptibility and vulnerability to contaminants. Data are also used by OGWDW to conduct analyses used in developing new policies, regulations, and guidance documents. When analyzing economic or financial impacts on the public water systems or consumers, EPA uses compliance data from SDWIS, together with other national survey data, to estimate the number of systems that would have to install treatment technologies or apply contamination reduction measures to reduce public health risks. Without such data, EPA would be unable to predict costs and benefits that systems would incur under new or revised regulations.
2(b)(ii) Users of the Data
The information collected by EPA is made available to the public upon request, via EPA’s public website (http://water.epa.gov/scitech/datait/databases/drink/sdwisfed/pivottables
.cfm) or by requesting the data via the Freedom of Information Act (40 CFR, Chapter 1, Part 2). Other organizations that utilize the data include:
Staff from other EPA programs (such as Superfund, the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act, and the Office of Enforcement and Compliance (OECA))
The Federal Emergency Management Administration
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Military bases
Farmers Home Administration
Department of Interior
Department of Housing and Urban Development
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
White House Task Forces
American Water Works Association (AWWA)
Association of Metropolitan Water Agencies (AMWA)
National Rural Water Association (NRWA)
National Association of Water Companies (NAWC)
Association of State Drinking Water Administrators (ASDWA)
Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC)
3 NON-DUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA
EPA has made an effort to ensure that the data collection efforts associated with this ICR are not duplicated. EPA has consulted state environmental programs, other federal agencies, and regulated entities, such as PWSs and their representative trade associations. To the best of EPA's knowledge, data currently required by the SDWA and its drinking water regulations, codified at 40 CFR Parts 141 and 142, are not available from any other source.
3(b) Public Notice Required Prior to ICR Submission to OMB
To comply with the 1995 Amendments to the PRA, EPA solicited public comment on this ICR for a 60-day period before it was submitted to OMB (80 CFR 17040, March 31, 2015). Specifically, EPA published a notice in the Federal Register (FR) requesting comment on the estimated respondent burden and other aspects of this ICR (Appendix A). EPA did not receive any comments during the 60-day comment period.
An additional FR notice will be published prior to submission of this ICR to OMB. The public comment period for this additional notice is 30 days.
As part of the revision of the PWSS ICR, in May 2015 EPA consulted with representatives of PWSs and states regarding the accuracy of EPA’s burden estimates. The groups consulted were NAWC, NRWA, AWWA, AMWA, and ASDWA. EPA received comments from ASDWA. ASDWA’s comments were incorporated into this ICR to the extent possible. The end of each appendix to the ICR contains a table summarizing EPA’s previous and revised burden estimates for the relevant rule.
3(d) Effects of Less Frequent Collection
EPA has considered a wide range of alternatives for frequency of data collection. EPA has chosen to require the least frequent collection that remains consistent with the overall goal of protecting public health. If data are collected less frequently, primacy agencies may not identify in a timely fashion significant contaminant concentrations that might threaten the health and safety of drinking water consumers.
For some rules, the primacy agency has discretion in adjusting monitoring schedules, where possible, by granting waivers or reducing the monitoring frequency and/or sites. Monitoring frequencies vary based on the following:
Type of contaminant.
Type and size of system.
System vulnerability.
Contaminant history.
Factors contributing to DBP formation.
This ICR does not request any exemptions from the general guidelines specified in the Paperwork Reduction Act.
No confidential information will be collected as a result of this ICR.
No information of a sensitive nature will be collected as a result of this ICR.
4 RESPONDENTS AND INFORMATION REQUESTED
Data associated with this ICR are collected and maintained at the PWS, state, and federal levels. Respondents include:
Owners/operators of PWSs, who must report to their primacy agency.
Primacy agencies, and EPA Regions that act as primacy agencies in Indian lands and states that do not have primacy.
The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) code for PWSs is 22131. The NAICS codes for state agencies that include drinking water programs are 92411 (Administration of Air and Water Resources and Solid Waste Management Programs) or 92312 (Administration of Public Health Programs). Ancillary systems (i.e., those that supplement the function of other establishments like factories, power plants, mobile home parks, etc.) cannot be categorized in a single NAICS code. For ancillary systems, the NAICS code is that of the primary establishment or industry.
The data items that respondents will collect in implementing their responsibilities under the chemical-related drinking water regulations included in this ICR are summarized below.
Each PWS is required to report to its primacy agency monitoring results received from laboratories. As required by 40 CFR 141.33, PWSs must either maintain analytical reports or transfer the following information regarding sample results:
Date, place, and time of sampling.
Name of the person who collected the sample.
Identification of the sample as a routine distribution system sample, check sample, raw or process water sample, or other special purpose sample.
Date of analysis.
Laboratory and person responsible for performing analysis.
Contaminants for which the analysis was performed.
Analytical technique/method used.
Results of the analysis.
PWSs are required to submit and keep records on additional information such as public education on lead, monitoring plans, waiver applications, and disinfection calculations.
Exhibit 2 further describes the respondent information collection requirements covered by the DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR.
PWS Recordkeeping and Reporting Requirements
Requirement |
Regulatory Citation |
Frequency/ Retention Period |
General Requirements (apply to all regulations) |
||
Reporting |
|
|
Except where a different period is specified in an individual drinking water regulation, PWSs are required to submit the following to the state: |
||
Results of any test measurement or analysis required in 40 CFR Part 141. |
40 CFR 141.31(a) |
At the end of the required monitoring period |
Failure to comply with any NPDWR, including failure to monitor. |
40 CFR 141.31(b) and (c) |
As necessary, unless state lab performs analysis and reports results to state |
Copies of records required to be maintained under 40 CFR 141.33 and/or copies of documents that the state is entitled to under section 1445 of SDWA or state law. |
40 CFR 141.31(e) |
As requested |
Recordkeeping |
||
Except where a different period is specified in an individual drinking water regulation, PWSs are required to retain the following information: |
||
Records of bacteriological, or chemical analyses and related information. |
40 CFR 141.33(a) |
5 years for bacteriological data; 10 years for chemical data
|
Records of actions taken by the PWS to correct violations of NPDWRs. |
40 CFR 141.33(b) |
3 years after last action taken related to the violation |
Copies of any written reports, summaries, or communications relating to sanitary surveys. |
40 CFR 141.33(c) |
10 years |
Records concerning a variance or exemption granted. |
40 CFR 141.33(d) |
5 years following the expiration of the variance or exemption |
Stage 1 DBPR |
||
Reporting |
|
|
Report to the state specified sampling information (including MCL or MRDL exceedances) about disinfectants, disinfection byproducts (DBPs), and DBP precursors. |
40 CFR 141.134(a) through (d) |
Quarterly or as necessary for systems sampling less frequently than quarterly |
Develop and submit application to state for approval of alternative minimum total organic carbon (TOC) removal levels. |
40 CFR 141.135(b)(3)and (4) |
As necessary |
Develop and submit application to state for approval of waiver of enhanced coagulation requirements. |
40 CFR 141.135(b)(4)(v) |
One time |
Stage 2 DBPR |
||
Reporting |
|
|
Develop and submit an Initial Distribution System Evaluation (IDSE) Plan and Report or 40/30 certification or very small system waiver. |
40 CFR 141.600 |
One time |
Recordkeeping |
|
|
Records of IDSE Reports |
40 CFR 141.601(c)(4) |
Ten years |
Results of operational evaluations to be discussed with states |
40 CFR 141.626 |
Ten years |
Chemical Phase Rules (Phases II, IIB, and V) |
||
Reporting |
||
Apply to state for asbestos monitoring waiver. |
40 CFR 141.23(b)(2) and (4) |
Every 3 years, if applicable |
Apply to state for inorganic compound (IOC) monitoring waiver. |
40 CFR 141.23(c)(2) and (3) |
Every 9 years, if applicable |
Apply to the state to conduct more frequent IOC monitoring. |
40 CFR 141.23(h) |
One time, if applicable |
Apply to state for volatile organic compounds (VOC) monitoring waiver. |
40 CFR 141.24(f)(7) and (10) |
Every 6 years or frequency specified by state, if applicable |
Apply to state for synthetic organic compound (SOC) monitoring waiver. |
40 CFR 141.24(h)(5) and 141.24(h)(7)(iv) |
Every 3 years, if applicable |
Notify state of MCL exceedances. |
40 CFR 141.23(m) through (o) |
As necessary |
Submit written treatment technique certification to state regarding acrylamide and epichlorohydrin levels. |
40 CFR 141.111 |
Annually, if applicable |
Radionuclides |
||
Reporting |
||
Notify state of MCL exceedances for contaminants specified in 40 CFR 141.66(b)-(e). |
40 CFR 141.26(c)(5) |
As necessary |
SWTR (only disinfection residual monitoring and associated activities) |
||
Unfiltered Systems – Reporting |
||
Disinfection information specified in 40 CFR 141.74(b) |
40 CFR 141.75(a)(2) |
Within 10 days after the end of each month the system serves water to the public |
Filtered Systems - Reporting |
|
|
Disinfection information specified in 40 CFR 141.74(c) |
40 CFR 141.75(b)(2) |
Within 10 days after the end of each month the system serves water to the public |
Arsenic Rule |
||
Subject to general requirements as listed above. |
||
Lead and Copper Rule, Including October 2008 Short Term Revisions |
||
Reporting |
||
Report to the state any information required by the treatment provisions in Subpart I (especially 40 CFR 141.90). |
40 CFR 141.80(i) |
As required |
Tap water and water quality parameters (WQP) monitoring requirements
|
||
Water systems that exceed the lead action level must reevaluate lead service lines (LSLs) classified as “replaced” through testing if they resume lead service line replacement (LSLR) programs. |
40 CFR 141.84(b) & (c) |
As necessary |
Allows systems with less than 5 taps to take one sample per tap if approved by state. |
40 CFR 141.86 (c) 141.80(c)(3)(v) |
One time |
Report the specified information for all tap water samples and all WQP samples. |
40 CFR 141.90(a)(1) |
End of the applicable monitoring period |
Provide written documentation to the state identifying standing times and locations for enough non-first-draw samples to make up its sampling pool under 40 CFR 141.86(b)(5). |
40 CFR 141.90(a)(2)(i) |
As necessary |
If the state has waived prior approval of non-first-draw sample sites selected by the system, identify, in writing, each site that did not meet the six-hour minimum standing time and the length of standing time for that particular substitute sample. |
40 CFR 141.90(a)(2)(ii) |
As necessary |
For a water system deemed to have optimized corrosion control, a water system subject to reduced monitoring, or a water system subject to a monitoring waiver, send written documentation to the state describing any addition of a new source or any change in water treatment. |
40 CFR 141.81(b)(3)(iii);
|
As necessary |
For a water system, prohibit systems that exceed the lead action level from initiating or remaining on reduced monitoring based solely on results of WQP monitoring |
40 CFR 141.86(d)(4)(vi)(B)
|
As necessary |
For any small water system applying for a monitoring waiver, provide documentation to the state demonstrating that it meets the waiver criteria. |
40 CFR 141.90(a)(4)(i) |
As necessary |
For each small system desiring to maintain its monitoring waiver, provide written information to the state. |
40 CFR 141.90(a)(4)(ii) |
Every 9 years |
For each small system with a monitoring waiver, provide written notification to the state if the system is no longer free of lead-containing or copper-containing materials. |
40 CFR 141.90(a)(4)(iii) |
As necessary, within 60 days after becoming aware of change |
For each ground water system that limits WQP monitoring to a subset of entry points, provide written correspondence to the state that identifies selected entry points and includes information sufficient to demonstrate that the sites are representative of water quality and treatment conditions throughout the system. |
40 CFR 141.90(a)(5) |
One time, as necessary |
Provide the specified information to the state if the state calculates the 90th percentile concentrations. |
40 CFR 141.90(h)(2) |
End of monitoring period |
Source water monitoring reporting requirements
|
||
Report the sampling results for all source water samples collected in accordance with 40 CFR 141.88. |
40 CFR 141.90(b)(1) |
End of monitoring period |
Specify any site which was not sampled during the previous monitoring period and explain why the sampling point has changed. |
40 CFR 141.90(b)(2) |
As necessary, end of monitoring period
|
Corrosion control treatment reporting requirements
|
||
For systems demonstrating optimized corrosion control, provide the state information demonstrating that the PWS has conducted activities equivalent to the applicable corrosion control steps. |
40 CFR 141.81(b)(2), 141.90(c)(1) |
One time, as necessary |
For systems demonstrating optimized corrosion control, submit results of tap water monitoring and source water monitoring. |
40 CFR 141.81(b)(3) |
As necessary |
For systems deemed to have optimized corrosion control, notify the state in writing prior to any change in treatment or of the addition of a new source. |
40 CFR 141.81(b)(3)(iii) 141.86(d)(4)(vii); 141.86(g)(4)(iii); 141.90(a)(3)
|
As necessary |
Submit monitoring results that show two consecutive monitoring periods that meet both lead and copper action levels. |
40 CFR 141.81(c) |
As necessary |
Request in writing a modification of optimal CCT. |
40 CFR 141.82(h) |
As necessary
|
For systems required to evaluate the effectiveness of CCTs, report the information required by 40 CFR 141.82(c). |
40 CFR 141.90(c)(3) |
As necessary |
For systems required to install optimal corrosion control, submit a letter certifying that the system has completed installation. |
40 CFR 141.90(c)(4) |
As necessary |
Source water treatment reporting requirements
|
||
Provide to the state a recommendation regarding source water treatment. |
40 CFR 141.83(a)(1), 40 CFR 141.83(b)(1), 40 CFR 141.90(d)(1) |
As necessary, within 6 months of exceeding action level
|
Request in writing a modification of source water treatment or maximum permissible lead and copper concentrations. |
40 CFR 141.83(b)(6) |
As necessary |
For systems required to install source water treatment, submit a letter certifying that the system has completed installation of the designated treatment. |
40 CFR 141.90(d)(2) |
As necessary, within 24 months after state designates treatment
|
Public education program reporting requirements
|
||
Deliver written public education materials if a water system exceeds the lead action level based on tap water samples. |
40 CFR 141.85(a) & (c) |
As necessary, timing varies by type of system
|
Broadcast public service announcements if a CWS exceeds the lead action level based on tap water samples. |
40 CFR 141.85(b) & (c) |
As necessary |
Water systems that exceed the lead action level must provide information to additional at-risk populations and must conduct specified public education activities. Water systems must include a statement on lead in their CCR. Water systems certify to state that activities have been conducted. |
40 CFR 141.85(a) & (b);141.154 |
As necessary |
Apply to the state in writing to alter specified public education language (CWSs only). |
40 CFR 141.85(c)(7) |
As necessary |
Water systems must provide consumers who occupy homes or buildings that are part of the utility’s monitoring program, with testing results when their drinking water is tested for lead and copper. Water systems certify to state that results have been distributed. |
40 CFR 141.80(g); 141.85(d); 141.90(f)(3) |
As necessary |
For any water system that is subject to public education requirements, send written documentation to the state that contains specified information. |
40 CFR 141.90(f)(1) |
As necessary; end of each public education period |
Primacy agencies review and maintain records on monitoring results, approve monitoring plans, waivers, treatment changes, public education, and other documents submitted by PWSs. Primacy agencies report compliance and enforcement data to EPA, and apply to EPA for primacy to implement new drinking water regulations. Reporting and recordkeeping requirements for states are described in more detail in Exhibit 3.
Primacy Agency Recordkeeping and Reporting Requirements
Requirement |
Regulatory Citation |
Frequency/Retention Period |
General Requirements (apply to all regulations) |
||
Reporting |
||
Submit reports to the Administrator containing new violations by PWS and new enforcement actions by states that occurred during the previous quarter. |
40 CFR 142.15(a)(1) and (2) |
Quarterly |
Recordkeeping |
||
Maintain records of tests, measurements, analyses, decisions, and determinations performed on each PWS to determine compliance with applicable provisions of state primary drinking water regulations. |
40 CFR 142.14(a) |
Varies |
Retain files, which shall include for each PWS in the state, records of any state approvals and records of any enforcement actions. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(2) and (3) |
12 years |
Stage 1 DBPR |
||
Reporting |
||
Review and make determination regarding approval of application for use of alternative minimum TOC removal levels. |
40 CFR 141.135(b)(1) |
As necessary |
Review and make determination regarding application for approval of waiver of enhanced coagulation requirements. |
40 CFR 141.135(b)(4)(v) |
One time, as necessary |
Recordkeeping |
||
Records of the currently applicable or most recent state determinations, including all supporting information and an explanation of the technical basis for each decision, made under the following provisions of 40 CFR Part 141, Subpart L for the control of disinfectants and DBPs. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(12) |
12 years |
Records of systems that are installing granular activated carbon or membrane technology. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(12)(i) |
12 years |
Records of systems that are required, by the state, to meet alternative minimum TOC removal requirements or for whom the state has determined that the source water is not amenable to enhanced coagulation. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(12)(ii) |
12 years |
Records of Subpart H systems using conventional treatment meeting any of the alternative compliance criteria. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(12)(iii) |
12 years |
A register of qualified operators that have met the state requirements. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(12)(iv) |
12 years |
Records of systems with multiple wells considered to be one treatment plant. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(13) |
12 years |
Monitoring plans for Subpart H systems serving more than 3,300 persons. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(14) |
12 years |
List of laboratories approved for analyses. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(15) |
12 years |
List of systems required to monitor for disinfectants and DBPs in accordance with Part 141, Subpart L. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(16) |
12 years |
Stage 2 DBPR |
||
Recordkeeping |
|
|
A record of all current monitoring requirements and the most recent monitoring frequency decision pertaining to the contaminant. |
40 CFR 142.14(a)(8) |
In perpetuity, until replaced or revised |
Records of IDSE monitoring plans submitted by PWSs plus any modifications, until replaced by approved IDSE reports. |
40 CFR 142.14(a)(8)(i) |
In perpetuity, until replaced or revised |
Records of IDSE reports and 40/30 certifications and any modifications required by the state, until replaced or revised. |
40 CFR 142.14(a)(8)(ii) |
In perpetuity, until replaced or revised |
Operational evaluations submitted by a system. |
40 CFR 142.14(a)(8)(iii) |
Ten years |
Special Primacy Requirements |
|
|
An application for approval of a state program revision that adopts 40 CFR Part 141, Subpart L, must contain a description of how the state will accomplish the program requirements. |
40 CFR 142.16(h) |
One time |
Chemical Phase Rules (Phases II, IIB, and V) |
||
Reporting |
||
Make determination regarding asbestos waiver requests. |
40 CFR 141.23(b)(3) and (4) |
3 years, as necessary |
Make determination regarding IOC waiver requests. |
40 CFR 141.23(c)(2) through (4) |
9 years, as necessary |
Make determination regarding VOC waiver. |
40 CFR 141.24(f)(7), (8), and (10) |
6 years or frequency specified by state, as necessary |
Make determination regarding SOC waiver requests. |
40 CFR 141.24(h)(5) and (6) |
3 years, as necessary |
Recordkeeping |
||
Records for most recent vulnerability determination, including monitoring results and other data supporting the determination, the state’s findings, and any additional bases for such determination. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(4) |
In perpetuity or until more current vulnerability determination has been issued |
Records of all current monitoring requirements and most recent monitoring frequency decision pertaining to each contaminant, including the monitoring results and other data supporting the decision, the state’s findings, and any additional bases for such decision. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(5) |
In perpetuity or until a more recent monitoring frequency decision has been issued |
Records of most recent asbestos repeat monitoring determination, including monitoring results and other data supporting the determination, the state’s findings, and any additional bases for the determination and the repeat monitoring frequency. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(6) |
In perpetuity or until more current repeat monitoring determination has been issued |
Records of annual certifications received from systems pursuant to Part 141, Subpart K demonstrating the system’s compliance with the treatment techniques for acrylamide and/or epichlorohydrin. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(7) |
12 years |
Radionuclides |
||
Reporting |
||
Evaluate and draft written response for a system request to use historical monitoring data. |
40 CFR 141.26(a)(2)(ii)(C) |
As necessary |
Determine whether to designate a system as vulnerable and notify system of the determination. |
40 CFR 141.26(b)(1) |
As necessary |
Designate system using waters contaminated by nuclear facility effluent and notify system of determination. |
40 CFR 141.26(b)(2) |
As necessary |
Recordkeeping |
||
Subject to general requirements as listed above. |
||
SWTR (only disinfection residual monitoring and associated activities) |
||
Reporting |
||
Subject to general requirements as listed above |
||
Recordkeeping |
||
Records of disinfectant residual measurements and other parameters necessary to document disinfection effectiveness. |
40 CFR 142.14(a)(4)(i) |
1 year |
Records of decisions to allow an unfiltered or filtered PWS to sample residual disinfectant concentration at alternate locations if it also has ground water source(s). |
40 CFR 142.14(a)(4)(ii)(A)(4) and (6) |
40 years, or 1 year after decision is reversed or revised |
Records of any decision that a violation of monthly contact time (CT) compliance requirements was caused by circumstances that were unusual and unpredictable. |
40 CFR 142.14(a)(4)(ii)(B)(1) |
1 year |
Records of any decision that a violation of the disinfection effectiveness criteria was not caused by a deficiency in treatment of the source water. |
40 CFR 142.14(a)(4)(ii)(B)(2) |
1 year |
Records of any decision that failure to meet the disinfectant residual concentration requirements of 40 CFR 141.72(a)(3)(i) was caused by circumstances that were unusual and unpredictable. A copy of the decision must be provided to the system. |
40 CFR 142.14(a)(4)(ii)(C)(2) |
40 years, unless filtration is installed |
Records of decisions that an unfiltered or filtered system has no means for having a sample transported and analyzed for heterotrophic plate count by a certified laboratory under the requisite time and temperature conditions and that the system is providing adequate disinfection in the distribution system, so that the disinfection requirements do not apply, and the basis for the decision. A copy of the decision must be provided to the system. |
40 CFR 142.14(a)(4)(ii)(C)(9) and (10), respectively |
Until the decision is reversed or revised |
Records of decisions that a system using a disinfectant other than chlorine may use CT 99.9 values other than those in tables 2.1 or 3.1 and /or other operational parameters to determine if the minimum total inactivation rates are being met. A copy of the decision must be provided to the system. |
40 CFR 142.14(a)(4)(ii)(C)(13) |
Until the decision is reversed or revised |
Arsenic Rule |
|
|
Reporting |
|
|
Subject to general requirements as listed above |
|
|
Recordkeeping |
|
|
Subject to general requirements as listed above |
|
|
Lead and Copper Rule |
||
Reporting |
||
Notify the system after an approval decision has been made in regards to the system’s request to add a new source of water or change a treatment process prior to implementation. |
40 CFR 141.81(b)(3)(iii); 141.86(d)(4)(vii); 141.86(g)(4)(iii); 141.90(a)(3)
|
As necessary |
Provide written notice to PWSs explaining the basis for determining if the PWS has optimized corrosion control and specifying the water quality control parameters that represent optimal corrosion control. |
40 CFR 141.81(b)(2) |
As necessary |
Notify a system in writing of any determination requiring a system to repeat treatment steps previously completed. |
40 CFR 141.81(c) |
As necessary |
Specify corrosion control studies or optimal CCT (after a small or medium system exceeds the lead or copper action level). |
40 CFR 141.81(e)(2) |
Within 18 months (medium systems) or 24 months (small systems) of exceedance |
Designate optimal CCT (if a small or medium system has performed corrosion control studies). |
40 CFR 141.81(e)(4) |
As necessary, within 6 months of system completing studies |
For small and medium systems, designate optimal WQPs. |
40 CFR 141.81(e)(7) |
As necessary, within 6 months of system completing follow-up sampling |
Notify PWSs in writing of decisions on optimal CCT. |
40 CFR 141.82(d)(2) |
As necessary |
Modify determinations of optimal CCT in writing. |
40 CFR 141.82(h) |
As necessary or as requested |
Notify the system in writing of determinations regarding necessary source water treatment. |
40 CFR 141.83(a)(2),141.83(b)(2) |
As necessary, within 6 months of submission of monitoring results |
Notify the system in writing of designations for maximum permissible source water levels. |
40 CFR 141.83(a)(5), 141.83(b)(4) |
As necessary within 6 months of completing tap and source water monitoring. |
Provide in writing revised source water treatment or maximum permissible lead and copper concentrations along with a basis for the decision and an implementation schedule. |
40 CFR 141.83(b)(6) |
As necessary or as requested |
Review public education materials content and consult on activities. Review and track system certification. |
40 CFR 141.85(a) |
As necessary |
Notify a system in writing if a shorter LSLR schedule is required. |
40 CFR 141.84(e) |
As necessary, within 6 months after system triggered into LSLR |
Review and track system certification regarding distribution of tap samples to individual monitoring locations. |
40 CFR 141.80(g); 141.85(d); 141.90(f)(3) |
As necessary |
Notify the system of approval of non-first-draw sample sites. |
40 CFR 141.86(b)(5) |
As necessary |
If applicable, review system request and approve in writing or by site verification the number of taps for sampling. |
40 CFR 141.80(c)(3)(v); 141.86 (c) |
One time |
Specify sampling locations when a system is conducting reduced monitoring. |
40 CFR 141.86(c) |
As necessary |
Notify the system in writing when the state determines that a system is eligible to commence reduced monitoring. |
40 CFR 141.86(d)(4)(ii) & (iii) |
As necessary |
Notify system of alternate period for collecting reduced lead and copper tap samples. |
40 CFR 141.86(d)(4)(iv)(B) |
As necessary |
Document in writing the decision and rationale for invalidating a sample. |
40 CFR 141.86(f)(3) |
As necessary |
Notify the system in writing of its waiver determination and the conditions of the waiver. |
40 CFR 141.86(g)(3) |
As necessary |
Notify a system if its waiver has been revoked. |
40 CFR 141.86(g)(5)(iii) |
As necessary |
Review additional monitoring data and reports from systems that have exceeded the lead action level. |
40 CFR 141.86(d)(4)(vi)(B)
|
As necessary |
Report to EPA the following information related to each system’s compliance with lead and copper requirements:
|
||
For each large and medium PWS, all 90th percentile lead levels calculated during each monitoring period, and the first and last day of the monitoring period for which the 90th percentile lead level was calculated. |
40 CFR 142.15(c)(4)(iii)(A) |
Quarterly |
For each small PWS, the 90th percentile lead level calculated during each monitoring period in which the systems exceeds the lead action level, and the first and last day of each monitoring period in which an exceedance occurred. |
40 CFR 142.15(c)(4)(iii)(B) |
Quarterly |
For each PWS, the 90th percentile copper level calculated during each monitoring period in which the system exceeds the copper action level, and the first and last day of each monitoring period in which an exceedance occurred. |
40 CFR 142.15(c)(4)(iii)(C) |
Quarterly |
For each PWS for which the state has designated optimal WQPs or which the state has deemed to have optimized corrosion control, the date of the determination and the paragraph(s) under which the state made its determination. |
40 CFR 142.15(c)(4)(iii)(D) |
Quarterly |
For each PWS required to begin replacing LSLs, the date each system must begin replacement. |
40 CFR 142.15(c)(4)(iii)(E) |
Quarterly |
For each PWS that has implemented optimal corrosion control, completed applicable source water treatment requirements or completed LSLR requirements and the date of the state's determination that these requirements have been met. |
40 CFR 142.15(c)(4)(iii)(F) |
Quarterly |
Recordkeeping |
||
Maintain records of currently applicable or most recent state determinations, including all supporting information and explanation of technical basis for each decision. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8) |
12 years |
For any system deemed to be optimized, maintain records of any conditions imposed by the state to ensure the continued operation and maintenance of CCT in place. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8)(i) |
12 years |
Maintain records of decisions to require a system to conduct CCT studies. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8)(ii) |
12 years |
Maintain records of designations of optimal CCT. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8)(iii) |
12 years |
Maintain records of designations of optimal WQPs. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8)(iv) |
12 years |
Maintain records of decisions to modify a PWS’s optimal CCT or WQPs. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8)(v) |
12 years |
Maintain records of determinations of source water treatment. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8)(vi) |
12 years |
Maintain records of designations of maximum permissible concentrations of lead and copper in source water. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8)(vii) |
12 years |
Maintain records of determinations establishing shorter LSLR schedules. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8)(viii) |
12 years |
Maintain records of determinations of additional monitoring requirements and/or other actions required to maintain optimal corrosion control by systems monitoring for lead and copper at the tap less frequently than once every six months that change treatment or add a new source of water. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8)(ix) |
12 years |
Maintain records of system-specific decisions regarding the content of written public education materials and/or the distribution of these materials. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8)(x) |
12 years |
Maintain records of system-specific determinations regarding use of non-first-draw samples at NTNCWSs and CWSs that operate 24 hours a day. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8)(xi) |
12 years |
Maintain records of system-specific designations of sampling locations for systems subject to reduced monitoring. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8)(xii) |
12 years |
Maintain records of system-specific determinations pertaining to alternative sample collection periods for systems subject to reduced monitoring. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8)(xiii) |
12 years |
Maintain records of determinations of small system monitoring waivers, waiver recertifications, and waiver revocations. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8)(xiv) |
12 years |
Maintain records of determinations regarding representative entry point locations at ground water systems. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(8)(xv) |
12 years |
Maintain records of reports and any other information submitted by PWSs. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(9) |
12 years |
Maintain records of state activities to verify compliance with state determinations. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(10)(i) |
12 years |
Maintain records of state activities to verify compliance with the requirements related to partial LSLR and compliance with LSLR schedules. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(10)(ii) |
12 years |
Maintain records of state activities to invalidate tap water lead and copper samples. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(10)(iii) |
12 years |
Maintain records of each system’s currently applicable or most recently designated monitoring requirements. |
40 CFR 142.14(d)(11) |
12 years or until a new decision, determination, or designation has been issued |
4(b)(ii) Respondent Activities
PWSs and primacy agencies must complete the activities described in the sections below.
Public Water Systems
PWSs are required to monitor for compliance with the MCLs or MRDLs as established in 40 CFR Part 141, Subpart B. Public water system owners and operators are required to report laboratory results to the state at frequencies specified in EPA regulations. In addition, they are required to record, maintain, and report the analytical results of these monitoring efforts in accordance with 40 CFR Part 141, Subparts C and D. General activities carried out by PWSs implementing the regulations addressed in this ICR include:
Planning activities associated with rule implementation, such as establishing monitoring plans.
Data collection such as identifying sample sites and collecting samples.
Analyzing samples collected.
Processing, compiling, and reviewing information created.
Developing and distributing reports and other documents.
Recording and maintaining the information.
Specific activities are described in Exhibit 2.
Primacy Agencies
States are currently required to maintain records of state verification activities and each determination made and to report to EPA through SDWIS in accordance with state reporting requirements (section 142.14). Primacy agencies ensure the implementation of the rules covered by this ICR. To meet their responsibilities, the primacy agencies conduct the following activities:5
Coordinate with EPA.
Notify systems of requirements.
Make compliance determinations.
Provide training and technical assistance to PWSs.
Maintain data management systems.
Establish the monitoring schedules.
Review plans and specifications.
Enter monitoring and enforcement data.
Keep records and supporting information, including state determinations and explanations for technical decisions regarding rule implementation.
Following is a detailed description of monitoring and other data collection and reporting requirements for each of the drinking water rules included in this ICR (see also Exhibit 3).
Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule
The Stage 1 DBPR applies primarily to community water systems (CWSs) and nontransient noncommunity water systems (NTNCWSs) that add a chemical disinfectant anywhere in the treatment process. Transient noncommunity water systems (TNCWSs) that add a disinfectant are subject to requirements on chlorine dioxide only. The regulation establishes:
MCL for total trihalomethanes (TTHMs) (40 CFR 141.64).
MCLs for haloacetic acids (HAA5), bromate, and chlorite (40 CFR 141.64).
MRDLs for chlorine, chloramines, and chlorine dioxide (40 CFR 141.65).
Treatment techniques for DBP precursors (40 CFR 141.135).
Best Available Technologies (BATs) for controlling DBPs and disinfectants (40 CFR 141.64 and 141.65, respectively).
The information collection requirements necessary to comply with these requirements include monitoring, reporting, and recordkeeping. Public water systems must report the number of samples and the sampling site, date, and results of each sample taken in the last monitoring period. For many of the DBPs and disinfectants, systems must also calculate the running annual average of sample results to determine compliance with the MCL or MRDL. All systems are required to conduct compliance monitoring in this ICR period. The Stage 2 DBPR modified how compliance with the MCLs for TTHM and HAA5 is calculated. For public water systems that take samples at more than one sampling site, the MCL is now calculated based on a running annual average at each sampling location rather than by averaging the sampling results at different locations. Other Stage 1 DBPR requirements remain unchanged.
MAXIMUM CONTAMINANT LEVELS (MCLs)
TTHM and HAA5 MCLs
Small Subpart H6 Systems Serving Fewer Than 500 People
Routine Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). CWSs and NTNCWSs must take one sample per plant per year for both TTHM and HAA5.
Reduced Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). No reduced monitoring is allowed.
Compliance Requirements (40 CFR 141.133). If the average of samples taken during the year exceeds the MCL, the system must increase monitoring to one sample per plant per quarter. Compliance with the MCL is based on an annual arithmetic average.
Small Subpart H Systems Serving 500-9,999 People
Routine Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). CWSs and NTNCWSs must take one sample per plant per quarter for both TTHM and HAA5.
Reduced Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). Systems with annual average TTHM < 0.040 mg/L and HAA5 < 0.030 mg/L and source water TOC < 4.0 mg/L prior to treatment may reduce monitoring to one sample per plant per year. If a system exceeds 0.060 mg/L or 0.045 mg/L for TTHM or HAA5 respectively, it must revert to routine monitoring.
Large Subpart H Systems Serving at Least 10,000 People
Routine Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). CWSs and NTNCWSs must take four samples per plant per quarter for both TTHM and HAA5.
Reduced Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). Systems with annual average TTHM < 0.040 mg/L and HAA5 < 0.030 mg/L and source water TOC < 4.0 mg/L prior to treatment may reduce samples to one sample per plant per quarter. If a system exceeds 0.060 mg/L or 0.045 mg/L for TTHM or HAA5 respectively, it must revert to routine monitoring.
Small Ground Water Systems Serving Fewer Than 10,000 People
Routine Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). CWSs and NTNCWSs must take one sample per plant per year for both TTHM and HAA5.
Reduced Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). Systems with annual average TTHM < 0.040 mg/L and HAA5 < 0.030 mg/L for 2 consecutive years or TTHM < 0.020 / HAA5 < 0.015 for one year may reduce samples to one sample per plant per three-year monitoring cycle.
Compliance Requirements (40 CFR 141.133). If the average of samples taken during the year exceeds the MCL, the system must increase monitoring to one sample per plant per quarter. Compliance with the MCL is based on an annual arithmetic average.
Large Ground Water Systems Serving at Least 10,000 People
Routine Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). CWSs and NTNCWSs must take one sample per plant per quarter for both TTHM and HAA5.
Reduced Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). Systems with annual average TTHM < 0.040 mg/L and HAA5 < 0.030 mg/L may reduce samples to one sample per plant per year. If a system exceeds 0.060 mg/L or 0.045 mg/L for TTHM or HAA5 respectively, it must revert to routine monitoring.
Chlorite MCL
Chlorite is an inorganic DBP formed when drinking water is treated with chlorine dioxide. The MCL for chlorite is 1.0 mg/L. CWSs and NTNCWSs that use chlorine dioxide must conduct chlorite monitoring.
Routine Daily Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). Systems must take daily samples at the entrance to the distribution system. If any sample exceeds the MCL, the system must take additional samples the following day at the following three locations: as close as possible to the first customer; a location representative of average residence time; and a location reflecting the maximum residence time.
Routine Monthly Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). Each month, systems must take one sample at each of the three following distribution system locations: near the first customer, at a location representative of average residence time, and at a location reflecting maximum residence time in the distribution system.
Reduced Monthly Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). After one year of routine monitoring, systems may reduce to one 3-sample set per quarter if the MCL has not been exceeded during that year by any individual sample and the system has not been required to take any follow-up samples. A system may remain on reduced monitoring if all three of the individual chlorite samples do not exceed the MCL. If a system conducting reduced monitoring exceeds the MCL and the daily sample does not exceed the MCL, it must revert to routine monitoring.
Bromate MCL
Bromate is one of the principal byproducts of ozonation in source water containing bromide. The MCL for bromate is 0.010 mg/L. CWSs and NTNCWSs that use ozone for disinfection or oxidation must conduct bromate monitoring.
Routine Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). Systems must take one sample per month for each plant using ozone at the entrance to the distribution system while the ozonation system is in operation.
Reduced Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). A system may take one sample per plant per quarter if its annual average source water bromide concentration is less than 0.05 mg/L, based on a monthly measurement. If the running annual average bromide concentration is >0.05 mg/L, the system must conduct routine monitoring. The system must continue to monitor for bromide to remain on reduced bromate monitoring.
MAXIMUM RESIDUAL DISINFECTANT LEVELS (MRDLs)
Disinfectants are added during water treatment to control waterborne microbial contaminants. Some residual disinfectants will remain in water after treatment. Setting MRDLs protects public health by limiting the level of residual disinfectant in drinking water while ensuring sufficient disinfectant remains in the drinking water to protect against waterborne microbial contaminants.
Chlorine and Chloramines MRDLs
Chlorine is a widely used disinfectant. The MRDL for chlorine is 4.0 mg/L. Chloramines are formed when ammonia is added during chlorination to suppress formation of many byproducts. The MRDL for chloramines is 4.0 mg/L (measured as Cl2).
Routine Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). CWSs and NTNCWSs must take samples for the residual disinfectant levels at the same points in the distribution system and at the same time as total coliform samples.
Chlorine Dioxide MRDL
Chlorine dioxide is used primarily for the oxidation of taste- and odor-causing organic compounds in water. About 60 to 70 percent of the chlorine dioxide is converted to chlorite in the treatment process. This provision applies to CWSs, NTNCWSs, and TNCWSs.
Routine Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). Systems must take a daily sample at the entrance to the distribution system. If any sample exceeds the MRDL, the system must take three additional samples the following day in the distribution system.
DBP PRECURSORS
Subpart H systems employing conventional filtration must monitor for TOC and alkalinity in their source and finished water. These samples determine treatment technique requirements.
Routine Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). Systems must take one paired sample per month of TOC in source water and treated water. These samples must be taken simultaneously. Additionally, systems must take one alkalinity sample per month at the same time as the source water TOC sample.
Reduced Monitoring (40 CFR 141.132). Systems may take one paired sample per quarter if their average treated water TOC is less than 2.0 mg/L for two consecutive years or less than 1.0 mg/L for one year. The alkalinity sample is taken at the same time. If the average treated water TOC in these systems is > 2.0 mg/L, the public water system must conduct routine monitoring.
MONITORING PLANS
Under the Stage 1 DBPR, each public water system was required to develop a monitoring plan (40 CFR 141.132), and have the plan readily available to the public and the state. The state may require changes in any element of the system’s monitoring plan.
Stage 2 Disinfectants and Disinfectant Byproducts Rule
The Stage 2 DBPR builds on the 1998 Stage 1 DBPR by requiring reduced levels of disinfectant byproducts (DBPs) in distribution systems. The Stage 2 DBPR is designed to reduce DBP occurrence peaks in the distribution system. The numerical MCLs for the Stage 2 DBPR are the same as for the Stage 1 DBPR MCLs. In Stage 2 DBPR, the TTHM and HAA5 MCLs compliance is determined at each monitoring location, while Stage 1 DBPR requires a system to average results over all monitoring locations.
Each rule activity is described below. Implementation activities and IDSEs, along with Stage 2 monitoring plans, were completed during previous ICR periods.
Systems
Most PWSs will be involved in the following collection activities:
Additional Routine Monitoring
Under Stage 2 DBPR, public water systems determined the number of samples and the locations of the sampling sites to comply with the regulation. In some cases, the number of samples and locations remained the same as in Stage 1 DBPR. These activities continue during this ICR period and are based on the monitoring plan submitted during a previous ICR period. The compliance date varies based on system size and other factors. Systems activities are included below:
Conduct additional routine monitoring.
Determine if provisions for reduced monitoring are satisfied.
Determine if increased monitoring is required.
Operational Evaluations
A system exceeds an operational evaluation level at any monitoring location when the sum of the two previous quarters’ compliance monitoring results plus twice the current quarter’s result at one location, divided by 4, exceeds 80 μg/L for TTHM or 60 μg/L for HAA5. If an operational evaluation level is exceeded, systems must:
Conduct an operational evaluation.
Submit a written report to the state no later than 90 days after being notified of the analytical result that resulted in the operational evaluation level exceedances.
States
State officials serve as respondents when reporting compliance data to EPA. States are currently required to maintain records of verification activities and each determination made and report to EPA through SDWIS.
States are anticipated to be involved in several activities as described below. Note that state review of IDSE reports and proposed monitoring plans was completed during a previous ICR period.
Additional Routine Monitoring
Review and evaluate monitoring data submitted by systems.
Operational Evaluations
Review operational evaluations from systems.
Recordkeeping
In addition to existing recordkeeping requirements, states must follow Stage 2 DBPR specific recordkeeping requirements in section 142.14(a)(8) which include:
Any decisions made pursuant to IDSE and Stage 2 DBPR site requirements, until replaced or revised.
Records of IDSE reports and 40/30 certifications and any modifications required by the state, until replaced or revised.
Operational evaluations submitted by a system, for 10 years following submission.
Chemical Phase Rules
The chemical monitoring requirements apply only to CWSs and NTNCWSs, except that TNCWSs must sample for nitrate and nitrite. Monitoring requirements follow the standardized monitoring framework (SMF) schedule established by the rule. Under the SMF, 9-year compliance cycles were established; the first cycle lasted from January 1, 1993 to December 31, 2001; the second cycle began on January 1, 2002, and ends on December 31, 2010; and the third cycle began January 1, 2011 and will end December 31, 2019. Each nine-year cycle consists of three, 3-year compliance periods (e.g., from January 1, 2011, to December 31, 2013; from January 1, 2014, to December 31, 2016; and from January 1, 2017, to December 31, 2019).
The compounds and contaminants addressed by the Chemical Phase Rules are listed in Exhibit 4. A more detailed description of the monitoring requirements for inorganic compounds (IOCs), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and synthetic organic compounds (SOCs) follows.
Regulated Organic Compounds and Inorganic Chemicals
Phase of Regulation |
Inorganic Chemicals |
Synthetic Organic Compounds |
Volatile Organic Compounds |
Phase I7 |
N/A |
N/A |
Benzene Carbon tetrachloride p-Dichlorobenzene Trichloroethylene Vinyl Chloride 1,1,1-Trichloroethane 1,1-Dichloroethylene 1,2-Dichloroethane |
Phase II |
Asbestos Cadmium Chromium Fluoride Mercury Nitrate Nitrite Selenium
|
Alachlor Atrazine Carbofuran Chlordane Ethylene dibromide DBCP Heptachlor Heptachlor epoxide Lindane Methoxychlor Toxaphene Polychlorinated byphenyl 2,4-D 2,4,5-TP (Silvex) |
cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene Ethylbenzene Monochlorobenzene o-Dichlorobenzene Styrene Tetrachloroethylene Toluene trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene Xylenes 1,2-Dichloropropane
|
Phase IIB |
Barium |
Pentachlorophenol |
N/A |
Phase V |
Antimony Beryllium Cyanide Nickel (remanded) Thallium |
Benzo(a)pyrene Dalapon Di(2-ethylhexyl)-adipate Di(2-ethylhexyl)-phthalate Dinoseb Diquat Endothall Endrin Glyphosate Hexachlorobenzene Hexachlorocyclopentadiene Oxamyl Picloram Simazine 2,3,7,8-TCDD (Dioxin) |
Dichloromethane 1,1,2-Trichloroethane 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
|
Arsenic Rule |
Arsenic |
NA |
NA |
INORGANIC CHEMICALS
This section summarizes the IOC monitoring requirements for the last year of the second 3-year compliance period and the first two years of the third 3-year compliance period of the third 9-year compliance cycle. The third 9-year compliance cycle began on January 1, 2011, and the third 3-year compliance period begins on January 1, 2017. For the purposes of monitoring requirements, the IOCs regulated under Phases II and IIB are asbestos, barium, cadmium, chromium, fluoride, mercury, nitrite, nitrate, and selenium. The IOCs regulated by Phase V are antimony, beryllium, cyanide, and thallium. The MCL for nickel, which was initially included as part of Phase V, was remanded on February 9, 1995. This means that, while many water suppliers continue to monitor nickel levels in their water, there is currently no EPA legal limit on the amount of nickel in drinking water. Arsenic was regulated under the 1976 standards for IOCs but is now addressed separately in the Arsenic Rule.
During each 3-year compliance period, ground water systems must take one sample at each sampling point. Surface water systems must take one sample annually at each sampling point. If results from any sampling events are above the MCL, the PWS must begin quarterly sampling during the next calendar quarter. The PWS must continue quarterly sampling until the state determines that the samples are reliably and consistently below the MCL based on at least two consecutive quarterly samples for ground water systems and four consecutive quarters for surface water systems. Once the samples are reliably and consistently below the MCL, ground water systems are then required to sample triennially, and surface water systems must sample annually.
After three consecutive sampling rounds in which sampling results are below the MCL, a PWS may apply to the state for a waiver. Should the state grant a waiver, the PWS is required to sample only once every nine years. IOC waivers must be renewed every nine years.
VOLATILE ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
This section summarizes VOC monitoring requirements for most of the third 3-year compliance period of the third compliance cycle, as described in 40 CFR 141.24(f).
For VOCs, surface water systems must take one sample annually at each sampling point. During each three-year compliance period, ground water systems must take one sample at each sampling point (after initially sampling annually). If any sample exceeds the method detection limit (MDL) of 0.0005 mg/l, the PWS must begin quarterly monitoring during the next calendar quarter. Quarterly sampling must continue until the state determines that the samples are reliably and consistently below the MCL based on at least two consecutive quarterly samples for ground water systems and four consecutive quarters for surface water systems. However, if the detection that triggered the increased sampling exceeds the MCL, the PWS must take a minimum of four consecutive quarterly samples, regardless of whether it is served by ground water or surface water. Once the samples are reliably and consistently below the MCL, the state may reduce the sampling frequency to once per year, provided repeat sampling is conducted during the calendar quarter that previously yielded the highest analytical result.
Systems may apply to the state for a waiver after initial monitoring provided VOCs are not detected. The maximum waiver period for ground water sampling points is six years. The initial waiver must be renewed within the first three years of issuance, but subsequent waivers may be renewed at the end of the six-year period. A ground water system must collect one sample within the first compliance period and at least one sample during each six-year waiver period. For surface water systems, the maximum waiver period is three years, but there is no minimum federal sampling frequency. The state determines the sampling schedule for surface water systems with a three-year waiver.
SYNTHETIC ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
This section summarizes the SOC monitoring requirements for most of the third 3-year compliance period of the third compliance cycle, as described in 40 CFR 141.24(h).
Systems serving more than 3,300 people are required to take two SOC samples every three years. For systems that serve fewer than 3,300 people, one sample is required every three years. If a contaminant is detected at any sampling point, the water system must begin quarterly sampling during the next calendar quarter. Quarterly sampling must continue until the state determines that the samples are reliably and consistently below the MCL based on at least two consecutive quarterly samples for ground water systems and four consecutive quarters for surface water systems. However, if the detection that triggered the increased sampling exceeds the MCL, then the PWS must take a minimum of four consecutive quarterly samples, regardless of whether it is served by ground water or surface water. Once the samples are reliably and consistently below the MCL, the state may reduce the sampling frequency to once per year, provided repeat sampling is conducted during the calendar quarter that previously yielded the highest analytical result.
After three years of annual monitoring without SOC detections, systems may apply for a waiver. Waivers are effective for one compliance period (i.e., three years). They must be renewed in each subsequent compliance period, or the system must return to the sampling frequency specified for its size.
Radionuclides Rule
On December 7, 2000, EPA promulgated a revised radionuclides regulation. The revised rule completely supersedes the requirements established in the original 1976 Rule. The Radionuclides Rule, which is applicable only to CWSs, revised and amended 40 CFR Parts 141 and 142 and:
Sets an MCLG of zero for all radionuclides.
Maintains the 1976 gross alpha MCL of 15 PicoCuries per liter (pCi/L) (which includes combined radium-226/-228 and excludes uranium and radon).
Maintains the 1976 MCL of 5 pCi/L for combined radium-226 and radium-228.
Maintains the 1976 beta particle and photon radioactivity MCL of 4 millirem per year (mrem/yr).
Sets an MCL of 30 µg/L for uranium.
Establishes separate monitoring requirements for radium-226 and radium-228.
Maintains the beta/photon screening levels set in the 1976 Rule for vulnerable systems (as deemed by the state). Surface water systems serving greater than 100,000 persons will no longer be required to monitor unless they are deemed vulnerable.
Revises sampling, compliance, and monitoring waivers to SMF at entry points to the distribution system. States have discretion in grandfathering existing distribution system data for determining initial monitoring baselines.
Disinfectant Residual Monitoring and Associated Activities under the SWTR8
As mentioned earlier, the majority of the SWTR requirements, with the exception of disinfectant residual monitoring, are addressed in the Microbial Rules ICR. Specific disinfectant residual monitoring required by the SWTR and covered under this ICR includes:–
Periodic disinfectant residual monitoring from the distribution system for Subpart H systems. (40 CFR 141.74 (b)(6)(i) for unfiltered systems and 40 CFR 141.74(c)(3)(i) for systems that filter).
Continuous disinfectant residual monitoring at entry points into the distribution system. (40 CFR 141.74 (b)(5) for unfiltered systems and 40 CFR 141.74(c)(2) for systems that filter).9
Calculation of inactivation ratios for unfiltered systems using CT values (40 CFR 141.74 (b)(3)).10
Arsenic Rule
The Arsenic Rule was promulgated January 22, 2001, and requires that CWSs and NTNCWSs follow the SMF. As previously described for the Chemical Phases Rule, the SMF is conducted within the schedule of a 9-year compliance cycle. The compliance cycle is subsequently composed of three, 3-year periods.
Routine Monitoring
Groundwater systems must take a sample at each entry point to the distribution system once every three years; surface water systems must sample at each entry point annually. Triggered monitoring as a result of a violation requires the system to monitor quarterly beginning in the next quarter after the violation has occurred. Only after a system has taken two consecutive groundwater samples or four consecutive surface water samples and the state has determined that the system is “reliably and consistently” below the MCL (40 CFR 141.23(c)(8)) may the system return to routine monitoring.
The rule also allows systems to receive nine-year monitoring waivers. During the waiver period, a system must take a minimum of one sample. To receive a waiver, a system must demonstrate that during the previous three rounds of monitoring all results were less than the MCL and there was adequate source protection. Systems with waivers are expected to reapply during the current ICR period.
Lead and Copper Rule
CWSs and NTNCWSs are required to comply with the LCR. In general, the LCR requires each of these water systems to undertake the following activities:11
Plan monitoring and other activities.
Provide training to appropriate staff and to residents collecting samples.
Identify appropriate sampling sites and collect samples.
Review sample data, including the calculation of lead and copper 90th percentile levels.
Submit to the state monitoring data and any other documents or reports.
Record and maintain information.
In addition, some systems must submit corrosion control studies, recommend and submit information regarding the completion of CCT or source water treatment installation, conduct public education, or conduct LSL monitoring, notification, and replacement.
The short term revisions to the LCR apply to CWSs and NTNCWSs, as with the LCR. In addition to the LCR requirements, the revisions require systems to undertake the following activities:
Take additional tap samples for lead if the lead action level of 0.015 mg/L is exceeded.
Provide revised public education materials according to revised delivery requirements if the lead action level is exceeded, including a statement on lead in the CCR.
Notify the state before making long term treatment changes.
Notify customers of results of samples taken at their homes.
Retest LSLs previously exempted from replacement if the lead action level is exceeded.
5 INFORMATION COLLECTED — AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
As part of its supervisory responsibility, EPA maintains SDWIS and evaluates SDWIS data to determine system compliance. EPA personnel also reformat, distribute, and store these data for a number of uses, including responding to Congressional and public inquiries. EPA also oversees the EPA Regional and state programs, provides technical assistance, and develops policies designed to ensure consistent program implementation. EPA officials serve as respondents when testifying to Congress on the PWSS Program or in the courts for enforcement actions.
EPA’s requirements are outlined in Exhibit 5 below. Most of the burden and costs for these activities are addressed in the PWSS Program ICR (OMB No. 2040-0090). Section 5(a) of the PWSS Program ICR contains additional detail regarding the activities supported by the collection of SDWIS data described above. Details regarding potential burden and cost reductions in future ICR periods are provided in section 5(b) of the PWSS Program ICR.
EPA will also conduct primacy activities in states, tribes and territories that do not have primacy. Specifically, EPA will be involved in the following activities:
Mobilization, planning, and implementation.
Training PWS and consultant staff.
Analyzing and reviewing PWS data.
Making determinations concerning PWSs.
Compliance tracking.
Recordkeeping.
However, burden and costs for these activities are accounted for under the primacy agency burden (see section 6).
EPA Requirements
Requirement |
Regulatory Citation |
Frequency |
General Requirements (apply to all regulations) |
||
For states and other entities for which the Agency maintains primacy, the Agency must maintain the records and perform the reporting activities required of states. |
40 CFR 142.14 and 142.15 |
As necessary |
Review state request for approval of a program revision and notify state of determination regarding request. |
40 CFR 142.12(d)(3) |
One time, as necessary |
Stage 1 DBPR |
||
Subject to general requirements as listed above. |
||
Stage 2 DBPR |
||
Subject to general requirements as listed above. |
||
Chemical Phase Rules (Phases II, IIB, and V) |
||
Subject to general requirements as listed above. |
||
Radionuclides |
||
Subject to general requirements as listed above. |
||
SWTR (only disinfectant residual monitoring and associated activities) |
||
Subject to general requirements as listed above. |
||
Arsenic Rule |
||
Subject to general requirements as listed above. |
||
Lead and Copper Rule |
||
Subject to general requirements as listed above. |
||
5(b) Collection Methodology and Management
Primacy agencies must report data to EPA on a quarterly basis. These data include any new data and revisions or corrections to existing data. This information is maintained in SDWIS12, which contains the following:
Inventory data for each PWS.
Violations.
Enforcement actions and some follow-up activity.
Variances and exemptions (where applicable).
Primacy agencies primarily transmit SDWIS data to EPA electronically. In the District of Columbia, Wyoming, and Indian Lands (except for the Navajo Nation, which has primacy), results of system samples are sent directly to EPA.
SDWIS data support a number of rule implementation and program management activities, which promote consistent national program implementation. SDWIS data is used to identify compliance trends with specific regulations, prioritize public water systems that might require training and technical assistance to return to compliance, and provide insights into primacy agency’s interpretation of regulations.
All costs for rule-related data management activities are addressed in the PWSS Program ICR (OMB No. 2040-0090). Section 5(b) of the PWSS Program ICR contains additional detail regarding the activities supported by the previously described collection of SDWIS data.
In developing chemical monitoring rules contained in this ICR, EPA considered the requirement of the Small Business Regulatory Enforcement Fairness Act (SBREFA) to minimize the burden of information collections on small entities. Small entities include “small businesses,” “small organizations” and “small government jurisdictions.” These terms are defined below.13
A small business is any business that is independently owned and operated and not dominant in its field, as defined by the Small Business Administration regulations under section 3 of the Small Business Act.
A small organization is any non-profit enterprise that is independently owned and operated and not dominant in its field.
A small governmental jurisdiction is the government of a city, county, town, township, village, school district, or special district that has a population of fewer than 50,000. This definition may also include Indian Tribes.
The major requirement under SBREFA is a regulatory flexibility analysis of all rules that have a “significant economic impact on a substantial number of small entities.” This ICR is not associated with new rules. Therefore, this ICR is not subject to the SBREFA.
EPA has made significant efforts to minimize the burden for all respondents, particularly for small entities. These efforts are described below.
Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule
The Stage 1 DBPR includes requirements tailored to small systems such as reduced monitoring frequency for systems producing finished water below the MCLs and MRDLs, and allowing rule requirements to begin up to five years after promulgation of the rule.
Stage 2 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule
The Agency took specific steps to minimize the burden of the IDSE on PWSs. For example, the rule included a VSS waiver, which allowed PWSs serving fewer than 500 people to be waived from conducting the IDSE. Small systems required to conduct IDSE, collected fewer samples than larger systems. As with the Stage 1 DBPR, compliance monitoring requirements are based on population served, allowing small systems to collect fewer compliance samples.
Chemical Phase Rules
For the contaminants regulated under the Phase II regulation, the provisions established in the SMF are intended to minimize burden on small entities by allowing systems to composite as many as five samples and by allowing states to grant waivers, which reduce monitoring requirements.
For Phase V chemicals, EPA has taken steps to minimize the burden on PWSs by allowing systems serving fewer than 3,300 people to composite among different systems provided the five sample limit is maintained. Sample collection has also been simplified by allowing the same sampling locations to be used for all source water-related monitoring.
Radionuclides Rule
The monitoring requirements for radionuclides apply only to CWSs.
Disinfectant Residual Monitoring and Associated Activities under the SWTR
The rule allows systems serving 3,300 and fewer people to substitute grab sampling for continuous disinfectant residual monitoring. This enables small systems to avoid capital costs associated with continuous monitoring equipment. The number of compliance samples is based on the population served by the PWS. For example, systems serving 500 or fewer people are required to take one sample, while systems serving 2,501 to 3,300 people are required to take four samples.
Arsenic Rule
In the Arsenic Rule, states are able to grant monitoring waivers to systems that are reliably and consistently below the MCL. These waivers will reduce the compliance cost for some small systems and will decrease the number of times a system must conduct routine monitoring. The monitoring requirements still allow systems to composite up to five samples. Compositing samples allows systems to reduce the laboratory costs associated with monitoring.
Lead and Copper Rule
The LCR reduced to the extent practicable and appropriate the burden on small PWSs. The regulations include different compliance or reporting requirements such as allowing states to permit systems to take 1 sample per tap in systems that have fewer than 5 taps.
Exhibit 6 contains a summary of the collection schedules for each rule. Given the wide range of phase-in schedules for the respective rules, additional information may be obtained by consulting the individual rules for specific collection schedules.
Exhibit 6
Collection Schedule14
Rule |
Collection Commencement |
Disinfectant residual monitoring and associated activities for the SWTR |
1991/1993 (depending on filtration status) |
Phase II |
1993 |
Phase IIB |
1993 |
Phase V |
1996 |
Stage 1 DBPR |
2002/2004 (depending on system size and source) |
Stage 2 DBPR |
2006 |
Radionuclides Rule |
2003 |
Arsenic Rule |
2006/2007 (depending on source water) |
Lead and Copper Rule |
1994 |
6 ESTIMATING BURDEN AND COST OF COLLECTION
This section estimates the burden and cost to PWSs, primacy agencies, and EPA for complying with drinking water information collection requirements associated with chemical contaminant-related rulemakings. These rulemakings include the following:
Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule
Stage 2 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule
Chemical Phase Rules
Radionuclides
Disinfectant Residual Monitoring and Associated Activities under the Surface Water Treatment Rule15
Arsenic Rule
Lead and Copper Rule16
This section also discusses the assumptions used to estimate burden and costs and describes the change in annual burden, as compared with the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR. This ICR updates the annual burden and costs associated with these rulemakings for January 1, 2016 through December 31, 2018.
EPA is committed to accurately characterizing the burden and costs of rules it promulgates. Consequently, EPA has refined some of the assumptions for calculating the burden and costs associated with implementing the drinking water regulations contained in this ICR. For this update, many assumptions were revised based on program changes and well-documented changes in some data. To provide a comparable basis on which to calculate the requirements addressed by the DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR and to address inconsistencies, EPA applied uniform assumptions to all rules. The categories of assumptions are listed below.
Labor rates: For PWSs, a 2013 labor rate of $21.62 was obtained from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). An overhead rate of 60 percent was applied, resulting in an hourly rate of $34.59. For states, a 2013 labor rate of $28.50 was obtained from the BLS. An overhead rate of 60 percent was applied, resulting in an hourly rate of $45.60.
PWS inventory figures from the most recent frozen SDWIS database pull (October 2014).
Number of entry points per system, as reported in the 2006 Community Water System Survey (CWSS).
Number of plants per system, as reported in the 2006 CWSS.
In addition, EPA revised some of the estimates of burden for particular activities to reflect consultations with representatives of PWSs and states (see section 3(c).
6(a)(i) Burden to Public Water Systems
The annual PWS burden for January 1, 2016 through December 31, 2018 is estimated to be approximately 3.3 million hours. Exhibit 7 tabulates the annual burden hours on a rule-specific basis. Activity-level burden assumptions were carried forward from previous ICRs. If updated data such as system inventories and results of consultations on burden, were available, those data were used in burden calculations. Appendices B through H show the assumptions and detailed burden calculations for each rule. The following further describes the bases for the burden estimates for each rule.
Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule
Activities associated with the Stage 1 DBPR account for 0.50 million annual burden hours. The assumptions used to calculate the Stage 1 DBPR burden are based largely on assumptions from the September 1998 Information Collection Request for the National Primary Drinking Water Regulations: Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule (Stage 1 DBPR ICR). The burden for systems includes only monitoring. The specific burden for monitoring includes the following:
Paired TTHM/HAA5
Alkalinity and paired TOC
Bromate
Chloride Dioxide
Chlorite (both daily and monthly monitoring)
Chlorine or chloramines (in the distribution system)17
At this point, reduced monitoring burden has not been estimated for the above contaminants, with the exception of alkalinity and paired TOC monitoring, which carried forward reduced monitoring rate estimates from the September 1998 Stage 1 DBPR ICR. The Stage 2 DBPR burden estimates account for any additional monitoring that may be required in addition to monitoring already required under Stage 1 DBPR.
Section 6(f) describes the reasons for changes between the burden reported in the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR and this ICR. Detailed burden and cost calculations for the Stage 1 DBPR are provided in Appendix B.
Stage 2 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule
Over the 3 years covered by this ICR, the total national respondent burden to PWSs is estimated at 0.146 million labor hours, an annual average of 0.049 million hours (see Exhibit 7). IDSE activities were completed during a previous ICR period, as were Stage 2 compliance monitoring plans. The next two sections describe the burden estimates for the current ICR period in greater detail.
Additional Routine Compliance Monitoring
Systems began conducting additional routine compliance monitoring during the previous ICR period. This monitoring is in addition to monitoring required under the Stage 1 DBPR. This requirement is not applicable to the majority of the public water systems. The burden for monitoring takes into account any changes in TTHM and HAA5 monitoring requirements resulting from the IDSE conducted during a previous ICR period. All small PWSs, regardless of whether or not they conducted Cryptosporidium monitoring under the LT2ESWTR, began to comply with the Stage 2 MCLs previous to this ICR period. Estimated burden and costs are presented in Exhibits 13a through 13c of Appendix C.
Operational Evaluations
An operational evaluation must include an examination of distribution system operational practices and how these practices may be modified to reduce TTHM and HAA5 levels. Systems must discuss their evaluations with the primacy agency. Costs for operational evaluations are presented in Exhibit 13 of Appendix C. Systems with operational evaluations incur costs in the year that the operational level is exceeded. This began in the previous ICR period once systems had 1 year worth of compliance monitoring data, and continues forward in this ICR period.
Chemical Phase Rules
PWS activities associated with the Chemical Phase Rules account for a burden of 0.36 million hours per year. The burden estimate includes routine and reduced sampling for IOCs, VOCs, and SOCs under the schedules dictated by the SMF. The assumptions used to calculate the Chemical Phase Rule burden are based on assumptions from the 1993 PWSS Program ICR, which maintained most assumptions and burden estimates from the individual ICRs for the Phase II, IIB, and V rules, with an adjustment to the waiver rate assumptions (in the 2004 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR) to more accurately reflect actual waiver issuance rates. Section 6(f) describes the reasons for changes between the burden reported in the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR and this ICR. Appendix D summarizes the assumptions used to calculate the Chemical Phase Rule burden and provides the detailed burden and cost calculations.
Radionuclides Rule
Annual PWS burden for the Radionuclides Rule is estimated to be 45,631 hours. This is based on burden assumptions carried forward from the 2000 Radionuclides Rule ICR.
Monitoring burden is for the following contaminants:
Gross alpha
Beta and photon emitters
Combined radium-226/-228
Uranium
Section 6(f) describes the reasons for changes between the radionuclides burden reported in the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR and this ICR. Calculations for burden and costs for the Radionuclides Rule are included in Appendix E.
Disinfectant Residual Monitoring and Associated Activities under the SWTR
As stated previously, this ICR includes burden estimates only for the disinfection residual monitoring and associated activities required under the SWTR. The Microbial Rules ICR addresses the burden and costs for all other SWTR requirements. Implementation of the SWTR disinfection residual monitoring and associated activities is estimated to result in an annual PWS burden of 1.1 million hours. Included in the estimate is burden for:
Distribution system residual monitoring.
Calculation of inactivation ratio using CT values for unfiltered systems.
Measurement of pH and temperature, as necessary to calculate CT.
Entry point residual monitoring for filtered systems.
Entry point residual monitoring for unfiltered systems.
Section 6(f) describes the reasons for changes between the burden reported in the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR and this ICR. Appendix F summarizes the assumptions used to calculate the burden for disinfection residual monitoring and associated activities under SWTR and provides the detailed burden and cost calculations.
Arsenic Rule
This ICR addresses the burden and cost for arsenic monitoring, reporting, and recordkeeping for 2016 through 2018. PWSs monitor arsenic in accordance with the standard monitoring framework schedule. In this 3-year ICR period, systems with existing waivers are expected to incur burden for reapplying. Implementation of the Arsenic Rule is estimated to result in an annual PWS burden of 200,280 hours. Appendix G summarizes the assumptions used to calculate burden for the Arsenic Rule and provides the detailed burden and cost estimates.
Lead and Copper Rule
The average annual respondent burden is 1.1 million hours for reporting, recordkeeping, and public education activities of the LCR. Only CWSs and NTNCWSs incur a burden associated with LCR requirements. The burden accounts for the provisions of the short term revisions, which require that systems:
Take additional tap samples for lead if they are on reduced monitoring and the lead action level of 0.015 mg/L is exceeded.
Provide revised public education materials according to revised delivery requirements if the lead action level is exceeded, including a statement on lead in the CCR.
Notify the state before making long term treatment changes.
Notify customers of results of samples taken at customers’ homes.
Retest LSLs previously exempted from replacement if the lead action level is exceeded.
Section 6(f) describes the reasons for changes between the burden reported in the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR and this DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR. Appendix H summarizes the assumptions used to calculate the burden for the Lead and Copper Rule and provides the detailed burden and cost estimates.
6(a)(ii) Burden to Primacy Agencies
The annual burden for primacy agencies is estimated to be approximately 2.0 million hours. Exhibit 8 shows the annual burden hours on a rule-specific basis. Many other state activities, such as compliance assurance and data management, cannot be divided among specific rules and are included in the PWSS Program ICR as general primacy activities. The following briefly describes the bases for the burden estimates:
Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule
The annual state burden for the Stage 1 DBPR is expected to be 0.15 million hours. This reflects data entry and recordkeeping burden. Section 6(f) describes the reasons for changes between the Stage 1 DBPR burden reported in the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR and this ICR. Detailed calculations for burden and cost are shown in Appendix B.
Stage 2 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule
The annual state burden for the Stage 2 DBPR is expected to be 50,822 hours. This reflects reporting and recordkeeping burden for maintaining records and tracking compliance by systems. This ICR also includes burden for reviewing operational evaluations. States are assumed to have already completed their IDSE oversight activities and review of compliance monitoring plans.
Chemical Phase Rules
For states, the annual burden associated with the Chemical Phase Rules is estimated to be approximately 1.4 million hours. This reflects reporting and recordkeeping burden for routine and reduced sampling for IOCs, VOCs, and SOCs under the schedules dictated by the SMF. Estimates for primacy agency burden for the Chemical Phase Rules are based on State Workload Model18 assumptions carried forward from the 1993 PWSS Program ICR. Note that the burden associated with oversight of arsenic monitoring is discussed separately below. Section 6(f) describes the reasons for changes between the Chemical Phase Rules burden reported in the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR and this ICR. Detailed calculations for burden and cost are shown in Appendix D.
Radionuclides Rule
For the Radionuclides Rule, annual state burden is estimated to be 5,476 hours. The annual state burden is based on burden assumptions carried forward from the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR. Burden is calculated for primacy agency staff for recordkeeping, reporting, and compliance tracking and analysis requirements, based on the number of analyses conducted by PWSs. Section 6(f) describes the reasons for changes between the radionuclides burden reported in the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR and this ICR. Calculations for cost and burden for the Radionuclides Rule are included in Appendix E.
Disinfectant Residual Monitoring and Associated Activities under SWTR
As stated previously, this ICR includes burden estimates for only disinfectant residual monitoring and associated activity components of the SWTR. The Microbial Rules ICR addresses the burden and costs for the other SWTR requirements. Implementation of the SWTR disinfectant residual monitoring is expected to result in an annual state burden of 0.16 million hours. Included in this estimate is burden associated with reviewing data for—
Distribution system residual monitoring.
Calculation of inactivation ratio using CT values.
Measurement of pH and temperature, as necessary to meet requirements.
Entry point residual monitoring for filtered systems.
Entry point residual monitoring for unfiltered systems.
Estimates for primacy agency burden for the SWTR are based on assumptions carried forward from the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR. Section 6(f) describes the reasons for changes between the burden reported in the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR and this ICR. Detailed calculations for burden and cost are shown in Appendix F.
Arsenic Rule
For the Arsenic Rule, annual state burden is estimated to be 80,704 hours. The annual state burden is based on assumptions carried forward from the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR and the 2000 Arsenic Rule ICR. Burden is calculated for primacy agency staff for oversight of monitoring activities. Burden is based on recordkeeping, reporting, and compliance tracking and analysis. In this 3-year ICR period, states will additionally incur burden to review waiver applications submitted by systems with existing waivers. Section 6(f) describes the reasons for changes between burden reported in the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR and this ICR. Calculations for cost and burden for the Arsenic Rule are included in Appendix G.
Lead and Copper Rule
EPA estimates that the annual burden incurred by primacy agencies for activities associated with the lead and copper regulation is approximately 0.18 million hours. This estimate includes costs for employing a corrosion control expert and costs to review various letters and results submitted by water systems in accordance with the LCR. It includes the additional burden associated with the LCR short term revisions, which estimate that states will spend extra time reviewing systems’ plans for changing treatment or adding a new source. Further detail about these activities and associated burden and costs is provided in Appendix H.
6(b)(i) Cost to Public Water Systems
Exhibit 7 shows the annual costs for PWSs over the three-year ICR period. Annual costs are estimated at approximately $374 million, which consists of $116 million in labor costs, $5.5 million in capital, and $253 million in O&M (numbers may not add due to rounding).
Labor costs are based on the number of hours times the average hourly wage rate, including overhead. In addition to labor costs, there are O&M costs associated with the each of the rules covered by this ICR. These O&M costs reflect non-labor costs associated with sample shipping and analysis for each of the rules, as well as material costs associated with public education materials and postage. These costs vary by rule according to the frequency and cost of a particular analysis.
In addition to O&M costs, the requirements of one rule (i.e., SWTR) result in capital costs to affected PWSs. Capital costs are incurred to buy and replace monitoring equipment necessary for on-site analysis of disinfectant residuals and water pH. Capital costs are based on vendor estimates for both in-line and portable equipment, as required by regulations. Equipment costs are based on a seven-year replacement cycle. Details on the labor, capital, and O&M costs associated with each rule can be found in Appendices B through H.
6(b)(ii) Cost to Primacy Agencies
Exhibit 8 shows that the annual cost to primacy agencies is estimated at approximately $90 million, which is comprised almost exclusively of labor costs. There are some O&M costs associated with the LCR ($5,678). There are no primacy agency capital costs associated with this ICR.
Exhibit 7
Annual PWS Burden and Cost January 1, 2016 – December 31, 2018
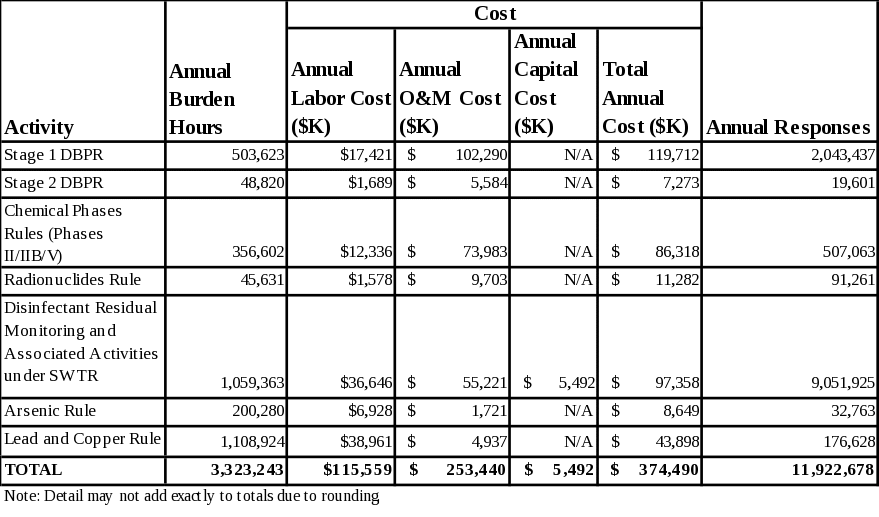
Annual Primacy Agency Burden and Cost January 1, 2016 – December 31, 2018
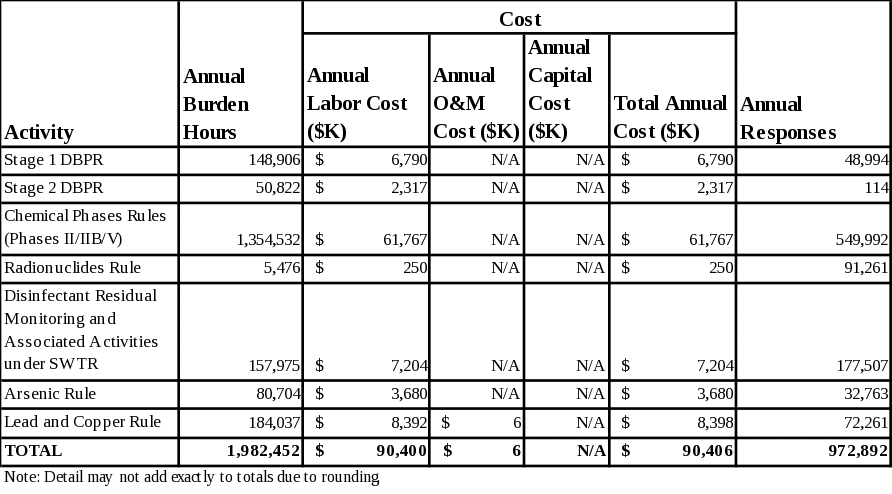
Burden and costs to the federal government are incurred by EPA’s drinking water program to assist states in implementing drinking water regulations. EPA burden and costs for general drinking water program implementation activities are accounted for under the PWSS Program ICR. Burden and costs included in the PWSS Program ICR cover all cross-cutting, non-rule specific, regulatory activities associated with compliance tracking, regulatory enforcement, and rule development activities.19
6(d) Estimating Respondent Universe and Total Burden and Costs
Respondents for this ICR include both PWSs and primacy agencies. This ICR estimates that the number of PWS respondents is 149,765 PWSs.20 However, all PWSs are not necessarily subject to each of the information collection requirements contained in this ICR. The regulations associated with each rule identify the numbers and types of PWSs that are subject to each particular provision. In addition to the PWS respondents, this ICR assumes 57 primacy agencies (50 states plus D.C., U.S. Territories, and the Navajo Nation).21 Therefore, the total number of respondents is 149,822. The total costs and burden for these respondents are summarized in Exhibits 8 and 9.
6(e) Bottom Line Burden Hours and Costs
The bottom line burden hours and costs for this ICR are presented in Exhibit 9. The total annual respondent burden associated with this ICR, which includes burden for PWSs and primacy agencies, is estimated to be approximately 5.3 million hours. The corresponding total annual respondent costs (labor, capital, and O&M) are estimated to be $464.9 million. The portion of the total annual respondent costs attributable to capital and O&M costs is $258.9 million.
Bottom Line Annual Burden and Cost ($K) January 1, 2016 – December 31, 2018
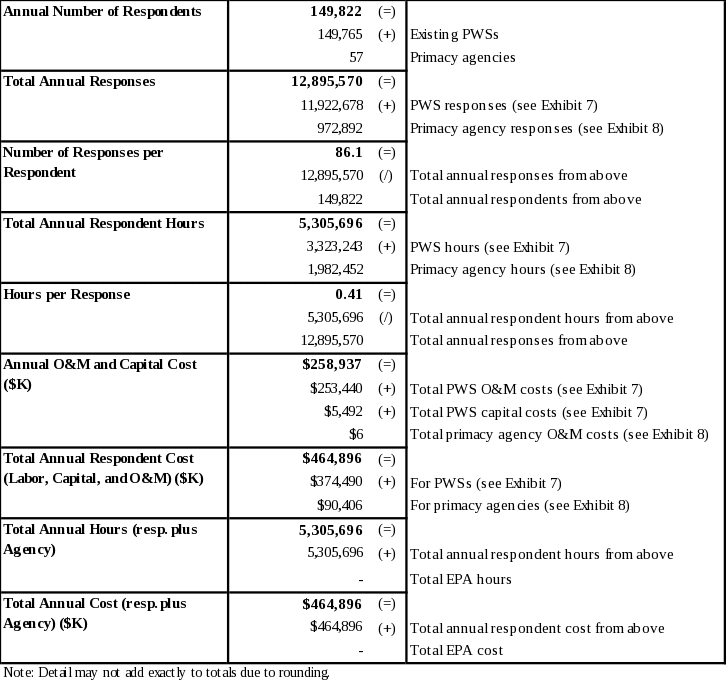
6(f) Reasons for Change in Burden
This section presents the change in burden and the reasons for the change in burden. The discussion is divided into two parts–
Section 6(f)(i) summarizes any restructuring adjustments being made for the addition of new stand-alone ICRs to the DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR. See Exhibit 11.
Section 6(f)(ii) summarizes other adjustments to the annual burden estimates associated with each rule in the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR. See Exhibits 12 through 14.
Exhibit 10 summarizes how each of these changes affects the overall burden inventory for the DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR.
Summary of Changes in Annual Burden (Includes both PWS and Primacy Agency Burden)
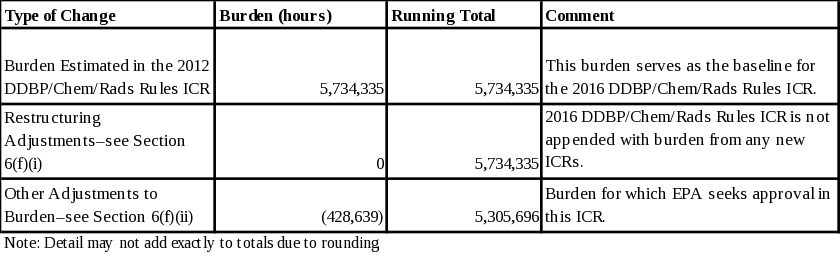
6(f)(i) Restructuring Adjustments
No restructuring adjustments are being made for the addition of new stand-alone ICRs to the DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR, as shown in Exhibit 11. In the next revision to the DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR any burden from relevant standalone ICRs that have expired will be newly incorporated into the DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR.
Restructuring Adjustments to the Annual Burden Inventory for the DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR (Includes both PWS and Primacy Agency Burden)
Action |
Annual Burden Hours |
Brief Explanation |
N/A |
5,734,335 |
Inventory for the 2012 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR carried forward as the baseline for 2016 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR, including PWS and state burden. |
Add |
0 |
2016 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR is not appended with burden from any new ICRs. |
Total |
5,734,335 |
2016 DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR inventory based on current burden inventories. |
6(f)(ii) Other Burden Adjustments
Changes in calculated burden are a result of updating relevant baseline information for each rule with the most current and accurate information available, such as PWS inventories, and incorporating the results of consultation with stakeholders. Where appropriate and available, estimated violation, waiver, and other associated rates have also been updated to reflect current information on rule compliance. Exhibits 12 and 13 summarize reasons for these changes and quantify the changes by rule. Burden adjustments associated with PWS activities resulted in a burden decrease of 0.46 million hours and are detailed in Exhibit 12. Burden adjustments for primacy agencies result in an increase of 0.04 million hours per year, as shown in Exhibit 13.
Adjustments to PWS Burden from Previous ICR Estimates
Activity |
Previous Annual Burden Estimate (Hours) |
2016 Annual |
Annual
Change in Burden |
Reason for Change in Annual Burden |
Stage 1 DBPR |
596,454 |
503,623 |
(92,831) |
The net change in the burden is attributed to the adjustments made in the modeling inputs to account for updated PWS inventory. Burden for ground water systems to calculated disinfectant residuals was reduced to remain consistent with comparable activities under the SWTR. |
Stage 2 DBPR |
30,842 |
48,820 |
17,978 |
The net change in the burden is attributed to the adjustments made in the modeling inputs to account for updated PWS inventory. In addition, all the Stage 2 DBPR requirements, such as operational evaluations and additional monitoring requirements, are applicable in this ICR period. |
Chemical Phases Rules (Phases II/IIB/V) |
365,561 |
356,602 |
(8,958) |
The net change in the burden is attributed to the adjustments made in the modeling inputs to account for updated PWS inventory |
Radionuclides |
14,448 |
45,631 |
31,182 |
The increase in burden is a result of the monitoring flexibility in the regulation which allows public water systems to monitoring on a 3, 6 or 9 year cycle based on initial monitoring results for each contaminant. Due to this flexibility, more public water systems are scheduled to monitor during this ICR period. |
Disinfectant Residual Monitoring and Associated Activities under SWTR |
1,039,257 |
1,059,363 |
20,107 |
The number of surface water systems has increased, resulting in an increase in the total burden associated with disinfectant residual monitoring requirements. |
Arsenic Rule |
71,761 |
200,280 |
128,519 |
The increase in burden is a result of the monitoring flexibility in the regulation which allows public water systems to monitoring on a 9 year cycle based on initial monitoring results. Due to this flexibility, more public water systems are scheduled to monitor during this ICR period. |
Lead and Copper Rule2 |
1,669,205 |
1,108,924 |
(560,281) |
The net change in the burden is attributed to the adjustments made in the modeling inputs to account for updated PWS inventory, as well as updated data on the number of action level exceedances. |
TOTAL2 |
3,787,528 |
3,323,243 |
(464,285) |
Adjusted PWS Burden |
Notes:
|
||||
Exhibit 13
Adjustments to Primacy Agency Burden from Previous ICR Estimates
Activity |
Previous Annual Burden
Estimate |
2016 Annual |
Annual
Change in Burden |
Reason for Change in Annual Burden |
Stage 1 DBPR |
148,335 |
148,906 |
571 |
The net change in the burden is attributed to the adjustments made in the modeling inputs to account for updated PWS inventory. States continue to incur annual data entry reporting and recordkeeping burden for combined DBP, TOC/alkalinity, and residual reporting. |
Stage 2 DBPR |
50,822 |
50,822 |
N/A |
States will continue recordkeeping and compliance activities for additional routine monitoring and operational evaluations. |
Chemical Phases Rules (Phases II/IIB/V) |
1,354,532 |
1,354,532 |
N/A |
The state burden for this rule is based on the State Workload Model, which has not changed. |
Radionuclides |
1,734 |
5,476 |
3,742 |
The increase in burden is a result of the monitoring flexibility in the regulation which allows public water systems to monitoring on a 3, 6 or 9 year cycle based on initial monitoring results for each contaminant. Due to this flexibility, more public water systems are scheduled to monitor during this ICR period and therefore increase the number of monitoring results submitted to the primacy agency. |
Disinfectant Residual Monitoring and Associated Activities under SWTR2 |
150,462 |
157,975 |
7,513 |
SWTR burden is calculated as a single value, and distributed between this ICR and the Microbials ICR. This burden is apportioned based on the relative proportion of burden hours for PWS activities covered under these ICRs. Additionally, the change in burden is attributable to updates to and QA of the model. |
Arsenic Rule |
18,765 |
80,704 |
61,939 |
The increase in burden is attributable to an increase in the number of samples taken in comparison to the previous ICR period; samples taken as part of a 9-year monitoring cycle are expected to occur during this ICR period. Additionally, systems are expected to submit waiver applications, which are also on a 9-year cycle. Note the increased system sampling and waiver applications result in an increase in state reporting and recordkeeping burden. The increase in burden is a result of the monitoring flexibility in the regulation which allows public water systems to monitoring on a 9 year cycle based on initial monitoring results. Due to this flexibility, more public water systems are scheduled to monitor during this ICR period, and therefore submit more monitoring results to the primacy agency. |
Lead and Copper Rule3 |
222,157 |
184,037 |
(38,120) |
The net change in the burden is attributed to the adjustments made in the modeling inputs to account for updated PWS inventory, as well as updated data on the number of action level exceedances. |
TOTAL2, 3 |
1,946,807 |
1,982,452 |
35,645 |
Adjusted Primacy Agency Burden |
Notes:
|
||||
Exhibit 14 shows the effect of these adjustments on the bottom line burden. Subtracting 0.46 million hours to account for the adjustment to the PWS burden and adding 0.04 million hours to account for the upward adjustment to the primacy burden yields 5.3 million hours.
Adjustments to Annual Burden Carried Forward from Previous ICR Estimates (Includes both PWS and Primacy Agency Burden)

6(g) Burden Statement
The public reporting burden for collections included in this ICR is detailed in Exhibit 14 above. The annual respondent burden is estimated to average approximately 5.3 million hours, of which 3.3 million hours are attributable to PWSs and 2.0 million hours to primacy agencies. These estimates include time for gathering information as well as developing and maintaining records.
Burden means the total time, effort, or financial resources expended by people to generate, maintain, retain, disclose, or provide information to or for a federal agency. This includes the time needed to review instructions; develop, acquire, install, and utilize technology, and systems for the purposes of collecting, validating, and verifying information, processing and maintaining information, and disclosing and providing information; adjust the existing ways to comply with any previously applicable instructions and requirements; train personnel to be able to respond to a collection of information; search data sources; complete and review the collection of information; and transmit or otherwise disclose the information. An agency may not conduct or sponsor, and a person is not required to respond to, a request for information collection unless it displays a currently valid OMB control number. The OMB control numbers for EPA’s regulations are listed in 40 CFR Part 9 and 48 CFR Chapter 15.
To comment on the Agency's need for this information, the accuracy of the provided burden estimates, and any suggested methods for minimizing respondent burden, including the use of automated collection techniques, EPA has established a public docket for this ICR under Docket ID Number EPA-HQ-OW-2011-0439, which is available for online viewing at www.regulations.gov, or in person viewing at the Water Docket in the EPA Docket Center (EPA/DC), WJC West, Room 3334, 1301 Constitution Ave., NW, Washington, DC. The EPA Docket Center Public Reading Room is open from 8:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m., Monday through Friday, excluding legal holidays. The telephone number for the Reading Room is (202) 566-1744, and the telephone number for the Water Docket is (202) 566-2426. An electronic version of the public docket is available at www.regulations.gov. This site can be used to submit or view public comments, to access the index listing of the contents of the public docket, and to access those documents in the public docket that are available electronically. When in the system, select “search,” then key in the Docket ID Number identified above. Comments can also be sent to the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs, Office of Management and Budget, 725 17th Street, NW, Washington, DC 20503, Attention: Desk Officer for EPA. Please include the EPA Docket ID Number (EPA-HQ-OW-2011-0439) and the OMB Control Number 2040-0204 in any correspondence.
1 Includes only the SWTR components relating to disinfectant residual monitoring and associated activities. All remaining SWTR requirements are included in the Microbial Rules ICR.
2 Includes only SWTR components relating to disinfectant residual monitoring and associated activities. All remaining SWTR requirements are included in the Microbial Rules ICR.
3 Disinfectant residual monitoring and associated activities are included in the DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR.
4 The burden associated with implementing the public notification requirements is currently addressed in the PWSS Program ICR (OMB No. 2040-0090).
5 Some of the general activities conducted by states are included in the PWSS Program ICR (OMB 2040-0090).
6 Subpart H systems include all PWSs using surface water or ground water under the direct influence of surface water as a source (40 CFR 141.2).
7 The Phase I rule contaminants were included for completeness. However, the Phase II rule superseded the Phase I rule. Some of the Phase I unregulated contaminants became regulated under Phase II and additional contaminants were added to the list of unregulated contaminants.
8 Includes only the rule components relating to disinfectant residual monitoring. The remaining SWTR requirements are included in the Microbial Rules ICR.
9 Systems that serve 3,300 or fewer people may take grab samples in lieu of providing continuous monitoring.
10 CT is the product of residual disinfectant concentration (C) in mg/l determined before or at the first customer, and the corresponding disinfectant contact time (T) in minutes. If a PWS applies disinfectants at more than one point prior to the first customer, it must determine the CT of each disinfectant sequence before or at the first customer to determine the total percent inactivation or total inactivation ratio.
11 For existing systems, some of these requirements may not fall within the collection period for this ICR. See Appendix H for detail related to assumptions and burden calculations for these activities.
12 The public can access the violation data in SDWIS online at http://water.epa.gov/scitech/datait/databases/drink/sdwisfed/howtoaccessdata.cfm.
13 These definitions were taken from section 601 of the Regulatory Flexibility Act (RFA).
14 Collection schedule is based on the commencement of monitoring requirements. Startup activities are typically completed prior to these dates.
15 The remaining SWTR requirements are included in the Microbial Rules ICR.
16 Includes LCR Short-term revisions.
17 Includes burden for ground water systems only. Disinfectant residual monitoring and associated activities for surface water systems are addressed by the SWTR.
18 New burden estimates from the revised State Workload Model will be incorporated into the subsequent DDBP/Chem/Rads Rules ICR. See section 5(b) of the PWSS ICR for additional information.
19 The EPA burden for activities where EPA acts as a primacy agent counts as primacy agency burden and is included in totals for primacy agency burden.
20 Source: SDWIS/FED Data from October 2014.
21 For several of these entities, primacy activities are actually implemented by EPA Regional offices. However, as a simplifying assumption, they are included with the states for respondent calculations under this ICR.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | Draft Information Collection Request for the Disinfectants/Disinfection Byproducts, Chemical, and Radionuclides Rules |
| Author | Katie Palanjian |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-24 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy