Form 1 TLP Grantee Survey Positive Youth Development
Evaluation of the Transition Living Program
Final Attachment J2 TLP Grantee Youth Development Survey
Youth Development Survey Interview Guide
OMB: 0970-0383
Attachment J2 – Survey of Youth Development Priorities
Survey of Youth Development Priorities
Thank you for taking the time to complete this survey. This survey is intended for research purposes ONLY. The information you share will help us to better understand how TLPs work with youth. The information reported is strictly confidential and will in no way affect HHS’s view of your program’s performance. The responses to the survey will be kept anonymous: neither the respondent nor the agency will be identified by name when we report findings from the study. |
The design of Transitional Living Programs (TLP) varies considerably from program to program, particularly with regard to specific program priorities and the degree of emphasis that is placed upon them. The purpose of this survey is to understand your program’s priorities for developing youth and how you work to achieve them. This survey focuses on 15 program priorities that may be more or less important to particular TLP programs. Not all programs pursue each priority, and programs vary significantly in the amount of emphasis they place on any given priority and the strategies used to pursue it. For example, programs may use specific program design features (such as program rules, youth development plans, and the provision of privileges) or they may provide particular types of services to promote the program’s key priorities.
For each priority, the survey asks two questions: (1) how important is the priority to your program and (2) what strategies do you use to pursue it. Please be as specific as possible in describing the features of your TLP program or the specific services you provide that are designed to achieve the program priorities. There are no “right” or “wrong” answers to these questions. We simply want to understand your program’s priorities and how you are pursuing them.
Priority 1: Helping Youth Bond with Others
Definition: Bonding is the emotional attachment and commitment a youth makes to relationships with other people. Strategies that encourage bonding can include program rules, other features of your program, or the specific services the program provides that might help youth build healthy relationships with staff, peers, family members, and other members of the community.
Q 1: On a scale of 1 to 10, how important is helping youth bond with others, in the design of your program and the types of services it chooses to offer?
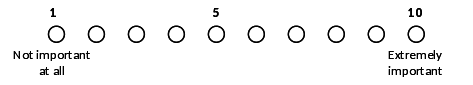
Q 2: [If Q1 = 5 or greater] What specific strategies, including program design features or services, does the program use to help youth build healthy relationships with other people?

Priority 2: Helping Youth Develop a Sense of Empowerment
Definition: Empowerment is the belief a youth has (whether or not accurate) that he or she can achieve desired goals through his or her own actions. Strategies that help create a sense of empowerment can include program rules, other features of your program, or the specific services the program provides that might help youth to feel that they are capable of achieving goals that they set for themselves.
Q 1: On a scale of 1 to 10, how important is creating a sense of empowerment in the design of your program and the types of services it chooses to offer?
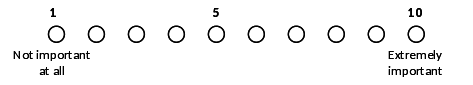
Q 2: [If Q1 = 5 or greater] What specific strategies, including program design features or services, does the program use to help youth create a sense of empowerment?

Priority 3: Helping Youth Develop Coping Skills
Definition: Coping skills help youth adapt to stressful events and change. Strategies that encourage coping skills can include program rules, other features of your program, or the specific services the program provides that might help youth to develop successful coping strategies (for example, behaviors or ways of thinking about things) that help them to succeed when facing difficult situations.
Q 1: On a scale of 1 to 10, how important is developing coping skills in the design of your program and the types of services it chooses to offer?
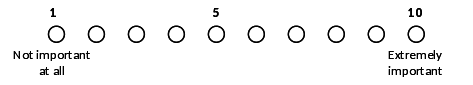
Q 2: [If Q1 = 5 or greater] What specific strategies, including program design features or services, does the program use to develop coping skills?

Priority 4: Helping Youth Have a Sense of Self-Determination
Definition: Self-determination is the ability of a youth to think for himself or herself and to act on that ability. Strategies that help create a sense of self-determination can include program rules, other features of your program, or the specific services you provide that might help youth to think and act for themselves and to believe that they can chart their own course.
Q 1: On a scale of 1 to 10, how important is creating a sense of self-determination in the design of your program and the types of services it chooses to offer?
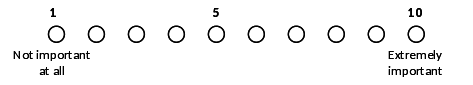
Q 2: [If Q1 = 5 or greater] What specific strategies, including program design features or services, does the program use to help youth develop a sense of self-determination?

Priority 5: Helping Youth Develop Critical Thinking Skills
Definition: Critical thinking skills refer to a youth’s ability to use logic, analytic thinking, and reasoning to solve problems, make decisions, and attain achievements, including academic acheivements. Strategies that help develop critical thinking skills can include program rules, other features of your program, or the specific services the program provides to help youth develop skills they need to be academically successful, or to help them to think logically, to problem-solve, and plan and set goals.
Q 1: On a scale of 1 to 10, how important is developing critical thinking skills in the design of your program and the types of services it chooses to offer?
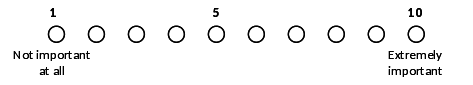
Q 2: [If Q1 = 5 or greater] What specific strategies, including program design features or services, does the program use to develop youths’ critical thinking skills?

Priority 6: Helping Youth Develop a Clear and Positive Identity
Definition: The formation of a clear and positive identity refers to a youth’s sense of self and his ability to acknowledge his own personal attributes, skills, and abilities, and his relationships to institutions and groups of people. Strategies to help create a clear and positive identity can include features of the way you run your program or specific services you provide that help youth to identify with their racial/ethnic groups or other social groups that support the development of a healthy and positive sense of self.
Q 1: On a scale of 1 to 10, how important is creating a clear and positive identity in the design of your program and the types of services it chooses to offer?
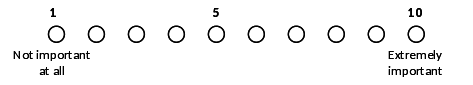
Q 2: [If Q1 = 5 or greater] What specific strategies, including program design features or services, does the program use to help youth form a clear and positive identity?

Priority 7: Helping Youth Develop Positive Social Behaviors
Definition: Positive social behaviors refer to the adoption of healthy beliefs and clear standards for behavior. Strategies that help create positive social behavior s can include program rules, other features of your program, or specific services you provide that help youth to develop clear standards for their behavior that reduce health risks (e.g., substance use and unprotected sexual activity) and encourage behaviors that will help them succeed in society (e.g., a strong work ethic and respect for others).
Q 1: On a scale of 1 to 10, how important is helping youth choose positive social behaviors in the design of your program and the types of services it chooses to offer?
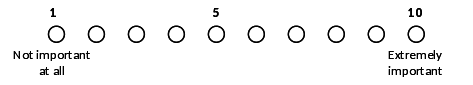
Q 2: [If Q1 = 5 or greater] What specific strategies, including program design features or services, does the program use to help youth develop positive social behaviors?

Priority 8: Helping Youth Develop Healthy Emotional Skills
Definition: Emotional skills refer to a youth’s ability to identify and respond to feelings and emotional reactions in him/herself and others. Strategies to help youth develop health emotional skills can include program rules, other features of your program, or specific services you provide that build and reinforce skills for identifying and managing one’s own feelings, understanding the feelings of others, controlling impulses, and tolerating frustration.
Q 1: On a scale of 1 to 10, how important is developing healthy emotional skills in the design of your program and the types of services it chooses to offer?
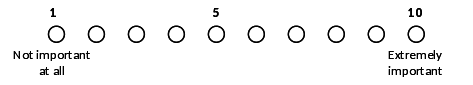
Q 2: [If Q1 = 5 or greater] What specific strategies, including program design features or services, does the program use to help youth develop healthy emotional skills?

Priority 9: Helping Youth Believe in the Future
Definition: Believing in the future refers to the ability of a young person to recognize his future potential, goals, options, choices, and long-range hopes. Strategies to help create a belief in the future can include features of the way you run your program or specific services you provide that help youth to develop a sense of hope and optimism regarding their future, a sense that they have options in life, and that, if they persevere, they can be successful.
Q 1: On a scale of 1 to 10, how important is creating a belief in the future in the design of your program and the types of services it chooses to offer?
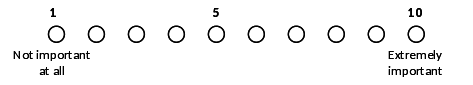
Q 2: [If Q1 = 5 or greater] What specific strategies, including program design features or services, does the program use to encourage youth to believe in the future?

Priority 10: Helping Youth Develop Social Skills
Definition: Social skills refer to the ability of a young person to interact and communicate well with others. Strategies to help develop social skills can include program rules, other features of your program, or specific services you provide that help youth to develop communication and other interpersonal skills such as how to be confident, how to resist pressure, and how to resolve conflicts.
Q 1: On a scale of 1 to 10, how important is developing social skills in the design of your program and the types of services it chooses to offer?
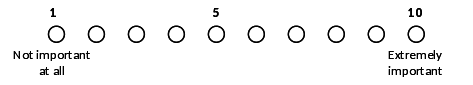
Q 2: [If Q1 = 5 or greater] What specific strategies, including program design features or services, does the program use to help youth develop social skills?

Priority 11: Providing Opportunities for Youth to Have Positive Social Involvement
Definition: Positive social involvement means that youth have access to events and activities across different social settings in which they can participate in positive ways. Strategies for providing opportunities for positive social involvement can include features of your program or specific services you provide that provide youth with opportunities that allow them to participate actively at school, with peers, in neighborhood or community groups, or with family.
Q 1: On a scale of 1 to 10, how important is offering youth opportunities for positive social involvement in the design of your program and the types of services it chooses to offer?
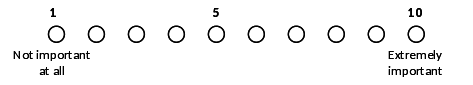
Q 2: [If Q1 = 5 or greater] What specific strategies, including program design features or services, does the program use to provide youth with opportunities for positive social involvement?

Priority 12: Helping Youth Develop Behavioral Skills
Definition: Behavioral skills refer to a youth’s ability to effectively act through nonverbal (e.g., facial expressions, style of dress, and gestures), as well as verbal methods. Strategies to help develop a young person’s behavioral skills can include features of your program or specific services you provide that build and reinforce behavioral skills.
Q 1: On a scale of 1 to 10, how important is developing behavioral skills in the design of your program and the types of services it chooses to offer?
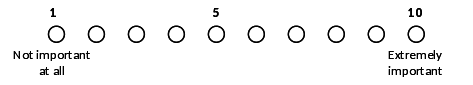
Q 2: [If Q1 = 5 or greater] What specific strategies, including program design features and/or services, does the program use to help youth develop behavioral skills?

Priority 13: Helping Youth Develop a Sense of Spirituality
Definition: A sense of spirituality can refer to both religious and non-religious forms of spiritual practice. Strategies that help create a youth’s sense of spirituality can include features of your program or specific services you provide that support youth in exploring a spiritual belief system or their spiritual identity, or encourage internal reflection or meditation, or a belief in a higher power.
Q 1: On a scale of 1 to 10, how important is creating a sense of spirituality in the design of your program and the types of services it chooses to offer?
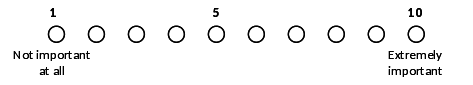
Q 2: [If Q1 = 5 or greater] What specific strategies, including program design features or services, does the program use to create a sense of spirituality in youth?

Priority 14: Recognizing the Positive Behavior of Youth
Definition: Recognizing positive behavior refers to the positive responses of those around the young person to his/her desirable behaviors. Strategies for recognizing positive behavior can include the approaches used by the program to acknowledge, reinforce, or reward positive behavior demonstrated by youth.
Q 1: On a scale of 1 to 10, how important is recognizing positive behavior in the design of your program and the types of services it chooses to offer?
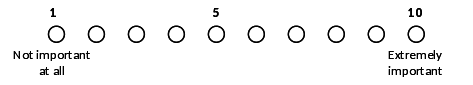
Q 2: [If Q1 = 5 or greater] What specific strategies, including program design features or services, does the program use to recognize positive behavior?

Priority 15: Helping Youth Develop Moral Skills
Definition: Moral skills refer to a youth’s ability to asses and respond to ethical, emotional and social justice issues. Strategies to help develop moral skills can include program rules or other features of your program that help youth develop a sense of right and wrong, empathy for others, respect for societal rules and standards, and a sense of social justice.
Q 1: On a scale of 1 to 10, how important is developing moral skills in the design of your program and the types of services it chooses to offer?
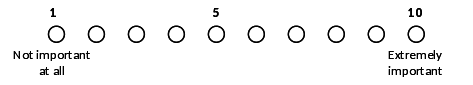
Q 2: [If Q1 = 5 or greater] What specific strategies, including program design features or services, does the program use to help youth develop moral skills?

Q31: Looking across all 15 priorities (see list below), please rank your program’s top 3 priorities.
Objective #1:
Objective #2:
Objective #3:
Priority 1: Helping Youth Bond with Others
Priority 2: Helping Youth Develop a Sense of Empowerment
Priority 3: Helping Youth Develop Coping Skills
Priority 4: Helping Youth Have a Sense of Self-Determination
Priority 5: Helping Youth Develop Critical Thinking Skills
Priority 6: Helping Youth Develop a Clear and Positive Identity
Priority 7: Helping Youth Develop Positive Social Behaviors
Priority 8: Helping Youth Develop Healthy Emotional Skills
Priority 9: Helping Youth Believe in the Future
Priority 10: Helping Youth Develop Social Skills
Priority 11: Providing Opportunities for Youth to Have Positive Social Involvement
Priority 12: Helping Youth Develop Behavioral Skills
Priority 13: Helping Youth Develop a Sense of Spirituality
Priority 14: Recognizing the Positive Behavior of Youth
Priority 15: Helping Youth Develop Moral Skills
Thank you for taking the time to complete this survey.
| File Type | application/msword |
| File Title | TLP Positive Youth Development Survey |
| Author | DARIA |
| Last Modified By | CortesA |
| File Modified | 2010-05-28 |
| File Created | 2010-03-01 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy