Electronic
Code of Federal Regulations
e-CFR
data is current as of July 19, 2017
|
§1910.66 Powered
platforms for building maintenance.
(a)
Scope.
This section covers powered platform installations permanently
dedicated to interior or exterior building maintenance of a
specific structure or group of structures. This section does not
apply to suspended scaffolds (swinging scaffolds) used to service
buildings on a temporary basis and covered under subpart D of this
part, nor to suspended scaffolds used for construction work and
covered under subpart L of 29 CFR part 1926. Building maintenance
includes, but is not limited to, such tasks as window cleaning,
caulking, metal polishing and reglazing.
(b)
Application—(1)
New
installations.
This section applies to all permanent installations completed
after July 23, 1990. Major modifications to existing installations
completed after that date are also considered new installations
under this section.
(2)
Existing
installations.
(i) Permanent installations in existence and/or completed before
July 23, 1990 shall comply with paragraphs (g), (h), (i), (j) and
appendix C to subpart I of this part.
(ii)
In addition, permanent installations completed after August 27,
1971, and in existence and/or completed before July 23, 1990,
shall comply with appendix D of this section.
(c)
Assurance.
(1) Building owners of new installations shall inform the employer
before each use in writing that the installation meets the
requirements of paragraphs (e)(1) and (f)(1) of this section and
the additional design criteria contained in other provisions of
paragraphs (e) and (f) of this section relating to: required load
sustaining capabilities of platforms, building components,
hoisting and supporting equipment; stability factors for
carriages, platforms and supporting equipment; maximum horizontal
force for movement of carriages and davits; design of carriages,
hoisting machines, wire rope and stabilization systems; and design
criteria for electrical wiring and equipment.
(2)
Building owners shall base the information required in paragraph
(c)(1) of this section on the results of a field test of the
installation before being placed into service and following any
major alteration to an existing installation, as required in
paragraph (g)(1) of this section. The assurance shall also be
based on all other relevant available information, including, but
not limited to, test data, equipment specifications and
verification by a registered professional engineer.
(3)
Building owners of all installations, new and existing, shall
inform the employer in writing that the installation has been
inspected, tested, and maintained in compliance with the
requirements of paragraphs (g) and (h) of this section and that
all anchorages meet the requirements of §1910.140(c)(13).
(4)
The employer shall not permit employees to use the installation
prior to receiving assurance from the building owner that the
installation meets the requirements contained in paragraphs (c)(1)
and (c)(3) of this section.
(d)
Definitions.
Anemometer
means an instrument for measuring wind velocity.
Angulated
roping
means a suspension method where the upper point of suspension is
inboard from the attachments on the suspended unit, thus causing
the suspended unit to bear against the face of the building.
Building
face roller
means a rotating cylindrical member designed to ride on the face
of the building wall to prevent the platform from abrading the
face of the building and to assist in stabilizing the platform.
Building
maintenance
means operations such as window cleaning, caulking, metal
polishing, reglazing, and general maintenance on building
surfaces.
Cable
means a conductor, or group of conductors, enclosed in a
weatherproof sheath, that may be used to supply electrical power
and/or control current for equipment or to provide voice
communication circuits.
Carriage
means a wheeled vehicle used for the horizontal movement and
support of other equipment.
Certification
means a written, signed and dated statement confirming the
performance of a requirement of this section.
Combination
cable
means a cable having both steel structural members capable of
supporting the platform, and copper or other electrical conductors
insulated from each other and the structural members by
nonconductive barriers.
Competent
person
means a person who, because of training and experience, is capable
of identifying hazardous or dangerous conditions in powered
platform installations and of training employees to identify such
conditions.
Continuous
pressure
means the need for constant manual actuation for a control to
function.
Control
means a mechanism used to regulate or guide the operation of the
equipment.
Davit
means a device, used singly or in pairs, for suspending a powered
platform from work, storage and rigging locations on the building
being serviced. Unlike outriggers, a davit reacts its operating
load into a single roof socket or carriage attachment.
Equivalent
means alternative designs, materials or methods which the employer
can demonstrate will provide an equal or greater degree of safety
for employees than the methods, materials or designs specified in
the standard.
Ground
rigging
means a method of suspending a working platform starting from a
safe surface to a point of suspension above the safe surface.
Ground
rigged davit
means a davit which cannot be used to raise a suspended working
platform above the building face being serviced.
Guide
button
means a building face anchor designed to engage a guide track
mounted on a platform.
Guide
roller
means a rotating cylindrical member, operating separately or as
part of a guide assembly, designed to provide continuous
engagement between the platform and the building guides or
guideways.
Guide
shoe
means a device attached to the platform designed to provide a
sliding contact between the platform and the building guides.
Hoisting
machine
means a device intended to raise and lower a suspended or
supported unit.
Hoist
rated load
means the hoist manufacturer's maximum allowable operating load.
Installation
means all the equipment and all affected parts of a building which
are associated with the performance of building maintenance using
powered platforms.
Interlock
means a device designed to ensure that operations or motions occur
in proper sequence.
Intermittent
stabilization
means a method of platform stabilization in which the angulated
suspension wire rope(s) are secured to regularly spaced building
anchors.
Lanyard
means a flexible line of rope, wire rope or strap which is used to
secure the body belt or body harness to a deceleration device,
lifeline or anchorage.
Lifeline
means a component consisting of a flexible line for connection to
an anchorage at one end to hang vertically (vertical lifeline), or
for connection to anchorages at both ends to stretch horizontally
(horizontal lifeline), and which serves as a means for connecting
other components of a personal fall arrest system to the
anchorage.
Live
load
means the total static weight of workers, tools, parts, and
supplies that the equipment is designed to support.
Obstruction
detector
means a control that will stop the suspended or supported unit in
the direction of travel if an obstruction is encountered, and will
allow the unit to move only in a direction away from the
obstruction.
Operating
control
means a mechanism regulating or guiding the operation of equipment
that ensures a specific operating mode.
Operating
device
means a device actuated manually to activate a control.
Outrigger
means a device, used singly or in pairs, for suspending a working
platform from work, storage, and rigging locations on the building
being serviced. Unlike davits, an outrigger reacts its operating
moment load as at least two opposing vertical components acting
into two or more distinct roof points and/or attachments.
Platform
rated load
means the combined weight of workers, tools, equipment and other
material which is permitted to be carried by the working platform
at the installation, as stated on the load rating plate.
Poured
socket
means the method of providing wire rope terminations in which the
ends of the rope are held in a tapered socket by means of poured
spelter or resins.
Primary
brake
means a brake designed to be applied automatically whenever power
to the prime mover is interrupted or discontinued.
Prime
mover
means the source of mechanical power for a machine.
Rated
load
means the manufacturer's recommended maximum load.
Rated
strength
means the strength of wire rope, as designated by its manufacturer
or vendor, based on standard testing procedures or acceptable
engineering design practices.
Rated
working load
means the combined static weight of men, materials, and suspended
or supported equipment.
Registered
professional engineer
means a person who has been duly and currently registered and
licensed by an authority within the United States or its
territories to practice the profession of engineering.
Roof
powered platform
means a working platform where the hoist(s) used to raise or lower
the platform is located on the roof.
Roof
rigged davit
means a davit used to raise the suspended working platform above
the building face being serviced. This type of davit can also be
used to raise a suspended working platform which has been
ground-rigged.
Rope
means the equipment used to suspend a component of an equipment
installation, i.e., wire rope.
Safe
surface
means a horizontal surface intended to be occupied by personnel,
which is so protected by a fall protection system that it can be
reasonably assured that said occupants will be protected against
falls.
Secondary
brake
means a brake designed to arrest the descent of the suspended or
supported equipment in the event of an overspeed condition.
Self
powered platform
means a working platform where the hoist(s) used to raise or lower
the platform is mounted on the platform.
Speed
reducer
means a positive type speed reducing machine.
Stability
factor
means the ratio of the stabilizing moment to the overturning
moment.
Stabilizer
tie
means a flexible line connecting the building anchor and the
suspension wire rope supporting the platform.
Supported
equipment
means building maintenance equipment that is held or moved to its
working position by means of attachment directly to the building
or extensions of the building being maintained.
Suspended
equipment
means building maintenance equipment that is suspended and raised
or lowered to its working position by means of ropes or
combination cables attached to some anchorage above the equipment.
Suspended
scaffold (swinging scaffold)
means a scaffold supported on wire or other ropes, used for work
on, or for providing access to, vertical sides of structures on a
temporary basis. Such scaffold is not designed for use on a
specific structure or group of structures.
Tail
line
means the nonsupporting end of the wire rope used to suspend the
platform.
Tie-in
guides
means the portion of a building that provides continuous positive
engagement between the building and a suspended or supported unit
during its vertical travel on the face of the building.
Traction
hoist
means a type of hoisting machine that does not accumulate the
suspension wire rope on the hoisting drum or sheave, and is
designed to raise and lower a suspended load by the application of
friction forces between the suspension wire rope and the drum or
sheave.
Transportable
outriggers
means outriggers designed to be moved from one work location to
another.
Trolley
carriage
means a carriage suspended from an overhead track structure.
Verified
means accepted by design, evaluation, or inspection by a
registered professional engineer.
Weatherproof
means so constructed that exposure to adverse weather conditions
will not affect or interfere with the proper use or functions of
the equipment or component.
Winding
drum hoist
means a type of hoisting machine that accumulates the suspension
wire rope on the hoisting drum.
Working
platform
means suspended or supported equipment intended to provide access
to the face of a building and manned by persons engaged in
building maintenance.
Wrap
means one complete turn of the suspension wire rope around the
surface of a hoist drum.
(e)
Powered
platform installations—Affected parts of buildings—(1)
General
requirements.
The following requirements apply to affected parts of buildings
which utilize working platforms for building maintenance.
(i)
Structural supports, tie-downs, tie-in guides, anchoring devices
and any affected parts of the building included in the
installation shall be designed by or under the direction of a
registered professional engineer experienced in such design;
(ii)
Exterior installations shall be capable of withstanding prevailing
climatic conditions;
(iii)
The building installation shall provide safe access to, and egress
from, the equipment and sufficient space to conduct necessary
maintenance of the equipment;
(iv)
The affected parts of the building shall have the capability of
sustaining all the loads imposed by the equipment; and,
(v)
The affected parts of the building shall be designed so as to
allow the equipment to be used without exposing employees to a
hazardous condition.
(2)
Tie-in
guides.
(i) The exterior of each building shall be provided with tie-in
guides unless the conditions in paragraph (e)(2)(ii) or
(e)(2)(iii) of this section are met.
Note:
See figure 1 in appendix B of this section for a description of a
typical continuous stabilization system utilizing tie-in guides.
(ii)
If angulated roping is employed, tie-in guides required in
paragraph (e)(2)(i) of this section may be eliminated for not more
than 75 feet (22.9 m) of the uppermost elevation of the building,
if infeasible due to exterior building design, provided an
angulation force of at least 10 pounds (44.4 n) is maintained
under all conditions of loading.
(iii)
Tie-in guides required in paragraph (e)(2)(i) of this section may
be eliminated if one of the guide systems in paragraph
(e)(2)(iii)(A), (e)(2)(iii)(B) or (e)(2)(iii)(C) of this section
is provided, or an equivalent.
(A)
Intermittent stabilization system. The system shall keep the
equipment in continuous contact with the building facade, and
shall prevent sudden horizontal movement of the platform. The
system may be used together with continuous positive building
guide systems using tie-in guides on the same building, provided
the requirements for each system are met.
(1)
The maximum vertical interval between building anchors shall be
three floors or 50 feet (15.3 m), whichever is less.
(2)
Building anchors shall be located vertically so that attachment of
the stabilizer ties will not cause the platform suspension ropes
to angulate the platform horizontally across the face of the
building. The anchors shall be positioned horizontally on the
building face so as to be symmetrical about the platform
suspension ropes.
(3)
Building anchors shall be easily visible to employees and shall
allow a stabilizer tie attachment for each of the platform
suspension ropes at each vertical interval. If more than two
suspension ropes are used on a platform, only the two
building-side suspension ropes at the platform ends shall require
a stabilizer attachment.
(4)
Building anchors which extend beyond the face of the building
shall be free of sharp edges or points. Where cables, suspension
wire ropes and lifelines may be in contact with the building face,
external building anchors shall not interfere with their handling
or operation.
(5)
The intermittent stabilization system building anchors and
components shall be capable of sustaining without failure at least
four times the maximum anticipated load applied or transmitted to
the components and anchors. The minimum design wind load for each
anchor shall be 300 (1334 n) pounds, if two anchors share the wind
load.
(6)
The building anchors and stabilizer ties shall be capable of
sustaining anticipated horizontal and vertical loads from winds
specified for roof storage design which may act on the platform
and wire ropes if the platform is stranded on a building face. If
the building anchors have different spacing than the suspension
wire rope or if the building requires different suspension
spacings on one platform, one building anchor and stabilizer tie
shall be capable of sustaining the wind loads.
Note:
See figure 2 in appendix B of this section for a description of a
typical intermittent stabilization system.
(B)
Button guide stabilization system.
(1)
Guide buttons shall be coordinated with platform mounted equipment
of paragraph (f)(5)(vi) of this section.
(2)
Guide buttons shall be located horizontally on the building face
so as to allow engagement of each of the guide tracks mounted on
the platform.
(3)
Guide buttons shall be located in vertical rows on the building
face for proper engagement of the guide tracks mounted on the
platform.
(4)
Two guide buttons shall engage each guide track at all times
except for the initial engagement.
(5)
Guide buttons which extend beyond the face of the building shall
be free of sharp edges or points. Where cables, ropes and
lifelines may be in contact with the building face, guide buttons
shall not interfere with their handling or operation.
(6)
Guide buttons, connections and seals shall be capable of
sustaining without damage at least the weight of the platform, or
provision shall be made in the guide tracks or guide track
connectors to prevent the platform and its attachments from
transmitting the weight of the platform to the guide buttons,
connections and seals. In either case, the minimum design load
shall be 300 pounds (1334 n) per building anchor.
Note:
See paragraph (f)(5)(vi) of this section for relevant equipment
provisions.
Note:
See figure 3 in appendix B of this section for a description of a
typical button guide stabilization system.
(C)
System utilizing angulated roping and building face rollers. The
system shall keep the equipment in continuous contact with the
building facade, and shall prevent sudden horizontal movement of
the platform. This system is acceptable only where the suspended
portion of the equipment in use does not exceed 130 feet (39.6 m)
above a safe surface or ground level, and where the platform
maintains no less than 10 pounds (44.4 n) angulation force on the
building facade.
(iv)
Tie-in guides for building interiors (atriums) may be eliminated
when a registered professional engineer determines that an
alternative stabilization system, including systems in paragraphs
(e)(2)(iii) (A), (B) and (C), or a platform tie-off at each work
station will provide equivalent safety.
(3)
Roof
guarding.
(i) Employees working on roofs while performing building
maintenance shall be protected by a perimeter guarding system
which meets the requirements of paragraph (c)(1) of §1910.23
of this part.
(ii)
The perimeter guard shall not be more than six inches (152 mm)
inboard of the inside face of a barrier, i.e. the parapet wall, or
roof edge curb of the building being serviced; however, the
perimeter guard location shall not exceed an 18 inch (457 mm)
setback from the exterior building face.
(4)
Equipment
stops.
Operational areas for trackless type equipment shall be provided
with structural stops, such as curbs, to prevent equipment from
traveling outside its intended travel areas and to prevent a
crushing or shearing hazard.
(5)
Maintenance
access.
Means shall be provided to traverse all carriages and their
suspended equipment to a safe area for maintenance and storage.
(6)
Elevated
track.
(i) An elevated track system which is located four feet (1.2 m) or
more above a safe surface, and traversed by carriage supported
equipment, shall be provided with a walkway and guardrail system;
or
(ii)
The working platform shall be capable of being lowered, as part of
its normal operation, to the lower safe surface for access and
egress of the personnel and shall be provided with a safe means of
access and egress to the lower safe surface.
(7)
Tie-down
anchors.
Imbedded tie-down anchors, fasteners, and affected structures
shall be resistant to corrosion.
(8)
Cable
stabilization.
(i) Hanging lifelines and all cables not in tension shall be
stabilized at each 200 foot (61 m) interval of vertical travel of
the working platform beyond an initial 200 foot (61 m) distance.
(ii)
Hanging cables, other than suspended wire ropes, which are in
constant tension shall be stabilized when the vertical travel
exceeds an initial 600 foot (183 m) distance, and at further
intervals of 600 feet (183 m) or less.
(9)
Emergency
planning.
A written emergency action plan shall be developed and implemented
for each kind of working platform operation. This plan shall
explain the emergency procedures which are to be followed in the
event of a power failure, equipment failure or other emergencies
which may be encountered. The plan shall also explain that
employees inform themselves about the building emergency escape
routes, procedures and alarm systems before operating a platform.
Upon initial assignment and whenever the plan is changed the
employer shall review with each employee those parts of the plan
which the employee must know to protect himself or herself in the
event of an emergency.
(10)
Building
maintenance.
Repairs or major maintenance of those building portions that
provide primary support for the suspended equipment shall not
affect the capability of the building to meet the requirements of
this standard.
(11)
Electrical
requirements.
The following electrical requirements apply to buildings which
utilize working platforms for building maintenance.
(i)
General building electrical installations shall comply with
§§1910.302 through 1910.308 of this part, unless
otherwise specified in this section;
(ii)
Building electrical wiring shall be of such capacity that when
full load is applied to the equipment power circuit not more than
a five percent drop from building service-vault voltage shall
occur at any power circuit outlet used by equipment regulated by
this section;
(iii)
The equipment power circuit shall be an independent electrical
circuit that shall remain separate from all other equipment within
or on the building, other than power circuits used for hand tools
that will be used in conjunction with the equipment. If the
building is provided with an emergency power system, the equipment
power circuit may also be connected to this system;
(iv)
The power circuit shall be provided with a disconnect switch that
can be locked in the “OFF” and “ON”
positions. The switch shall be conveniently located with respect
to the primary operating area of the equipment to allow the
operators of the equipment access to the switch;
(v)
The disconnect switch for the power circuit shall be locked in the
“ON” position when the equipment is in use; and
(vi)
An effective two-way voice communication system shall be provided
between the equipment operators and persons stationed within the
building being serviced. The communications facility shall be
operable and shall be manned at all times by persons stationed
within the building whenever the platform is being used.
(f)
Powered
platform installations—Equipment—(1)
General
requirements.
The following requirements apply to equipment which are part of a
powered platform installation, such as platforms, stabilizing
components, carriages, outriggers, davits, hoisting machines, wire
ropes and electrical components.
(i)
Equipment installations shall be designed by or under the
direction of a registered professional engineer experienced in
such design;
(ii)
The design shall provide for a minimum live load of 250 pounds
(113.6 kg) for each occupant of a suspended or supported platform;
(iii)
Equipment that is exposed to wind when not in service shall be
designed to withstand forces generated by winds of at least 100
miles per hour (44.7 m/s) at 30 feet (9.2 m) above grade; and
(iv)
Equipment that is exposed to wind when in service shall be
designed to withstand forces generated by winds of at least 50
miles per hour (22.4 m/s) for all elevations.
(2)
Construction
requirements.
Bolted connections shall be self-locking or shall otherwise be
secured to prevent loss of the connections by vibration.
(3)
Suspension
methods.
Elevated building maintenance equipment shall be suspended by a
carriage, outriggers, davits or an equivalent method.
(i)
Carriages.
Carriages used for suspension of elevated building maintenance
equipment shall comply with the following:
(A)
The horizontal movement of a carriage shall be controlled so as to
ensure its safe movement and allow accurate positioning of the
platform for vertical travel or storage;
(B)
Powered carriages shall not exceed a traversing speed of 50 feet
per minute (0.3 m/s);
(C)
The initiation of a traversing movement for a manually propelled
carriage on a smooth level surface shall not require a person to
exert a horizontal force greater than 40 pounds (444.8 n);
(D)
Structural stops and curbs shall be provided to prevent the
traversing of the carriage beyond its designed limits of travel;
(E)
Traversing controls for a powered carriage shall be of a
continuous pressure weatherproof type. Multiple controls when
provided shall be arranged to permit operation from only one
control station at a time. An emergency stop device shall be
provided on each end of a powered carriage for interrupting power
to the carriage drive motors;
(F)
The operating controls(s) shall be so connected that in the case
of suspended equipment, traversing of a carriage is not possible
until the suspended portion of the equipment is located at its
uppermost designed position for traversing; and is free of contact
with the face of the building or building guides. In addition, all
protective devices and interlocks are to be in the proper position
to allow traversing of the carriage;
(G)
Stability for underfoot supported carriages shall be obtained by
gravity, by an attachment to a structural support, or by a
combination of gravity and a structural support. The use of
flowing counterweights to achieve stability is prohibited.
(1)
The stability factor against overturning shall not be less than
two for horizontal traversing of the carriage, including the
effects of impact and wind.
(2)
The carriages and their anchorages shall be capable of resisting
accidental over-tensioning of the wire ropes suspending the
working platform, and this calculated value shall include the
effect of one and one-half times the stall capacity of the hoist
motor. All parts of the installation shall be capable of
withstanding without damage to any part of the installation the
forces resulting from the stall load of the hoist and one half the
wind load.
(3)
Roof carriages which rely on having tie-down devices secured to
the building to develop the required stability against overturning
shall be provided with an interlock which will prevent vertical
platform movement unless the tie-down is engaged;
(H)
An automatically applied braking or locking system, or equivalent,
shall be provided that will prevent unintentional traversing of
power traversed or power assisted carriages;
(I)
A manual or automatic braking or locking system or equivalent,
shall be provided that will prevent unintentional traversing of
manually propelled carriages;
(J)
A means to lock out the power supply for the carriage shall be
provided;
(K)
Safe access to and egress from the carriage shall be provided from
a safe surface. If the carriage traverses an elevated area, any
operating area on the carriage shall be protected by a guardrail
system in compliance with the provisions of paragraph (f)(5)(i)(F)
of this section. Any access gate shall be self-closing and
self-latching, or provided with an interlock;
(L)
Each carriage work station position shall be identified by
location markings and/or position indicators; and
(M)
The motors shall stall if the load on the hoist motors is at any
time in excess of three times that necessary for lifting the
working platform with its rated load.
(ii)
Transportable
outriggers.
(A) Transportable outriggers may be used as a method of suspension
for ground rigged working platforms where the point of suspension
does not exceed 300 feet (91.5 m) above a safe surface. Tie-in
guide system(s) shall be provided which meet the requirements of
paragraph (e)(2) of this section.
(B)
Transportable outriggers shall be used only with self-powered,
ground rigged working platforms.
(C)
Each transportable outrigger shall be secured with a tie-down to a
verified anchorage on the building during the entire period of its
use. The anchorage shall be designed to have a stability factor of
not less than four against overturning or upsetting of the
outrigger.
(D)
Access to and egress from the working platform shall be from and
to a safe surface below the point of suspension.
(E)
Each transportable outrigger shall be designed for lateral
stability to prevent roll-over in the event an accidental lateral
load is applied to the outrigger. The accidental lateral load to
be considered in this design shall be not less than 70 percent of
the rated load of the hoist.
(F)
Each transportable outrigger shall be designed to support an
ultimate load of not less than four times the rated load of the
hoist.
(G)
Each transportable outrigger shall be so located that the
suspension wire ropes for two point suspended working platforms
are hung parallel.
(H)
A transportable outrigger shall be tied-back to a verified
anchorage on the building with a rope equivalent in strength to
the suspension rope.
(I)
The tie-back rope shall be installed parallel to the centerline of
the outrigger.
(iii)
Davits. (A) Every davit installation, fixed or transportable,
rotatable or non-rotatable shall be designed and installed to
insure that it has a stability factor against overturning of not
less than four.
(B)
The following requirements apply to roof rigged davit systems:
(1)
Access to and egress from the working platform shall be from a
safe surface. Access or egress shall not require persons to climb
over a building's parapet or guard railing; and
(2)
The working platform shall be provided with wheels, casters or a
carriage for traversing horizontally.
(C)
The following requirements apply to ground rigged davit systems:
(1)
The point of suspension shall not exceed 300 feet (91.5 m) above a
safe surface. Guide system(s) shall be provided which meet the
requirements of paragraph (e)(2) of this section;
(2)
Access and egress to and from the working platform shall only be
from a safe surface below the point of suspension.
(D)
A rotating davit shall not require a horizontal force in excess of
40 pounds (177.9 n) per person to initiate a rotating movement.
(E)
The following requirements shall apply to transportable davits:
(1)
A davit or part of a davit weighing more than 80 pounds (36 kg)
shall be provided with a means for its transport, which shall keep
the center of gravity of the davit at or below 36 inches (914 mm)
above the safe surface during transport;
(2)
A davit shall be provided with a pivoting socket or with a base
that will allow the insertion or removal of a davit at a position
of not more than 35 degrees above the horizontal, with the
complete davit inboard of the building face being serviced; and
(3)
Means shall be provided to lock the davit to its socket or base
before it is used to suspend the platform.
(4)
Hoisting
machines.
(i) Raising and lowering of suspended or supported equipment shall
be performed only by a hoisting machine.
(ii)
Each hoisting machine shall be capable of arresting any overspeed
descent of the load.
(iii)
Each hoisting machine shall be powered only by air, electric or
hydraulic sources.
(iv)
Flammable liquids shall not be carried on the working platform.
(v)
Each hoisting machine shall be capable of raising or lowering 125
percent of the rated load of the hoist.
(vi)
Moving parts of a hoisting machine shall be enclosed or guarded in
compliance with paragraphs (a)(1) and (2) of §1910.212 of
this part.
(vii)
Winding drums, traction drums and sheaves and directional sheaves
used in conjunction with hoisting machines shall be compatible
with, and sized for, the wire rope used.
(viii)
Each winding drum shall be provided with a positive means of
attaching the wire rope to the drum. The attachment shall be
capable of developing at least four times the rated load of the
hoist.
(ix)
Each hoisting machine shall be provided with a primary brake and
at least one independent secondary brake, each capable of stopping
and holding not less than 125 percent of the lifting capacity of
the hoist.
(A)
The primary brake shall be directly connected to the drive train
of the hoisting machine, and shall not be connected through belts,
chains, clutches, or set screw type devices. The brake shall
automatically set when power to the prime mover is interrupted.
(B)(1)
The secondary brake shall be an automatic emergency type of brake
that, if actuated during each stopping cycle, shall not engage
before the hoist is stopped by the primary brake.
(2)
When a secondary brake is actuated, it shall stop and hold the
platform within a vertical distance of 24 inches (609.6 mm).
(x)
Any component of a hoisting machine which requires lubrication for
its protection and proper functioning shall be provided with a
means for that lubrication to be applied.
(5)
Suspended
equipment—(i)
General
requirements.
(A) Each suspended unit component, except suspension ropes and
guardrail systems, shall be capable of supporting, without
failure, at least four times the maximum intended live load
applied or transmitted to that component.
(B)
Each suspended unit component shall be constructed of materials
that will withstand anticipated weather conditions.
(C)
Each suspended unit shall be provided with a load rating plate,
conspicuously located, stating the unit weight and rated load of
the suspended unit.
(D)
When the suspension points on a suspended unit are not at the unit
ends, the unit shall be capable of remaining continuously stable
under all conditions of use and position of the live load, and
shall maintain at least a 1.5 to 1 stability factor against unit
upset.
(E)
Guide rollers, guide shoes or building face rollers shall be
provided, and shall compensate for variations in building
dimensions and for minor horizontal out-of-level variations of
each suspended unit.
(F)
Each working platform of a suspended unit shall be secured to the
building facade by one or more of the following methods, or by an
equivalent method:
(1)
Continuous engagement to building anchors as provided in paragraph
(e)(2)(i) of this section;
(2)
Intermittent engagement to building anchors as provided in
paragraph (e)(2)(iii)(A) of this section;
(3)
Button guide engagement as provided in paragraph (e)(2)(iii)(B) of
this section; or
(4)
Angulated roping and building face rollers as provided in
paragraph (e)(2)(iii)(C) of this section.
(G)
Each working platform of a suspended unit shall be provided with a
guardrail system on all sides which shall meet the following
requirements:
(1)
The system shall consist of a top guardrail, midrail, and a
toeboard;
(2)
The top guardrail shall not be less than 36 inches (914 mm) high
and shall be able to withstand at least a 100-pound (444 n) force
in any downward or outward direction;
(3)
The midrail shall be able to withstand at least a 75-pound (333 n)
force in any downward or outward direction; and
(4)
The areas between the guardrail and toeboard on the ends and
outboard side, and the area between the midrail and toeboard on
the inboard side, shall be closed with a material that is capable
of withstanding a load of 100 pounds (45.4 KG.) applied
horizontally over any area of one square foot (.09 m2).
The material shall have all openings small enough to reject
passage of life lines and potential falling objects which may be
hazardous to persons below.
(5)
Toeboards shall be capable of withstanding, without failure, a
force of at least 50 pounds (222 n) applied in any downward or
horizontal direction at any point along the toeboard.
(6)
Toeboards shall be three and one-half inches (9 cm) minimum in
length from their top edge to the level of the platform floor.
(7)
Toeboards shall be securely fastened in place at the outermost
edge of the platform and have no more than one-half inch (1.3 cm)
clearance above the platform floor.
(8)
Toeboards shall be solid or with an opening not over one inch (2.5
cm) in the greatest dimension.
(ii)
Two
and four-point suspended working platforms.
(A) The working platform shall be not less than 24 inches (610 mm)
wide and shall be provided with a minimum of a 12 inch (305 mm)
wide passage at or past any obstruction on the platform.
(B)
The flooring shall be of a slip-resistant type and shall contain
no opening that would allow the passage of life lines, cables and
other potential falling objects. If a larger opening is provided,
it shall be protected by placing a material under the opening
which shall prevent the passage of life lines, cables and
potential falling objects.
(C)
The working platfrom shall be provided with a means of suspension
that will restrict the platform's inboard to outboard roll about
its longitudinal axis to a maximum of 15 degrees from a horizontal
plane when moving the live load from the inboard to the outboard
side of the platform.
(D)
Any cable suspended from above the platform shall be provided with
a means for storage to prevent accumulation of the cable on the
floor of the platform.
(E)
All operating controls for the vertical travel of the platform
shall be of the continuous-pressure type, and shall be located on
the platform.
(F)
Each operating station of every working platform shall be provided
with a means of interrupting the power supply to all hoist motors
to stop any further powered ascent or descent of the platform.
(G)
The maximum rated speed of the platform shall not exceed 50 feet
per minute (0.3 ms) with single speed hoists, nor 75 feet per
minute (0.4 ms) with multi-speed hoists.
(H)
Provisions shall be made for securing all tools, water tanks, and
other accessories to prevent their movement or accumulation on the
floor of the platform.
(I)
Portable fire extinguishers conforming to the provisions of
§§1910.155 and 1910.157 of this part shall be provided
and securely attached on all working platforms.
(J)
Access to and egress from a working platfrom, except for those
that land directly on a safe surface, shall be provided by stairs,
ladders, platforms and runways conforming to the provisions of
subpart D of this part. Access gates shall be self-closing and
self-latching.
(K)
Means of access to or egress from a working platform which is 48
inches (1.2 m) or more above a safe surface shall be provided with
a guardrail system or ladder handrails that conform to the
provisions of subpart D of this part.
(L)
The platform shall be provided with a secondary wire rope
suspension system if the platform contains overhead structures
which restrict the emergency egress of employees. A horizontal
lifeline or a direct connection anchorage shall be provided as
part of a personal fall arrest system that meets the requirements
of subpart I of this part for each employee on such a platform.
(M)
A vertical lifeline shall be provided as part of a personal fall
arrest system that meets the requirements of subpart I of this
part for each employee on a working platform suspended by two or
more wire ropes, if the failure of one wire rope or suspension
attachment will cause the platform to upset. If a secondary wire
rope suspension is used, vertical lifelines are not required for
the personal fall arrest system, provided that each employee is
attached to a horizontal lifeline anchored to the platform.
(N)
An emergency electric operating device shall be provided on roof
powered platforms near the hoisting machine for use in the event
of failure of the normal operating device located on the working
platform, or failure of the cable connected to the platform. The
emergency electric operating device shall be mounted in a secured
compartment, and the compartment shall be labeled with
instructions for use. A means for opening the compartment shall be
mounted in a break-glass receptable located near the emergency
electric operating device or in an equivalent secure and
accessible location.
(iii)
Single
point suspended working platforms.
(A) The requirements of paragraphs (f)(5)(ii) (A) through (K) of
this section shall also apply to a single point working platform.
(B)
Each single point suspended working platform shall be provided
with a secondary wire rope suspension system which will prevent
the working platform from falling should there be a failure of the
primary means of support, or if the platform contains overhead
structures which restrict the egress of the employees. A
horizontal life line or a direct connection anchorage shall be
provided as part of a personal fall arrest system that meets the
requirements of subpart I of this part for each employee on the
platform.
(iv)
Ground-rigged
working platforms.
(A) Groundrigged working platforms shall comply with all the
requirements of paragraphs (f)(5)(ii) (A) through (M) of this
section.
(B)
After each day's use, the power supply within the building shall
be disconnected from a ground-rigged working platform, and the
platform shall be either disengaged from its suspension points or
secured and stored at grade.
(v)
Intermittently
stabilized platforms.
(A) The platform shall comply with paragraphs (F)(5)(ii) (A)
through (M) of this section.
(B)
Each stabilizer tie shall be equipped with a “quick
connect-quick disconnect” device which cannot be accidently
disengaged, for attachment to the building anchor, and shall be
resistant to adverse environmental conditions.
(C)
The platform shall be provided with a stopping device that will
interrupt the hoist power supply in the event the platform
contacts a stabilizer tie during its ascent.
(D)
Building face rollers shall not be placed at the anchor setting if
exterior anchors are used on the building face.
(E)
Stabilizer ties used on intermittently stabilized platforms shall
allow for the specific attachment length needed to effect the
predetermined angulation of the suspended wire rope. The specific
attachment length shall be maintained at all building anchor
locations.
(F)
The platform shall be in continuous contact with the face of the
building during ascent and descent.
(G)
The attachment and removal of stabilizer ties shall not require
the horizontal movement of the platform.
(H)
The platform-mounted equipment and its suspension wire ropes shall
not be physically damaged by the loads from the stabilizer tie or
its building anchor. The platform, platform mounted equipment and
wire ropes shall be able to withstand a load that is at least
twice the ultimate strength of the stabilizer tie.
Note:
See figure II in appendix B of this section for a description of a
typical intermittent stabilization system.
(vi)
Button-guide
stabilized platforms.
(A) The platform shall comply with paragraphs (f)(5)(ii) (A)
through (M) of this section.
(B)
Each guide track on the platform shall engage a minimum of two
guide buttons during any vertical travel of the platform following
the initial button engagement.
(C)
Each guide track on a platform that is part of a roof rigged
system shall be provided with a storage position on the platform.
(D)
Each guide track on the platform shall be sufficiently
maneuverable by platform occupants to permit easy engagement of
the guide buttons, and easy movement into and out of its storage
position on the platform.
(E)
Two guide tracks shall be mounted on the platform and shall
provide continuous contact with the building face.
(F)
The load carrying components of the button guide stabilization
system which transmit the load into the platform shall be capable
of supporting the weight of the platform, or provision shall be
made in the guide track connectors or platform attachments to
prevent the weight of the platform from being transmitted to the
platform attachments.
Note:
See figure III in appendix B of this section for a description of
a typical button guide stabilization system.
(6)
Supported
equipment.
(i) Supported equipment shall maintain a vertical position in
respect to the face of the building by means other than friction.
(ii)
Cog wheels or equivalent means shall be incorporated to provide
climbing traction between the supported equipment and the building
guides. Additional guide wheels or shoes shall be incorporated as
may be necessary to ensure that the drive wheels are continuously
held in positive engagement with the building guides.
(iii)
Launch guide mullions indexed to the building guides and retained
in alignment with the building guides shall be used to align drive
wheels entering the building guides.
(iv)
Manned platforms used on supported equipment shall comply with the
requirements of paragraphs (f)(5)(ii)(A), (f)(5)(ii)(B), and
(f)(5)(ii) (D) through (K) of this section covering suspended
equipment.
(7)
Suspension
wire ropes and rope connections.
(i) Each specific installation shall use suspension wire ropes or
combination cable and connections meeting the specification
recommended by the manufacturer of the hoisting machine used.
Connections shall be capable of developing at least 80 percent of
the rated breaking strength of the wire rope.
(ii)
Each suspension rope shall have a “Design Factor” of
at least 10. The “Design Factor” is the ratio of the
rated strength of the suspension wire rope to the rated working
load, and shall be calculated using the following formula:
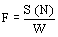
View
or download PDF
Where:
F
= Design factor
S
= Manufacturer's rated strength of one suspension rope
N
= Number of suspension ropes under load
W
= Rated working load on all ropes at any point of travel
(iii)
Suspension wire rope grade shall be at least improved plow steel
or equivalent.
(iv)
Suspension wire ropes shall be sized to conform with the required
design factor, but shall not be less than 5⁄16
inch (7.94 mm) in diameter.
(v)
No more than one reverse bend in six wire rope lays shall be
permitted.
(vi)
A corrosion-resistant tag shall be securely attached to one of the
wire rope fastenings when a suspension wire rope is to be used at
a specific location and will remain in that location. This tag
shall bear the following wire rope data:
(A)
The diameter (inches and/or mm);
(B)
Construction classification;
(C)
Whether non-preformed or preformed;
(D)
The grade of material;
(E)
The manufacturer's rated strength;
(F)
The manufacturer's name;
(G)
The month and year the ropes were installed; and
(H)
The name of the person or company which installed the ropes.
(vii)
A new tag shall be installed at each rope renewal.
(viii)
The original tag shall be stamped with the date of the
resocketing, or the original tag shall be retained and a
supplemental tag shall be provided when ropes are resocketed. The
supplemental tag shall show the date of resocketing and the name
of the person or company that resocketed the rope.
(ix)
Winding drum type hoists shall contain at least three wraps of the
suspension wire rope on the drum when the suspended unit has
reached the lowest possible point of its vertical travel.
(x)
Traction drum and sheave type hoists shall be provided with a wire
rope of sufficient length to reach the lowest possible point of
vertical travel of the suspended unit, and an additional length of
the wire rope of at least four feet (1.2 m).
(xi)
The lengthening or repairing of suspension wire ropes is
prohibited.
(xii)
Babbitted fastenings for suspension wire rope are prohibited.
(8)
Control
circuits, power circuits and their components.
(i) Electrical wiring and equipment shall comply with subpart S of
this part, except as otherwise required by this section.
(ii)
Electrical runway conductor systems shall be of a type designed
for use in exterior locations, and shall be located so that they
do not come into contact with accumulated snow or water.
(iii)
Cables shall be protected against damage resulting from
overtensioning or from other causes.
(iv)
Devices shall be included in the control system for the equipment
which will provide protection against electrical overloads, three
phase reversal and phase failure. The control system shall have a
separate method, independent of the direction control circuit, for
breaking the power circuit in case of an emergency or malfunction.
(v)
Suspended or supported equipment shall have a control system which
will require the operator of the equipment to follow predetermined
procedures.
(vi)
The following requirements shall apply to electrical protection
devices:
(A)
On installations where the carriage does not have a stability
factor of at least four against overturning, electrical contact(s)
shall be provided and so connected that the operating devices for
the suspended or supported equipment shall be operative only when
the carriage is located and mechanically retained at an
established operating point.
(B)
Overload protection shall be provided in the hoisting or
suspension system to protect against the equipment operating in
the “up” direction with a load in excess of 125
percent of the rated load of the platform; and
(C)
An automatic detector shall be provided for each suspension point
that will interrupt power to all hoisting motors for travel in the
“down” direction, and apply the primary brakes if any
suspension wire rope becomes slack. A continuous-pressure
rigging-bypass switch designed for use during rigging is
permitted. This switch shall only be used during rigging.
(vii)
Upper and lower directional switches designed to prevent the
travel of suspended units beyond safe upward and downward levels
shall be provided.
(viii)
Emergency stop switches shall be provided on remote controlled,
roof-powered manned platforms adjacent to each control station on
the platform.
(ix)
Cables which are in constant tension shall have overload devices
which will prevent the tension in the cable from interfering with
the load limiting device required in paragraph (f)(8)(vi)(B) of
this section, or with the platform roll limiting device required
in paragraph (f)(5)(ii)(C) of this section. The setting of these
devices shall be coordinated with other overload settings at the
time of design of the system, and shall be clearly indicated on or
near the device. The device shall interrupt the equipment travel
in the “down” direction.
(g)
Inspection
and tests—(1)
Installations
and alterations.
All completed building maintenance equipment installations shall
be inspected and tested in the field before being placed in
initial service to determine that all parts of the installation
conform to applicable requirements of this standard, and that all
safety and operating equipment is functioning as required. A
similar inspection and test shall be made following any major
alteration to an existing installation. No hoist in an
installation shall be subjected to a load in excess of 125 percent
of its rated load.
(2)
Periodic
inspections and tests.
(i) Related building supporting structures shall undergo periodic
inspection by a competent person at intervals not exceeding 12
months.
(ii)
All parts of the equipment including control systems shall be
inspected, and, where necessary, tested by a competent person at
intervals specified by the manufacturer/supplier, but not to
exceed 12 months, to determine that they are in safe operating
condition. Parts subject to wear, such as wire ropes, bearings,
gears, and governors shall be inspected and/or tested to determine
that they have not worn to such an extent as to affect the safe
operation of the installation.
(iii)
The building owner shall keep a certification record of each
inspection and test required under paragraphs (g)(2)(i) and (ii)
of this section. The certification record shall include the date
of the inspection, the signature of the person who performed the
inspection, and the number, or other identifier, of the building
support structure and equipment which was inspected. This
certification record shall be kept readily available for review by
the Assistant Secretary of Labor or the Assistant Secretary's
representative and by the employer.
(iv)
Working platforms and their components shall be inspected by the
employer for visible defects before every use and after each
occurrence which could affect the platform's structural integrity.
(3)
Maintenance
inspections and tests.
(i) A maintenance inspection and, where necessary, a test shall be
made of each platform installation every 30 days, or where the
work cycle is less than 30 days such inspection and/or test shall
be made prior to each work cycle. This inspection and test shall
follow procedures recommended by the manufacturer, and shall be
made by a competent person.
(ii)
The building owner shall keep a certification record of each
inspection and test performed under paragraph (g)(3)(i) of this
section. The certification record shall include the date of the
inspection and test, the signature of the person who performed the
inspection and/or test, and an identifier for the platform
installation which was inspected. The certification record shall
be kept readily available for review by the Assistant Secretary of
Labor or the Assistant Secretary's representative and by the
employer.
(4)
Special
inspection of governors and secondary brakes.
(i) Governors and secondary brakes shall be inspected and tested
at intervals specified by the manufacturer/supplier but not to
exceed every 12 months.
(ii)
The results of the inspection and test shall confirm that the
initiating device for the secondary braking system operates at the
proper overspeed.
(iii)
The results of the inspection and test shall confirm that the
secondary brake is functioning properly.
(iv)
If any hoisting machine or initiating device for the secondary
brake system is removed from the equipment for testing, all
reinstalled and directly related components shall be reinspected
prior to returning the equipment installation to service.
(v)
Inspection of governors and secondary brakes shall be performed by
a competent person.
(vi)
The secondary brake governor and actuation device shall be tested
before each day's use. Where testing is not feasible, a visual
inspection of the brake shall be made instead to ensure that it is
free to operate.
(5)
Suspension
wire rope maintenance, inspection and replacement.
(i) Suspension wire rope shall be maintained and used in
accordance with procedures recommended by the wire rope
manufacturer.
(ii)
Suspension wire rope shall be inspected by a competent person for
visible defects and gross damage to the rope before every use and
after each occurrence which might affect the wire rope's
integrity.
(iii)
A thorough inspection of suspension wire ropes in service shall be
made once a month. Suspension wire ropes that have been inactive
for 30 days or longer shall have a thorough inspection before they
are placed into service. These thorough inspections of suspension
wire ropes shall be performed by a competent person.
(iv)
The need for replacement of a suspension wire rope shall be
determined by inspection and shall be based on the condition of
the wire rope. Any of the following conditions or combination of
conditions will be cause for removal of the wire rope:
(A)
Broken wires exceeding three wires in one strand or six wires in
one rope lay;
(B)
Distortion of rope structure such as would result from crushing or
kinking;
(C)
Evidence of heat damage;
(D)
Evidence of rope deterioration from corrosion;
(E)
A broken wire within 18 inches (460.8 mm) of the end attachments;
(F)
Noticeable rusting and pitting;
(G)
Evidence of core failure (a lengthening of rope lay, protrusion of
the rope core and a reduction in rope diameter suggests core
failure); or
(H)
More than one valley break (broken wire).
(I)
Outer wire wear exceeds one-third of the original outer wire
diameter.
(J)
Any other condition which the competent person determines has
significantly affected the integrity of the rope.
(v)
The building owner shall keep a certification record of each
monthly inspection of a suspension wire rope as required in
paragraph (g)(5)(iii) of this section. The record shall include
the date of the inspection, the signature of the person who
performed the inspection, and a number, or other identifier, of
the wire rope which was inspected. This record of inspection shall
be made available for review by the Assistant Secretary of Labor
or the Assistant Secretary's representative and by the employer.
(6)
Hoist
inspection.
Before lowering personnel below the top elevation of the building,
the hoist shall be tested each day in the lifting direction with
the intended load to make certain it has sufficient capacity to
raise the personnel back to the boarding level.
(h)
Maintenance—(1)
General
maintenance.
All parts of the equipment affecting safe operation shall be
maintained in proper working order so that they may perform the
functions for which they were intended. The equipment shall be
taken out of service when it is not in proper working order.
(2)
Cleaning.
(i) Control or power contactors and relays shall be kept clean.
(ii)
All other parts shall be kept clean if their proper functioning
would be affected by the presence of dirt or other contaminants.
(3)
Periodic
resocketing of wire rope fastenings.
(i) Hoisting ropes utilizing poured socket fastenings shall be
resocketed at the non-drum ends at intervals not exceeding 24
months. In resocketing the ropes, a sufficient length shall be cut
from the end of the rope to remove damaged or fatigued portions.
(ii)
Resocketed ropes shall conform to the requirements of paragraph
(f)(7) of this section.
(iii)
Limit switches affected by the resocketed ropes shall be reset, if
necessary.
(4)
Periodic
reshackling of suspension wire ropes.
The hoisting ropes shall be reshackled at the nondrum ends at
intervals not exceeding 24 months. When reshackling the ropes, a
sufficient length shall be cut from the end of the rope to remove
damaged or fatigued portions.
(5)
Roof
systems.
Roof track systems, tie-downs, or similar equipment shall be
maintained in proper working order so that they perform the
function for which they were intended.
(6)
Building
face guiding members.
T-rails, indented mullions, or equivalent guides located in the
face of a building shall be maintained in proper working order so
that they perform the functions for which they were intended.
Brackets for cable stabilizers shall similarly be maintained in
proper working order.
(7)
Inoperative
safety devices.
No person shall render a required safety device or electrical
protective device inoperative, except as necessary for tests,
inspections, and maintenance. Immediately upon completion of such
tests, inspections and maintenance, the device shall be restored
to its normal operating condition.
(i)
Operations—(1)
Training.
(i) Working platforms shall be operated only by persons who are
proficient in the operation, safe use and inspection of the
particular working platform to be operated.
(ii)
All employees who operate working platforms shall be trained in
the following:
(A)
Recognition of, and preventive measures for, the safety hazards
associated with their individual work tasks.
(B)
General recognition and prevention of safety hazards associated
with the use of working platforms, including the provisions in the
section relating to the particular working platform to be
operated.
(C)
Emergency action plan procedures required in paragraph (e)(9) of
this section.
(D)
Work procedures required in paragraph (i)(1)(iv) of this section.
(E)
Personal fall arrest system inspection, care, use and system
performance.
(iii)
Training of employees in the operation and inspection of working
platforms shall be done by a competent person.
(iv)
Written work procedures for the operation, safe use and inspection
of working platforms shall be provided for employee training.
Pictorial methods of instruction, may be used, in lieu of written
work procedures, if employee communication is improved using this
method. The operating manuals supplied by manufacturers for
platform system components can serve as the basis for these
procedures.
(v)
The employer shall certify that employees have been trained in
operating and inspecting a working platform by preparing a
certification record which includes the identity of the person
trained, the signature of the employer or the person who conducted
the training and the date that training was completed. The
certification record shall be prepared at the completion of the
training required in paragraph (i)(1)(ii) of this section, and
shall be maintained in a file for the duration of the employee's
employment. The certification record shall be kept readily
available for review by the Assistant Secretary of Labor or the
Assistant Secretary's representative.
(2)
Use.
(i) Working platforms shall not be loaded in excess of the rated
load, as stated on the platform load rating plate.
(ii)
Employees shall be prohibited from working on snow, ice, or other
slippery material covering platforms, except for the removal of
such materials.
(iii)
Adequate precautions shall be taken to protect the platform, wire
ropes and life lines from damage due to acids or other corrosive
substances, in accordance with the recommendations of the
corrosive substance producer, supplier, platform manufacturer or
other equivalent information sources. Platform members which have
been exposed to acids or other corrosive substances shall be
washed down with a neutralizing solution, at a frequency
recommended by the corrosive substance producer or supplier.
(iv)
Platform members, wire ropes and life lines shall be protected
when using a heat producing process. Wire ropes and life lines
which have been contacted by the heat producing process shall be
considered to be permanently damaged and shall not be used.
(v)
The platform shall not be operated in winds in excess of 25 miles
per hour (40.2 km/hr) except to move it from an operating to a
storage position. Wind speed shall be determined based on the best
available information, which includes on-site anemometer readings
and local weather forecasts which predict wind velocities for the
area.
(vi)
On exterior installations, an anemometer shall be mounted on the
platform to provide information of on-site wind velocities prior
to and during the use of the platform. The anemometer may be a
portable (hand held) unit which is temporarily mounted during
platform use.
(vii)
Tools, materials and debris not related to the work in progress
shall not be allowed to accumulate on platforms. Stabilizer ties
shall be located so as to allow unencumbered passage along the
full length of the platform and shall be of such length so as not
to become entangled in rollers, hoists or other machinery.
(j)
Personal
fall protection.
Employees on working platforms shall be protected by a personal
fall arrest system meeting the requirements of subpart I of this
part and as otherwise provided by this standard.
Appendix
A to §1910.66, Guidelines (Advisory)
1.
Use
of the Appendix.
Appendix A provides examples of equipment and methods to assist
the employer in meeting the requirements of the indicated
provision of the standard. Employers may use other equipment or
procedures which conform to the requirements of the standard. This
appendix neither adds to nor detracts from the mandatory
requirements set forth in §1910.66.
2.
Assurance.
Paragraph (c) of the standard requires the building owner to
inform the employer in writing that the powered platform
installation complies with certain requirements of the standard,
since the employer may not have the necessary information to make
these determinations. The employer, however, remains responsible
for meeting these requirements which have not been set off in
paragraph (c)(1).
3.
Design
Requirements.
The design requirements for each installation should be based on
the limitations (stresses, deflections, etc.), established by
nationally recognized standards as promulgated by the following
organizations, or to equivalent standards:
AA—The
Aluminum Association, 818 Connecticut Avenue, NW., Washington, DC,
20006
Aluminum
Construction Manual
Specifications
For Aluminum Structures
Aluminum
Standards and Data
AGMA—American
Gear Manufacturers Association, 101 North Fort Meyer Dr., Suite
1000, Arlington, VA 22209
AISC—American
Institute of Steel Construction, 400 North Michigan Avenue,
Chicago, IL 60611
ANSI—American
National Standards Institute, Inc., 1430 Broadway, New York, NY
10018
ASCE—American
Society of Civil Engineers, 345 East 47th Street, New York, NY
10017
ASME—American
Society of Mechanical Engineers, 345 East 47th Street, New York,
NY 10017
ASTM—American
Society for Testing and Materials, 1916 Race Street, Philadelphia,
PA 19103
AWS—American
Welding Society, Inc., Box 351040, 550 NW. LeJeunne Road, Miami,
FL 33126
JIC—Joint
Industrial Council, 2139 Wisconsin Avenue NW., Washington, DC
20007
NEMA—National
Electric Manufacturers Association, 2101 L Street, NW.,
Washington, DC 20037
4.
Tie-in-guides.
Indented mullions, T-rails or other equivalent guides are
acceptable as tie-in guides in a building face for a continuous
stabilization system. Internal guides are embedded in other
building members with only the opening exposed (see Figure 1 of
appendix B). External guides, however, are installed external to
the other building members and so are fully exposed. The minimum
opening for tie-in guides is three-quarters of an inch (19 mm),
and the minimum inside dimensions are one-inch (25 mm) deep and
two inches (50 mm) wide.
Employers
should be aware of the hazards associated with tie-in guides in a
continuous stabilization system which was not designed properly.
For example, joints in these track systems may become extended or
discontinuous due to installation or building settlement. If this
alignment problem is not corrected, the system could jam when a
guide roller or guide shoe strikes a joint and this would cause a
hazardous situation for employees. In another instance, faulty
design will result in guide rollers being mounted in a line so
they will jam in the track at the slightest misalignment.
5.
Building
anchors (intermittent stabilization system).
In the selection of the vertical distance between building
anchors, certain factors should be given consideration. These
factors include building height and architectural design, platform
length and weight, wire rope angulation, and the wind velocities
in the building area. Another factor to consider is the material
of the building face, since this material may be adversely
affected by the building rollers.
External
or indented type building anchors are acceptable. Receptacles in
the building facade used for the indented type should be kept
clear of extraneous materials which will hinder their use. During
the inspection of the platform installation, evidence of a failure
or abuse of the anchors should be brought to the attention of the
employer.
6.
Stabilizer
tie length.
A stabilizer tie should be long enough to provide for the planned
angulation of the suspension cables. However, the length of the
tie should not be excessive and become a problem by possibly
becoming entangled in the building face rollers or parts of the
platform machinery.
The
attachment length may vary due to material elongation and this
should be considered when selecting the material to be used.
Consideration should also be given to the use of ties which are
easily installed by employees, since this will encourage their
use.
7.
Intermittent
stabilization system.
Intermittent stabilization systems may use different equipment,
tie-in devices and methods to restrict the horizontal movement of
a powered platform with respect to the face of the building. One
acceptable method employs corrosion-resistant building anchors
secured in the face of the building in vertical rows every third
floor or 50 feet (15.3 m), whichever is less. The anchors are
spaced horizontally to allow a stabilization attachment
(stabilizer tie) for each of the two platform suspension wire
ropes. The stabilizer tie consists of two parts. One part is a
quick connect-quick disconnect device which utilizes a
corrosion-resistant yoke and retainer spring that is designed to
fit over the building anchors. The second part of the stabilizer
tie is a lanyard which is used to maintain a fixed distance
between the suspension wire rope and the face of the building.
In
this method, as the suspended powered platform descends past the
elevation of each anchor, the descent is halted and each of the
platform occupants secures a stabilizer tie between a suspension
wire rope and a building anchor. The procedure is repeated as each
elevation of a building anchor is reached during the descent of
the powered platform.
As
the platform ascends, the procedure is reversed; that is, the
stabilizer ties are removed as each elevation of a building anchor
is reached. The removal of each stabilizer tie is assured since
the platform is provided with stopping devices which will
interrupt power to its hoist(s) in the event either stopping
device contacts a stabilizer during the ascent of the platform.
Figure
2 of appendix B illustrates another type of acceptable
intermittent stabilization system which utilizes retaining pins as
the quick connect-quick disconnect device in the stabilizer tie.
8.
Wire
Rope Inspection.
The inspection of the suspension wire rope is important since the
rope gradually loses strength during its useful life. The purpose
of the inspection is to determine whether the wire rope has
sufficient integrity to support a platform with the required
design factor.
If
there is any doubt concerning the condition of a wire rope or its
ability to perform the required work, the rope should be replaced.
The cost of wire rope replacement is quite small if compared to
the cost in terms of human injuries, equipment down time and
replacement.
No
listing of critical inspection factors, which serve as a basis for
wire rope replacement in the standard, can be a substitute for an
experienced inspector of wire rope. The listing serves as a user's
guide to the accepted standards by which ropes must be judged.
Rope
life can be prolonged if preventive maintenance is performed
regularly. Cutting off an appropriate length of rope at the end
termination before the core degrades and valley breaks appear
minimizes degradation at these sections.
9.
General
Maintenance.
In meeting the general maintenance requirement in paragraph (h)(1)
of the standard, the employer should undertake the prompt
replacement of broken, worn and damaged parts, switch contacts,
brushes, and short flexible conductors of electrical devices. The
components of the electrical service system and traveling cables
should be replaced when damaged or significantly abraded. In
addition, gears, shafts, bearings, brakes and hoisting drums
should be kept in proper alignment.
10.
Training.
In meeting the training requirement of paragraph (i)(1) of the
standard, employers should use both on the job training and formal
classroom training. The written work procedures used for this
training should be obtained from the manufacturer, if possible, or
prepared as necessary for the employee's information and use.
Employees
who will operate powered platforms with intermittent stabilization
systems should receive instruction in the specific ascent and
descent procedures involving the assembly and disassembly of the
stabilizer ties.
An
acceptable training program should also include employee
instruction in basic inspection procedures for the purpose of
determining the need for repair and replacement of platform
equipment. In addition, the program should cover the inspection,
care and use of the personal fall protection equipment required in
paragraph (j)(1) of the standard.
In
addition, the training program should also include emergency
action plan elements. OSHA brochure #1B3088 (Rev.) 1985, “How
to Prepare for Workplace Emergencies,” details the basic
steps needed to prepare to handle emergencies in the workplace.
Following
the completion of a training program, the employee should be
required to demonstrate competency in operating the equipment
safely. Supplemental training of the employee should be provided
by the employer, as necessary, if the equipment used or other
working conditions should change.
An
employee who is required to work with chemical products on a
platform should receive training in proper cleaning procedures,
and in the hazards, care and handling of these products. In
addition, the employee should be supplied with the appropriate
personal protective equipment, such as gloves and eye and face
protection.
11.
Suspension
and Securing of Powered Platforms (Equivalency).
One acceptable method of demonstrating the equivalency of a method
of suspending or securing a powered platform, as required in
paragraphs (e)(2)(iii), (f)(3) and (f)(5)(i)(F), is to provide an
engineering analysis by a registered professional engineer. The
analysis should demonstrate that the proposed method will provide
an equal or greater degree of safety for employees than any one of
the methods specified in the standard.
Appendix
B to §1910.66—Exhibits (Advisory)
The
three drawings in appendix B illustrate typical platform
stabilization systems which are addressed in the standard. The
drawings are to be used for reference purposes only, and do not
illustrate all the mandatory requirements for each system.
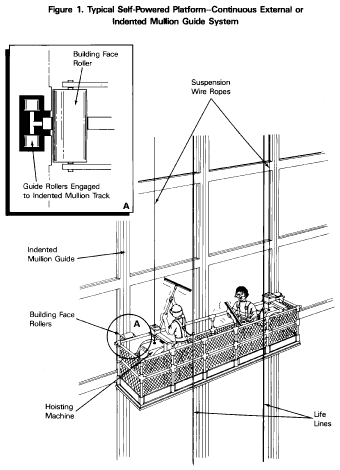
View
or download PDF
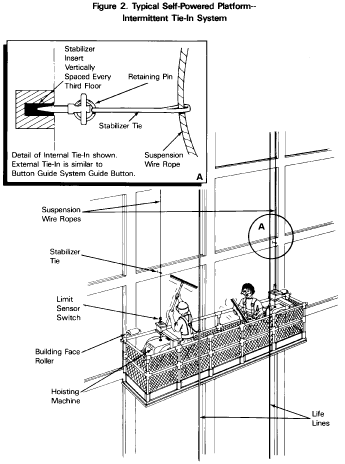
View
or download PDF
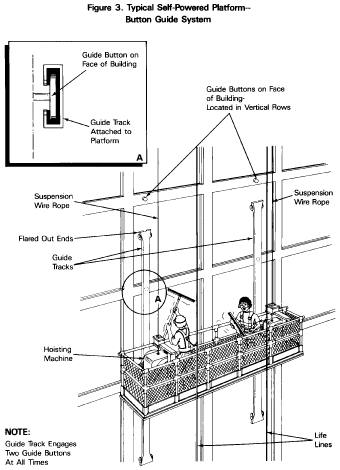
View
or download PDF
Appendix
C to §1910.66 [Reserved]
Appendix
D to §1910.66—Existing Installations (Mandatory)
Use
of the Appendix
Appendix
D sets out the mandatory building and equipment requirements for
applicable permanent installations completed after August 27,
1971, and no later than July 23, 1990 which are exempt from the
paragraphs (a), (b)(1), (b)(2), (c), (d), (e), and (f) of this
standard. The requirements in appendix D are essentially the same
as unrevised building and equipment provisions which previously
were designated as 29 CFR 1910.66 (a), (b), (c) and (d) and which
were effective on August 27, 1971.
Note:
All existing installations subject to this appendix shall also
comply with paragraphs (g), (h), (i), (j) and appendix C of the
standard 29 CFR 1910.66.
(a)
Definitions
applicable to this appendix—(1)
Angulated
roping.
A system of platform suspension in which the upper wire rope
sheaves or suspension points are closer to the plane of the
building face than the corresponding attachment points on the
platform, thus causing the platform to press against the face of
the building during its vertical travel.
(2)
ANSI.
American National Standards Institute.
(3)
Babbitted
fastenings.
The method of providing wire rope attachments in which the ends of
the wire strands are bent back and are held in a tapered socket by
means of poured molten babbitt metal.
(4)
Brake—disc
type.
A brake in which the holding effect is obtained by frictional
resistance between one or more faces of discs keyed to the
rotating member to be held and fixed discs keyed to the stationary
or housing member (pressure between the discs being applied
axially).
(5)
Brake—self-energizing
band type.
An essentially undirectional brake in which the holding effect is
obtained by the snubbing action of a flexible band wrapped about a
cylindrical wheel or drum affixed to the rotating member to be
held, the connections and linkages being so arranged that the
motion of the brake wheel or drum will act to increase the tension
or holding force of the band.
(6)
Brake—shoe
type.
A brake in which the holding effect is obtained by applying the
direct pressure of two or more segmental friction elements held to
a stationary member against a cylindrical wheel or drum affixed to
the rotating member to be held.
(7)
Building
face rollers.
A specialized form of guide roller designed to contact a portion
of the outer face or wall structure of the building, and to assist
in stabilizing the operators' platform during vertical travel.
(8)
Continuous
pressure.
Operation by means of buttons or switches, any one of which may be
used to control the movement of the working platform or roof car,
only as long as the button or switch is manually maintained in the
actuating position.
(9)
Control.
A system governing starting, stopping, direction, acceleration,
speed, and retardation of moving members.
(10)
Controller.
A device or group of devices, usually contained in a single
enclosure, which serves to control in some predetermined manner
the apparatus to which it is connected.
(11)
Electrical
ground.
A conducting connection between an electrical circuit or equipment
and the earth, or some conducting body which serves in place of
the earth.
(12)
Guide
roller.
A rotating, bearing-mounted, generally cylindrical member,
operating separately or as part of a guide shoe assembly, attached
to the platform, and providing rolling contact with building
guideways, or other building contact members.
(13)
Guide
shoe.
An assembly of rollers, slide members, or the equivalent, attached
as a unit to the operators' platform, and designed to engage with
the building members provided for the vertical guidance of the
operators' platform.
(14)
Interlock.
A device actuated by the operation of some other device with which
it is directly associated, to govern succeeding operations of the
same or allied devices.
(15)
Operating
device.
A pushbutton, lever, or other manual device used to actuate a
control.
(16)
Powered
platform.
Equipment to provide access to the exterior of a building for
maintenance, consisting of a suspended power-operated working
platform, a roof car, or other suspension means, and the requisite
operating and control devices.
(17)
Rated
load.
The combined weight of employees, tools, equipment, and other
material which the working platform is designed and installed to
lift.
(18)
Relay,
direction.
An electrically energized contactor responsive to an initiating
control circuit, which in turn causes a moving member to travel in
a particular direction.
(19)
Relay,
potential for vertical travel.
An electrically energized contactor responsive to initiating
control circuit, which in turn controls the operation of a moving
member in both directions. This relay usually operates in
conjunction with direction relays, as covered under the
definition, “relay, direction.”
(20)
Roof
car.
A structure for the suspension of a working platform, providing
for its horizontal movement to working positions.
(21)
Roof-powered
platform.
A powered platform having the raising and lowering mechanism
located on a roof car.
(22)
Self-powered
platform.
A powered platform having the raising and lowering mechanism
located on the working platform.
(23)
Traveling
cable.
A cable made up of electrical or communication conductors or both,
and providing electrical connection between the working platform
and the roof car or other fixed point.
(24)
Weatherproof.
Equipment so constructed or protected that exposure to the weather
will not interfere with its proper operation.
(25)
Working
platform.
The suspended structure arranged for vertical travel which
provides access to the exterior of the building or structure.
(26)
Yield
point.
The stress at which the material exhibits a permanent set of 0.2
percent.
(27)
Zinced
fastenings.
The method of providing wire rope attachments in which the splayed
or fanned wire ends are held in a tapered socket by means of
poured molten zinc.
(b)
General
requirements.
(1) Design requirements. All powered platform installations for
exterior building maintenance completed as of August 27, 1971, but
no later than [insert date, 180 days after the effective date],
shall meet all of the design, construction and installation
requirements of part II and III of the “American National
Standard Safety Requirements for Powered Platforms for Exterior
Building Maintenance ANSI A120.1-1970” and of this appendix.
References shall be made to appropriate parts of ANSI A120.1-1970
for detail specifications for equipment and special installations.
(2)
Limitation.
The requirements of this appendix apply only to electric powered
platforms. It is not the intent of this appendix to prohibit the
use of other types of power. Installation of powered platforms
using other types of power is permitted, provided such platforms
have adequate protective devices for the type of power used, and
otherwise provide for reasonable safety of life and limb to users
of equipment and to others who may be exposed.
(3)
Types
of powered platforms.
(i) For the purpose of applying this appendix, powered platforms
are divided into two basic types, Type F and Type T.
(ii)
Powered platforms designated as Type F shall meet all the
requirements in part II of ANSI A 120.1-1970, American National
Standard Safety Requirements for Powered Platforms for Exterior
Building Maintenance. A basic requirement of Type F equipment is
that the work platform is suspended by at least four wire ropes
and designed so that failure of any one wire rope will not
substantially alter the normal position of the working platform.
Another basic requirement of Type F equipment is that only one
layer of hoisting rope is permitted on winding drums. Type F
powered platforms may be either roof-powered or self-powered.
(iii)
Powered platforms designated as Type T shall meet all the
requirements in part III of ANSI A120.1-1970 American National
Standard Safety Requirements for Powered Platforms for Exterior
Building Maintenance, except for section 28, Safety Belts and Life
Lines. A basic requirement of Type T equipment is that the working
platform is suspended by at least two wire ropes. Failure of one
wire rope would not permit the working platform to fall to the
ground, but would upset its normal position. Type T powered
platforms may be either roof-powered or self-powered.
(iv)
The requirements of this section apply to powered platforms with
winding drum type hoisting machines. It is not the intent of this
section to prohibit powered platforms using other types of
hoisting machines such as, but not limited to, traction drum
hoisting machines, air powered machines, hydraulic powered
machines, and internal combustion machines. Installation of
powered platforms with other types of hoisting machines is
permitted, provided adequate protective devices are used, and
provided reasonable safety of life and limb to users of the
equipment and to others who may be exposed is assured.
(v)
Both Type F and Type T powered platforms shall comply with the
requirements of appendix C of this standard.
(c)
Type
F powered platforms—(1)
Roof
car, general.
(i) A roof car shall be provided whenever it is necessary to move
the working platform horizontally to working or storage positions.
(ii)
The maximum rated speed at which a power traversed roof car may be
moved in a horizontal direction shall be 50 feet per minute.
(2)
Movement
and positioning of roof car.
(i) Provision shall be made to protect against having the roof car
leave the roof or enter roof areas not designed for travel.
(ii)
The horizontal motion of the roof cars shall be positively
controlled so as to insure proper movement and positioning of the
roof car.
(iii)
Roof car positioning devices shall be provided to insure that the
working platform is placed and retained in proper position for
vertical travel and during storage.
(iv)
Mechanical stops shall be provided to prevent the traversing of
the roof car beyond its normal limits of travel. Such stops shall
be capable of withstanding a force equal to 100 percent of the
inertial effect of the roof car in motion with traversing power
applied.
(v)(a)
The operating device of a power-operated roof car for traversing
shall be located on the roof car, the working platform, or both,
and shall be of the continuous pressure weather-proof electric
type. If more than one operating device is provided, they shall be
so arranged that traversing is possible only from one operating
device at a time.
(b)
The operating device shall be so connected that it is not operable
until:
(1)
The working platform is located at its uppermost position of
travel and is not in contact with the building face or fixed
vertical guides in the face of the building; and
(2)
All protective devices and interlocks are in a position for
traversing.
(3)
Roof
car stability.
Roof car stability shall be determined by either paragraph (c)(3)
(i) or (ii) of this appendix, whichever is greater.
(i)
The roof car shall be continuously stable, considering overturning
moment as determined by 125 percent rated load, plus maximum dead
load and the prescribed wind loading.
(ii)
The roof car and its anchorages shall be capable of resisting
accidental over-tensioning of the wire ropes suspending the
working platform and this calculated value shall include the
effect of one and one-half times the value. For this calculation,
the simultaneous effect of one-half wind load shall be included,
and the design stresses shall not exceed those referred to in
paragraph (b)(1) of this appendix.
(iii)
If the load on the motors is at any time in excess of three times
that required for lifting the working platform with its rated load
the motor shall stall.
(4)
Access
to the roof car.
Safe access to the roof car and from the roof car to the working
platform shall be provided. If the access to the roof car at any
point of its travel is not over the roof area or where otherwise
necessary for safety, then self-closing, self-locking gates shall
be provided. Access to and from roof cars must comply with the
requirements of subpart D of this part.
(5)
Means
for maintenance, repair, and storage.
Means shall be provided to run the roof car away from the roof
perimeter, where necessary, and to provide a safe area for
maintenance, repairs, and storage. Provisions shall be made to
secure the machine in the stored position. For stored machines
subject to wind forces, see special design and anchorage
requirements for “wind forces” in part II, section
10.5.1.1 of ANSI A120.1-1970 American National Standard Safety
Requirements for Powered Platforms for Exterior Building
Maintenance.
(6)
General
requirements for working platforms.
The working platform shall be of girder or truss construction and
shall be adequate to support its rated load under any position of
loading, and comply with the provisions set forth in section 10 of
ANSI A120.1-1970, American National Standard Safety Requirements
for Powered Platforms for Exterior Building Maintenance.
(7)
Load
rating plate.
Each working platform shall bear a manufacturer's load rating
plate, conspicuously posted; stating the maximum permissible rated
load. Load rating plates shall be made of noncorrosive material
and shall have letters and figures stamped, etched, or cast on the
surface. The minimum height of the letters and figures shall be
one-fourth inch.
(8)
Minimum
size.
The working platform shall have a minimum net width of 24 inches.
(9)
Guardrails.
Working platforms shall be furnished with permanent guard rails
not less than 36 inches high, and not more than 42 inches high at
the front (building side). At the rear, and on the sides, the rail
shall not be less than 42 inches high. An intermediate guardrail
shall be provided around the entire platform between the top
guardrail and the toeboard.
(10)
Toeboards.
A four-inch toeboard shall be provided along all sides of the
working platform.
(11)
Open
spaces between guardrails and toeboards.
The spaces between the intermediate guardrail and platform
toeboard on the building side of the working platform, and between
the top guardrail and the toeboard on other sides of the platform,
shall be filled with metalic mesh or similar material that will
reject a ball one inch in diameter. The installed mesh shall be
capable of withstanding a load of 100 pounds applied horizontally
over any area of 144 square inches. If the space between the
platform and the building face does not exceed eight inches, and
the platform is restrained by guides, the mesh may be omitted on
the front side.
(12)
Flooring.
The platform flooring shall be of the nonskid type, and if of open
construction, shall reject a 9⁄16
-inch diameter ball, or be provided with a screen below the floor
to reject a 9⁄16
-inch diameter ball.
(13)
Access
gates.
Where access gates are provided, they shall be self-closing and
self-locking.
(14)
Operating
device for vertical movement of the working platform.
(i) The normal operating device for the working platform shall be
located on the working platform and shall be of the continuous
pressure weatherproof electric type.
(ii)
The operating device shall be operable only when all electrical
protective devices and interlocks on the working platform are in
position for normal service and, the roof car, if provided, is at
an established operating point.
(15)
Emergency
electric operative device.
(i) In addition, on roof-powered platforms, an emergency electric
operating device shall be provided near the hoisting machine for
use in the event of failure of the normal operating device for the
working platform, or failure of the traveling cable system. The
emergency operating device shall be mounted in a locked
compartment and shall have a legend mounted thereon reading: “For
Emergency Operation Only. Establish Communication With Personnel
on Working Platform Before Use.”
(ii)
A key for unlocking the compartment housing the emergency
operating device shall be mounted in a break-glass receptacle
located near the emergency operating device.
(16)
Manual
cranking for emergency operation.
Emergency operation of the main drive machine may be provided to
allow manual cranking. This provision for manual operation shall
be designed so that not more than two persons will be required to
perform this operation. The access to this provision shall include
a means to automatically make the machine inoperative electrically
while under the emergency manual operation. The design shall be
such that the emergency brake is operative at or below governor
tripping speed during manual operation.
(17)
Arrangement
and guarding of hoisting equipment.
(i) Hoisting equipment shall consist of a power-driven drum or
drum contained in the roof car (roof-powered platforms) or
contained on the working platform (self-powered platform).
(ii)
The hoisting equipment shall be power-operated in both up and down
directions.
(iii)
Guard or other protective devices shall be installed wherever
rotating shafts or other mechanisms or gears may expose personnel
to a hazard.
(iv)
Friction devices or clutches shall not be used for connecting the
main driving mechanism to the drum or drums. Belt or chain-driven
machines are prohibited.
(18)
Hoisting
motors.
(i) Hoisting motors shall be electric and of weather-proof
construction.
(ii)
Hoisting motors shall be in conformance with applicable provisions
of paragraph (c)(22) of this appendix, Electric Wiring and
Equipment.
(iii)
Hoisting motors shall be directly connected to the hoisting
machinery. Motor couplings, if used, shall be of steel
construction.
(19)
Brakes.
The hoisting machine(s) shall have two independent braking means,
each designed to stop and hold the working platform with 125
percent of rated load.
(20)
Hoisting
ropes and rope connections.
(i) Working platforms shall be suspended by wire ropes of either 6
× 19 or 6 × 37 classification, preformed or
nonpreformed.
(ii)
[Reserved]
(iii)
The minimum factor of safety shall be 10, and shall be calculated
by the following formula:
F
= S × N/W
Where
S
= Manufacturer's rated breaking strength of one rope.
N
= Number of ropes under load.
W
= Maximum static load on all ropes with the platform and its rated
load at any point of its travel.
(iv)
Hoisting ropes shall be sized to conform with the required factor
of safety, but in no case shall the size be less than 5⁄16
inch diameter.
(v)
Winding drums shall have at least three turns of rope remaining
when the platform has landed at the lowest possible point of its
travel.
(vi)
The lengthening or repairing of wire rope by the joining of two or
more lengths is prohibited.
(vii)
The nondrum ends of the hoisting ropes shall be provided with
individual shackle rods which will permit individual adjustment of
rope lengths, if required.
(viii)
More than two reverse bends in each rope is prohibited.
(21)
Rope
tag data.
(i) A metal data tag shall be securely attached to one of the wire
rope fastenings. This data tag shall bear the following wire rope
data:
(a)
The diameter in inches.
(b)
Construction classification.
(c)
Whether nonpreformed or preformed.
(d)
The grade of material used.
(e)
The manufacturer's rated breaking strength.
(f)
Name of the manufacturer of the rope.
(g)
The month and year the ropes were installed.
(22)
Electrical
wiring and equipment.
(i) All electrical equipment and wiring shall conform to the
requirements of subpart S of this Part, except as modified by ANSI
A120.1—1970 “American National Standard Safety
Requirements for Powered Platforms for Exterior Building
Maintenance” (see §1910.6). For detail design
specifications for electrical equipment, see part 2, ANSI
A120.1-1970.
(ii)
All motors and operation and control equipment shall be supplied
from a single power source.
(iii)
The power supply for the powered platform shall be an independent
circuit supplied through a fused disconnect switch.
(iv)
Electrical conductor parts of the power supply system shall be
protected against accidental contact.
(v)
Electrical grounding shall be provided.
(a)
Provisions for electrical grounding shall be included with the
power-supply system.
(b)
Controller cabinets, motor frames, hoisting machines, the working
platform, roof car and roof car track system, and noncurrent
carrying parts of electrical equipment, where provided, shall be
grounded.
(c)
The controller, where used, shall be so designed and installed
that a single ground or short circuit will not prevent both the
normal and final stopping device from stopping the working
platform.
(d)
Means shall be provided on the roof car and working platform for
grounding portable electric tools.
(e)
The working platform shall be grounded through a grounding
connection in a traveling cable. Electrically powered tools
utilized on the working platform shall be grounded.
(vi)
Electrical receptacles located on the roof or other exterior
location shall be of a weatherproof type and shall be located so
as not to be subject to contact with water or accumulated snow.
The receptacles shall be grounded and the electric cable shall
include a grounding conductor. The receptacle and plug shall be a
type designed to avoid hazard to persons inserting or withdrawing
the plug. Provision shall be made to prevent application of cable
strain directly to the plug and receptacle.
(vii)
Electric runway conductor systems shall be of the type designed
for use in exterior locations and shall be located so as not to be
subject to contact with water or accumulated snow. The conductors,
collectors, and disconnecting means shall conform to the same
requirements as those for cranes and hoists in subpart S of this
Part. A grounded conductor shall parallel the power conductors and
be so connected that it cannot be opened by the disconnecting
means. The system shall be designed to avoid hazard to persons in
the area.
(viii)
Electrical protective devices and interlocks of the weatherproof
type shall be provided.
(ix)
Where the installation includes a roof car, electric contact(s)
shall be provided and so connected that the operating devices for
the working platform shall be operative only when the roof car is
located and mechanically retained at an established operating
point.
(x)
Where the powered platform includes a powered-operated roof car,
the operating device for the roof car shall be inoperative when
the roof car is mechanically retained at an established operating
point.
(xi)
An electric contact shall be provided and so connected that it
will cause the down direction relay for vertical travel to open if
the tension in the traveling cable exceeds safe limits.
(xii)
An automatic overload device shall be provided to cut off the
electrical power to the circuit in all hoisting motors for travel
in the up direction, should the load applied to the hoisting ropes
at either end of the working platform exceed 125 percent of its
normal tension with rated load, as shown on the manufacturer's
data plate on the working platform.
(xiii)
An automatic device shall be provided for each hoisting rope which
will cut off the electrical power to the hoisting motor or motors
in the down direction and apply the brakes if any hoisting rope
becomes slack.
(xiv)
Upper and lower directional limit devices shall be provided to
prevent the travel of the working platform beyond the normal upper
and lower limits of travel.
(xv)
Operation of a directional limit device shall prevent further
motion in the appropriate direction, if the normal limit of travel
has been reached.
(xvi)
Directional limit devices, if driven from the hoisting machine by
chains, tapes, or cables, shall incorporate a device to disconnect
the electric power from the hoisting machine and apply both the
primary and secondary brakes in the event of failure of the
driving means.
(xvii)
Final terminal stopping devices of the working platform:
(a)
Final terminal stopping devices for the working platform shall be
provided as a secondary means of preventing the working platform
from over-traveling at the terminals.
(b)
The device shall be set to function as close to each terminal
landing as practical, but in such a way that under normal
operating conditions it will not function when the working
platform is stopped by the normal terminal stopping device.
(c)
Operation of the final terminal stopping device shall open the
potential relay for vertical travel, thereby disconnecting the
electric power from the hoisting machine, and applying both the
primary and secondary brakes.
(d)
The final terminal stopping device for the upper limit of travel
shall be mounted so that it is operated directly by the motion of
the working platform itself.
(xviii)
Emergency stop switches shall be provided in or adjacent to each
operating device.
(xix)
Emergency stop switches shall:
(a)
Have red operating buttons or handles.
(b)
Be conspicuously and permanently marked “Stop.”
(c)
Be the manually opened and manually closed type.
(d)
Be positively opened with the opening not solely dependent on
springs.
(xx)
The manual operation of an emergency stop switch associated with
an operating device for the working platform shall open the
potential relay for vertical travel, thereby disconnecting the
electric power from the hoisting machine and applying both the
primary and secondary brakes.
(xxi)
The manual operation of the emergency stop switch associated with
the operating device for a power-driven roof car shall cause the
electrical power to the traverse machine to be interrupted, and
the traverse machine brake to apply.
(23)
Requirements
for emergency communications.
(i) Communication equipment shall be provided for each powered
platform for use in an emergency.
(ii)
Two-way communication shall be established between personnel on
the roof and personnel on the stalled working platform before any
emergency operation of the working platform is undertaken by
personnel on the roof.
(iii)
The equipment shall permit two-way voice communication between the
working platform and
(a)
Designated personnel continuously available while the powered
platform is in use; and
(b)
Designated personnel on roof-powered platforms, undertaking
emergency operation of the working platform by means of the
emergency operating device located near the hoisting machine.
(iv)
The emergency communication equipment shall be one of the
following types:
(a)
Telephone connected to the central telephone exchange system; or
(b)
Telephones on a limited system or an approved two-way radio
system, provided designated personnel are available to receive a
message during the time the powered platform is in use.
(d)
Type
T powered platforms—(1)
Roof
car.
The requirements of paragraphs (c)(1) through (c)(5) of this
appendix shall apply to Type T powered platforms.
(2)
Working
platform.
The requirements of paragraphs (c)(6) through (c)(16) of this
appendix apply to Type T powered platforms.
(i)
The working platform shall be suspended by at least two wire
ropes.
(ii)
The maximum rated speed at which the working platform of
self-powered platforms may be moved in a vertical direction shall
not exceed 35 feet per minute.
(3)
Hoisting
equipment.
The requirements of paragraphs (c) (17) and (18) of this appendix
shall apply to Type T powered platforms.
(4)
Brakes.
Brakes requirements of paragraph (c)(19) of this appendix shall
apply.
(5)
Hoisting
ropes and rope connections.
(i) Paragraphs (c)(20) (i) through (vi) and (viii) of this
appendix shall apply to Type T powered platforms.
(ii)
Adjustable shackle rods in subparagraph (c)(20)(vii) of this
appendix shall apply to Type T powered platforms, if the working
platform is suspended by more than two wire ropes.
(6)
Electrical
wiring and equipment.
(i) The requirements of paragraphs (c)(22) (i) through (vi) of
this appendix shall apply to Type T powered platforms. “Circuit
protection limitation,” “powered platform electrical
service system,” all operating services and control
equipment shall comply with the specifications contained in part
2, section 26, ANSI A120.1-1970.
(ii)
For electrical protective devices the requirements of paragraphs
(c)(22) (i) through (viii) of this appendix shall apply to Type T
powered platforms. Requirements for the “circuit potential
limitation” shall be in accordance with specifications
contained in part 2, section 26, of ANSI A120.1-1970.
(7)
Emergency
communications.
All the requirements of paragraph (c)(23) of this appendix shall
apply to Type T powered platforms.
[54
FR 31456, July 28, 1989, as amended at 61 FR 9235, Mar. 7, 1996;
72 FR 7190, Feb. 14, 2007; 81 FR 82998, Nov. 18, 2016]
|


