Revised Final OMB Supporting Statement for 10 CFR 36
Revised Final OMB Supporting Statement for 10 CFR 36.docx
10 CFR Part 36 - Licenses and Radiation Safety Requirements for Irradiators
OMB: 3150-0158
FINAL OMB SUPPORTING STATEMENT
FOR
10 CFR PART 36
"LICENSES AND RADIATION SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
FOR IRRADIATORS"
(3150-0158)
---
EXTENSION
Description of the Information Collection
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission's (NRC) regulations in Title 10 of the Code of Federal Regulations (10 CFR) Part 36, contain requirements for the issuance of a license authorizing the use of sealed sources containing radioactive materials in irradiators used to irradiate objects or materials for a variety of purposes in research, industry, and other fields. This part also contains the radiation safety requirements for operating irradiators. These regulations were issued pursuant to the Atomic Energy Act of 1954, as amended, and the Energy Reorganization Act of 1974, as amended.
The regulations in 10 CFR Part 36 (as described in Subpart A) apply to panoramic, dry or wet storage irradiators, and underwater irradiators in which both the source and the products being irradiated are under water. They do not cover self-contained dry-source-storage irradiators, medical uses of sealed sources (such as teletherapy), or nondestructive testing (such as industrial radiography). The irradiators covered by this part have dose rates that exceed 5 grays (500 rads) per hour at 1 meter from the radioactive sealed sources in air or in water, as applicable for the irradiator type.
Subpart B of this part covers specific licensing requirements for obtaining a license or a license exemption. Subpart C lists the design and performance criteria for irradiators, including special requirements for sealed sources installed, licenses issued, and irradiator construction begun after July 1, 1993. The requirements for operating irradiators are covered in Subpart D. These include operator training, written operating and emergency procedures, personnel monitoring, radiation surveys, inspection, and maintenance. The records and reports required to ensure that the irradiator is being safely operated so that it poses no danger to the health and safety of the general public and the irradiator employees are listed in Subpart E.
A. Justification
1. Need for and Practical Utility of the Information Collection
The records that 10 CFR Part 36 requires the licensees to maintain will be used by the NRC or Agreement State inspectors to evaluate compliance with NRC regulations to ensure that public health and safety are protected. The reports required by 10 CFR Part 36 will be used to alert the NRC to any special problems that may be a threat to health and safety so that adequate protective actions can be taken.
The need for practical utility of the specific information collection requirements
of 10 CFR Part 36 are identified in Appendix A-10 CFR Part 36, Information Collection Requirements.
2. Agency Use of Information
Reports of operational data surrounding several significant safety occurrences at irradiators have been utilized by the NRC to develop the presently used safety criteria and license conditions. These requirements have precluded a repetition of these events at facilities and have resulted in safe operation of licensed facilities. The NRC's Office of Nuclear Material Safety and Safeguards (NMSS) monitors the operation of the irradiators in conjunction with regional staff assigned to inspect and monitor these facilities. The reports containing timely operational data are essential in order to ensure safe operation. If the reports indicate the possibility of a continuing hazard at the irradiator, the NRC will take action. In many situations an emergency inspection may be carried out. The records that 10 CFR Part 36 requires the licensees to maintain are reviewed during inspections, license renewals, and license amendment reviews to evaluate compliance with NRC radiation safety requirements for irradiators.
3. Reduction of Burden Through Information Technology
There are no legal obstacles to reducing the burden associated with this information collection. The NRC encourages respondents to use information technology when it would be beneficial to them. The NRC has issued Guidance for Electronic Submissions to the NRC which provides direction for the electronic transmission and submittal of documents to the NRC. Electronic transmission and submittal of documents can be accomplished via the following avenues: the Electronic Information Exchange process, which is available from the NRC's “Electronic Submittals” Web page, by Optical Storage Media (e.g. CD-ROM, DVD), by facsimile or by e-mail. It is estimated that approximately 4 percent of the potential responses are filed electronically.
4. Effort to Identify Duplication and Use Similar Information
No sources of similar information are available. There is no duplication of requirements.
5. Effort to Reduce Small Business Burden
While a number of the licensees are considered small businesses under the NRC's current definitions, all licensees have the same responsibility for safe operation of their irradiators. Therefore, there is no way to reduce the burden on small businesses by less frequent or less complete records or reports while maintaining the required level of safety.
Consequences to Federal Program or Policy Activities if the Collection Is Not
Collected or is Conducted Less Frequently
If the information is not collected, the NRC will not have a way to assess whether this category of licensee is operating within the radiation safety requirements applicable to the use of licensed material in irradiators.
7. Circumstances Which Justify Variation From OMB Guidelines
NRC Section 36.83 (b) requires licensees to submit significant safety events in a manner which varies from OMB guidelines.
Section 36.83 (b) requires the licensee to report significant safety events by telephone within 24 hours and in writing within 30 days: (1) in case emergency actions are necessary to reduce the hazard; (2) in case an emergency NRC inspection is necessary to ensure the problem is being handled properly; and (3) in case the problem is important enough that other licensees should be promptly informed.
Records that must be retained longer than 3 years are contained in Sections 36.81(a), 36.81(b), 36.81(d), 36.81(e), 36.81(k), 36.81(l), and 36.81(m). The justifications are as follows:
Section 36.81(a) requires that the licensee keep a copy of the current license, including the license conditions, documents incorporated by reference, and amendments, until license termination. It would be difficult to comply with the conditions of a license if there were no written record of the commitments the licensee has made.
Section 36.81(b) requires that the licensee keep records of each individual’s training, tests, and safety reviews provided to meet the requirements of Sections 36.51 (except Section 36.51(e)) until 3 years after the individual terminates work. The record retention is necessary for assuring that individuals who are currently working or who have recently worked in the facility are properly trained and the training records can be reviewed in accordance with the requirements.
Section 36.81(d) requires that the licensee keep a copy of the current written operating and emergency procedures until license termination. Written procedures are considered necessary to operate the irradiator safely and to protect the health and safety of the public and irradiator employees in the event of an emergency.
Section 36.81(e) restates, as a reminder, an existing 10 CFR Part 20 requirement that personnel dosimeters results be kept until license termination. This requirement is necessary to verify that the irradiator operators and other individuals for whom monitoring is required have not exceeded the dose limits in 10 CFR Part 20.
Section 36.81(k) restates, as a reminder, the requirements of Sections 30.51 and 30.41 for records of receipt, transfer, and disposal of all licensed sealed sources. These records are required for tracking the location of all byproduct material licensed under the Atomic Energy Act of 1954, as amended, and under Title II of the Energy Reorganization Act of 1974.
Section 36.81(l) requires that the licensee retain the design checks required by Section 36.39 and the construction control checks required by Section 36.41 until the license for the facility is terminated. As long as the facility is in operation, records of the design and construction of its principal safety features are important in maintaining and demonstrating the safety of the facility. In addition, they would be useful for correcting problems in the case where a vendor discovered a design flaw.
Section 36.81(m) restates, as a reminder, the existing requirements in Section 30.35(g) that the licensee keep records of information important to the safe and effective decommissioning of the facility until the site is released for unrestricted use. The information in these records is necessary for the safe and effective decommissioning of the facility.
8. Consultations Outside the NRC
Opportunity for public comment on the information collection requirements for this clearance package was published in the Federal Register on July 27, 2017 (82 FR34998). NRC emailed 4 licensees and no comments were received.
9. Payment or Gift to Respondents
Not applicable.
10. Confidentiality of Information
Confidential and proprietary information is protected in accordance with NRC regulations at 10 CFR 9.17(a) and 10 CFR 2.390(b).
11. Justification for Sensitive Questions
No sensitive information is requested under these regulations.
12. Estimated Burden and Burden Hour Cost
The estimates are based on submittals to and reviews by NRC in past years. The cost to licensees and applicants is calculated for 2017 at a rate of $263/hour for the professional staff that prepares the technical reports and records in response to the 10 CFR Part 36 information collection requirements.
The regulations in 10 CFR Part 36 establish licensing and radiation safety requirements for irradiator licensees, which include training requirements. As such, a number of the requirements under this Part represent third-party disclosure notifications, in which the licensees are providing training information to workers. In this renewal, third-party disclosure notifications have been captured as such in the burden tables.
Estimated Annual Cost to Respondents
NRC Licensees: The burden for NRC licensees to respond to the collection is shown in Tables 1, 2, and 3. The total burden for NRC licensees is 6,088 hours (93 hours reporting + 4,585 hours annual recordkeeping + 1,410 hours third-party disclosures) at a cost of $1,601,144 (6,088 hours x $263/hour).
Agreement State Licensees: The recordkeeping and reporting burden on the
Agreement State licensees is based on several assumptions, including:
The Agreement States implement 10 CFR Part 36 in exactly the same manner as the NRC.
The Agreement States license 6 times the number of irradiators that are covered by 10 CFR Part 36 than the NRC.
The frequency of incidents requiring reports from Agreement State licensees is the same for the NRC licensees.
The burden for Agreement State licensees to respond to the collection is shown in Tables 4, 5 and 6. The total burden for Agreement State licensees is 36,524 hours (554 hours reporting + 27,510 hours annual recordkeeping + 8,460 hours third-party disclosures) at a cost of $9,605,812 (36,524 hours x $263/hour).
Total Estimated Burden: 42,612 hours (647 reporting hours + 32,095 recordkeeping hours + 9,870 third-party disclosure hours).
NRC Licensees Agreement State Licensees
Reporting (hours) 93 554
Recordkeeping (hours) 4,585 27,510
Third-Party Disclosures (hours) 1,410 8,460
Total (hours) 6,088. 36,524
Total number of respondents: 70 (10 NRC licensees and 60 Agreement State
licensees).
Total number of responses: 2,389.3 (9.3 for reporting [2.8 NRC licensee and 6.5 Agreement State licensees], 70 for recordkeepers [10 NRC licensees and 60 Agreement State Licensees], and 2,310 for third-party disclosures [330 NRC licensees and 1,980 Agreement State licensees])
13. Estimate of Other Additional Costs
The quantity of records to be maintained is roughly proportional to the recordkeeping
burden. Based on the number of pages maintained for a typical clearance, the records
storage cost has been determined for 2017 to be equal to 0.0004 times the
recordkeeping burden cost. Therefore, the storage cost for this clearance is $3,376.39 (32,095 recordkeeping hours x 0.0004 x $263).
14. Estimated Annualized Cost to the Federal Government
The estimated burden on the NRC to review the records and reports is based on the frequency the NRC inspects the 10 CFR Part 36 licensees.
Number of
Category Licensees Inspection Cycle
Irradiators - Other, less than 3 Every 3 Years
10,000 Curies
Irradiators - Other, greater than 7 Yearly
10,000 Curies
The annual burden on the NRC to review records is estimated to be 8 hours per licensee per year, or 76 hours for the 9.5 NRC licensees inspected per year (7 licensees per year + 3 licensees every 3 years = 9.5 per year). The annual burden to review reports submitted by these licensees is estimated to be an additional 76 hours per year. The total is 152 hours per year. At a cost of $263 per hour, the total annual cost to the NRC is $39,976 per year. The annualized cost is based on staff's best estimate.
15. Reasons for Changes in Burden or Cost
The overall burden has increased by 8,564 hours from 34,048 to 42,612 hours due to an increased in the number of respondents from 56 to 70. This is due to a total increase of 14 irradiator licenses from NRC and Agreement State licensees from the 2014 numbers. The cost estimates have changed since the last clearance, as a result of a decrease in the fee rate per hour from $272 to $263/hour. The burden hour increase, 8564 hours, relates to an estimated average burden of 612 burden hours per respondent per year, multiplied by the 14 new respondents.”
16. Publication for Statistical Use
None.
17. Reason for Not Displaying the Expiration Date
The requirement is contained in a regulation. Amending the Code of Federal
Regulations to display information that, in an annual publication, could become obsolete would be unduly burdensome and too difficult to keep current.
18. Exceptions to the Certification Statement
None.
B. COLLECTIONS OF INFORMATION EMPLOYING STATISTICAL METHODS
Statistical methods are not used in this collection of information.
Table 1: NRC Licensee Recordkeeping Requirements for Part 36
Section |
Number of Recordkeepers |
Hours Per Recordkeeper |
Total Annual Burden Hours |
Cost @ $263 /Hr |
36.21(a)(1) |
10 |
0.5 |
5 |
$1,315 |
36.53(a), (b) |
10 |
60 |
600 |
$157,800 |
36.81(a) |
10 |
2 |
20 |
$5,260 |
36.81(b) |
10 |
20 |
200 |
$52,600 |
36.81(c) |
10 |
2 |
20 |
$5,260 |
36.81(d) |
10 |
40 |
400 |
$105,200 |
36.81(e) |
10 |
Addressed under OMB # 3150-0014 |
||
36.81(f) |
10 |
20 |
200 |
$52,600 |
36.81(g) |
10 |
4 |
40 |
$10,520 |
36.81(h) |
10 |
10 |
100 |
$26,300 |
36.81(i) |
10 |
200 |
2,000 |
$526,000 |
36.81(j) |
10 |
20 |
200 |
$52,600 |
36.81(k) |
10 |
Addressed under OMB # 3150-0017 |
||
36.81(l) |
10 |
80 |
800 |
$210,400 |
36.81(m) |
10 |
Addressed under OMB # 3150-0017 |
||
TOTALS |
10 |
458.5 |
4,585 |
$1,205,855 |
Table 2: NRC Licensee Reporting Requirements for Part 36
Section |
Description |
Number of Licensees |
Estimated Annual Responses |
Burden Hrs Per Response |
Total Annual Burden (Hrs) |
Cost @ $263 |
36.11 - See OMB clearance No. 3150-0120 |
Application for Specific License |
10 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
36.13(b),(c),(d),(e),(f),(g), and (h) - See OMB clearance 3150-0120 |
Requirements for Specific license |
10 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
36.17(a), (b) |
Application for exemption |
10 |
1 |
8 |
8 |
2,104 |
36.19 (a) and (b) |
Request for written statements |
10 |
0.5 |
10 |
5 |
1,315 |
36.69(a), (b) |
Irradiation of explosives or flammable materials |
10 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
36.83(a), (b) |
Reports |
10 |
0.8 |
100 |
80 |
21,040 |
TOTALS |
|
10 |
2.8 |
|
93 |
$24,459 |
Notes: * Burden calculates only those events that would not be reported under 30.50(b).
Table 3: NRC Licensee Third-Party Disclosures for Part 36
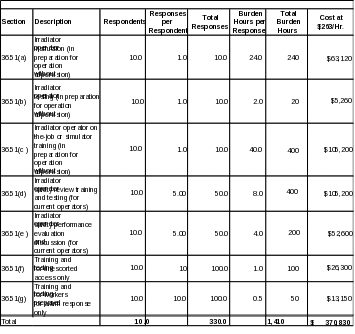
Table 4: Agreement State Licensee Recordkeeping Requirements for Part 36
Section |
Number of Recordkeepers |
Hours Per Recordkeeper |
Total Annual Burden Hours |
Cost @ $263/Hr |
36.21(a)(1) |
60 |
0.5 |
30 |
$7,890 |
36.53(a), (b) |
60 |
60.0 |
3,600 |
$946,800 |
36.81(a) |
60 |
2.0 |
120 |
$31,560 |
36.81(b) |
60 |
20.0 |
1,200 |
$315,600 |
36.81(c) |
60 |
2.0 |
120 |
$31,560 |
36.81(d) |
60 |
40.0 |
2,400 |
$631,200 |
36.81(e) |
60 |
Addressed under OMB # 3150-0014 |
||
36.81(f) |
60 |
20.0 |
1,200 |
$315,600 |
36.81(g) |
60 |
4.0 |
240 |
$63,120 |
36.81(h) |
60 |
10.0 |
600 |
$157,800 |
36.81(i) |
60 |
200.0 |
12,000 |
$3,156,000 |
36.81(j) |
60 |
20.0 |
1,200 |
$315,600 |
36.81(k) |
60 |
Addressed under OMB # 3150-0017 |
||
36.81(l) |
60 |
80.0 |
4,800 |
$1,262,400 |
36.81(m) |
60 |
Addressed under OMB # 3150-0017 |
||
TOTALS |
60 |
|
27,510 |
$7,235,130 |
Table 5: Agreement State Licensee Reporting Requirements for Part 36
Section |
Description |
Number of Licensees |
Estimated Annual Responses |
Burden Hrs Per Response |
Total Annual Burden (Hrs) |
Cost @ $263 |
36.11 - See OMB clearance No. 3150-0120 |
Application for Specific License |
60 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
$0 |
36.13(b),(c),(d),(e),(f),(g), and (h) - See OMB clearance 3150-0158 |
Requirements for Specific license |
60 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
$0 |
36.17(a), (b) |
Application for exemption |
60 |
3 |
8 |
24 |
$6,312 |
36.19 (a) and (b) |
Request for written statements |
60 |
3 |
10 |
30 |
$7,890 |
36.69(a), (b) |
Irradiation of explosives or flammable materials |
60 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
36.83(a), (b) |
Reports |
60 |
5 |
100 |
500 |
$131,500 |
TOTALS |
|
60 |
6.5 |
|
554 |
$145,702 |
Notes: * Burden calculates only those events that would not be reported under ' 30.50(b).
Table 6: Agreement State Licensee Third-Party Disclosures for Part 36
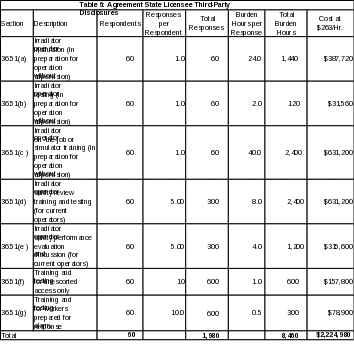
Appendix A- 10 CFR Part 36, Information Collection Requirements
Section 36.11 states how a person may file an application for a specific license
authorizing the use of a sealed source in an irradiator on NRC Form 313, "Application for Material License," and where the application must be mailed. The information on NRC Form 313 is used by the NRC to determine whether the applicant's equipment, procedures, and personnel are adequate to protect public health and safety. NRC Form 313 has previously been cleared under OMB Clearance No. 3150-0120, which should be referred to for additional supporting information, burden and cost data.
Section 36.13 describes the information that must be included in an application for a specific license for an irradiator if it is to be approved. This information is reviewed by the NRC staff to determine if the applicant's training program, operating and emergency procedures, organizational structure, radiation safety program, personnel qualifications, and inspection and maintenance procedures will provide adequate protection of the public health and safety.
Section 36.17(a) allows an applicant to apply for an exemption from the requirements in 10 CFR Part 36. This information is used by the Commission to grant exemptions from the requirements in this part as long as they are authorized by law and will not endanger life or property or the common defense and security.
Section 36.17(b) allows applicants for a license or for amendment of a license authorizing use of teletherapy-type units for irradiation of materials or objects to include proposed alternatives to the requirements in this part in their application. The Commission reviews this information to determine if the applicant provides adequate rationale for the proposed alternatives and demonstrates that they are likely to provide an adequate level of safety for workers and the public. The requests in Section 36.17 are part of the application process under Section
36.13 and, thus, the burden is covered under that section.
Section 36.19(a) and (b) allows the Commission to request additional information. Paragraph (a) of this section allows the Commission to request any additional information that NRC may need to determine whether or not the application should be granted or denied. Paragraph (b) allows the Commission to request written statements to determine whether a license should be modified, suspended, or revoked. This section codifies a requirement (found in Section 182 of the Atomic Energy Act) that licensees must supply any additional information required by NRC to assure that health and safety will be protected.
Additional information is sometimes needed to clarify information submitted in the
application, or to rectify deficiencies in proposed or existing programs for
protection of the public health and safety, the common defense and security, or the environment. The additional information submitted is reviewed by various NRC organizational units to assess the adequacy of the applicant's physical
plant, procedures, and plans for protection of the public health and safety. The NRC review and the findings therefrom form the basis for NRC decisions concerning the issuance, modification, or revocation of licenses authorizing the use of sealed sources containing radioactive materials in irradiators.
Section 36.21(a)(1) requires that sealed sources installed after July 1, 1993, must have a certificate of registration issued under 10 CFR 32.210. The certificate of registration demonstrates that the source design has been reviewed and approved by either the NRC or an Agreement State.
Section 36.51(a), (b), and (c) list requirements that individuals must fulfill before they are permitted to operate an irradiator without a supervisor present. Paragraph (a) of this section requires that before an individual is permitted to operate an irradiator without a supervisor present, the individual must be instructed in:
(1) The fundamentals of radiation protection applied to irradiators;
(2) The requirements of parts 19 and 36 of NRC regulations that are relevant to the irradiator;
(3) The operation of the irradiator;
(4) Those operating and emergency procedures listed in 36.53 that the individual is responsible for performing;
(5) Case histories of accidents or problems involving irradiators.
Paragraph (b) requires that before an individual is permitted to operate an irradiator without a supervisor present, the individual shall pass a written test on the instruction received consisting primarily of questions based on the licensee’s operating and emergency procedures that the individual is responsible for performing and other operations necessary to safely operate the irradiator without supervision.
Paragraph (c) requires that before an individual is permitted to operate an irradiator without a supervisor present, the individual must have received
on-the-job training or simulator training in the use of the irradiator as described in the license application and shall demonstrate the ability to perform those portions of the operating and emergency procedures that he or she is to perform.
These training requirements listed in 36.51(a), (b), and (c) ensure that individuals permitted to operate the irradiator without supervision have been adequately prepared for their responsibilities.
Section 36.51(d) and (e) list requirements that must be completed at least annually for irradiator operators. Paragraph (d) of this section requires that the licensee shall conduct safety reviews for irradiator operators at least annually. The licensee shall give each operator a brief written test on the information. Each safety review must include, to the extent appropriate: (1) any changes in operating and emergency procedures since the last review; (2) any changes in regulations and license conditions since the last review; (3) reports on recent
accidents, mistakes, or problems that have occurred at irradiators, if any; (4) relevant results of inspections of operator safety performance; (5) relevant results of the facility’s inspection and maintenance checks; and (6) a drill to practice an emergency or abnormal event procedure.
Paragraph (e) of this section requires that the licensee shall evaluate the safety performance of each irradiator operator at least annually to ensure that regulations, license conditions, and operating and emergency procedures are followed. The licensee shall discuss the results of the evaluation with the operator on how to correct any mistakes or deficiencies observed.
These training requirements listed in 36.51(d) and (e) ensure that licensees provide updated their irradiator operators with updated safety information and changes to regulations, as well as evaluate their safety performance at least annually. The purpose is to ensure continued safe operation of the irradiator.
Section 36.51(f) requires that individuals who will be permitted unescorted access to the radiation room of the irradiator or the area around the pool of an underwater irradiator, but who have not received the training required for operators and the radiation safety officer, shall be instructed and tested in any precautions they should take to avoid radiation exposure, any procedures or parts of procedures listed in 36.53 that they are expected to perform or comply with, and their proper response to alarms required in this part. The purpose of these requirements is to ensure that unescorted individuals (without operator or radiation safety officer training) are prepared safely perform their responsibilities and access potentially high-radiation areas.
Section 36.51(g) requires that individuals who must be prepared to respond to alarms required by 36.23(b), 36.23(i), 36.27(a), 36.29(a), 36.29(b), and 36.59(b) shall be trained and tested on how to respond. Each individual shall be retested at least once a year. The purpose of this requirement is to ensure that individuals who must be prepared to respond to alarms are adequately trained to safely perform their responsibilities.
Section 36.53(a) requires licensees to have and follow written operating procedures. Paragraph (a) lists the operating, monitoring, surveying, testing, and inspection procedures that must be addressed in the licensee's written operating procedures. The procedures ensure there is a standard way of safely operating the irradiator that can be followed by all personnel and reviewed by NRC inspectors.
Section 36.53(b) requires licensees to have and follow emergency or abnormal event procedures, appropriate for the irradiator type. Paragraph (b) lists the types of emergency or abnormal events that must be addressed in the licensee's written emergency procedures. The purpose is to have preplanned, approved procedures for responding to emergencies.
Section 36.69(a) prohibits the irradiation of explosive material, unless the licensee has applied for and received prior written approval. The purpose of this section is to assure that the licensee can demonstrate that detonation of the explosive would not rupture the sealed sources, injure personnel, damage safety systems, or cause radiation overexposures of personnel.
Section 36.69(b) prohibits the irradiation of more than small quantities of flammable material (flash point below 140 degrees F) in panoramic irradiators unless the licensee has received prior written authorization from the Commission. The application must demonstrate that the licensee can control a fire in the radiation room without damage to the sealed sources or safety systems and without radiation overexposures of personnel.
Section 36.81 states the records that a licensee must maintain and the retention periods for these records. These are as follows:
a) A copy of the license, license conditions, documents incorporated into a
license by reference, and amendments thereto until superseded or until the
NRC terminates the license. These documents must be maintained so that
the licensee has a record of the commitments that it has made and must
comply with.
b) Records of each individual's training, tests, and safety evaluations provided to
meet the requirements of Section 36.51 (except Section 36.51(e)) until 3 years
after the individual terminates work. The records allow NRC inspectors to
verify that the irradiator operators have received the required training.
c) Records of the annual evaluations of the safety performance of irradiator
operators required by Section 36.51(e) for 3 years after the evaluation. The
records allow NRC inspectors to verify that the licensee has been evaluating
the performance of its operators.
d) A copy of the current operating and emergency procedures required by
Section 36.53, until superseded or the NRC terminates the license. Records
of the radiation safety officer's review and approval of changes in the
procedures must be retained for 3 years from the date of the change. The
records allow the operators to have access to an up-to-date set of written
operating procedures, so that they can operate the irradiator properly and
safely. The procedures may be discarded immediately after a new or revised
procedure is approved.
e) Personnel dosimeters results required by Section 36.55, until the license is
terminated by the Commission. The records allow NRC inspectors to verify
that the licensee is complying with the NRC's radiation dose limits. This
requirement in 10 CFR Part 36 is a reminder to licensees of the requirement
in Section 20.2106, which is covered under OMB Clearance No. 3150-0014.
f) Records of radiation surveys required by Section 36.57 for 3 years from the
date of the survey. The records allow NRC inspectors to verify that the
required radiation surveys have been done and radiation dose limits are
being complied with.
g) Records of radiation survey meter calibrations required by Section 36.57 and
pool water conductivity meter calibrations required by Section 36.63(b) for 3
years from the date of each calibration. The records allow the NRC
inspectors to verify that required calibrations have been performed.
h) Records of the results of leak tests required by Section 36.59(a) and the
results of contamination checks required by Section 36.59(b) for 3 years
from the date of each test. The records allow NRC inspectors to verify that
the required tests to detect radioactive contamination have been done.
I) Records of inspection and maintenance checks required by Section 36.61 for
3 years. The records allow NRC inspectors to verify that the licensee is
making necessary checks to maintain the irradiator in safe working condition.
j) Records of major malfunctions, significant defects, operating difficulties or
irregularities, and major operating problems that involve required radiation
safety equipment for 3 years after the repairs are completed. These records
allow NRC inspectors to verify that the irradiator is being properly maintained
and repaired. The records also allow NRC to identify generic problems that
may decrease safety.
k) Records of the receipt, transfer, and disposal of licensed sealed sources, as required by Sections 30.51 and 30.41. This is a reminder that the
requirements of Sections 30.51 and 30.41 must be met. (Agreement States
must have requirements compatible with those of Sections 30.51 and 30.41.)
For Section 30.51 recordkeeping requirements for byproduct materials, the
licensee shall retain each record of receipt as long as the material is
possessed and 3 years following transfer or disposal of the material. The
licensee who transfers the material shall retain each record of transfer for 3
years after each transfer unless a specific part in this chapter dictates
otherwise. The licensee who disposes of the material shall retain each
record of disposal until the license is terminated. These records allow NRC
to track the possession, use, and location of byproduct material. The
collection of this information has been previously cleared under
OMB Clearance No. 3150-0017.
l) Records of the design checks required by Section 36.39 and the construction
control checks required by Section 36.41 until the license is terminated. The
records must be signed and dated. The title or qualification of the person
signing must be included. These records allow NRC inspectors to assure
that the irradiator was properly and carefully designed and constructed.
m) Records related to decommissioning of the irradiator as required by Section
30.35(g) until the site is released for unrestricted use. This reference is
added for completeness to remind the licensee that 10 CFR Part 30 requires
certain records that are related to decommissioning. The information in these
records is necessary for the safe and effective decommissioning of the
facility.
Section 36.83(a) requires that, in addition to any other NRC reporting requirements, the licensee shall report the following events if not reported under other parts of NRC regulations:
(1) Source stuck in unshielded position.
(2) Any fire or explosion in radiation room.
(3) Damage to the source racks.
(4) Failure of the cable or drive mechanism used to move the source racks.
(5) Inoperability of the access control system.
(6) Detection of a radiation source by the product exit monitor.
(7) Detection of radioactive contamination attributable to licensed
radioactive material.
(8) Structural damage to the pool liner or walls.
(9) Abnormal water loss or leakage from the source storage pool.
(10) Pool water conductivity exceeding 100 microsiemens per centimeter.
Section 36.83(b) requires that the events listed in Section 36.83(a) must be reported by telephone within 24 hours as described in Section 30.50(c)(1), and in writing within 30 days as described in Section 30.50(c)(2). The purposes of these reports are to ensure that the licensee has properly corrected a potentially hazardous situation and to determine if any class of irradiators might have generic safety problems that should be corrected.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | FINAL OMB SUPPORTING STATEMENT FOR |
| Author | tud |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-21 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy