Attachment 2 - claims analysis results
CMS-10675_Attachment_2_Results_from_Claims_Analysis_051818_508.docx
Evaluation of the CMS Quality Improvement Organizations: Medication Safety and Adverse Drug Event Prevention (CMS-10675)
Attachment 2 - claims analysis results
OMB: 0938-1356
CMS-10675 Attachment 2
Readmission Rates for Medicare Beneficiaries Using High-Risk Medications (HRM) by Provider’s Participation in the QIN-QIO Program to Prevent Adverse Drug Events: Results from Preliminary Analysis of Medicare Claims (QIN-QIO Implementation Begins January 2015)
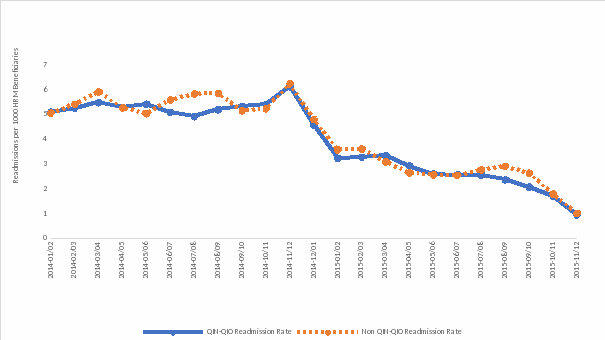
Figure 1. All-Cause Readmissions, HRM Beneficiaries*
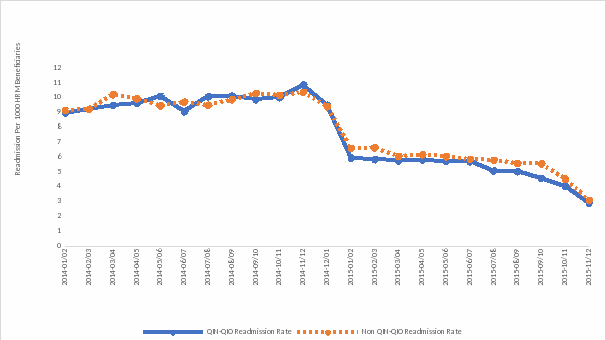
Figure 2. Readmissions Related to Anticoagulants per 1,000 HRM Beneficiaries
Figure 3. Readmissions Related to Diabetes Agents per 1,000 HRM Beneficiaries

Figure 4. Readmissions Related to Opioids per 1,000 HRM Beneficiaries
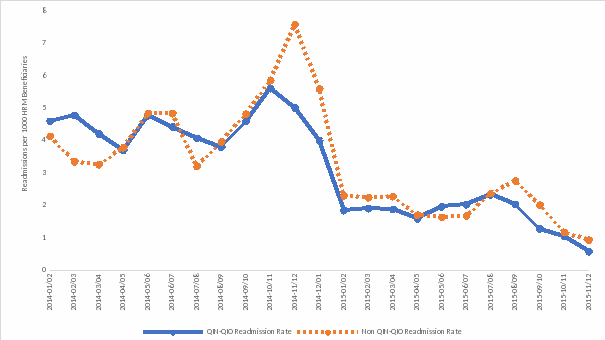
* Readmissions due to any cause were reduced more for beneficiaries exposed to the QIN-QIO program compared to beneficiaries in the Non-QIN-QIO group by about 8% (OR = 0.92 [95% CI, 0.88-0.96] p <.0001). No statistically significant differences between groups were observed for readmission rates due to specific drug classes.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | Attachment 2: Readmission Rates for Medicare Beneficiaries Using High-Risk Medications (HRM) by Provider’s Participation in the |
| Subject | Annual survey of quality improvement activities in CMS nursing homes both participating in and not participating in the QIN-QIO |
| Author | Booz Allen Hamilton |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-20 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy