SSB_NEARS_20190515 updated
SSB_NEARS_20190515 updated.docx
National Environmental Assessment Reporting System (NEARS)
OMB: 0920-0980
National Environmental Assessment Reporting System (NEARS)
OMB Control No. 0920-0980 (Expiration Date: 08/31/2019)
Revision
Supporting Statement Part B –
Collections of Information Employing Statistical Methods
Program Official: Laura G. Brown, Ph.D.
Title: Lead Behavioral Scientist
Phone: 770-488-4332
Email: [email protected]
Fax: 770-488-7310
Date: May 15, 2019
Table of Contents
B.1. Respondent Universe and Sampling Methods 3
B.2. Procedures for the Collection of Information 3
B.3. Methods to Maximize Response Rates and Deal with No Response 5
B.4. Test of Procedures or Methods to be Undertaken 5
Part B. Collections of Information Employing Statistical Methods
B.1. Respondent Universe and Sampling Methods
Statistical methods will not be used to select respondents for this data collection. All food safety programs in the United States (U.S.) will be invited to participate; however, participation is voluntary. Programs that participate in NEARS will report data on all outbreaks occurring in their jurisdictions. We expect that program participation will increase over time. However, until all eligible programs are participating, a limitation of our data will be that it applies to only those jurisdictions participating in NEARS.
State, local, tribal, and territorial food safety programs will report data into NEARS. There are approximately 3,000 such food safety programs in the U.S.
Although the data reported through this system are collected by food safety programs, they are not collected on food safety programs or personnel. Instead, they are collected primarily on foodborne illness outbreaks. Specifically, data collected by food safety programs during their investigation of foodborne illness outbreaks will be reported into NEARS. These data will provide information on environmental factors associated with outbreaks.
Data on all outbreaks occurring in the jurisdictions of participating food safety programs (the NEARS ‘catchment area’) will be reported to NEARS. Thus, we will be utilizing a convenience sample of voluntary participating programs and not obtaining a statistical sample. In the future, should a nationally representative program evolve, we may be able to generalize our data. Currently, we will describe the population of outbreaks solely in the NEARS catchment area and the environmental factors associated with them, and we will not generalize the data as nationally representative.
B.2. Procedures for the Collection of Information
Data Collection
Prior to collecting data, all food safety program personnel participating in NEARS will be encouraged to attend training for NEARS. These staff will be encouraged to attend a Skype Meeting (i.e., webinar) training session conducted by CDC staff (Attachment 4). This training is voluntary and will cover identifying environmental factors, logging in and entering data into the web-based NEARS data entry system, and troubleshooting problems. There will be no website, form, or presentation document associated with this training. Instead, CDC personnel will be guiding participants through the NEARS data entry system. Attachment 4 contains a brief description of the training.
Although not a requirement, food safety program personnel participating in NEARS will also be encouraged to complete CDC’s Environmental Assessment Training Series (EATS) (Attachment 5). This e-Learning course provides training on how to use a systems approach in foodborne illness outbreak environmental assessments. Participants acquire in-depth skills and knowledge to investigate foodborne illness outbreaks as a member of a larger outbreak response team, identify an outbreak’s environmental causes, and recommend appropriate control measures. The course is presented in the context of a simulated virtual environment where participants can interact and practice the skills being learned. Attachment 5 contains a brief description of the training.
There are two data collection activities. For the first activity, participating food safety programs will record all their environmental assessment data using pen-and -paper form (Attachment 6) and then enter all their data into the secure NEARS web-based system (Attachment 7). The respondents for this activity are the food safety program personnel participating in NEARS. This activity will be done once for each outbreak.
The second activity is the manager interview that will be conducted at each establishment associated with an outbreak (Attachment 8). The respondents for this activity are the retail food managers of the outbreak establishments. Manager interviews are a routine part of outbreak investigations; however, food safety program personnel participating in NEARS conduct a structured interview, and will thus conduct their interviews slightly differently than they would if they were not participating in NEARS.
Data analysis results will be shared informally with participating sites through annual data summary reports and presentations during NEARS quarterly webinars. Results will also be shared with other stakeholders (e.g., NORS Team) and the food safety and environmental public health community through presentations at meetings and conferences, peer-reviewed publications in scientific journals, and possibly ‘plain language’ summaries on the CDC website. Results will be presented in aggregate form.
The results will be used to develop recommendations for food safety and environmental public health programs and the retail food industry. For example, if data collection identifies specific environmental antecedents are associated with certain foodborne outbreaks, CDC can develop recommendations that address these unsafe polices and/or practices and disseminate the information to environmental public health programs and the retail food industry.
Quality Control Procedures
CDC personnel will periodically review the data from each site, and perform quality assurance procedures to check for data entry errors. They will provide reports to each program about the quality of their data. CDC personnel will use these reports to highlight weaknesses in data and recommend ways to improve the quality of the data.
Potential Biases
The act of observing workers during environmental assessments may influence their performance and behavior on work-related tasks. In other words, the workers may not respond naturally when they know they are being observed. However, for the most part, those collecting these data will be experienced and will take measures (such as remaining unobtrusive and engaging in activities that will place workers more at ease) to minimize this bias when possible.
The manager interview data may be influenced by social desirability bias - the tendency for people to report greater levels of socially desirable behavior (such as safe food preparation practices) than they actually engage in, or to report their best behavior rather than their typical or worst behavior.
Any presentation of these data will acknowledge these potential biases and include a discussion of how they impact data interpretation.
B.3. Methods to Maximize Response Rates and Deal with No Response
Program Response
We have been and will continue to engage in activities to promote and encourage food safety program participation in NEARS. We have presented at multiple conferences attended by those responsible for outbreak investigation (e.g., National Environmental Health Association, Council to Improve Foodborne Outbreak Response, etc.). We will hold informational conference calls with programs interested in NEARS. During these calls, we will attempt to identify barriers to NEARS participation and address those barriers. Our goal is to achieve close to 100% participation in NEARS.
B.4. Test of Procedures or Methods to be Undertaken
Development of Revisions
A work group of experienced foodborne outbreak investigators and NEARS participants developed the proposed revisions to the instrument, after extensive discussion. Thus, the revisions and discussions were based on the collective experience and expertise of these investigators. For example, added questions were ones that these investigators have regularly used in the course of their investigations, and many of the clarification revisions were ones investigators have had to regularly make in the field to obtain the desired data. Thus, although these revisions were not formally cognitively tested, we feel confident that the revisions will lead to improved flow and comprehension, and higher quality data. Nevertheless, we will regularly obtain feedback from NEARS users on the data collection instrument and experience, and routinely assess data quality, and will respond to any identified issues.
Future Revisions
The data collection instrument to be used for the NEARS was previously developed by the Environmental Health Specialists Network (EHS-Net) (See Attachments 6, 7, and 8). As food safety programs beyond the EHS-Net participants continue using the instrument, we expect that they will identify some components of the instrument that need revision. We expect these revisions to be minor. We plan to review respondents’ revision comments and questions on an annual basis to determine the nature and scope of requested revisions. Annual review of data may also reveal minor needed changes. Should we identify the need for changes to the data collection instruments, we will submit a nonmaterial or non-substantive change request to OMB for approval. For major changes to the instruments or methods, a full revision information collection request (ICR) will be submitted for Paperwork Reduction Act (PRA) clearance.
Data Analysis Plan
The three main goals of this data collection are to:
Describe foodborne illness outbreaks and outbreak responses.
Describe environmental factors (environmental antecedents and contributing factors) associated with outbreaks.
Describe the associations between environmental antecedents and contributing factors to outbreaks.
To address the first goal of this data collection, describe foodborne illness outbreaks and outbreak responses, we will conduct descriptive analyses (frequencies, means, etc.) to describe:
outbreaks (Table B.4.1 contains the variables included in these descriptive analyses)
outbreak responses (Table B.4.2 contains the variables included in these descriptive analyses).
Table B.4.1. Variables included in descriptive analyses of outbreaks
Question Number |
Question |
Justification |
I_1 |
Did the exposure(s) take place in a single or multiple locations? |
Describe where the outbreak took place. |
I_2 |
Did the exposure(s) occur in a single state or multiple states? |
|
I_3 |
Did the exposure(s) happen in a single county/township/parish or multiple counties/ townships/parishes? |
|
I_4 |
How many food service establishment locations within your jurisdiction were associated with this outbreak? |
|
I_5 |
How many environmental assessments conducted at foodservice establishments in your jurisdiction as part of this outbreak? |
Describe whether environmental assessments were conducted. |
I_5a |
Why were no environmental assessments conducted in your jurisdiction as a part of this outbreak? |
Describe barriers to conducting environmental assessments. |
I_6 |
How many non-food service establishments within your jurisdiction were associated with this outbreak? |
Describe whether any non-food service establishments were associated with the outbreak. |
I_6a |
How many environmental assessments were conducted at non-food service establishments in your jurisdiction as part of this outbreak? |
Describe how many environmental assessments were conducted in non food service establishments. |
I_7 |
Was a primary agent identified (suspected or confirmed) in this outbreak? |
Describe the agent and serotype. |
I_7a |
What was the identified agent?
|
|
I_7b |
Was a serotype identified for this outbreak? |
|
I_7c |
What was the identified serotype? |
|
I_8 |
Was this outbreak reported to a state or local Communicable Disease Surveillance Program? |
This information will be used to help connect the NEARS data to existing epidemiological and laboratory data reported to the state. |
I_8a |
Select the state or local surveillance system(s) where this outbreak was reported. |
|
I_9 |
Was this outbreak reported to a national surveillance system? |
This information will be used to help connect the NEARS data to existing epidemiological and laboratory data reported to other national surveillance systems. |
I_9a |
Select the national surveillance system(s) where this outbreak was reported and record the corresponding reporting number. |
|
I_10 |
Was a specific ingredient or multi-ingredient food suspected or confirmed in this outbreak? |
Describe ingredients and foods associated with the outbreak. |
I_10a |
If an ingredient/food was not suspected or confirmed, explain why this outbreak was considered foodborne. |
|
I_11 |
Provide any comments that would help describe the foods involved in this outbreak. |
|
Va_1 |
What is the name of the suspected or confirmed ingredient / food vehicle? |
|
Va_2 |
Is this food a single specific ingredient or multi-ingredient? |
|
I_11 |
Were any contributing factors identified in this outbreak? |
Describe contributing factors to the outbreak. |
VII_1 |
Which contributing factors was identified? |
|
VII_2 |
In your judgment, was this the primary contributing factor to this outbreak? |
|
VII_3 |
Briefly explain why this is a contributing factor in this outbreak. |
|
VII_4 |
When did this factor most likely occur? |
|
Va_3 |
Select the reason that best describes how this single specific ingredient or multi ingredient food was implicated in the outbreak. |
Describes the type of information used to determine the food associated with the outbreak. |
Va_4 |
Which best describes the food preparation process used for this specific ingredient or multi-ingredient food before consumption? |
Describe the preparation of the suspected ingredient/food associated with the outbreak. |
Va_5 |
During the likely time the ingredient/food was prepared, were any events noted that appeared to be different from the ordinary operating circumstances or procedures, as described by managers and/or workers? |
Describe the circumstances of the outbreak. |
Va_5a |
How would those differing events best be characterized? |
|
V1_1 |
Describe the agent found in the sample. |
Describe sample agents. |
VI_2 |
Where was the sample taken? |
|
VI_3 |
Provide any other information about the sample. |
Table B.4.2 Variables included in descriptive analyses of outbreak responses
Question Number |
Question |
Justification |
I_12 |
What activities were conducted during the outbreak investigation to try to identify the contributing factors? |
Describe outbreak investigation activities. |
I_13 |
Please rate the quality of communication between the food regulatory program and the communicable disease control program during this outbreak investigation. |
Describe communication during the outbreak investigation. |
I_16 |
Were any immediate control measures implemented for this outbreak? |
Describe outcomes of the outbreak investigation. |
I_16a |
If control measures were implemented, briefly describe this measures. |
Describe outcomes of the outbreak investigation. |
II_1 |
Date the establishment was identified for an environmental assessment |
Describe how long it takes to respond to outbreaks with an environmental assessment. |
II_2 |
Date of first contact with establishment management |
|
II_3 |
Number of visits to the establishment to complete this environmental assessment |
Describe environmental assessment responses. |
II_4 |
Number of contacts with the establishment other than visits to complete this environmental assessment |
|
II_7 |
Was a translator needed to communicate with the kitchen manager during the environmental assessment? |
Describe whether language and communication are issues in collecting information for environmental assessments. |
II_7a |
Was a translator used to communicate with the kitchen manager? |
|
II_8 |
Was a translator needed to communicate with the food workers during the environmental assessment? |
|
II_8a |
Was a translator used to communicate with the food workers? |
|
II_13 |
Were any samples taken in the establishment? |
Describe sampling practices |
II_13a |
Where were they taken? |
|
II_13b |
What foods or ingredients were sampled? |
|
III_1a |
How long was the interview? |
|
III_1 |
Date the manager interview was initiated |
Describe the time from identification/contact until specific environmental assessment activities are conducted. |
IV_1a |
How long was the observation? |
|
IV_1 |
Date the observation was initiated |
To address the second goal of this data collection, describe environmental factors associated with outbreaks, we will conduct descriptive analyses (frequencies, means, etc.) to describe
environmental antecedents (see Table B.4.3 for the variables included in these descriptive analyses and their environmental antecedent classifications [economics, equipment, food, people, processes])
contributing factors (examined by category: contamination, proliferation, and survival; see Table B.4.4 for the variables included in these descriptive analyses).
The list and descriptions of all contributing factors can be found in Attachment 3.
NEARS collects data on a number of environmental antecedent variables. These variables were chosen for inclusion in NEARS because existing hypotheses, theories or data suggest that they may be related to food safety and/or foodborne illness outbreaks.
Table B.4.3. Variables included in descriptive analyses of environmental antecedents
Question Number |
Question |
Justification |
Classification |
|
I_14 |
What were the environmental antecedents of this outbreak? |
Describe the underlying causes of the outbreak.
|
Economics, Equipment, Food People, Processes
|
|
I_15 |
Briefly describe any other information about the underlying causes of the outbreak |
|||
II_5 |
Facility type |
Describe facility type. |
Process |
|
II_6 |
How many critical violations/priority foundation items were noted during the last routine inspection? |
Describe critical violations. |
Equipment, People, Process |
|
II_9 |
Establishment type |
Describe establishment type. |
Process |
|
II_10 |
Do customers have direct access to unpackaged food such as a buffet line or salad bar in this establishment? |
Describe customer access to unpackaged food. |
People |
|
II_11 |
Does the establishment serve raw or undercooked animal products (example, oysters or raw shell eggs) in any menu item? |
Describe whether this food safety risk exists and whether customers are notified of this risk. |
Food, Process |
|
II_11a |
Is a consumer advisory regarding the risk of consuming raw or undercooked animal products provided? |
People |
||
II_11a1 |
Where is the consumer advisory located? |
People |
||
II_12 |
Which one of the options best describes the menu for this establishment? |
Describe the establishment menu. |
Food, Process |
|
III_2 |
Is this an independent establishment or a chain establishment? |
Describe establishment ownership. |
People, Process |
|
III_3 |
Approximately how many meals are served here daily? |
Describe volume of business. |
Economics, People, Process |
|
III_4 |
What is the establishment’s busiest day, in terms of number of meals served? |
|||
III_5 |
Are any foods prepared or partially prepared at a commissary or other location? |
Describe whether foods are prepared at commissaries. |
Process |
|
III_6 |
Other than daily specials, when was the last time food items were added to your menu(s)? |
Describe whether food items have been added to the menu. |
Food, People, Process |
|
III_7 |
Approximately how long have you been employed as a kitchen manager in this establishment? |
Describe manager experience.
|
People, Process |
|
III_8 |
Approximately how long have you worked as a kitchen manager? |
|||
III_9 |
How many kitchen managers, including you, are currently employed in this establishment? |
Describe ratio of managers to workers (measure of worker supervision). |
People |
|
III_10 |
What language(s) do you and other managers in this establishment speak fluently? |
Describe manager/worker communication/language barriers.
|
People |
|
III_11 |
What languages do you and other managers speak at work? |
|||
III_12 |
In your opinion, how well do you communicate verbally with your food workers, very well, somewhat well or not well at all? |
|||
III_13 |
Do any kitchen managers receive food safety training? |
Describe manager food safety training. |
People |
|
III_13a |
How many kitchen managers have had food safety training? |
|||
III_13b |
What type of food safety training do kitchen managers (you) receive? |
|||
III_14 |
Does this establishment require that kitchen managers have a food safety certification? |
Describe food safety certification. |
People |
|
III_15 |
Are any kitchen managers, including you, food safety certified? |
|||
III_15a |
How many kitchen managers in this establishment, including yourself, are food safety certified by an ANSI accredited program such as ServSafe National Registry of Food Safety Professionals/Environmental Health Testing or Thomson Prometric? |
|||
III_15b |
How often is there a certified kitchen manager present during hours of operation? |
|||
III_16 |
How many food workers do you have? |
Describe staff size. |
People, Process |
|
III_16a |
What language(s) do food workers in this establishment speak fluently? |
Describe manager/worker communication/language barriers.
|
People |
|
III_16b |
What languages do food workers speak at work? |
|
||
III_16c |
Do any food workers receive food safety training? |
Describe food worker food safety training. |
People |
|
III_16c1 |
How many food workers have had food safety training? |
|||
III_16c2 |
What type of food safety training do food workers receive? |
|||
III_17 |
Does this establishment have a policy or schedule for |
Describe cleaning and glove use policies.
|
Process
|
|
III_17a |
Cleaning cutting boards? |
|||
III_17b |
Cleaning food slicers? |
|||
III_17c |
Cleaning food preparation tables? |
|||
III_17d |
After a worker or customer vomits and/or has diarrhea in the establishment? |
|||
III_17e |
Frequently touched customer surfaces? |
|||
III_17f |
Are any of these policies written? |
|||
III_17f1 |
Which ones? |
|||
III_18 |
Does this establishment have a policy for disposable glove use? |
|||
III_18a |
Does the glove use policy require that food workers wear gloves? |
|||
III_18a1 |
When they have cuts or other injuries? |
|||
III_18a2 |
When handling ready-to-eat foods? |
|||
III_18a3 |
When handling raw meat or poultry? |
|||
III_18a4 |
At all times while working in the kitchen? |
|||
III_18b |
Is the policy written? |
|
|
|
III_19 |
Does this establishment have a policy to take the temperature of any incoming food products? |
Describe temperature taking policies. |
Process |
|
III_20 |
Excluding incoming products, does this establishment have a policy to take food temperatures? |
|||
III_21 |
When food workers say they are ill, do you typically ask if they are experiencing certain symptoms? |
Describe ill worker and sick leave policies. |
Process, People |
|
III_22 |
Does this establishment have a policy or procedures that requires food workers to tell a manager when they are ill? |
|||
III_22a |
Is this policy in writing? |
|||
III_22b |
Does this policy require ill workers to tell managers what their symptoms are? |
|||
III_22c |
Does this policy specify certain symptoms that ill workers are required to tell managers about? |
|||
III_25c1 |
What are those symptoms? |
|||
III_23 |
Does this establishment have a policy or procedure to restrict or exclude ill workers from working? |
|||
III_23a |
Is this policy in writing? |
|||
III_23b |
Does this policy specify the specific symptoms that would prompt excluding or restricting ill workers from working? |
|||
III_23b1 |
What are those symptoms? |
|||
III_24 |
Do any kitchen managers (including you) ever get paid when they miss work because they are ill? |
|||
III_24a |
How many kitchen managers get paid when they miss work because they are ill? |
|||
III_25 |
Do any food workers ever get paid when work is missed because they are ill? |
|||
III_25a |
How many food workers get paid when they miss work because they are ill? |
|||
IV_2 |
How many hand sinks are in the employee restrooms? |
Describe availability of handwashing sinks, supplies and equipment, and handwashing and handwashing behavior |
Equipment, People |
|
IV_2a |
Is warm water (minimum 100°F) available at all employee restroom hand sinks? |
|
||
IV_2b |
Is soap available at (or near) all employee restroom hand sinks? |
|
||
IV_2c |
Are paper or cloth drying towels or electric hand dryers available at (or near) all employee restroom hand sinks? |
|
||
IV_3 |
How many hand sinks are located in the work area? |
|
||
IV_3a |
Is warm water (minimum 100°F) available at all hand sinks in the work area? |
|
||
IV_3b |
Is soap available at (or near) all employee restroom hand sinks in the work area? |
|
||
IV_3c |
Are paper or cloth drying towels or electric hand dryers available at (or near) all hand sinks in the work area? |
|
||
IV_4 |
If workers are observed washing hands, do the hand washes include water, hand cleanser, appropriate drying methods and are they for the appropriate length of time (approximately)? |
|
||
|
IV_5 |
How many cold storage units are in the establishment? |
Describe cold storage units and their temperatures. |
Equipment |
|
|
|
IV_5a |
Which types of units did you observe? |
|
|
|
|
|
IV_6 |
Were any foods observed in cold holding? |
|
|
||
|
IV_6a |
Were the temperatures of all foods measured in cold holding at 41°F or below? |
|
|
||
|
IV_7 |
Are any food workers using gloves while handling food? |
Describe glove practices. |
Equipment, People |
|
|
|
IV_8 |
Is there a supply of disposable gloves available in the establishment? |
Describe glove availability. |
Economics, Equipment |
|
|
|
IV_9 |
Are food workers using any methods besides gloves to prevent bare hand contact with ready-to-eat food? |
Describe other bare hand contact prevention practices. |
Equipment, people |
|
|
|
IV_9a |
If methods besides gloves are used: What methods? |
|
|
||
|
IV_10 |
Are any food workers handling ready-to-eat foods with bare hands? |
Describe bare hand contact practices. |
People |
|
|
|
IV_12 |
Are there records to indicate that the temperatures of incoming ingredients are being taken and recorded? |
Describe temperature taking and recording practices. |
People |
|
|
|
IV_13 |
Are there records to indicate that the temperatures of foods, excluding incoming ingredients, are being taken and recorded? |
|
|
||
|
IV_13 |
Is there any evidence of direct cross contamination of raw animal products with ready to eat foods? |
Describe practices that could lead to cross contamination. |
People, Process |
|
|
|
IV_13a |
Describe cross contamination evidence. |
|
|
||
|
IV_14 |
Were any hot foods observed in cooling? |
Describe food cooling practices. |
Process |
|
|
|
IV_14a |
What cooling method(s) are used? |
|
|
||
|
IV_14b |
Were the cooling methods properly implemented? |
|
|
||
|
IV_15 |
Were any foods observed in hot holding? |
Describe food holding and cooking practices. |
People, Process |
|
|
|
IV_15a |
Were the temperatures of all foods measured in hot holding at 135°F or above? |
|
|||
|
IV_16 |
Were any foods observed during cooking? |
|
|||
|
IV_16a |
Were the temperatures of all foods measured during cooking at or above the recommended temperatures? |
|
|||
|
IV_17 |
Were any thermometers observed in food preparation areas to measure food temperatures? |
|
|||
|
IV_17a |
Were any thermometers observed being used? |
|
|||
|
IV_18 |
Were any of these materials observed for cleaning/sanitizing food contact surfaces and in-place equipment? |
Describe cleaning practices. |
People, Process |
|
|
|
IV_18a |
Are all wet wiping cloths stored in sanitizer solution between uses? |
|
|||
|
IV_18b |
Pick one sanitizer bucket (or bottle) and test sanitizer concentration. Is it in the proper range? |
|
|||
|
IV_19 |
What does the establishment use to clean dishes, utensils, or other food equipment that is not cleaned in place? |
Describe dishwashing practices. |
Equipment, Process |
|
|
|
IV_19a |
Does the wash cycle reach the temperatures recommended for the mechanical washing machine? |
|
|||
|
IV_19b |
How is sanitization achieved? |
|
|||
|
IV_191 |
Does the sanitizing cycle reach the temperatures recommended for sanitization? |
|
|||
|
IV_19b2 |
Does the chemical sanitizing cycle have the required levels of chemical sanitizer recommended for the machine? |
|
|||
|
IV_19c |
What type of sink is used for manual washing? |
|
|||
|
IV_19d |
Are dishes, utensils, etc. washed, rinsed, and sanitized (either with heat or chemical) properly? |
|
|||
|
IV_19d1 |
Is a santitizing method properly implemented? |
|
|||
|
IV_20 |
Did you observe signs and instructions posted in the establishment? |
Describe signs.
|
People, Process |
|
|
|
IV_20a |
Did any use pictures or symbols to communicate a message? |
|
|||
|
IV_20b |
What languages did you observe on signs or instructions posted for food workers? |
|
|||
IV_21 |
Did you observe any of these items for responding to vomit and/or diarrheal incidents? |
Describe equipment for cleaning after vomiting/diarrheal incidents |
Equipment |
|||
IV_21a |
Were any of these things located together? |
|||||
IV_24 |
Is a certified manager present at the time of data collection? |
Describe manager training |
People |
|||
IV_25 |
Does the written employee health policy or procedure…. |
Describe employee health policy |
Process |
|||
Va_1 |
What is the name of the suspected or confirmed ingredient/food vehicle? |
Describe and classify food ingredients linked with the outbreak.
|
Food |
|||
Va_2 |
Is this food a single specific ingredient or multi-ingredient? |
|||||
Va_3 |
Select the reason that best describes how this single specific ingredient or multi-ingredient food was implicated in the outbreak. |
|||||
Va_4 |
Which of the following best describes the food preparation process used for this specific ingredient or multi-ingredient food before consumption? |
Describe and classify the food prep processes that the establishment used to prepare the suspected/confirmed vehicle. |
Food, Process |
|||
Va_5 |
During the likely time the ingredient/food was prepared, were any events noted that appeared to be different from the ordinary operating circumstances or procedures, as described by managers and/or workers? |
Out-of-the ordinary events can lead to potential food safety risks. These data will identify and describe these events. |
Economics, Equipment, Food People, Processes
|
|||
Va_5a |
How would these events best be characterized? |
|||||
Vb_1 |
Name of ingredient |
Describe and classify food ingredients linked with the outbreak.
|
Food, Process |
|||
Vb_2 |
If any information is present that shows this ingredient is an important food item or from an unapproved source or recall, describe. |
|||||
Vb_3a |
Select poultry type |
|||||
Vb_3b |
Select seafood type |
|||||
Vb_3c |
Select beef, pork, lamb, other meat type |
|||||
Vb_3d |
Poultry, seafood, beef, pork, lamb, other meat, Select best description of product upon arrival at the food service establishment |
|||||
Vb_3e |
Dairy, Select best description of product upon arrival at the food service establishment |
|||||
Vb_3f |
Eggs, Select best description of product upon arrival at the food service establishment |
|||||
Vb_3g |
Plant or plant product, Select type |
|||||
Vb_3h |
Produce, Select produce type |
|||||
Vb_3i |
Plant or plant product, Select best description of product upon arrival at the food service establishment |
|||||
Vb_3j |
Describe other ingredient |
|||||
To address the third goal of this data collection, describe the associations between environmental antecedents and contributing factors, we will conduct tests for association and logistic regression models.
Analysis will involve bivariate tests for association between individual environmental antecedent (explanatory) variables and the contributing factor (outcome) variables. Odds ratios will be calculated to assess the strength and direction of the bivariate relationships. For those bivariate associations found to be statistically significant at p<.30, the environmental antecedent variables will be used as candidate “predictors” to examine their multivariate relationships with the contributing factor variables. Multivariable logistic regression will be used to model for the effects that these environmental antecedent variables have in explaining the variations observed in the contributing factor variables. This type of analysis allows us to determine which environmental antecedents contribute to the presence of the contributing factor, and the relative degree of impact that each environmental antecedent has in the presence of that contributing factor. A separate model will be developed for each contributing factor analyzed.
Table B.4.5 describes the study questions designed to address this third goal of this data collection and the data collection variables designed to answer those questions. Note that we will likely create composite environmental antecedent variables based on the individual variables listed in the table.
Table B.4.5. Study questions and the data collection variables designed to answer those questions
Study Question |
Environmental Antecedent Variables |
Contributing Factors |
How are specific environmental antecedents related to contamination contributing factors? |
II_5, II_6, II_7 (a), II_8 (a), II_9, II_10, II_12, III_2, III_3, III_4, III_5, III_6, III_7, III_8, III_9, III_10, III_11, III_12, III_13 (a, b), III_14, III_15 (a, b), III_16 (a, b, c, c1, c2), III_17 (a, b, c, d, e, f, f1), III_18 (a, b), III_21, III_22 (a, b, c, c1), III_23 (a, b, b1), III_24 (a), III_25 (a), III_26 (a), IV_2 (a, b, c), IV_3 (a, b, c), IV_4, IV_7, IV_8, IV_9 (a), IV_10, IV_13 (a), IV_17 (a, b), IV_18 (a, b), IV_19 (a, b, b1, b2, c, d, d1), IV_20 (a, b), IV_21, IV_22 (a), IV_23, IV_24, IV_25 |
C1-C15
|
How are specific environmental antecedents related to proliferation contributing factors? |
II_5, II_6, II_7 (a), II_8 (a), II_9, II_11, II_12, III_2, III_3, III_4, III_5, III_6, III_7, III_8, III_9, III_10, III_11, III_12, III_13 (a, b), III_14, III_15 (a, b), III_16 (a, b, c, c1, c2), III_17 (a, b, c, d, e, f, f1), III_19, III_20, IV_5 (a), IV_6 (a), IV_11, IV_12, IV_14 (a, b), IV_15 (a), IV_16 (a), IV_17 (a) |
P1-P12 |
How are specific environmental antecedents related to survival contributing factors? |
II_5, II_6, II_7 (a), II_8 (a), II_9, II_11 (a, a1), II_12, III_2, III_3, III_4, III_5, III_6, III_7, III_8, III_9, III_10, III_11, III_12, III_13 (a, b), III_14, III_15 (a, b), III_16 (a, b, c, c1, c2), III_17, III_18, III_20, III_26 (a), IV_16 (a), IV_17 (a), IV_22 (a), IV_23 |
S1-S5 |
Table B.4.6 is a table shell that illustrates how we might analyze and present the data examining the bivariate relationships between specific environmental antecedents and the contributing factor of bare-hand contact with ready-to-eat food by a food worker who is suspected to be infectious (contributing factor C10).
Table B.4.6. Example Table Shell: Environmental antecedent variables associated with the outcome variable of whether the contributing factor of bare-hand contact with ready-to-eat food by an infectious food worker was identified, bivariate analyses
Environmental antecedent variables |
Bare hand contact with food by infectious food worker (C10) identified as a contributing factor |
|
|
OR (95% CI) |
P |
Number of meals served daily (III_3) |
|
|
<300 |
x.xx (ref) |
.xxx |
>300 |
x.xx |
|
Food worker training provided (III_20) |
|
|
No |
x.xx (ref) |
.xxx |
Yes |
x.xx |
|
Paid sick leave provided (III_28) |
|
|
No |
x.xx (ref) |
.xxx |
Yes |
x.xx |
|
Establishment has ill worker policy (III_26) |
|
|
No |
x.xx (ref) |
.xxx |
Yes |
x.xx |
|
Disposable gloves are available in establishment (IV_8) |
|
|
No |
x.xx (ref) |
.xxx |
Yes |
x.xx |
|
Hand sink is available in work area (IV_2) |
|
|
No |
x.xx (ref) |
.xxx |
Yes |
x.xx |
|
OR=Odds Ratio, P=probability level
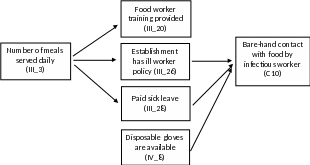
Below is an example figure demonstrating results from a multivariate analysis of the associations between environmental antecedents and the contributing factor of bare-hand contact with ready-to-eat food by an infectious food worker. This type of analysis allows us to determine the relationships among environmental antecedents and between environmental antecedents and contributing factors. It allows us to determine the direct and indirect effects of each environmental antecedent on the contributing factor. A separate model would be developed for each contributing factor analyzed.
Figure B.4.1. Example Figure - Environmental antecedent variables associated with the outcome variable of whether the contributing factor of bare-hand contact with ready-to-eat food by an infectious worker was identified, multivariate analyses
B.5. Individuals Consulted on Statistical Aspects and Individuals Collecting and/or Analyzing Data
The following persons were primarily responsible for designing the instrument; however, Laura Brown and Adam Kramer will be primarily responsible for analyzing data.
Data Collection Designers and Analysts
Laura Green Brown, Ph.D.
Behavioral Scientist
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
National Center for Environmental Health
Division of Environmental Health Science and Practice
Water, Food, and Environmental Health Services Branch
4770 Buford Hwy, NE (F58)
Atlanta, GA 30341
770-488-4332
Carol Selman, MPH (Retired)
Senior Public Health Advisor
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
National Center for Environmental Health
Division of Environmental Health Science and Practice
Water, Food, and Environmental Health Services Branch
4770 Buford Hwy, NE (F58)
Atlanta, GA 30341
770-488-4352
Erik W. Coleman, MPH
Health Scientist (Informatics)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
National Center for Environmental Health
Division of Environmental Health Science and Practice
Water, Food, and Environmental Health Services Branch
4770 Buford Hwy, NE (F58)
Atlanta, GA 30341
770-488-3438
Adam Kramer, ScD
Environmental Science Officer
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
National Center for Environmental Health
Division of Environmental Health Science and Practice
Water, Food, and Environmental Health Services Branch
4770 Buford Hwy, NE (F58)
Atlanta, GA 30341
770-488-3438
References
Brown, L, Hoover, E, Selman, C, Coleman, E, Schurz Rogers, H. Outbreak characteristics associated with identification of contributing factors to foodborne illness outbreaks. Epi Infect. 2017;1:1-9.
Dewey-Mattia D, Manikonda K, Hall AJ, Wise ME, Crowe SJ. Surveillance for Foodborne Disease Outbreaks — United States, 2009–2015. MMWR Surveill Summ 2018;67(No. SS-10):1–11.
Scallan E, Hoekstra RM, Angulo FJ, Tauxe RV, Widdowson M-A, Roy SL, et al. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—major pathogens. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011; 17:7–15.
Scallan E, Griffin PM, Angulo FJ, Tauxe RV, Hoekstra RM. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—unspecified agents. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011; 17:16–22.
Attachments
Attachment 1A. Authorizing Legislation 42 U.S.C. § 241
Attachment 1B. Authorizing Legislation 21 U.S.C § 2201
Attachment 2. 60-day Federal Register Notice
Attachment 3. Definition of Contributing Factors to Foodborne Illness Outbreaks
Attachment 4. NEARS Food Safety Program Training Webinar
Attachment 5. NEARS e-Learning on Environmental Assessment Foodborne Illness Outbreaks (screenshots)
Attachment 6. NEARS Data Recording Instrument Word
Attachment 7. NEARS Data Recording and Manager Interview Web Entry (screenshots)
Attachment 8. NEARS Manager Interview
Attachment 9. Research Determination Form
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 0000-00-00 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy