2019 OMB Final Supporting Statement -Collection of Research Code Non-Disclosure Agreement Information
2019 OMB Final Supporting Statement -Collection of Research Code Non-Disclosure Agreement Information.doc
Collection of Research Code Non-Disclosure Agreement Information
OMB: 3150-0240
FINAL SUPPORTING STATEMENT FOR
COLLECTION OF RESEARCH CODE NON- DISCLOSURE AGREEMENT INFORMATION (3150-XXXX)
NEW
Description of the Information Collection
The collection instrument is a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) used for domestic and foreign entities to obtain and use the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s (NRC’s) nuclear safety analytical computer codes. These computer codes are used to model and evaluate fuel behavior, reactor kinetics, thermal-hydraulic conditions, severe accident progression, time-dependent dose for design-basis accidents, emergency preparedness and response, health effects, radionuclide transport, and materials performance during various operating and postulated accident conditions. Foreign and domestic licensees, universities, and corporations requesting access to the codes must provide the following information on the NDA:
Name of entity requesting access
Ownership (foreign or domestic) of entity requesting access
Name of person completing the form
Title
Position
Email address
Citizenship of requestor
Mailing address
Company website (if applicable)
Planned use of codes
NRC Contractor number (if applicable)
Entities submit revised NDAs when that user no longer requires access to the codes.
The NDA also includes terms and conditions for code use, and asks for notification to NRC of code errors, code modifications, and updated user information. An officially signed and executed NDA of users agreeing to the terms and conditions is current NRC practice for allowing access to NRC-developed computer codes. Once the NDA has been signed, received, reviewed, and accepted, the requesting individual or organization is given access to the requested code.
The information is mandatory to obtain a benefit (access to the codes). NRC has the authority to request this information under Section 161c of the Atomic Energy Act of 1954, which states, “In the performance of its functions the Commission is authorized to…make such studies and investigations, obtain such information, and hold such meetings or hearings as the Commission may deem necessary or proper to assist it in exercising any authority provided in this Act, or in the administration or enforcement of this Act, or any regulations or
orders issued thereunder.”
JUSTIFICATION
Need For and Practical Utility of the Collection of Information
The information collection enables the NRC to ensure that proper procedures and agreements are in place to guide the distribution and use of these codes according to NRC and U.S. Government policies and international agreements such as import-export restrictions and intellectual property rights. Further information collection on code errors and modifications by code users permits NRC to maintain control and quality of its codes in a timely and efficient manner. The NDA is stored in the Agencywide Documents Access and Management System (ADAMS) for easy retrievability and traceability.
Adhering to a practice where users of the code are required to sign an NDA provides the following key benefits to NRC:
Highlights the terms by which users will not release NRC-developed computer codes to a third party without NRC consent and approval.
Ensures authenticity and pedigree of NRC computer codes and code results by requiring users to rename a modified code version with a somewhat different name (provided NRC has authorized the development of a modified version).
Prohibits foreign entities from using the code for the commercial application in the development of a new reactor design or for commercial use in the United States unless performed by its U.S. subsidiary.
Makes no warranty by NRC, expressed or implied, or assumes any legal liability or responsibility for any use, or the results of such use, or of any information, product, or process included in or calculated by the code, or represents that the use would not infringe privately-owned rights.
Requires a description of the intended use of the code ensuring the use of the code is not inconsistent with the mission of the NRC.
Stipulates that code errors be communicated to NRC code developers as well as any nonproprietary improvements or modifications made to the code, including a summary of the impact on representative code calculations.
Makes all users requesting computer codes identify their country of citizenship to determine eligibility (U.S. citizens and U.S. permanent residents are automatically eligible).
Agency Use of Information
The NRC will use the information collected to:
Verify that code users meet all statutory and regulatory requirements.
Improve the codes.
Maintain code integrity.
Reduction of Burden Through Information Technology
The NRC has issued Guidance for Electronic Submissions to the NRC which provides direction for the electronic transmission and submittal of documents to the NRC. Electronic transmission and submittal of documents can be accomplished via the following avenues: the Electronic Information Exchange process, which is available from the NRC’s “Electronic Submittals” Web page, by Optical Storage Media (e.g. CD-ROM, DVD), by facsimile, or by e-mail. Code users have the option of submitting code errors via e-mail to a resource inbox or through a Bugzilla tracking system, which is operated by Sandia National Laboratories on behalf of the NRC. It is estimated that, approximately 100 percent of the responses are filed electronically.
Effort to Identify Duplication and Use Similar Information
No sources of similar information are available. There is no duplication of requirements.
Effort to Reduce Small Business Burden
No small businesses are affected by the information collection requirements.
Consequences to Federal Program or Policy Activities if the Collection Is Not Conducted or Is Conducted Less Frequently
The information collection enables the NRC to ensure that proper procedures and agreements are in place to guide the distribution and use of these codes according to NRC and U.S Government policies and international agreements such as import- export restrictions and intellectual property rights. If the information were not collected…the requestor does not receive access to the code(s), and the NRC would lose control to who has access to the codes.
Circumstances Which Justify Variation from OMB Guidelines
There are no variations from OMB guidelines.
The following are the circumstances and justifications apply to the information collection:
Information is collected more often than quarterly: The participants submit a non-disclosure agreement whenever they decide to request access to NRC’s code(s). Once the NDA is approved and the code is distributed to the participant, NRC expects that further information be submitted as required by the NDA including notification of code errors, modifications to the code, and updating of user information.
Proprietary trade secrets or similar confidential information are required: Nuclear power plants and engineering corporations are sensitive about sharing their plant and component design information. This information provided to the NRC and included in codes will be treated as proprietary information to the information providers.
Consultations Outside the NRC
Opportunity for public comment on the information collection requirements for this clearance package was published in the Federal Register on April 16, 2019 (84 FR 15640). NRC received no comments. NRC also contacted 6 licensees and people within the code user base by email/phone and there were no comments received.
Payment or Gift to Respondents
Not Applicable.
Confidentiality of Information
Confidential and proprietary information is protected in accordance with the NRC regulations at 10 CFR 9.17(a) and 10 CFR 2.390(b).
The information being collected under this clearance includes Personally Identifiable Information. This information is necessary to ensure the proper identification of the individual providing the information. The NRC’s Privacy Officer reviewed the information collection and determined that it does not need to be included in a System of Records Notice.
Justification for Sensitive Questions
Not Applicable.
Estimated Burden and Burden Hour Cost
The total estimated cost for the information collection is 640 hours annually, based on the following assumptions:
The NRC staff estimates that the NRC will receive approximately 436 NDAs annually from the following entities:
Licensees/NPPs (Foreign and domestic): 110
Universities (Foreign and domestic): 165
Corporations (Foreign and domestic): 105
Members of the public (Foreign and domestic): 8
Technical support organizations (Foreign): 48
A total of 436 NDAs are expected to be submitted annually. Each NDA is estimated to take 1 hour to complete and submit.
The participating code users are expected to incur the following annual additional burdens, if applicable:
Submissions of code errors:
116 per year, estimated time is 1 hour per submittal.
Submissions of code improvements or modifications 35 per year, estimated time is 1 hour per submittal.
Updating list of code users
53 per year, estimated time is 1 hour per submittal.
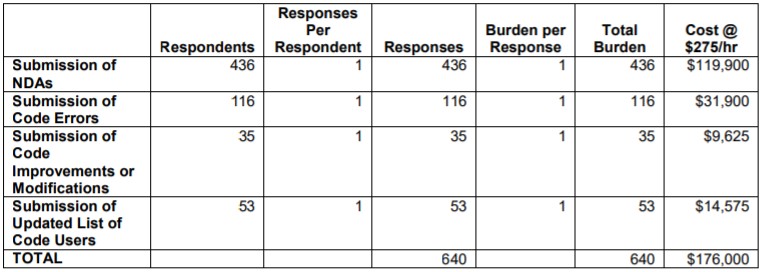
The $275 hourly rate used in the burden estimates is based on the Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s fee for hourly rates as noted in 10 CFR 170.20 “Average cost per professional staff-hour.” For more information on the basis of this rate, see the Revision of Fee Schedules; Fee Recovery for Fiscal Year 2018 (83 FR 29622, June 25, 2018).
Estimate of Other Additional Costs
There are no additional costs.
Estimated Annualized Cost to the Federal Government
The staff has developed estimates of annualized costs to the Federal Government related to the conduct of this collection of information. These estimates are based on staff experience and subject matter expertise and include the burden needed to review, analyze, and process the collected information and any relevant operational expenses.
NRC staff are the ones receiving and reviewing NDAs to determine who has access.
The NRC solicited the services of maintaining the database of providing technical support with the average annual cost of $185,075.
Reasons for Change in Burden or Cost
This is a new collection to collect NDA information that imposes 640 hours of burden to code users. The information collected on the NDAs will be used by the NRC to verify that code users meet all statutory and regulatory requirements for access to the codes. Information submitted voluntarily about code errors and modifications will be used to improve the codes and maintain code integrity.
Publication for Statistical Use
Not applicable.
Reason for Not Displaying the Expiration Date
The expiration date will be displayed.
Exceptions to the Certification Statement
None.
| File Type | text/rtf |
| Last Modified By | SYSTEM |
| File Modified | 2019-11-01 |
| File Created | 2019-11-01 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy