571ss13
571ss13.docx
General Hazardous Waste Facility Standards (Renewal)
OMB: 2050-0120
SUPPORTING STATEMENT FOR
OMB CONTROL NO. 2050-0120
"GENERAL HAZARDOUS WASTE FACILITY STANDARDS"
September 2020
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
1(a) Title and Number of the Information Collection 3
1(b) Characterization of the Information Collection 3
2. NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION
2(a) Need and Authority for the Collection 6
2(b) Use and Users of the Data 7
3. NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA
3(a) Nonduplication 9
3(b) Consultations 9
3(c) Public Notice 10
3(d) Effects of Less Frequent Collection 10
3(e) General Guidelines 10
3(f) Confidentiality 11
3(g) Sensitive Questions 11
4. THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED
4(a) Respondents/NAICS Codes 11
4(b) Information Requested 12
5. THE INFORMATION COLLECTED—AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
5(a) Agency Activities 48
5(b) Collection Methodology and Management 50
5(c) Small Entity Flexibility 50
5(d) Collection Schedule 50
6. ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF THE COLLECTION
6(a) Estimating Respondent Burden 53
6(b) Estimating Respondent Cost 53
6(c) Estimating Agency Burden and Cost 54
6(d) Respondent Universe and Total Respondent Burden and Costs 54
6(e) Bottom Line Burden Hours and Costs 63
6(f) Reasons for Change in Burden 63
6(g) Burden Statement 63
1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
1(a) TITLE AND NUMBER OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
This ICR is entitled “General Hazardous Waste Facility Standards,” EPA ICR #1571.13, OMB Control No. 2050-0120.
1(b) SHORT CHARACTERIZATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
Section 3004 of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), as amended, requires that the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) develop standards for hazardous waste treatment, storage and disposal facilities (TSDFs) as may be necessary to protect human health and the environment. Subsections 3004(a) (1), (3), (4), (5) and (6) specify that these standards include, but not be limited to, the following requirements:
Maintaining records of all hazardous wastes identified or listed under Subtitle C that are treated, stored, or disposed of, and the manner in which such wastes were treated, stored, or disposed of;
Operating methods, techniques, and practices for treatment, storage, or disposal of hazardous waste;
Location, design, and construction of such hazardous waste treatment, disposal, or storage facilities;
Contingency plans for effective action to minimize unanticipated damage from any treatment, storage, or disposal of any such hazardous waste; and
Maintaining or operating such facilities and requiring such additional qualifications as to ownership, continuity of operation, training for personnel, and financial responsibility as may be necessary or desirable.
The regulations implementing these requirements are codified in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 40, Parts 264 and 265. A brief summary of the information collection requirements associated with each TSDF regulation for the above areas is provided below. A more specific discussion of the data elements and respondent activities associated with each of the information collection requirements is presented in Section 4.
2. NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION
2(a) NEED AND AUTHORITY FOR THE COLLECTION
This section describes the need and authority for each type of information collection analyzed in this ICR.
GENERAL FACILITY OPERATING REQUIREMENTS
(1) Foreign Shipment Import Report
EPA promulgated regulations in §§264.12(a) and 265.12(a) requiring owners and operators of hazardous waste facilities that have arranged to receive hazardous wastes from foreign sources to notify the Regional Administrator in writing at least four weeks prior to the expected date of arrival of the shipments at the facility. EPA uses information in the foreign shipment import report to determine: (1) whether hazardous wastes will be transported safely to the United States, and (2) whether the waste will be managed in a manner that is protective of human health and the environment. The foreign shipment import report requirement contributes to EPA's goal of minimizing detrimental impacts to the environment resulting from the unsafe transportation and management of hazardous waste.
(2) Notice of Appropriate Permits
Section 264.12(b) requires the owner or operator of a facility receiving off-site waste to send a one-time notice to the generator stating that he or she has the appropriate permits, and will accept the waste the generator is shipping. The owner or operator must retain a copy of the notice at the facility. The notice is needed to ensure that waste is being managed properly. EPA may examine the notices during inspections to ensure that the notifications are being transmitted.
(3) Notice of Part 264 or 265 and Part 270 Requirements
Sections 264.12(c) and 265.12(b) require owners and operators transferring ownership of a facility during its operating life, or of a disposal facility during the post-closure care period, to notify the new owner or operator in writing of the requirements of 40 CFR Parts 264 and 270. This information is needed to help new owners and operators understand applicable regulations and facilitate compliance.
(4) Waste Analysis
EPA promulgated regulations in §§264.13(a) (1) and 265.13(a) (1) requiring owners or operators to obtain a detailed chemical and physical analysis of a representative sample of the waste that will be received. EPA and the owner or operator use information obtained in the waste analysis sample to determine: 1) whether a facility can adequately handle incoming waste, and 2) whether the waste is really what the generator claims it to be. The owner or operator also uses information obtained from the waste analysis to determine whether there are any potential dangers from handling the waste. The waste analysis requirement contributes to EPA's goal of preventing releases or reactions of hazardous waste on-site.
(5) Waste Analysis Plan
Sections 264.13(b) and 265.13(b) state that the owner or operator of a hazardous waste facility must develop and follow a written waste analysis plan that describes the procedures to be used in obtaining a detailed chemical and physical analysis of the waste. EPA uses the waste analysis plan as a planning tool to ensure the quality of information obtained from the waste analysis samples required in 264.13(a)(1) and 265.13(a)(1).
(6) Inspection Schedule
EPA promulgated regulations in §§264.15(d) and 265.15(d) requiring the owner or operator of a facility to record inspections in an inspection log or summary. EPA and owners and operators use information in the inspection log to determine whether facility equipment is safe for handling hazardous waste. The inspection requirement contributes to EPA's goal of preventing hazardous waste constituents from being released into the environment due to faulty or deteriorated equipment.
(7) Personnel Training
Sections 264.16(d) and 265.16(d) require owners and operators to maintain copies of personnel training documents and records at their facilities. Both EPA and owners and operators use information in personnel training records to determine whether employees have acquired the necessary expertise to perform their jobs. EPA also reviews personnel records to determine whether employees are receiving a level of training that is commensurate with their duties and responsibilities as well as their ability to respond to any emergency situations at the facility. Requiring owners and operators to maintain personnel training documents decreases the likelihood that employees are unqualified to handle hazardous waste or respond to emergencies. The personnel recordkeeping requirement contributes to EPA's goal of minimizing the potential for employee-related mistakes that may threaten human health and the environment.
(8) Documentation of Compliance for Ignitable, Reactive or Incompatible Wastes
Section 264.17(c) states that any owner or operator who treats, stores, or disposes of ignitable or reactive wastes, or mixes incompatible wastes, must document compliance with §264.17(a) and (b), which require certain precautions to prevent reactions. EPA uses information in the documentation of compliance to determine whether facilities are operating in a manner that is protective of human health and the environment. The documentation requirement contributes to EPA's goal of minimizing damage from the treatment, storage, or disposal of hazardous waste.
(9) Construction Quality Assurance Plan
Section 265.19(b) requires each owner or operator of a surface impoundment, waste pile, or landfill to develop a written construction quality assurance (CQA) plan that identifies steps that will be used to monitor and document the quality of materials and the condition and manner of their installation. The CQA plan helps to ensure proper structural stability and integrity of all unit components, and proper construction of all units.
RECORDKEEPING REQUIREMENTS
EPA promulgated regulations in 40 CFR 264.73 and 265.73 directing owners or operators of hazardous waste treatment, storage, or disposal facilities to keep a written operating record at the facility. Other recordkeeping requirements under 40 CFR Parts 264 and 265, Subpart E, include submitting copies of records of waste disposal locations and quantities under §§264.73(b)(2) and 265.73(b)(2) to the Regional Administrator and local land authority upon closure of the facility (§§264.74(c) and 265.74(c)). In addition, 40 CFR 264.37(b) requires facilities to document in the operating record any refusal of State
or local authorities to enter into arrangements for emergency situations. EPA uses information collected pursuant to these regulations to select appropriate corrective action and cleanup measures should an unanticipated release of hazardous waste occur. EPA compliance officials refer to the operating record to determine the following: 1) what cleanup measures are appropriate and 2) whether operating requirements can be better tailored to the needs of a particular site. EPA anticipates that the owner or operator will use information included in the operating record to prevent receiving, or placing in proximity, wastes that are incompatible with other wastes that are likely to ignite or explode. Requiring facilities to develop and maintain an operating record and conduct the recordkeeping activities contributes to EPA's goal of minimizing damage to the environment due to the treatment, storage, or disposal of hazardous waste.
CONTINGENCY PLAN AND EMERGENCY REPORTING AND RECORDKEEPING REQUIREMENTS
Section 3004(a) (5) of RCRA, as amended, requires EPA to develop standards for contingency plans for effective action to minimize damage from any treatment, storage, or disposal of any such hazardous waste. EPA codified regulations that address this statutory requirement in 40 CFR Parts 264 and 265. 40 CFR §§264.51 through 264.54 and 264.56 and 265.51 through 265.54 and 265.56 require all owners and operators of hazardous waste facilities to prepare and maintain contingency plans, and to notify State and local authorities and prepare and emergency reports whenever an imminent or actual emergency situation occurs. EPA reviews the contingency plan and emergency reports to determine whether a facility has developed adequate procedures to respond to unplanned sudden or non-sudden releases of hazardous waste or hazardous constituents to air, soil, or surface water. Notifications to State and local authorities facilitate remedial actions and evacuations, if necessary. Requiring facilities to develop and maintain contingency plans and prepare emergency response reports and notifications contributes to EPA's goal of minimizing damage from the treatment, storage, or disposal of hazardous waste.
CLOSURE AND POST-CLOSURE REQUIREMENTS
EPA promulgated regulations in 40 CFR Parts 264 and 265, Subpart G (§§264.112, 264.115, 264.116, 264.118-120 and 265.112, 265.113, 265.115, 265.116, and 265.118-120), that require owners and operators to develop closure and post-closure plans, amend these plans when appropriate, and submit
to EPA closure certifications and post-closure notices. EPA reviews information in the closure and post-closure plans to determine whether closure and post-closure activities will comply with the regulatory requirements. EPA uses information in the closure certifications to determine that closure took place in accordance with the approved closure plan. EPA, local authorities, and potential purchasers of a closed facility review information included in the post-closure notices to determine what future uses of the site will not lead to a release of hazardous waste.
In addition, 40 CFR 264.113 and 265.113 allow owners and operators to apply for allowances and extensions during the closure period by preparing and submitting demonstrations. These demonstrations are needed to ensure that any activities taking place during closure are protective of human health and the environment.
Requiring facilities to comply with these regulations contributes to EPA's goal of ensuring that all hazardous waste management facilities are closed in a manner that minimizes the need for post-closure maintenance, and controls, minimizes, or eliminates post-closure escape of waste, leachate, contaminated rainfall, or waste decomposition products to ground or surface waters and the atmosphere to the extent necessary to protect human health and the environment.
FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS
Section 3004(a) (6) of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act of 1976 (RCRA), as amended, requires EPA to promulgate regulations that include requirements respecting "the maintenance of operations of such facilities and requiring such additional qualifications as to ... financial responsibility (including financial responsibility for corrective action) as may be necessary or desirable."
(1) Closure and Post-Closure Financial Assurance Requirements
The need for financial assurance of closure and post-closure care is indicated by the numerous instances of environmental damage resulting from abandonment of hazardous waste management (HWM) facilities and other failures by owners and operators to provide adequately for closure and post-closure care. The likelihood of such failure is increased by the fact that the costs for closure and post-closure care are expected to commence when the economic value of the facility is either at a minimum or nonexistent. For most disposal facilities, post-closure care will extend for at least 30 years beyond the operating life of the facility.
EPA believes that significant numbers of owners and operators would lack the ability to provide for closure and post-closure care without effective requirements for financial assurance. Consequently, the Agency developed 40 CFR Parts 264 and 265, Subpart H financial responsibility requirements for closure and post-closure care. (The requirements in Part 264, Subpart H, are identical to the requirements in Part 265, Subpart H. The remainder of this supporting statement will use the reference to Subpart H as referring to both the Part 264 and Part 265 financial responsibility requirements.)
(2) Liability Requirements
The liability requirements are designed to assure that funds will be available during the operating life of a facility from which third parties can seek compensation for bodily injury and property damage arising from the operation of the facility. The liability requirements are necessary for several reasons. First, the requirements provide protection to human health and the environment by assuring that funds are available to owners and operators to compensate for damage caused by accidents at hazardous waste facilities, including payments for bodily injury and property damage. In addition, the Agency believes that without liability coverage requirements, there would be less public confidence in and greater opposition to proposed and existing hazardous waste facilities. The liability requirements also result in other potential benefits for human health and the environment: the incentive, in the form of lower insurance premiums, to improve design and operation of the facility, and the oversight that insurers provide over facility operations.
CONDITIONS APPLICABLE TO ALL PERMITS
EPA promulgated conditions applicable to all permits at 40 CFR Part 270, Subpart C. Information collected under this authority is needed to ensure that permittees are complying with permit conditions, and to determine whether cause exists for modifying, revoking and reissuing, or modifying a permit.
2(b) USE AND USERS OF THE DATA
GENERAL FACILITY OPERATING REQUIREMENTS
(1) Foreign Shipment Import Report, Notice of Appropriate Permit(s), and
Notice of Part 264 and Part 270 Requirements
EPA uses foreign shipment import reports to determine the quantities and types of hazardous wastes being imported from abroad. Information in the foreign shipment import report also allows EPA to determine whether hazardous wastes will be safely transported and managed.
Generators use notices of appropriate permits to ensure that their waste is being managed by a permitted facility. Owners and operators of TSDFs must keep the notices in the operating record, and these notices may be reviewed by EPA during facility inspections.
New owners and operators use the notice of Part 264 and Part 270 requirements to improve their understanding of applicable regulations.
(2) Waste Analysis, Waste Analysis Plan, Inspection Schedule, and
Documentation of Compliance
The waste analysis and waste analysis plan, as well as the inspection schedule and documentation of compliance for ignitable or incompatible wastes, are primarily internal recordkeeping requirements used by owners and operators of facilities to assure that they can adequately handle incoming waste, to assure that the incoming waste is really what the generator claims it to be, and to prevent undetected releases or reactions of hazardous waste on-site. Much of the information in the waste analysis plan will also be used to provide a quality assurance check on both the generator and the owners' and operators' facilities.
(3) Personnel Training
Both EPA and owners and operators use information in the personnel training records to ensure that personnel acquire the necessary expertise to perform their jobs. During inspections, EPA reviews job descriptions and training documents to determine whether each person is receiving a level of training that is commensurate with the person's duties and responsibilities as well as the ability to respond to any emergency situations at the facility.
RECORDKEEPING REQUIREMENTS
The facility owner or operator uses information included in the operating record and waste disposal location and quantity records to prevent the facility from receiving or placing in proximity wastes that are incompatible or that are likely to ignite or explode. If an unanticipated release of hazardous waste occurs, the owner or operator may review information in the operating record to determine the composition of the waste. Reviewing information in the operating record facilitates the owner's or operator's selection of an appropriate corrective action and cleanup measure. By providing facility-specific data, the operating record also enables EPA compliance officials to determine whether operating requirements can be better tailored to the needs of a particular site.
CONTINGENCY PLAN AND EMERGENCY REPORTING AND RECORDKEEPING REQUIREMENTS
Local emergency response teams, certain hazardous waste generators, treatment, storage, and disposal facility owners or operators, and EPA use information included in the contingency plan to assure an appropriate response to any unplanned release of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents. EPA reviews information in the contingency plan and emergency report to determine whether additional site-specific emergency provisions are necessary.
CLOSURE AND POST-CLOSURE REQUIREMENTS
EPA uses information contained in closure and post-closure plans to determine whether an owner or operator's planned closure and post-closure activities will comply with environmental regulations. EPA officials use information contained in closure certifications to ensure that the owner or operator closed his/her facility according to the specifications outlined in the approved closure plan. EPA uses information contained in demonstrations to ensure that any activities taking place during the closure period are protective of human health and the environment. Local authorities, EPA, and potential purchasers of a closed facility review information included in post-closure notices to ensure that new owners or operators will not use land in a manner that will lead to a release of hazardous waste into the environment.
FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS
The closure, post-closure care, and liability coverage financial instruments submitted by the owner or operator are reviewed by EPA to determine compliance with the applicable Subpart H regulations. This review involves determinations of the validity of the instrument, acceptability of the financial assurance provider, adequacy of the instrument amount, and fulfillment of the other regulatory requirements. The information is also used to direct funds for closure, post-closure care, and liability coverage in the event of default or bankruptcy of a facility owner or operator.
CONDITIONS APPLICABLE TO ALL PERMITS
EPA uses data collected from permitted facilities to evaluate compliance with the terms of the permit and to decide whether cause exists for modifying, revoking and reissuing, or terminating the permit. By collecting this information, EPA ensures that permitted facilities are operating in a manner protective to human health and the environment.
3. NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATION, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA
3(a) NONDUPLICATION
Most of the information required by the regulation is not available from any source but the respondents. To avoid duplicating previous work, EPA is allowing respondents to draw upon similar analyses in compiling data for waste analysis and testing requirements, provided the information meets the requirements specified in the regulations.
3(b) CONSULTATIONS
The following consultants were contacted on the burden estimates for this ICR.
Mike Davis Chemical Waste Management (205) 652-8100
John Dyer U.S. Ecology (800) 239-3943
Timothy Orton Energy Solution (801) 649-2144
Kathleen Shoemaker Clean Harbors (870) 864-3711
There are no changes to the burden calculations based on these consultations.
3(c) PUBLIC NOTICE
In compliance with the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995, EPA issued a public notice in the Federal Register on March 26, 2020 (85 FR 17057), and provided a 60 day comment period. One comment was received but it was about the coronavirus pandemic and not about the ICR.
3(d) EFFECTS OF LESS FREQUENT COLLECTION
EPA has carefully considered the burden imposed upon the regulated community by the general facility standards. EPA is confident that those activities required of respondents are necessary, and to the extent possible, have attempted to minimize the burden imposed. EPA believes strongly that if the minimum requirements specified under the regulations are not met, neither the facilities nor EPA can ensure that hazardous wastes are being properly managed, and do not pose a serious threat to human health and the environment.
3(e) GENERAL GUIDELINES
In general, the information collection requirements covered by this ICR adhere to the guidelines stated in the 1995 Paperwork Reduction Act as amended, OMB's implementing regulations, EPA's Information Collection Review Handbook, and other applicable OMB guidance. However, certain general facility regulations listed below require TSDFs to retain records for more than three years. As explained below, EPA believes that maintenance of these records for longer than three years meets substantial needs to protect human health and the environment.
GENERAL FACILITY OPERATING STANDARDS
(1) General Inspection Requirements
The general inspection requirements require the owner or operator to keep inspection records at the facility for at least three years from the date of inspection. Keeping inspection records for longer than three years may be advisable to keep track of any long standing violations or continued areas of concern regarding potential spills, leaks or mismanagement of the hazardous wastes.
(2) Personnel Training
Training records on current employees must be kept at the facility until closure of the facility. Records of former employees must be held for at least three years after the date the employee left the facility. Keeping these records will provide documentation of preparations made for handling hazardous waste, and allow the facility to keep up to date on its employee training.
OPERATING RECORD
Owners or operators are required to maintain an operating record at the facility until closure. This record will help ensure compliance with the hazardous waste regulations, and make it easier to locate the cause of any potential hazardous waste leak or spill.
CLOSURE/POST-CLOSURE PLANS
Owners or operators are required to keep a copy of the closure plan at the facility until closure. The owner or operator is also required to keep the certification of closure at the facility until the facility is released from financial assurance requirements for closure. These requirements assure that the facility is closing in accordance with the regulations at the least possible risk to human health and the environment.
3(f) CONFIDENTIALITY
Section 3007(b) of RCRA and 40 CFR Part 2, Subpart B, which define EPA’s general policy on the public disclosure of information, contain provisions for confidentiality. EPA does not anticipate requesting any confidential information.
3(g) SENSITIVE QUESTIONS
No questions of a sensitive nature are included in any of the information collection requirements.
4. THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED
4(a) RESPONDENTS/NAICS CODES
The following is a list of North American Industrial Classification System (NAICS) codes associated with industries most likely affected by the information collection requirements covered under this ICR.
323110 Commercial Lithographic Printing
323114 Quick Printing
325131 Inorganic Dye and Pigment Manufacturing
325188 All Other Basic Inorganic Chemical Manufacturing
325998 All Other Miscellaneous Chemical Product Manufacturing
331311 Alumina refining
325211 Plastics Material and Resins Manufacturing
32551 Paint and Coating Manufacturing
32511 Petrochemical Manufacturing
32512 Industrial Gas Manufacturing
325188 All Other Inorganic Chemical Manufacturing
325193 Ethyl Alcohol Manufacturing
325199 All Other Basic Organic Chemical Manufacturing
325998 All Other Miscellaneous Chemical Product Manufacturing
311942 Spice and Extract Manufacturing
32411 Petroleum Refineries
332813 Electroplating, Plating, Polishing, Anodizing and Coloring
33271 Machine Shops
332991 All Other Miscellaneous Fabricated Metal Product Manufacturing
333319 Other Commercial or Service Industry Machinery Manufacturing Accessories
333999 All Other General Purpose Machinery Manufacturing
336399 All Other Motor Vehicle Part Manufacturing
334 Computer and Electronic Product Manufacturing
336 Transportation Equipment Manufacturing
48422 Specialized Freight (except Used Goods) Trucking, Local
56211 Waste Collection
22111 Electric Power Generation
22112 Fossil Fuel Electric Power Generation
22132 Sewage Treatment Facilities
56292 Materials Recovery Facilities
56221 Waste Treatment and Disposal
42271 Petroleum Bulk Stations and Terminals
45431 Fuel Dealers
4411 Automobile Dealers
4471 Gasoline Stations
811111 General Automotive Repair
4(b) INFORMATION REQUESTED
The following subsections summarize the data items and respondent activities required for each of the information collection requirements discussed in this ICR. The information collection requirements are divided into seven categories:
General facility operating requirements;
Recordkeeping requirements;
Contingency plan and emergency reporting and recordkeeping requirements;
Closure and post-closure requirements;
Financial requirements;
Corrective action management unit requirements; and
Conditions applicable to all permits.
GENERAL FACILITY OPERATING REQUIREMENTS
(1) Foreign Shipment Import Report
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.12(a) and 265.12(a) require owners or operators that have arranged to receive hazardous wastes from foreign sources to notify the Regional Administrator in writing at least four weeks prior to the expected date of arrival of the shipments at the facility. Data items that should be included in this notification include:
Description of the type and quantity of waste to be received;
Date shipment is expected to arrive; and
Description of how imported waste will be managed at the facility.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with the foreign shipment report requirements, respondents must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Collect data; and
Prepare and submit the notification.
(2) Notice of Appropriate Permits
(i) Data item:
Section 264.12(b) requires the owner or operator of a facility that receives off-site waste to inform the generator in writing that he or she has the appropriate permits, and will accept, the waste the generator is shipping. This notice must be sent to the generator before receiving the first shipment of waste. The owner or operator must retain a copy of the notice at the facility.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with Section 264.12(b), respondents must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare and submit the one-time notice; and
Retain a copy of the notice.
(3) Notice of Part 264 and Part 270 Requirements
(i) Data item:
Sections 264.12(c) and 265.12(b) require owners or operators transferring ownership of a facility during its operating life, or of a disposal facility during the post-closure care period, to notify the new owner or operator in writing of the requirements of 40 CFR Part 264 or 265 and Part 270. This notice must be submitted before the transfer in ownership.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with sections 264.12(c) and 265.12(b), respondents must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations; and
Prepare and submit the notice.
(4) Waste Analysis
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.13(a) (1) and 265.13(a) (1) require an owner or operator to obtain a detailed chemical and physical analysis of any hazardous waste he or she intends to treat, store, or dispose. Sections 264.13(a) (2) and 265.13(a) (2) state that the analysis may include data, either existing or published, developed under 40 CFR Part 261, as well as existing data on the hazardous waste or hazardous waste generated from similar processes.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with sections 264.13(a) (1) and 265.13(a) (1), respondents must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Collect data; and
Perform waste analysis (sampling, testing).
(5) Waste Analysis Plan
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.13(b)-(c) and 265.13(b)-(c) state that an owner or operator of a hazardous waste facility must develop and follow a written waste analysis plan that describes the procedures to be used in obtaining a detailed chemical and physical analysis of the waste. The owner or operator is required to keep the waste analysis plan at the facility. At a minimum, the plan must include the following information:
Parameters for which each hazardous waste will be analyzed and the rationale for the selection of these parameters;
Sampling method used to obtain a representative sample of the waste to be analyzed;
Frequency with which the initial analysis of the waste will be reviewed or repeated to ensure that the analysis is accurate and up to date;
For off-site facilities, the waste analyses that hazardous waste generators have agreed to supply;
Where applicable, the methods which will be used to meet additional waste analysis requirements for specific waste management methods as specified in §§264.17, 264.314, 264.341, 264.1034(d), 264.1063(d), 265.200, 265.225, 265.252, 265.273, 265.314, 265.341, 265.375, 265.402, 265.1034(d), 265.1063(d), and 268.7; For surface impoundments exempted from land disposal restrictions under Section 268.4(a) procedures and schedules for:
-- The sampling of impoundment contents;
-- The analysis of test data;
-- The annual removal of residues which are not delisted under
§260.22 or which exhibit a characteristic of hazardous waste and meet the requirements specified in §§264.13(b)(7)(iii)(A),(B),(B)(1) or (B)(2) and 265.13(b)(7)(iii)(A), (B), (B)(1), or (B)(2); and
For off-site facilities, the procedures used to inspect and analyze each movement of hazardous waste received at the facility, as required under §§264.13(c) and 265.13(c), including:
-- Procedures that will be used to determine the identity of each
movement of waste managed at the facility; and
-- The sampling method which will be used to obtain a representative
sample of the waste to be identified, if the identification method includes sampling.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Since permitted facilities submit the waste analysis plan with the Part B permit application, activities associated with developing and modifying the waste analysis plan are discussed in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Applications, Special Permits, and Permit Modifications ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0009). However, prior to submitting a permit application, an interim status facility must prepare a waste analysis plan. Therefore, preparation and modification of waste analysis plans for interim status facilities will be discussed in this ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0120). In addition to the development of the plan, this ICR will also focus on activities associated with the recordkeeping aspects of the regulations for both permitted and interim status facilities.
To meet the recordkeeping requirement outlined in §§264.13(b) and 265.13(b), owners or operators must file the waste analysis plan at the facility. Activities associated with developing a waste analysis plan include:
Reading the regulations;
Collecting the data required in the waste analysis plan;
Writing the waste analysis plan;
Maintaining the plan (e.g., photocopying and filing); and
Modifying the waste analysis plan (for new and existing interim status facilities).
(6) Inspection Schedule
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.15(b)(1) and 265.15(b)(1) require owners and operators to develop and follow a written schedule for monitoring equipment that is important in preventing, detecting, or responding to environmental or human health hazards. At a minimum, the inspection schedule must include the terms and frequencies called for in §§264.174, 264.194, 264.195, 264.226, 264.253, 264.254, 264.303, 264.347, 264.602, 264.1033, 264.1052, 264.1053, 264.1058, 265.174, 265.193, 265.195, 265.226, 265.347, 265.377, 265.403, 265.1033, 265.1052, 265.1053, and 265.1058 and must identify the types of problems that are to be investigated during the inspection.
Section 264.15(d) and 265.15(d) state that an owner or operator must record inspections conducted according to the written schedule developed pursuant to §§264.15(b)(1) and 265.15(b)(1) in an inspection log or summary that is to be maintained at the facility. The inspection log or summary must contain the following data items:
Date and time of inspection;
Name of inspector;
Notation of the observations made; and
Date and nature of any repairs or other remedial action.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Since permitted facilities submit the inspection schedule with the Part B permit application, activities associated with developing and modifying the schedule are discussed in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Applications, Special Permits, and Permit Modifications ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0009). Prior to submitting a permit application, interim status facilities must prepare an inspection schedule; preparation of and modification to the inspection schedule for these facilities will be discussed in this ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0120). This ICR will also focus on activities associated with the recordkeeping aspects of the regulations for both permitted and interim status facilities.
To meet the requirements outlined in §§264.15(d) and 265.15(d), the owner or operator must conduct the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Develop an inspection schedule (new interim status facilities only);
Maintain and modify the inspection schedule at the facility (new and existing interim facilities only); and
Record problems identified during inspections in the inspection log
(7) Personnel Training
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.16(d) and 265.16(d) require an owner or operator to maintain copies of personnel training documents and records at the facility. These documents should include the following data items:
Job title for each position at the facility related to hazardous waste management, and the name of the employee filling each job;
Written job description for each position, which includes the necessary skill, education, or other qualifications and duties of employees assigned to each position;
Written description of the type and amount of both introductory and continuing training that will be given to each person filling a position; and records that document that the training or job experience required have been given to, and completed by, facility personnel.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondent activities associated with Sections 264.16(d) and 265.16(d) include:
Reading the regulations;
Collecting the data items listed above; and
Maintaining (e.g., photocopying and filing) the information at the facility.
(8) Documentation of Compliance for Ignitable, Reactive, or Incompatible Wastes
(i) Data items:
Section 264.17(c) states that the owner or operator of a hazardous waste facility must take precautions to prevent accidental ignition or reaction of ignitable or reactive waste. The owner or operator of a permitted facility must document compliance with the requirements outlined in §§264.17(a) and (b). The documentation may be based on references to published scientific or engineering literature, data from trial tests (e.g., bench scale or pilot scale tests), waste analyses (as specified in §264.13), or the results of the treatment of similar wastes by similar treatment processes and under similar operating conditions.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondent activities associated with Section 264.17(c) include:
Reading the regulations;
Collecting and documenting the data items mentioned above; and
Maintaining (e.g., photocopying and filing) documentation at the facility.
(9) Construction Quality Assurance Plan
(i) Data items:
Section 265.19(b) requires any owner or operator of an interim status surface impoundment, waste pile, or landfill to develop a written construction quality assurance (CQA) plan that identifies steps that will be used to monitor and document the quality of materials and the condition and manner of their installation. [Permitted facilities must also develop a CQA plan for surface impoundments, waste piles, and landfills. Activities associated with CQA plans at permitted facilities are burdened in the Part B Permit Application, Permit Modifications, and Special Permits ICR, OMB Control No. 2050-0009.] The CQA plan must include the following information:
Identification of applicable units, and a description of how they will be constructed;
Identification of key personnel in the development and implementation of the CQA plan, and CQA officer qualifications;
A description of inspection and sampling activities for all unit components, including observations and tests that will be used before, during, and after construction to ensure that the construction materials and the installed unit components meet design specifications. This description must cover:
- Sampling size and locations;
- Frequency of testing;
- Data evaluation procedures;
- Acceptance and rejection criteria for construction materials;
- Plans for implementing corrective measures; and
- Data or other information to be recorded and retained in the operating record under §265.73.
The owner or operator also must prepare and submit a certification signed by the CQA officer at least 30 days prior to receiving waste that the CQA plan has been successfully carried out and that the unit meets the requirements of §§265.221(a), 265.254, or 265.301(a).
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with Section 265.19, owners and operators must:
Read the regulations;
Prepare the CQA plan;
Prepare the certification;
Submit materials to EPA; and
Maintain records of the materials.
RECORDKEEPING REQUIREMENTS
(1) Operating Record Requirements
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.73 and 265.73 outline specific operating recordkeeping requirements that are imposed on TSDFs. This ICR covers the requirements found at §264.73(b) (1)-(16) and §265.73(b) (1)-(16), which state that the operating record must contain the following data items:
A description and the quantity of each hazardous waste received, and the method(s) and date(s) of its treatment, storage, or disposal at the facility as required by Appendix I;
The location of each hazardous waste within the facility and the quantity at each location. For disposal facilities, the location and quantity of each hazardous waste must be recorded on a map or diagram of each cell or disposal area;
Records and results of waste analyses performed;
Summary reports and details of all incidents that require implementing the contingency plan;
Records and results of inspection reports (which must be kept for three years);
Monitoring, testing, or analytical data and corrective action where required;
Copies of written notices (for off-site facilities) certifying that the facility is permitted and will accept the waste the generator is shipping;
Closure cost estimates and, for disposal facilities, post-closure cost estimates;
A certification by the permittee, no less often than annually, that the permittee has a program in place to reduce the volume and toxicity of hazardous waste that he generates to the degree determined by the permittee to be economically practicable; and the proposed method of treatment, storage, or disposal that is the practicable method currently available to the permittee which minimizes the present and future threat to human health and the environment;
Records of the quantities (and date of placement) for each shipment of hazardous waste placed in land disposal units under an extension to the effective date of any land disposal restriction, or a certification, and the applicable notice required by a generator;
Documents stating refusal of State or local authorities to enter into arrangements to address emergency situations;
Records of hazardous waste application dates and rates; and
Maps detailing (1) the exact location, dimensions, and depths of each cell with respect to permanently surveyed benchmarks, and (2) the contents of each cell and the approximate location of each hazardous waste type within each cell.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with sections 264.73 and 265.73, 264.37, 264.279 and 265.279, and 264.309 and 265.309, owners or operators are required to maintain a written operating record at the facility. Respondent activities associated with maintaining an operating record include maintaining (e.g., photocopying and filing) the data items listed above.
(2) Other Recordkeeping and Reporting Requirements
Sections 264.74(c) and 265.74(c) require owners or operators to submit to the Regional Administrator and local land authority a copy of the records of waste disposal locations and quantities under §§264.73(b)(2) and 265.73(b)(2) upon closure of the facility. Since this information is submitted upon closure of the facility, data items and respondent activities are included in the closure/post-closure section.
CONTINGENCY PLAN AND EMERGENCY REPORTING REQUIREMENTS
Contingency Plan Requirements
Data items:
Sections 264.51 and 265.51 require owners or operators to have a contingency plan for their facilities and sections 264.53(a) and 265.53(a) require the owner or operator to maintain a copy of an updated contingency plan at the facility. Sections 264.52 and 265.52 outline the data elements that should be included in this plan:
A description of the arrangements agreed to by local police departments, fire departments, hospitals, contractors, and State and local emergency response teams to coordinate emergency services;
An updated list of the names, addresses, and phone numbers (office and home) of all persons qualified to act as emergency coordinators;
An updated list of all emergency equipment at the facility and the location, physical description, and capabilities of the emergency equipment. The contingency plan should also indicate where the emergency equipment will be required; and
An evacuation plan for facility personnel where there is a possibility that evacuation may be necessary.
In addition, sections 264.53(b) and 265.53(b) require owner/operators to submit a copy of the contingency plan and all revisions to all local police departments, fire departments, hospitals, and State and local emergency response teams that may be called upon to provide emergency services.
Respondent activities:
Since permitted facilities submit the contingency plan with the Part B permit application, activities associated with developing and modifying the contingency plan are discussed in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Applications, Special Permits, and Permit Modifications ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0009). Interim status facilities must prepare contingency plans prior to submitting a permit application; therefore, preparation of the contingency plan for these facilities is covered under this ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0120). This ICR also includes submittal of the plan to State and local authorities and recordkeeping activities for both permitted and interim status facilities.
In order to comply with contingency plan requirements, owners or operators are required to perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Collect the data required in the contingency plan;
Write the contingency plan (new interim status facilities only);
Submit the contingency plan to State and local authorities;
Maintain (e.g., photocopy and file) the contingency plan; and
Amend the contingency plan when appropriate.
[Although permitted and interim-status facilities must comply with appropriate requirements for amending a contingency plan, this ICR addresses only interim status facilities amending their plans. As mentioned, permitted facilities amending their plans must comply with sections 264.54 and submit a permit modification under section 270.42. These permitted facilities are addressed in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Applications, Special Permits, and Permit Modifications, ICR OMB Control No. 2050-0009].
(2) Emergency Reporting and Recordkeeping Requirements
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.56(a) (2) and 265.56(a) (2) require owners and operators to immediately notify State and local authorities with designated response roles of an imminent or actual emergency situation. Sections 264.56(d)(1) and 265.56(d)(1) require owners and operators to notify local authorities if his or her assessment of a release, fire, or explosion indicates that evacuation of local areas may be advisable.
Sections 264.56(d) (2) and 265.56(d) (2) require the facility emergency coordinator to notify the on-scene coordinator or the National Response Center of any release, fire, or explosion that could threaten human health or the environment outside the facility. The emergency notification report must include the following information:
Name and telephone number of reporter;
Name and address of facility;
Time and type of incident;
Name and quantity of material(s) involved;
The extent of injuries; and
Possible hazards to human health or the environment outside the facility.
Sections 264.56(i) and 265.56(i) state that the owner or operator should notify the Regional Administrator and appropriate State and local authorities that their facility is in compliance with §§264.56(h) and 265.56(h) before resuming operations in the affected area(s) of the facility.
Within 15 days of the incident, owners and operators are required, under Sections 264.56(j) and 265.56(j) to submit a written report ("owner/operator emergency report") on the incident to the Regional Administrator. The report must include the following data items:
Name, address, and telephone number of the owner or operator;
Name, address, and telephone number of the facility;
Date, time, and type of incident;
Name and quantity of material(s) involved;
The extent of injuries;
An assessment of actual or potential hazards to human health or the environment; and
Estimated quantity and disposition of recovered material that resulted from the incident.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with the reporting requirements of §264.56(a) (2) and §265.56(a) (2), owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Submit the required notification of an imminent or actual emergency situation to State and/or local authorities.
In order to comply with the reporting requirements of §264.56(d) (1) and §265.56(d) (1), owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Notify local authorities of the owner or operator's recommendation to evacuate local areas.
In order to comply with the reporting requirements of §264.56(d) (2) and §265.56(d) (2), owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Notify the on-scene coordinator or the National Response Center of any release.
In order to prepare an emergency report under §264.56(d) (2) and §265.56(d) (2), emergency coordinators must conduct the following activities:
Collect the information required in the emergency report; and
Write the emergency notification report.
In order to prepare an owner/operator's emergency report under §264.56(j) and §265.56(j), owners and operators must conduct the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Collect the information required in the emergency report; and
Prepare and submit the emergency report.
In addition to preparing an emergency report, the owner or operator must notify the Regional Administrator that the facility is in compliance with §§264.56(h) and 265.56(h) before resuming operations in affected areas of the facility. In order to comply with this requirement, respondents must conduct the following activities:
Compile information that demonstrates that all affected areas are in compliance; and
Prepare and submit a letter notifying the Regional Administrator of this compliance.
Sections 264.56 and 265.56 require the owner/operator to note in the operating record the time, date, and details of any incident that requires implementing the contingency plan (§§264.56(j) and 265.56(j)). Respondent activities associated with this requirement are burdened in the respondent activity section for the operating record requirements.
CLOSURE AND POST-CLOSURE REQUIREMENTS
(1) Closure Plan
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.112(a) and 265.112(a) state that an owner or operator must have a written closure plan. The closure plan must include the following data items:
A description of how each hazardous waste management unit at the facility will be closed in accordance with §§264.111 and 265.111;
A description of how final closure of the facility will be conducted in accordance with §§264.111 and 265.111. The description must identify the maximum extent of operations which will be unclosed during the active life of the facility;
An estimate of the maximum inventory of hazardous wastes ever on-site over the active life of the facility. This should include a detailed description of the methods to be used during partial closures and final closure such as methods for removing, transporting, treating, storing, or disposing of all hazardous wastes, and identification of the type(s) of off-site hazardous waste management units to be used, if applicable;
A detailed description of the steps needed to remove or decontaminate all hazardous waste residues and contaminated containment system components, equipment, structures, and soils during partial and final closure;
A detailed description of other activities necessary during the closure period to ensure that all partial closures and final closure satisfy the closure performance standards, including ground-water monitoring, leachate collection, and run-on and run-off control;
A schedule for closure of each hazardous waste management unit and for final closure of the facility. The schedule must include, at a minimum:
-- The total time required to close each hazardous waste
management unit; and
-- The time required for intervening closure activities which will allow tracking of the progress of partial and final closure; and
For facilities that use trust funds to establish financial assurance under §§264.143 and 265.143, or 264.145 and 265.145, and that are expected to close prior to the expiration of the permit, an estimate of the expected year of final closure.
Certain permitted surface impoundments and waste piles from which the owner or operator intends to remove or decontaminate the hazardous waste at partial or final closure are required by Sections 264.228(c)(1)(ii) and 264.258(c)(1)(ii) to have contingent closure plans. In addition, owners or operators of tank systems or drip pads that intend to remove or decontaminate hazardous waste at partial or final closure are required to submit contingent closure plans as specified in sections 264.197(c)(1) and 265.197(c)(1), and 264.575(c)(1)(i)and 265.445(c)(1)(i), respectively.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Since permitted facilities submit the closure plan and contingency closure plans with the Part B permit application, activities associated with developing and modifying the closure plan are discussed in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Applications, Special Permits, and Permit Modifications ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0009). Prior to submitting a permit application, interim status facilities must prepare a closure plan. Therefore, preparation of and modification to the closure plan for interim status facilities will be covered in this ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0120). This ICR will also include activities associated with the recordkeeping aspects of the regulations for both permitted and interim status facilities.
Maintaining the closure plan at the facility is the only respondent activity associated with the recordkeeping aspects of this regulation. Respondent activities associated with developing a closure plan include:
Reading the regulations;
Conducting an inventory of the hazardous waste present;
Recording results of inventory;
Writing descriptions for the necessary activities;
Estimating final closure; and
Writing the closure schedule.
(2) Notification and Amendment of Closure Plan
(i) Data items:
Permit modifications for permitted facilities under section 264.112(c) are included in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Applications, Special Permits, and Permit Modifications ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0009). Under section 265.112(c), owners or operators of interim status facilities may amend the closure plan at any time prior to notification of partial or final closure of the facility. An owner or operator with an approved closure plan must submit a written request to EPA to authorize a change in the approved closure plan. The owner or operator must amend the closure plan at least 60 days prior to the proposed change in the facility design or operation, or no later than 60 days after an unexpected event has occurred which has affected the closure plan. An owner or operator with an approved closure plan must submit the amended plan to EPA.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Interim status facilities with approved closure plans must prepare and submit a notification of amendment, amend the plan, and submit the plan to EPA, pursuant to section 265.112(c).
(3) Partial Closure and Final Closure Notification
(i) Data items:
Under Section 264.112(d)(1), owners or operators of permitted facilities must notify the Regional Administrator of imminent closure intentions. Section 265.112(d)(1) requires owners or operators of interim status facilities with approved closure plans to notify EPA of closure in writing within a specified period of time before closure of the unit. Section 265.112(d)(1) also requires owners or operators of interim status facilities to submit a closure plan to the Regional Administrator prior to closure. In addition, section 265.112(d)(3) requires owners or operators of interim status facilities to submit the closure plan to the Regional Administrator no later than 15 days after termination of interim status.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Under section 264.112(d)(1) or 265.112(d)(1) permitted and interim status facilities must prepare and submit a notification to EPA of imminent closure. Interim status facilities also must submit a closure plan under section 265.112(d)(1) or 265.112(d)(3).
(4) Extensions and Allowances During the Closure Period
(i) Data items:
Under 40 CFR 264.113 and 265.113, owners and operators may prepare demonstrations in support of certain extensions and allowances during the closure period. Sections 264.113(a) and 265.113(a) allow owners and operators to request an extension for the treatment, storage, or removal of hazardous waste. To receive such an extension, the owner or operator must request a permit modification and demonstrate the following:
Treatment, storage, and removal activities will, of necessity, take longer than 90 days to complete; or
The hazardous waste management unit or facility has the capacity to receive additional hazardous or non-hazardous wastes; there is a likelihood that operations will be recommenced within one year; and closure of the unit would be incompatible with continued operation of the site; and
The owner or operator has taken and will continue to take all steps necessary to prevent threats to human health and the environment, including compliance with all applicable permit requirements.
Sections 264.113(b) and 265.113(b) allow owners and operators to request an extension of the closure period. To receive such an extension, the owner or operator must request a permit modification and demonstrate the following:
Partial of final closure activities will, of necessity, take longer than 180 days to complete; or
The hazardous waste management unit or facility has the capacity to receive additional hazardous or non-hazardous wastes; there is a reasonable likelihood that operations will be recommenced within one year; and closure of the unit would be incompatible with continued operation of the site; and
The owner or operator has taken and will continue to take all steps necessary to prevent threats to human health and the environment, including compliance with all applicable permit requirements.
Sections 264.113(d) and 265.113(d) allow owners and operators to request an allowance to receive only non-hazardous wastes in a landfill, land treatment, or surface impoundment unit after the final receipt of hazardous waste. To receive such an allowance, the owner or operator must request a permit modification, and include the following demonstrations and information:
The unit has the existing design capacity as indicated on the part A application to receive non-hazardous wastes;
There it a reasonable likelihood that operations will be recommenced within one year after the final receipt of hazardous wastes;
The non-hazardous wastes will not be incompatible with any remaining wastes in the unit or facility;
Closure of the unit would be incompatible with continued operation of the site;
The owner or operator is operating and will continue to operate in compliance with all applicable permit requirements;
The request to modify the permit includes an amended waste analysis plan, ground-water monitoring and response program, human exposure assessment, closure and post-closure plans, updated cost estimates and demonstrations of financial assurance for closure and post-closure care, and changes in closure activities.
(ii) Respondent activities:
The burden associated with developing a permit modification for such an extension or allowance is addressed in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Application, Permit Modifications, and Special Permits ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0009). Other respondent activities associated with obtaining an extension or allowance include the following:
Reading the regulations;
Preparing and submitting the demonstration for an extension for treatment, storage, or removal of hazardous waste;
Preparing and submitting the demonstration for an extension of the closure period; and
Preparing and submitting the demonstration for receiving non-hazardous wastes.
(5) Closure Certification
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.115 and 265.115 require owners or operators to submit to the Regional Administrator a certification that the unit or facility has been closed in accordance with the specifications in the approved closure plan. Documentation supporting the independent registered professional engineer's certification must be furnished to the Regional Administrator upon request before he or she releases the owner or operator from the financial assurance requirements for closure under §§264.143(i) and 265.143(h).
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to certify that the unit or facility has been closed in accordance with the specifications in the approved closure plan, respondents must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Have a registered professional engineer inspect the facility; and
Collect documentation to support the certification and submit the certification.
(6) Survey Plat
(i) Data item:
Sections 264.116 and 265.116 require an owner or operator to submit to the Regional Administrator a survey plat indicating the location and dimensions of landfill cells or other hazardous waste disposal units with respect to permanently surveyed benchmarks.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with §264.116 and §265.116, respondents must have a professional land surveyor prepare and certify a survey plat, and submit the plat to the Regional Administrator.
(7) Post-Closure Plan
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.118(a) and 265.118(a) state that the owner or operator of a hazardous waste disposal facility must have a written post-closure plan. Surface impoundments and waste piles from which the owner or operator intends to remove or decontaminate the hazardous waste at partial or final closure are required by §§264.228(c)(1)(ii) and 264.258(c)(1)(ii) to have contingent post-closure plans submitted with the Part B permit application. In addition, owners or operators of tank systems or drip pads that intend to remove or decontaminate the hazardous waste at partial or final closure are required to submit a contingent post-closure plan, as specified in sections 264.197(c)(2) and 265.197(c)(2), and 264.575(c)(1)(ii) and 265.445(c)(1)(ii), respectively. Section 265.118 requires owners or operators to maintain a copy of the post-closure plan at the facility.
Data items included in the post-closure plan are listed below:
A description of the facility's monitoring activities and frequencies at which they will be performed to comply with Subparts F, K, L, M, N, and X during the post-closure care period;
A description of the planned maintenance activities, and frequencies at which they will be performed;
The name, address, and phone number of the person or office to contact about the hazardous waste disposal unit or facility during the post-closure care period; and
A copy of the approved post-closure plan, to be provided to the Regional Administrator upon request, until final closure of the facility.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Since permitted facilities submit post-closure and contingent post-closure plans with the Part B permit application, activities associated with developing these post-closure plans are discussed in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Applications, Special Permits, and Permit Modifications ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0009). Prior to submitting a permit, interim status facilities must develop a post-closure plan. Therefore, preparation of these plans for interim status facilities will be covered in this ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0120). This ICR will also focus on activities associated with the recordkeeping aspects of the regulations for both permitted and interim status facilities.
Section 265.118(e) requires an interim status facility owner or operator to submit a post-closure plan to the Regional Administrator no later than 15 days after termination of interim status, except when a permit is issued simultaneously with termination of interim status, or the facility is issued a judicial decree or final order under §3008 of RCRA to cease receiving hazardous wastes or close. If the Regional Administrator does not approve the plan, the owner or operator must modify the plan or submit a new plan for approval.
In order to comply with the post-closure plan requirements, respondents must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Collect the necessary information;
Prepare and submit the post-closure plan or contingent post-closure plan, if applicable (new interim status facilities only); and
Maintain the plan.
(8) Notification and Amendment of Post-Closure Plan Under 265.118(d)(1)-(3)
(i) Data items:
Section 265.118(d)(1)-(3) requires owners or operators of interim status facilities to submit written requests to authorize changes to approved post closure plans, and requires submittal of modified plans to the Regional Administrator. Under section 264.118(d)(1)-(3), permitted facilities must request permit modifications to authorize and make changes to approved post-closure plans. Such permit modifications are included in ICR OMB Control No. 2050-0009.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Interim status facilities must:
Prepare a notification of amendment;
Amend the plan; and
Submit these data items to EPA, as required by section 265.118(d)(1)-(3).
(9) Amendment of Post-Closure Plan Under 265.118(d)(4), (f), and (g)(1)
(i) Data items:
Under 40 CFR 265.118(d)(4), if the Regional Administrator determines that an owner or operator of a surface impoundment or waste pile who intended to remove all hazardous wastes at closure must close the facility as a landfill, the owner or operator must submit to the Regional Administrator within 90 days of the determination a post-closure plan for approval. If the Regional Administrator requests modifications to the plan, the owner or operator must submit the modified plan no later than 60 days after the Regional Administrator's request or no later than 90 days if the unit is a surface impoundment or waste pile not previously required to prepare a contingent closure plan.
Under section 265.118(f), if the Regional Administrator does not approve the plan, he or she must provide the owner or operator with a detailed written statement of reasons for the refusal. The owner or operator must modify the plan or submit a new plan within 30 days after receiving such written statement.
Under section 265.118(g)(1), the owner or operator may prepare and submit a petition to the Regional Administrator to extend or reduce the post-closure period applicable to a hazardous waste management unit or facility, or to alter the requirements of the post-closure care period.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with sections 265.118(d)(4) and 265.118(f), respondents must perform the following activities:
Prepare an amended post-closure plan;
Submit the amended plan to EPA; and
Modify and resubmit plan, if not approved by EPA
In order to obtain an extension or reduction of the post-closure period, per section 265.118(g)(1), respondents must prepare a petition and submit it to EPA. (Permitted facilities are covered in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Applications, Specific Permits and Permit Modifications ICR, OMB Control No. 2050-0009.)
(10) Hazardous Waste Disposal Records
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.119(a) and 265.119(a) require owners or operators to submit to the local zoning authority, or to the authority with jurisdiction over local land use, and to the Regional Administrator a record of the type, location, and quantity of hazardous wastes disposed of within each cell or other disposal unit of the facility.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with sections 264.119(a) and 265.119(a), respondents must perform the following activities:
Determine the specifications of the hazardous waste activity; and
Establish, submit, and maintain (i.e., photocopying and filing) a record of the activity.
(11) Hazardous Waste Notation Certification
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.119(b)(2) and 265.119(b)(2) require owners or operators to submit to the Regional Administrator a signed certification that they have recorded the notation required in §§264.119(b)(1) and 265.119(b)(1), including a copy of the document in which the notation has been placed.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with sections 264.119(b)(2) and 265.119(b)(2), respondents must record the notation on the deed, and develop and submit the certification to the Regional Administrator.
(12) Post-Closure Permit Modification
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.119(c) and 265.119(c) state that if an owner wishes to remove hazardous wastes and residues, liners, or contaminated soils, he or she must request a modification to the post-closure permit and demonstrate that removal of hazardous waste will satisfy the criteria of §§264.117(c) and 265.118(g). For permitted facilities, the modification will be done through the permit modification process and will be covered by the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Applications, Special Permits, and Permit Modifications ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondent activities associated with modification of the post-closure permit include:
Reading the regulations;
Preparing a request for modification; and
Demonstrating compliance through a written document or some other form of notification.
(13) Post-Closure Care Certification
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.120 and 265.120 state that owners or operators must submit to the Regional Administrator a certification that the post-closure care period for the facility was performed in accordance with the specifications in the approved closure plan. Documentation supporting the independent registered professional engineer's certification must be furnished to the Regional Administrator upon request before he or she releases the owner from the financial assurance requirements for closure under §§264.145(i) and 265.145(h).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondent activities associated with certifying completion of post-closure care include:
Reading the regulations;
Obtaining certification of compliance from an independent registered professional engineer;
Maintaining a copy of the certification; and
Submitting the necessary documentation to the Regional Administrator as required.
FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS
(1) Financial Responsibility for Corrective Action
(i) Data item:
Sections 264.101(b) and 264.101(c) require owners and operators of facilities containing solid waste management units (SWMUs) to institute corrective action as necessary, and to provide assurances of financial responsibility for completing such corrective action. This assurance must contain the documented assurances of financial responsibility in the permit for the means of corrective action chosen.
(ii) Respondent activity:
In order to comply with sections 264.101(b) and 264.101(c), respondents must prepare and submit to the Regional Administrator, with the permit, documented assurances of financial responsibility for the corrective action chosen to be implemented.
(2) Cost Estimates for Closure and Post-Closure Care
Data items
Sections 264.142, 265.142, 264.144, and 265.144 require owners and operators to maintain a detailed written estimate of the cost of facility closure or post-closure care, in accordance with the requirements specified in §§264.142(a), 265.142(a), 264.144(a), and 265.144(a), respectively. Section 264.144 only applies to owners or operators of disposal surface impoundments, disposal miscellaneous units, land treatment units, or landfill units, or owners or operators of surface impoundments or waste piles required to prepare contingency closure and post-closure plans, while Section 265.144 applies to owners or operators of interim status hazardous waste disposal units. These estimates must include the following data items:
A written estimate containing:
-- The costs of final closure at the point in the facility's active life
when the extent and manner of its operation would make closure the most expensive, as indicated by its closure plan (§§264.142(a)(1) and 265.142(a)(1)); or
-- The annual cost of post-closure monitoring and maintenance of the
facility in accordance with the applicable post-closure regulations specified in §§264.144(a) and 265.144(a);
Estimates of the following cost, as required under §264.258(c)(2) for waste piles only:
-- The cost of complying with the contingent closure plan or the
contingent post-closure plan, but not the cost of expected closure under §264.258(c)(2);
Estimates of the following cost, as required under §§264.197(c)(3) and 265.197(c)(3) for tank systems only:
-- The cost of complying with the contingent closure plan and the
contingent post-closure plan, if those costs are greater than the costs of complying with the closure plan prepared for the expected closure under §§264.197(a) and 265.197(a).
Estimates of the following cost, as required under §264.228(c)(2) for surface impoundments, §§264.575(c)(2) and 265.445(c)(2) for drip pads, and §264.258(c)(2) for waste piles:
-- The cost of complying with the contingent closure plan and the
contingent post-closure plan, but not the cost of expected closure under §§264.228(a) for surface impoundments, 264.575(a) or 265.445(a) for drip pads, and 264.258(a) for waste piles.
Costs to owners or operators of hiring a third party to conduct closure or post-closure care at the facility;
An adjustment of the closure or post-closure cost estimate for inflation within sixty days of the anniversary date of the establishment of the financial instrument(s) used to assure financial responsibility for closure (thirty days in the case of owners or operators using the financial test or corporate guarantee)(§§264.142(b), 265.142(b), 264.144(b), and 265.144(b)); and
A revision of the closure or post-closure cost estimate no later than thirty days after a modification has been made to the closure or post-closure plan which increases the closure or post-closure cost (§§264.142(c), 265.142(c), 264.144(c), and 265.144(c)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owners and operators will need to engage in several activities in order to collect and maintain the data required by §§264.142, 265.142, 264.144, and 265.144:
Reading the regulations;
Collecting data;
Preparing the written cost estimate;
Periodically adjusting the cost estimate to include inflation and/or revisions to the closure or post-closure plan; and
Maintaining at the facility the latest closure or post-closure cost estimate and any subsequent adjustments.
(3) Financial Assurance for Closure and Post-Closure Care
Owners or operators are required to establish and provide evidence of financial assurance for facility closure (§§264.143 and 265.143) and post-closure care (§§264.145 and 265.145). Several financial instruments are described throughout these sections for the purpose of establishing financial assurance:
(a) Closure or Post-Closure Trust Fund
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.143(a), 265.143(a), 264.145(a), and 265.145(a) explain that owners or operators may establish a closure or post-closure trust fund in order to comply with §§264.143, 265.143, 264.145, and 265.145 requirements. Data items for establishing and providing evidence of a closure or post-closure trust fund include:
A trust agreement in compliance with §§264.143(a)(2)-(8) and (10), 265.143(a)(2)-(8) and (10), 264.145(a)(2)-(8) and (11), and 265.145(a)(2)-(8) and (11); and
For post-closure trust funds, a formal certification of acknowledgment (§§264.145(a)(2) and 265.145(a)(2)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owners and operators establishing a trust fund in order to comply with the closure and post-closure financial assurance requirements of sections 264.143, 265.143, 264.145, and 265.145 will need to engage in the following respondent activities:
Reading the regulations;
Establishing a closure or post-closure trust fund, in compliance with §§264.143(a)(2)-(8) and (10), 265.143(a)(2)-(8) and (10), 264.145(a)(2)-(8) and (11), and 265.145(a)(2)-(8) and (11);
Submitting an originally signed duplicate of the trust agreement to the EPA Regional Administrator (owners or operators of new facilities must submit this at least sixty days prior to receiving hazardous waste for treatment, storage, or disposal);
Submitting the formal certification of acknowledgment required for post-closure trust funds; and
For owners and operators of new facilities, submitting a receipt for the first payment under the trust agreement before the initial receipt of hazardous wastes.
(b) Surety Bond Guaranteeing Payment into a Closure or Post-Closure Trust Fund
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.143(b), 265.143(b), 264.145(b), and 265.145(b) allow owners and operators to establish surety bonds in order to comply with the financial assurance requirements of Sections 264.143, 265.143, 264.145, and 265.145. Establishing surety bonds that guarantee payment into a closure or post-closure trust fund will entail the collection of the following data items:
A surety bond and trust agreement indicating the conditions of payment into the closure or post-closure standby trust fund specified in §§264.143(b)(2)-(6) and (8), 265.143(b)(2)-(6) and (8), 264.145(b)(2)-(6) and (8), and 265.145(b)(2)-(6) and (8); and
Evidence of an increase or decrease in the closure or post-closure cost estimate that may require the penal sum of the surety bond to be increased or decreased accordingly (§§264.143(b)(7), 265.143(b)(7), 264.145(b)(7), and 265.145(b)(7)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
In collecting these data items, owners and operators will need to engage in the following respondent activities:
Reading the regulations;
Establishing a surety bond and trust agreement that comply with the financial assurance requirements of §§264.143, 265.143, 264.145, and 265.145;
Submitting originally signed duplicates of the surety bond and trust agreement to the Regional Administrator (for new facilities, these must be submitted at least sixty days before receiving hazardous waste for disposal);
Submitting evidence of and obtaining approval from the Regional Administrator for alternate financial assurance mechanisms, in the case of cancellation of the bond by the surety;
Increasing the penal sum amount, in the case of a corresponding increase in the closure or post-closure cost estimate; and
Submitting evidence of such an increase in the closure or post-closure cost estimate to the Regional Administrator.
(c) Surety Bond Guaranteeing Performance of Closure or Post-Closure Care
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.143(c) and 264.145(c) allow owners or operators of permitted facilities to comply with §§264.143 and 264.145 requirements by obtaining a surety bond that guarantees performance of closure or post-closure care. Data items for this option include:
A surety bond and trust agreement indicating the conditions of payment into the standby trust fund specified in §§264.143(c)(2)-(6) and (8) and 264.145(c)(2)-(6) and (9); and
Evidence of an increase in the closure or post-closure cost estimate that may require the penal sum of the surety bond to be increased or decreased accordingly (§§264.143(c)(7) and 264.145(c)(7)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
In collecting these data items, owners and operators will need to engage in the following respondent activities:
Reading the regulations;
Obtaining a surety bond and trust agreement that comply with the financial assurance requirements of §§264.143 and 264.145;
Submitting originally signed duplicates of the surety bond and trust agreement to the Regional Administrator (for new facilities, these must be submitted at least sixty days prior to receiving hazardous wastes for disposal);
Submitting evidence of and obtaining approval from the Regional Administrator for alternate financial assurance mechanisms, in the case of cancellation of the bond by the surety;
Increasing the penal sum amount, in the case of a corresponding increase in the closure or post-closure cost estimate; and
Submitting evidence of such an increase in the closure or post-closure cost estimate to the Regional Administrator.
(d) Closure or Post-Closure Letter of Credit
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.143(d), 265.143(c), 264.145(d), and 265.145(c) specify that owners or operators may obtain an irrevocable standby letter of credit in order to satisfy financial assurance requirements. Data items for this information collection include:
A letter of credit from an issuing institution authorized to issue letters of credit and whose letter-of-credit operations are regulated and examined by a Federal or State agency;
A trust agreement indicating the conditions of payment into the standby trust fund specified in §§264.143(d)(2)-(4) and (6), 265.143(c)(2)-(4) and (6), 264.145(d)(2)-(6), and 265.145(c)(2)-(6);
Notification from the issuing institution to the owner/operator and EPA of a decision not to extend the expiration date mailed at least 120 days before the current expiration date of the letter of credit (§§264.143(d)(5) and 265.143(c)(5));
A letter (to accompany the letter of credit) from the owner or operator providing the following information:
-- The number, issuing institution, and date of the letter of credit;
-- The EPA identification number, name, and address of the facility; and
-- The amount of funds assured for closure of or post-closure care for the facility by the letter of credit; and
Evidence of an increase in the closure or post-closure cost estimate that may require the amount of credit to be increased accordingly (§§264.143(d)(7), 265.143(c)(7), 264.145(d)(7), and 265.145(c)(7)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owners or operators will need to engage in the following activities in order to satisfy the financial assurance requirements with a closure or post-closure letter of credit:
Reading the regulations;
Obtaining a letter of credit from an issuing institution and establishing the stand-by trust fund;
Writing a letter from the owner or operator to accompany the letter of credit;
Submitting the following documents to the Regional Administrator:
-- The letter of credit (in the case of new permitted facilities, this must be submitted at least sixty days prior to receiving hazardous waste for treatment, storage, or disposal, pursuant to §§264.143(d)(1) and 264.145(d)(1));
-- The accompanying letter from the owner or operator; and
-- An originally signed duplicate of the trust agreement;
Increasing the amount of the letter of credit, in the case of corresponding increase in the closure or post-closure cost estimate; and
Submitting evidence of such an increase in the closure or post-closure cost estimate to the Regional Administrator.
(e) Closure or Post-Closure Insurance
(i) Data items:
Owners or operators may satisfy the financial assurance requirements for closure or post-closure care by establishing closure or post-closure insurance according to §§264.143(e), 265.143(d), 264.145(e), and 265.145(d). Data items for this information collection include:
A closure or post-closure insurance policy (identified by a certificate of insurance) that meets the requirements specified in §§264.143(e)(1)-(4) and (8), 265.143(d)(1)-(4) and (8), 264.145(e)(1)-(5) and (8), or 265.145(d)(1)-(5) and (8);
In the case of some interim status facilities, a letter from an insurer stating that an owner or operator is being considered for a closure insurance policy (§§265.143(d)(1) and 265.145(d)(1)); and
Evidence of an increase in the closure or post-closure cost estimate that may require the face amount of the insurance policy to be increased accordingly (§§264.143(e)(7), 265.143(d)(7), 264.145(e)(7), and 265.145(d)(7)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Collecting this data will entail the following respondent activities:
Reading the regulations;
Obtaining a closure or post-closure insurance policy that satisfies the requirements of §§264.143, 265.143, 264.145, or 265.145;
Submitting a certificate of this insurance policy to the Regional Administrator (for new facilities, this must be submitted at least sixty days prior to receiving hazardous wastes for treatment, storage, or disposal);
In the case of some interim status facilities, submitting a letter from an insurer stating that the insurer is considering issuance of an insurance certificate (in this case, owners or operators must submit the certificate of insurance within ninety days of the effective date of these regulations); and
Submitting evidence of an increase in the current closure or post-closure cost estimate that may require the face amount of the insurance policy to be modified accordingly.
(f) Financial Test and Corporate Guarantee for Closure or
Post-Closure Care
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.143(f), 265.143(e), 264.145(f), and 265.145(e) allow owners and operators to satisfy closure or post-closure financial assurance requirements by demonstrating financial strength using the financial test specified in these sections. Data items for this demonstration include:
A letter signed by the owner's or operator's chief financial officer and worded as specified in §264.151(f);
A copy of an independent certified public accountant's report on examination of the owner's or operator's financial statements for the latest completed fiscal year;
A special report from the owner's or operator's independent certified public accountant to the owner or operator covering the specifications outlined in §§264.143(f)(3)(iii), 265.143(e)(3)(iii), 264.145(f)(3)(iii), or 265.145(e)(3)(iii);
If an extension of submission of the above documents is sought, a letter from the owner's or operator's chief financial officer to the Regional Administrator of each Region in which facilities to be covered under the financial test are located. This letter, allowed only under §§265.143(e)(4) and 265.145(e)(4), must contain the following data items:
-- A request for the extension;
-- A certification that the chief financial officer believes that the owner or operator meets the criteria of the financial test;
-- For each facility to be covered by the test, the EPA identification number, name, address, and current closure and post-closure cost estimates to be covered by the test;
-- A specification of the date (no later than ninety days after the end of such fiscal year) when the owner or operator will submit the documents specified in §§265.143(e)(3) and 265.145(e)(3); and
-- A certification that the year-end financial statements of the owner or operator for such fiscal year will be audited by an independent certified public accountant;
Annual updates of the above data items;
A notice of intent to establish alternative financial assurance, if the owner or operator fails the financial test and no longer meets the requirements of §§264.143(f)(1), 265.143(e)(1), 264.145(f)(1), or 265.145(e)(1);
Reports of financial conditions as required by the Regional Administrator (§§264.143(f)(7), 265.143(e)(7), 264.145(f)(7), and 265.145(e)(7));
If applicable, a written guarantee from the parent corporation of the owner or operator that satisfies financial assurance requirements (§§264.143(f)(10), 265.143(e)(10), 264.145(f)(10), or 265.145(e)(10)); and
Notification from the insurer to the owner/operator and EPA of a decision to cancel, terminate, or fail to renew the policy (§§264.145(f)(11)(ii) and 265.143(e)(11)(ii)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owners or operators will need to engage in the following respondent activities in order to collect the data required by these sections:
Reading the regulations;
Writing the letter signed by the chief financial officer;
Submitting the following documents to the Regional Administrator (for new facilities, these documents must be submitted at least sixty days prior to receiving hazardous waste for treatment, storage, or disposal):
-- The letter signed by the chief financial officer;
-- A copy of the independent certified public accountant's report; and
-- The special report from the independent certified public accountant;
Submitting updated information annually;
If applicable, writing and submitting a notice, by certified mail, to the Regional Administrator of intent to establish other financial assurance;
Writing and submitting additional reports of financial condition at any time, as directed by the Regional Administrator; and
If applicable, submitting the corporate guarantee from the parent corporation of the owner or operator.
(g) Use of a Financial Mechanism for Multiple Facilities
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.143(h), 265.143(g), 264.145(h), and 265.145(g) specify that owners or operators may use one of the above financial assurance mechanisms to meet the requirements of §§264.143, 265.143, 264.145, or 265.145 for more than one facility. In such cases, the owner and operator must provide the following data items for each facility:
EPA identification number, name, and address; and
The amount of funds for closure or post-closure care assured by the mechanism.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of these sections, owners and operators will need to engage in the following activities:
Reading the regulations;
Submitting the data items listed above to the Regional Administrator; and
If the facilities covered by the mechanism are located in more than one Region, submitting identical evidence of financial assurance to all the applicable Regional Administrators.
(4) Liability Requirements
(a) Coverage for Sudden or Nonsudden Accidental Occurrences
Data items:
Sections 264.147(a) and 265.147(a) specify that owners and operators of hazardous waste treatment, storage, and disposal facilities must demonstrate financial responsibility for bodily injury and property damage to third parties caused by sudden accidental occurrences arising from operations of the facility or group of facilities. Similarly, §§264.147(b) and 265.147(b) require owners or operators of surface impoundments, landfills, land treatment facilities managing hazardous wastes, or combinations of such facilities to demonstrate financial responsibility for bodily injury and property damage to third parties caused by nonsudden accidental occurrences arising from facilities' operations. In order to comply with these sections, owners or operators will need to gather the following data items:
Liability coverage demonstrated by one of the following documents (data items for these documents are described in full in the following sections):
-- A liability insurance policy (§§264.147(a)(1), 265.147(a)(1), 264.147(b)(1), or 265.147(b)(1)), accompanied by a signed duplicate original of a Hazardous Waste Facility Liability Endorsement or a
Certificate of Liability Insurance (§§264.147(a)(1) and 264.147(b)(1) only);
-- Written evidence of passing a financial test or a written
guarantee for liability coverage from the owner's or operator's parent corporation, a firm whose parent corporation is the parent corporation of the owner or operator, or a firm with a "substantial business relationship" with the owner or operator (§§264.147(a)(2), 265.147(a)(2), 264.147(b)(2), and 265.147(b)(2));
-- A letter of credit for liability coverage (§§264.147(a)(3),
265.147(a)(3), 264.147(b)(3), and 265.147(b)(3));
-- A surety bond for liability coverage (§§264.147(a)(4),
265.147(a)(4), 264.147(b)(4), and 265.147(b)(4));
-- A trust fund for liability coverage (§§264.147(a)(5), 265.147(a)(5),
264.147(b)(5), and 265.147(b)(5)); or
-- A combination of insurance, financial test, guarantee, letter of
credit, surety bond, and trust fund (§§264.147(a)(6), 265.147(a)(6), 264.147(b)(6), and 265.147(b)(6));
A written notification to the Regional Administrator whenever a claim or verification of a valid claim for bodily injury or property damages caused by the operation of a hazardous waste treatment, storage, or disposal facility is made against the owner or operator (§§264.147(a)(7), 265.147(a)(7), 264.147(b)(7), and 265.147(b)(7)); and
A written notification to the Regional Administrator whenever the amount of financial assurance for liability coverage under one of the above-mentioned instruments is reduced, contingent on a claim or verification of a valid claim (§§264.147(a)(7), 265.147(a)(7), 264.147(b)(7), and 265.147(b)(7)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owners or operator will need to engage in the following activities in order to comply with the information collection requirements of §§264.147(a) and (b), and 265.147(a) and (b):
Read the regulations;
Establish liability coverage using one of the financial instruments listed above;
Submit appropriate evidence of such financial instruments to the Regional Administrator (in the case of new facilities establishing liability insurance, this must be submitted at least sixty days before receiving hazardous wastes for treatment, storage, or disposal, according to §§264.147(a)(1)(i) and 265.147(b)(1)(i));
Prepare, write, and submit a notification to the Regional Administrator whenever a claim for bodily injury is made against the owner or operator; and
Prepare, write, and submit a notification to the Regional Administrator whenever the amount of financial assurance for liability coverage is reduced.
Submission of the two notifications listed immediately above will only occur in the event of a claim; therefore, if no accidental releases occur, owners or operators may never need to submit these notifications.
(b) Liability Insurance
(i) Data item:
Sections 264.147(a)(1), 264.147(b)(1), 265.147(a)(1), and 265.147(b)(1) require owners or operators to submit a duplicate of the endorsement or certificate of insurance, and, if requested by the Regional Administrator, a duplicate of the insurance policy.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owners or operators will need to engage in the following activities to complete the requirements for this option:
Reading the regulations;
Obtaining an insurance policy amended by attachment of the Hazardous Waste Facility Liability Endorsement or evidenced by a Certificate of Liability Insurance and meeting other specifications outlined in §§264.147(a)(1), 264.147(b)(1), 265.147(a)(1), or 265.147(b)(1);
Submitting a signed duplicate original of the endorsement or the certificate of insurance to the Regional Administrator, or Regional Administrators if the facilities are located in more than one Region; and
If requested by the Regional Administrator, submitting a signed duplicate original of the insurance policy (for new facilities this must be submitted at least sixty days before receiving hazardous waste for treatment, storage, or disposal).
(c) Variance of Financial Responsibility Regulations
(i) Data item:
Section 265.147(c) provides for a variance from the financial responsibility requirements if the owner or operator can demonstrate that the required levels of financial responsibility are not consistent with the degree and duration of risk associated with treatment, storage, or disposal at the facility. The request for a variance must be submitted in writing to EPA, and may include technical and engineering information that is deemed necessary by the Regional Administrator.
(ii) Respondent Activity:
Owners and operators that wish to apply for a variance must prepare and submit information in support of the variance.
(d) Financial Test for Liability Coverage
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.147(f) and 265.147(f) allow owners or operators to satisfy liability requirements by passing a financial test. Data items for these sections include:
A letter signed by the owner's or operator's chief financial officer and worded as specified in §264.151(g); if the financial test is also being used to demonstrate closure or post-closure financial assurance, the letter specified in §264.151(g) must be submitted to cover both forms of financial responsibility;
A copy of an independent certified public accountant's report on examination of the owner's or operator's financial statements for the latest completed fiscal year;
A special report from the owner's or operator's independent certified public accountant to the owner or operator covering the specifications outlined in §§264.147(f)(3)(iii) and 265.147(f)(3)(iii);
If an extension of submission of the above documents is sought, a letter from the owner's or operator's chief financial officer to the Regional Administrator of each Region in which facilities to be covered under the financial test are located. This letter, allowed only under §265.147(f)(4), must contain the following data items:
-- A request for the extension;
-- A certification that the chief financial officer believes that the owner
or operator meets the criteria of the financial test;
-- For each facility to be covered by the test, the EPA identification
number, name, address, and current closure and post-closure cost estimates to be covered by the test;
-- A specification of the date (no later than ninety days after the end
of such fiscal year) when the owner or operator will submit the documents specified in §§265.147(f)(3); and
-- A certification that the year-end financial statements of the owner
or operator for such fiscal year will be audited by an independent certified public accountant;
Annual updates of the above data items; and
Should the owner or operator fail the test and no longer meet the requirements of §§264.147(f)(1) or 265.147(f)(1), evidence of insurance obtained for the entire amount of required liability coverage specified in §§264.147 and 265.147.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owners or operators will need to engage in the following respondent activities in order to collect the data required by these sections:
Reading the regulations;
Writing the letter signed by the chief financial officer;
Submitting the following documents to the Regional Administrator (for new facilities, these documents must be submitted at least sixty days prior to receiving hazardous waste for treatment, storage, or disposal):
-- The letter signed by the chief financial officer;
-- A copy of an independent certified public accountant's report; and
-- The special report from an independent certified public accountant;
Submitting updated information annually; and
Should the owner or operator fail the test and no longer meet §§264.147 or 265.147 requirements, submitting evidence to the Regional Administrator of insurance obtained for the entire amount of required liability coverage specified in these sections.
(e) Guarantee for Liability Coverage
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.147(g) and 265.147(g) allow owners or operators to meet liability requirements by obtaining a written guarantee, under the conditions specified in §§264.147(g)(2) and 265.147(g)(2). Data items for this option include:
A certified copy of a written guarantee from the direct or higher-tier parent corporation of the owner or operator, a firm whose parent corporation is the parent corporation of the owner or operator, or a firm with a "substantial business relationship" with the owner or operator;
In the case of corporations incorporated in the United States, a written statement from applicable Attorney(s) General or Insurance Commissioners to EPA indicating that a guarantee executed as described in the regulations is a legally valid and enforceable obligation in that State (§§264.147(g)(2) and 265.147(g)(2));
In the case of corporations incorporated outside the United States, identification by the non-U.S. corporation of a registered agent for service of process in each State in which the facility covered by the guarantee is located and in the State in which it has its principal place of business, and a written statement from applicable Attorney(s) General or Insurance Commissioner of each applicable State indicating that a guarantee executed as described in the regulations is a legally valid and enforceable obligation in that State (§§264.147(g)(2) and 265.147(g)(2)); and
A letter from the guarantor's chief financial officer as specified in §§264.147(f)(3) and 265.147(f)(3) that demonstrates that the guarantor has passed the financial test.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owners or operators will need to engage in the following respondent activities in order to collect the data required by these sections:
Reading the regulations;
Obtaining a written guarantee from the direct or higher-tier parent corporation of the owner or operator, a firm whose parent corporation is the parent corporation of the owner or operator, or a firm with a "substantial business relationship" with the owner or operator;
Submitting a certified copy of this written guarantee to the Regional Administrator along with the items specified in §§264.147(f)(3) and 265.147(f)(3); and
Submitting a letter from the guarantor's chief financial officer as specified in §§264.147(f)(3) and 265.147(f)(3) that demonstrates that the guarantor has passed the financial test.
(f) Letter of Credit for Liability Coverage
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.147(h) and 265.147(h) allow owners or operators to satisfy financial requirements for liability by obtaining the following data item:
An irrevocable standby letter of credit that conforms to applicable requirements and is submitted from a financial institution with the authority to issue letters of credit, whose letter of credit operations are regulated and examined by a Federal or State agency, and whose letters of credit meet the requirements of §264.147(h).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owners or operators using this option to satisfy financial assurance for liability will need to engage in the following activities:
Reading the regulations;
Obtaining the standby letter of credit described above; and
Submitting a copy of this letter of credit to the Regional Administrator.
(g) Surety Bond for Liability Coverage
(i) Data item:
Sections 264.147(i) and 265.147(i) allow owners or operators to satisfy financial requirements for liability. Under sections 264.147(i)(4) and 265.147(i)(4), a surety bond may be used to satisfy the requirements of this section only if the applicable Attorneys General or Insurance Commissioners have submitted a written statement to EPA that a surety bond executed as described in the regulations is a legally valid and enforceable obligation in that State. The owner/operator must obtain a surety bond (and other information, where applicable) that conforms to the requirements specified in §§264.147(i) and 265.147(i).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owners or operators using this option to satisfy financial assurance for liability will need to engage in the following activities:
Reading the regulations;
Obtaining the surety bond described above; and
Submitting a copy of this surety bond to the Regional Administrator.
(h) Trust Fund for Liability Coverage
(i) Data item:
Sections 264.147(j) and 265.147(j) allow owners or operators to satisfy financial requirements for liability by establishing a trust fund that conforms to the requirements specified in §§264.147(j) and 265.147(j).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owners or operators using this option to satisfy financial assurance for liability will need to engage in the following activities:
Reading the regulations;
Establishing the trust fund described above; and
Submitting an originally signed duplicate of the trust agreement to the Regional Administrator.
(i) Adjustments by the Regional Administrator
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.147(d) and 265.147(d) allow Regional Administrators to adjust the level of financial responsibility required under §§264.147 and 265.147 in order to protect human health and the environment. Respondents will need to furnish the following data items should Regional Administrators make such a determination:
Any information which the Regional Administrator requests to determine whether cause exists for such adjustments of level or type of coverage; and
If the Regional Administrator decides to adjust the level or type of coverage, the data elements necessary for a permit modification (detailed in ICR OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owners or operators will need to engage in the following activities in order to satisfy the information collection requirements of this section:
Reading the regulations;
Submitting to the Regional Administrator any requested information; and
Preparing, writing, and submitting a permit modification if the Regional Administrator decides to adjust level or type of coverage (specific respondent activities for permit modifications are detailed in ICR OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
(5) Incapacity of Owners or Operators, Guarantors, or Financial Institutions
(i) Data item:
Sections 264.148 and 265.148 require owners or operators to submit, if applicable, a notification of the commencement of a voluntary or involuntary proceeding under Title 11 (Bankruptcy), U.S. Code, naming the owner or operator as debtor (if the guarantor is named as the debtor, the collection of this data is the guarantor's responsibility).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Activities for this data collection will include:
Reading the regulations; and
Submitting, by certified mail, a notice to the Regional Administrator indicating the commencement of bankruptcy proceedings in which the owner or operator or guarantor is named as debtor.
(6) Use of State-Required Mechanisms
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.149 and 265.149 allow owners or operators to use State-required financial assurance mechanisms to meet §§264.143, 264.145, 264.147, 265.143, 265.145, or 265.147 requirements. Data items for this option include:
A letter from the owner or operator requesting that the State-required mechanism be considered acceptable for meeting the requirements of this subpart;
Evidence of the establishment of a State-required mechanism, including the following information:
-- The facility's EPA identification number, name, and address; and
-- The amount of funds for closure or post-closure care or liability
coverage assured by the mechanism; and
Any additional information required by the Regional Administrator in order to make the determination.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Activities for this data collection will include:
Reading the regulations; and
Submitting to the Regional Administrator:
-- The letter from the owner or operator;
-- Written evidence of the establishment of a State-required financial
assurance mechanism; and
-- Any additional information requested by the Regional
Administrator.
(7) State Assumption of Responsibility
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.150 and 265.150 require owners or operators to notify EPA when a State assumes legal responsibility or assures availability of funds for an owner's or operator's compliance with the closure, post-closure care, or liability requirements of this part. Data items to be collected in this case include:
A letter from the owner or operator requesting that the State's assumption of responsibility be considered acceptable for meeting the requirements of this subpart;
A letter from the State describing the nature of the State's assumption of responsibility, including the following information:
-- The facility's EPA identification number, name, and address; and
-- The amount of funds for closure or post-closure care or liability
coverage that are guaranteed by the State; and
Any additional information which the Regional Administrator deems necessary to make the determination whether the State's assumption of responsibility is acceptable.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Activities for this data collection will include:
Reading the regulations; and
Submitting to the Regional Administrator:
-- The letter from the owner or operator; and
-- The letter from the State describing the State's assumption of
responsibility and including the information specified above; and
Submitting any additional information requested by the Regional Administrator.
(8) Subpart F and G Requirements (§§266.70 and 266.80)
Sections 266.70(d) and 266.80(b)(2) explain that two specific groups of respondents are also subject to Parts 264 and 265 financial assurance requirements:
Persons who generate, transport, or store recyclable materials that are reclaimed to recover economically significant amounts of gold, silver, platinum, palladium, iridium, osmium, rhodium, ruthenium, or any combination of these; and
Owners or operators of facilities that store spent lead acid batteries before reclaiming them.
CONDITIONS APPLICABLE TO ALL PERMITS
(i) Data items:
40 CFR Part 270, Subpart C specifies conditions applicable to all permitted facilities. 40 CFR 270.30(h) requires owners and operators of permitted facilities to furnish any relevant information requested by EPA to determine whether cause exists for modifying, revoking and reissuing, or terminating a permit, or to determine compliance with the permit. Section 270.30(j)(2) and (3) requires permittees to retain records of all monitoring information, copies of all reports required by the permit, the certification required by §264.73(b)(9), and records of all data used to complete the application for a period of at least three years from the date of the sample, measurement, report, certification, or application. [These requirements are burdened in the section entitled "Operating Record" of this ICR.] In addition, section 270.30(l) specifies the following reporting requirements, which are applicable to all permitted facilities:
Prompt notice of planned physical alternations or additions (§270.30(l)(1));
Notice of planned changes or activities which may result in noncompliance with permit requirements (§270.30(l)(2));
Letter certifying that the facility has been constructed or modified in compliance with the permit (§270.30(l)(2)(i);
Monitoring reports, submitted at the intervals specified in the permit (§270.30(l)(4));
Reports of compliance or noncompliance with, or any progress reports on, interim and final requirements contained in any compliance schedule of the permit, submitted no later than 14 days following each schedule date (§270.30(l)(5));
A report containing information concerning a release that may threaten drinking water supplies (§270.30(l)(6)(i)(A), or information concerning a release, fire, or explosion which could threaten human health or the environment outside the facility (§270.30(l)(6)(i)(B)), within 24 hours from the time the permittee becomes aware of the circumstances. Such a report must include the following information:
-- Name, address, and telephone number of the owner or operator;
-- Name, address, and telephone number of the facility;
-- Date, time, and type of incident;
-- Name and quantity of material(s) involved;
-- The extent of injuries, if any;
-- An assessment of actual or potential hazards to the environment
and human health outside the facility; and
-- Estimated quantity and disposition of recovered material that
resulted from the incident.
A written notice within five days of noncompliance, or a written report within 15 days, that includes a description of the noncompliance and its cause, the period of noncompliance, the anticipated time the noncompliance is expected to continue, and steps taken to reduce, eliminate, and prevent reoccurrence of the noncompliance (§270.30(l)(6)(iii);
Report of any manifest discrepancy, as required by §264.72 (§270.30(l)(7). [This requirement is burdened in "Requirements for Generators, Transporters, and Waste Management Facilities Under the RCRA Hazardous Waste Manifest System", ICR OMB Control No. 2050-0039.];
Report of any receipt of unmanifested waste, as required by §264.76 (§270.30(l)(8)). [This requirement is burdened in "Requirements for Generators, Transporters, and Waste Management Facilities Under the RCRA Hazardous Waste Manifest System", ICR OMB Control No. 2050-0039.];
A biennial report covering facility activities, as required by §264.75 (§270.30(l)(9)). [This requirement is burdened in the "Hazardous Waste Report ICR", ICR OMB Control No. 2050-0024.]
Report of other noncompliance not submitted with monitoring reports, compliance schedule reports, and reports of releases, fires, or explosions (§270.30(l)(10)); and
For cases where the permittee becomes aware that he or she failed to submit any relevant facts in a permit application, or submitted incorrect information in any permit application or report, corrected or new information (§270.30(l)(11)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with 40 CFR Part 270, Subpart C, owners and operators of permitted facilities must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations; and
Prepare and submit the required information as described above.
5. THE INFORMATION COLLECTED--AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
The following subsections discuss how EPA will collect the information, what activities EPA will perform once the information has been received, and how EPA will manage the information it collects. The subsections also include a discussion of how the information collection requirements affect small entities.
5(a) AGENCY ACTIVITIES
GENERAL FACILITY OPERATING STANDARDS
Although the information is not formally submitted to EPA, EPA may review information collected from the requirements outlined in Subpart E during facility inspections. Therefore, this analysis assumes that the Agency will spend a minimal amount of review time annually at each facility.
The requirements for the foreign shipment import report, however, state that owners or operators must notify the Regional Administrator of the anticipated collection of hazardous waste. In turn, the Agency must review the information included in the notification.
RECORDKEEPING REQUIREMENTS
Only one Agency activity is associated with the operating record requirements: on-site review of the record.
CONTINGENCY PLAN AND EMERGENCY REPORTING REQUIREMENTS
(1) Contingency Plan
Two Agency activities are associated with the development and amendment of the contingency plan: reviewing the contingency plan during on-site inspections and reviewing revisions to the contingency plan.
(2) Emergency Reporting Requirements
Agency activities associated with emergency reporting requirements include reviewing documents in the owners' or operators' and emergency coordinators' emergency reports.
CLOSURE AND POST-CLOSURE REQUIREMENTS
Agency activities associated with the regulations promulgated in 40 CFR, Parts 264 and 265, Subpart G, include reviewing the following data items:
Closure plans;
Closure plan amendment notifications;
Partial/final closure notifications;
Closure extensions and allowances;
Survey plats;
Post-closure plans;
Post-closure plan amendment notifications;
Post-closure plan modifications;
Hazardous waste disposal records; and
Post-closure permit modifications.
FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS
EPA uses the cost estimates and financial assurance mechanisms to ensure compliance with Subpart H. In the event that an owner or operator is unable or unwilling to perform closure or post-closure activities or to pay third-party damages, EPA will draw upon the mechanisms. The cost estimates are normally retained by the owner or operator during interim status; they are submitted to the Region or authorized State as part of the permit process.
The financial assurance instruments for closure, post-closure care, and liability coverage, with standard wording, are submitted by the owner or operator (or the third-party financial entity) to the Region or authorized State that serves the area and where the facility is located. These submissions must be made by the effective date of the regulations for existing facilities -- July 6, 1982 (Assurance) and July 15, 1982 (Liability) -- and sixty days before the initial receipt of hazardous wastes at new facilities. There was a phase-in period for nonsudden coverage for existing facilities. January 16, 1985 was the final phase-in date.
When financial assurance information is submitted, EPA conducts a review for completeness, then enters the information into the RCRIS data base. The EPA Regional or State offices establish a file for each applicant that contains the submissions. The financial instruments are maintained in a secure area.
Submissions are tabulated in the EPA Regional Offices and Headquarters and are used by Agency management to oversee implementation of the RCRA financial responsibility requirements. The information is also shared with States to assist them in implementing their hazardous waste management programs. There are no plans to publish information obtained under the Subpart H financial requirements.
CONDITIONS APPLICABLE TO ALL PERMITS
EPA reviews all information submitted at intervals specified in the permit. This information includes monitoring reports and reports on compliance or noncompliance with compliance schedules. EPA also reviews information that may be submitted on occasion by facilities, if necessary. Such information includes notices of planned physical alterations or additions; notices of planned changes or activities; letters certifying compliance; information concerning releases, fires, or explosions; reports of other noncompliance; and corrected or new information.
5(b) COLLECTION METHODOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
To collect and analyze the information discussed in this ICR, EPA keeps records of and reviews all of the information submitted. Authorized States and EPA Regions enter the information into electronic data base systems. States coordinate with the EPA Regions and OSW Headquarters to supply EPA with the data reported for inclusion in the RCRAInfo national database.
5(c) SMALL ENTITY FLEXIBILITY
When promulgating the regulations covered under this ICR, EPA considered developing separate and simplified requirements for small businesses. Since small facilities conduct operations that are equally as hazardous to the environment as those conducted by larger facilities, EPA determined that small businesses should be required to comply with the same regulations as large businesses. As a result of this interpretation, no specific requirements are outlined for smaller facilities.
5(d) COLLECTION SCHEDULE
GENERAL FACILITY STANDARDS
The reporting requirements outlined in the regulations will vary according to individual facility circumstances (e.g., when receiving hazardous waste from a foreign source).
RECORDKEEPING REQUIREMENTS
Since the operating record is maintained at the facility, discussion of a collection schedule is not applicable. Copies of records of waste disposal are submitted to EPA upon closure of the facility.
CONTINGENCY PLAN AND EMERGENCY REPORTING REQUIREMENTS
The contingency plan is collected when the permittee submits the Part B permit application. A discussion of the contingency plan collection schedule for permitted facilities is included in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Applications, Special Permits, and Permit Modifications ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0009). Since interim status facilities are not required to submit their contingency plans to EPA, discussion of a collection schedule for these facilities is not applicable.
The owner or operator must submit a written report of any incident that requires implementation of the contingency plan within 15 days after the incident occurs. The emergency coordinator must immediately notify the appropriate authorities of an imminent or actual emergency situation.
CLOSURE AND POST-CLOSURE REQUIREMENTS
Permitted facilities submit their closure and post-closure plans to EPA when submitting a Part B permit application. A discussion addressing collection schedules for permitted facilities is included in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Applications, Special Permits, and Permit Modifications ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
Interim status closure and post-closure plans must be submitted according to the following schedules:
The owner or operator must submit the closure plan to the Regional Administrator at least 180 days prior to the date on which he or she expects to begin closure of the first surface impoundment, waste pile, land treatment, or landfill unit, or final closure if it involves such a unit, whichever is earlier;
The owner or operator must submit the closure plan to the Regional Administrator at least 45 days prior to the date on which he or she expects to begin final closure of a facility with only tanks, container storage, or incinerator units;
Owners or operators with approved closure plans must notify the Regional Administrator in writing at least 60 days prior to the date on which they expect to begin closure of a surface impoundment, waste pile, landfill, or land treatment unit, or final closure of a facility involving such a unit;
Owners and operators with approved closure plans must notify the Regional Administrator in writing at least 45 days prior to the date on which they expect to begin final closure of a facility with only tanks, container storage, or incinerator units;
The owner or operator must submit the closure plan to the Regional Administrator no later than 15 days after:
-- Termination of interim status except when a permit is issued
simultaneously with termination of interim status; or
-- Issuance of a judicial decree or final order under §3008 of RCRA
to cease receiving hazardous wastes or close
If the Regional Administrator does not approve the closure plan, he or she shall provide the owner or operator with a detailed written statement of reasons for the refusal and the owner or operator must modify the plan or submit a new plan for approval within 30 days after receiving such written statement;
An owner or operator of a surface impoundment or waste pile that intends to remove all hazardous waste at closure must prepare a post-closure plan and submit it to the Regional Administrator within 90 days of the date that the owner or operator or Regional Administrator determines that the hazardous waste management unit or facility must be closed as a landfill, subject to the requirements of §§265.117 through 265.120;
If an owner or operator of a surface impoundment or a waste pile who intended to remove all hazardous wastes at closure in accordance with §265.228(b) or §265.258(a) is required to close as a landfill in accordance with §265.310, the owner or operator must submit a post-closure plan within 90 days of the determination by the owner or operator or Regional Administrator that the unit must be closed;
If the Regional Administrator determines that an owner or operator of a surface impoundment or waste pile who intended to remove all hazardous wastes at closure must close the facility as a landfill, the owner or operator must submit a post-closure plan for approval to the Regional Administrator within 90 days of the determination;
The owner or operator must submit the post-closure plan to the Regional Administrator at least 180 days before the date he or she expects to begin partial or final closure of the first hazardous waste disposal unit. The date he "expects to begin closure" of the first hazardous waste disposal unit must be either within 30 days after the date on which the hazardous waste management unit receives the known final volume of hazardous waste or, if there is a reasonable possibility that the hazardous waste management unit will receive additional hazardous wastes, no later than one year after the date on which the unit received the most recent volume of hazardous wastes; and
The owner or operator must submit his post-closure plan to the Regional Administrator no later than 15 days after:
-- Termination of interim status except when a permit is issued
simultaneously with termination of interim status; or
-- Issuance of a judicial decree or final order under §3008 of RCRA
to cease receiving hazardous wastes or close.
Both interim status and permitted facilities are required to request approval for post-closure plan modifications. Since permitted facilities must submit permit modifications to authorize changes to their post-closure plans, a discussion addressing scheduling requirements for permitted facilities' modifications to the post-closure plan is included in ICR OMB Control No. 2050-0009. The following is a schedule for interim status facilities:
An owner or operator with an approved post-closure plan must submit the modified plan to the Regional Administrator at least 60 days prior to the proposed change in facility design or operation, or no more than 60 days after an unexpected event has occurred which has affected the post-closure plan; and
If the Regional Administrator requests modifications to the post-closure plan, the owner or operator with an approved post-closure plan must submit the modified plan to the Regional Administrator no later than 60 days of the request from the Regional Administrator.
Both interim status and permitted facilities are required to submit closure certifications, survey plats, and post-closure notices according to the following schedules:
The owner or operator must submit a certification of closure to the Regional Administrator within 60 days of completion of closure for each hazardous waste surface impoundment, waste pile, land treatment, and landfill unit and within 60 days of final closure;
No later than the submission of the certification of closure, the owner or operator must submit to the Regional Administrator a survey plat;
If the Regional Administrator does not approve the post-closure plan, he shall provide the owner or operator with a detailed written statement of reasons for the refusal and the owner or operator must modify the plan or submit a new plan for approval within 30 days after receiving such written statement;
The owner or operator must submit a post-closure notice to the Regional Administrator within 60 days of certification of closure for each hazardous waste disposal unit;
No later than 60 days after certification of closure of each hazardous waste disposal unit, the owner or operator must submit to the Regional Administrator a record of the type, location, and quantity of hazardous wastes disposed of within each cell or other disposal unit of the facility; and
No later than 60 days after the completion of the established post-closure care period for each hazardous waste disposal unit, the owner or operator must submit to the Regional Administrator a certification that the post-closure care period for the unit was performed in accordance with the specifications in the approved post-closure plan.
FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS
For closure and post-closure cost estimates, owners or operators must prepare initial cost estimates for activities identified in the closure and post-closure plans. Thereafter, owners or operators must provide annual adjustments of these cost estimates to account for inflation. Also, owners or operators may be required to prepare new cost estimates, if changes in the closure or post-closure plan increase closure or post-closure costs. This burden will vary from facility to facility.
For closure and post-closure care financial instruments, owners or operators must initially establish a financial instrument(s) assuring the cost of closure and post-closure care. Thereafter, owners or operators must annually check the amount covered by the instrument(s) to make sure it equals the adjusted cost estimate, and change the amount assured accordingly.
For liability coverage requirements, owners or operators of facilities identified in §§264.147 and 265.147 must initially demonstrate liability coverage for sudden and nonsudden accidents during the facilities' active life. Some of the financial instruments for liability coverage require additional reporting on an annual basis; for example, owners or operators must annually submit documentation to EPA supporting the use of the financial test or guarantee. Furthermore, owners or operators may also have to provide information due to varying circumstances; for example, whenever a claim for bodily injury or property damages caused by a hazardous waste treatment, storage, or disposal facility is made.
CONDITIONS APPLICABLE TO ALL PERMITS
EPA collects information from permitted facilities at intervals specified in the permit. EPA may also collect other information if the Agency determines that it needs information to determine whether a permit should be terminated, revoked and reissued, or modified. EPA may collect additional information from permitted facilities if noncompliance with permit conditions occurs.
6. ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF THE COLLECTION
6(a) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT BURDEN
Table 2 presents the bottom line burden for respondents. The 6 exhibits referred to in the Table are spreadsheets in an excel file attached to this supporting statement. Table 3 presents the burden for State Agencies, the breakdown of that burden is explained in exhibit 7 of the same excel file.
6(b) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT COSTS
LABOR COSTS
For the private sector, EPA estimates an average hourly respondent labor cost (including fringe and overhead) of $131.20 for legal staff, $77.55 for managerial staff, $57.79 for technical staff, and $34.76 for clerical staff. These wage rates are based on the rates from last renewal, multiplied by an inflation rate of 3.4% to bring them up to 2018 rates.
For State Agencies, EPA estimates an average hourly respondent labor cost (including fringe and overhead) of $63.48 for legal staff, $59.59 for managerial staff, $35.65 for technical staff, and $22.74 for clerical staff. These labor costs were obtained from EPA ICR Number 0976.18.
CAPITAL COSTS
EPA estimates that all new facilities and facilities with new Part B permits will incur capital costs associated with purchasing file storage systems for maintaining records. EPA realizes that facilities will likely use different and various file storage systems (e.g., file cabinets, CD-ROM, off-site storage, etc) and store their files on different media (paper, microfiche, electronic files, etc). For purposes of estimating these capital costs across all facilities, EPA has made the conservative assumption that every facility will store their files in paper form in file cabinets.
In addition, EPA estimates that during the facilities’ operating and post-closure periods each facility will store an average 48,000 pieces of paper. Therefore, the average facility will need to purchase three 5-drawer lateral file cabinets that each hold 16,000 pieces of paper. As the current market price for such a file cabinet is $680, each facility would therefore purchase $2,040 worth of file cabinets.
OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE COSTS
EPA also estimates that facilities will incur operations and maintenance (O&M) costs such as postage costs for submitting information to EPA, purchased material costs, and various lump-sum purchased service costs. These O&M costs are expected to be incurred on an ongoing, annual, or periodic basis per the associated regulatory requirement and assumptions in this ICR.
Postage costs are estimated at $0.55 per one ounce letter, $6.95 per submittal for flat-rate by priority mail, and $12.40 per submittal that must be sent by registered, priority mail.
EPA estimates purchased material costs/and or lump-sum purchased service costs for waste analysis, specifically $1,000 per analysis for non-commercial facilities and $400 per analysis for commercial facilities.
EPA estimates lump-sum purchased service costs for certain inspections and/or certifications that must be completed by independent professionals, specifically $1,000 per inspection/certification by an independent registered professional engineer and $750 per survey/certification by a professional land surveyor.
6(c) ESTIMATING AGENCY BURDEN AND COST
EPA estimates the Agency hour and cost burden associated with the information collection requirements covered in this ICR. EPA estimates an average hourly labor cost of $95.02 for legal staff (GS15, Step 5), $83.84 for managerial staff (GS-15, Step 1), $60.32 for technical staff (GS-13, Step 1), and $25.73 for clerical staff (GS-06, Step 1). To derive these hourly estimates, EPA referred to the General Schedule (GS) Salary Table 2020. This publication summarizes the unloaded (base) hourly rate for various labor categories in the Federal Government. EPA then applied the standard government overhead factor of 1.6 to the unloaded rate to derive loaded hourly rates.
6(d) RESPONDENT UNIVERSE AND TOTAL RESPONDENT BURDEN AND COST
RESPONDENT UNIVERSE
Table 1 presents the estimated universe of facilities that are affected by the General Facility Standard requirements. These numbers were obtained from RCRAInfo.1
TABLE 1
Estimated Universe of Facilities Affected by General Facility Standard Requirements
|
Permitted |
Interim Status |
Total |
All Facilities (Operating & Closed/Post Closed) |
1133 |
8 |
1141 |
Operating Facilities |
563 |
3 |
566 |
Commercial |
318 |
1 |
319 |
Non-Commercial |
245 |
2 |
247 |
Closed Facilities (New Annual Closures) |
7 |
0 |
7 |
Post-Closed Facilities |
563 |
5 |
568 |
Land Disposal Facilities (Op. & Cl/P-Cl) |
451 |
5 |
456 |
Operating LDFs |
47 |
1 |
48 |
Closed LDFs (New Annual Closures) |
1 |
0 |
1 |
Post-Closed LDFs |
403 |
4 |
407 |
Closed or Post-Closed LDFs |
404 |
4 |
408 |
Facilities with Incinerators |
42 |
0 |
42 |
Treatment and Storage Only Facilities |
429 |
2 |
431 |
New Interim Status |
NA |
0 |
0 |
New Part B Permits (Incl. New Construction) |
0 |
NA |
0 |
Facilities Who Intend to Close Annually |
7 |
0 |
7 |
LDFs Who Intend to Close Annually |
3 |
0 |
3 |
Facilities Who Intend to Post-Close Annually |
32 |
0 |
32 |
LDFs Who Intend to Post-Close Annually |
3 |
0 |
3 |
Facilities Completing Post-Closure Annually |
0 |
0 |
0 |
GENERAL FACILITY OPERATING REQUIREMENTS
(1) Foreign Shipment Import Report
Based on previous experience, EPA estimates that approximately six percent of the operating respondent universe will submit foreign shipment import reports annually.
(2) Notice of Appropriate Permits
EPA estimates that approximately 12 percent of operating TSDFs accept off-site waste. These commercial facilities must submit a one-time notice to these generators before accepting their waste.
(3) Notice of Part 264 or Part 265, and Part 270 Requirements
EPA estimates that approximately one percent of all facilities will experience a transfer in ownership each year. The owners and operators of these facilities will be required to submit a notice of Part 264 or 265 and Part 270 requirements to the new owner or operator of the facility.
(4) Waste Analysis
Only operating facilities are required to conduct waste analysis testing. EPA believes that the commercial incinerator and land disposal sites have the greatest responsibility for waste analysis. Based on previous experience, EPA estimates that commercial incinerator and land disposal facilities will conduct testing 50 times a year, while the remaining operating facilities will conduct this analysis twice a year.
(5) Waste Analysis Plan
This ICR assumes that existing interim status and permitted facilities have already developed a waste analysis plan. Therefore, only new interim and permitted facilities will develop waste analysis plans. EPA estimates that no new interim facilities will be entering the universe whereas the 13 newly permitted facilities will have to prepare a waste analysis plan. In addition to preparing a waste analysis plan, these 13 facilities must also maintain (i.e., photocopy and file) the plan at the facility.
EPA also assumes that 20 percent of all operating facilities will modify the plan and maintain the modified plan each year.
(6) Inspection Schedule
This ICR assumes that existing interim status and permitted facilities have already developed an inspection schedule. Therefore, only new permitted and interim status facilities will develop inspection schedules. EPA estimates that no new interim and 13 new permitted facilities will enter the universe during the period covered by this ICR.
In addition to preparing an inspection schedule, new permitted facilities must also maintain (i.e., photocopy, file, and update) the schedule at the facility. EPA estimates that five percent of all operating facilities and facilities undergoing closure or post-closure will modify their inspection schedules annually and maintain the modified inspection schedule. All operating facilities are required to record problems in an inspection log.
(7) Personnel Training
This ICR assumes that existing interim status and permitted facilities have already collected the information necessary to prepare a personnel training record. Therefore, only new interim status facilities and newly constructed permitted facilities will be required to collect information regarding their employees' training experiences. EPA estimates that no new interim status facilities will join the universe during the period covered by this ICR. Newly constructed facilities with Part B permits will have to read the regulations and collect information.
All operating and newly constructed facilities must also maintain (i.e., photocopy, file, and update) their training records.
(8) Documentation of Compliance for Ignitable, Reactive, or Incompatible Wastes
Based on previous experience, EPA estimates that 40 percent of the permitted operating universe will have to maintain documentation of compliance for ignitable, reactive, or incompatible wastes.
(9) Construction Quality Assurance Plan
This ICR assumes that existing permitted and interim status facilities have submitted their construction quality assurance plan to EPA. Therefore, only new interim status facilities will be required to submit the CQA plan. EPA estimates that no new facilities will obtain interim status during the period covered by this ICR.
RECORDKEEPING REQUIREMENTS
Operating Record
Excluding the inspection information requirements, only operating facilities are required to comply with the operating record recordkeeping requirements. There are sixteen information components of the operating record requirements contained in 40 CFR §§264.73(b)(1)-(16) and 265.73(b)(1)-(16). Some of the requirements apply only to certain types of facilities:
Facilities must document any refusal of State and local agencies to enter into arrangements to address emergency situations (§264.37(b)). EPA estimates that only one percent of all operating facilities will be required to comply with this regulation.
Facilities that have emergency incidents requiring implementation of the contingency plan must maintain (i.e., photocopy and file) written documentation of the incident (§§264.73(b)(4) and 265.73(b)(4)). EPA estimates that only one percent of all operating facilities will be required to comply with this regulation.
Both operating and post-closure facilities are required to maintain updated inspection information in the operating record (§§264.73(b)(5) and (265.73(b)(5)).Only land disposal facilities and incinerator facilities are required to collect and record monitoring data (§264.73(b)(6)) in the operating record.
Only land disposal facilities and incinerator facilities are required to collect and record monitoring data (§264.73(b)(6)) in the operating record.
Only facilities that receive hazardous waste from an off-site source (except where the owner or operator is also the generator) are required to maintain (i.e., photocopy and file) notices for generators verifying that they have a permit to handle the hazardous waste they are receiving (§§264.73(b)(7) and (265.73(b)(7)). Thus, EPA has determined that 12 percent of the operating universe, including non-commercial facilities, will need to maintain, in the operating record, the notice to generators.
All facilities must maintain updated information in the operating record closure cost estimates. However, only land disposal facilities must maintain post-closure cost estimates (§§264.73(b)(8) and (265.73(b)(8)). EPA expects that all permitted and interim status facilities will have to maintain closure cost estimates. Permitted and interim status operating land disposal facilities will also need to maintain post-closure cost estimates.
All operating land disposal facilities must also maintain records of the quantities (and date of placement) for each shipment of hazardous waste placed in land disposal units under an extension to the effective date of any land disposal restriction, or a certification, and the applicable notice required by the generator (§§264.73(b)(10) and (265.73(b)(10)).
Only off-site TSDFs are required to maintain (i.e., photocopy and file) a copy of the notice, and the certification and demonstration, if applicable, required by the generator or owner or operator in the operating record (§§264.73(b)(11), (13) and (15) and (265.73(b)(11), (13) and 15)). Thus EPA has determined that five percent of the operating universe will need to maintain (i.e., photocopy and file) this information in the operating record.
Only on-site TSDFS are required to maintain (i.e., photocopy and file) the information contained in the notice (except the manifest number), and the certification and demonstration if applicable, required by the generator or owner or operator (§§264.73(b)(12), (14) and (16) and (265.73(b)(12), (14) and (16)). EPA had determined that 95 percent of the operating universe will need to maintain (i.e. photocopy and file) this information in the operating record.
The remaining requirements (§§264.73(b)(1)-(3) and (9) and (265.73(b)(1)-(3), and (9)) apply to
the entire universe of operating facilities.
CONTINGENCY PLAN AND EMERGENCY REPORTING REQUIREMENTS
Contingency Plan
For this ICR, the Agency assumes that existing interim status and permitted facilities have already prepared contingency plans. Therefore, only new interim status facilities will be required to prepare a contingency plan. (Modifications to contingency plans of permitted facilities are covered under the hazardous Waste Part B Permit Application, Special Permits, and Permit Modifications ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0009)).
EPA estimates that no new facilities will obtain interim status during the period covered by this ICR
(OMB Control No. 2050-0120), or submit the contingency plan to all local police and fire departments, hospitals, and State and
local response teams.
Emergency Reporting And Recordkeeping
Based on program experience, the Agency estimates that one percent of all facilities with experience an emergency situation each year that will require the help of State or local authorities with
designated response roles. Therefore, emergency coordinators at permitted and interim status facilities will be required to notify these authorities of an actual or imminent emergency situation (§§264.56(a)(2) and (265.56(a)(2)).
EPA estimates that one percent of those facilities experiencing an emergency situation will have a release, fire, or explosion for which the emergency coordination determines that is may be advisable to
evacuate local areas.
EPA estimates that one percent of facilities will notify either a government official designated as the on-scene coordinator or the National Response Center of a release, fire, or explosion (§§264.56(d)(2) and 265.56(d)(2)). EPA estimates that only one percent of all facilities will have emergency incidents requiring implementation of the contingency plan and will be required to prepare an emergency report.
All owners and operators experiencing an emergency situation are required to notify the Regional Administrator that the facility is in compliance with §265.56(h) before resuming operation in the affected
areas. The owner operator must also submit a written report to the Regional Administrator 15 days
after the incident (§§264.56(j) and 265.56(j)). The respondent burden for recording emergency details in the operating record is covered in the operating record section.
CLOSURE AND POST-CLOSURE REQUIREMENTS
Reading the Regulations
The only facilities that are expected to read the closure requirements will be the newly permitted facilities. Land disposal facilities are expected to read the post-closure regulations.
Closure Plans
Since existing interim status and permitted facilities have already developed closure and post-closure plans, activities associated with developing closure/pose-closure plans apply to newly interim
status facilities only. EPA expects no new facilities to develop and submit closure plans.
Closure Plan Amendment
Based on previous experience, EPA estimates that five percent of operating or closing interim
status facilities, such as facilities converting waste piles to containment building, will amend their closure plans annually and will submit a request to the Regional Administrator to authorize a change
in the closure plan. Since closure plan amendments for permitted facilities are associated with permit modifications, amendments and discussed in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Application, Special
Permits, and Permit Modifications ICR, OMB Control No. 2050-0009.
Partial Closure and Final Closure Notification
Owners and operators of all permitted and interim status facilities who intend to close their facility annually must notify EPA of closure. In addition, owners and operators of the interim status facilities must also submit their closure plans to EPA.
Extensions and Allowances During the Closure Period
Of the total number of facilities that will be closing, EPA estimates that 20 percent will request an extension for the treatment, storage, or removal of hazardous waste (§§264.113(a) and 265.113(a)). EPA estimates that an additional 20 percent will request an extension for completing closure activities. EPA also estimates that an additional five percent of all closing facilities will request an allowance to receive non-hazardous wastes in a land-based unit after the final receipt of hazardous waste (§§264.113(d) and 265.113(d)).
Closure Certification
EPA estimates that all of the permitted and interim status facilities that will be closing annually will complete a certification of closure.
Survey Plat
EPA estimates that 50 percent of the land disposal facilities that will be closing annually will submit a survey plat to the Regional Administrator.
(8) Post-Closure Plan
Existing permitted land disposal facilities already have approved post-closure plans. Therefore, only new interim status land disposal facilities will develop post-closure plans. EPA estimates that no new interim status land disposal facilities will prepare a post-closure plan annually. In addition to preparing a post-closure plan, all permitted and interim status land disposal facilities must also maintain (i.e., photocopy, file, and update) the post-closure plan at the facility.
(9) Notification and Amendment of Post-Closure Plan Under 265.118(d)
Since respondent activities associated with permit modifications are discussed in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Applications, Special Permits, and Permit Modifications ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0009), this ICR focuses on interim status facilities' activities associated with notification of a post-closure amendment. EPA estimates that 20 percent of interim status facilities that will be undergoing post-closure, or two facilities, will amend their post-closure plans and submit written notification of a change in the approved post-closure plans.
(10) Amendment of Post-Closure Plan Under 265.118(d)(4), (f), and (g)(1)
In some cases, the Regional Administrator will require owners or operators of surface impoundments or waste piles who intend to remove all hazardous wastes at closure to modify their post-closure plans. EPA expects that ten percent of interim status facilities that are undergoing post-closure will be required to modify their post-closure plan. EPA estimates that the Agency will reject ten percent of these plans, which will require approximately no facilities to modify its plan or submit a new plan.
In some cases, facilities will request that the Agency extend or reduce the post-closure period applicable to a hazardous waste management unit or facility, or to alter the requirements of the post-closure care period. EPA estimates that 20 percent of interim status facilities that are undergoing post-closure (two facilities), will prepare and submit such a request.
(11) Hazardous Waste Disposal Records
All owners and operators who close their land disposal facilities annually must submit hazardous waste disposal records.
(12) Hazardous Waste Notation Certification
All owners and operators who close their land disposal facilities annually must submit a certification that they have recorded the notation required in §§264.119(b)(2) and 265.119(b)(2).
(13) Post-Closure Plan Modifications
EPA does not expect that any interim status facilities will subject to section 265.119(c) during the effective period of this ICR.
(14) Post-Closure Care Certification
Since the post-closure care period lasts for 30 years, except for those facilities that qualify for "early outs," EPA does not expect many owners/operators to submit certifications of post-closure care during the period covered by this ICR. Based on previous experience, EPA estimates that no facilities will complete post-closure care and be required to submit certifications.
FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS
(1) Reading the Regulations
All operating and newly constructed facilities are expected to read the financial requirements regulations.
(2) Financial Responsibility for Corrective Action
Because financial responsibility for corrective action is required under Part 264, only permitted facilities are included in the burden estimate. EPA estimates that 80 percent of permitted facilities completed a RCRA Facility Assessment (RFA) that indicated that further investigation, or a RCRA Facility Investigation (RFI), was necessary. Because such further investigation will entail the submission of corrective action financial assurance documentation, EPA concludes that 80 percent of the permitted facilities will need to meet corrective action financial responsibility requirements. These facilities will need to include this financial assurance documentation in their permit renewals; because most TSDF permits are valid for five years, EPA estimates that each year approximately 20 percent will submit financial assurance documentation for corrective action. EPA estimates that ten percent of these facilities per year will need to provide the additional demonstration of denied permission to implement corrective action beyond facility boundaries.
(3) Cost Estimates for Closure and Post-Closure Care
Closure and post-closure plan amendments for permitted facilities are associated with permit modifications, such amendments are instead discussed in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Applications, Special Permits, and Permit Modifications ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0009). The burden covered in this ICR is for respondents to collect data, to prepare closure and post-closure care cost estimates, and to maintain these estimates at the facility.
(4) Financial Assurance for Closure or Post-Closure Care
Because evidence of establishing a financial instrument for closure or post-closure care is submitted with the Part B permit application, such activities for permitted facilities are discussed in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Applications, Special Permits, and Permit Modifications ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0009). However, prior to submitting a permit application, interim status facilities must present evidence of an established financial instrument for closure or post-closure care under §§265.143 and 265.145. Only new interim facilities will have to choose between the financial test for liability coverage and the other coverage options. EPA estimates that no new interim facilities will join the universe in the period this ICR covers.
EPA projects that two percent of existing facilities amend closure and post-closure financial instruments due to changes in the cost estimates or plans. Finally, all facilities covered under the financial test will need to submit annual updates; accordingly, 50 percent of existing facilities will submit this update.
(5) Liability Requirements
EPA calculates the number of respondents for demonstrating liability coverage in a manner similar to determining the number of closure and post-closure care respondents. Because evidence of establishing a financial instrument for liability coverage is submitted with the Part B permit application, such activities for permitted facilities are discussed in the Hazardous Waste Part B Permit Applications, Special Permits, and Permit Modifications ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0009). However, prior to submitting a permit application, interim status facilities must present evidence of an established financial instrument for liability coverage under §265.147. Therefore, preparation of the required evidence for interim status facilities is covered by this ICR. In addition, the burden associated with annual updates or modifications to financial instruments for liability coverage is covered by this ICR.
Only new interim facilities will have to choose between the liability coverage options. EPA estimates that no new interim facilities will join the universe in the period this ICR covers.
EPA expects that all existing TSDFs using the financial test or guarantee will submit the financial test documentation on an annual basis for review. EPA estimates that one percent of all facilities will become bankrupt and will need to submit evidence of insurance.
(6) Other Requirements
For activities relating to State-required mechanisms and State assumption of responsibility, EPA estimates that one percent of interim status facilities (permitted facilities are included in ICR OMB Control No. 2050-0009), will be included in the respondent burden estimate. EPA estimates that of these facilities, only one percent (approximately zero interim status facilities) will be required by EPA to furnish additional information under the State assumption of responsibility requirements.
CONDITIONS APPLICABLE TO ALL PERMITS
EPA estimates that each year 20 percent of permitted facilities will submit a permit modification at the request of the Agency. These permittees will be required to furnish any relevant information requested by EPA to determine whether cause exists to modify, revoke and reissue, or terminate a permit, or to determine compliance with a permit.
EPA estimates that 15 percent of permitted facilities will annually submit a notice of physical alterations or additions. Of these facilities, 50 percent will submit a notice of planned changes that may result in noncompliance with permit requirements. Of these facilities, 50 percent will submit a letter certifying that the facility has been constructed or modified in compliance with the terms of the permit.
EPA estimates that all permitted facilities with land-based units and incinerators must submit monitoring reports. EPA further estimates that one percent will be required to prepare and submit reports of compliance and noncompliance with the compliance schedule at intervals specified in the permit.
EPA estimates that one percent of all permitted facilities will experience a release, fire, or explosion that may threaten drinking water supplies, human health, or the environment outside the facility. These facilities will be required to submit a report within 24 hours of the incident and a more detailed written notice or report within 5 or 15 days, respectively, of the incident.
EPA estimates that two percent of all permitted facilities will be required to submit reports of other noncompliance that are not submitted with monitoring reports, compliance schedule reports, and reports of releases, fires, and explosions. An additional one percent will submit amended information that was incorrect or omitted during an initial submittal.
6(e) BOTTOM LINE BURDEN HOURS AND COSTS
The total respondent burden and costs associated with all of the information collection activities covered in this ICR can be calculated by adding the burdens from Tables 2 and 3. EPA estimates that the total annual respondent burden for all activities covered in the ICR is approximately 558,042 hours, at an annual cost of $337,223.
6(f) REASONS FOR CHANGE IN BURDEN
The previous ICR had a burden of 583,237 hours. There is decrease of 25,195 hours with this renewal. This decrease is due to a decrease in the overall number of interim status facilities. This decrease is not due to a program change, but is due to the Agency’s push to have facilities leave interim status and enter permitted status, as well as facilities wishing to close to enter post-closure status. This has led to a dramatic decrease in the number of interim status facilities, as well as increased the number of facilities in post-closure.
6(g) BURDEN STATEMENT
The annual public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 400 hours per respondent, and the annual public recordkeeping burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 80 hours per respondent. Burden means the total time, effort, or financial resources expended by persons to generate, maintain, retain, or disclose or provide information to or for a Federal agency. This includes the time needed to review instructions; develop, acquire, install, and utilize technology and systems for the purposes of collecting, validating, and verifying information, processing and maintaining information, and disclosing and providing information; adjust the existing ways to comply with any previously applicable instructions and requirements; train personnel to be able to respond to a collection of information; search data sources; complete and review the collection of information; and transmit or otherwise disclose the information. An agency may not conduct or sponsor, and a person is not required to respond to, a collection of information unless it displays a currently valid OMB control number. The OMB control numbers for EPA’s regulations are listed in 40 CFR Part 9 and 48 CFR Chapter 15.
To comment on EPA 's need for this information, the accuracy of the provided burden estimates, and any suggested methods for minimizing respondent burden, including the use of automated collection techniques, EPA has established a public docket for this ICR under Docket ID Number EPA-HQ-OLEM-2018-0690, which is available for online viewing at www.regulations.gov, or in person viewing at the RCRA Docket in the EPA Docket Center (EPA/DC), EPA West, Room B102, 1301 Constitution Avenue, NW, Washington, D.C. The EPA Docket Center Public Reading Room is open from 8:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m., Monday through Friday, excluding legal holidays. The telephone number for the Reading Room is (202) 566-1744, and the telephone number for the RCRA Docket is (202) 566-0270. An electronic version of the public docket is available at www.regulations.gov. This site can be used to submit or view public comments, access the index listing of the contents of the public docket, and to access those documents in the public docket that are available electronically. When in the system, select “search,” then key in the Docket ID Number identified above. Also, you can send comments to the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs, Office of Management and Budget, 725 17th Street, NW, Washington, D.C. 20503, Attention: Desk Officer for EPA. Please include the EPA Docket ID Number EPA-HQ-OLEM-2018-0690 and OMB Control Number 2050-0120 in any correspondence.
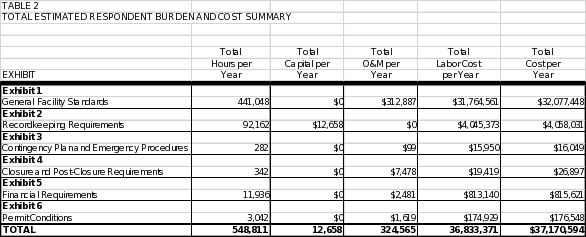
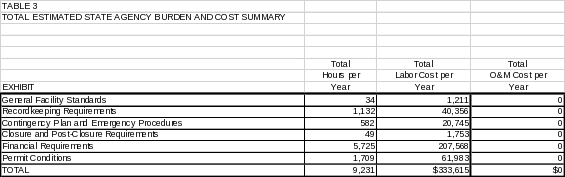
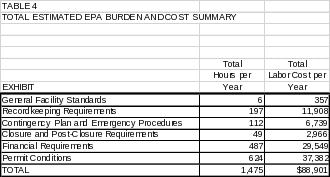
1 RCRAInfo database public site is available at https://rcrapublic.epa.gov/rcrainfoweb/action/main-menu/view
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | SUPPORTING STATEMENT FOR |
| Author | ctsuser |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-13 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy