1572ss13
1572ss13.docx
Hazardous Waste Specific Unit Requirements and Special Waste Processes and Types (Renewal)
OMB: 2050-0050
SUPPORTING STATEMENT FOR
INFORMATION COLLECTION REQUEST OMB CONTROL NO. 2050-0050
“HAZARDOUS WASTE SPECIFIC UNIT REQUIREMENTS
AND
SPECIAL WASTE PROCESSES AND TYPES”
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
1(a) TITLE AND NUMBER OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 4
1(b) SHORT CHARACTERIZATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 4
2. NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION
2(a) NEED AND AUTHORITY FOR THE COLLECTION 4
2(b) PRACTICAL UTILITY AND USERS OF THE DATA 5
3. NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA
3(a) NONDUPLICATION 5
3(b) PUBLIC NOTICE REQUIRED PRIOR TO ICR SUBMISSION TO OMB 5
3(c) CONSULTATIONS 5
3(d) EFFECTS OF LESS FREQUENT COLLECTION 5
3(e) GENERAL GUIDELINES 5
3(f) CONFIDENTIALITY 6
3(g) SENSITIVE QUESTIONS 6
4. THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED
4(a) RESPONDENTS/NAICS CODES 6
4(b) INFORMATION REQUESTED 7
5. THE INFORMATION COLLECTED -- AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
5(a) AGENCY ACTIVITIES 119
5(b) COLLECTION METHODOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT 124
5(c) SMALL ENTITY FLEXIBILITY 124
5(d) COLLECTION SCHEDULE 125
6. ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF THE COLLECTION
6(a) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT BURDEN 128
6(b) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT COSTS 128
6(c) ESTIMATING AGENCY BURDEN AND COST 129
6(d) ESTIMATING THE REPONDENT UNIVERSE AND TOTAL BURDEN AND COST 130
6(e) BOTTOM LINE BURDEN HOURS AND COSTS 131
6(f) REASONS FOR CHANGE IN BURDEN 132
6(g) BURDEN STATEMENT 132
EXHIBITS 133
1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
1(a) TITLE AN D NUMBER OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
Hazardous Waste Specific Unit Requirements and Special Waste Processes and Types, OMB Control No. 2050-0050, EPA ICR Number 1572.13
1(b) SHORT CHARACTERIZATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
Section 3004 of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) of 1976, as amended, requires that the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency develop standards for hazardous waste treatment, storage, and disposal facilities (TSDFs), as may be necessary, to protect human health and the environment. Section 3004, Subsections (1), (3), (4), (5), and (6) specify that these standards include, but not be limited to, the following requirements:
(1) Maintaining records of all hazardous wastes identified or listed under this title which are treated, stored, or disposed of, ... and the manner in which such wastes were treated, stored, or disposed of;
(3) Treatment, storage, or disposal of all such waste received by the unit pursuant to such operating methods, techniques, and practices as may be satisfactory to the Administrator;
(4) The location, design, and construction of such hazardous waste treatment, disposal, or storage facilities;
(5) Contingency plans for effective action to minimize unanticipated damage from any treatment, storage, or disposal of any such hazardous waste; and
(6) The maintenance or operation of such facilities and requiring such additional qualifications as to ownership, continuity of operation, training for personnel, and financial responsibility as may be necessary or desirable.
The regulations implementing these requirements are published in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 40, Parts 261, 264, 265, and 266, Subpart F.
Section 4(b) of this ICR contains a more detailed description of the information collection requirements, including the data items and respondent activities associated with each requirement.
2. NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION
2(a) NEED AND AUTHORITY FOR THE COLLECTION
This subsection establishes the need and legal authority for each information collection covered in this ICR. All of the collection requirements covered in this ICR have been published in 40 CFR Parts 261, 264 and 265, Subparts I through DD, and 40 CFR Part 266, Subpart F. With each collection covered in this ICR, EPA is aiding the goal of complying with its statutory mandate under RCRA to develop standards for hazardous waste TSDFs, as may be necessary, to protect human health and the environment. Section 2(b) lists each information collection along with its regulatory citation, and provides precise information regarding the decisions EPA makes with the information provided by the respondents.
2(b) PRACTICAL UTILITY AND USERS OF THE DATA
The information in this section is used for the following:
Monitor compliance
Assure hazardous waste is handled properly
Assure human health and the environment is protected
3. NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA
The information collections covered in this ICR are not available from sources other than the respondents. EPA’s Office of Solid Waste (and authorized States in lieu of EPA) is the only Office within the Agency collecting this information, and no other Federal agency or department collects this information. In addition, the Office of Solid Waste in partnership with the States has systematically reorganized its information collection structure to eliminate gaps or duplication.
3(b) PUBLIC NOTICE REQUIRED PRIOR TO ICR SUBMISSION TO OMB
In compliance with the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995, EPA issued a public notice on March 24, 2022 (87 FR 16728). EPA received no comments on this ICR in response to the Federal Register notice.
EPA consulted with the following members of the regulated community that are respondents for the information collection request. Consultations were conducted with: Clean Harbors, US Ecology, Inc., Chemical Waste Management, and Diversified Scientific Services, Inc. No burden estimates were revised as a result of these consultations.
3(d) EFFECTS OF LESS FREQUENT COLLECTION
EPA has carefully considered the burden imposed upon the regulated community by the specific unit and by special waste processes and types regulations. Consequently, EPA is confident that those activities required of all respondents are necessary, and to the extent possible, has minimized the burden imposed. EPA believes strongly that if the minimum requirements specified under the regulations are not met, EPA will be unable to fulfill its statutory mandate under RCRA to protect public health and the environment.
These collections will not include activities specified in 5 CFR 1320.5(d)(2) that require special justification.
3(f) CONFIDENTIALITY
Section 3007(b) of RCRA and 40 CFR Part 2, Subpart B, which define EPA’s general policy on the public disclosure of information, contain provisions for confidentiality. EPA also ensures that the information collection procedures comply with the Privacy Act of 1974 and the OMB Circular 108. EPA does not anticipate requesting any confidential information.
No questions of a sensitive nature are included in any of the information collection requirements.
4. THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED
4(a) RESPONDENTS UNIVERSE AND NAICS CODES
The following is a list of North American Industrial Classification System (NAICS) codes associated with the respondents most likely to be affected by the information collection requirements detailed in this ICR.
211112 Natural Gas Liquid Extraction
221111 Hydroelectric Power Generation
221112 Fossil Fuel Electric Power Generation
221113 Nuclear Electric Power Generation
221119 Other Electric Power Generation
221121 Electric Bulk Power Transmission and Control
221122 Electric Power Distribution
22132 Sewage Treatment Facilities
311942 Spice and Extract Manufacturing
323110 Commercial Litographic Printing
323114 Quick Printing
32411 Petroleum Refineries
32511 Petrochemical Manufacturing
32512 Industrial Gas Manufacturing
325131 Inorganic Dye and Pigment Manufacturing
325188 All Other Basic Inorganic Chemical Manufacturing
325193 Ethyl Alcohol Manufacturing
325199 All Other Basic Organic Chemical Manufacturing
325211 Plastics Material and Resin Manufacturing
32551 Paint and Coating Manufacturing
325998 All Other Miscellaneous Chemical Product and Preparation Manufacturing
331311 Alumina Refining
33271 Machine Shops
332813 Electroplating, Plating, Polishing, Anodizing, and Coloring
332999 All Other Miscellaneous Fabricated Metal Product Manufacturing
333319 Other Commercial and Service Industry Machinery Manufacturing
333999 All Other Miscellaneous General Purpose Machinery Manufacturing
33422 Radio and Television Broadcasting and Wireless Communications Equipment Manufacturing
33431 Audio and Video Equipment Manufacturing
334418 Printed Circuit Assembly (Electronic Assembly) Manufacturing
334419 Other Electronic Component Manufacturing
336211 Motor Vehicle Body Manufacturing
336312 Gasoline Engine and Engine Parts Manufacturing
336322 Other Motor Vehicle Electrical and Electronic Equipment Manufacturing
33633 Motor Vehicle Steering and Suspension Components (except Spring) Manufacturing
33634 Motor Vehicle Brake System Manufacturing
33635 Motor Vehicle Transmission and Power Train Parts Manufacturing
336399 All Other Motor Vehicle Parts Manufacturing
42271 Petroleum Bulk Stations and Terminals
44111 New Car Dealers
44112 Used Car Dealers
44711 Gasoline Stations with Convenience Store
44719 Other Gasoline Stations
454311 Heating Oil Dealers
454312 Liquefied Petroleum Gas (Bottled Gas) Dealers
48411 General Freight Trucking, Local
48421 Used Household and Office Goods Moving
48422 Specialized Freight (except Used Goods) Trucking, Local
562111 Solid Waste Collection
562112 Hazardous Waste Collection
562119 Other Waste Collection
562211 Hazardous Waste Treatment and Disposal
562212 Solid Waste Landfill
562213 Solid Waste Combustors and Incinerators
562219 Other Non-hazardous Waste Treatment and Disposal
56292 Materials Recovery Facilities
811111 General Automotive Repair
The following subsection presents the data items and respondent activities required for each of the broad information collection areas introduced in the previous section.
CONTAINERS
Permitted facilities:
Regulations
Each owner/operator regulated under 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart I is expected to read the regulations.
Inspections
40 CFR 264.174 requires owners and operators of permitted containers to conduct inspections of the areas where the containers are stored. Data items and respondent activities associated with these requirements are covered in this ICR. However, the burden for recordkeeping the applicable data items is covered in the “General Hazardous Waste Facility Standards ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0120).
(i) Data item:
The data item required to comply with these requirements includes:
• Documentation pertaining to the weekly inspection of the areas where the containers are stored. During each inspection, owners and operators must look for leaks and for deterioration caused by corrosion or other factors.
(ii) Respondent activity: Respondents must perform the following activity in documenting to the operating record of the facility the inspection of the area where the containers are stored:
• Record all inspection data.
TANK SYSTEMS
Permitted facilities:
Regulations
Each owner/operator regulated under 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart J is expected to read the regulations.
No-free-liquids demonstration
40 CFR 264.190(a) releases tank system owner/operators from the requirements of §§ 264.193 (containment and detection of releases) provided that the tanks are located in buildings with impermeable floors and are used to store or treat wastes that contain no free liquids. Owner/operators must demonstrate the absence of free liquids by using EPA Method 9095 (Paint Filter Liquids Test) as described in “Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Wastes, Physical/Chemical Methods” (EPA Publication No. SW-846) in order to be exempt from these requirements.
(i) Data item:
The data item for demonstrating the absence of free liquids includes:
• Results of the Paint Filter Liquids Test, performed as specified in SW-846.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities in performing this demonstration:
• Perform the Paint Filter Liquids Test as required and file test results at the facility.
Assessment of existing tank systems’ integrity
Under 40 CFR 264.191 owner/operators of facilities with tank systems that (1) store or treat waste that becomes hazardous after July 14, 1986 and (2) do not meet the secondary containment requirements of 40 CFR 264.193 must determine that the tank systems are sufficient for storing or treating hazardous waste.
(i) Data items:
Data items for this determination include:
• For each tank system, a written assessment that has been reviewed and certified by an independent, qualified registered professional engineer in accordance with 40 CFR 270.11(d). At a minimum, the assessment must consider the following:
-- The design standards to which the tank and ancillary equipment were constructed;
-- Hazardous characteristics of the waste(s) that has been and will be handled;
-- Existing corrosion protection measures;
-- The tank’s documented or estimated age; and
-- Results of a leak test performed as specified in 40 CFR 264.191(b)(5)(i) and (ii).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities in assessing their tank systems:
• Perform the leak test as specified in 40 CFR 264.191(b)(5)(i) and (ii);
• Write or have written an assessment certified by an independent, qualified, registered professional engineer that attests to the tank system’s integrity and file the assessment at the unit.
Design and installation of new tank systems or components
40 CFR 264.192 requires owner/operators of new tank systems or components to obtain a written assessment attesting that the tank system is acceptable for storing and treating hazardous waste. Since permitted facilities submit this assessment with their part B permit application, activities associated with obtaining and submitting a written assessment are covered in the “Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
40 CFR 264.192(g) requires owner/operators to obtain and keep on file at the unit statements written by those who designed the tank system and supervised its construction. These
statements will verify that the system was designed and constructed properly.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• Maintaining records of statements written by those who certify the tank system’s design and supervise its installation. These must verify that the system was designed and installed according to the regulatory requirements, and that any needed repairs were performed. They must also include the certification statement as required in 40 CFR 270.11(d).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities in complying with these requirements:
• Obtain written statements from those who certified the design of the tank system and supervised its installation and maintain the written statements at the unit.
Containment and detection requirements
Equivalent containment device
40 CFR 264.193(d) requires all secondary containment for tank systems to include one or more of the following devices: a liner; a vault; a double-walled tank; or an equivalent device, as approved by the Regional Administrator. The regulations do not specify the means by which respondents will obtain approval of their equivalent containment devices. Though some respondents may choose to use a previously-approved containment device, this ICR assumes that owner/operators will submit to the Regional Administrator written information regarding the design and type of device, as well as additional information that may be necessary to substantiate a claim that the device is equivalent to a liner, vault, or double-walled tank. Since permitted facilities submit an applications for obtaining equivalent containment device approval with their part B permit application, data items and activities associated with preparing and submitting this information are covered in the Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
Exemption from 24-hour leak detection requirements
40 CFR 264.193(e)(3)(iii) requires secondary containment systems to have a leak detection system that will detect a release within 24 hours. If owner/operators can demonstrate that existing technologies or site conditions will not allow detection within 24 hours, they may use a leak detection system that will detect failure or contamination “at the earliest practicable time.” Since permitted facilities submit applications for exemption from 24-hour leak detection requirements with their part B permit application, data items and activities associated with preparing and submitting this information are covered in the “Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
Variance from secondary containment requirements
40 CFR 264.193(g) allows owner/operators to obtain a variance from all secondary containment requirements if they can demonstrate to the Regional Administrator that (1) alternative design and operating practices, together with location characteristics, will prevent the migration of hazardous constituents into the ground water or surface water as effectively as secondary containment or (2) if a release does migrate to ground or surface water, that the release will pose no substantial hazard. Since permitted facilities submit an applications for variances from secondary containment requirements with their part B permit application, data items and activities associated with preparing and submitting this information are covered in the “Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
Annual leak tests and inspections
40 CFR 264.193(i) requires owner/operators, until they meet the secondary containment requirements, to conduct annual leak tests on the tank system and ancillary equipment and/or develop a schedule and procedures for assessing their tanks. Records of the tests and assessments must be kept on file at the facility. Data items and respondent activities associated with these requirements are covered in this ICR. However, the burden for recordkeeping the applicable data items is covered in “General Hazardous Waste Facility Standards ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0120).
(i) Data item:
The data item required for these recordkeeping requirements is:
• A record of the results of the leak tests and/or inspections required under 40 CFR 264.193(i).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities in filing a record of the assessment results:
• For non-enterable underground tanks, conduct a leak test that meets the requirements of 40 CFR 264.191(b)(5), or other method approved or required by the Regional Administrator;
• For all other tanks and ancillary equipment, conduct the annual leak test (above) or develop a schedule and procedure, in accordance with 40 CFR 264.193(i)(2), for assessing the overall condition of the tank system. This assessment must be performed by an independent, qualified, registered professional engineer and record all inspection and/or test results.
Responses to leaks or spills; disposition of leaking or unfit-for-use tank systems
Exemption from the 24-hour waste removal requirement
40 CFR 264.196 requires a tank system or secondary containment system from which there has been a spill to be removed from service immediately. Paragraph (b) of that section requires owner/operators, within 24 hours, to remove enough waste from the system to prevent further release and allow for inspection and repair of the tank. If the owner/operator can demonstrate that it is not possible to do so within 24 hours, the waste may be removed at the earliest practicable time.
(i) Data item:
The data item required for this demonstration includes:
• Any such evidence sufficient to show that, within 24 hours, the owner/operator cannot remove enough waste from the system to prevent further release and allow for system inspection and repair.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities in making this demonstration:
• Compile evidence showing that, within 24 hours, enough waste cannot be removed from the system to prevent further release and allow for system inspection and repair and submit the evidence to the Regional Administrator.
Release notifications and reports; major repair certifications
40 CFR 264.196(d) requires facilities to comply with certain reporting requirements in the case of a leak or spill. Owner/operators must notify the Regional Administrator of any release to the environment (except as defined in 40 CFR 264.196(d)(2)) within 24 hours of detection,1 and submit a detailed report within 30 days. In addition, where the leak or spill is caused by major system damage, 40 CFR 264.196(f) requires that owner/operators submit to the Regional Administrator a certification of major repairs. This documents that the system has been repaired and is capable of handling hazardous waste without release, and must be submitted to the Regional Administrator within 7 days of returning the system to use.
(i) Data items:
Data items required for release notifications and reports include:
• A notification to the Regional Administrator that there has been a release;
• A report to the Regional Administrator containing the following information:
-- The release’s likely migration route;
-- The surrounding soil characteristics;
-- The results of any monitoring or sampling conducted in connection with the release (if not available within 30 days, results must be submitted as soon as practicable);
-- The release’s proximity to down gradient drinking water, surface water, and population areas; and
-- A description of the response actions taken or planned.
Data items required for a certification of major repairs include:
• A certification by an independent, qualified, registered professional engineer in accordance with 40 CFR 270.11(d) that the repaired system is capable of handling hazardous wastes without release for the intended life of the system.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities in preparing and submitting release notifications and reports:
• Within 24 hours of detection, notify the Regional Administrator that there has been a release;
• Within 30 days of detection, prepare a detailed report for submission to the Regional Administrator. In order to do so, owner/operators must:
-- Determine the release’s likely migration route;
-- Provide information on the surrounding soil characteristics;
-- Conduct appropriate monitoring or sampling;
-- Determine the release’s proximity to down gradient drinking water, surface water, and population areas;
-- Describe the response actions taken or planned and compile and submit the report to the Regional Administrator.
Respondents must perform the following activities in preparing and submitting a certification of major repairs:
• Obtain a certification in accordance with 40 CFR 270.11(d); and
• Within 7 days of returning the system to use, submit the certification to the Regional Administrator.
Closure and post-closure care
Decontamination demonstration
40 CFR 264.197 regulates tank system closure and post-closure care. Paragraph (a) stipulates that the closure plan, closure activities, cost estimates for closure, and financial responsibility for tank systems must meet all of the requirements of 40 CFR Part 264, Subparts G and H. Tank systems will be required to submit a decontamination of soils demonstration under §264.197(b) and §265.197(b). All other information collection requirements for tank system closure and post-closure care are contained in ICR Number 1571, “General Hazardous Waste Facility Standards.”
(i) Data items:
No specific data items are to be included in this demonstration.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities in performing this demonstration:
• Prepare decontamination demonstration and submit demonstration to EPA.
Air emission standards
40 CFR 264.200 requires owners and operators of permitted facilities to manage all hazardous waste placed in a tank in accordance with the applicable requirements of 40 CFR part 264, Subparts AA, BB, and CC. All data items and respondent activities under Subparts AA and BB, as applicable to tanks, are covered later in this ICR under process vents and equipment leaks, respectively. Data items and respondent activities under Subpart CC, as applicable to tanks, are covered in the Supporting Statement for OMB Control No. 2060-0318: “Standards of Performance for Air Emission Standards for Tanks, Surface Impoundments and Containers, 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart CC and 40 CFR Part 265, Subpart CC.”
SURFACE IMPOUNDMENTS
Permitted facilities:
Regulations
Each owner/operator regulated under 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart K is expected to read the regulations.
Design and operating requirements
Under 40 CFR 264.221, facilities will need to submit information to EPA or the authorized State if they seek an exemption from the liner and/or leachate system requirements specified in §264.221(a), (c), or (e). Since permitted facilities submit applications for exemption from the liner and/or leachate system requirements with their part B permit application, data items and activities associated with preparing and submitting applications for exemption from the liner and/or leachate system requirements are covered in the “Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
Calculating average daily flow rates
To determine if the action leakage rate has been exceeded, the owner or operator of the surface impoundment must use the weekly or monthly flow rates from the monitoring data obtained under §264.226(d) and calculate average daily flow rates (in gallons per acre per day), in accordance with §264.222(b). Unless EPA specifies otherwise, the average daily flow rates for each sump must be calculated weekly during the active life and closure period, and monthly during the post‑closure care period, if the unit is closed in accordance with section 264.228(b), and when required under section 264.226(d).
(i) Data item:
The data item required to comply with this requirement is:
• Estimate of the average daily flow rates weekly during the active life and closure period, and monthly during the post‑closure care period.
(ii) Respondent activity:
Respondents must perform the following activity:
• Calculate the average daily flow rates as required by §264.222(b).
Completion and submittal of the Response Action Plan and recordkeeping of response actions
Section 264.223(a) require the owner or operator of each new surface impoundment unit, each replacement of an existing surface impoundment unit, and each lateral expansion of a surface impoundment unit subject to section 264.221(a) to prepare a Response Action Plan (RAP). The plan must set forth the actions to be taken if the action leakage rate has been exceeded. It must describe, at a minimum, the actions required under §264.223(b). Permitted facilities and facilities seeking initial permits must submit the RAP for EPA approval in a Part B permit application or modification before the receipt of waste. Data items and respondent activities associated with preparing and submitting the RAP are covered in the “Part B Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
Action leakage reporting
In the event the flow rate into the leak detection system exceeds the action leakage rate (ALR), section 264.223(b) requires the owner or operator to undertake the following activities.
(i) Data items:
Data items required to comply with this requirement include:
• Notification to the Regional Administrator, in writing, of the exceedance within seven days of the determination;
• Submittal of a preliminary written assessment to the Regional Administrator within 14 days of the determination, as to the amount of liquids, likely sources of liquids, possible location, size and cause of any leaks, and short-term actions taken and planned;
• Determination of, to the extent practicable, the location, size, and cause of any leaks;
• Determination as to whether waste receipt should cease or be curtailed;
Determination as to whether any waste should be removed from the unit for inspection, repairs, or controls, and whether or not the unit should be closed;
• Determination of any other short‑term and longer‑term actions to be taken to mitigate or stop any leaks; and
• Submittal to the Regional Administrator, within 30 days after the notification that the action leakage rate has been exceeded, the results of the analyses specified, the results of actions taken, and actions planned. As long as the ALR is exceeded, the owner or operator must submit to the Regional Administrator monthly reports summarizing the results of any remedial actions taken and actions planned.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities as specified in the RAP:
• Notify the Regional Administrator, in writing, of the exceedance within seven days of the determination, as required by §264.223(b)(1);
• Submit a preliminary written assessment to the Regional Administrator within 14 days of the determination, as required by §264.223(b)(2);
• Determine, to the extent practicable, the location, size and cause of any leak, as required by §264.223(b)(3);
• Determine whether waste receipt should cease or be curtailed;
Determine whether any waste should be removed from the unit for inspection, repairs, or controls, and whether or not the unit should be closed;
• Determine any other short‑term and longer‑term actions to be taken to mitigate or stop any leaks, as required by §264.223(b)(5); and
• Submit to the Regional Administrator, within 30 days after the notification that the ALR has been exceeded, the results of the analyses specified in paragraphs(b)(3), (4), and (5), the results of the actions taken, and actions planned, and monthly thereafter as required by §264.223(b)(6).
Remediation determination analyses
Under 40 CFR 264.223(b)(3), (4), and (5), owners and operators must make leak and/or remediation determinations.
(i) Data items:
Data items required to comply with the requirements include:
• Assessment of the source liquids and amounts of liquids by source;
• Execution of a fingerprint, hazardous constituent, of other analyses of the liquids in the leak detection system to identify the source of liquids and possible location of any leaks, and the hazard and mobility of the liquid; and
• Assessment of the seriousness of any leaks in terms of potential for escaping into the environment.
OR
• Documentation as to why assessments above are not needed.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities when conducting remediation determination analyses:
• Perform the following activities to make leak and/or remediation determinations:
-- Assess the source of liquids and amounts of liquids, as required by sections 264.223(c)(1)(i);
-- Conduct a fingerprint, hazardous constituent, or other analyses, as required by section 264.223(c)(1)(ii) and assess the seriousness of any leaks, as required by sections 264.223(c)(1)(ii).
OR
-- Document why assessments above are not needed, as required by §264.223(c)(1)(iii).
Dike re-certification
Under 40 CFR 264.226(c) surface impoundment owner/operators must, prior to issuance of a permit and after any extended period of time in which the impoundment was not in use, obtain a certification from a qualified engineer that the impoundment’s dike has sufficient structural integrity. Since permitted facilities submit these certifications prior to or with their part B permit application, data items and activities associated with preparing and submitting these certifications are covered in the “Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009). The burden associated with re-certifying dikes after extended periods of non-use is covered in this ICR.
(i) Data item:
The data item required to comply with this requirement includes:
• A certification from a qualified engineer that the impoundment’s dike, including any portion of the dike that provides freeboard, has structural integrity according to the standards detailed in §264.226(c)(1) and (2).
(ii) Respondent activities:
To fulfill this requirement, permittees will need to perform the following activities:
• Obtain the certification from a qualified engineer and file and maintain certification and related data at the unit.
Monitoring and inspection
Section 264.226(a) and (b) require owners and operators of facilities that use surface impoundments to inspect their units and to record the specified inspection activities. Data items and respondent activities associated with these requirements are covered in this ICR. However, the burden for recordkeeping the applicable data items is covered in “General Hazardous Waste Facility Standards ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0120).
Data items:
Data items required to comply with these requirements include:
Records pertaining to inspections done during the construction and installation of liners (except in the case of existing portions of surface impoundments exempt form §264.221(a)) and cover systems (e.g., membranes, sheets, or coatings) for uniformity, damage, and imperfections (e.g., holes, cracks, thin spots, or foreign materials) (§264.226(a));
Records pertaining to the inspection of synthetic liners and covers to ensure tight seams and joints an the absence of tears, punctures, or blisters immediately after construction and installation (§264.226(a));
Records pertaining to the inspection of soil-based and admixed liners and covers for imperfections including lenses, cracks, channels, root holes, or other structural non-uniformities that may cause an increase in the permeability of the liner or cover immediately after construction and installation (§264.226(a)); and
Records pertaining to the inspection of the surface impoundment weekly and after storms while it is operation to detect evidence of any of the following (§264.226(b)):
-- Deterioration, malfunctions, or improper operation of overtopping control systems;
-- Sudden drops in the level of the impoundment’s contents; and
-- Severe erosion or other signs of deterioration in dikes or other containment devices.
(ii) Respondent activity:
Respondents must perform the following activity for actions associated with monitoring and inspections:
Emergency repairs and contingency plans
40 CFR 264.227 details criteria applicable to during emergency situations (i.e., those in which there is a precipitous drop in liquid levels or the impoundment is known to be leaking).
In addition, §264.227(d)(2)(ii) stipulates that no surface impoundment that contains a liner system and has been removed from service under §264.227(a)(1) may be restored to service unless the repaired liner system is certified by an engineer as meeting the design specifications approved in the permit.
(i) Data items:
For each surface impoundment removed from service under §264.227(a) owner/operators must, in addition to complying with other requirements, provide the following data item:
• A written notification to the Regional Administrator of a surface impoundment’s removal from service.
The data item required under §264.227(d)(2)(ii) includes:
• A certification by a qualified engineer that the repaired liner system meets the design specifications approved in the permit.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to complete this notification, permittees will need to engage in the following activities:
• Within seven days, notify the Regional Administrator in writing of a surface impoundment’s removal from service and file and maintain related data.
Respondents must perform the following activities in recertifying dikes:
• Obtain certification of the dike’s sufficient structural integrity; and
• Maintain the certification on file.
OR
• Obtain a liner repair certification, as required under §264.227(d)(2)(ii); and
• Maintain the certification on file.
Closure
Under 40 CFR 264.113(e) an owner or operator of a hazardous waste surface impoundment that is not in compliance with the liner and leachate collection system requirements in 42 U.S.C. 3004(o)(1) and 3005(j)(1) or 2 U.S.C. 3004(o)(2) or (3) or 3005(j)(2), (3),(4), or (13) must implement closure and corrective action measures.
(i) Data items:
The data items required to comply with these requirements are:
• A contingent corrective measures plan, unless a corrective action plan has already been submitted under;
• A plan for removing hazardous wastes in compliance with paragraph (e)(2) of this section;
• An extension request, based on a demonstration that the removal of hazardous wastes will, of necessity, take longer than the allotted period to complete and that an extension will not pose a threat to human health and the environment; and
• A semi-annual report to the Regional Administrator that describes the progress of the corrective action program.
(ii) Respondent activities:
• Prepare and submit a contingent corrective measures plan in accordance with §264.113(e)(1)(i);
• Prepare and submit a hazardous waste removal plan in accordance with §264.113(e)(1)(ii);
• Prepare and submit an extension request, as specified in §264.113(e)(3); and
• Prepare and submit a corrective action report twice per year, as required by §264.113(e)(5).
Special requirements for hazardous wastes F020, F021, F022, F023, F026, and F027
40 CFR 264.231 prohibits placing F020, F021, F022, F023, F026, and F027 wastes in any surface impoundment unless the owner/operator operates the impoundment in accordance with a management plan approved by the Regional Administrator. Since the waste management plan is submitted with the Part B permit application, data items and respondent activities associated with this requirement are covered in the “Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (1573).
Air emission standards
40 CFR 264.232 requires owners and operators of permitted facilities to manage all hazardous waste placed in a surface impoundment in accordance with the applicable requirements of 40 CFR part 264, Subparts BB and CC. All data items and respondent activities under Subpart BB, as applicable to surface impoundments, are covered later in this ICR under equipment leaks. Data items and respondent activities under Subpart CC, as applicable to surface impoundments, are covered in the Supporting Statement for OMB Control No. 2060-0318: “Standards of Performance for Air Emission Standards for Tanks, Surface Impoundments and Containers, 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart CC and 40 CFR Part 265, Subpart CC.”
WASTE PILES
Permitted facilities:
Regulations
Each owner/operator regulated under 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart L is expected to read the regulations.
Exemption from design and operating requirements
40 CFR 264.251(a) requires owner/operators to comply with the provisions in 40 CFR 264.251. Under 40 CFR 264.251(a), owner/operators with waste piles subject to Subpart L are required to have liners and leachate collection and removal systems sufficient to prevent any waste migration for the active life of the pile (including the closure period). This citation also details design, construction, and installation requirements for the liners and collection systems. 40 CFR 264.251(b) exempts waste piles from the requirements in §264.251(a) if the owner/operator can demonstrate to the Regional Administrator that alternate design and operating practices, together with location characteristics, will prevent hazardous constituents from migrating into the ground or surface water at any future time. Since permitted facilities submit applications for exemption from 40 CFR 264.251 with their part B permit application, data items and activities associated with this exemption are covered in the “Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
Variance from design and operating requirements
40 CFR 264.251(d) allows owner/operators of waste piles to seek a variance from the liner/leachate system requirements by submitting an alternative design or operating practices, as long as the alternative complies with the requirements given in section 264.251(d). Since permitted facilities submit applications for variance from 40 CFR 264.251 with their part B permit application, data items and activities associated with this variance are covered in the “Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
Calculating average daily flow rates
To determine if the action leakage rate has been exceeded, the owner or operator of the waste pile must use the weekly flow rates from the monitoring data obtained under §264.254(c) and calculate average daily flow rates (in gallons per acre per day), in accordance with §264.252(b). Unless EPA specifies otherwise, the average daily flow rates for each sump must be calculated weekly during the active life and closure period.
(i) Data item:
The data item required to comply with this requirement is:
• Estimate of the average daily flow rates weekly during the active life and closure period.
(ii) Respondent activity:
Respondents must perform the following activity:
• Calculate the average daily flow rates as required by §264.252(b).
Completion and submittal of the Response Action Plan and recordkeeping of response actions
Section 264.253(a) requires the owner or operator of each new waste pile unit, each replacement of an existing waste pile unit, and each lateral expansion of a waste pile unit subject to section 264.253(c) or (d) to prepare and submit to EPA a Response Action Plan (RAP). The plan must set forth the actions to be taken if the action leakage rate has been exceeded. It must describe, at a minimum, the actions required under §264.253(b). Permitted facilities and facilities seeking initial permits must submit the RAP for EPA approval in a Part B permit application or modification before the receipt of waste. Data items and respondent activities associated with preparing and submitting the RAP are covered in the “Part B Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
Action leakage reporting
In the event the flow rate into the leak detection system exceeds the action leakage rate, section 264.253(b) requires the owner or operator to collect the following data items.
(i) Data items:
The following data items are required if the action leakage rate is exceeded:
• Notification to the Regional Administrator, in writing, of the exceedance within seven days of the determination;
• Submittal of a preliminary written assessment to the Regional Administrator within 14 days of the determination, as the amount of liquids, likely sources of liquids, possible location, size and cause of any leaks, and short‑term actions taken and planned;
• Determination of, to the extent practicable, the location, size, and cause of any leaks;
• Determination as to whether waste receipt should cease or be curtailed;
Determination as to whether any waste should be removed from the unit for inspection, repairs, or controls, and whether or not the unit should be closed;
• Determination of any other short‑term and longer‑term actions to be taken to mitigate or stop any leaks; and
• Submittal to the Regional Administrator, within 30 days after the notification that the action leakage rate has been exceeded, the results of the analyses specified, the results of actions taken, and actions planned. As long as the ALR is exceeded, the owner or operator must submit to the Regional Administrator monthly reports summarizing the results of any remedial actions taken and actions planned.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities as outlined in the RAP:
• Notify the Regional Administrator, in writing, of the exceedance within seven days of the determination, as required by §264.253(b)(1);
• Submit a preliminary written assessment to the Regional Administrator within 14 days of the determination, as required by §264.253(b)(2);
• Determine, to the extent practicable, the location, size and cause of any leak, as required by §264.253(b)(3);
• Determine whether waste receipt should cease or be curtailed;
Determine whether any waste should be removed from the unit for inspection, repairs, or controls, and whether or not the unit should be closed;
• Determine any other short‑term and longer‑term actions to be taken to mitigate or stop any leaks, as required by §264.253(b)(5); and
• Submit to the Regional Administrator, within 30 days after the notification that the ALR has been exceeded, the results of the analyses specified in paragraphs (b)(3), (4), and (5), the results of the actions taken, and actions planned, and monthly thereafter as required by §264.253(b)(6).
Remediation determination analyses
Under 40 CFR 264.253(b)(3), (4), and (5), owners and operators must make leak and/or remediation determinations.
(i) Data items:
Data items required to comply with these requirements include:
• Assessment of the source liquids and amounts of liquids by source;
• Execution of a fingerprint, hazardous constituent, of other analyses of the liquids in the leak detection system to identify the source of liquids and possible location of any leaks, and the hazard and mobility of the liquid; and
• Assessment of the seriousness of any leaks in terms of potential for escaping into the environment.
OR
• Documentation as to why assessments above are not needed.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities when conducting remediation determination analyses:
• Perform the following activities to make leak and/or remediation determinations:
-- Assess the source of liquids and amounts of liquids, as required by sections 264.253(c)(1)(i);
-- Conduct a fingerprint, hazardous constituent, or other analyses, as required by sections 264.253(c)(1)(ii); and
-- Assess the seriousness of any leaks, as required by sections 264.253(c)(1)(ii).
OR
-- Document why assessments above are not needed, as required by §264.253(c)(1)(iii).
Monitoring and inspections
Section 264.254(a) and (b) require owners and operators of facilities that use waste piles to inspect their units and to record the specified inspection activities. Data items and respondent activities associated with these requirements are covered in this ICR. However, the burden for recordkeeping the applicable data items is covered in “General Hazardous Waste Facility Standards ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0120).
(i) Data items:
Data items required to comply with these requirements include:
Records pertaining to inspections done during the construction and installation of liners (except in the case of existing portions of surface impoundments exempt form §264.251(a)) and cover systems (e.g., membranes, sheets, or coatings) for uniformity, damage, and imperfections (e.g., holes, cracks, thin spots, or foreign materials) (§264.254(a));
Records pertaining to the inspection of synthetic liners and covers to ensure tight seams and joints an the absence of tears, punctures, or blisters immediately after construction and installation (§264.254(a));
Records pertaining to the inspection of soil-based and admixed liners and covers for imperfections including lenses, cracks, channels, root holes, or other structural non-uniformities that may cause an increase in the permeability of the liner or cover immediately after construction and installation (§264.254(a)); and
Records pertaining to the inspection of the waste pile weekly and after storms while it is operation to detect evidence of any of the following (§264.254(b)):
-- Deterioration, malfunctions, or improper operation of run-on and run-off control systems;
-- Proper functioning of wind dispersal control systems, where present; and
-- The presence of leachate in and proper functioning of leachate collection and removal systems, where present.
(ii) Respondent activity:
Respondents must perform the following activity for actions associated with monitoring and inspections:
Special requirements for hazardous wastes F020, F021, F022, F023, F026, and F027
40 CFR 264.259 prohibits placing F020, F021, F022, F023, F026, and F027 wastes in any waste pile unless the owner/operator operates the waste pile in accordance with a management plan approved by the Regional Administrator. Since the waste management plan is submitted with the Part B permit application, data items and respondent activities associated with this requirement are covered in the “Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (1573).
LAND TREATMENT
Permitted facilities:
Regulations
Each owner/operator regulated under 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart M is expected to read the regulations.
Food-chain crops
40 CFR 264.276 regulates the growth of food-chain crops at permitted hazardous waste land treatment facilities. Since the owner/operator must make the demonstrations outlined in §264.276(a) prior to submitting the Part B permit application, data items and activities associated with this demonstration are covered in the “Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009). The burden associated with maintaining (i.e., filing and photocopying) this documentation is covered in this ICR.
Under section 264.276(b)(2)(iii), owner/operators must develop and maintain an operating plan that demonstrates how the animal feed will be distributed to preclude ingestion by humans.
(i) Data items:
Operating plan that demonstrates how the animal feed will be distributed to preclude ingestion by humans.
(ii) Respondent activities:
• Maintain food-chain crop documentation at the facility and develop and maintain an operating plan.
Unsaturated-zone monitoring
Owner/operators of permitted facilities subject to the unsaturated-zone monitoring requirements of 40 CFR 264.278 must establish an unsaturated-zone monitoring program to determine whether hazardous constituents migrate out of the treatment zone. These owner/operators must notify EPA whenever they determine that there is a statistically significant increase of hazardous constituents below the treatment zone, and must (1) submit a permit modification application to modify the operating practices at the unit, or (2) submit a report to EPA demonstrating that the source of the increase is not the regulated unit. If, however, the demonstration does not show that a source other than the regulated units or some error in sampling, analysis, or evaluation caused the increase in hazardous constituents, the owner/operator must submit the permit modification request within the specified time period.
(i) Data items:
Data items for these requirements include:
• Notification of statistically significant increases of hazardous waste constituents below the treatment zone. This notification must be made within seven days and must include information on what constituents have shown statistically significant increases (§264.278(g)(1));
• An application for a permit modification, submitted within 90 days, to modify operating practices at the unit in order to maximize the success of degradation, transformation, or immobilization processes in the treatment zone (§264.278(g)(2));
• Notification of intent to demonstrate that the increase was not caused by the regulated units. This notification must be submitted within seven days of identifying the increase (§264.278(h)(1)); and
• A report, submitted within 90 days, demonstrating that a source other than the regulated units caused the increase or that the increase resulted from error in sampling, analysis, or evaluation (§264.278(h)(2)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities in complying with these notification, report, and application requirements:
• Prepare and submit a notice of statistically significant increases in the concentration of hazardous constituents;
• Prepare and submit notice of intent to make a demonstration under 40 CFR 264.278(h); and
• Prepare and submit a report demonstrating that a source other than the regulated units caused the increase or that the increase resulted from error in sampling, analysis, or evaluation.
Closure and post-closure care
40 CFR 264.280 regulates closure and post-closure care at hazardous waste land treatment facilities. The regulations require owner/operators to provide EPA with certification of closure when unit closure is completed. The regulations also allow exemptions from both the requirement to establish a vegetative cover (§264.280(a)(8)), and the post-closure care requirements (§264.280(c)) if facilities make the appropriate demonstrations.
(i) Data items:
Data items for these requirements include:
• Certification by an independent qualified scientist, in lieu of an independent registered professional engineer, that the unit has been closed in accordance with the specifications in the approved closure plan (§264.280(b)); and
• For exemption from the vegetative cover and post-closure requirements, a demonstration that the level of hazardous constituents in the treatment zone soil does not exceed the background value of those constituents by a statistically significant amount (§264.280(d)). This demonstration may be submitted at any time during the closure or post-closure care periods.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities in complying with these requirements:
• Obtain certification of closure from a qualified scientist;
• Submit the certification(s) to EPA and if applying for a demonstration under §264.280(d), prepare the demonstration and submit it to EPA.
Special requirements for hazardous wastes F020, F021, F022, F023, F026, and F027
40 CFR 264.283 prohibits placing F020, F021, F022, F023, F026, and F027 wastes in any land treatment unit unless the owner/operator operates the unit in accordance with a management plan approved by the Regional Administrator. Since the waste management plan is submitted with the Part B permit application, data items and respondent activities associated with this requirement are covered in the “Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (1573).
LANDFILLS
Permitted facilities:
Regulations
Each owner/operator regulated under 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart N is expected to read the regulations.
Calculating average daily flow rates
To determine if the action leakage rate has been exceeded, section 264.302(b) requires the owner or operator of each landfill unit to use the weekly or monthly flow rates from the monitoring data obtained under §264.303(c)(2) and calculate average daily flow rates (in gallons per acre per day). Unless EPA specifies otherwise, the average daily flow rates for each sump must be calculated weekly during the active life and closure period, and monthly during the post‑closure care period, if the unit is closed in accordance with section 264.310(b)(3), and when required under section 264.303(c)(1).
(i) Data item:
The data item required to comply with these requirements is:
• Estimate of the average daily flow rates weekly during the active life and closure period, and monthly during the post‑closure care period.
(ii) Respondent activity:
Respondents must perform the following activity:
• Calculate the average daily flow rates as required by §264.302(b).
Monitoring and inspection
Section 264.303(a) and (b) require owners and operators of facilities that have landfills to inspect their units and to record the specified inspection activities. Data items and respondent activities associated with these requirements are covered in this ICR. However, the burden for recordkeeping the applicable data items is covered in “General Hazardous Waste Facility Standards ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0120).
(i) Data items:
Data items required to comply with these requirements include:
Records pertaining to inspections done during the construction and installation of liners (except in the case of existing portions of surface impoundments exempt form §264.301(a)) and cover systems (e.g., membranes, sheets, or coatings) for uniformity, damage, and imperfections (e.g., holes, cracks, thin spots, or foreign materials) (§264.303(a));
Records pertaining to the inspection of synthetic liners and covers to ensure tight seams and joints an the absence of tears, punctures, or blisters immediately after construction and installation (§264.303(a));
Records pertaining to the inspection of soil-based and admixed liners and covers for imperfections including lenses, cracks, channels, root holes, or other structural non-uniformities that may cause an increase in the permeability of the liner or cover immediately after construction and installation (§264.303(a)); and
Records pertaining to the inspection of the waste pile weekly and after storms while it is operation to detect evidence of any of the following (§264.303(b)):
-- Deterioration, malfunctions, or improper operation of run-on and run-off control systems;
-- Proper functioning of wind dispersal control systems, where present; and
-- The presence of leachate in and proper functioning of leachate collection and removal systems, where present.
(ii) Respondent activity:
Respondents must perform the following activity for actions associated with monitoring and inspections:
Completion and submittal of the Response Action Plan and recordkeeping of response actions
Section 264.304(a) requires the owner or operator of each new landfill unit, each replacement of an existing landfill unit, and each lateral expansion of a landfill unit subject to section 264.301(c) or (d) to prepare a Response Action Plan (RAP). The plan must set forth the actions to be taken if the action leakage rate has been exceeded. It must describe, at a minimum, the actions required under §264.303(b). Permitted facilities and facilities seeking initial permits must submit the RAP for EPA approval in a Part B permit application or modification before the receipt of waste. Data items and respondent activities associated with preparing and submitting the RAP are covered in the “Part B Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
Action leakage reporting
40 CFR 264.304(b) requires owners and operators to collect certain information in the event the flow rate into the leak detection system exceeds the action leakage rate.
(i) Data items:
The following data items are required if the action leakage rate is exceeded:
• Notification to the Regional Administrator, in writing, of the exceedance within seven days of the determination;
• Submittal of a preliminary written assessment to the Regional Administrator within 14 days of the determination, as the amount of liquids, likely sources of liquids, possible location, size and cause of any leaks, and short‑term actions taken and planned; Determination of, to the extent practicable, the location, size, and cause of any leaks;
• Determination as to whether waste receipt should cease or be curtailed;
Determination as to whether any waste should be removed from the unit for inspection, repairs, or controls, and whether or not the unit should be closed;
• Determination of any other short‑term and longer‑term actions to be taken to mitigate or stop any leaks; and
• Submittal to the Regional Administrator, within 30 days after the notification that the action leakage rate has been exceeded, the results of the analyses specified, the results of actions taken, and actions planned. As long as the ALR is exceeded, the owner or operator must submit to the Regional Administrator monthly reports summarizing the results of any remedial actions taken and actions planned.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities as outlined in the RAP:
• Notify the Regional Administrator, in writing, of the exceedance within seven days of the determination, as required by §264.304(b)(1);
• Submit a preliminary written assessment to the Regional Administrator within 14 days of the determination, as required by §264.304(b)(2);
• Determine, to the extent practicable, the location, size and cause of any leak, as required by §264.304(b)(3);
• Determine whether waste receipt should cease or be curtailed;
Determine whether any waste should be removed from the unit for inspection, repairs, or controls, and whether or not the unit should be closed;
• Determine any other short‑term and longer‑term actions to be taken to mitigate or stop any leaks, as required by §264.304(b)(5); and
• Submit to the Regional Administrator, within 30 days after the notification that the ALR has been exceeded, the results of the analyses specified in paragraphs(b)(3), (4), and (5), the results of the actions taken, and actions planned, and monthly thereafter as required by §264.304(b)(6).
Remediation determination analyses
Under 40 CFR 264.304(b)(3), (4) and (5), owners and operators must make leak and/or remediation determinations.
(i) Data items:
Data items required to comply with these requirements include:
• Assessment of the source liquids and amounts of liquids by source;
• Execution of a fingerprint, hazardous constituent, of other analyses of the liquids in the leak detection system to identify the source of liquids and possible location of any leaks, and the hazard and mobility of the liquid; and
• Assessment of the seriousness of any leaks in terms of potential for escaping into the environment.
OR
• Documentation as to why assessments above are not needed.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities to make leak and/or remediation determinations:
• Perform the following activities to make leak and/or remediation determinations:
-- Assess the source of liquids and amounts of liquids, as required by section 264.304(c)(1)(i);
-- Conduct a fingerprint, hazardous constituent, or other analyses, as required by section 264.304(c)(1)(ii); and
-- Assess the seriousness of any leaks, as required by section 264.304(c)(1)(ii).
OR
-- Document why assessments above are not needed, as required by §264.304(c)(1)(iii).
Special requirements for bulk and containerized liquids
40 CFR 264.314(b) prohibits disposing bulk or containerized liquid hazardous waste or hazardous waste containing free liquids in any landfill. 40 CFR 264.314(c) requires owner/operators to demonstrate the absence or presence of free liquids in bulk or containerized waste using EPA Method 9095 (Paint Filter Liquids Test) as described in “Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Wastes, Physical/Chemical Methods” (EPA Publication No. SW-846).
In addition, 40 CFR 264.314(e) prohibits placing non-hazardous liquid waste in a landfill unless the landfill owner/operator can demonstrate to the Regional Administrator, or the Regional Administrator determines, that: (1) the only reasonably available alternative is placing the waste in another landfill that contains or is expected to contain hazardous waste, and (2) placing the waste in the owner/operator’s landfill will not risk contaminating any underground source of drinking water. The regulations do not specify the exact form this demonstration must take; depending on the circumstances surrounding each demonstration, the effort and data required to gain an exemption may vary. This ICR assumes that owner/operators will present information regarding (1) the situational constraints that necessitate disposing the waste in a landfill containing hazardous waste (e.g., the lack of access to any other suitable disposal arrangement), and (2) hydrogeological and other information sufficient to show that doing so cannot contaminate any underground source of drinking water.
(i) Data items:
The data items for demonstrating the absence of free liquids include:
• Results of the Paint Filter Liquids Test, performed as specified in SW-846.
The data items required for the demonstration under 40 CFR 264.314(e) include:
• Information sufficient to show that the only reasonably available alternative to placing the waste in the owner/operator’s landfill would be to place the waste in another landfill
or unlined surface impoundment that contains or is expected to contain hazardous waste; and
• Information sufficient to show that placing the waste in the owner/operator’s landfill will not present a risk of contamination of any underground source of drinking water.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities in performing the no-free-liquids demonstration:
• Record and file the observation results.
Respondents must perform the following activities in order to gain an exemption from the requirements in §264.314(e):
• Gather the information necessary to make the demonstration and submit the information to the Regional Administrator.
Special requirements for hazardous wastes F020, F021, F022, F023, F026, and F027
40 CFR 264.317 prohibits placing F020, F021, F022, F023, F026, and F027 wastes in any landfill unless the landfill is operated in accordance with a management plan approved by the Regional Administrator. Since the waste management plan is submitted with the Part B permit application, data items and respondent activities associated with this requirement are covered in the “Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
INCINERATORS
Permitted facilities:
Regulations
Each owner/operator regulated under 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart O is expected to read the regulations.
Applicability
40 CFR Part 264, Subpart O presents permitted status hazardous waste incinerator standards. Section 264.340(b) exempts incinerator owner/operators from these regulations. Since the owner/operator submits applicability exemptions with the Part B Permit Application, data items and respondent activities associated with this requirement are covered in the “Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
Notification of intent to burn hazardous wastes
40 CFR 264.343(a)(2) requires owner/operators to notify the Regional Administrator prior to burning EPA Hazardous Waste Codes F020, F021, F022, F023, F026, and F027.
(i) Data items:
No specific data items are to be included in this notification.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with 40 CFR 264.343(a)(2), owners/operators must perform the following activities:
• Prepare notification of intent to burn wastes and submit notification to the Regional Administrator.
Monitoring and inspections
40 CFR 264.347(a), (b) and (c) detail the monitoring and inspection requirements for Subpart O incinerators. Data items and respondent activities associated with these requirements are covered in this ICR. However, the burden for recordkeeping the applicable data items is covered in the “General Hazardous Waste Facility Standards ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0120).
(i) Data items:
Data items required to comply with these requirements include:
-- Combustion temperature, waste feed rate, and the indicator of combustion gas velocity specified in the facility permit must be monitored on a continuous basis;
-- CO must be monitored on a continuous basis at a point in the incinerator downstream of the combustion zone and prior to release to the atmosphere; and
-- Upon request by the Regional Administrator, sampling and analysis of the waste and exhaust emissions must be conducted to verify that the operating requirements established in the permit achieve the performance standards of §264.343;
Records pertaining to thorough visual inspections, conducted at least daily, of the incinerator and associated equipment (pumps, valves, conveyors, pipes, etc.) for leaks, spills, fugitive emissions, and signs of tampering (§264.347(b)); and
Records pertaining to operational testing, conducted at least weekly, of the emergency waste feed cutoff system and associated alarms to verify operability (§264.347(c));
OR
• A demonstration for exemption under §264.347(c) from the requirements to test the emergency waste feed cutoff system and associate alarms on a weekly basis; and
Records pertaining to operational testing, conducted at least monthly, of the emergency waste feed cutoff system and associated alarms to verify operability (§264.347(c)).
(ii) Respondent activity:
Respondents must perform the following activity in order to be exempt from these requirements:
• Record all inspection data.
DRIP PADS
Generators:
Regulations
Each respondent regulated under 40 CFR Part 261 is expected to read the regulations.
Equipment cleaning or replacement plan
40 CFR 261.35(b) requires owners and operators of facilities that generate wastes from wood preserving processes to either prepare, sign, and follow an equipment cleaning plan, or prepare, sign, and follow an equipment replacement plan. In addition, generators must document equipment cleaning and replacement in accordance with §261.35(b)(1)(iii). Generators must also maintain records documenting all equipment cleaning or replacement (§261.35(c)).
(i) Data item:
The data item required to comply with these requirements include:
Documentation of equipment cleaning and replacement.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities in gathering this data:
• Prepare and follow an equipment cleaning plan;
OR
• Prepare and follow an equipment replacement plan;
OR
• Document cleaning and replacement; and
• Maintain documentation of equipment cleaning and replacement.
Permitted facilities:
Regulations
Each owner/operator regulated under 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart W is expected to read the regulations.
Contingency plan
40 CFR 264.570 requires owners and operators of facilities that use new or existing drip pads to convey treated wood drippage, precipitation, and/or surface water run-on to an associated collection system. The requirements are not applicable, however, to the management of infrequent and incidental drippage in storage yards provided that the owner or operator maintains and complies with a written contingency plan that describes how the owner or operator will respond immediately to the discharge of such infrequent and incidental drippage.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• Contingency plan describing how the owner or operator will do the following: (1) clean up the drippage; (2) document the cleanup of the drippage; (3) retain documents regarding cleanup for three years; and (4) manage the contaminated media in a manner consistent with Federal regulations (§264.570(c)(1)).
(ii) Respondent activity:
To comply with §264.570(c)(1), respondents must perform the following activity:
• Develop and maintain a contingency plan for discharge of drippage, including documentation of drippage.
Assessment of existing drip pad integrity
40 CFR 264.571(a) requires that for each existing drip pad as defined in §264.570, the owner or operator must evaluate the drip pad and determine that it meets all of the requirements of this Subpart, except the requirements for liners and leak detection systems of §264.573(b).
(i) Data item:
The data item for this evaluation includes:
• A written assessment of the drip pad, reviewed and certified by an independent, qualified registered professional engineer that attests to the results of the evaluation.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.571(a), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Obtain a written, certified assessment of the drip pad;
• Maintain on file the written assessment of the drip pad and review, update, and re-certify the assessment annually.
Plan for upgrading, repairing, and modifying the drip pad
40 CFR 264.571(b) requires that the owner or operator develop a written plan for upgrading, repairing, and modifying the drip pad to meet the requirements of §264.573(b) and must submit this plan no later than two years before the date that all repairs, upgrades, and modifications will be complete. This written plan must describe all changes to be made to the drip pad. Upon completion of all repairs and modifications, the owner or operator must submit the as-built drawing with certification by and independent, qualified engineer attesting that the drip pad conforms to the drawings, as specified in 40 CFR 264.571(c).
(i) Data items:
The data items for these requirements include:
• A written plan reviewed and certified by an independent qualified, registered professional engineer; and
• As-built drawings for the drip pad together with a certification by an independent, qualified registered professional engineer attesting that the drip pad conforms to the drawings.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.571(b)-(c), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Develop and submit to the Regional Administrator a written certified plan;
• Maintain a written assessment of the plan and obtain and submit as-built drawings and a certification.
Design and operating requirements
40 CFR 264.573 specifies design and operating requirements for owners and operators of facilities with drip pads. Sections 264.573(a), (b), (g), (i), and (k) include information collection requirements associated with the design, construction, operation, and maintenance of the drip pads.
(i) Data items:
The data items required to comply with these requirements include:
• A written assessment of the drip pad, reviewed and certified by an independent, qualified registered professional engineer that attests to the results of the evaluation. The assessment must be reviewed, updated, and recertified annually. The evaluation must document the extent to which the drip pad meets the design and operating standards of this section (§264.573(a)(4)(ii));
• Documentation in the unit’s operating log of the date and time of any leakage collected and removed from the leakage collection system immediately above the liner that is designed, constructed, maintained, and operated to collect leakage from the drip pad (§264.573(b)(3));
• Certification from an independent, qualified registered professional engineer stating that the drip pad design meets the requirements of §264.573 (§264.573(g));
• Documentation in the unit’s operating log of the date and time of each weekly cleaning of the drip pad and the cleaning procedure used (§264.573(i)); and
• Records sufficient to document that all treated wood is held on the pad following treatment in accordance with this requirement (§264.573(k)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.573(a), (b), (g), (i), and (k), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Obtain and maintain a written certified assessment of a new drip pad;
• Update and maintain the written certified assessment of the drip pad annually;
• Maintain documentation of the date and time of any leakage collected and removed from the leakage collection system immediately above the liner;
Obtain and maintain a certification from an independent, qualified registered professional engineer stating that the drip pad design meets the requirements of §264.573;
• Maintain documentation of the date and time of each weekly cleaning of the drip pad and maintain records that all treated wood is held on the drip pad after treatment.
Emergency response
40 CFR 264.573(m) requires that throughout the active life of the drip pad, the owner or operator must repair within a reasonably prompt period of time any condition detected that may have caused or has caused a release of hazardous waste.
(i) Data items:
The data items for this requirement include:
• A record of discovery of each condition in the unit operating log;
A 24-hour notification;
• Written notification of the condition to the Regional Administrator within 10 working days of the discovery, providing a description of the steps that will be taken to repair the drip pad, and clean up any leakage, and the schedule for accomplishing this work; and
• Written notification with a certification to the Regional Administrator showing that all repairs and clean up have been completed according to the written plan submitted.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.573(m), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Enter a record of discovery for each condition;
Notify EPA of each condition within 24 hours;
• Provide written notification to EPA within 10 working days; and
• Prepare and submit a report with certification to EPA when all repairs and clean up are complete.
Facility operating record
40 CFR 264.573(n) requires that the owner or operator of a unit with drip pads must maintain as part of the unit’s operating log, documentation of past operating and waste handling practices.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement is:
• Documentation of past operating and waste handling practices, which must include identification of preservative formulations used in the past, a description of drippage management practices, and a description of treated wood storage and handling practices.
(ii) Respondent activity:
To comply with §264.573(n), respondents must perform the following activity:
• Maintain documentation of past operating and waste handling practices.
Inspections
40 CFR 264.574 requires that during construction or installation, liners and cover systems (e.g., membranes sheets, or coatings) must be inspected for uniformity, damage, and imperfections (e.g., holes, cracks, thin spots, or foreign materials). Data items and respondent activities associated with these requirements are covered in this ICR. However, the burden for recordkeeping the applicable data items is covered in the “General Hazardous Waste Facility Standards ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0120).
(i) Data items:
The data items for this requirement include:
• Inspection of liners immediately after construction or installation with certification by an independent qualified, registered professional engineer. Also, drip pads must be inspected weekly while in operation; and
• Certifications of inspection must be maintained at the unit as part of the unit’s operating record.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.574 respondents must perform the following activity:
• Inspect and certify liners immediately after construction or installation and inspect and certify liners on a weekly basis.
MISCELLANEOUS UNITS (Permitted Facilities Only)
Because developing and following a written schedule for inspecting equipment is covered in the “General Hazardous Waste Facility Standards ICR” ( OMB Control No. 2050-0120), submitting a biennial report is covered in the “Biennial Report ICR” (EPA ICR Number 976), preparing an unmanifested waste report is covered in the “Manifest ICR” (EPA ICR Number 801), preparing release, fire, explosion, and closure reports are covered in the “General Hazardous Waste Facility Standards ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0120), and documenting post-closure care procedures for closed miscellaneous units that have contaminated soils or ground water are covered in the “Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009), these data items and activities associated with them are not covered in this ICR. The only burden covered in this ICR for respondents regulated under 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart X is for reading the regulations.
PROCESS VENTS
Permitted facilities:
Regulations
Each owner/operator regulated under 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart AA is expected to read the regulations.
Control device operation documentation
40 CFR 264.1033(j) requires owner/operators to prepare documentation describing the operation of control devices different from those specified in §264.1033(f), (g), and (h) and identifying process parameters that indicate proper operation and maintenance of those control devices.
(i) Data items:
The data items for this determination include:
• Information describing the control device operation; and
• Information on the process parameter or parameters that will be used to indicate proper operation and maintenance of the control device.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1033(j), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Gather information on control device operation and process parameters;
• Document control device operation and process parameter information;
• Reassess control device operation documentation;
• Modify control device operation documentation, if necessary; and
• Maintain documentation at the unit (required under §264.1035(e)).
Waste determination
40 CFR 264.1034(d)(2) requires owner/operators to document waste determinations that are based on knowledge of the waste rather than testing.
(i) Data items:
Data items required for documenting waste determinations are not specified, but may include the following:
• Production process information documenting that no organic compounds are used;
• Waste generation information documenting that the waste is generated by a process identical to a process at the same or another unit that has previously been demonstrated by direct measurement to generate a waste stream having a total organic content less than 10 ppmw; and
• Prior specification analysis results on the same waste stream where it can be documented that no process changes have occurred since the specification analysis was conducted that could affect the waste total organic concentration.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1034(d)(2), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Gather information on production processes, waste generation, and specification analysis;
• Document information on production processes, waste generation, and specification analysis and maintain documentation at the unit.
Facility operating record
Implementation schedule
Under 40 CFR 264.1035(b)(1), owner/operators of facilities that comply with the provisions of §264.1033(a)(2) are required to record the following information in the unit operating record.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• An implementation schedule that includes dates by which the closed-vent system and control device will be installed and in operation. The schedule must also include a rationale of why the installation cannot be completed at an earlier date;
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1035(b)(1), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Prepare and reassess the implementation schedule;
• File and maintain the implementation schedule; and
• Modify the implementation schedule, if necessary.
Up-to-date documentation of compliance with the process vent standards in §264.1032
Under 40 CFR 264.1035(b)(2), owner/operators are required to record the following information in the unit operating record to document up-to-date compliance with §264.1032.
(i) Data items:
The data items for this requirement include:
Information and data identifying all affected process vents, annual throughput and operating hours of each affected unit, estimated emission rates for each affected vent and for the overall unit, and the approximate location within the unit of each affected unit; and
Information and data supporting determinations of vent emissions and emission reductions achieved by add-on control devices based on engineering calculations or source tests.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1035(b)(2), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Prepare and reassess documentation of compliance;
• File and maintain documentation of compliance; and
• Modify documentation of compliance, if necessary.
Performance test plan
Under 40 CFR 264.1035(b)(3), owners/operators that choose to use test data to determine the organic removal efficiency or total organic compound concentration achieved by the control device are required to record the following information in the unit operating record.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• A performance test plan that includes the following information:
-- A description of how it is determined that the planned test is going to be conducted when the hazardous waste management unit is operating at the highest load or capacity level reasonably expected to occur. This shall include the estimated or design flow rate and organic content of each vent stream and define the acceptable operating ranges of key process and control device parameters during the test program;
-- A detailed engineering description of the closed-vent system and control device, including:
- Manufacturer’s name and model number of control device;
- Type, capacity, and dimensions of control device;
- Dimensions of the control device and construction materials
-- A detailed description of sampling and monitoring procedures, including sampling and monitoring locations in the system, the equipment to be used, sampling and monitoring frequency, and planned analytical procedures for sample analysis.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1035(b)(3), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Prepare and reassess performance test plan;
• File and maintain performance test plan; and
• Modify performance test plan, if necessary.
Documentation of compliance with §264.1033
Under 40 CFR 264.1035(b)(4), owner/operators are required to record the following information in the unit operating record to document compliance with §264.1033.
(i) Data items:
The data items for this requirement include:
A list of all information references and sources used in preparing the documentation;
Records including the dates of each compliance test required by §264.1033(k);
If engineering calculations are used, a design analysis, specifications, drawings, schematics, and piping and instrumentation diagrams based on the appropriate sections of “APTI Course 415: Control of Gaseous Emissions” or other engineering texts acceptable to the Regional Administrator that present basic control device design information. Documentation provided by the control device manufacturer or vendor that describes the control device design in accordance with paragraphs (b)(4)(iii)(A) through (b)(4)(iii)(G) of this section may be used;
A statement signed and dated by the owner/operator certifying that the operating parameters used in the design analysis reasonably represent the conditions that exist when the hazardous waste management unit is or would be operating at the highest load or capacity level reasonably expected to occur;
A statement signed and dated by the owner/operator certifying that the control device is designed to operate at an efficiency of 95 percent or greater unless the total organic concentration limit of §264.1032(a) is achieved at an efficiency less than 95 percent or the total organic emission limits of §264.1032(a) for affected process vents at the unit can be attained by a control device involving vapor recovery at an efficiency less than 95 weight percent. A statement provided by the control device manufacturer or vendor certifying that the control equipment meets the design specifications may be used to comply with this requirement; and
If performance tests are used to demonstrate compliance, all test results.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1035(b)(4), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Prepare and reassess documentation of compliance;
• File and maintain documentation of compliance; and
• Modify documentation of compliance, if necessary.
Design, monitoring, operation, and inspection information
Under 40 CFR 264.1035(c), owner/operators are required to record the following information in the unit operating record for each closed-vent system and control device required to comply with §264.1033.
(i) Data items:
Data items for this requirement include:
Description and date of each modification that is made to the closed-vent system or control device design;
Identification of operating parameter, description of monitoring device, and diagram of monitoring sensor location or locations used to comply with §§ 264.1033(f)(1) and (f)(2);
Monitoring, operating and inspection information required by paragraphs (f) through (k) of §264.1033;
Date, time, and duration of each period that occurs while the control device is operating when any monitored parameter exceeds the value established in the control device design analysis;
Explanation for each period recorded under paragraph (4) of the cause for control device operating parameter exceeding the design value and the measures implemented to correct the control device operation;
For a carbon adsorption system operated subject to requirements specified in §§ 264.1033(g) or 264.1033(h)(2), date when existing carbon in the control device is replaced with fresh carbon;
For a carbon adsorption system operated subject to requirements specified in §264.1033(h)(1), a log recording the following information:
-- Date and time when control device is monitored for carbon breakthrough and the monitoring device reading; and
-- Date existing carbon in control device is replaced with fresh carbon;
Date of each control device startup and shutdown;
Where an owner or operator designates any components of a closed-vent system as unsafe to monitor pursuant to §264.1033(o), the owner or operator must record in a log that is kept in the facility operating record: the identification of closed-vent system components that are designated unsafe to monitor pursuant to §265.1033(o), an explanation for each closed-vent system component stating why the closed-vent system component is unsafe to monitor, and the plan for monitoring each closed-vent system component; and
When each leak is detected as specified in §264.1033(l), record the following information:
-- The instrument identification number, the closed-vent system component identification number, and the operator name, initials, or identification number;
-- The date the leak was detected and the date of first attempt to repair the leak;
-- The date of successful repair of the leak;
-- Maximum instrument reading measured by Method 21 of 40 CFR part 60, appendix A after it is successfully repaired or determined to be nonrepairable; and
-- “Repair delayed” and the reason for the delay if a leak is not repaired within 15 calendar days after discovery of the leak.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1035(c), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Prepare and reassess design, monitoring, operation, and inspection information;
• File and maintain design, monitoring, operation, and inspection information; and
• Modify design, monitoring, operation, and inspection information, if necessary.
Determination of applicability of §264.1032
Under 40 CFR 264.1035(f), owner/operators are required to record the following information in the unit operating record used to determine the applicability of §264.1032 process vent standards.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• Up-to-date information and data used to determine whether or not a process vent is subject to the requirements in §264.1032 including supporting documentation as required by §264.1034(d)(2) when application of the knowledge of the nature of the hazardous waste stream or the process by which it was produced is used.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1035(f), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Prepare and reassess determination of applicability;
• File and maintain determination of applicability;
• Modify determination of applicability, if necessary.
Semiannual report of control device monitoring events
40 CFR 264.1036 requires owner/operators with control devices that have exceeded or operated outside of the design specifications as defined in §264.1035(c)(4) for more than 24 hours or flares that have operated with visible emissions as defined in §264.1033(d) to submit a semiannual report to the Regional Administrator. The report must contain the following information:
• The EPA identification number, name, and address of the unit;
• Dates when the control device exceeded or operated outside of the design specifications as indicated by the control device monitoring required by §264.1033(f) which were not corrected within 24 hours;
• Dates when a flare operated with visible emissions as defined in §264.1033(d) and as determined by Method 22 monitoring;
• The duration and cause of each control device exceedance or visible emissions; and
• Corrective measures taken for each control device exceedance or visible emissions.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
A semiannual report.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1036, respondents must perform the following activities:
• Prepare the semiannual report and submit the semiannual report to the Regional Administrator.
EQUIPMENT LEAKS
Permitted facilities:
Regulations
Each owner/operator regulated under Part 264 is expected to read the regulations.
Notification to implement the alternate valve standard specified in §264.1061(a)
40 CFR 264.1061(b)(1) requires owners or operators that have decided to implement the alternative standard for valves specified in §264.1061(a) to notify the Regional Administrator.
(i) Data items:
No specific data items are to be included in this notification.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1061(b)(1), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Prepare notification and submit notification to the Regional Administrator.
Notification to discontinue implementing the alternative valve standard specified in §264.1061(a)
40 CFR 264.1061(d) requires owners or operators that no longer wish to implement the alternative standard for valves specified in §264.1061(a) to notify the Regional Administrator.
(i) Data items:
No specific data items are to be included in this notification.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1061(d), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Prepare notification and submit notification to the Regional Administrator.
Notification to implement the alternative valve standard specified in §§ 264.1062(b)(2), or §264.1062(b)(3)
40 CFR 264.1062(a)(2) requires owners or operators that have decided to implement the alternative standard for valves specified in §§ 264.1062(b)(2) or 264.1062(b)(3) to notify the Regional Administrator.
(i) Data items:
No specific data items are to be included in this notification.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1062(a)(2), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Prepare notification and submit notification to the Regional Administrator.
Non-hazardous waste documentation
40 CFR 264.1063(d)(3) requires owners or operators that determining that each piece of equipment does or does not contain hazardous waste with organic concentration that equals or exceeds 10 percent waste to document the determination if it was based on knowledge rather than testing.
(i) Data items:
Data items required for documenting waste determinations are not specified, but may include the following:
• Production process information documenting that no organic compounds are used;
• Waste generation information documenting that the waste is generated by a process identical to a process at the same or another unit that has previously been demonstrated by direct measurement to generate a waste stream having a total organic content less than 10 ppmw; and
• Prior specification analysis results on the same waste stream where it can be documented that no process changes have occurred since the specification analysis was conducted that could affect the waste total organic concentration.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1063(d)(3), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Gather information on production processes, waste generation, and specification analysis;
• Document information on production processes, waste generation, and specification analysis and maintain documentation at the unit.
Facility operating record
Equipment record
Under 40 CFR 264.1064(b)(1), owner/operators are required to record the following information in the unit operating record for each piece of equipment to which Subpart BB applies.
(i) Data items:
Data items for this requirement include:
Equipment identification number and hazardous waste management unit identification;
Approximate locations within the unit;
Type of equipment;
Percent-by-weight total organics in the hazardous waste stream at the equipment;
Hazardous waste state at the equipment; and
Method of compliance with the standard.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1064(b)(1), respondents must perform the following activities:
Prepare and reassess equipment record;
File and maintain equipment record; and
Modify equipment record, if necessary.
Implementation schedule
Under 40 CFR 264.1064(b)(2), owner/operators of facilities that comply with the provisions of §264.1033(a)(2) are required to record the following information in the unit operating record.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• An implementation schedule that includes dates by which the closed-vent system and control device will be installed and in operation. The schedule must also include a rationale of why the installation cannot be completed at an earlier date.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1064(b)(2), respondents must perform the following activities:
Prepare and reassess implementation schedule;
File and maintain implementation schedule; and
Modify implementation schedule, if necessary.
Performance test plan
Under 40 CFR 264.1064(b)(3), owner/operators that choose to use test data to demonstrate the organic removal efficiency or total organic compound concentration achieved by the control device are required to record the following information in the unit operating record.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• A performance test plan as specified in §264.1035(b)(3).
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1064(b)(3), respondents must perform the following activities:
Prepare and reassess performance test plan;
File and maintain performance test plan; and
Modify performance test plan, if necessary.
Documentation of compliance with §264.1060
Under 40 CFR 264.1064(b)(4), owner/operators are required to record the following information in the unit operating record.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• Documentation of compliance with §264.1060, including detailed design documentation or performance test results specified in §264.1035(b)(4).
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1064(b)(4), respondents must perform the following activities:
Prepare and reassess documentation of compliance;
File and maintain documentation of compliance; and
Modify documentation of compliance, if necessary.
Leak inspection log
Under 40 CFR 264.1064(d), owner/operators are required to record the following information in the unit operating record.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• When each leak is detected as specified in §§ 264.1052, 264.1053, 264.1057, and 264.1058, an inspection log that includes the following information:
-- Instrument and operator identification numbers and the equipment identification number;
-- The date evidence of a potential leak was found in accordance with §264.1058(a);
-- The date the leak was detected and the dates of each attempt to repair the leak;
-- Repair methods applied in each attempt to repair the leak;
-- “Above 10,000” if the maximum instrument reading measured by the methods specified in §264.1063(b) after each repair attempt is equal to or greater than 10,000 ppm;
-- “Repair delayed” and the reason for the delay if a leak is not repaired within 15 calendar days after discovery of the leak;
-- Documentation supporting the delay of repair of a valve in compliance with §264.1059(c);
-- The signature of the owner or operator (or designate) whose decision it was that repair could not be effected without a hazardous waste management unit shutdown;
-- The expected date of successful repair of the leak if a leak is not repaired within 15 calendar days; and
-- The date of successful repair of the leak.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1064(d), respondents must perform the following activities:
Prepare and reassess leak inspection log;
File and maintain leak inspection log; and
Modify leak inspection log, if necessary.
Design, monitoring, operation, and inspection information
Under 40 CFR 264.1064(e), owner/operators are required to record the following information in the unit operating record for each closed-vent system and control device required to comply with §264.1060.
(i) Data items:
Data items for this requirement include:
Description and date of each modification that is made to the closed-vent system or control device design;
Identification of operating parameter, description of monitoring device, and diagram of monitoring sensor location or locations used to comply with §§ 264.1033(f)(1) and (f)(2);
Monitoring, operating and inspection information required by paragraphs (f) through (k) of §264.1033;
Date, time, and duration of each period that occurs while the control device is operating when any monitored parameter exceeds the value established in the control device design analysis;
Explanation for each period recorded under paragraph (4) of the cause for control device operating parameter exceeding the design value and the measures implemented to correct the control device operation;
For a carbon adsorption system operated subject to requirements specified in §§ 264.1033(g) or 264.1033(h)(2), date when existing carbon in the control device is replaced with fresh carbon;
For a carbon adsorption system operated subject to requirements specified in §264.1033(h)(1), a log recording the following information:
-- Date and time when control device is monitored for carbon breakthrough and the monitoring device reading; and
-- Date when existing carbon in the control device is replaced with fresh carbon; and
Date of each control device startup and shutdown.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1064(e), respondents must perform the following activities:
Prepare and reassess design, monitoring, operation, and inspection information;
File and maintain design, monitoring, operation, and inspection information; and
Modify design, monitoring, operation, and inspection information, if necessary.
Monitoring and inspection information for other control devices
Under 40 CFR 264.1064(f), owner/operators are required to record the following information in the unit operating record for a control device other than a thermal vapor incinerator, catalytic vapor incinerator, flare, boiler, process heater, condenser, or carbon adsorption system.
(i) Data items:
Data items for this requirement include:
• Recordkeeping information specified by the Regional Administrator.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1064(f), respondents must perform the following activities:
Prepare and reassess monitoring and inspection information;
File and maintain monitoring and inspection information; and
Modify monitoring and inspection information, if necessary.
Equipment log
Under 40 CFR 264.1064(g), owner/operators are required to record the following information in the unit operating record.
(i) Data items:
Data items for this requirement include:
• A log recording the following information for all equipment subject to §§ 264.1052 through 264.1060:
-- A list of identification numbers (except welded fittings) for equipment subject to the standards of Subpart BB;
-- A list of identification numbers for equipment that the owner or operator elects to designate for no detectable emissions, as indicated by an instrument reading of less than 500 ppm above background, under §§ 264.1052(e), 264.1053(i), and 264.1057(f);
-- Signed designation of this equipment as subject to the requirements of §§ 264.1052(e), 264.1053(i), and 264.1057(f) by the owner or operator;
-- A list of equipment identification numbers for pressure relief devices required to comply with §264.1054(a);
-- The dates of each compliance test required in §§ 264.1052(e), 264.1053(i), 264.1054, and 264.1057(f);
-- The background level measured during each compliance test;
-- The maximum instrument reading measured at the equipment during each compliance test;
-- A list of identification numbers for equipment in vacuum service; and
-- Identification either by list or location (area or group) of equipment that contains or contacts hazardous waste with an organic concentration of at least 10 percent by weight for less than 300 hours per calendar year.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1064(g), respondents must perform the following activities:
Prepare and reassess equipment log;
File and maintain equipment log; and
Modify equipment log, if necessary.
Valve log for all valves subject to §264.1057(g) and (h)
Under 40 CFR 264.1064(h), owner/operators are required to record the following information in the unit operating record.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• A log for valves subject to §264.1057(g) and (h), including the following:
-- List of identification numbers for valves designated as unsafe to monitor, an explanation for each valve stating why the valve is unsafe to monitor, and the plan for monitoring each valve; and
-- List of identification numbers for valves designated as difficult to monitor, an explanation for each valve stating why the valve is difficult to monitor, and the planned schedule for monitoring each valve.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1064(h), respondents must perform the following activities:
Prepare and reassess valve log;
File and maintain valve log; and
Modify valve log, if necessary.
Valve log for all valves subject to §264.1062
Under 40 CFR 264.1064(i), owner/operators are required to record the following information in the unit operating record.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• For all valves complying with §264.1062, a log containing the following information:
-- A schedule for monitoring and the percent of valves found leaking during each monitoring period.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1064(i), respondents must perform the following activities:
Prepare and reassess valve log;
File and maintain valve log; and
Modify valve log, if necessary.
Criteria log
Under 40 CFR 264.1064(j), owner/operators are required to record the following information in the unit operating record.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• A criteria log containing the following information:
-- Criteria required in §§ 264.1052(d)(5)(ii) and 264.1053(e)(2) and an explanation of the design criteria; and
-- Any changes to these criteria and the reasons for these changes.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1064(j), respondents must perform the following activities:
Prepare and reassess criteria log;
File and maintain criteria log; and
Modify criteria log, if necessary.
Exemption log
Under 40 CFR 264.1064(k), owner/operators are required to record the following information in the unit operating record.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• An exemption log containing the following information:
-- An analysis determining design capacity of the hazardous waste management unit;
-- A statement listing hazardous waste influent to and effluent from each hazardous waste management unit subject to §§ 264.1052 through 264.1060 and an analysis determining whether these hazardous wastes are heavy liquids; and
-- An up-to-date analysis and the supporting information and data used to determine whether or not equipment is subject to the requirements in §§ 264.1052 through 264.1060. The record shall include supporting documentation as required by §264.1063(d)(3) when application of the knowledge of the nature of the hazardous waste stream or the process by which it was produced is used.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1064(k), respondents must perform the following activities:
Prepare and reassess exemption log;
File and maintain exemption log; and
Modify exemption log, if necessary.
Semiannual report of control device monitoring events
40 CFR 264.1065 requires owner/operators with control devices that have exceeded or operated outside of the design specifications as defined in §264.1035(c)(4) for more than 24 hours or flares that have operated with visible emissions as defined in §264.1033(d) to submit a semiannual report to the Regional Administrator. The report must contain the following information:
• The EPA identification number, name, and address of the unit;
• For each month during the semiannual reporting period:
-- The equipment identification number of each valve for which a leak was not repaired as required in §264.1057(d);
-- The equipment identification number of each pump for which a leak was not repaired as required in §§ 264.1052(c) and (d)(6); and
-- The equipment identification number of each compressor for which a leak was not repaired as required in §264.1053(g);
• Dates of hazardous waste management unit shutdowns that occurred within the semiannual reporting period; and
• For each month during the semiannual reporting period, dates when the control device installed as required by §§ 264.1052, 264.1053, 264.1054, or 264.1055 exceeded or operated outside the design specifications and was not corrected within 24 hours, the duration and cause of each exceedance, and any corrective measures taken.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
A semiannual report
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1065, respondents must perform the following activities:
• Prepare the semiannual report and submit the semiannual report to the Regional Administrator.
CONTAINMENT BUILDINGS
Permitted facilities:
Regulations
Each owner/operator regulated under 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart DD is expected to read the regulations.
Demonstration that unit meets the standards of Subpart DD
Under §264.1101(b)(4), for existing units other than 90-day generator units, EPA may delay the secondary containment requirement for up to two years, based on a demonstration by the owner/operator that the unit substantially meets the standards of this Subpart. In making a demonstration, the owner/operator must meet the requirements of §264.1101(b)(4)(i) and (ii).
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• A demonstration that the unit substantially meets the standards of Subpart DD, if the owner/operator wants the secondary containment requirement to be delayed. The demonstration must include:
-- Written notice of the request, describing the unit and its operating practices with specific reference to the performance of existing containment systems and specific plans for retrofitting the unit with secondary containment;
-- Response to comments from the Regional Administrator; and
-- Fulfillment of the terms of the revised plan, if such plans are approved by EPA.
(ii) Respondent activity:
To comply with §264.1101(b)(4), respondents must perform the following activity:
• Demonstrate that the unit substantially meets the standards of Subpart DD, if the owner/operator wants the secondary containment requirement to be delayed, as required by or §264.1101(b)(4).
Certification and response procedures
Pursuant to §264.1101(c)(2), owner/operators of all containment units placed into operation prior to the effective date of the rule must obtain and maintain in the operating record (on-site files for generators who are not formally required to have operating records) a certification by a qualified registered professional engineer. The certification must certify that the containment building design meets the requirements of §§264.1101(a) through (c). Throughout the active life of the containment building, if the owner/operator detects a condition that could lead to or has caused a release of hazardous waste, s/he must repair the condition promptly, in accordance with the procedures in §264.1101(c)(3). The owner/operator must also inspect and record in the unit operating record, at least once every seven days, data gathered from monitoring equipment and leak detection equipment as well as the containment building and the area immediately surrounding the containment building to detect signs of releases of hazardous waste, as required by §264.1101(c)(4).
(i) Data items:
Data items for this requirement include:
• Certification by a qualified registered professional engineer that the containment building design meets the requirements of §264.1101(a) through (c);
• Upon the owner/operator’s detecting a condition that has caused a release:
-- A record of discovery of the release into the unit operating record;
-- A schedule for accomplishing cleanup and repairs;
-- Notification to the Regional Administrator of the condition within 7 days after the discovery of the condition;
-- A written notice with a description of the steps taken to repair the containment building, and a schedule for accomplishing the work; and
-- Notification to the Regional Administrator in writing and a verification signed by a qualified, registered professional engineer that the repairs and cleanup have been completed according to the written plan submitted in accordance with paragraph (c)(3)(i)(D) of this section; and
• Data from monitoring and leak detection equipment, the containment building, and the area immediately surrounding the containment building.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with §264.1101(c), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Obtain a certification by a qualified registered professional engineer and place this certification in the unit’s operating record, as required by §264.1101(c)(2);
• Upon detecting a condition that has caused a release, the owner/operator must perform the following activities, as required by §264.1101(c)(3)(i):
-- Enter a record of discovery of the release into the unit’s operating record, as required by §264.1101(c)(3)(i)(A);
-- Establish a schedule for accomplishing cleanup and repairs, as required by §264.1101(c)(3)(i)(C);
-- Notify the Regional Administrator of the condition within 7 days after the discovery of the condition, as required by §264.1101(c)(3)(i)(D);
-- Provide to EPA within 14 days a written notice with a description of the steps taken to repair the containment building, and a schedule for accomplishing the work, as required by §264.1101(c)(3)(i)(D); and
-- Upon completing all repairs and cleanup, notify the Regional Administrator in writing and provide a verification signed by a qualified, registered professional engineer that the repairs and cleanup have been completed according to the written plan submitted in accordance with paragraph (c)(3)(i)(D) of this section, as required by §264.1101(c)(3)(i)(D)(iii); and
• Inspect and record in the unit’s operating record, at least once every seven days, data from monitoring and leak detection equipment, the containment building, and the area immediately surrounding the containment building, as required by §264.1101(c)(4).
Operating procedures for areas without secondary containment
Under 40 CFR 264.1101(d)(3), owners/operators of containment buildings that contain areas with and without secondary containment must maintain in the unit’s operating log a written description of the operating procedures used to maintain the integrity of areas without secondary containment.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• A written description of the operating procedures used to maintain the integrity of areas without secondary containment.
(ii) Respondent activity:
To comply with §264.1101(d)(3), respondents must perform the following activities:
• Maintain in the unit’s operating log a written description of the operating procedures used to maintain the integrity of areas without secondary containment, as required by §264.1101(d)(3).
Demonstration for exemption from secondary containment requirements
Under 40 CFR 264.1101(e), the owner/operator of a permitted containment building may obtain a waiver from secondary containment from EPA. In order to obtain this waiver, the owner/operator has to demonstrate that the only free liquids in the unit are limited amounts of dust suppression liquids required to meet occupational health and safety requirements, or that containment of managed wastes and liquids can be assured without a secondary containment system.
(i) Data item:
The data item for this requirement includes:
• A demonstration that the only free liquids in the unit are limited amounts of dust suppression liquids required to meet occupational health and safety requirements and that containment of managed wastes and liquids can be assured without a secondary containment system, if applicable.
(ii) Respondent activity:
To comply with §264.1101(e), respondents must perform the following activity:
• Demonstrate that only free liquids in the unit are limited amounts of dust suppression liquids and that containment of managed wastes and liquids can be assured without a containment system, if the owner/operator wants EPA to waive secondary containment requirements for a permitted containment building, as provided by §264.1101(e).
SPECIFIC HAZARDOUS WASTE RECOVERY/RECYCLING FACILITIES
Regulations
Each owner/operator regulated under 40 CFR Part 266 is expected to read the regulations.
Recyclable materials utilized for precious metal recovery
40 CFR 266.70(c) requires those who store recycled materials regulated under 40 CFR Part 266, Subpart F to keep records showing that they are not accumulating the materials speculatively (as defined in 261.1(c)).
(i) Data items:
The data items for this recordkeeping requirement are:
• Information showing the volume of recycled materials regulated under 40 CFR Part 266, Subpart F that are stored at the beginning of the calendar year;
• The amount of materials regulated under 40 CFR Part 266, Subpart F that are generated or received during the calendar year; and
• The amount of materials regulated under 40 CFR Part 266, Subpart F that are remaining at the end of the calendar year.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities to comply with this requirement:
• Record the information specified in 40 CFR 266.70(c) and file and maintain the information.
5. THE INFORMATION COLLECTED -- AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
The following subsections discuss how EPA (and authorized States in lieu of EPA) will collect information, what activities EPA (and authorized States in lieu of EPA) will perform once the information has been received, and how EPA will manage the information it collects. The subsections also include a discussion of how information collection requirements affect small entities.
“Agency” in this section means EPA and the authorized States in lieu of EPA. The agency activities associated with respondent reporting are discussed below. This analysis assumes that there are no agency activities associated with recordkeeping activities (i.e., filing and maintaining documentation at the respondent’s unit) because documentation is not formally submitted to the agency. Although EPA will examine unit records during periodic inspections as activities that are a part of EPA’s overall compliance and enforcement program, the cost associated with their activities is not attributed to the Subparts covered in this ICR. In addition, review of items submitted with Part B permit applications are covered in the “Part B Permit Application, Permit Modification, and Special Permits ICR” (OMB Control No. 2050-0009).
TANK SYSTEMS
Permitted facilities:
Agency activities associated with requirements for owners and operators of permitted tank systems include the following:
• Reviewing information submitted for exemption from 24-hour waste removal requirement;
• Reviewing release notifications and reports;
• Reviewing major repair certifications; and
• Reviewing decontamination demonstrations.
SURFACE IMPOUNDMENTS
Permitted facilities:
Agency activities associated with requirements for owners and operators of permitted surface impoundments include the following:
• Reviewing written action leakage rate exceedance notifications;
• Reviewing leakage reports;
• Entering RAP data into a data base;
• Reviewing notifications of surface impoundment removal from service;
• Reviewing contingent corrective measures plans;
• Reviewing hazardous waste removal plans;
• Reviewing extension requests; and
• Reviewing corrective action reports.
WASTE PILES
Permitted facilities:
Agency activities associated with requirements for owners and operators of permitted waste piles include the following:
• Reviewing written action leakage rate exceedance notifications;
• Reviewing leakage reports; and
• Entering RAP data into a data base.
LAND TREATMENT
Permitted facilities:
Agency activities associated with the requirements for permitted land treatment facilities include the following:
• Reviewing notifications of significant increases of hazardous constituents below the treatment zone;
• Reviewing notifications of intent to demonstrate that regulated unit is not the source of increase in hazardous constituents below the treatment zone;
• Reviewing demonstrations that regulated unit is not the source of increase in hazardous constituents below the treatment zone;
• Reviewing §264.280(d) demonstrations; and
• Reviewing closure certifications.
LANDFILLS
Permitted facilities:
Agency activities associated with the requirements for permitted land treatment facilities include the following:
• Reviewing written action leakage rate exceedance notifications;
• Reviewing leakage reports;
• Entering RAP data into a data base; and
• Reviewing demonstrations for placing non-hazardous liquid waste in landfills (§264.314(e)).
INCINERATORS
Permitted facilities:
Agency activities associated with the requirements for permitted incinerators consist of reviewing notifications of intent to burn hazardous wastes F020, F021, F022, F023, F026 and F027, and reviewing demonstrations for exemption from emergency waste feed cutoff system testing requirements.
DRIP PADS
Permitted facilities:
Agency activities associated with 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart W include:
• Reviewing plans for updating, repairing, and modifying the drip pad; and
• Reviewing release notifications and reports.
PROCESS VENTS
Permitted facilities:
Agency activities associated with the requirements for permitted facilities with process vents include reviewing semiannual reports.
EQUIPMENT LEAKS
Permitted facilities:
Agency activities associated with the requirements for permitted facilities with equipment subject to Subpart BB include:
• Reviewing notifications to implement the alternate valve standard specified in §264.1061(a));
• Reviewing notifications to discontinue implementing the alternate valve specified in §264.1061(a));
• Reviewing notifications to implement the alternate valve standard specified in §§ 264.1062(b)(2) or (b)(3)); and
• Reviewing semiannual reports.
CONTAINMENT BUILDINGS
Permitted facilities:
Agency activities associated with the requirements for permitted facilities with containment buildings subject to Subpart DD include:
• Collecting written notices of requests for delay of secondary containment;
• Reviewing and commenting on plans to retrofit a unit;
• Reviewing responses to comments and approving/disapproving a delay;
• Receiving notifications of release;
• Reviewing written notices, descriptions, or remedial steps, and schedules for cleanup;
• Reviewing information and determining if a unit must be removed from service;
• Notifying owner/operator in writing of determination;
• Reviewing verification of cleanup; and
• Reviewing no-free-liquid demonstrations.
5(b) COLLECTION METHODOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
Respondents are required to submit certain documentation to the agency as discussed in Section 4. The submitted documents are maintained by the receiving agency. The agency enters select data about the respondents’ facilities and the submitted documents into RCRAInfo; RCRAInfo is EPA’s comprehensive information system which provides access to data supporting the implementation and management of the RCRA hazardous waste program.
EPA does not anticipate that many small businesses will be engaging in the types of activities covered in this ICR. However, to the extent that there are small entities with, for example, a regulated hazardous waste tank system, they are subject to the same standards as larger entities. EPA has been directed by Congress to promulgate standards to protect public health and the environment. In cases where small businesses engage in activities that endanger the environment, EPA believes it is alleviating its responsibility to respond to its Congressional mandate by exempting them from regulation.
TANK SYSTEMS
Permitted facilities:
As described in §264.196(d), releases to the environment must be reported to the Regional Administrator within 24 hours. Furthermore, within 30 days of detection of a release to the environment, a facility must submit a report to the Regional Administrator. In addition, the certification of major repairs (required under §264.196(f)) must be submitted within 7 days of returning the repaired tank system to use.
SURFACE IMPOUNDMENTS
Permitted facilities:
Notification of removal of a surface impoundment from service must be submitted to the Regional Administrator within 7 days after detection of a release. Notification of an exceedance of the action leakage rate must be submitted to EPA within seven days, and a preliminary written assessment identifying the amount of liquids, likely sources, etc., must be submitted within 14 days of the determination of exceedance. Within 30 days after the notification of ALR exceedance, the analysis results must be submitted, along with the results of any actions taken, and actions planned.
WASTE PILES
Permitted facilities:
Notification of an exceedance of the action leakage rate must be submitted to EPA within seven days, and a preliminary written assessment identifying the amount of liquids, likely sources, etc., must be submitted within 14 days of the determination of exceedance. Within 30 days after the notification of ALR exceedance, the analysis results must be submitted, along with the results of any actions taken, and actions planned.
LAND TREATMENT
Permitted facilities:
Notification of statistically significant contaminant increases must be submitted to the Regional Administrator within 7 days of determination. Notification of intent to make a demonstration under §264.278(h) must be submitted to the Regional Administrator within 7 days of the above determination, and the demonstration must be submitted within 90 days. Certification of closure must be submitted within 60 days of closure in accordance with §265.115. Demonstrations for exemption from §264.280(a)(8) and (c) may be submitted at any time during the closure or post-closure period, depending on the desire of the owner or operator to submit such a demonstration.
LANDFILLS
Permitted facilities:
Notification of an exceedance of the action leakage rate must be submitted to EPA within seven days, and a preliminary written assessment identifying the amount of liquids, likely sources, etc., must be submitted within 14 days of the determination of exceedance. Within 30 days after the notification of ALR exceedance, the analysis results must be submitted, along with the results of any actions taken, and actions planned.
DRIP PADS
Permitted facilities:
Notification of a condition detected that may have caused or has caused a release of hazardous waste must be submitted to the EPA within 10 working days of the discovery.
PROCESS VENTS
Permitted facilities:
Owner/operators submit semiannual reports to EPA on dates specified by the Regional Administrator.
EQUIPMENT LEAKS
Permitted facilities:
Owner/operators submit semiannual reports to EPA on dates specified by the Regional Administrator.
CONTAINMENT BUILDINGS
Permitted facilities:
Owner/operators must submit notification of any condition that has caused a release within 7 days after the discovery of the condition. A description of the steps taken to repair the containment building, and a schedule for accomplishing the work must be submitted to EPA within 14 days after discovery of the condition.
6. ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF THE COLLECTION
EPA estimates respondent burden for both private respondents (private sector businesses and industries) and non-federal governments respondents (includes State, County, Municipal, District, and Tribal governments). Table 1 presents the estimated number of RCRA facilities with each specific type of existing permitted units that are expected to comply annually with the information collection requirements covered in this ICR.
EPA derived these data for this ICR from RCRAInfo. RCRAInfo is EPA's comprehensive information system which provides access to data supporting the implementation and management of the RCRA Subtitle C hazardous waste program. The data is entered into the system by States and EPA. RCRAInfo allows the Permitting Program to track facilities through the permitting process and communicate their performance and progress.
6(a) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT BURDEN
EPA estimates respondent burden for units associated with all requirements covered in this ICR in Exhibit 1 for private respondents and Exhibit 2 for non-federal governments respondents. The exhibits address the following specific unit requirements:
6(b) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT COSTS
Labor Rates
The labor wage rates used to estimate costs to respondents were calculated as shown in the following table. The 2022 average wage rates from are the average wage rates are reported in the Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2020 National Occupational Employment and Wage Estimate, released May 2020, and updated to 2022 levels.
Labor Category |
Non-loaded 2022 hourly rate |
Fringe benefits loading multiplier |
Overhead loading multiplier |
Loaded Hourly rate |
1. Legal |
$71.59 |
1.43 |
1.336 |
$136.77 |
2. Managerial |
$60.45 |
1.43 |
1.336 |
$115.49 |
3. Technical |
$46.58 |
1.43 |
1.336 |
$88.99 |
4. Clerical |
$18.16 |
1.43 |
1.336 |
$34.69 |
For the State respondent labor rates, EPA estimates an average hourly State labor cost (including fringe and overhead) of $67.67 for legal staff, $63.52 for managerial staff, $38.00 for technical staff, and $24.24 for clerical staff. These State labor costs were obtained from a previously approved ICR and updated to 2022 levels using Employment Cost Indexes developed by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Capital Costs
EPA assumes that all facilities with permitted units already possess file storage systems, either for electronic or paper filing. Therefore, no capital costs will be incurred during the three year period of this ICR.
Operation and Maintenance Costs
EPA also estimates that facilities will incur operation and maintenance (O&M) costs. O&M costs include postage for submittals of information or notices. EPA estimates that facilities will incur $5.75 in postage costs for every submittal to EPA, based on the mailing cost of $7.50 for a two-pound package. O&M costs also include purchased material costs and/or lump-sum purchased service costs (e.g., waste analyses, inspection/certification by an independent registered professional engineer). From O&M costs in Exhibits 1 and 2 (see Subsection 6(e)), EPA estimates that the total annual O&M cost for conducting respondent activities covered in the ICR is $1,733,951.
6(c) ESTIMATING AGENCY BURDEN AND COST
EPA estimates an average hourly labor cost (labor plus overhead) of $86.54 for legal staff, $62.27 for managerial staff, $43.68 for technical staff, and $26.56 for clerical staff. To derive these estimates, EPA used the General Schedule (GS) Salary Table 2022. For purposes of this ICR, EPA assigned staff the following government service levels:
Legal Staff GS‑15, Step 1
Managerial Staff GS‑13, Step 1
Technical Staff GS‑11, Step 1
Clerical Staff GS‑6, Step 1
To derive hourly estimates, EPA divided annual compensation estimates by 2,080, which is the number of hours in the Federal work‑year. EPA then multiplied hourly rates by the standard government overhead factor of 1.6.
6(d) ESTIMATING THE RESPONDENT UNIVERSE AND TOTAL BURDEN AND COST
Respondent Universe
EPA estimates respondent burden for both private respondents (private sector businesses and industries) and non-federal governments respondents (includes State, County, Municipal, District, and Tribal governments).
Table 1 presents the estimated number of RCRA facilities with permitted units for each specific unit type that are expected to comply annually with the information collection requirements covered in this ICR. For example, if a facility has one container, three tank units and two incinerators, it counts as one for each specific unit type – one for tanks, one for containers, and one for incinerators. This facility would have units subject to three different specific unit type regulations (Subparts I, J, and O).
As shown in the Table 1, EPA estimates that annually a total of 919 facilities with specific unit types will be subject to the information collection requirements covered in this ICR. In addition, there are 1,172 Process Vents and Equipment Leaks.
Table 1
-
Specific Unit Type
Number of Facilities
with Permitted Units
Private
State/Local
Total
Subpart I - Containers
427
21
448
Subpart J – Tank Systems
331
4
335
Subpart K - Surface Impoundments
25
0
25
Subpart L - Waste Piles
5
0
5
Subpart M - Land Treatment
4
0
4
Subpart N - Landfills
39
1
40
Subpart O - Incinerators
42
0
42
Subpart W - Drip Pads
0
0
0
Subpart DD - Containment Buildings
20
0
20
TOTAL
893
26
919
(below are number of units, not facilities)
Number of Permitted Units
Private
State/Local
Total
Subpart AA - Process Vents
397
0
397
Subpart BB - Equipment Leaks
773
2
775
TOTAL
1,170
2
1,172
6(e) BOTTOM LINE BURDEN HOURS AND COSTS
Based on the universe data presented in Table 1, EPA estimates private respondent and non-federal governments respondent burden and costs associated with all the requirements covered in this ICR in Exhibits 1 and 2, respectively. A discussion of the private and non-federal governments burden estimates presented in these exhibits follows; the data in the discussion is the sum of the respective private respondent and non-federal governments respondent burdens.
Respondent and Agency bottom line burden hours and costs are summarized in this subsection. The bottom line burden hours and cost to respondents and agencies are based on a three-year time-span over which the ICR is effective.
Respondent Tally
Exhibits 1 and 2 below summarize, respectively, the total annual private and non-federal governments respondent burdens and costs associated with all the requirements covered in this ICR. Exhibit 4 summarizes the total annual state agency burdens and costs. For the sum of the three exhibits, EPA estimates the total annual respondent burden to be 377,427 hours at a total annual cost of $23,872,056, of which $1,733,951 is O&M costs.
Agency Tally
Exhibit 3 below summarizes the total annual EPA burden and cost associated with all the requirements covered in this ICR. EPA estimates the total annual agency burden to be 689 hours at a total annual cost of $30,104.
6(f) REASONS FOR CHANGE IN BURDEN
There is an increase in burden of 21,122 hours over the previous ICR. This increase is due to an increase in the number of Subpart AA and BB units.
6(g) BURDEN STATEMENT
Burden means the total time, effort, or financial resources expended by persons to generate, maintain, retain, or disclose or provide information to or for a Federal agency. This includes the time needed to review instructions; develop, acquire, install, and utilize technology and systems for the purposes of collecting, validating, and verifying information, processing and maintaining information, and disclosing and providing information; adjust the existing ways to comply with any previously applicable instructions and requirements; train personnel to be able to respond to a collection of information; search data sources; complete and review the collection of information; and transmit or otherwise disclose the information. An agency may not conduct or sponsor, and a person is not required to respond to, a collection of information unless it displays a currently valid OMB control number. The OMB control numbers for EPA’s regulations are listed in 40 CFR Part 9 and 48 CFR Chapter 15.
To comment on the Agency’s need for this information, the accuracy of the provided burden estimates, and any suggested methods for minimizing respondent burden, including the use of automated collection techniques, EPA has established a public docket for this ICR under Docket ID No. EPA-HQ-OLEM-2018-0757, which is available for public viewing at the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) Docket in the EPA Docket Center (EPA/DC), EPA West, Room 3334, 1301 Constitution Ave., NW, Washington, DC. The EPA/DC Public Reading Room is open from 8:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m., Monday through Friday, excluding legal holidays. The telephone number for the Reading Room is (202) 566-1744, and the telephone number for the RCRA Docket is (202) 566-0270. An electronic version of the public docket is available through http://www.regulations.gov by entering the Docket ID above in the search form. Use http://www.regulations.gov to submit or view public comments, access the index listing of the contents of the public docket, and to access those documents in the public docket that are available electronically. Once in the system, select “search,” then key in the docket ID number identified above.
Also, you can send comments to the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs, Office of Management and Budget, 725 17th Street, NW, Washington DC 20503, Attention: Desk Officer for EPA. Please include the EPA Docket ID No. EPA-HQ-OLEM-2018-0757 and OMB Control No. 2050-0050 in any correspondence.
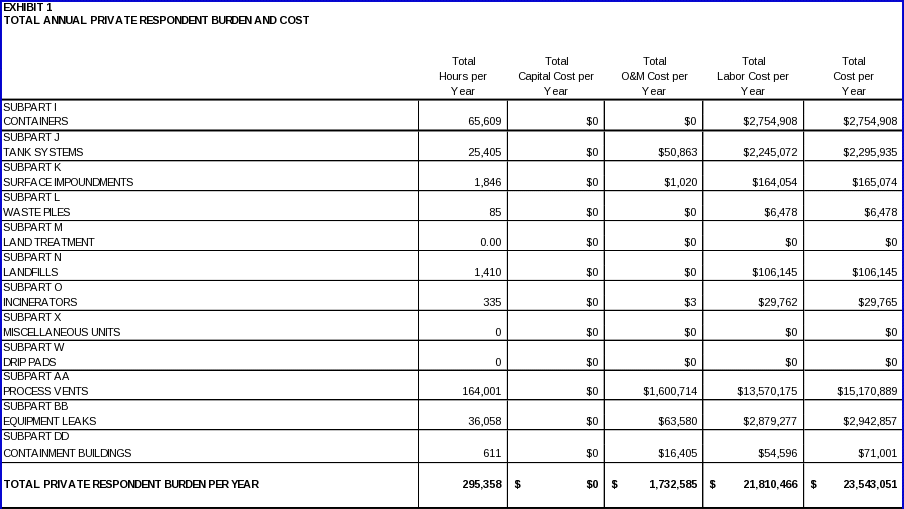
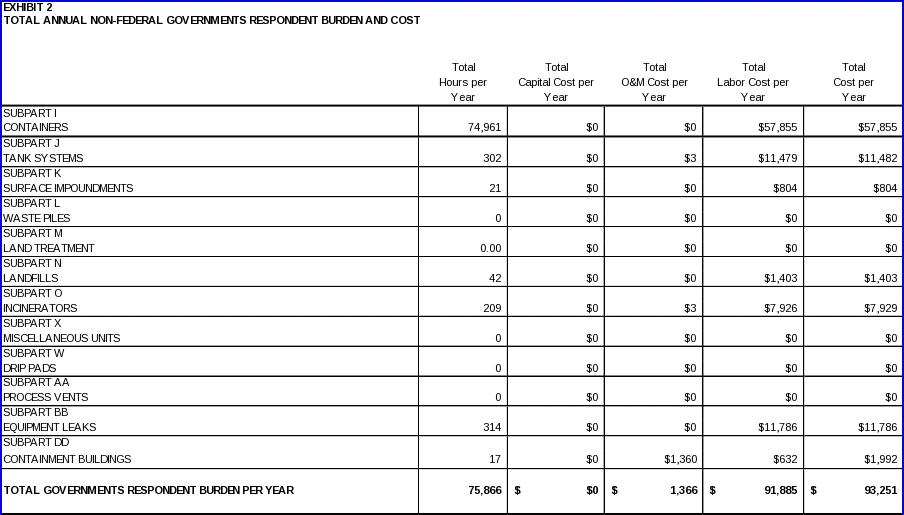
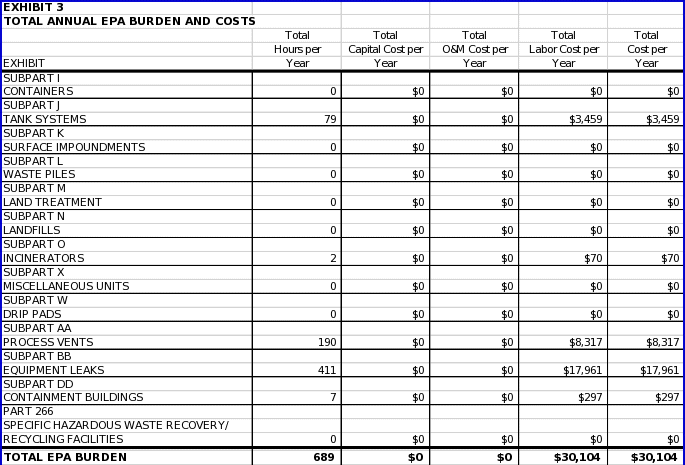
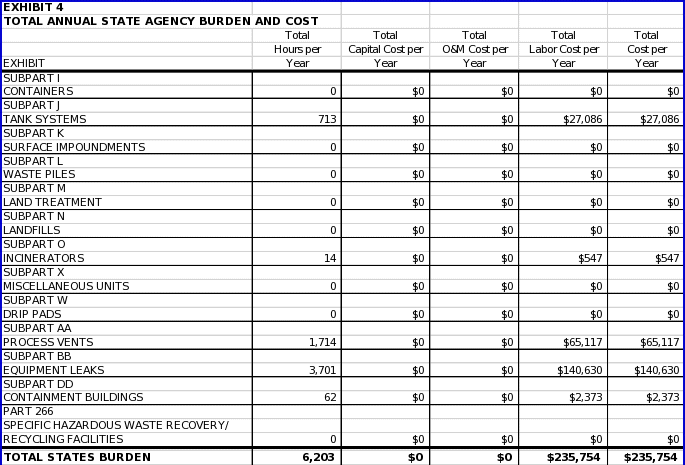
APPENDIX
EXHIBITS 5 – 25
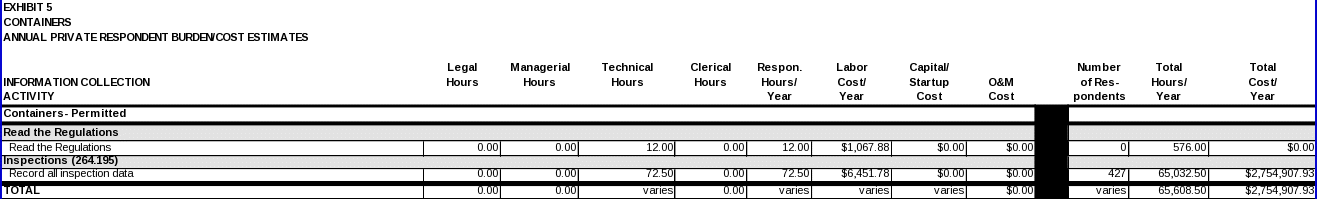
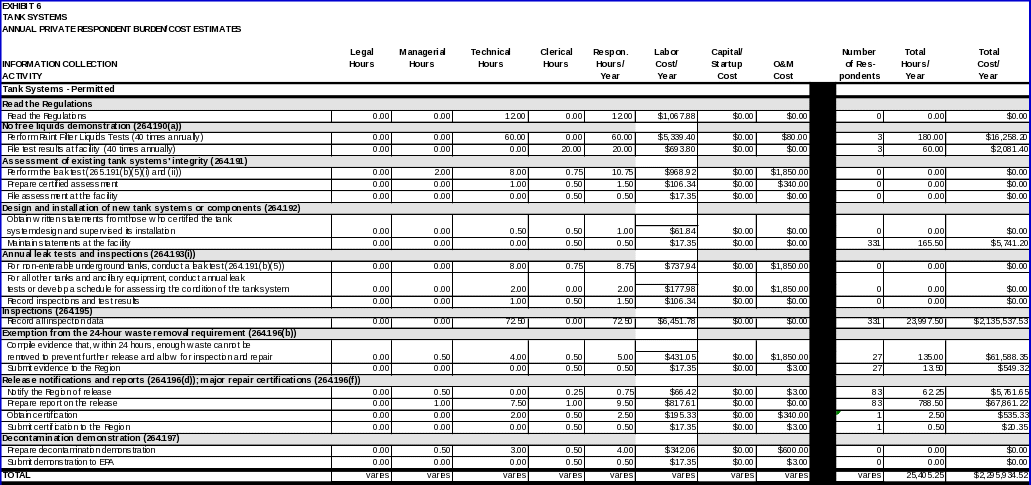
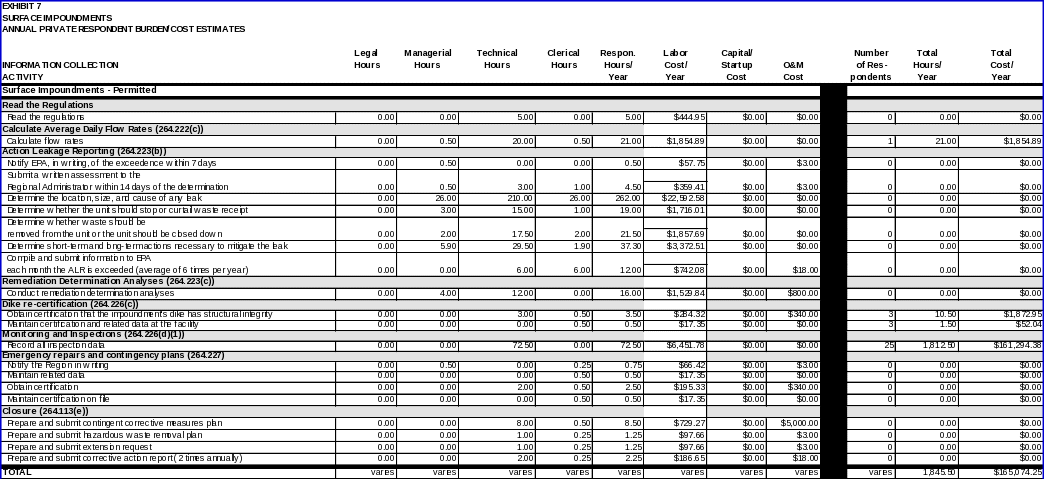
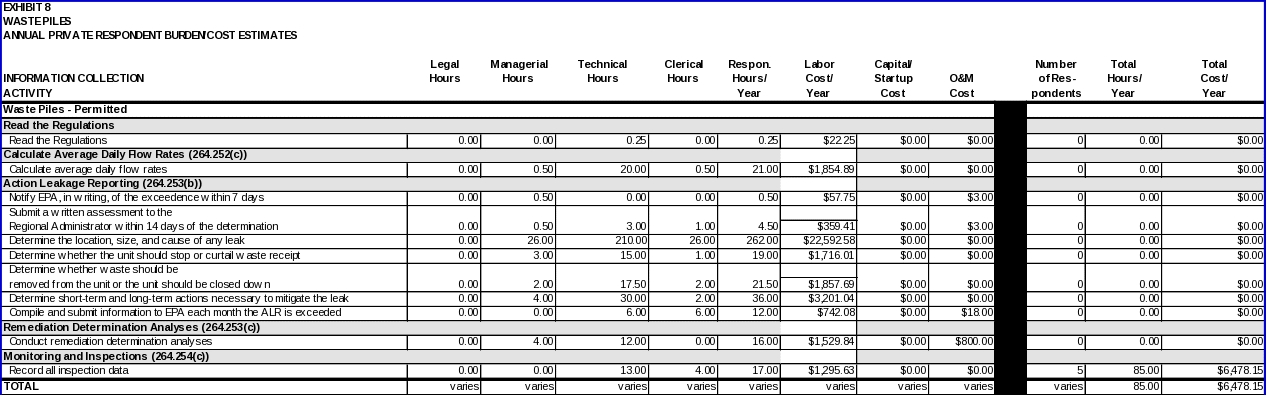
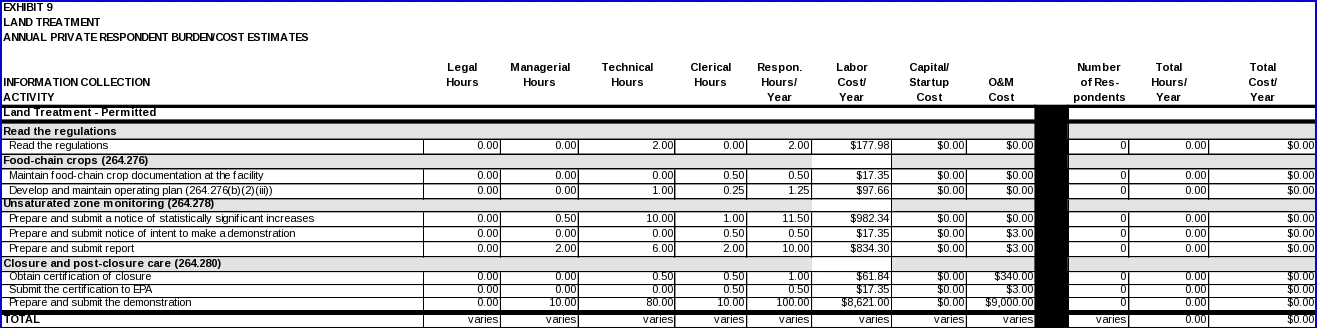

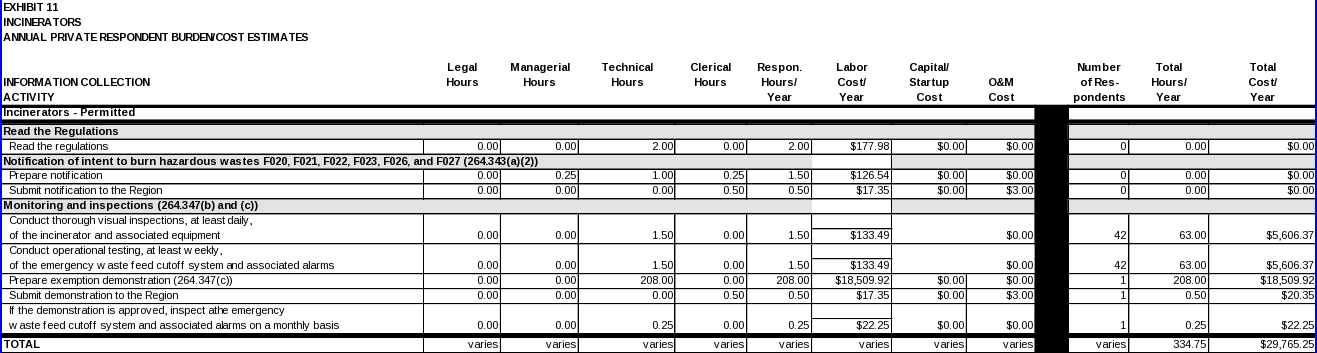
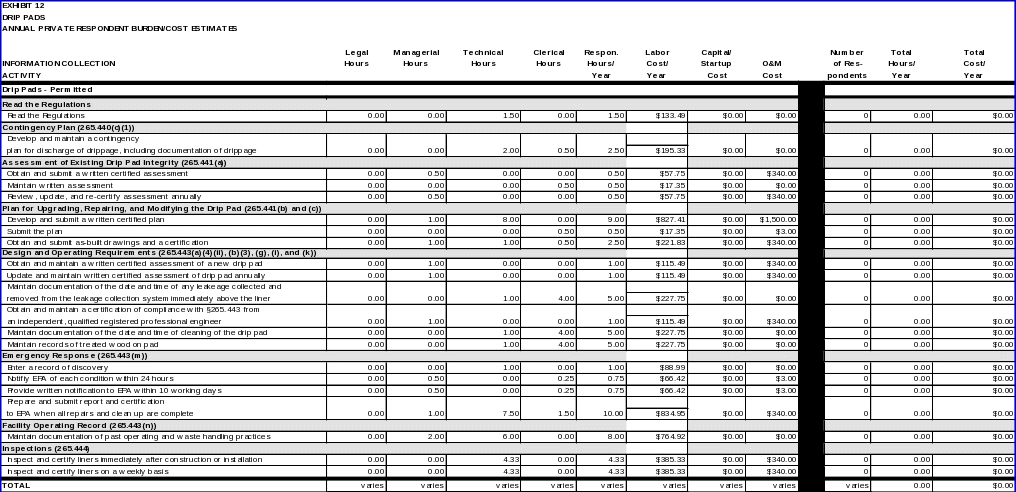
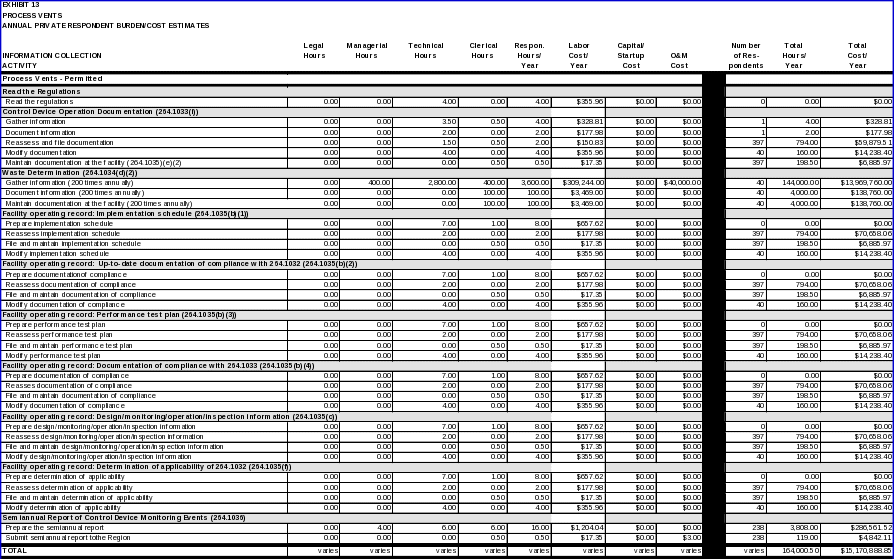

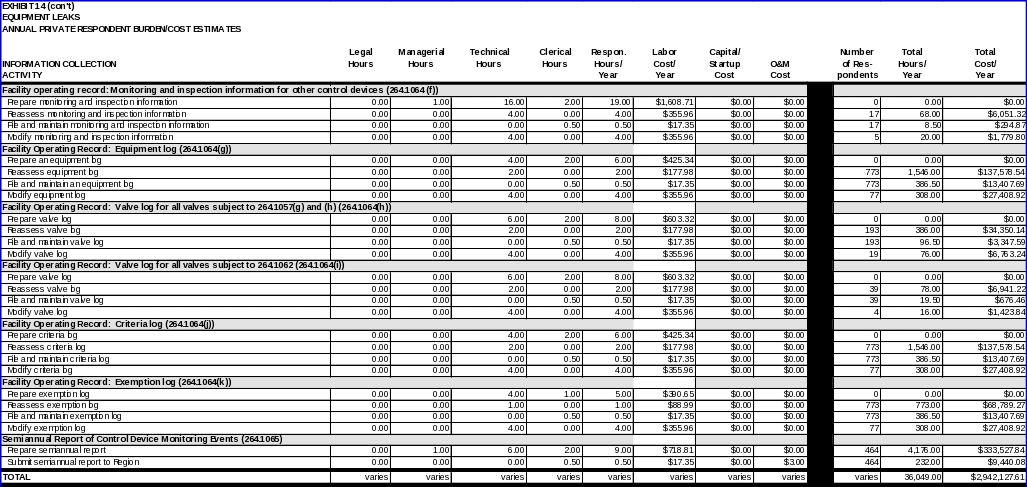
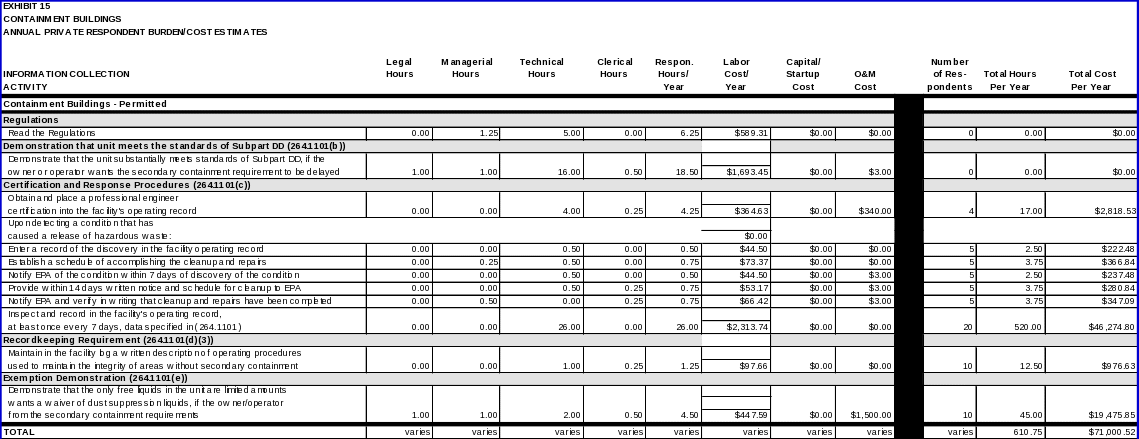
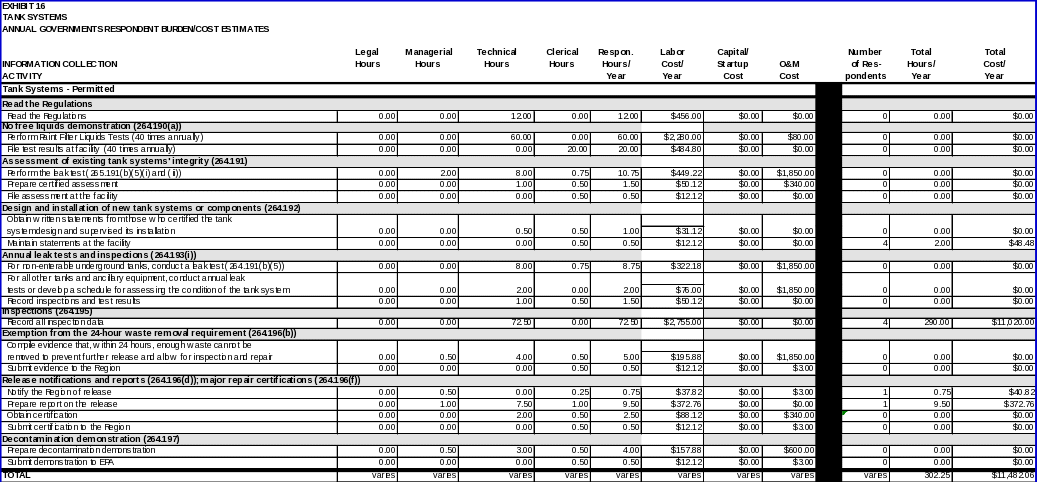
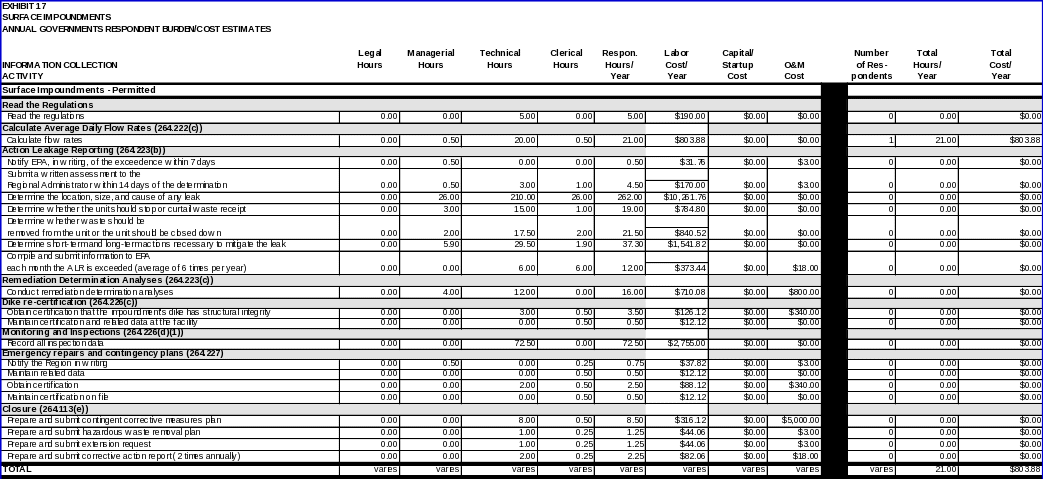
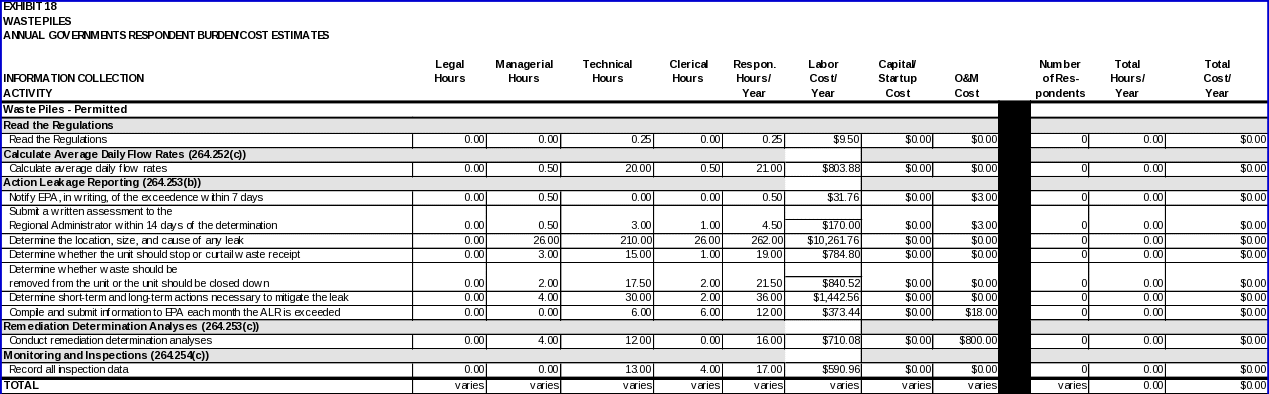
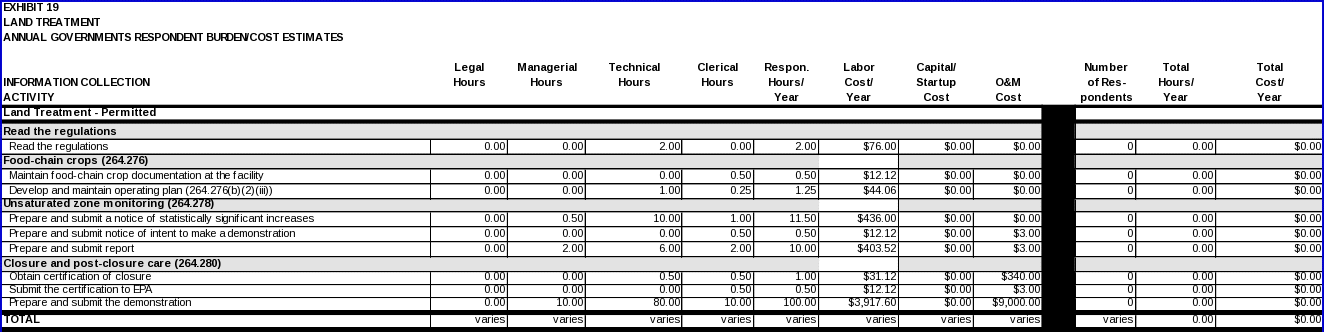
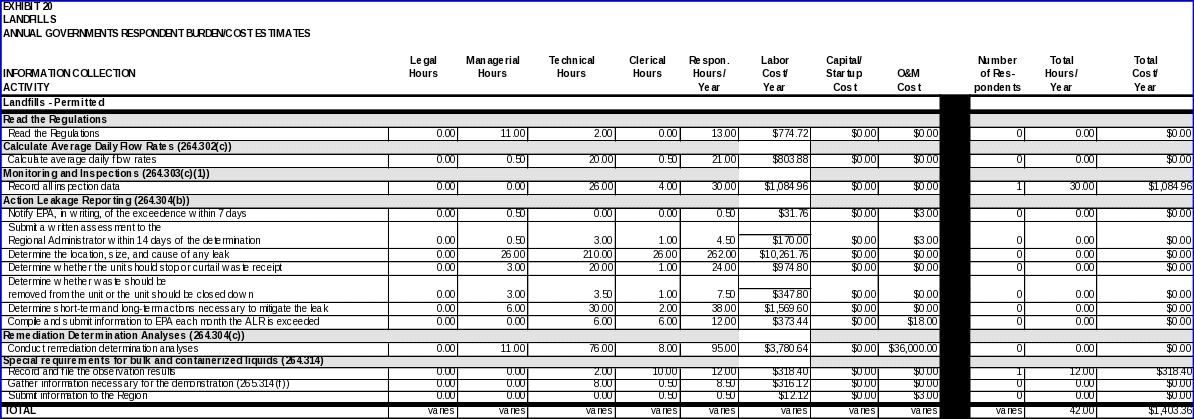
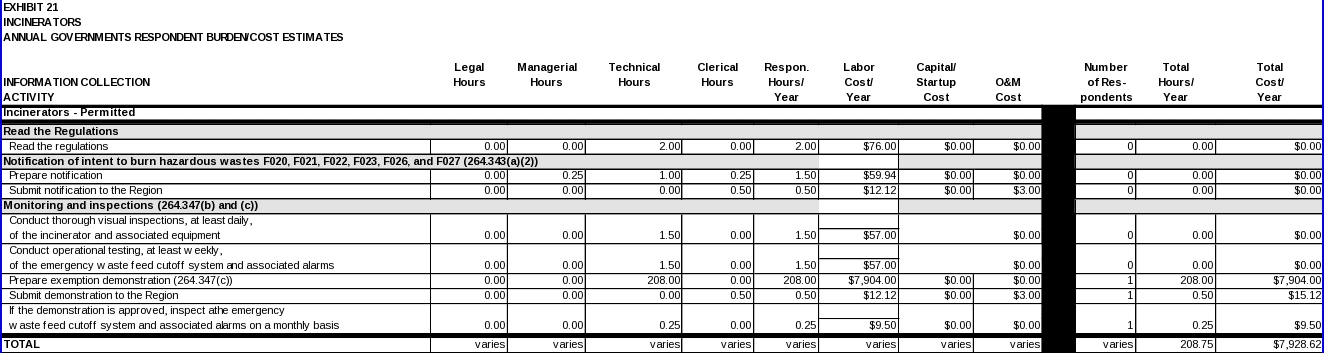
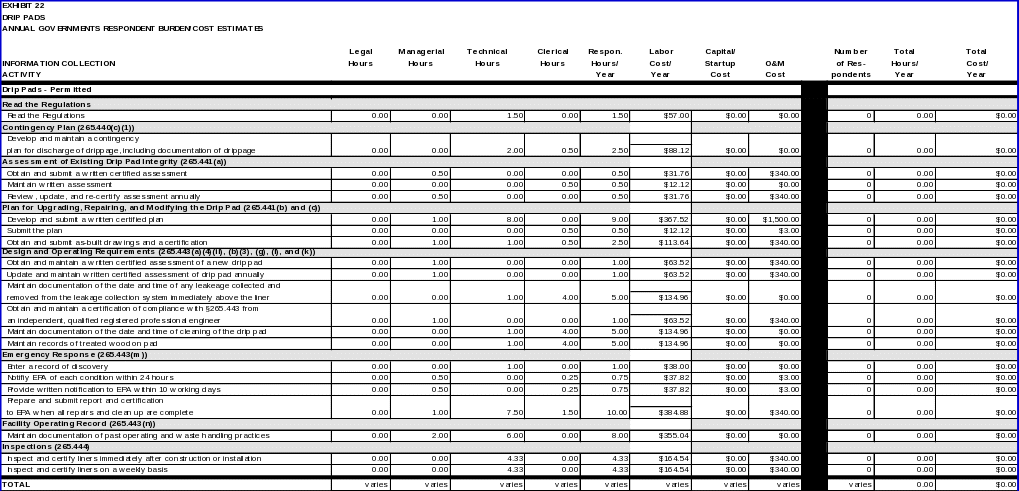
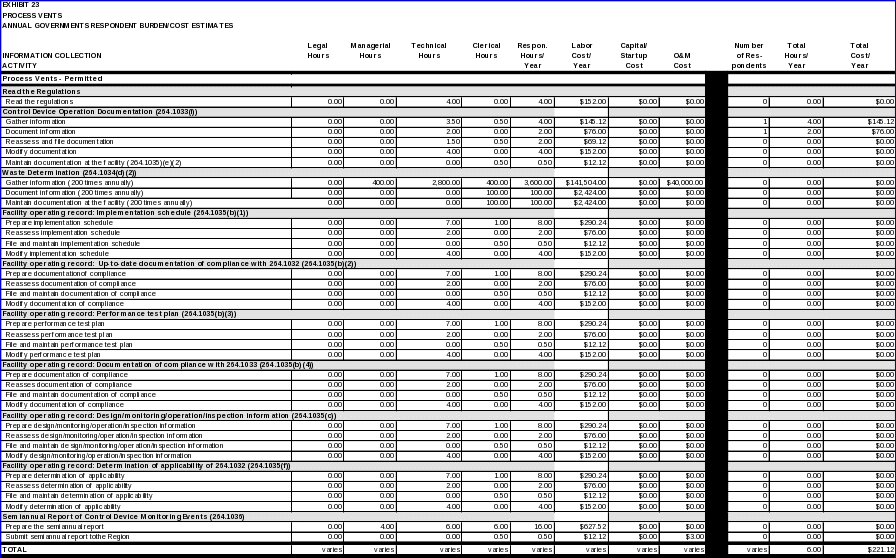

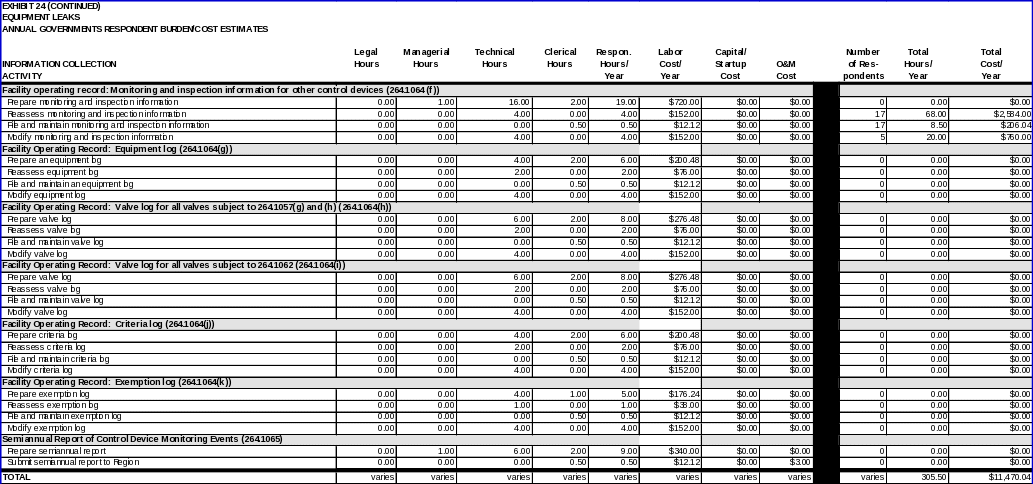
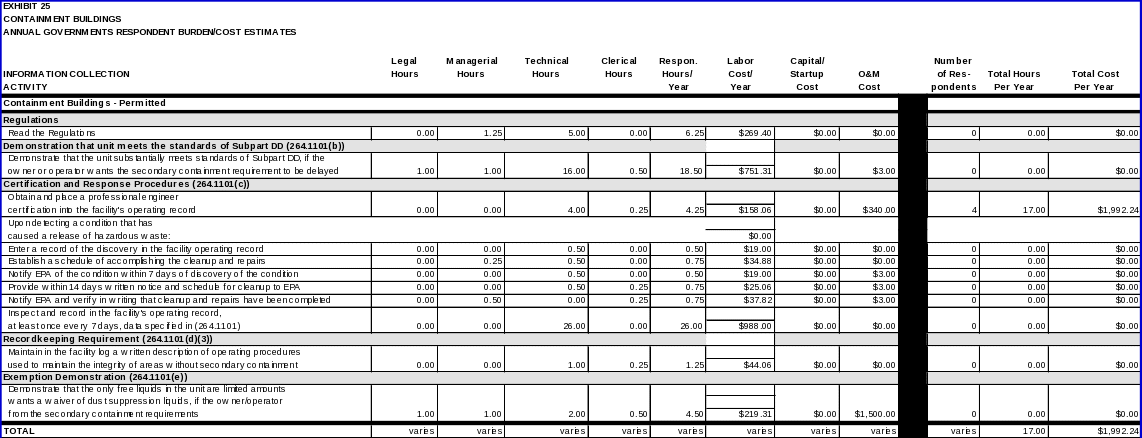
1 If the release has been reported pursuant to 40 CFR Part 302 (CERCLA §103), that report will satisfy this requirement.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2023-08-29 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy