1573ss16
1573ss16.docx
Part B Permit Application, Permit Modifications, and Special Permits (Renewal)
OMB: 2050-0009
SUPPORTING STATEMENT FOR
INFORMATION COLLECTION REQUEST OMB CONTROL NO. 2050-0009
"PART B PERMIT APPLICATION, PERMIT MODIFICATIONS,
AND SPECIAL PERMITS"
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
1(a) Title of the Information Collection 1
1(b) Short Characterization/Abstract 1
2. NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION
2(a) Need/Authority for the Collection 3
2(b) Practical Utility/Users of the Data 9
3. NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA
3(a) Nonduplication 11
3(b) Public Notice Required Prior to ICR Submission to OMB 11
3(c) Consultations 11
3(d) Effects of Less Frequent Collection 12
3(e) General Guidelines 12
3(f) Confidentiality 12
3(g) Sensitive Questions 12
4. THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED
4(a) Respondents/SIC Codes 12
4(b) Information Requested 14
THE INFORMATION COLLECTED ‑‑ AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION
METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
5(a) Agency Activities 84
5(b) Collection Methodology and Management 93
5(c) Small Entity Flexibility 93
5(d) Collection Schedule 93
6. ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF THE COLLECTION
6(a) Estimating Respondent Burden 97
6(b) Estimating Respondent Costs 97
6(c) Estimating State Agency Burden and Cost 98
6(d) Estimating the Respondent Universe and Total Burden and Costs 99
6(e) Bottom Line Burden Hours and Cost Tables 111
6(f) Reasons for Change in Burden 130
6(g) Burden Statement 130
1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
1(a) Title and Number of the Information Collection
This ICR is titled "Part B Permit Application, Permit Modifications, and Special Permits," ICR number 1573.16, OMB Control Number 2050-0009.
1(b) Short Characterization
The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) of 1976, as amended by the Hazardous and Solid Waste Amendments (HSWA) of 1984, requires EPA to establish a national regulatory program to insure that hazardous wastes are managed in a manner protective of human health and the environment. Specifically, the statute requires EPA to promulgate regulations that establish performance standards and permitting requirements applicable to hazardous waste treatment, storage, and disposal facilities (TSDFs). Section 3004 of Subtitle C establishes performance standards applicable to these facilities. Section 3005 requires EPA to promulgate regulations requiring these facilities to obtain a permit. In the event permit modifications are proposed by an applicant or EPA, modifications must conform to the requirements under Sections 3004 and 3005. The regulations implementing these requirements are codified at 40 CFR Parts 264 and 270.
This ICR provides a comprehensive discussion of the requirements for owner/operators of TSDFs submitting applications for a Part B permit or permit modification. The information collections contained in this ICR are divided into three sections: demonstrations and exemptions from requirements (40 CFR Part 264), contents of the Part B application (40 CFR Part 270), and permit modifications and special permits (40 CFR Part 270).
2. NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION
2(a) Need and Authority for the Collection
This section describes the need and authority for each type of information collection analyzed in this ICR.
Demonstrations and Exemptions from Requirements
Releases from Regulated Units and Specific Unit Requirements
EPA promulgated a number of regulations in 40 CFR Part 264 providing owner/operators the opportunity to submit demonstrations to exempt their facilities from certain requirements. In Part 264.90, EPA promulgated regulations allowing owner/operators to obtain an exemption from the Subpart F requirements regarding releases into the uppermost aquifer. In Parts 264.193, 264.221, 264.251, 264.272, 264.301, and 264.344, EPA promulgated regulations outlining the requirements for owner/operators petitioning to exempt units (tank systems, surface impoundments, waste piles, land treatment, landfills, and incinerators) at their facilities from specific requirements. EPA needs this information to evaluate the accuracy and completeness of petitions for exemptions submitted by owner/operators. These requirements insure that only facilities fully protective of human health and the environment are granted exemptions and contribute to EPA’s goal of preventing contamination of the environment from hazardous waste treatment, storage, and disposal practices.
Contents of the Part B Application
General Information
EPA promulgated regulations in §270.1(c)(5) allowing owner/operators of surface impoundments, land treatment units, and waste piles closing by removal or decontamination under Part 265 standards to petition the Regional Administrator for a determination that a post‑closure permit is not required. The owner/operator will need to demonstrate that the particular unit does not require a post‑closure permit because its closure met the applicable Part 264 closure standards. Similar to the exemption provisions in 40 CFR Part 264 (discussed in previous section), EPA needs this information to evaluate the accuracy and completeness of the claims made in the petitions for exemptions submitted by owner/operators. These requirements contribute to EPA’s goal of ensuring that hazardous waste management facilities are closed in a manner fully protective of human health and the environment.
Permit Application
Section 3019 of RCRA requires EPA to promulgate regulations requiring owner/operators of facilities that store, treat, or dispose of hazardous waste in a surface impoundment or landfill to submit information on the potential for the public to be exposed to hazardous wastes or hazardous constituents through releases related to the unit (40 CFR §270.10(j)). EPA needs this information to comprehensively evaluate the potential risk posed by facilities seeking permits. This information aids EPA’s in meeting its goal of ascertaining and minimizing risks to human health and the environment from hazardous waste management facilities.
General Requirements, General Facility Standards, Financial Assurance, Ground‑Water Protection, Regulated Units, and Other Requirements
RCRA Section 3005 requires EPA to promulgate regulations detailing informational requirements for owner/operators submitting Part B permit applications. EPA promulgated these requirements in 40 CFR Parts 264 and 270:
Section 270.14(a) allows owner/operators to petition EPA for relief from submission of information prescribed in Part B on a case‑by‑case basis by demonstrating that such information cannot be provided to the extent required.
Section 270.14(b)(1)‑(14) requires owner/operators of hazardous waste management facilities to submit information on compliance with general facility standards in their Part B permit applications.
Sections 270.14 ‑ .16 require owner/operators of new facilities to submit detailed written estimates of the cost of facility closure and post‑closure care in accordance with the requirements of §§264.142(a) and 264.144(a), respectively.
Sections 270.14 ‑ .16 also require owner/operators to establish and provide evidence of financial assurance for facility closure (§264.143) and post‑closure (§264.145). Owner/operators can establish financial assurance with a number of financial instruments.
Section 264.14(b)(17) requires owner/operators to document the amount of insurance meeting specifications detailed in §264.147(a) and, if applicable, §264.147(b), that are in effect before initial receipt of hazardous waste for treatment, storage, or disposal.
Section 270.14(b)(18) requires owner/operators to provide proof of coverage by a State financial mechanism in compliance with §§264.149 or 264.150, where appropriate. Section 264.149 allows owner/operators to use State‑required financial assurance mechanisms to meet §§264.143, 264.145, or 264.147 requirements. Section 264.150 requires owner/operators to notify EPA when a State assumes legal responsibility or assures availability of funds for an owner/operator’s compliance with the closure, post‑closure care, or liability requirements of this part.
Section 270.14(b)(19) requires owner/operators to provide a topographic map showing a distance of 1000 feet around the facility. EPA also promulgated regulations in §270.14(b)(21) requiring owner/operators of land disposal facilities that have received approval for a case‑by‑case extension under §268.5 or a petition under §268.6 to submit a copy of the notice of approval for the extension or petition with their Part B permit application.
Section 270.14(c)(1) ‑ (5) requires owner/operators to submit additional information to EPA regarding protection of ground water when applying for a Part B permit. The information required includes information on site‑specific characteristics, and a ground‑water monitoring program as required under §264.97. The monitoring program must include sampling and analysis procedures, sampling intervals, and statistical methods to be used in evaluating ground‑water monitoring data.
Section 270.14(c)(6) requires that if the presence of hazardous constituents has not been detected in the ground water at the time of permit application, the owner/operator must submit to EPA sufficient information, supporting data, and analyses to establish a detection monitoring program meeting the requirements of §264.98. This information includes information required by EPA to determine the parameters or constituents to be monitored under the detection monitoring program, as well as information for determining appropriate time periods for identifying contamination.
Section 270.14(c)(7) requires that if the presence of hazardous constituents has been detected in the ground water at the point of compliance at the time of the permit application, the owner/operator must submit to EPA sufficient information, supporting data, and analyses to establish a compliance monitoring program meeting the requirements of §264.99. Section 264.99 requires owner/operators to submit to EPA all information necessary to determine a reasonable time period for identifying significant evidence of increased contamination during compliance monitoring.
Section 270.14(c)(8) requires that if hazardous constituents have been measured in the ground water which exceed the concentration limits established under §264.94 Table 1, or if ground‑water monitoring conducted at the time of permit application under §§265.90 through 265.94 at the waste boundary indicates the presence of hazardous constituents from the facility in ground water over background concentrations, the owner/operator must submit to EPA sufficient information, supporting data, and analyses to establish a corrective action program which meets the requirements of §264.100.
Section 270.14(d) establishes Part B information requirements for solid waste management units.
EPA needs the various Part B permit information to evaluate the compliance of facilities with the permitting standards. These requirements contribute to EPA’s goal of insuring that hazardous waste management facilities are operated in a manner fully protective of human health and the environment.
Specific Part B Information Requirements
EPA promulgated regulations in 40 CFR Part 270 requiring owner/operators to submit specific additional information for various units at their facilities. These requirements are specified for owner/operators of facilities that perform the following activities:
Store containers of hazardous waste (§270.15);
Use tanks to store or treat hazardous waste (§270.16);
Store, treat, or dispose of hazardous waste in surface impoundments (§270.17);
Store or treat hazardous waste in waste piles (§270.18);
Incinerate hazardous waste (§270.19);
Use land treatment to dispose of hazardous waste (§270.20);
Dispose of hazardous waste in landfills (§270.21);
Treat, store, or dispose of hazardous waste in miscellaneous units (§270.23);
Release organic emissions from process vents and leaks from equipment (§§270.24 and 270.25); and
Collect, treat, or store hazardous waste on drip pads (§270.26).
EPA needs this information to evaluate each of the facility units included in permit applications. This information contributes to EPA’s goal of safe management of hazardous waste.
Schedules of Compliance
EPA promulgated regulations in §270.33 detailing informational requirements for owner/operators developing schedules of compliance leading to compliance with the Act and regulations. EPA needs this information to determine whether schedules of compliance are reasonable.
Permit Modifications and Special Permits
Permit Modifications
EPA promulgated regulations in 40 CFR Part 270 outlining procedures for modification and transfer of permits:
Compliance with Class 1 modification requirements and submittal of specific financial and contractual information before transferring ownership or operational control of a facility (§270.40(b));
Specified procedures for owner/operators submitting permit modifications at the request of the Agency (§270.41);
Specified procedures for owner/operators applying for Class 1 permit modifications (§270.42(a)), and owner/operators applying for Class 2 or 3 permit modifications (§270.42(b) ‑ (c));
Specified procedures for owner/operators requesting a classification of a permit modification (§270.42(d)); and
Specified procedures for owner/operators applying for temporary authorization (§270.42(e)), and for owner/operators handling newly regulated wastes hazardous or managing waste in newly regulated units (§270.42(g)).
EPA needs this information to comprehensively evaluate whether requests for modifications or transfer of ownership should be granted. The permit modification procedures contribute to EPA’s goal of providing a role for the public in the permitting process. In general, these informational requirements aid in meeting EPA’s goal of ascertaining and minimizing risks to human health and the environment from hazardous waste management facilities.
In 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart S, EPA promulgated regulations for corrective action management units (CAMUs). EPA needs to collect information from facilities that are engaged in, or will be initiating, corrective action to effectively designate CAMUs.
Expiration and Continuation of Permits
EPA promulgated regulations in §§270.50 and 270.51 requiring owner/operators to renew their Part B permit. In order to renew an expiring permit, owner/operators must submit an application containing the information required under §270.14 and the applicable sections of §§270.15 through 270.29. The permit renewal process provides EPA with an opportunity to complete an extensive review of the facility permit to determine whether the terms of the permit continue to provide the most appropriate mechanism for protecting human health and the environment.
Special Forms of Permits
EPA promulgated regulations in §270.60 and §§270.62 through 270.65 creating additional forms of permits. Informational requirements are specified for these permits in the following sections:
Permits by rule (§270.60);
Hazardous waste incinerator permits (§270.62);
Permits for land treatment demonstrations using filed test or laboratory analyses (§270.63);
Interim permits for UIC wells (§270.64); and
Research, development, and demonstration permits (§270.65).
EPA needs this information to comprehensively evaluate permit applications. These informational requirements contribute EPA’s goal of ascertaining and minimizing risks to human health and the environment from hazardous waste management facilities.
Interim Status
Termination of Interim Status
EPA promulgated regulations at 40 CFR Part 270, Subpart G covering interim status facilities. Section 270.73 requires land disposal facilities that become subject to permit requirements as a result of statutory or regulatory amendments to submit within 12 months a Part B permit application and a certification that the facility is in compliance with all applicable ground‑water monitoring and financial responsibility requirements. EPA needs this information to ensure that such facilities come under permit conditions and are operated in a manner protective of human health and the environment.
2(b) Practical Utility and Use and Users of Data
This section describes the users of the collected data and how the information will be used.
Demonstrations and Exemptions from Requirements
Releases from Regulated Units and Specific Unit Requirements
EPA uses the information submitted by owner/operators in their exemption petitions to evaluate these demonstrations fully. Owner/operators of facilities must establish that they do not need to comply with the applicable requirements to be protective of human health and the environment.
Contents of the Part B Application
General Information
EPA uses the required information to fully evaluate petitions submitted by owner/operators for their exemptions from post‑closure permit requirements. Owner/operators of facilities must establish that the facility was closed in a manner protective of human health and the environment.
Permit Application
EPA uses information on exposure potential to minimize any risks to human health from hazardous waste management facilities. If EPA determines that a facility poses a substantial risk to human health, EPA may request that the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry conduct a health assessment.
General Requirements, General Facility Standards, Financial Assurance, Ground‑Water Protection, Regulated Units, and Other Requirements
EPA uses the information requirements in 40 CFR Parts 264 and 270 for owner/operators submitting Part B applications to evaluate compliance with various elements of the regulations. For example, the general facility standards informational requirements provide EPA with information demonstrating compliance with standards regarding the facility’s contingency plan, the inspection schedule, and security procedures. EPA uses the financial assurance information requirements to evaluate the facility owner’s financial ability to close the facility, to maintain the facility after closure, and to respond to any contingencies. Both EPA and the owner/operators use the ground‑water protection information to evaluate the state of the underlying ground water, the adequacy of the monitoring program, and whether hazardous constituents are present in the ground water.
Specific Part B Information Requirements
EPA uses information regarding specific units at facilities to evaluate the adequacy of each unit to manage hazardous wastes. Additional information is required because each of the different types of hazardous waste management units presents different risks to the environment and consequently requires different standards. EPA reviews the submittals of each type of hazardous waste management unit to evaluate whether it is designed, built, and operated in a manner protective of human health and the environment. EPA uses the information required for process vents and equipment leaks to ensure compliance with air emissions standards.
Schedules of Compliance
Owner/operators use schedules of compliance to develop a list of activities needed to come into compliance with the applicable regulations. EPA uses performance test plans and documentation of compliance to ensure that design and operating procedures are in accordance with air emissions standards.
Permit Modifications and Special Permits
Permit Modifications
EPA uses permit information to evaluate the initial permit applications and any subsequent requests for modifications. The public may also use draft EPA permit and permit modification determinations which incorporate data submitted by facilities to assess hazardous waste management facilities being developed in their communities.
EPA reviews data collected from facilities undergoing or scheduled to undergo corrective action to designate CAMUs at the facility.
Expiration and Continuation of Permits
EPA uses permit renewal applications to ensure that the terms of the facility permit remain protective of human health and the environment.
Special Forms of Permits
EPA uses the information requirements for these permits to determine compliance with the regulations. EPA needs this information to comprehensively evaluate whether applicant facilities are protective of human health and the environment.
Interim Status
Termination of Interim Status
EPA uses certifications collected from land disposal facilities to ensure that the facility can satisfy ground‑water monitoring and financial responsibility requirements and be operated in a manner protective of human health and the environment.
3. NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA
3(a) Nonduplication
There are no other Federal agencies with a permit program for hazardous waste facilities. Authorized States must modify their programs only after EPA promulgates Federal standards that are more stringent than the existing Federal standards. Section 3009 of RCRA allows States to impose standards more stringent than or in addition to those in the Federal program. In order to obtain authorization, a State must agree to have reporting requirements that are equivalent to EPA’s requirements. Facilities in authorized States will need to maintain records and submit reports to comply only with the States’ requirements; there is no parallel information submitted to EPA.
3(b) Public Notice Required Prior to ICR Submission to OMB
In compliance with the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995, EPA issued a public notice in the Federal Register on June 13, 2022 (87 FR 35764) and provided a 60 day comment period for this ICR. No comments were received.
3(c) Consultations
The following were contacted for consultation of burden estimates:
Safety Clean |
Kelly Dale Taylor |
US Ecology |
Noel Bailey |
Envirite |
Colletta Campbell |
All those contacted said burden estimates were accurate. No change to the burden estimates resulted from these consultations.
3(d) Effects of Less Frequent Collection
EPA has sought to reduce the reporting frequency to the minimum that is necessary to ensure compliance with the rules. It would not be possible to collect this information less frequently and still assure that the requirements of permit regulations are met by owner/operators. The reporting frequency is essential to assure that the effect of any changes in the permit contents are made known to EPA.
3(e) General Guidelines
The information collection does not include any information collection activities that exceed the Paperwork Reduction Act, OMB’s General Guidelines and regulations under 5 CFR 1320.5(d)(2).
Information is not collected more often than quarterly.
Responses are not required in less than 30 days.
Respondents are not required to submit more than one original and two copies of any document.
The collection does not provide for remuneration of respondents.
The collection does not require records to be kept for more than three years.
The collection is not in conjunction with a statistical survey.
Provisions for small businesses and other small entities are appropriate.
Confidentiality is protected.
3(f) Confidentiality
Section 3007(b) of RCRA and 40 CFR Part 2, Subpart B, which define EPA’s general policy on public disclosure of information, contain provisions for confidentiality. EPA does not anticipate requesting any confidential information.
3(g) Sensitive Questions
No questions of a sensitive nature are included in any of the information collection requirements.
4. THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED
4(a) Respondents and NAICS Codes
The following is a list of NAICS codes associated with the facilities most likely to be affected by the Part B permit application and permit modifications under this ICR:
22132 Sewage Treatment Facilities
32411 Petroleum Refineries
32511 Petrochemical Manufacturing
32512 Industrial Gas Manufacturing
32551 Paint and Coating Manufacturing
32551 Paint and Coating Manufacturing
33271 Machine Shops
33422 Radio and Television Broadcasting and Wireless Communications Equipment Manufacturing
33633 Motor Vehicle Steering and Suspension Components (except Spring) Manufacturing
33634 Motor Vehicle Brake System Manufacturing
33635 Motor Vehicle Transmission and Power Train Parts Manufacturing
42271 Petroleum Bulk Stations and Terminals
44111 New Car Dealers
44112 Used Car Dealers
44711 Gasoline Stations with Convenience Store
44719 Other Gasoline Stations
48411 General Freight Trucking, Local
48421 Used Household and Office Goods Moving
48422 Specialized Freight (except Used Goods) Trucking, Local
56292 Materials Recovery Facilities
221111 Hydroelectric Power Generation
221112 Fossil Fuel Electric Power Generation
221113 Nuclear Electric Power Generation
221119 Other Electric Power Generation
221121 Electric Bulk Power Transmission and Control
221122 Electric Power Distribution
311942 Spice and Extract Manufacturing
323110 Commercial Lithographic Printing
323114 Quick Printing
325131 Inorganic Dye and Pigment Manufacturing
325188 All Other Basic Inorganic Chemical Manufacturing
325188 All Other Inorganic Chemical Manufacturing
325193 Ethyl Alcohol Manufacturing
325199 All Other Basic Organic Chemical Manufacturing
325211 Plastics Material and Resin Manufacturing
325998 All Other Miscellaneous Chemical Product Manufacturing
331311 Alumina Refining
332813 Electroplating, Plating, Polishing, Anodizing, and Coloring
332999 All Other Miscellaneous Fabricated Metal Product Manufacturing
333319 Other Commercial and Service Industry Machinery Manufacturing
333999 All Other General Purpose Machinery Manufacturing
334418 Printed Circuit/Electronics Assembly Manufacturing
334419 Other Electronic Component Manufacturing
336211 Motor Vehicle Body Manufacturing
336312 Gasoline Engine and Engine Parts Manufacturing
336322 Other Motor Vehicle Electrical and Electronic Equipment Manufacturing
336399 All Other Motor Vehicle Part Manufacturing
454311 Heating Oil Dealers
454312 Liquefied Petroleum Gas (Bottled Gas) Dealers
562111 Solid Waste Collection
562112 Hazardous Waste Collection
562119 Other Waste Collection
562211 Hazardous Waste Treatment and Disposal
562212 Solid Waste Landfills
562213 Solid Waste Combustors and Incinerators
562219 Other Nonhazardous Waste Treatment and Disposal
811111 General Automotive Repair
4(b) Information Requested
Demonstrations and Exemptions from Requirements
Releases from Regulated Units
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 264.90 allows owner/operators of facilities that treat, store, or dispose of hazardous waste to obtain an exemption from the Subpart F requirements regarding releases into the uppermost aquifer. Owner/operators must submit one of the following demonstrations to EPA in order to obtain an exemption:
A demonstration that the unit meets the conditions of §§264.90(b)(2) (i) ‑ (vii); or
A demonstration, pursuant to §264.280(d), that the treatment zone of a land treatment unit that qualifies as a regulated unit does not contain levels of hazardous constituents that are above background levels of those constituents by an amount that is statistically significant, and that an unsaturated zone monitoring program meeting the requirements of §264.278 has not shown a statistically significant increase in hazardous constituents below the treatment zone during the operating life of the unit (§264.90(b)(3)) ; or
A demonstration that there is no potential for migration of liquid from a regulated unit to the uppermost aquifer during the active life of the regulated unit (including the closure period) and the post‑closure care period specified under §264.117 (§264.90(b)(4)). This demonstration must be certified by a qualified geologist or geotechnical engineer.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to provide these demonstrations, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare and submit the appropriate demonstration;
If submitting a no‑migration demonstration under §264.90(b)(4), obtain certification from a qualified geologist or geotechnical engineer; and
File a copy of the demonstration at the facility.
Specific Unit Requirements
(1) Tank Systems
(i) Data Items:
Section 264.193 requires that certain tank systems, including all new tank systems, be equipped with a secondary containment system in order to prevent the release of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents to the environment. Owner/operators may obtain a variance from the secondary containment requirements of this section by submitting a notification and demonstration in accordance with §§264.193(h)(1) and 264.193(g), respectively. Owner/operators may also submit demonstrations for a variance from the 24‑hour leak detection requirements (§§264.193(c)(3) and 264.193(e)(3)(iii)) and the 24‑hour waste removal requirement (§264.193(c)(4)). In addition, owner/operators must submit information for an equivalent secondary containment device, where appropriate. Data items associated with these requirements include the following:
A notification of intent to conduct and submit a demonstration for a variance from the secondary containment requirements (§264.193(h)(1)). The notification must include a description of the steps necessary to conduct the demonstration and a timetable for completing each of the steps;
A demonstration that alternate design and operating practices, together with location characteristics, will prevent the migration of any hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituent into the ground water or surface water at least as effectively as secondary containment during the active life of the tank system. This demonstration must include the information required under §264.193(g)(1)(i)‑(iv); or
A demonstration that in the event of a release that does migrate to ground water or surface water, no substantial present or potential hazard will be posed to human health or the environment. Because new tank systems cannot obtain exemption from the secondary containment requirements by submitting this demonstration, this ICR assumes that no respondents will submit this demonstration (§264.193(g)(2));
For secondary containment systems (§264.193(c)(3)) and double‑walled tanks (§264.193(e)(3)(iii)), a demonstration that existing detection technologies or site conditions will not allow detection of a release within 24 hours;
A demonstration that removal of the released waste or accumulated precipitation cannot be accomplished within 24 hours (§264.193(c)(4));
A written description of an equivalent secondary containment device if such a device is to be used in lieu of those listed under §264.193(d)(1) through (3); and
Records of the assessments conducted in accordance with §§264.193(i) (1)‑(3) (§264.193(i)(4)). This recordkeeping requirement is included in the General Facility Standards ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0120).
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of this section, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare and submit the notification of intent to make a demonstration;
Prepare and submit the demonstration under §264.193(g)(1);
Prepare and submit the demonstration for exemption from the 24‑hour leak detection requirement;
Prepare and submit the demonstration for exemption from the 24‑hour waste removal requirement;
Prepare and submit a written description of the equivalent secondary containment device; and
File copies of the demonstrations at the facility.
(2) Surface Impoundments
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 264.221 provides owner/operators of surface impoundments with the opportunity to obtain an exemption from the liner and double liner requirements of §§264.221(a) and (c), respectively. An owner or operator of a leak detection system that is not located completely above the seasonal high table must submit a demonstration under §264.221(c)(4). Owner/operators may also obtain a waiver of the double liner requirements for any monofill under §264.221(e). In addition, owner/operators of any replacement surface impoundment unit may submit information under §264.221(f) in support of an exemption from §264.221(c). Data items associated with the requirements of this section include the following:
To obtain an exemption from the liner requirements of §264.221(a), a demonstration that alternative design and operating practices, together with location characteristics, will prevent the migration of any hazardous constituents into the ground water or surface water at any future time. This demonstration must contain the information required under §264.221(b)(1)‑(4). Because all surface impoundments are now required to have double liners, this ICR assumes that no respondents will submit this demonstration;
For a leak detection system that is not located completely above the seasonal high water table, a demonstration that the operation of the leak detection system will not be adversely affected by the presence of ground water, as required under §264.221(c)(4);
To obtain an exemption from the double liner and leachate collection and removal system requirements of §264.221(c), a demonstration that alternative design and operating practices, together with location characteristics, will prevent the migration of any hazardous constituent into the ground water or surface water at least as effectively as the double liner collection system (§264.221(d));
To obtain a waiver of the double liner requirement for monofills (§264.221(e)), the owner/operator must demonstrate to the EPA that:
‑‑ The monofill contains only hazardous wastes from foundry furnace emission controls or metal casting molding sand, and such wastes do not contain constituents which would render the wastes hazardous for reasons other than the toxicity characteristic; and
‑‑ The monofill possesses the following qualities:
At least one liner for which there is no evidence that such liner is leaking;
Located more than one quarter mile from an underground source of drinking water as defined in ‘144.3; and
Complies with generally applicable ground‑water monitoring requirements for facilities with permits under RCRA section 3005(c); or
‑‑ The monofill is located, designed and operated so as to assure that there will be no migration of any hazardous constituent into ground water or surface water at any future time; and
For a replacement surface impoundment unit for which an exemption from §264.221(c) is sought, information demonstrating that the unit was constructed in compliance with the design standards of RCRA sections 3004(o)(1)(A)(i) and (o)(5), and information supporting the claim that the liner is functioning as designed (§264.221(f)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of this section, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare and submit the demonstration supporting an exemption from the liner requirement of §264.221(a);
Prepare and submit the demonstration for the leak detection system (§264.221(c)(4);
Prepare the demonstration for exemption from the §264.221(c) double liner and leachate collection and removal system requirements (§264.221(d);
Prepare and submit the demonstration for a waiver of the double liner requirements for monofills;
Prepare and submit the information supporting an exemption for a replacement unit; and
File a copy of the demonstrations at the facility.
(3) Waste Piles
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 264.251(b) allows owner/operators of existing waste piles to obtain an exemption from the liner and leachate collection system requirements of §264.251(a). 40 CFR 264.251(c)(5) requires owner/operators of a leak detection system that is not located completely above the seasonal high water table to demonstrate that the operation of the leak detection system will not be adversely affected by the presence of ground water. 40 CFR 264.251(d) allows owner/operators of new waste pile units, lateral expansions, replacement units constructed after January 29, 1992 to obtain an exemption from the double liner and leachate collection system requirements of §264.251(c). In addition, owner/operators of any replacement waste pile unit may submit information under §264.251(f) in support of an exemption from §264.251(c). Data items associated with the requirements of this section include:
To obtain an exemption from the liner requirements of §264.251(a), a demonstration that includes the following information:
‑‑ Information regarding the nature and quantity of the wastes;
‑‑ The proposed alternative design and operation;
‑‑ The facility’s hydrogeologic setting, including attenuative capacity and thickness of the liners and soils present between the pile and ground water or surface water; and
‑‑ All other factors that would influence the quality and mobility of the leachate produced and the potential for it to migrate to ground water or surface water.
For owner/operators of leak detection systems that are not located completely above the seasonal high water table, a demonstration that the operation of the leak detection system will not be adversely affected by the presence of ground water;
To obtain an exemption from the double liner and leachate collection and removal system requirements of §264.251(c), a demonstration that alternative design and operating practices, together with location characteristics will: (1) prevent the migration of any hazardous constituents into the ground water or surface water at least as effectively as the liners and leachate collection and removal systems; and (2) allow detection of leaks of hazardous constituents through the top liner at least as effectively; and
For a replacement waste pile unit for which an exemption from §264.251(c) is sought, information demonstrating that the unit was constructed in compliance with the design standards of RCRA sections 3004(o)(1)(A)(i) and (o)(5), and information supporting the claim that the liner is functioning as designed (§264.251(f)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of this section, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare and submit the demonstration supporting an exemption from the liner requirement of §264.251(a);
Prepare and submit the demonstration for the leak detection system;
Prepare and submit the demonstration for exemption from the double liner and leachate collection and removal system requirements of §264.251(c);
Prepare and submit the information supporting an exemption for a replacement unit; and
File a copy of the demonstration(s) at the facility.
(4) Land Treatment
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 264.272 requires owner/operators of land treatment units to submit a treatment demonstration to EPA, prior to application of the waste to the treatment zone, showing that hazardous constituents in the waste can be completely degraded, transformed, or immobilized (§264.272(a)). In making this demonstration, the owner/operator may use field tests, laboratory analyses, available data, or, in the case of existing units, operating data.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of this section, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare and submit the demonstration; and
File a copy of the demonstration at the facility.
(5) Landfills
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 264.301 provides owner/operators of landfills with the opportunity to obtain an exemption from the liner and/or double liner and leachate collection and removal system requirements of §§264.301(a) and (c), respectively. 40 CFR 264.301(c)(5) requires owner/operators of a leak detection system that is not located completely above the seasonal high water table to demonstrate that the operation of the leak detection system will not be adversely affected by the presence of ground water. Owner/operators may also obtain a waiver of the double liner requirements for any monofill under §264.301(e). In addition, owner/operators of any replacement waste pile unit may submit information under §264.301(f) in support of an exemption from §264.301(c). Data items associated with the requirements of this section include the following:
To obtain exemption from the liner requirements of §264.301(a), a demonstration that alternative design and operating practices, together with location characteristics, will prevent the migration of any hazardous constituents into the ground water or surface water at any future time (§264.301(b)). Because landfills are now required to have double liners, this ICR assumes that no respondents will submit this demonstration;
For owner/operators of leak detection systems that are not located completely above the seasonal high water table, a demonstration that the operation of the leak detection system will not be adversely affected by the presence of ground water (§264.301(c)(5));
To obtain exemption from the double liner and leachate collection and removal system requirements of §264.301(c), a demonstration that alternative design and operating practices, together with location characteristics, will prevent the migration of any hazardous constituent into the ground water or surface water at least as effectively as the double liner collection system (§264.301(d)); and
To obtain a waiver of the double liner requirement for a monofill (§264.301(e)), the owner/operator must demonstrate to the EPA that:
‑‑ The monofill contains only hazardous wastes from foundry furnace emission controls or metal casting molding sand, and such wastes do not contain constituents which would render the wastes hazardous for reasons other than the toxicity characteristic; and
‑‑ The monofill possesses the following qualities:
At least one liner for which there is no evidence that such liner is leaking;
Located more than one quarter mile from an underground source of drinking water as defined in ‘144.3; and
Complies with generally applicable ground‑water monitoring requirements for facilities with permits under RCRA section 3005(c); or
‑‑ The monofill is located, designed and operated so as to assure that there will be no migration of any hazardous constituent into ground water or surface water at any future time; and
For a replacement landfill unit for which an exemption from §264.301(c) is sought, information demonstrating that the unit was constructed in compliance with the design standards of RCRA sections 3004(o)(1)(A)(i) and (o)(5), and information supporting the claim that the liner is functioning as designed (§264.301(f)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of this section, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare and submit the demonstration for an exemption from the liner requirement of §264.301(a);
Prepare and submit the demonstration for the leak detection system;
Prepare and submit the demonstration for an exemption from the double liner and leachate collection and removal system requirements of §264.301(c);
Prepare and submit the demonstration for a waiver of the double liner requirements for monofills;
Prepare and submit the information supporting an exemption for a replacement unit; and
File a copy of the demonstration(s) at the facility.
(6) Incinerators
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 264.344 requires that the period beginning with initial introduction of hazardous waste to the incinerator and ending with initiation of the trial burn not exceed a duration of 720 hours operating time for treatment of hazardous waste. However, EPA may extend the duration of this period once for up to 720 additional hours if the owner/operator can demonstrate good cause for the extension.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of this section, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare and submit the demonstration; and
File a copy of the demonstration at the facility.
Contents of the Part B Application
General Information
(i) Data items:
Under 40 CFR 270.1(c)(5), owner/operators of surface impoundments, land treatment units, and waste piles closing by removal or decontamination under Part 265 standards who have not submitted a Part B application for a post‑closure permit may petition EPA for a determination that a post‑closure permit is not required because the closure meets the applicable Part 264 closure standards. The petition must include the following information:
Data demonstrating that closure by removal or decontamination standards were met; or
Data demonstrating that the unit closed under State requirements that met or exceeded the applicable Part 264 closure‑by‑removal standard.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondent activities associated with §270.1(c)(5) include reading the regulations, developing and submitting the petition, and filing a copy of the petition at the facility.
Permit Application
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.10(j) requires that Part B permit applications submitted by owner/operators of facilities that store, treat, or dispose of hazardous waste in a surface impoundment or landfill be accompanied by information on the potential for the public to be exposed to hazardous wastes or hazardous constituents through releases related to the unit. The data items for this requirement include the following information:
Potential for releases from both normal operations and accidents at the unit, including releases associated with transportation to or from the unit;
The potential pathways of human exposure to hazardous wastes or constituents resulting from the releases described above; and
The potential magnitude and nature of the human exposure resulting from such releases.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondent activities associated with §270.10(j) include reading the regulations, collecting and submitting the required data, and filing the data at the facility.
General Requirements
(i) Data items:
Under 40 CFR 270.14(a), owner/operators may obtain from EPA relief from submission of information prescribed in Part B on a case‑by‑case basis by demonstrating that such information cannot be provided to the extent required.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondent activities associated with the demonstration submitted under §270.14(a) include reading the regulations, preparing and submitting the demonstration, and filing the demonstration at the facility.
General Facility Standards
(i) Data items:
Under 40 CFR 270.14(b) (1)‑(14), owner/operators of hazardous waste management facilities must submit in their Part B permit applications information on compliance with general facility standards. Data items required under these sections include the following:
A general description of the facility (§270.14(b)(1));
Chemical and physical analyses of the hazardous waste to be handled at the facility. At a minimum, these analyses should contain all the information that must be known to treat, store, or dispose of the wastes properly in accordance with Part 264 (§270.14(b)(2));
A waste analysis plan describing the procedures that will be carried out to comply with §264.13(a). The plan should contain information required under §264.13(b) (1)‑(7) and, for off‑site facilities, the information required under §264.13(c) (§270.14(b)(3));
A description of the security procedures and equipment required by §264.14, or a justification demonstrating the reasons for requesting a waiver of this requirement (§270.14(b)(4)). To obtain a waiver, owner/operators must demonstrate to EPA that:
‑‑ Physical contact with the waste, structures, or equipment within the active portion of the facility will not injure unknowing or unauthorized persons or livestock which may enter the active portion of the facility; and
‑‑ Disturbance of the waste or equipment, by the unknowing or unauthorized entry of persons or livestock onto the active portion of a facility, will not cause a violation of the requirements of this part;
A general inspection schedule, as required under §264.15(b), for monitoring equipment that is important in preventing, detecting, or responding to environmental or human health hazards (§270.14(b)(5)). Where applicable, the inspection schedule should include the specific requirements in §§264.174, 264.193(i), 264.195, 264.226, 264.254, 264.273, 264.303 and 264.602, and should identify the types of problems that are to be investigated during the inspection;
If an exemption from special equipment requirements is sought under §264.32, a demonstration that none of the hazards posed by waste handled at the facility could require the use of equipment required under §§264.32(a) through (d) (§270.14(b)(6));
If an exemption from the aisle space requirements of §264.35 is sought, a demonstration that the aisle space is not needed to allow the unobstructed movement of personnel, fire protection equipment, spill control equipment, and decontamination equipment to any area of the facility operating in an emergency (§270.14(b)(6));
A contingency plan as required under sections 264.51, 264.52 and 264.53(a). Data elements that should be included in this plan are listed below:
‑‑ A description of the arrangements agreed to by local police departments, fire departments, hospitals, contractors, and State and local emergency response teams to coordinate emergency services;
‑‑ An updated list of the names, addresses, and phone numbers (office and home) of all persons qualified to act as emergency coordinators;
‑‑ An updated list of all emergency equipment at the facility and the location, physical description, and capabilities of the emergency equipment. The contingency plan should also indicate where the emergency equipment will be required; and
‑‑ An evacuation plan for facility personnel where there is a possibility that evacuation may be necessary;
A description of procedures, structures, or equipment used at the facility for the following purposes:
‑‑ To prevent hazards in unloading operations;
‑‑ To prevent runoff from hazardous waste handling areas to other areas of the facility or environment, or to prevent flooding;
‑‑ To prevent contamination of water supplies;
‑‑ To mitigate effects of equipment failure and power outages; and
‑‑ To prevent undue exposure of personnel to hazardous waste;
A description of precautions taken under §264.17 to prevent accidental ignition or reaction of ignitable, reactive, or incompatible wastes, including documentation demonstrating compliance with §264.17(c) (§270.14(b)(9)). The documentation may be based on references to published scientific or engineering literature, data from trial tests, waste analyses, or the results of the treatment of similar wastes by similar treatment processes and under similar operating conditions;
A description of traffic patterns, estimated volume, and control (§270.14(b)(10));
Facility location information (§270.14(b)(11)). At a minimum, the location information provided must include:
‑‑ An identification of the political jurisdiction in which the facility is proposed to be located;
‑‑ If the facility is proposed to be located in an area listed in Appendix VI of Part 264, a demonstration of compliance with the seismic standard as defined under §264.18(a). This demonstration may be made using either published geologic data or data obtained from field investigations carried out by the applicant;
‑‑ An identification of whether the facility is located within a 100‑year floodplain. The identification must include the following information:
The source of data for the determination;
A copy of the relevant Federal Insurance Administration (FIA) flood map, if used, or the calculations and maps used where an FIA map is not available; and
An identification of the 100‑year flood level and any other special flooding factors which must be considered in designing, constructing, operating, or maintaining the facility to withstand washout from a 100‑year flood;
‑‑ Facilities located in a 100‑year floodplain may submit a demonstration for exemption from design and operating standards under §264.18(b). The demonstration must establish the following:
Procedures are in effect which will cause the waste to be removed safely, before flood waters can reach the facility, to a location where the wastes will not be vulnerable to flood waters; or
For existing surface impoundments, waste piles, land treatment units, landfills, and miscellaneous units, no adverse effects on human health or the environment will result if washout occurs;
‑‑ Owner/operators of facilities located in the 100‑year floodplain that are not exempt from the design and operating standards under §264.18(b) must provide the following information:
Engineering analysis to indicate the various hydrodynamic and hydrostatic forces expected to result at the site as consequence of a 100‑year flood; and
Structural or other engineering studies showing the design of operational units and flood protection devices at the facility and how these will prevent washout; or
If applicable, a detailed description of procedures to be followed to remove hazardous waste to safety before the facility is flooded;
‑‑ Existing facilities not in compliance with §264.18(b) must provide a plan showing how the facility will be brought into compliance, along with a schedule for compliance;
An outline of both the introductory and continuing training programs used to prepare persons to operate or maintain the facility in a safe manner as required to demonstrate compliance with §264.16, and a brief description of how training will be designed to meet actual job tasks in accordance with the requirements in §264.16(a)(3) (§270.14(b)(12));
A closure plan as required under §§264.112 and 264.197 (§270.14(b)(13)). The closure plan must include the information required under §264.112(b) (1)‑(7). Owner/operators must also submit a written post‑closure plan under §§264.118 and 264.197, where applicable, which contains the information required under §264.118(b) (1)‑(3). In addition, certain owner/operators of tanks, surface impoundments, waste piles, and drip pads may also need to submit a contingent closure and contingent post‑closure plan under sections 264.197(c), 264.228(c), 264.258(c), and 264.575(c), respectively; and
For hazardous waste disposal units that have been closed, documentation that the post‑closure notices required under §264.119 have been filed (§270.14(b)(14)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to provide the data items listed above, respondents must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare a written description of the facility;
Collect the analytical information required under §270.14(b)(2) and prepare a written report of the analyses conducted;
Collect the data required in the waste analysis plan;
Write the waste analysis plan;
Prepare the description of security procedures and equipment; or
Prepare a demonstration for a waiver of the security procedures and equipment requirements;
Develop an inspection schedule;
If applicable, prepare a demonstration for exemption from special equipment requirements;
If applicable, prepare a demonstration for exemption from aisle space requirements;
Collect the data required in the contingency plan;
Write the contingency plan;
Prepare the description of procedures, structures, or equipment;
Prepare a description of precautions to prevent accidental ignition or reaction of ignitable, reactive, or incompatible wastes;
Prepare a description of traffic patterns, estimated volume, and control;
Compile and document the facility location information required under §270.14(b)(11);
If the facility is proposed to be located in an area listed in Appendix VI, prepare a demonstration of compliance with the seismic standard;
For facilities in a 100‑year floodplain, prepare a demonstration for exemption from design and operating standards under §264.18(b);
For facilities in a 100‑year floodplain that are not exempt from §264.18(b), prepare an engineering analysis and engineering studies;
For facilities not in compliance with §264.18(b), a compliance plan and schedule of compliance;
Prepare outline of personnel training programs and description of training design;
Write descriptions of the necessary closure activities;
Estimate final closure;
Write the closure schedule;
Collect the necessary information for post‑closure requirements;
Write the post‑closure plan;
Prepare and submit documentation that post‑closure notices have been submitted;
Submit the general facility standards information; and
File a copy of the documentation at the facility.
Financial Assurance
(1) Cost Estimates for Closure and Post‑Closure Care
(i) Data items:
Sections 270.14(b)(15) and (16) require owner/operators to submit a detailed written estimate of the cost of facility closure and post‑closure care in accordance with the requirements of §§264.142(a) and 264.144(a), respectively. These estimates must include the following data items:
A written estimate containing:
‑‑ The costs of final closure at the point in the facility’s active life when the extent and manner of its operation would make closure the most expensive, as indicated by its closure plan (§264.142(a)(1));
‑‑ The annual cost of post‑closure monitoring and maintenance of the facility in accordance with the applicable post‑closure regulations specified in §264.144(a);
‑‑ The costs for tanks under §264.197(c)(3), for surface impoundments under §264.228(c)(2), for waste piles under §264.258(c)(2), and drip pads under §264.575(c)(2), of contingent closure and post‑closure, if required; and
Costs to the owner or operator of hiring a third party to conduct closure or post‑closure care at the facility (or on‑site disposal costs, if owner/operator can demonstrate that on‑site disposal capacity will exist at all times throughout the facility’s life (§264.142(a)(2)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Since cost estimates for closure and post‑closure care are submitted with the Part B permit application, activities associated with developing the estimates are discussed in this ICR. However, prior to submitting a permit application, interim status facilities must prepare closure and post‑closure cost estimates under §§265.142 and 265.144, respectively. Therefore, preparation of the closure and post‑closure cost estimates for interim status facilities are discussed in the General Facility Standards ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0120).
Owner/operators will need to engage in the following activities in order to collect the data required by §§264.142 and 264.144:
Read the regulations;
Collect data; and
Prepare the written cost estimates.
(2) Financial Assurance for Closure and Post‑Closure Care
(i) Data items:
Sections 270.14(b) (15) and (16) also require owner/operators to establish, and provide evidence of, financial assurance for facility closure (§264.143) and post‑closure care (§264.145). Because evidence of financial assurance is submitted with the Part B permit application, activities associated with obtaining financial assurance are discussed in this ICR. However, prior to submitting a Part B permit application, interim status facilities must prepare evidence of financial assurance for closure and post‑closure care under §§265.143 and 265.145, respectively. Therefore, the activities associated with preparing evidence of closure and post‑closure financial assurance for interim status facilities are discussed in the General Facility Standards ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0120).
Several financial instruments may be used for the purpose of establishing financial assurance for closure and post‑closure care. These financial instruments include the following:
Closure or post‑closure trust fund (§§264.143(a) and 264.145(a));
Surety bond guaranteeing payment into a closure or post‑closure trust fund (§§264.143(b) and 264.145(b));
Surety bond guaranteeing performance of closure or post‑closure care (§§264.143(c) and 264.145(c));
Closure or post‑closure letter of credit (§§264.143(d) and 264.145(d));
Closure or post‑closure insurance (§§264.143(e) and 264.145(e)); and
Financial test and corporate guarantee for closure or post‑closure care (§§264.143(f) and 264.145(f)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with the requirements concerning financial assurance for closure and post‑closure care, respondents must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations; and
Obtain and submit documentation of financial assurance.
(3) Use of a Financial Mechanism for Multiple Facilities
(i) Data items:
Sections 264.143(h) and 264.145(h) specify that owner/operators may use one of the above financial assurance mechanisms to meet the requirements of §§264.143 or 264.145 for more than one facility. In such cases, the owner/operator must provide the following data items for each facility:
EPA identification number, name, and address; and
The amount of funds for closure or post‑closure care assured by the mechanism.
(ii) Respondent activities:
The information required under this section will be submitted with the information provided by the owner/operator to establish one of the financial assurance mechanisms listed above. Therefore, this ICR assumes that any respondent activities related to the requirements of this section are already covered under the previous sections.
(4) Liability Requirements
Section 270.14(b)(17) requires owner/operators of new facilities to provide documentation showing the amount of insurance meeting the specification of §264.147(a) and, if applicable, §264.147(b), that the owner/operator plans to have in effect before initial receipt of hazardous waste for treatment, storage, or disposal.
(a) Coverage for Sudden or Nonsudden Accidental Occurrences
(i) Data items:
Section 264.147(a) requires owner/operators of hazardous waste TSDFs, or a group of such facilities, to demonstrate financial responsibility for bodily injury and property damage to third parties caused by sudden accidental occurrences arising from operations at the facility or group of facilities. Section 264.147(b) requires owner/operators of surface impoundments, landfills, and land treatment facilities managing hazardous wastes, or combinations of such facilities to demonstrate financial responsibility for bodily injury and property damage to third parties caused by nonsudden accidental occurrences rising from facilities’ operations. In order to comply with these requirements, owner/operators will need to gather the following data items:
A liability insurance policy (§§264.147(a)(1) and 264.147(b)(1)), accompanied by a signed duplicate original of a Hazardous Waste Facility Liability Endorsement or a Certificate of Liability Insurance;
Written evidence of passing a financial test or a written guarantee for liability coverage from the owner/operator’s parent corporation (§§264.147(a)(2) and 264.147(b)(2));
A letter of credit for liability coverage (§§264.147(a)(3) and 264.147(b)(3));
A surety bond for liability coverage (§§264.147(a)(4) and 264.147(b)(4));
A trust fund for liability coverage (§§264.147(a)(5) and 264.147(b)(5)); or
A combination of insurance, financial test, guarantee, letter of credit, surety bond, and trust fund (§§264.147(a)(6) and 264.147(b)(6)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of these sections, owner/operators will need to perform the following activities:
Read the regulations; and
Obtain and submit documentation of liability coverage using one of the financial instruments listed above.
(b) Request for Variance
(i) Data item:
Section 264.147(c) allow owner/operators to obtain a variance from EPA if they can demonstrate that the levels of financial responsibility required for sudden and nonsudden accidental occurrences are not consistent with the degree and duration of risk associated with treatment, storage, or disposal at the facility or group of facilities. The data item for this demonstration is:
A request for a variance submitted as part of the permit application under §270.14(b)(17) for new facilities, or pursuant to the procedures for permit modification under §§270.41(a)(5) and 124.5. This request may include technical and engineering information as deemed necessary by EPA.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owner/operators will need to engage in the following activities in requesting a variance:
Read the regulations; and
Prepare and submit the request for variance, including any technical or engineering information required by EPA.
(c) Adjustments by the Regional Administrator
(i) Data items:
Section §264.147(d) allows EPA to adjust the level of financial responsibility required under §264.147 in order to protect human health and the environment. Respondents will need to furnish the following data items should EPA decide to make such a determination:
Any information that EPA requests to determine whether cause exists for such adjustments of level or type of coverage; and
If the Regional Administrator decides to adjust the level or type of coverage, the data elements necessary for a permit modification. The activities and estimated burden and cost associated with permit modifications are included under the section on permit modifications below.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owner/operators will need to engage in the following activities in order to satisfy the information collection requirements of this section:
Read the regulations; and
Prepare and submit to EPA any requested information.
(5) Coverage by a State Financial Mechanism
(i) Data items:
Section 270.14(b)(18) requires owner/operators to provide proof of coverage by a State financial mechanism in compliance with §§264.149 or 264.150, where appropriate. Section 264.149 allows owner/operators to use State‑required financial assurance mechanisms to meet §§264.143, 264.145, or 264.147 requirements. Section 264.150 requires owner/operators to notify EPA when a State assumes legal responsibility or assures availability of funds for an owner/operator’s compliance with the closure, post‑closure care, or liability requirements of this part. Data items associated with these requirements include the following:
A letter from the owner/operator requesting the following:
‑‑ The State‑required mechanism be considered acceptable for meeting the requirements of this subpart; or
‑‑ The State’s assumption of responsibility be considered acceptable for meeting the requirements of this subpart;
Evidence of the establishment of a State‑required mechanism or a letter from the State describing the nature of the State’s assumption of responsibility. Each of these data items should include the following information:
‑‑ The facility’s EPA identification number, name, and address; and
‑‑ The amount of funds for closure or post‑closure care or liability coverage assured by the mechanism; and
Any additional information required by EPA in order to make the determination.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondent activities associated with the requirements of §264.149 include the following:
Read the regulations;
Submit the letter from the owner/operator;
Submit written evidence of the establishment of a State‑required financial assurance mechanism or letter from the State describing the State’s assumption of responsibility and including the information specified above; and
Submit any additional information requested by EPA.
Other Requirements
(1) Topographical Map
(i) Data items:
Section 270.14(b)(19) requires owner/operators to provide a topographic map showing a distance of 1000 feet around the facility. The map shall clearly show the following information:
Map scale and date;
100‑year floodplain area;
Surface waters including intermittent streams;
Surrounding land uses;
A wind rose;
Orientation of the map;
Legal boundaries of the facility site;
Access control;
Injection and withdrawal wells both on‑site and off‑site;
Buildings; treatment, storage, or disposal operations; or other structure;
Barriers for drainage or flood control; and
Location of operational units within the facility site, where hazardous waste is (or will be) treated, stored, or disposed (including equipment cleanup areas);
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities in order to provide the topographic map:
Read the regulations;
Collect the necessary information; and
Develop and submit the map.
(2) Case‑By‑Case Extensions and Petitions to Allow Land Disposal of a Waste Prohibited Under Subpart C of Part 268
(i) Data items:
Under §270.14(b)(21), owner/operators of land disposal facilities that have received approval for a case‑by‑case extension under §268.5 or a petition under §268.6 must submit a copy of the notice of approval for the extension or petition with their Part B permit application.
(ii) Respondent activities:
The burden associated with developing the extension application or petition is addressed in Land Disposal Restrictions ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0085). To provide a copy of these documents for the Part B permit application, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations; and
Prepare and submit copy of the notice of approval.
Ground‑Water Protection
(1) General Ground‑Water Monitoring Requirements
(i) Data items:
Sections 270.14(c) (1)‑(5) require owner/operators to submit additional information to EPA regarding protection of ground water when applying for a Part B permit. The information required includes information on site‑specific characteristics, and a ground‑water monitoring program as required under §264.97. The monitoring program must include sampling and analysis procedures, sampling intervals, and statistical methods to be used in evaluating ground‑water monitoring data. To fulfill the requirements of these sections, owner/operators must submit the following data items:
A summary of the ground‑water monitoring data obtained during the interim status period under §§265.90 through 265.94, where applicable (§270.14(c)(1));
Identification of the uppermost aquifer and aquifers hydraulically interconnected beneath the facility property, including ground‑water flow direction and rate, and the basis for such identification (§270.14(c)(2));
On the topographic map required under §270.14(b)(19), a delineation of the following:
‑‑ The waste management area;
‑‑ The property boundary;
‑‑ The proposed "point of compliance" as defined under §264.95;
‑‑ The proposed location of ground‑water monitoring wells as required under §264.97; and
‑‑ Identification of aquifers, as required above;
A description of any plume of contamination that has entered the ground water from a regulated unit at the time the application is submitted (§270.14(c)(4)). The description should:
‑‑ Delineate the extent of the plume on the topographic map required under §270.14(b)(19); and
‑‑ Identify the concentration of each Appendix IX (40 CFR Part 264) constituent throughout the plume or identify the maximum concentrations of each Appendix IX constituent in the plume;
A description of the proposed ground‑water sampling and analysis procedures as required under §264.97. At a minimum these procedures must include:
‑‑ Procedures and techniques for sample collection, sample preservation and shipment, analytical procedures, and chain of custody control (§264.97(d));
‑‑ Sampling and analytical methods appropriate for ground‑water sampling and accurate measurement of hazardous constituents in ground‑water samples (§264.97(e)); and
‑‑ Procedures for determining the ground‑water surface elevation each time ground water is sampled (§264.97(f));
A statistical method to be used in evaluating ground‑water monitoring data for each hazardous constituent. The method specified will be one of those listed under §264.97(h)(1) through (4), or another statistical test method submitted in accordance with §264.97(h)(5). In specifying the type of statistical method to be used, the owner/operator may also be required to supply the following information:
‑‑ Where practical quantification limits (pql’s) are used, the pql must be submitted to EPA for approval;
‑‑ If a control chart approach is used to evaluate ground‑water monitoring data, the specific type of control chart and its associated parameter values shall be submitted to EPA for approval; and
‑‑ If a tolerance interval or a prediction interval is used to evaluate ground‑water monitoring data, the levels of confidence and, for tolerance intervals, the percentage of the population that the interval must contain shall contain must be submitted to EPA for approval; and
A record of all ground‑water monitoring data collected in accordance with §264.97(g). This information must be recorded in the facility operating record. Therefore, the burden associated with this requirement is included in the General Facility Standards ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0120).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities to provide the information required in these sections:
Read the regulations;
Summarize ground‑water monitoring data obtained during the interim status period under §§265.90 through 265.94;
Collect and document the hydrogeologic information required under §270.14(c)(2);
Add the required information to the topographical map required under §270.14(b)(19);
Prepare a description of plume contamination, where applicable;
Develop a ground‑water sampling and analysis procedure;
Determine the appropriate statistical method to be used;
Submit the ground‑water monitoring program; and
File copies of the submitted information on file at the facility.
(2) Detection Monitoring Program
(i) Data items:
Section 270.14(c)(6) requires that if the presence of hazardous constituents has not been detected in the ground water at the time of permit application, the owner/operator must submit to EPA sufficient information, supporting data, and analyses to establish a detection monitoring program meeting the requirements of §264.98. This information includes data required by EPA to determine the parameters or constituents to be monitored under the detection monitoring program, as well as information for determining appropriate time periods for identifying contamination. The information submitted should include the following items:
Information required to determine the parameters or constituents to be monitored under the detection monitoring program, including:
‑‑ The types, quantities, and concentrations of constituents in wastes managed at the regulated unit;
‑‑ The mobility, stability, and persistence of waste constituents or their reaction products in the unsaturated zone beneath the waste management area;
‑‑ The detectability of indicator parameters, waste constituents, and reaction products in ground water; and
‑‑ The concentrations or values and coefficients of variation of proposed monitoring parameters or constituents in the ground‑water background;
Detailed plans and an engineering report describing the proposed ground‑water monitoring system, in accordance with the requirements of §264.97;
Background values for each proposed monitoring parameter or constituent, or procedures to calculate such values (§270.14(c)(6)(iii));
A description of proposed sampling, analysis and statistical comparison procedures to be utilized in evaluating ground‑water monitoring data (§270.14(c)(6)(iv)). The requirements associated with providing this information are discussed in the previous section on General Ground‑Water Monitoring Requirements; and
Information required to determine a reasonable time period for identifying significant evidence of contamination, including information on the complexity of the statistical test and the availability of laboratory facilities for performing the analysis of ground‑water samples (§264.98(f)(2)).
[Note: If the owner or operator determines pursuant to paragraph (f) that there is statistically significant evidence of contamination for chemical parameters or hazardous constituents at any monitoring well at the compliance point, he or she must submit to EPA an application for a Class 2 or 3 permit modification to establish a compliance monitoring program under section 264.99. This activity is currently burdened in the Facility Ground‑Water Monitoring Requirements ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0033).]
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of this section, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Compile the information required to determine monitoring parameters or constituents;
Prepare the plans and engineering report describing the proposed ground‑water monitoring system;
Establish background values for each proposed monitoring parameter or constituent, or procedures for determining such values;
Compile the information required to determine a reasonable time period for identifying significant evidence of contamination;
Submit the required information; and
Maintain copies of all submitted information on file at the facility.
(3) Compliance Monitoring Program
(i) Data items:
Section §270.14(c)(7) requires that if the presence of hazardous constituents has been detected in the ground water at the point of compliance at the time of the permit application, the owner/operator must submit to EPA sufficient information, supporting data, and analyses to establish a compliance monitoring program meeting the requirements of §264.99. Section 264.99 requires owner/operators to submit to EPA all information necessary to determine a reasonable time period for identifying significant evidence of increased contamination during compliance monitoring. The information submitted to EPA should include the following items:
A description of the wastes previously handled at the facility (§270.14(c)(7)(i));
A characterization of the contaminated ground water, including concentrations of hazardous constituents (§270.14(c)(7)(ii));
A list of hazardous constituents for which compliance monitoring will be undertaken in accordance with §§264.97 and 264.99 (§270.14(c)(7)(iii));
Proposed concentration limits for each hazardous constituent, based on the criteria set forth in §264.94(a), including a justification for establishing any alternate concentration limits (§270.14(c)(7)(iv));
Detailed plans and an engineering report describing the proposed ground‑water monitoring system, in accordance with the requirements of §264.97 (§270.14(c)(7)(v));
A description of proposed sampling, analysis and statistical comparison procedures to be used in evaluating ground‑water monitoring data (§270.14(c)(7)(vi)). The requirements associated with providing this information are discussed in the previous section on General Ground‑Water Monitoring Requirements;
Information necessary to determine a reasonable time period for identifying significant evidence of increased contamination, including information on the complexity of the statistical test and the availability of laboratory facilities for performing the analysis of ground‑water samples (§264.99(d)(2)); and
An engineering feasibility plan for a corrective action program necessary to meet the requirements of §264.100 (§270.14(a)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities to provide the information required in this section:
Read the regulations;
Provide a description of wastes previously handled at the facility;
Provide a characterization of contaminated ground water;
Develop a list of hazardous constituents for which compliance monitoring will be undertaken in accordance with §§264.97 and 264.99;
Develop proposed concentration limits for each hazardous constituent, and a justification for establishing any alternate concentration limits;
Prepare plans and engineering report describing the proposed ground‑water monitoring system;
Compile the information necessary to determine a reasonable time period for identifying significant evidence of increased contamination;
Develop an engineering feasibility plan for corrective action;
Submit the required information; and
Maintain copies of all submitted information on file at the facility.
(4) Corrective Action Program
(i) Data items:
Section 270.14(c)(8) requires that if hazardous constituents have been measured in the ground water which exceed the concentration limits established under §264.94 Table 1, or if ground‑water monitoring conducted at the time of permit application under §§265.90 through 265.94 at the waste boundary indicates the presence of hazardous constituents from the facility in ground water over background concentrations, the owner/operator must submit to EPA sufficient information, supporting data, and analyses to establish a corrective action program which meets the requirements of §264.100. The information submitted should include the following:
A characterization of the contaminated ground water, including concentrations of hazardous constituents;
The concentration limit for each hazardous constituent found in the ground water as set forth in §264.94;
Detailed plans and an engineering report describing the corrective action to be taken;
A description of how the ground water monitoring program will demonstrate the adequacy of the corrective action;
If applicable, a schedule for submittal of the information required in §§270.14(c)(8)(iii) and (iv) in the permit. The owner/operator must obtain written authorization from EPA prior to submittal of the complete permit application; and
A demonstration that alternate concentration limits will protect human health and the environment. The demonstration should include the information listed under §270.14(c)(8) (i)‑(v). Owner/operators that submit such a demonstration are not required to submit information to establish a corrective action program. Instead, these owner/operators must submit sufficient information to establish a compliance monitoring program meeting the requirements of §264.99 and §270.14(c)(6).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Respondents must perform the following activities to provide the information required in this section:
Read the regulations;
Prepare a characterization of the contaminated ground water;
Develop a concentration limit for each hazardous constituent;
Prepare the detailed plans and engineering report describing corrective action;
Prepare a description of how the ground‑water monitoring program will demonstrate the adequacy of the corrective action;
If applicable, prepare a schedule for submittal of the information required in §§270.14(c)(8)(iii) and (iv) in the permit;
If applicable, prepare a demonstration that alternate concentration limits will protect human health and the environment;
Submit the required information; and
File copies of the submitted information at the facility.
Solid Waste Management Units
(i) Data items:
Section 270.14(d) establishes Part B information requirements for solid waste management units. Data items associated with these requirements are listed below:
Information on each solid waste management unit, including the following:
‑‑ The location of the unit on the topographic map required under §270.14(b)(19);
‑‑ Designation of the type of unit;
‑‑ General dimensions and structural description;
‑‑ When the unit was operated; and
‑‑ Specification of all wastes that have been managed at the unit, to the extent available;
All available information pertaining to any release of hazardous wastes or hazardous constituents from such unit or units (§270.14(d)(2)); and
Results of sampling and analysis, where the Director ascertains that a RCRA Facility Assessment is necessary.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to provide the data items listed above, respondents must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Compile the information required for each solid waste management unit under §270.14(d)(1);
Compile information pertaining to any releases from the unit(s);
Prepare and submit results of sampling and analysis;
Submit the required information; and
File copies of the submitted information at the facility.
Specific Part B Information Requirements
(1) Containers
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.15 requires owner/operators of facilities that store containers of hazardous waste to provide the following additional information:
A description of the containment system to demonstrate compliance with §264.175 (§270.15(a)). This description must, at a minimum, include the following information:
‑‑ Basic design parameters, dimensions, and materials of construction;
‑‑ How the design promotes drainage or how containers are kept from contact with standing liquids in the containment system;
‑‑ Capacity of the containment system relative to the number and volume of containers to be stored;
‑‑ Provisions for preventing or managing run‑on; and
‑‑ How accumulated liquids can be analyzed and removed to prevent overflow;
For storage areas that store containers holding wastes that do not contain free liquids, a demonstration of compliance with §264.175(c) (§270.15(b)). The demonstration must include:
‑‑ Test procedures and results or other documentation or information to show that the wastes do not contain free liquids; and
‑‑ A description of how the storage area is designed or operated to drain and remove liquids or how containers are kept from contact with standing liquids;
Sketches, drawings, or data demonstrating compliance with §264.176 (location of buffer zone and containers holding ignitable or reactive wastes) and §264.177(c) (location of incompatible wastes), where applicable (§270.15(c)); and
Where incompatible wastes are stored or otherwise managed in containers, a description of the procedures used to ensure compliance with §§264.177 (a) and (b), and 264.17 (b) and (c) (§270.15(d)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of §270.15, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare a written description of the containment system;
Prepare the no free liquids demonstration;
Document compliance with §264.176 and §264.177;
Provide a written description of procedures used to ensure compliance with §§264.177 (a) and (b), and 264.17 (b) and (c);
Submit the required information; and
File copies of the submitted information at the facility.
(2) Tank Systems
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.16 requires owner/operators of facilities that use tanks to store or treat hazardous waste to provide the following additional information:
An assessment of existing tank system’s integrity (§270.16(a)). Section 264.191 requires that an owner/operator of an existing tank system that does not have secondary containment meeting the requirements of §264.193 must provide a written assessment of their tank system’s integrity. The assessment must include the information required under §264.191(b) (1)‑(5) and must be certified by an independent, qualified engineer in accordance with §270.11(d); or
An assessment of new tank system’s integrity (§270.16(a)). Section 264.192 requires owner/operators of a new tank system or component to provide EPA with a written assessment, in accordance with §270.11(d), attesting that the tank system has sufficient structural integrity and is acceptable for the storing and treating of hazardous waste. The assessment should include the information required under §264.192(a) (1)‑(5) and must be certified by an independent, qualified registered professional engineer;
Dimensions and capacity of each tank (§270.16(b));
Description of feed systems, safety cutoff, bypass systems, and pressure controls (e.g., vents) (§270.16(c));
A diagram of piping, instrumentation, and process flow for each tank system (§270.16(d));
A description of materials and equipment used to provide external corrosion protection, as required under §264.192(a)(3)(ii) (§270.16(e));
For new tank systems, a detailed description of how the tank system(s) will be installed in compliance with §264.192(b), (c), (d), and (e) (§270.16(f));
Detailed plans and description of how the secondary containment system for each tank system is or will be designed, constructed, and operated to meet the requirements of §264.193(a), (b), (c), (d), (e), and (f) (§270.16(g));
A description of controls and practices to prevent spills and overflows, as required under §264.194(b) (§270.16(i)); and
For tank systems in which ignitable, reactive, or incompatible wastes are to be stored or treated, a description of how operating procedures and tank system and facility design will achieve compliance with the requirements of §§264.198 and 264.199 (§270.16(j)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of §270.16, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Conduct an assessment of the new or existing tank system;
Write the assessment;
Compile the information required under §270.16 (b)‑(e);
Provide a description of tank system installation;
Prepare a description of how the secondary containment system for each tank system is or will be designed, constructed, and operated to meet the requirements of §264.193(a), (b), (c), (d), (e), and (f);
Prepare a description of controls and practices to prevent spills and overflows;
Prepare a description of how operating procedures and tank system and facility design will achieve compliance with the requirements of §§264.198 and 264.199;
Submit the required information; and
File copies of the submitted information at the facility.
(3) Surface Impoundments
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.17 requires owner/operators of facilities that store, treat or dispose of hazardous waste in surface impoundments to provide the following additional information:
A list of the hazardous wastes places or to be placed in each surface impoundment (§270.17(a));
Detailed plans and an engineering report describing how the surface impoundment is or will be designed, constructed, operated and maintained to meet the requirements of §264.221 (§270.17(b)). This submission must address the following items as specified in §264.221:
‑‑ The liner system;
‑‑ The double liner and leak (leachate) detection, collection, and removal system, if required;
‑‑ For a leak detection system located in a saturated zone, the system’s design, operation, and location in relation to the saturated zone;
‑‑ The construction quality assurance plan (§264.19);
‑‑ Proposed action leakage rate;
‑‑ Response action plan;
‑‑ Prevention of overtopping; and
‑‑ Structural integrity of dikes;
A description of how each surface impoundment, including the liner and cover systems and appurtenances for control of overtopping, will be inspected in order to meet the requirements of §264.226(a) and (b) (§270.17(c)). This information should be included in the inspection plan submitted under §270.14(b)(5);
A certification by a qualified engineer which attests to the structural integrity of each dike, as required under §264.226(c) (§270.17(d)). For new units, the owner/operator must submit a statement by a qualified engineer that he or she will provide such a certification upon completion of construction in accordance with the plans and specifications;
A description of the procedure to be used for removing a surface impoundment from service, as required under §264.227(b) and (c) (§270.17(e)). This information should be included in the contingency plan submitted under §270.14(b)(7);
A description of how hazardous waste residues and contaminated materials will be removed from the unit at closure, as required under §264.228(a)(1). For any wastes not to be removed from the unit upon closure, the owner/operator must submit detailed plans and an engineering report describing how §264.228(a)(2) and (b) will be complied with (§270.17(f)). This information should be included in the closure plan and, where applicable, the post‑closure plan submitted under §270.14(b)(13);
If ignitable or reactive wastes are to be placed in a surface impoundment, an explanation of how §264.229 will be complied with (§270.17(g));
If incompatible wastes, or incompatible wastes and materials, will be placed in a surface impoundment, an explanation of how §264.230 will be complied with (§270.17(h)); and
A waste management plan for EPA Hazardous Waste Nos. F020, F021, F022, F023, F026, and F027 describing how the surface impoundment is or will be designed, constructed, operated, and maintained to meet the requirements of §264.231. This submission must address the following items as specified in §264.231:
‑‑ The volume, physical, and chemical characteristics of the wastes, including their potential to migrate through soil or to volatilize or escape into the atmosphere;
‑‑ The attenuative properties of underlying and surrounding soils or other materials;
‑‑ The mobilizing properties of other materials co‑disposed with these wastes; and
‑‑ The effectiveness of additional treatment, design, or monitoring techniques.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of §270.17, owner/operator must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Develop plans and an engineering report describing how the surface impoundment will be designed, constructed, operated and maintained;
Prepare a description of inspection procedures and incorporate the description into the inspection plan;
Obtain a certification or statement from a qualified engineer;
Prepare a description of procedures for removing the surface impoundment from service, and incorporate the description into the contingency plan;
Prepare a description of how hazardous waste residues and contaminated materials will be removed from the unit at closure, and incorporate the description into the closure and post‑closure plans;
Provide plans and an engineering report describing how §§264.228(a)(2) and (b) will be complied with, and incorporate the description into the closure and post‑closure plans;
Prepare an explanation of how §264.229 will be complied with for ignitable or reactive wastes;
Prepare an explanation of how §264.230 will be complied with for incompatible wastes;
Prepare a waste management plan for F‑wastes;
Submit the required information; and
File a copy of the required information at the facility.
(4) Waste Piles
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.18 requires owner/operators of facilities that store or treat hazardous waste in waste piles to provide the following additional information:
A list of hazardous wastes placed or to be placed in each waste pile (§270.18(a));
If an exemption from §264.251 (liner and leachate collection requirements) or Subpart F of Part 264 (ground‑water monitoring) is sought as provided by §264.250(c) or §264.90(b)(2), respectively, an explanation of how the standards of §264.250(c) will be complied with or detailed plans and an engineering report describing how the requirements of §264.90(b)(2) will be complied with (§270.18(b));
Detailed plans and an engineering report describing how the pile is or will be designed, constructed, operated and maintained to meet the requirements of §264.251 (§270.18(c)). This submission must address the following items:
‑‑ The liner system;
‑‑ The double liner and leak (leachate) detection, collection, and removal system, if required;
‑‑ For a leak detection system located in a saturated zone, the system’s design, operation, and location in relation to the saturated zone;
‑‑ The construction quality assurance plan;
‑‑ Proposed action leakage rate;
‑‑ Response action plan;
‑‑ Control of run‑on and run‑off;
‑‑ Management of collection and holding units associated with run‑on and run‑off control systems; and
‑‑ Control of wind dispersal of particulate matter, where applicable;
A description of how each waste pile, including the liner and appurtenances for control of run‑on and run‑off, will be inspected in order to meet the requirements of §264.254(a) and (b) (§270.18(d)). This information should be included in the inspection plan submitted under §270.14(b)(5);
If treatment is carried out on or in the pile, details of the process and equipment used, and the nature and quality of the residuals (§270.18(e));
If ignitable or reactive wastes are to be placed in a waste pile, an explanation of how the requirements of §264.256 will be complied with (§270.18(f));
If incompatible wastes, or incompatible wastes and materials, will be placed in a waste pile, an explanation of how §264.257 will be complied with (§270.18(g));
A description of how hazardous waste residues and contaminated materials will be removed from the waste pile at closure, as required under §264.258(a). For any waste not to be removed from the waste pile upon closure, the owner/operator must submit detailed plans and an engineering report describing how §264.310(a) and (b) will be complied with (§270.18(h)). This information should be included in the closure plan and, where applicable, the post‑closure plan submitted under §270.14(b)(13); and
A waste management plan for EPA Hazardous Waste Nos. F020, F021, F022, F023, F026, and F027 describing how a waste pile that is not enclosed (as defined in §264.250(c)) is or will be designed, constructed, operated, and maintained to meet the requirements of §264.259 (§270.18(i)). This submission must address the following items as specified in §264.259:
‑‑ The volume, physical, and chemical characteristics of the wastes to be disposed in the waste pile, including their potential to migrate through soil or to volatilize or escape into the atmosphere;
‑‑ The attenuative properties of underlying and surrounding soils or other materials;
‑‑ The mobilizing properties of other materials co‑disposed with these wastes; and
‑‑ The effectiveness of additional treatment, design, or monitoring techniques.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of §270.18, owner/operator must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare a list of hazardous wastes placed or to be placed in each waste pile;
If an exemption from §264.251 is sought, prepare an explanation of how §264.250(c) will be complied with;
If an exemption under §264.90(b) is sought, prepare an engineering report describing how §264.90(b)(2) will be complied with;
Develop plans and an engineering report describing how the waste pile is or will be designed, constructed, operated and maintained;
Prepare a description of inspection procedures and incorporate the description into the inspection plan;
If applicable, describe the process and equipment used to treat the pile, and identify the nature and quality of residuals;
Prepare an explanation of how §264.256 will be complied with for ignitable or reactive wastes;
Prepare an explanation of how §264.257 will be complied with for incompatible wastes;
Prepare a description of hazardous waste residues and contaminated materials that will be removed from the pile at closure, and incorporate the description into the closure and post‑closure plans;
Provide plans and an engineering report describing how §§264.310(a) and (b) will be complied with, and incorporate the description into the closure and post‑closure plans;
Prepare a waste management plan for F‑wastes;
Submit the required information; and
File a copy of the required information at the facility.
(5) Incinerators
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.19, 270.62(b)(2), and 270.62(b)(6)‑(8) require owner/operators of facilities that incinerate hazardous waste to provide the following additional information:
When seeking an exemption under §264.340 (b) or (c) for ignitable, corrosive, or reactive wastes:
‑‑ Documentation that the waste is listed as a hazardous waste in 40 CFR Part 261, Subpart D solely because it is ignitable or corrosive, or both (§270.19(a)(1)); or
‑‑ Documentation that the waste is listed as a hazardous waste in 40 CFR Part 261, Subpart D solely because it is reactive for characteristics other than those listed in §261.23(a) (4) and (5), and will not be burned when other hazardous wastes are present in the combustion zone (§270.19(a)(2)); or
‑‑ Documentation that the waste is a hazardous waste solely because it possesses the characteristic of ignitability, corrosivity, or both, as determined by the tests for characteristics of hazardous waste under 40 CFR Part 261, Subpart C (§270.19(a)(3)); or
‑‑ Documentation that the waste is a hazardous waste solely because it possesses the reactivity characteristics listed in §261.23(a) (1), (2), (3), (6), (7), or (8), and that it will not be burned when other hazardous wastes are present in the combustion zone (§270.19(a)(4)); or
A trial burn plan or the results of a trial burn, in accordance with §270.62 (§270.19(b)). The information required includes:
‑‑ A proposed trial burn plan. The plan must include the information listed under §270.62(b)(2) (i)‑(viii) (§270.19(b)); or
‑‑ The results of a trial burn, including certified documentation of the results of the trial burn (§270.62(b)(6)) and certification that the trial burn has been carried out in accordance with the approved trial burn plan (§270.62(b)(7)); and
‑‑ All data collected during any trial burn (§270.62(b)(8)); or
In lieu of a trial burn, the following information as required under §270.19(c):
‑‑ An analysis of each waste or mixture of wastes to be burned, including:
Heat value of the waste in the form and composition in which it will be burned;
Viscosity (if applicable), or description of physical form of the waste;
An identification of any hazardous organic constituents listed in 40 CFR Part 261, Appendix VIII, which are present in the waste to be burned, except that the applicant need not analyze for constituents listed in 40 CFR Part 261, Appendix VIII which would reasonably not be expected to be found in the waste. The constituents excluded from the analysis must be identified and the basis for their exclusion stated;
An approximate quantification of the hazardous constituents identified in the waste, within the precision produced by the analytical methods specified in "Test Methods for the Evaluation of Solid Waste, Physical/Chemical Methods"; and
A quantification of those hazardous constituents in the waste which may be designated as Principal Organic Hazardous Constituents (POHCs) based on data submitted from other trial or operational burns which demonstrate compliance with the performance standards in §264.343.
‑‑ A detailed engineering description of the incinerator, including:
Manufacturer’s name and model number of incinerator, and type of incinerator;
Linear dimension of incinerator unit including cross sectional area of combustion chamber;
Description of auxiliary fuel system;
Capacity of prime mover;
Description of automatic waste feed cutoff system(s);
Stack gas monitoring and pollution control monitoring system;
Nozzle and burner design;
Construction materials; and
Location and description of temperature, pressure, and flow indicating devices and control devices.
‑‑ A description and analysis of the waste to be burned compared with the waste for which data from operational or trial burns are provided to support the contention that a trial burn is not needed. The data should include those items listed in §270.19(c)(1). This analysis should specify the POHCs which the applicant has identified in the waste for which a permit is sought, and any differences from the POHCs in the waste for which burn data are provided;
‑‑ The design and operating conditions of the incinerator unit to be used, compared with that for which comparative burn data are available;
‑‑ A description of the results submitted from any previously conducted trial burn(s) including:
Sampling and analysis techniques used to calculate performance standards in §264.343; and
Methods and results of monitoring temperatures, waste feed rates, carbon monoxide, and an appropriate indicator of combustion gas velocity (including a statement concerning the precision and accuracy of this measurement);
‑‑ The expected incinerator operation information to demonstrate compliance with §§264.343 and 264.345, including:
Expected carbon monoxide level in the stack exhaust gas;
Waste feed rate;
Combustion zone temperature;
Indication of combustion gas velocity;
Expected stack gas volume, flow rate, and temperature;
Computed residence time for waste in the combustion zone;
Expected hydrochloric acid removal efficiency;
Expected fugitive emissions and their control procedures; and
Proposed waste feed cut‑off limits based on the identified significant operating parameters;
‑‑ Waste analysis data, including that submitted in §270.19(c)(1), sufficient to allow EPA to specify as permit POHCs those constituents for which destruction and removal efficiencies will be required.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of §270.19, owner/operator must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare documentation for ignitable, corrosive, or reactive wastes as required under §270.19(a) (1)‑(4); or
Prepare a trial burn plan; or
Prepare a report on the results of a trial burn; or
Prepare an analysis of each waste or mixture of wastes to be burned;
Prepare a detailed engineering description of the incinerator;
Prepare a description and analysis of the waste to be burned and compare the data with data collected from operational or trial burns are provided to support the contention that a trial burn is not needed;
Document the design and operating conditions of the incinerator unit to be used compared with that for which comparative burn data are available;
Prepare a description of the results submitted from any previously conducted trial burn(s);
Compile the expected incinerator operation information to demonstrate compliance with §§264.343 and 264.345;
Provide waste analysis data sufficient to allow EPA to identify permit POHCs;
Submit the required information; and
File a copy of the required information at the facility.
(6) Land Treatment
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.20 requires owner/operators of facilities that use land treatment to dispose of hazardous waste to provide the following additional information:
A description of plans to conduct a treatment demonstration as required under §264.272 (§270.20(a)). The description must include the following information:
‑‑ The wastes for which the demonstration will be made and the potential hazardous constituents in the waste;
‑‑ The data sources to be used to make the demonstration; and
‑‑ Any specific laboratory or field test that will be conducted, including the information required under §270.20(a)(3) (i)‑(iv).
A description of the land treatment program, as required under §264.271 (§270.20(b)). This information must be submitted with the plans for the treatment demonstration, and updated following the treatment demonstration. The land treatment program must address the following items:
‑‑ The wastes to be land treated;
‑‑ Design measures and operating practices necessary to maximize treatment in accordance with §264.273(a), including the information required under §270.20(b)(2) (i)‑(iv);
‑‑ Provisions for unsaturated zone monitoring, including the information required under §270.20(b)(3) (i)‑(vii);
‑‑ A list of hazardous constituents reasonably expected to be in, or derived from, the wastes to be land treated based on waste analysis performed pursuant to §264.13; and
‑‑ The proposed dimensions of the treatment zone;
A description of how the unit is or will be designed, constructed, operated, and maintained in order to meet the requirements of §264.273 (§270.20(c)). This submission must address the following items:
‑‑ Control of run‑on;
‑‑ Collection and control of run‑off;
‑‑ Minimization of run‑off of hazardous constituents from the treatment zone;
‑‑ Management of collection and holding facilities associated with run‑on and run‑off control systems;
‑‑ Periodic inspection of the unit. This information should be included in the inspection plan submitted under §270.14(b)(5); and
‑‑ Control of wind dispersal of particulate matter, if applicable;
If food‑chain crops are to be grown in or on the treatment zone of the land treatment unit, a description of how the demonstration required under §264.276(a) will be conducted (§270.20(d)). This submission should include the following information:
‑‑ Characteristics of the food‑chain crop for which the demonstration will be made;
‑‑ Characteristics of the waste, treatment zone, and waste application method and rate to be used in the demonstration;
‑‑ Procedures for crop growth, sample collection, sample analysis, and data evaluation; and
‑‑ Characteristics of the comparison crop including the location and conditions under which it was or will be grown;
If food‑chain crops are to be grown, and cadmium is present in the land‑treated waste, a description of how the requirements of §264.276(b) will be complied with (§270.20(e));
A description of the vegetative cover to be applied to closed portions of the facility, and a plan for maintaining such cover during the post‑closure care period, as required under §264.280(a)(8) and §264.280(c)(2) (§270.20(f)). This information should be included in the closure plan and, where applicable, the post‑closure care plan submitted under §270.14(b)(13);
If ignitable or reactive wastes will be placed in or on the treatment zone, an explanation of how the requirements of §264.281 will be complied with (§270.20(g));
If incompatible wastes, or incompatible wastes and materials, will be placed in or on the same treatment zone, an explanation of how §264.282 will be complied with (§270.20(h)); and
A waste management plan for EPA Hazardous Waste Nos. F020, F021, F022, F023, F026, and F027 describing how a land treatment facility is or will be designed, constructed, operated, and maintained to meet the requirements of §264.283 (§270.20(i)). This submission must address the following items as specified in §264.283:
‑‑ The volume, physical, and chemical characteristics of the wastes, including their potential to migrate through soil or to volatilize or escape into the atmosphere;
‑‑ The attenuative properties of underlying and surrounding solids or other materials;
‑‑ The mobilizing properties of other materials co‑disposed with these wastes; and
‑‑ The effectiveness of additional treatment, design, or monitoring techniques.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of §270.20, owner/operator must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare a description of plans to conduct a treatment demonstration;
Prepare a description of a land treatment program;
Prepare a description of how the unit is or will be designed, constructed, operated, and maintained;
If applicable, prepare a description of how the demonstration under §264.276(a) will be conducted;
If applicable, prepare a description of how the requirements of §264.276(b) will be complied with;
Prepare a description of the vegetative cover to be applied to closed portions of the facility and incorporate this information into the post‑closure care plan;
Develop a plan for maintaining the vegetative cover during post‑closure care period and incorporate this plan into the post‑closure plan;
Prepare an explanation of how §264.281 will be complied with for ignitable and reactive wastes;
Prepare an explanation of how §264.282 will be complied with for incompatible wastes;
Prepare a waste management plan for F‑wastes;
Submit the required information; and
File a copy of the required information at the facility.
(7) Landfills
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.21 requires owner/operators of facilities that dispose of hazardous waste in landfills to provide the following additional information:
A list of the hazardous wastes placed or to be placed in each landfill or landfill cell (§270.21(a));
Detailed plans and an engineering report describing how the landfill is or will be designed, constructed, operated and maintained to comply with the requirements of §264.301 (§270.21(b)). This submission must address the following items as specified in §264.301:
‑‑ The liner system and leachate collection and removal system (except for an existing portion of a landfill);
‑‑ The double liner and leak (leachate) detection, collection, and removal system, if required;
‑‑ For a leak detection system located in a saturated zone, the system’s design, operation, and location in relation to the saturated zone;
‑‑ The construction quality assurance plan;
‑‑ Proposed action leakage rate;
‑‑ Response action plan;
‑‑ Control of run‑on and run‑off;
‑‑ Management of collection and holding facilities associated with run‑on and run‑off control systems; and
‑‑ Control of wind dispersal of particulate matter, where applicable;
If an exemption from Subpart F of Part 264 is sought, as provided by §264.302(a), the owner/operator must submit detailed plans and an engineering report explaining the location of the saturated zone in relation to the landfill, the design of a double‑liner system that incorporates a leak detection system between the liners, and a leachate collection and removal system above the liners (§270.21(c));
A description of how each landfill, including the liner and cover systems, will be inspected in order to meet the requirements of §264.303 (a) and (b) (§270.21(d)). This information should be included in the inspection plan submitted under §270.14(b)(5);
Detailed plans and an engineering report describing the final cover which will be applied to each landfill or landfill cell at closure in accordance with §264.310(a), and a description of how each landfill will be maintained and monitored after closure in accordance with §264.310(b) (§270.21(e)). This information should be included in the closure and post‑closure plans submitted under §270.14(b)(13);
If ignitable or reactive wastes will be landfilled, an explanation of how the standards of §264.312 will be complied with (§270.21(f));
If incompatible wastes, or incompatible wastes and materials will be landfilled, an explanation of how §264.313 will be complied with (§270.21(g));
If containers of hazardous waste are to be landfilled, an explanation of how the requirements of §264.315 or §264.316, as applicable, will be complied with (§270.21(i)); and
A waste management plan for EPA Hazardous Waste Nos. F020, F021, F022, F023, F026, and F027 describing how a landfill is or will be designed, constructed, operated, and maintained to meet the requirements of §264.317 (§270.21(j)). This submission must address the following items as specified in §264.317:
‑‑ The volume, physical, and chemical characteristics of the wastes, including their potential to migrate through soil or to volatilize or escape into the atmosphere;
‑‑ The attenuative properties of underlying and surrounding solids or other materials;
‑‑ The mobilizing properties of other materials co‑disposed with these wastes; and
‑‑ The effectiveness of additional treatment, design, or monitoring techniques.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of §270.21, owner/operator must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare a list of hazardous wastes places or to be placed in each landfill or landfill cell;
Prepare plans and an engineering report describing how the landfill is or will be designed, constructed, operated and maintained;
If applicable, prepare the plans and an engineering report required under §270.21(c);
Prepare a description of how the landfill will be inspected, and incorporate this description into the inspection plan;
Prepare plans and an engineering report describing the final cover which will be applied to each landfill or landfill cell at closure, and incorporate this description into the closure and post‑closure plans;
Prepare a description of how each landfill will be maintained and monitored after closure, and incorporate this description into the closure and post‑closure plans;
Prepare an explanation of how the standards of §264.312 will be complied with for ignitable or reactive wastes;
Prepare an explanation of how §264.313 will be complied with for incompatible wastes;
Prepare an explanation of how §264.315 or §264.316 will be complied with for landfilled containers of hazardous waste;
Prepare a waste management plan for F‑wastes;
Submit the required information; and
File a copy of the required information at the facility.
(8) Miscellaneous Units
40 CFR 270.23 requires owner/operators of facilities that treat, store, or dispose of hazardous waste in miscellaneous units to provide the following additional information:
A detailed description of the unit being used or proposed for use, including the following:
‑‑ Physical characteristics, materials of construction, and dimensions of the unit;
‑‑ Detailed plans and engineering reports describing how the unit will be located, designed, constructed, operated, maintained, monitored, inspected, and closed to comply with the requirements of §§264.601 and 264.602; and
‑‑ For disposal units, a detailed description of the plans to comply with the post‑closure requirements of §264.603;
Detailed hydrologic, geologic, and meteorologic assessments and land‑use maps for the region surrounding the site that address and ensure compliance of the unit with each factor in the environmental performance standards of §264.601 (§270.23(b));
Information on the potential pathways of exposure of humans or environmental receptors to hazardous waste or hazardous constituents and on the potential magnitude and nature of such exposures (§270.23(c)); and
For any treatment unit, a report on a demonstration of the effectiveness of the treatment based on laboratory or field data (§270.23(d)).
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of §270.23, owner/operator must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare a detailed description of the unit being used or proposed for use;
Prepare hydrologic, geologic, and meteorologic assessments and land‑use maps;
Compile information on the potential exposure pathways of humans or environmental receptors to hazardous waste or hazardous constituents and on the potential magnitude and nature of exposure;
Prepare a report on a demonstration of the effectiveness of treatment;
Submit the required information; and
File a copy of the required information at the facility.
(9) Process Vents and Equipment Leaks
(i) Data items:
Sections 270.24 and 270.25 require owner/operators of facilities that have process vents subject to Subpart AA of Part 264 and/or equipment subject to Subpart BB of Part 264 to provide EPA with additional information in their Part B application. Owner/operators of facilities with process vents subject to Subpart AA must provide the following information:
For facilities that cannot install a closed‑vent system and control device to comply with Part 264 Subpart AA on the effective date that the facility becomes subject to the provisions of Parts 264 or 265 Subpart AA, an implementation schedule as specified in §264.1033(a)(2) (270.24(a));
Documentation of compliance with the process vents standards in §264.1032. Documentation of compliance should include the information listed in §270.24(b)(1)‑(3);
Where an owner/operator applies for permission to use a control device other than a thermal vapor incinerator, catalytic vapor incinerator, flare, boiler, process heater, condensator, or carbon adsorption system to comply with §264.1032, and chooses to use test data to determine the organic removal efficiency or the total organic compound concentration achieved by the control device, a performance test plan as specified in §264.1035(b)(3) (§270.24(c)); and
Documentation of compliance with §264.1033, that includes the information contained in §270.24(d)(1)‑(5).
Owner/operators of facilities with equipment subject to Subpart BB must provide the following information:
For each piece of equipment to which Subpart BB of Part 264 applies, provide the following information (§270.25(a)(1)‑(6)):
‑‑ Equipment identification number and hazardous waste management unit identification;
‑‑ Approximate equipment locations within the facility;
‑‑ Type of equipment;
‑‑ Percent by weight total organics in the hazardous waste stream at the equipment;
‑‑ Hazardous waste state at the equipment; and
‑‑ Method of compliance with the standard;
For facilities that cannot install a closed‑vent system and control device to comply with the provisions of Part 264 Subpart BB on the effective date that the facility becomes subject to the provisions of Parts 264 or 265 Subpart BB, an implementation schedule as specified in §264.1033(a)(2) (§270.25(b));
Where an owner/operator applies for permission to use a control device other than a thermal vapor incinerator, catalytic vapor incinerator, flare, boiler, process heater, condenser, or carbon adsorption system and chooses to use test data to determine the organic removal efficiency or the total organic compound concentration achieved by the control device, a performance test plan as specified in §264.1035(b)(3) (§270.25(c));
Documentation to demonstrate compliance with §264.1052 through §264.1059, which includes records required under §264.1064; and
Documentation to demonstrate compliance with §264.1060, which includes the information contained in §270.25(e)(1)‑(5).
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of §§270.24 and 270.25, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Write and submit an implementation schedule;
Prepare and submit documentation of compliance with process vent standards in §§264.1032 and 264.1033;
Write and submit a performance test plan;
Compile and submit equipment information;
Prepare and submit documentation of compliance with §§264.1052 through §264.1059; and
Prepare and submit documentation of compliance with §264.1060.
(10) Drip Pads
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.26(a)‑(c) requires owner/operators of facilities that use drip pads to collect, treat, or store hazardous waste to provide the following additional information:
A list of hazardous wastes placed or to be placed on each drip pad;
If an exemption is sought to 40 CFR Part 264, subpart F, as provided by §264.90, detailed plans and an engineering report describing how the requirements of §264.90(b)(2) will be met. [This requirement has already been burdened in this ICR. See "Releases from Regulated Units"];
Detailed plans and an engineering report describing how the drip pad is or will be designed, constructed, operated, and maintained to meet the requirements of §264.573, including as‑built drawings and specifications. This submission must address the following items as specified in §264.571:
‑‑ The design characteristics of the drip pad;
‑‑ The liner system;
‑‑ The leakage detection system;
‑‑ Practices designed to maintain drip pads;
‑‑ The associated collection system;
‑‑ Control of run‑on and run‑off to the drip pad;
‑‑ The interval at which drippage and other materials will be removed from the associated collection system and a statement demonstrating that the interval will be sufficient to prevent overflow onto the drip pad;
‑‑ Procedures for cleaning the drip pad at least once every seven days to ensure the removal of accumulated waste residues and other materials;
‑‑ Operating practices and procedures that will be followed to ensure that tracking of hazardous waste or waste constituents off the drip pad due to activities by personnel or equipment is minimized;
‑‑ Procedures for ensuring that, after removal from the treatment vessel, treated wood is held on the drip pad until drippage has ceased, including recordkeeping practices;
‑‑ Provisions for ensuring that collection and holding units associated with the run‑on and run‑off control systems are emptied or otherwise managed as soon as possible after storms to maintain design capacity of the system;
‑‑ Details of any treatment process used, and the nature and quality of the residuals;
‑‑ A description of how each drip pad will be inspected;
‑‑ A certification, signed by an independent, qualified registered professional engineer, stating that the drip pad design meets the requirements of §264.573(a)‑(f); and
‑‑ A description of how hazardous waste residues and contaminated materials will be removed from the drip pad at closure.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with the requirements of §270.26, the owner or operator must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare and submit a list of hazardous wastes; and
Develop and submit plans and an engineering report that include the items listed above.
Schedules of Compliance
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.33 requires owner/operators to specify in the permit a schedule of compliance leading to compliance with the Act and regulations, where appropriate. Data items required under this section include the following:
A schedule of compliance (§270.33(a)). The schedule must include the following information:
‑‑ A requirement for compliance as soon as possible;
‑‑ Interim requirements and the dates for their achievement, if the permit establishes a schedule of compliance which exceeds 1 year from the date of permit issuance;
‑‑ Interim dates for the submission of reports of progress toward completion of the interim requirements and a projected completion date, if the time necessary for completion of any interim requirement is more than 1 year and is not readily divisible into stages for completion; and
‑‑ A requirement that no later than 14 days following each interim date and the final date of compliance, the permittee shall notify EPA in writing of compliance or noncompliance with the interim or final requirements;
If the permittee decides to cease conducting regulated activities at a given time within the term of a permit which has already been issued, an application for a permit modification that contains a new or additional schedule leading to timely cessation of activities (§270.33(b)(1)). Permit modifications are discussed in the permit modification section of this ICR;
If the decision to cease conducting regulated activities is made before issuance of a permit whose term will include the termination date, a schedule leading to termination which will ensure timely compliance with applicable requirements (§270.33(b)(2));
If the permittee is undecided whether to cease conducting regulated activities, he or she may apply for a permit or submit an application for a permit modification to establish two schedules of compliance. The two schedules shall contain information as outlined in §270.33(b)(3) (i)‑(iv). Permit modifications are discussed in the permit modification section of this ICR; and
If the permittee decides to cease conducting regulated activities, written evidence of a firm public commitment to cease conducting regulated activities.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with the requirements of §270.33, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Develop and submit a schedule of compliance;
Develop and submit an alternative schedule of compliance under §270.33(b)(2));
Develop and submit an application for two schedules of compliance; and
Document and submit evidence of firm public commitment to cease conducting regulated activities.
Permit Modifications and Special Permits
Permit Modifications
(1) Transfer of Permits
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.40(b) explains that changes in the ownership or operational control of a facility may be made as a Class 1 modification with prior written approval of EPA. The requirements associated with applying for a Class 1 modification are discussed in this ICR under §270.42(a). In addition to the Class 1 modification requirements, owner/operators must also submit the following information in order to transfer ownership or operational control of a facility:
A written agreement containing a specific date for transfer of permit responsibility between the current and new permittees; and
A demonstration that the new owner/operator is complying with the requirements of Subpart H (financial requirements), within 6 months of the date of the change of ownership or operational control of the facility. The requirements associated with this demonstration are discussed in this ICR under §§270.14(b) (15) and (16).
(ii) Respondent activities:
In complying with the requirements of this section, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations; and
Prepare and submit the written agreement.
(2) Permit Modification at the Request of the Agency
(i) Data items:
EPA has the authority under §270.41 to modify any permit when certain causes for modification exist, including substantial alterations to the facility, new information not available at the time of permitting, new statutory requirements or regulations, and events over which the permittee has little or no control and for which there is no reasonable remedy. Facilities required to submit a Agency‑initiated permit modification will submit a Class 2 or Class 3 permit modification as described under §270.42.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In complying with the requirements for Agency‑initiated permit modifications, respondents must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare and submit the modification request;
Prepare and submit proof of public notice; and
File a record of the permit modification request at the facility.
(3) Permit Modification at the Request of the Permittee
(a) Class 1 Modifications
(i) Data items:
In making an application for a Class 1 permit modification under §270.42(a), owner/operators must provide the following information:
A notification to EPA concerning the permit modification within 7 calendar days after the change is put into effect (§270.42(a)(i)). The notice should specify the changes being made to the permit conditions or supporting documents referenced by the permit and must explain why these changes are necessary;
Applicable information required by §§270.13 through 270.21, 270.62, and 270.63 (§270.42(a)(i)); and
A written notification of the modification to all persons on the facility mailing list and the appropriate units of State and local governments (§270.42(a)(ii)). This notification must be made within 90 calendar days after the change is put into effect. For the Class 1 modifications that require prior EPA approval, the notification must be made within 90 calendar days after EPA approves the request.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In complying with the requirements for Class 1 permit modifications, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare and submit the notification required under §270.42(a)(i);
Prepare and submit the applicable information required by §§270.13 through 270.21, 270.62, and 270.63;
Prepare and submit written notification to all persons on the mailing list and the appropriate units of State and local governments; and
File a record of the permit modification request and supporting documents at the facility.
(b) Class 2 and 3 Modifications
(i) Data items:
In making an application for a Class 2 or 3 permit modification under §270.42(b) or §270.42(c), respectively, owner/operators must provide the following information:
A modification request, submitted to EPA, that:
‑‑ Describes the exact change to be made to the permit conditions and supporting documents referenced by the permit;
‑‑ Identifies that the modification is a Class 2 modification;
‑‑ Explains why the modification is needed; and
‑‑ Provides the applicable information required by §§270.13 through 270.21, 270.62, and 270.63;
A written notification of the modification request to all persons on the facility mailing list and the appropriate units of State and local governments, and publication of the notice in a major local newspaper of general circulation. The notice must be mailed and published within 7 days before or after the date of submission of the modification request, and must contain the information listed in §270.42(b)(2) (i)‑(vi) or §270.42(c)(2) (i)‑(vi). In addition, the permittee must provide to EPA evidence of the mailing and publication; and
A record of the permit modification request and supporting documents, placed in a location accessible to the public in the vicinity of the permitted facility.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In complying with the requirements for Class 2 or 3 permit modifications, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare and submit the modification request;
Prepare and distribute a written notification of the modification request;
Provide for newspaper publication of the notice;
Prepare and submit to EPA proof of public notice; and
File a record of the permit modification request and supporting documents.
(c) Request for Classification of a Permit Modification
(i) Data item:
For modifications that are not explicitly listed in appendix I of section 270.42(d)(1), the permittee may submit a Class 3 modification request, or he or she may request that the Director review the modification and classify it as a Class 1 or Class 2 modification. For such a request, the permittee must provide the Agency with the necessary information to support the requested classification.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To request a classification for a permit modification, the permittee must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations; and
Prepare and submit information to support the requested classification.
(4) Temporary Authorizations
(i) Data items:
In making an application for temporary authorization under 40 CFR 270.42(e), owner/operators must supply the following information:
A temporary authorization request containing the following information listed under §270.42(e)(2)(ii) (A)‑(C):
‑‑ A description of the activities to be conducted under the temporary authorization;
‑‑ An explanation of why the temporary authorization is necessary; and
‑‑ Sufficient information to ensure compliance with 40 CFR Part 264 standards; and
A written notification of the temporary authorization request to all persons on the facility mailing list and to the appropriate units of State and local governments (§270.42(e)(2)(iii). This notification must be made within 7 days of submission of the authorization request.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In complying with the requirements for temporary authorization, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare and submit a temporary authorization request; and
Prepare and distribute notification of the temporary authorization request to all persons on the facility mailing list and to the appropriate units of State and local governments.
(5) Newly Listed or Identified Wastes
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.42(g) allows owner/operators of facilities to continue to manage hazardous wastes listed or identified under Part 261, or to continue to manage hazardous waste in units newly regulated as hazardous waste management units if they meet specific conditions and submit the following information:
A Class 1 permit modification on or before the date of the waste or unit becomes subject to the new requirement;
A Class 2 or 3 permit modification request within 180 days of the effective date of the rule listing or identifying the waste, or subjecting the unit to RCRA Subtitle C management standards; and
In the case of land disposal units, a certification that the unit is in compliance with all applicable Part 265 ground‑water monitoring and financial assurance requirements 12 months after the effective date of the rule listing or identifying the waste, or subjecting the unit to RCRA Subtitle C management standards.
(ii) Respondent activities:
To comply with these requirements, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Submit a Class 1 permit modification;
Submit a Class 2 or 3 permit modification request within 180 days of the effective date of the rule; and
For land disposal units, submit a certification that the unit is in compliance with all applicable standards 12 months after the effective date of the rule.
(6) Corrective Action Management Units
(i) Data item:
In 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart S, EPA promulgated regulations for corrective action management units (CAMUs). Section 264.552(d) requires owner/operators to prepare and submit information to EPA, upon request, that enables EPA to designate a CAMU. Section 264.552(g) provides for owner/operators of permitted facilities to modify their permit to incorporate a CAMU.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with section 264.552(d), owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations; and
Prepare and submit information to enable EPA to designate a CAMU.
Expiration and Continuation of Permits
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.50 explains that all RCRA permits must be renewed no later than 10 years after the date of issuance. Under §270.51, owner/operators renewing an expiring permit must submit an application containing the information required under §270.14 and the applicable sections of §§270.15 through 270.29.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owner/operators submitting a Part B permit renewal application must perform the same activities as owner/operators of new facilities submitting their first permit application, as described above.
Special Forms of Permits
(1) Permits By Rule
40 CFR 270.60 states that ocean disposal barges or vessels, injection wells, and publicly owned treatment works (POTWs) will be deemed to have a RCRA permit if the conditions listed under §270.60 (a)‑(c) are met. In complying with these sections, owner/operators of POTWs or ocean disposal barges or vessels must submit all information required under §§264.11, 264.71, 264.72, 264.73(a) and (b)(1), 264.75, and 264.76. In addition, owner/operators of POTWs must submit the information required under §264.101. Owner/operators of injection wells must also submit the information required under §264.101, as well as the information required under §270.14(d). The specific information requirements of these sections and the respondent burden associated with them are discussed in the Notification ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0028), the Manifests ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0039), the General Facility Standards ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0120), or in other sections of this ICR.
(2) Hazardous Waste Incinerator Permits
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.62 requires owner/operators of hazardous waste incinerators to provide a proposed trial burn plan and trial burn results as part of the Part B permit application. Specific requirements associated with the proposed trial burn and its results are included in this ICR under the requirements for §270.19. In addition to these requirements, applicants for a hazardous waste incinerator permit must also submit the following information with their Part B application:
For an extension of the operational period beyond 720 hours, a request demonstrating why good cause exists for such an extension (270.62(a));
A statement suggesting the conditions necessary to operate in compliance with the performance standards of §264.343 during the period following completion of physical construction (§270.62(a)(1)). This statement should include, at a minimum, restrictions on waste constituents, waste feed rates and the operating parameters identified in §264.345;
A statement identifying the conditions necessary to operate in compliance with the performance standards of §264.343 during the period following completion of the trial burn period and prior to final modification of the permit conditions to reflect the trial burn results (§270.62(c)(1)). The statement should include, at a minimum, restrictions on waste constituents, waste feed rates, and the operating parameters in §264.345; and
A certification, in the form of a signature, on behalf of the applicant must be provided on all submissions by a person authorized to sign a permit application or report under §270.11 (§270.62(b)(9).
(ii) Respondent activities:
In complying with the requirements of this section, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare and submit the extension request;
Provide on all submissions the signature of a person authorized to sign a permit application or a report; and
Prepare and submit the required statements.
(3) Permits for Land Treatment Demonstrations Using Field Test or Laboratory Analyses
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.63 allows owner/operators to obtain a treatment demonstration permit for the purpose of meeting the requirements of §264.272. The permit may be issued either as a treatment or disposal permit covering only the field test or laboratory analyses, or as a two‑phase facility permit covering the field tests, or laboratory analyses, and design construction, operation and maintenance of the land treatment unit. When owner/operators who have been issued a two‑phase permit have completed the treatment demonstration, they must submit the following information in accordance with §270.63(c):
A certification, signed by a person authorized to sign a permit application report under §270.11, that the field tests or laboratory analyses have been carried out in accordance with the conditions specified in phase one of the permit for conducting such tests or analyses; and
All data collected during the field tests or laboratory analyses. This information must be submitted to EPA within 90 days of completion of those tests and analyses unless EPA approves a later date.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In complying with the requirements of this section, owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations;
Prepare and submit the certification; and
Compile and submit the data collected during the field tests or laboratory analyses.
(4) Interim Permits for UIC Wells
40 CFR 270.64 states that EPA may issue a permit to any Class I UIC well injecting hazardous wastes within a State in which no UIC program has been approved or promulgated. Any such permit shall apply and insure compliance with all applicable requirements of 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart R. However, these Subpart R regulations have not yet been promulgated. Therefore, there are no activities associated with this section.
(5) Research, Development, and Demonstration Permits
(i) Data items:
40 CFR 270.65 allows EPA to issue a research, development, and demonstration permit for any hazardous waste treatment facility which proposes to utilize an innovative and experimental hazardous waste treatment technology or process for which permit standards for such experimental activity have not been promulgated under Part 264 or 266. Applicants for this type of permit must submit the same information required for a Part B permit, as discussed above.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Owner/operators applying for a research, development, and demonstration permits must perform the same activities as owner/operators applying for a Part B permit, as described above.
Interim Status
Termination of Interim Status
(i) Data item:
40 CFR section 270.73(d) states that interim status terminates 12 months after an existing land disposal facility comes under permit requirements resulting from statutory or regulatory amendments, unless the facility submits a Part B application before the 12‑month period expires and certifies that the facility is in compliance with all applicable ground‑water monitoring and financial responsibility requirements. The submittal of the Part B application has already been burdened in this ICR.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In order to comply with section 270.73(d), owner/operators must perform the following activities:
Read the regulations; and
Prepare and submit the certification.
5. THE INFORMATION COLLECTED ‑‑ AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
5(a) Agency Activities
Demonstrations and Exemptions from Requirements
Releases from Regulated Units
Agency activities associated with demonstrations for the exemption of facility owner/operators from Subpart F requirements regarding releases into the uppermost aquifer include reviewing and evaluating demonstrations, reviewing certifications (from qualified biologists or geotechnical engineers) of no‑migration demonstrations under §264.90(b)(4), and entering the information into a data base.
Specific Unit Requirements
(1) Tank Systems
Agency activities associated with tank system requirements include reviewing notifications of intent to make a demonstration, demonstrations under §264.193(g)(1), demonstrations for exemption from the 24‑hour leak detection requirement and/or the 24‑hour waste removal requirement, and written descriptions of equivalent secondary containment devices; and entering the information into a data base.
(2) Surface Impoundments
Agency activities associated with surface impoundment requirements include reviewing demonstrations for exemption from the double liner requirement (§264.221(d)), and demonstrations for a waiver of double liner requirements for monofills, and entering the information into a data base.
(3) Waste Piles
Agency activities associated with waste pile requirements include reviewing demonstrations for exemption from the liner and leachate collection system requirements of §264.251(b) and demonstrations for exemption from the double liner and leachate collection system requirements of §264.251(d), and entering the information into a data base.
(4) Land Treatment
Agency activities associated with land treatment requirements include reviewing and evaluating demonstrations and entering the information into a data base.
(5) Landfills
Agency activities associated with landfill requirements include reviewing and evaluating demonstrations and entering the information into a data base.
(6) Incinerators
Agency activities associated with incinerator requirements include reviewing demonstrations and entering the information into a data base.
Contents of the Part B Application
General Information
Agency activities associated with petitioning the Regional Administrator for a determination that a post‑closure permit is not required because the closure (of surface impoundments, land treatment units, and waste piles closing by removal or decontamination under Part 265 standards) meets applicable Part 264 closure standards include reviewing and approving petitions and entering the information into a data base.
Permit Application
Agency activities associated with the requirement that Part B permit applications submitted by owner/operators of facilities that store, treat, or dispose of hazardous waste in a surface impoundment of landfill be accompanied by information on the potential for the public to be exposed to hazardous wastes or hazardous constituents through releases related to the unit include reviewing the required data and entering the information into a data base.
General Requirements
Agency activities associated with demonstrations by owner/operators to obtain allowance from Regional Administrators to submit information prescribed in Part B on a case‑by‑case basis include reviewing and approving demonstration and entering the information into a data base.
General Facility Standards
Agency activities associated with the requirement that owner/operators of hazardous waste management facilities submit in their Part B permit applications information on compliance with general facility standards include reviewing the required information and entering it into a data base.
Financial Assurance
(1) Cost Estimates for Closure and Post‑Closure Care
Agency activities associated with cost estimates for closure and post‑closure care include reviewing written cost estimates and entering the information into a data base. Agency activities associated with post‑closure cost estimates for interim status facilities are discussed in the General Facility Standards (OMB Control No. 2050-0120).
(2) Financial Assurance for Closure and Post‑Closure Care
Agency activities associated with the requirements for financial assurance for closure and post‑closure care include reviewing the documentation of financial assurance submitted by the respondent and entering the information into a data base.
(3) Use of a Financial Mechanism for Multiple Facilities
The information required under this section will be submitted with the information provided by the owner/operator to establish financial assurance mechanisms. Therefore, this ICR assumes that any agency activities related to the requirements of this section are already covered under the previous sections.
(4) Liability Requirements
(a) Coverage for Sudden or Nonsudden Accidental Occurrences
Agency activities associated with the establishment of liability coverage for sudden or nonsudden accidental occurrences include reviewing the information submitted and entering information into a data base.
(b) Request for Variance
Agency activities associated with allowing owners/operators to obtain a variance from EPA include reviewing requests for variance, including any technical or engineering information required by EPA.
(c) Adjustments by the Regional Administrator
Agency activities associated with allowing the Agency to adjust the level of financial responsibility required under §264.147 to protect human health and the environment include reviewing any information requested by the Agency and, if the Agency decides to adjust the level or type of coverage, permit modifications. The Agency burden associated with permit modifications is discussed below under the section entitled "Permit Modifications."
(5) Coverage by a State Financial Mechanism
Agency activities associated with establishing coverage by State financial mechanisms include reviewing letters from owner/operators, written evidence of the establishment of State‑required financial assurance mechanisms, or letters from the State describing the State’s assumption of responsibility and including the information specified above, and any additional information requested by EPA.
Other Requirements
(1) Topographical Map
Agency activities associated with the requirement that owner/operators must provide a topographical map include reviewing the topographical map.
(2) Case‑By‑Case Extensions and Petitions to Allow Land Disposal of a Waste Prohibited Under Subpart C of Part 268
Agency activities associated with the requirement that owner/operators of land disposal facilities that have received approval for a case‑by‑case extension under §268.5 or a petition under §268.6 submit a copy of the notice of approval for the extension or petition with their Part B permit application include reviewing the notice of approval.
Ground‑Water Protection
(1) General Ground‑Water Monitoring Requirements
Agency activities associated with general ground‑water monitoring requirements include reviewing and approving the ground‑water monitoring program.
(2) Detection and Monitoring Programs
Agency activities associated with the requirement that owner/operators develop a detection monitoring program if the presence of hazardous constituents has not been detected in the ground water at the time of permit application include reviewing all information submitted, and entering the information into a data base.
(3) Compliance Monitoring Program
Agency activities associated with the requirement that owner/operators develop a detection monitoring program if the presence of hazardous constituents has been detected in the ground water at the point of compliance at the time of permit application include reviewing all information submitted, and entering the information into a data base.
(4) Corrective Action Program
Agency activities associated with the establishment of a corrective action program include reviewing all information submitted, and if applicable, reviewing schedules of information required in §§270.14(c)(8)(iii) and (iv) in the permit and demonstrations that alternate concentration limits will protect human health and the environment. EPA will also enter the information into a data base.
Solid Waste Management Units
Agency activities associated with Part B information requirements for solid waste management units include reviewing all required information and entering it into a data base.
Specific Part B Information Requirements
(1) Containers
Agency activities associated with information requirements for owner/operators of facilities that store containers of hazardous waste include reviewing written descriptions of containment systems, no free liquids demonstrations, documentation of compliance with §264.176 and §264.177, and written descriptions of procedures used to ensure compliance with §264.177(a) and (b), and 264.17(b) and(c); and entering the information into the data base.
(2) Tank Systems
Agency activities associated with information requirements for owner/operators of facilities that use tanks to store or treat hazardous waste include reviewing assessments of new or existing tank systems, information required under §270.16(b)‑(e), descriptions of tank system installations, descriptions of how the secondary containment system for each tank system is or will be designed, constructed, and operated, descriptions of controls and practices to prevent spills and overflows, and descriptions of how operating procedures and tank system and facility design will achieve compliance with the requirements of §§264.198 and 264.199; and entering the information into a data base.
(3) Surface Impoundments
Agency activities associated with information requirements for owner/operators of facilities that store, treat, or dispose of hazardous waste in surface impoundments include reviewing the following information: plans and engineering reports describing how surface impoundments will be designed, constructed, operated, and maintained; descriptions of inspection procedures that are included in inspection plans; certifications or statements from qualified engineers; in contingency plans, descriptions of procedures for removing surface impoundments from service; in closure and post‑closure plans, descriptions of hazardous waste residues and contaminated materials that will be removed from the unit at closure and plans and engineering reports describing compliance with §§264.228(a)(2) and (b); explanations of how §264.229 will be complied with for ignitable or reactive wastes; explanations of how §264.230 will be complied with for incompatible wastes; and waste management plans for F‑wastes. The Agency will also enter the information into a data base.
(4) Waste Piles
Agency activities associated with information requirements for owner/operators of facilities that store or treat hazardous waste in waste piles include reviewing the following information: explanations of how §264.250(c) will be complied with if an exemption from §264.251 is sought; engineering reports describing how §264.90(b)(2) will be complied with if an exemption from Subpart F of Part 264 is sought; plans and engineering reports describing how the waste pile will be designed, constructed, operated, and maintained; in inspection plans, descriptions of inspection procedures; if applicable, descriptions of processes and equipment used to treat piles, and descriptions of the nature and quantity of residuals; explanations of how §264.256 will be complied with for ignitable or reactive wastes; explanations of how §264.257 will be complied with for incompatible wastes; in post‑closure plans, descriptions of hazardous waste residues and contaminated materials to be removed from piles at closure; in closure and post‑closure plans, plans and engineering reports describing how §§264.310(a) and (b) will be complied with; and waste management plans for F‑wastes. The Agency will also enter the information into a data base.
(5) Incinerators
Agency activities associated with information requirements for owner/operators of facilities that incinerate hazardous wastes include reviewing the following information: documentation for ignitable, corrosive, or reactive wastes as required under §270.19(a) (1)‑(4); trial burn plans; reports on results of trial burns; and information submitted in lieu of a trial burn. The Agency will also enter the information into a data base.
(6) Land Treatment
Agency activities associated with information requirements for owner/operators of facilities that use land treatment to dispose of hazardous waste include reviewing the following information: descriptions of plans to conduct treatment demonstrations; descriptions of land treatment programs; descriptions of how the units are or will be designed, constructed, operated, and maintained; if applicable, descriptions of how demonstrations under §264.276(a) will be conducted; if applicable, descriptions of how the requirements of §264.276(b) will be complied with; in post‑closure care plans, descriptions of vegetative cover to be applied to closed portions of facilities; in post‑closure plans, plans for maintaining vegetative cover during the post‑closure care period; explanations of how §264.281 will be complied with for ignitable and reactive wastes; explanations of how §264.282 will be complied with for incompatible wastes; and waste management plans for F‑wastes. The Agency will also enter the information into a data base.
(7) Landfills
Agency activities associated with information requirements for owner/operators of facilities that dispose of hazardous waste in landfills include reviewing the following information: list of hazardous wastes in each landfill or landfill cell; plans and engineering reports describing how the landfill is or will be designed, constructed, operated, and maintained; if applicable, plans and engineering reports required under §270.21(c); in inspection plans, descriptions of how landfills will be inspected; in closure and post‑closure plans, plans and engineering reports describing the final cover which will be applied to each landfill or landfill cell at closure; in closure and post‑closure plans, descriptions of how each landfill will be maintained and monitored after closure; explanations of how standards of §264.312 will be complied with for ignitable or reactive wastes; explanations of how §264.313 will be complied with for incompatible wastes; explanations of how §264.315 or §264.316 will be complied with for landfilled containers of hazardous waste; and waste management plans for F‑wastes. The Agency will also enter the information into a data base.
(8) Miscellaneous Units
Agency activities associated with information requirements for owner/operators of facilities that treat, store, or dispose of hazardous waste in miscellaneous units include reviewing the following information: detailed descriptions of units being used or proposed for use; hydrologic, geologic, and meteorologic assessments and land‑use maps; information on the potential exposure pathways of humans or environmental receptors to hazardous waste or hazardous constituents and on the potential magnitude and nature of exposure; and reports on demonstrations of the effectiveness of treatment. The Agency will also enter the information into a data base.
(9) Process Vents and Equipment Leaks
Agency activities associated with the requirements for process vents and equipment leaks include reviewing implementation schedules, documentation of compliance with §§264.1052‑.1059, 264.1060, .1032 and .1033, performance test plans, and equipment information. The Agency will also enter the information into a data base.
(10) Drip Pads
Agency activities associated with the requirements for drip pads include reviewing lists of hazardous wastes placed or to be placed on each drip pad, reviewing plans and engineering reports, and entering the information into a data base.
Schedules of Compliance
Agency activities associated with the requirement that owner/operators specify in permits a schedule of compliance leading to compliance with the Act and regulations, where appropriate, include reviewing the following information: schedules of compliance, alternative schedules of compliance under §270.33(b)(2), applications for two schedules of compliance, and evidence of firm public commitment to cease conducting regulated activities. The Agency will also enter the information into a data base.
Permit Modifications and Special Permits
Permit Modifications
(1) Transfer of Permits
Agency activities associated with the transfer of permits includes reviewing written agreements and entering the information into a data base.
(2) Permit Modification at the Request of the Agency
Agency activities associated with Agency‑initiated permit modifications include reviewing the modification request and entering the information into a data base.
(3) Permit Modification at the Request of the Permittee
(a) Class 1 Modifications
Agency activities associated with applications for Class 1 permit modifications include reviewing notifications required under §270.42(a)(i), and applicable information required by §§270.13 through 270.21, 270.62, and 270.63, and entering the information into a data base.
(b) Class 2 and 3 Modifications
Agency activities associated with applications for Class 2 or 3 permit modifications include reviewing modifications requests and written notifications, and entering the information into a data base.
(c) Request for Classification of a Permit Modification
Agency activities associated with requests for classification of a permit modification include reviewing the information submitted in support of a request, making a determination on the request, and entering the information into a data base.
(4) Temporary Authorizations
Agency activities associated with applications for temporary authorization include reviewing temporary authorization requests and entering the information into a data base.
(5) Newly Regulated Wastes and Units
Agency activities associated with the requirement that to be authorized to continue managing wastes listed or identified under 40 CFR Part 261 owner/operators of land disposal units certify that units are in compliance with all applicable Part 265 ground‑water monitoring and financial responsibility requirements include reviewing certifications.
(6) Corrective Action Management Units
EPA must review information submitted for the designation of a CAMU.
Expiration and Continuation of Permits
Agency activities associated with renewing existing permits include conducting the same activities as they would for initial permit applications.
Special Forms of Permits
(1) Permits By Rule
The specific information requirements and agency activities for this section are discussed in the Notification ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0028), the Manifests ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0039), and the General Facility Standards ICR (OMB Control No. 2050-0120).
(2) Hazardous Waste Incinerator Permits
Agency activities associated with the requirement that owner/operators of hazardous waste incinerators applying for permits submit information in addition to the trial burn plan include reviewing requests to extend the operational period, reviewing the required statements and certifications, and entering the information into a data base.
(3) Permits for Land Treatment Demonstrations Using Field Test or Laboratory Analyses
Agency activities associated with the requirement that owner/operators who have been issued a two‑phase permit and have completed treatment demonstrations submit information in accordance with §270.63(c) include reviewing certifications and data collected during field tests or laboratory analyses, and entering the information into a data base.
(4) Interim Permits for UIC Wells
There are no Agency activities associated with this section.
(5) Research, Development, and Demonstration Permits
Agency activities associated with research, development, and demonstration permits for hazardous waste treatment facilities proposing to utilize innovative and experimental treatment technologies or processes for which permit standards for such experimental activity have not been promulgated under Part 264 or 266 conduct the same activities as they would for a Part B permit.
Interim Status
Termination of Interim Status
Agency activities associated with interim status facilities include reviewing each certification that an interim status facility is in compliance with all applicable ground‑water monitoring and financial responsibility requirements.
5(b) Collection Methodology and Management
In collecting and analyzing the information required for Part B permit applications, permit modifications and special permits, EPA uses state‑of‑the‑art electronic equipment such as personal computers and applicable data base software, when appropriate.
5(c) Small Entity Flexibility
Some respondents will be small organizations. In certain cases they will be able to complete recordkeeping, reporting, and application requirements in less time than large organizations because their permits will not be as detailed, or they will not be required to conduct as many monitoring activities or submit as many reports because they have fewer activities requiring monitoring and reporting. However, a parallel does not always exist between the size of an organization and the amount of time needed to maintain records or submit reports. For example, a chemical landfill may be classified as a small business, but the facility employs numerous processes that necessitate a detailed application and supporting records and reporting. EPA has taken steps to minimize the burdens for all facilities whether they are small businesses or not.
5(d) Collection Schedule
Demonstrations and Exemptions from Requirements
Because the regulations do not provide a specific time frame for submitting exemption demonstrations, this ICR assumes that all demonstrations are submitted along with the Part B application. However, tank system owner/operators must notify EPA of their intent to submit a demonstration for a variance from secondary containment (40 CFR 264.193(h)(1)) as follows:
For existing tank systems, at least 24 months prior to the date that secondary containment must be provided; and
For new tank systems, at least 30 days prior to entering into a contract for installation.
In addition, the demonstration for a variance must be completed within 180 days after notifying the Regional Administrator of an intent to conduct the demonstration.
Contents of the Part B Application
Owner/operators of existing TSDFs may be required to submit their Part B application at any time after promulgation of Phase II. Owner/operators may voluntarily submit their Part B application at any time. Owner/operators of new TSDFs must submit their Part B application at least 180 days before physical construction is expected to commence.
This ICR assumes that all information required under §270.14 through §270.29 is submitted along with the Part B application, with the following exceptions:
General Information
Owners/operators of surface impoundments, land treatment units, and waste piles closing by removal or decontamination under Part 265 standards may submit a petition to EPA for a determination that a post‑closure permit is not required. If the owner/operator has not submitted a Part B application for a post‑closure permit, the owner/operator may petition the EPA for a determination that a post‑closure permit is not required. If the owner/operator has submitted a Part B application for a post‑closure permit, the owner/operator may request a determination based on information contained in the application. The collection schedule for these activities will vary, but submissions should be made to EPA within a reasonable time frame.
Financial Assurance
(1) Cost Estimates for Closure and Post‑Closure Care
Cost estimates and documentation of financial instruments for closure and post‑closure care must be submitted to EPA at least 60 days prior to the initial receipt of hazardous waste for treatment, storage, or disposal. Insurance documentation must be submitted within the same time frame. Respondents must also submit any requested information and permit modifications to EPA within a reasonable time, if EPA decides that an adjustment is necessary.
Owner/operators of new facilities must submit proof of coverage by a State financial mechanism to EPA at least 60 days before the date on which hazardous waste is first received for treatment, storage, or disposal. If a State assumes legal responsibility for a facility’s compliance with the closure, post‑closure care, or liability requirements, the owner/operator must submit evidence of this to EPA within a reasonable time.
Permit Modifications and Special Permits
Permit Modifications
(1) Transfer of Permits
Upon a change of ownership or operational control of a facility, the new owner/operator must submit a revised permit application to EPA no later than 90 days prior to the scheduled change. When a transfer of ownership or operational control occurs, the old owner/operator will comply with the requirements of 40 CFR Part 264, Subpart H until the new owner/operator has demonstrated that he or she is complying with the requirements of that Subpart. The new owner/operator must demonstrate compliance with Subpart H requirements within six months of the date of the change of ownership or operational control of the facility.
(2) Permit Modification at the Request of the Agency
Permit modifications made at the request of the Agency are submitted according to the time frame discussed below for permit modifications made at the request of the permittee.
(3) Permit Modification at the Request of the Permittee
(a) Class 1 Modifications
The permittee must notify EPA concerning the Class 1 modification by certified mail or other means that establishes proof of delivery within seven calendar days after the change is put into effect. The permittee must also send a notice of the modification to all persons on the facility mailing list within 90 calendar days after the change. For Class 1 modifications that require prior EPA approval, the notification must be made within 90 calendar days after EPA approves the request.
(b) Class 2 and 3 Modifications
The permittee must send a notice of the Class 2 or 3 modification request to all persons on the facility mailing list and publish the notice in a major newspaper of general circulation within seven days before or after the date of submission of the modification request.
(c) Requests for Classification of a Permit Modification
For permit modifications that are not specifically listed in appendix I of section 270.42, a permittee may submit information in support of a request for a Class 1 or Class 2 permit modification. The permittee must submit this information and receive the Agency’s determination before making the modification.
(4) Temporary Authorizations
The permittee must send a notice regarding the temporary authorization request to all persons on the facility mailing list. This notification must be made within seven days of the submission of the authorization request.
(5) Newly Listed or Identified Wastes
The permittee is authorized to continue managing wastes listed or identified as hazardous waste if the owner/operator submits a Class 1 modification request on or before the date on which the waste becomes subject to the new requirements. In the case of Class 2 and 3 modifications, owner/operators must submit a complete permit modification request within 180 days after the effective date of the listing or the waste identification in order to maintain the permit authorization.
(6) Corrective Action Management Units
EPA collects information used to designate a CAMU for the purpose of implementing corrective action requirements under section 264.101 and RCRA section 3008(h). There is no specific collection schedule.
Special Forms of Permits
(1) Hazardous Waste Incinerator Permits
An owner or operator must submit a request for extension of the operational period if he or she believes that an incinerator unit requires more than 720 hours of operating time to bring it to the point of readiness for a trial burn.
(2) Permits for Land Treatment Demonstrations Using Field Test or Laboratory Results
Owners/operators must submit a certification that the field tests or laboratory analyses have been carried out to EPA within 90 days of the completion of those tests or analyses, unless EPA approves a later date.
Interim Status
Termination of Interim Status
An owner or operator of a land disposal facility that becomes subject to permit requirements must submit, within 12 months of becoming subject to regulation, a Part B application and a certification that the facility is in compliance with all applicable ground‑water monitoring and financial responsibility requirements.
6. ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF COLLECTION
6(a) Estimating Respondent Burden
EPA estimates annual respondent burden hours associated with all of the information collection requirements covered in this ICR in Exhibits 1 through 3. These exhibits detail the number of hours required to conduct each discrete information collection activity. Exhibit 4 provides the annual bottom‑line respondent burden associated with all information collection requirements included in this ICR.
6(b) Estimating Respondent Cost
(i) Estimating Labor Costs
EPA estimates an average hourly respondent labor cost (including overhead) of $121.19 for legal staff, $86.16 for managerial staff, $41.51 for technical staff, and $24.31 for clerical staff. These wage rates are based on the rates from last renewal, multiplied by an inflation rate of 3.4% to bring them up to 2022 rates.
(ii) Estimating Capital Costs
EPA estimates that facilities complying with Part 270 will incur capital costs associated with some of the respondent activities. These capital costs include the cost of purchasing equipment, such as file cabinets, photocopiers, and monitoring equipment. Exhibits 1 through 3 detail these costs, if any, for each discrete information collection activity. Exhibit 4 provides the annual bottom-line respondent capital cost associated with all information collection requirements included in this ICR.
(iii) Estimating Operations and Maintenance (O&M) Costs
In complying with Part 270 requirements, facilities may incur operations and maintenance (O&M) costs associated with some respondent activities. O&M costs include mail submittals, purchased materials costs, and certain lump-sum purchased service costs. Exhibits 1 through 3 detail these costs, if any, for each discrete information collection activity. Exhibit 4 provides the annual bottom-line respondent O&M cost associated with all information collection requirements included in this ICR.
6(c) Estimating State Agency Burden and Costs
Forty-eight (48) States are authorized for the Part B permit program. The two States that are not authorized, Alaska and Iowa, have not received any Part B permits for the last 15 years. EPA estimates the State Agency hour and cost burden associated with all information collection requirements covered in this ICR in Exhibits 5 through 7. These exhibits detail the number of hours required to conduct each discrete information collection activity. Exhibit 8 provides the annual bottom‑line State Agency burden associated with all information collection requirements included in this ICR.
As shown in the exhibit, EPA estimates an average hourly State agency labor cost (including overhead) of $64.64 for legal staff, $60.68 for managerial staff, $36.30 for technical staff, and $23.17 for clerical staff. These wage rates are based on the rates from last renewal, multiplied by an inflation rate of 3.4% to bring them up to 2022 rates.
6(d) Estimating the Respondent Universe and Total Burden and Costs
Table 1 presents the estimated annual universe of facilities subject to the various types of RCRA permitting requirements covered in this ICR. Table 2 presents the estimated annual universe of facilities and units covered by RCRA Part B permit applications. Table 3 presents the estimated annual universe estimates of facilities and units covered by a RCRA post-closure permit applications.
Table 1
Estimated Annual
Universe of Facilities Affected by RCRA Part B and |
|||
Description |
Number of Facilities |
||
Private |
State/Local |
Total |
|
PART B PERMIT APPLICATIONS |
|||
Total facilities submitting Part B permit applications |
6 |
0 |
6 |
Interim facilities submitting Part B permit applications |
0 |
0 |
0 |
New facilities submitting Part B permit applications |
6 |
0 |
6 |
POST-CLOSURE PERMIT APPLICATIONS |
|||
Facilities applying for post-closure permits |
10 |
0 |
10 |
PERMIT MODIFICATIONS AND SPECIAL TYPES OF PERMITS |
|||
Total facilities submitting Part B permit modifications |
33 |
0 |
33 |
Permit transfers |
2 |
0 |
2 |
Agency-initiated modifications |
1 |
0 |
1 |
Permittee-initiated modifications (Class 1) |
19 |
0 |
19 |
Permittee-initiated modifications (Class 2 or 3) |
11 |
0 |
11 |
RCRAInfo, Permit and Handler Modules. Data current as of September 2022.
Table 2
Estimated Annual
Universe of Facilities and Units |
||||||
Unit Type |
Number of Facilities |
Number of Units |
||||
Private |
State |
Total |
Private |
State |
Total |
|
Containers |
15 |
0 |
15 |
46 |
0 |
46 |
Tank Systems |
15 |
0 |
15 |
98 |
0 |
98 |
Incinerators |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
Land Disposal Units |
9 |
0 |
9 |
14 |
0 |
14 |
Surface Impoundments |
2 |
0 |
2 |
9 |
0 |
9 |
Waste Piles |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Land Treatment Units |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Landfills |
3 |
0 |
3 |
5 |
0 |
5 |
Miscellaneous Units |
4 |
0 |
4 |
8 |
0 |
8 |
RCRAInfo, Permit and Handler Modules. Data current as of September 2022.
Table 3
Estimated Annual
Universe of Facilities and Units |
||||||
Unit Type |
Number of Facilities |
Number of Units |
||||
Private |
State |
Total |
Private |
State |
Total |
|
Containers |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Tank Systems |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
Incinerators |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Land Disposal Units |
12 |
0 |
12 |
23 |
0 |
23 |
Surface Impoundments |
4 |
0 |
4 |
10 |
0 |
10 |
Waste Piles |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
Land Treatment Units |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
Landfills |
6 |
0 |
6 |
11 |
0 |
11 |
Miscellaneous Units |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
RCRAInfo, Permit and Handler Modules. Data current as of September 2022.
Demonstrations and Exemptions from Requirements
Exhibit 1 details the universe of facilities affected by each discrete information collection activity associated with this group of requirements. In addition, Exhibit 1 presents the total burden and cost for each of these information collection activities based on this number of affected facilities and the burden and cost estimates developed under Sections 6(a) and 6(b).
Contents of the Part B Application
Exhibit 2 details the universe of facilities affected by each discrete information collection activity associated with this group of requirements. In addition, Exhibit 2 presents the total burden and cost for each of these information collection activities based on this number of affected facilities and the burden and cost estimates developed under Sections 6(a) and 6(b).
Permit Modifications and Special Permits
Exhibit 3 details the universe of facilities affected by each discrete information collection activity associated with this group of requirements. In addition, Exhibit 3 presents the total burden and cost for each of these information collection activities based on this number of affected facilities and the burden and cost estimates developed under Sections 6(a) and 6(b).
6(e) Bottom Line Burden Hours and Cost Tables
Annual Respondent Burden
|
Respondents |
Responses |
Hours |
O&M/Capital Costs |
Total Annual Cost |
Private Sector |
106 |
1,898 |
18,510 |
$3,761,707 |
$4,723,589 |
State Agencies |
48 |
380 |
930 |
$0 |
$193,147 |
Total |
154 |
2,278 |
19,440 |
$3,761,707 |
$4,916,736 |
6(f) Reasons for Change in Burden
The overall annual burden associated with the Part B requirements is 19,440 hours, which is a decrease of 646 hours under the previous version of this ICR. This difference is due to the smaller number of affected facilities, based on the current information and reporting requirements from the RCRAInfo database.
6(g) Burden Statement
The annual public reporting and recordkeeping burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 9.75 hours per response. Burden means the total time, effort, or financial resources expended by persons to generate, maintain, retain, or disclose or provide information to or for a Federal agency. This includes the time needed to review instructions; develop, acquire, install, and utilize technology and systems for the purposes of collecting, validating, and verifying information, processing and maintaining information, and disclosing and providing information; adjust the existing ways to comply with any previously applicable instructions and requirements; train personnel to be able to respond to a collection of information; search data sources; complete and review the collection of information; and transmit or otherwise disclose the information. An agency may not conduct or sponsor, and a person is not required to respond to, a collection of information unless it displays a currently valid OMB control number. The OMB control numbers for EPA's regulations are listed in 40 CFR part 9 and 48 CFR chapter 15.
To comment on the Agency's need for this information, the accuracy of the provided burden estimates, and any suggested methods for minimizing respondent burden, including the use of automated collection techniques, EPA has established a public docket under Docket ID Number EPA-HQ-OLEM-2018-0758, which is available for online viewing at www.regulations.gov, or in person viewing at the EPA Docket Center (EPA/DC), EPA West, Room 3334, 1301 Constitution Avenue, NW, Washington, D.C. The EPA Docket Center Public Reading Room is open from 8:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m., Monday through Friday, excluding legal holidays. The telephone number for the Reading Room is (202) 566‑1744.
An electronic version of the public docket is available at http://www.regulations.gov. This site can be used to submit or view public comments, access the index listing of the contents of the public docket, and to access those documents in the public docket that are available electronically. When in the system, select "search," then key in the Docket ID Number identified above. Also, you can send comments to the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs, Office of Management and Budget, 725 17th Street, NW, Washington, D.C. 20503, Attention: Desk Officer for EPA. Please include the EPA Docket ID Number EPA-HQ-OLEM-2018-0758, and OMB Control Number 2050–0009 in any correspondence.
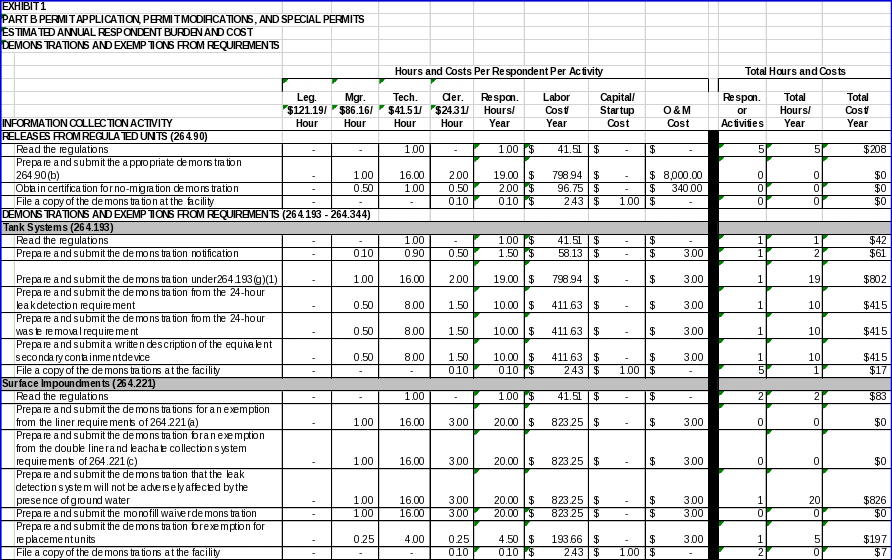
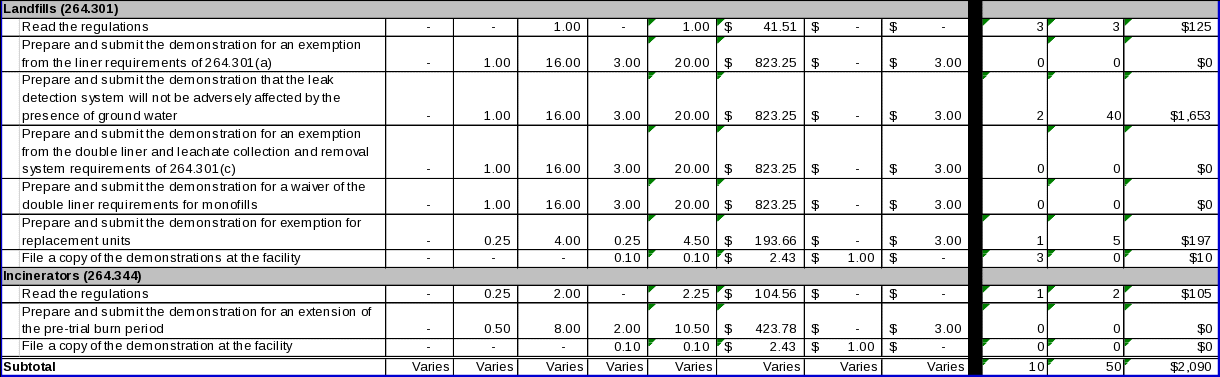
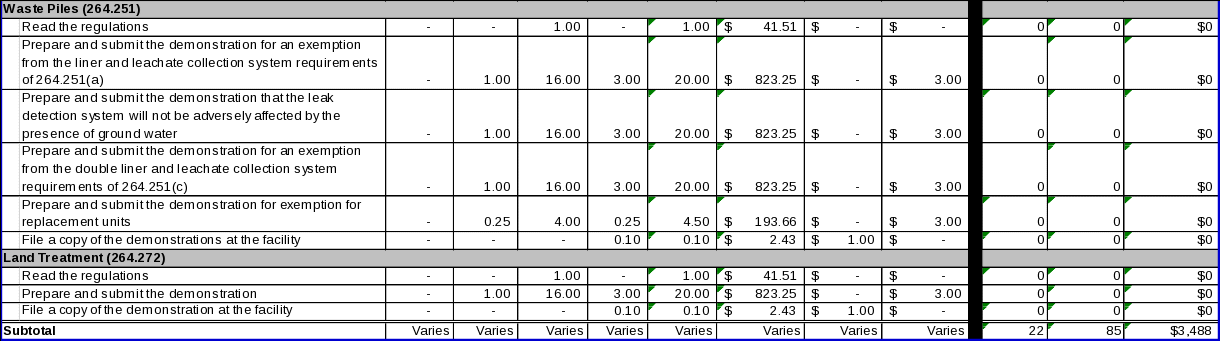
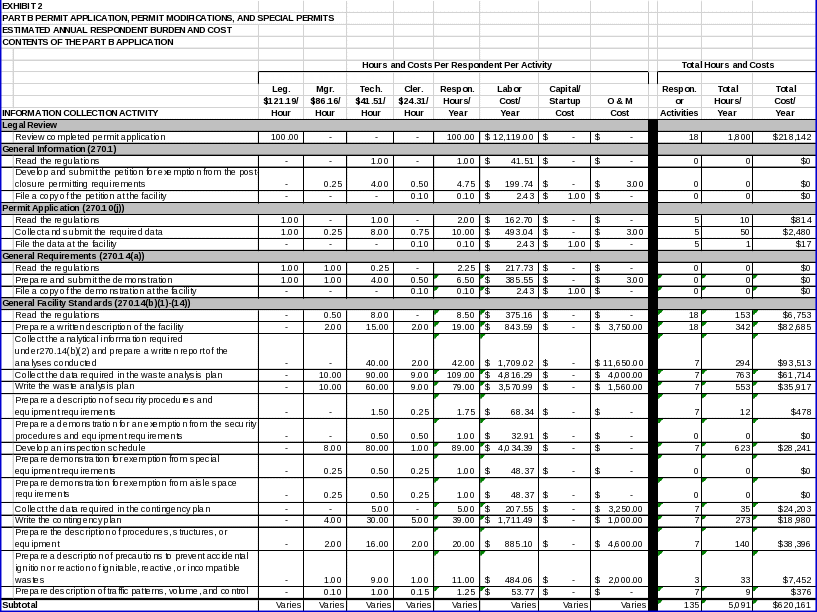
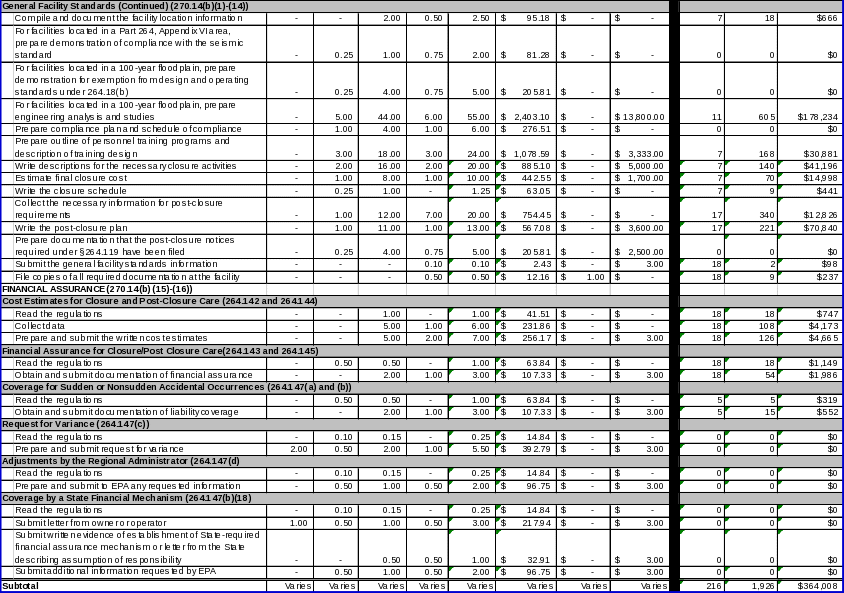
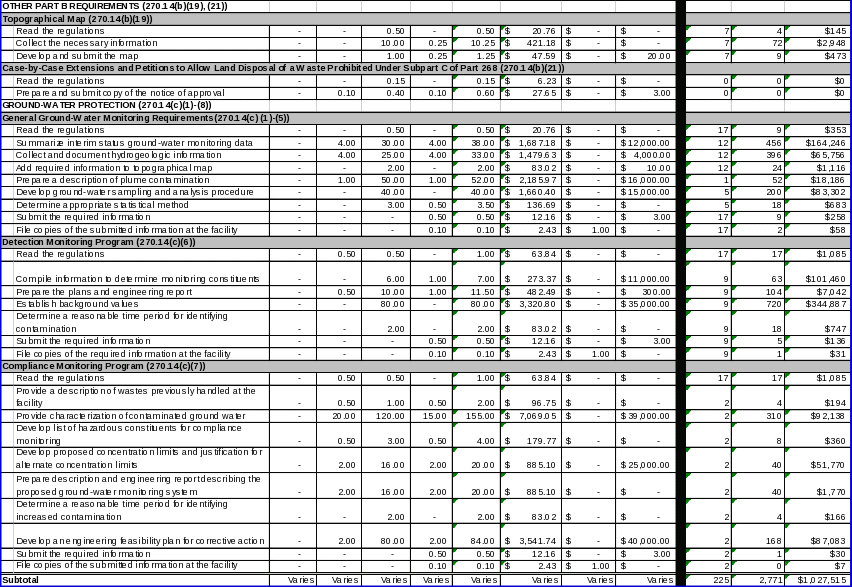
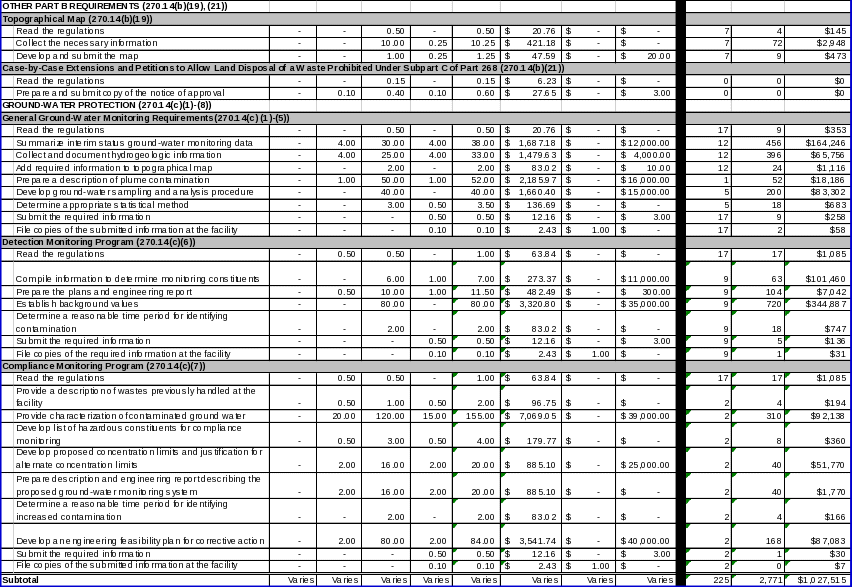
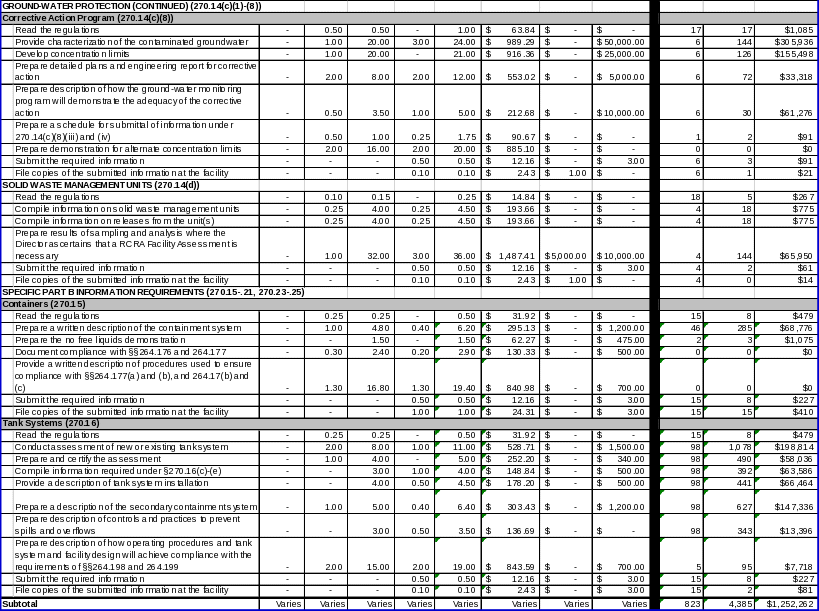

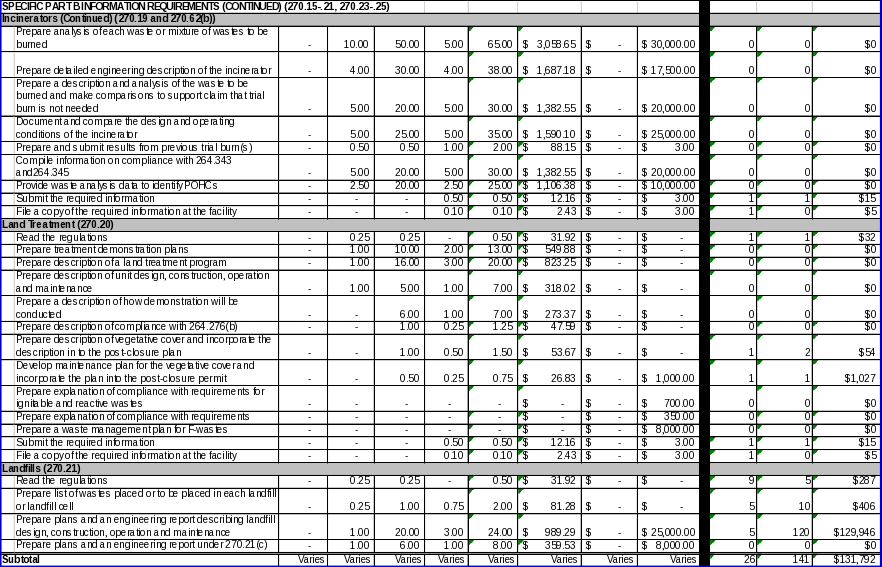
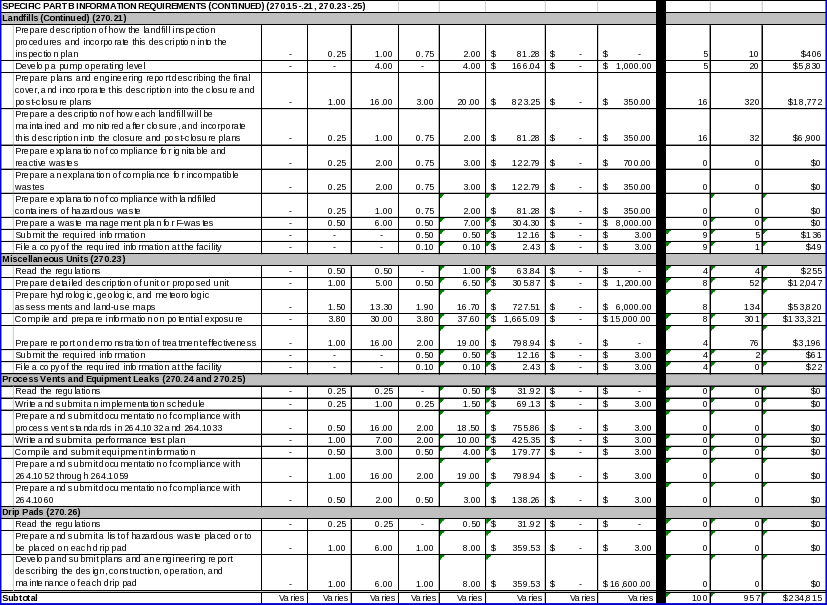

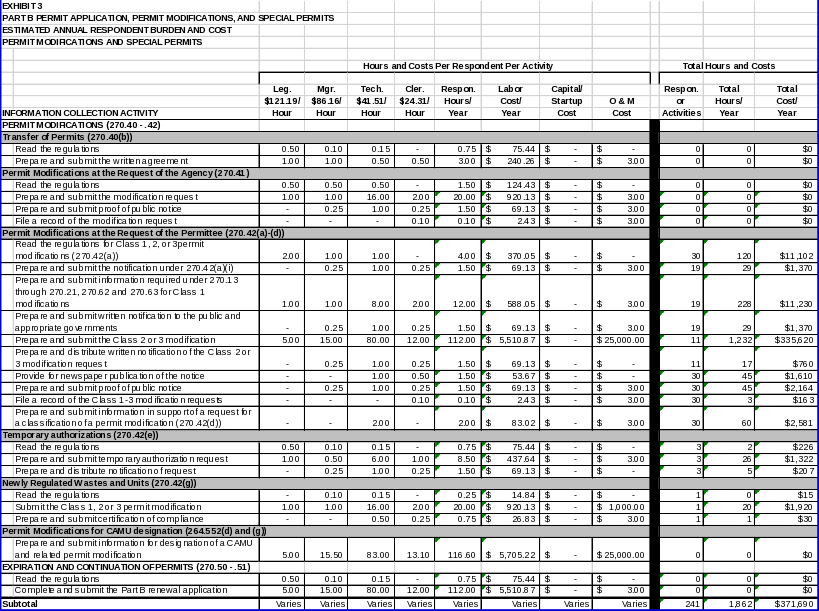
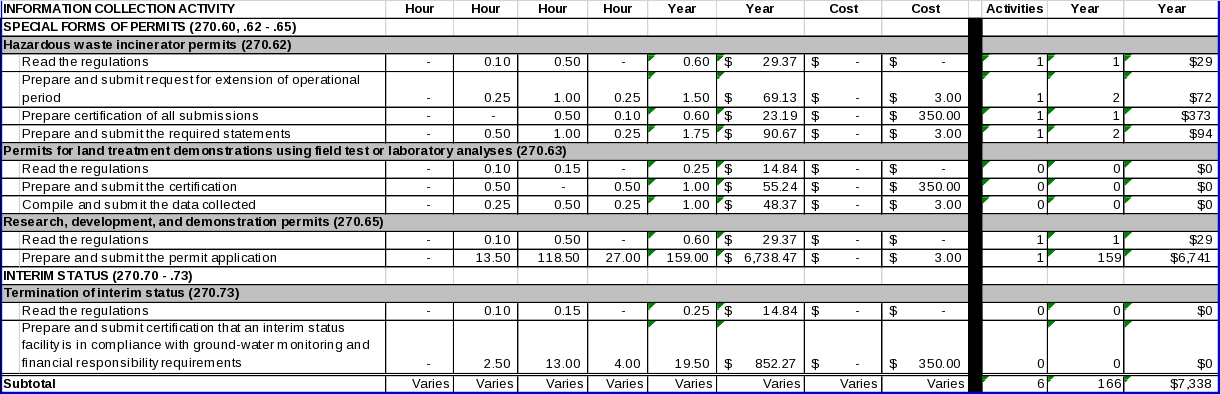
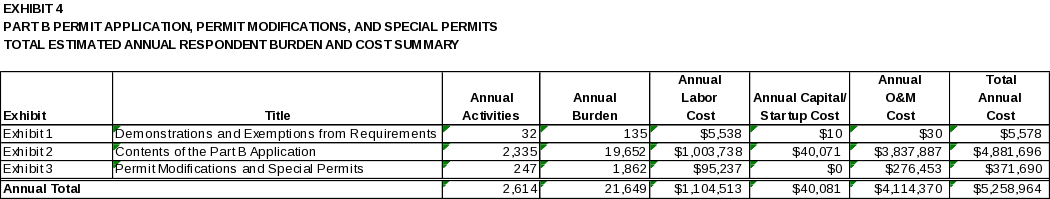
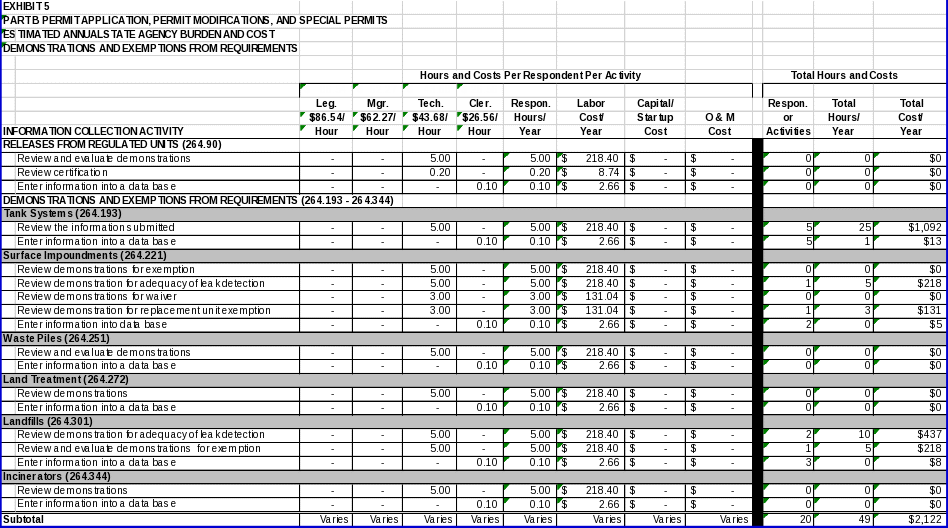
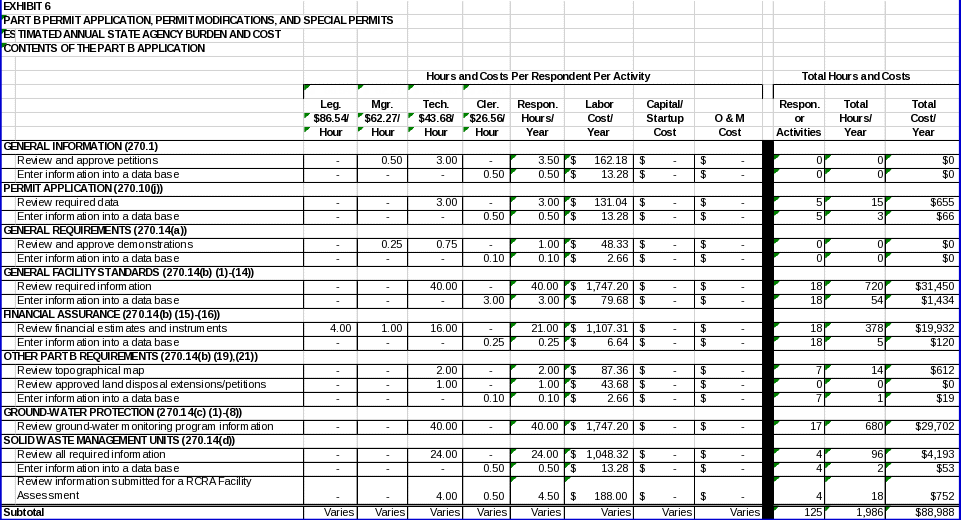
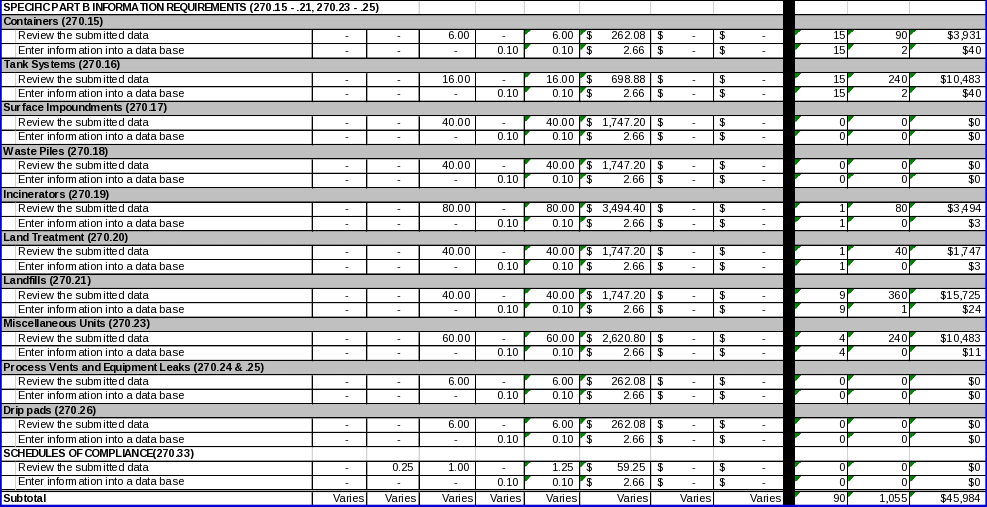
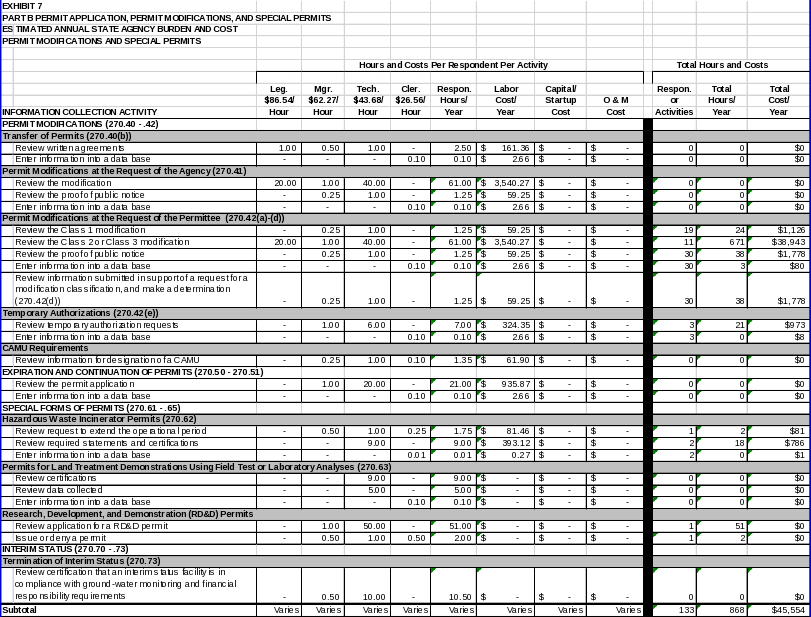
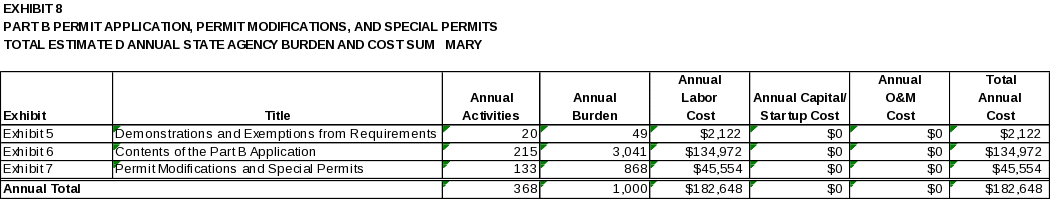
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2023-08-27 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy