Appendix A to L _ 29 CFR 1915.1001
Appendix A to L_ 29 CFR Part 1915.1001.docx
Asbestos in Shipyards Standard (29 CFR 1915.1001)
Appendix A to L _ 29 CFR 1915.1001
OMB: 1218-0195
Appendix A to §1915.1001—OSHA Reference Method (Mandatory)
This mandatory appendix specifies the procedure for analyzing air samples for asbestos, and specifies quality control procedures that must be implemented by laboratories performing the analysis. The sampling and analytical methods described below represent the elements of the available monitoring methods (such as appendix B to this section, the most current version of the OSHA method ID-160, or the most current version of the NIOSH Method 7400) which OSHA considers to be essential to achieve adequate employee exposure monitoring while allowing employers to use methods that are already established within their organizations. All employers who are required to conduct air monitoring under paragraph (f) of this section are required to utilize analytical laboratories that use this procedure, or an equivalent method, for collecting and analyzing samples.
Sampling and Analytical Procedure
1. The sampling medium for air samples shall be mixed cellulose ester filter membranes. These shall be designated by the manufacturer as suitable for asbestos counting. See below for rejection of blanks.
2. The preferred collection device shall be the 25-mm diameter cassette with an open-faced 50-mm extension cowl. The 37-mm cassette may be used if necessary but only if written justification for the need to use the 37-mm filter cassette accompanies the sample results in the employee's exposure monitoring record. Other cassettes such as the Bell-mouth may be used within the limits of their validation. Do not reuse or reload cassettes for asbestos sample collection.
3. An air flow rate between 0.5 liter/min and 5 liters/min shall be selected for the 25-mm cassette. If the 37-mm cassette is used, an air flow rate between 1 liter/min and 5 liters/min shall be selected.
4. Where possible, a sufficient air volume for each air sample shall be collected to yield between 100 and 1,300 fibers per square millimeter on the membrane filter. If a filter darkens in appearance or if loose dust is seen on the filter, a second sample shall be started.
5. Ship the samples in a rigid container with sufficient packing material to prevent dislodging the collected fibers. Packing material that has a high electrostatic charge on its surface (e.g., expanded polystyrene) cannot be used because such material can cause loss of fibers to the sides of the cassette.
6. Calibrate each personal sampling pump before and after use with a representative filter cassette installed between the pump and the calibration devices.
7. Personal samples shall be taken in the “breathing zone” of the employee (i.e., attached to or near the collar or lapel near the worker's face).
8. Fiber counts shall be made by positive phase contrast using a microscope with an 8 to 10× eyepiece and a 40 to 45× objective for a total magnification of approximately 400× and a numerical aperture of 0.65 to 0.75. The microscope shall also be fitted with a green or blue filter.
9. The microscope shall be fitted with a Walton-Beckett eyepiece graticule calibrated for a field diameter of 100 micrometers (±2 micrometers).
10. The phase-shift detection limit of the microscope shall be about 3 degrees measured using the HSE phase shift test slide as outlined below.
a. Place the test slide on the microscope stage and center it under the phase objective.
b. Bring the blocks of grooved lines into focus.
Note: The slide consists of seven sets of grooved lines (ca. 20 grooves to each block) in descending order of visibility from sets 1 to 7, seven being the least visible. The requirements for asbestos, tremolite, anthophyllite, and actinolite counting are that the microscope optics must resolve the grooved lines in set 3 completely, although they may appear somewhat faint, and that the grooved lines in sets 6 and 7 must be invisible. Sets 4 and 5 must be at least partially visible but may vary slightly in visibility between microscopes. A microscope that fails to meet these requirements has either too low or too high a resolution to be used for asbestos, tremolite, anthophyllite, and actinolite counting.
c. If the image deteriorates, clean and adjust the microscope optics. If the problem persists, consult the microscope manufacturer.
11. Each set of samples taken will include 10% field blanks or a minimum of 2 field blanks. These blanks must come from the same lot as the filters used for sample collection. The field blank results shall be averaged and subtracted from the analytical results before reporting. A set consists of any sample or group of samples for which an evaluation for this standard must be made. Any samples represented by a field blank having a fiber count in excess of the detection limit of the method being used shall be rejected.
12. The samples shall be mounted by the acetone/triacetin method or a method with an equivalent index of refraction and similar clarity.
13. Observe the following counting rules.
a. Count only fibers equal to or longer than 5 micrometers. Measure the length of curved fibers along the curve.
b. In the absence of other information, count all particles as asbestos that have a length-to-width ratio (aspect ratio) of 3 to 1 or greater.
c. Fibers lying entirely within the boundary of the Walton-Beckett graticule field shall receive a count of 1. Fibers crossing the boundary once, having one end within the circle, shall receive the count of one half ( 1⁄2 ). Do not count any fiber that crosses the graticule boundary more than once. Reject and do not count any other fibers even though they may be visible outside the graticule area.
d. Count bundles of fibers as one fiber unless individual fibers can be identified by observing both ends of an individual fiber.
e. Count enough graticule fields to yield 100 fibers. Count a minimum of 20 fields; stop counting at 100 fields regardless of fiber count.
14. Blind recounts shall be conducted at the rate of 10 percent.
Quality Control Procedures
1. Intra-laboratory program. Each laboratory and/or each company with more than one microscopist counting slides shall establish a statistically designed quality assurance program involving blind recounts and comparisons between microscopists to monitor the variability of counting by each microscopist and between microscopists. In a company with more than one laboratory, the program shall include all laboratories and shall also evaluate the laboratory-to-laboratory variability.
2. a. Interlaboratory program. Each laboratory analyzing asbestos, tremolite, anthophyllite, and actinolite samples for compliance determination shall implement an interlaboratory quality assurance program that as a minimum includes participation of at least two other independent laboratories. Each laboratory shall participate in round robin testing at least once every 6 months with at least all the other laboratories in its interlaboratory quality assurance group. Each laboratory shall submit slides typical of its own work load for use in this program. The round robin shall be designed and results analyzed using appropriate statistical methodology.
b. All laboratories should participate in a national sample testing scheme such as the Proficiency Analytical Testing Program (PAT), the Asbestos Registry sponsored by the American Industrial Hygiene Association (AIHA).
3. All individuals performing asbestos, tremolite, anthophyllite, and actinolite analysis must have taken the NIOSH course for sampling and evaluating airborne asbestos, tremolite, anthophyllite, and actinolite dust or an equivalent course.
4. When the use of different microscopes contributes to differences between counters and laboratories, the effect of the different microscope shall be evaluated and the microscope shall be replaced, as necessary.
5. Current results of these quality assurance programs shall be posted in each laboratory to keep the microscopists informed.
Appendix B to §1915.1001—Detailed Procedures for Asbestos Sampling and Analysis (Non-mandatory)
Matrix: |
Air |
OSHA Permissible Exposure Limits: |
|
Time Weighted Average |
0.1 fiber/cc |
Excursion Level (30 minutes) |
1.0 fiber/cc |
Collection Procedure: |
|
A known volume of air is drawn through a 25-mm diameter cassette containing a mixed-cellulose ester filter. The cassette must be equipped with an electrically conductive 50-mm extension cowl. The sampling time and rate are chosen to give a fiber density of between 100 to 1,300 fibers/mm2 on the filter. |
|
Recommended Sampling Rate |
0.5 to 5.0 liters/minute (L/min) |
Recommended Air Volumes: |
|
Minimum |
25 L |
Maximum |
2,400 L |
Analytical Procedure: A portion of the sample filter is cleared and prepared for asbestos fiber counting by Phase Contrast Microscopy (PCM) at 400X.
Commercial manufacturers and products mentioned in this method are for descriptive use only and do not constitute endorsements by USDOL-OSHA. Similar products from other sources can be substituted.
1. Introduction
This method describes the collection of airborne asbestos fibers using calibrated sampling pumps with mixed-cellulose ester (MCE) filters and analysis by phase contrast microscopy (PCM). Some terms used are unique to this method and are defined below: Asbestos: A term for naturally occurring fibrous minerals. Asbestos includes chrysotile, crocidolite, amosite (cummingtonite-grunerite asbestos), tremolite asbestos, actinolite asbestos, anthophyllite asbestos, and any of these minerals that have been chemically treated and/or altered. The precise chemical formulation of each species will vary with the location from which it was mined. Nominal compositions are listed:
Chrysotile |
Mg3Si2O5(OH)4 |
Crocidolite |
Na2Fe32 + Fe23 + Si8O22(OH)2 |
Amosite |
(Mg,Fe)7Si8O22(OH)2 |
Tremolite-actinolite |
Ca2(Mg,Fe)5Si8O22(OH)2 |
Anthophyllite |
(Mg,Fe)7Si8O22(OH)2 |
Asbestos Fiber: A fiber of asbestos which meets the criteria specified below for a fiber.
Aspect Ratio: The ratio of the length of a fiber to it's diameter (e.g. 3:1, 5:1 aspect ratios).
Cleavage Fragments: Mineral particles formed by comminution of minerals, especially those characterized by parallel sides and a moderate aspect ratio (usually less than 20:1).
Detection Limit: The number of fibers necessary to be 95% certain that the result is greater than zero.
Differential Counting: The term applied to the practice of excluding certain kinds of fibers from the fiber count because they do not appear to be asbestos.
Fiber: A particle that is 5 µm or longer, with a length-to-width ratio of 3 to 1 or longer.
Field: The area within the graticule circle that is superimposed on the microscope image.
Set: The samples which are taken, submitted to the laboratory, analyzed, and for which, interim or final result reports are generated.
Tremolite, Anthophyllite, and Actinolite: The non-asbestos form of these minerals which meet the definition of a fiber. It includes any of these minerals that have been chemically treated and/or altered.
Walton-Beckett Graticule: An eyepiece graticule specifically designed for asbestos fiber counting. It consists of a circle with a projected diameter of 100 ±2 µm (area of about 0.00785 mm2) with a crosshair having tic-marks at 3-µm intervals in one direction and 5-µm in the orthogonal direction. There are marks around the periphery of the circle to demonstrate the proper sizes and shapes of fibers. This design is reproduced in figure 1. The disk is placed in one of the microscope eyepieces so that the design is superimposed on the field of view.
1.1. History
Early surveys to determine asbestos exposures were conducted using impinger counts of total dust with the counts expressed as million particles per cubic foot. The British Asbestos Research Council recommended filter membrane counting in 1969. In July 1969, the Bureau of Occupational Safety and Health published a filter membrane method for counting asbestos fibers in the United States. This method was refined by NIOSH and published as P & CAM 239. On May 29, 1971, OSHA specified filter membrane sampling with phase contrast counting for evaluation of asbestos exposures at work sites in the United States. The use of this technique was again required by OSHA in 1986. Phase contrast microscopy has continued to be the method of choice for the measurement of occupational exposure to asbestos.
1.2. Principle
Air is drawn through a MCE filter to capture airborne asbestos fibers. A wedge shaped portion of the filter is removed, placed on a glass microscope slide and made transparent. A measured area (field) is viewed by PCM. All the fibers meeting defined criteria for asbestos are counted and considered a measure of the airborne asbestos concentration.
1.3. Advantages and Disadvantages
There are four main advantages of PCM over other methods:
(1) The technique is specific for fibers. Phase contrast is a fiber counting technique which excludes non-fibrous particles from the analysis.
(2) The technique is inexpensive and does not require specialized knowledge to carry out the analysis for total fiber counts.
(3) The analysis is quick and can be performed on-site for rapid determination of air concentrations of asbestos fibers.
(4) The technique has continuity with historical epidemiological studies so that estimates of expected disease can be inferred from long-term determinations of asbestos exposures.
The main disadvantage of PCM is that it does not positively identify asbestos fibers. Other fibers which are not asbestos may be included in the count unless differential counting is performed. This requires a great deal of experience to adequately differentiate asbestos from non-asbestos fibers. Positive identification of asbestos must be performed by polarized light or electron microscopy techniques. A further disadvantage of PCM is that the smallest visible fibers are about 0.2 µm in diameter while the finest asbestos fibers may be as small as 0.02 µm in diameter. For some exposures, substantially more fibers may be present than are actually counted.
1.4. Workplace Exposure
Asbestos is used by the construction industry in such products as shingles, floor tiles, asbestos cement, roofing felts, insulation and acoustical products. Non-construction uses include brakes, clutch facings, paper, paints, plastics, and fabrics. One of the most significant exposures in the workplace is the removal and encapsulation of asbestos in schools, public buildings, and homes. Many workers have the potential to be exposed to asbestos during these operations.
About 95% of the asbestos in commercial use in the United States is chrysotile. Crocidolite and amosite make up most of the remainder. Anthophyllite and tremolite or actinolite are likely to be encountered as contaminants in various industrial products.
1.5. Physical Properties
Asbestos fiber possesses a high tensile strength along its axis, is chemically inert, non-combustible, and heat resistant. It has a high electrical resistance and good sound absorbing properties. It can be weaved into cables, fabrics or other textiles, and also matted into asbestos papers, felts, or mats.
2. Range and Detection Limit
2.1. The ideal counting range on the filter is 100 to 1,300 fibers/mm2. With a Walton-Beckett graticule this range is equivalent to 0.8 to 10 fibers/field. Using NIOSH counting statistics, a count of 0.8 fibers/field would give an approximate coefficient of variation (CV) of 0.13.
2.2. The detection limit for this method is 4.0 fibers per 100 fields or 5.5 fibers/mm2. This was determined using an equation to estimate the maximum CV possible at a specific concentration (95% confidence) and a Lower Control Limit of zero. The CV value was then used to determine a corresponding concentration from historical CV vs fiber relationships. As an example:
Lower Control Limit (95% Confidence) = AC—1.645(CV)(AC)
Where:
AC = Estimate of the airborne fiber concentration (fibers/cc) Setting the Lower Control Limit = 0 and solving for CV:
0 = AC—1.645(CV)(AC)
CV = 0.61
This value was compared with CV vs. count curves. The count at which CV = 0.61 for Leidel-Busch counting statistics (8.9.) or for an OSHA Salt Lake Technical Center (OSHA-SLTC) CV curve (see appendix A for further information) was 4.4 fibers or 3.9 fibers per 100 fields, respectively. Although a lower detection limit of 4 fibers per 100 fields is supported by the OSHA-SLTC data, both data sets support the 4.5 fibers per 100 fields value.
3. Method Performance—Precision and Accuracy
Precision is dependent upon the total number of fibers counted and the uniformity of the fiber distribution on the filter. A general rule is to count at least 20 and not more than 100 fields. The count is discontinued when 100 fibers are counted, provided that 20 fields have already been counted. Counting more than 100 fibers results in only a small gain in precision. As the total count drops below 10 fibers, an accelerated loss of precision is noted.
At this time, there is no known method to determine the absolute accuracy of the asbestos analysis. Results of samples prepared through the Proficiency Analytical Testing (PAT) Program and analyzed by the OSHA-SLTC showed no significant bias when compared to PAT reference values. The PAT samples were analyzed from 1987 to 1989 (N = 36) and the concentration range was from 120 to 1,300 fibers/mm2.
4. Interferences
Fibrous substances, if present, may interfere with asbestos analysis.
Some common fibers are:
fiberglass
anhydrate
plant fibers
perlite veins
gypsum
some synthetic fibers
membrane structures
sponge spicules
diatoms
microorganism
wollastonite
The use of electron microscopy or optical tests such as polarized light, and dispersion staining may be used to differentiate these materials from asbestos when necessary.
5. Sampling
5.1. Equipment
5.1.1. Sample assembly (The assembly is shown in figure 3). Conductive filter holder consisting of a 25-mm diameter, 3-piece cassette having a 50-mm long electrically conductive extension cowl. Backup pad, 25-mm, cellulose. Membrane filter, mixed-cellulose ester (MCE), 25-mm, plain, white, 0.4 to 1.2-µm pore size.
Notes: (a) DO NOT RE-USE CASSETTES.
(b) Fully conductive cassettes are required to reduce fiber loss to the sides of the cassette due to electrostatic attraction.
(c) Purchase filters which have been selected by the manufacturer for asbestos counting or analyze representative filters for fiber background before use. Discard the filter lot if more than 4 fibers/100 fields are found.
(d) To decrease the possibility of contamination, the sampling system (filter-backup pad-cassette) for asbestos is usually preassembled by the manufacturer.
(e) Other cassettes, such as the Bell-mouth, may be used within the limits of their validation.
5.1.2. Gel bands for sealing cassettes.
5.1.3. Sampling pump.
Each pump must be a battery operated, self-contained unit small enough to be placed on the monitored employee and not interfere with the work being performed. The pump must be capable of sampling at the collection rate for the required sampling time.
5.1.4. Flexible tubing, 6-mm bore.
5.1.5. Pump calibration.
Stopwatch and bubble tube/burette or electronic meter.
5.2. Sampling Procedure
5.2.1. Seal the point where the base and cowl of each cassette meet with a gel band or tape.
5.2.2. Charge the pumps completely before beginning.
5.2.3. Connect each pump to a calibration cassette with an appropriate length of 6-mm bore plastic tubing. Do not use luer connectors—the type of cassette specified above has built-in adapters.
5.2.4. Select an appropriate flow rate for the situation being monitored. The sampling flow rate must be between 0.5 and 5.0 L/min for personal sampling and is commonly set between 1 and 2 L/min. Always choose a flow rate that will not produce overloaded filters.
5.2.5. Calibrate each sampling pump before and after sampling with a calibration cassette in-line (Note: This calibration cassette should be from the same lot of cassettes used for sampling). Use a primary standard (e.g. bubble burette) to calibrate each pump. If possible, calibrate at the sampling site.
Note: If sampling site calibration is not possible, environmental influences may affect the flow rate. The extent is dependent on the type of pump used. Consult with the pump manufacturer to determine dependence on environmental influences. If the pump is affected by temperature and pressure changes, correct the flow rate by using the formula shown in the section “Sampling Pump Flow Rate Corrections” at the end of this appendix.
5.2.6. Connect each pump to the base of each sampling cassette with flexible tubing. Remove the end cap of each cassette and take each air sample open face. Assure that each sample cassette is held open side down in the employee's breathing zone during sampling. The distance from the nose/mouth of the employee to the cassette should be about 10 cm. Secure the cassette on the collar or lapel of the employee using spring clips or other similar devices.
5.2.7. A suggested minimum air volume when sampling to determine TWA compliance is 25 L. For Excursion Limit (30 min sampling time) evaluations, a minimum air volume of 48 L is recommended.
5.2.8. The most significant problem when sampling for asbestos is overloading the filter with non-asbestos dust. Suggested maximum air sample volumes for specific environments are:
Environment |
Air vol. (L) |
Asbestos removal operations (visible dust) |
100 |
Asbestos removal operations (little dust) |
240 |
Office environments |
400 to 2,400 |
Caution: Do not overload the filter with dust. High levels of non-fibrous dust particles may obscure fibers on the filter and lower the count or make counting impossible. If more than about 25 to 30% of the field area is obscured with dust, the result may be biased low. Smaller air volumes may be necessary when there is excessive non-asbestos dust in the air.
While sampling, observe the filter with a small flashlight. If there is a visible layer of dust on the filter, stop sampling, remove and seal the cassette, and replace with a new sampling assembly. The total dust loading should not exceed 1 mg.
5.2.9. Blank samples are used to determine if any contamination has occurred during sample handling. Prepare two blanks for the first 1 to 20 samples. For sets containing greater than 20 samples, prepare blanks as 10% of the samples. Handle blank samples in the same manner as air samples with one exception: Do not draw any air through the blank samples. Open the blank cassette in the place where the sample cassettes are mounted on the employee. Hold it open for about 30 seconds. Close and seal the cassette appropriately. Store blanks for shipment with the sample cassettes.
5.2.10. Immediately after sampling, close and seal each cassette with the base and plastic plugs. Do not touch or puncture the filter membrane as this will invalidate the analysis.
5.2.11 Attach and secure a sample seal around each sample cassette in such a way as to assure that the end cap and base plugs cannot be removed without destroying the seal. Tape the ends of the seal together since the seal is not long enough to be wrapped end-to-end. Also wrap tape around the cassette at each joint to keep the seal secure.
5.3. Sample Shipment
5.3.1. Send the samples to the laboratory with paperwork requesting asbestos analysis. List any known fibrous interferences present during sampling on the paperwork. Also, note the workplace operation(s) sampled.
5.3.2. Secure and handle the samples in such that they will not rattle during shipment nor be exposed to static electricity. Do not ship samples in expanded polystyrene peanuts, vermiculite, paper shreds, or excelsior. Tape sample cassettes to sheet bubbles and place in a container that will cushion the samples in such a manner that they will not rattle.
5.3.3. To avoid the possibility of sample contamination, always ship bulk samples in separate mailing containers.
6. Analysis
6.1. Safety Precautions
6.1.1. Acetone is extremely flammable and precautions must be taken not to ignite it. Avoid using large containers or quantities of acetone. Transfer the solvent in a ventilated laboratory hood. Do not use acetone near any open flame. For generation of acetone vapor, use a spark free heat source.
6.1.2. Any asbestos spills should be cleaned up immediately to prevent dispersal of fibers. Prudence should be exercised to avoid contamination of laboratory facilities or exposure of personnel to asbestos. Asbestos spills should be cleaned up with wet methods and/or a High Efficiency Particulate-Air (HEPA) filtered vacuum.
Caution: Do not use a vacuum without a HEPA filter—It will disperse fine asbestos fibers in the air.
6.2. Equipment
6.2.1. Phase contrast microscope with binocular or trinocular head.
6.2.2. Widefield or Huygenian 10X eyepieces (NOTE: The eyepiece containing the graticule must be a focusing eyepiece. Use a 40X phase objective with a numerical aperture of 0.65 to 0.75).
6.2.3. Kohler illumination (if possible) with green or blue filter.
6.2.4. Walton-Beckett Graticule, type G-22 with 100 ±2 µm projected diameter.
6.2.5. Mechanical stage. A rotating mechanical stage is convenient for use with polarized light.
6.2.6. Phase telescope.
6.2.7. Stage micrometer with 0.01-mm subdivisions.
6.2.8. Phase-shift test slide, mark II (Available from PTR optics Ltd., and also McCrone).
6.2.9. Precleaned glass slides, 25 mm × 75 mm. One end can be frosted for convenience in writing sample numbers, etc., or paste-on labels can be used.
6.2.10. Cover glass #11⁄2 .
6.2.11. Scalpel (#10, curved blade).
6.2.12. Fine tipped forceps.
6.2.13. Aluminum block for clearing filter (see appendix D and figure 4).
6.2.14. Automatic adjustable pipette, 100- to 500-µL.
6.2.15. Micropipette, 5 µL.
6.3. Reagents
6.3.1. Acetone (HPLC grade).
6.3.2. Triacetin (glycerol triacetate).
6.3.3. Lacquer or nail polish.
6.4. Standard Preparation
A way to prepare standard asbestos samples of known concentration has not been developed. It is possible to prepare replicate samples of nearly equal concentration. This has been performed through the PAT program. These asbestos samples are distributed by the AIHA to participating laboratories.
Since only about one-fourth of a 25-mm sample membrane is required for an asbestos count, any PAT sample can serve as a “standard” for replicate counting.
6.5. Sample Mounting
Note: See Safety Precautions in Section 6.1. before proceeding. The objective is to produce samples with a smooth (non-grainy) background in a medium with a refractive index of approximately 1.46. The technique below collapses the filter for easier focusing and produces permanent mounts which are useful for quality control and interlaboratory comparison.
An aluminum block or similar device is required for sample preparation.
6.5.1. Heat the aluminum block to about 70 °C. The hot block should not be used on any surface that can be damaged by either the heat or from exposure to acetone.
6.5.2. Ensure that the glass slides and cover glasses are free of dust and fibers.
6.5.3. Remove the top plug to prevent a vacuum when the cassette is opened. Clean the outside of the cassette if necessary. Cut the seal and/or tape on the cassette with a razor blade. Very carefully separate the base from the extension cowl, leaving the filter and backup pad in the base.
6.5.4. With a rocking motion cut a triangular wedge from the filter using the scalpel. This wedge should be one-sixth to one-fourth of the filter. Grasp the filter wedge with the forceps on the perimeter of the filter which was clamped between the cassette pieces. DO NOT TOUCH the filter with your finger. Place the filter on the glass slide sample side up. Static electricity will usually keep the filter on the slide until it is cleared.
6.5.5. Place the tip of the micropipette containing about 200 µL acetone into the aluminum block. Insert the glass slide into the receiving slot in the aluminum block. Inject the acetone into the block with slow, steady pressure on the plunger while holding the pipette firmly in place. Wait 3 to 5 seconds for the filter to clear, then remove the pipette and slide from the aluminum block.
6.5.6. Immediately (less than 30 seconds) place 2.5 to 3.5 µL of triacetin on the filter (Note: Waiting longer than 30 seconds will result in increased index of refraction and decreased contrast between the fibers and the preparation. This may also lead to separation of the cover slip from the slide).
6.5.7. Lower a cover slip gently onto the filter at a slight angle to reduce the possibility of forming air bubbles. If more than 30 seconds have elapsed between acetone exposure and triacetin application, glue the edges of the cover slip to the slide with lacquer or nail polish.
6.5.8. If clearing is slow, warm the slide for 15 min on a hot plate having a surface temperature of about 50 °C to hasten clearing. The top of the hot block can be used if the slide is not heated too long.
6.5.9. Counting may proceed immediately after clearing and mounting are completed.
6.6. Sample Analysis
Completely align the microscope according to the manufacturer's instructions. Then, align the microscope using the following general alignment routine at the beginning of every counting session and more often if necessary.
6.6.1. Alignment
(1) Clean all optical surfaces. Even a small amount of dirt can significantly degrade the image.
(2) Rough focus the objective on a sample.
(3) Close down the field iris so that it is visible in the field of view. Focus the image of the iris with the condenser focus. Center the image of the iris in the field of view.
(4) Install the phase telescope and focus on the phase rings. Critically center the rings. Misalignment of the rings results in astigmatism which will degrade the image.
(5) Place the phase-shift test slide on the microscope stage and focus on the lines. The analyst must see line set 3 and should see at least parts of 4 and 5 but, not see line set 6 or 6. A microscope/microscopist combination which does not pass this test may not be used.
6.6.2. Counting Fibers
(1) Place the prepared sample slide on the mechanical stage of the microscope. Position the center of the wedge under the objective lens and focus upon the sample.
(2) Start counting from one end of the wedge and progress along a radial line to the other end (count in either direction from perimeter to wedge tip). Select fields randomly, without looking into the eyepieces, by slightly advancing the slide in one direction with the mechanical stage control.
(3) Continually scan over a range of focal planes (generally the upper 10 to 15 µm of the filter surface) with the fine focus control during each field count. Spend at least 5 to 15 seconds per field.
(4) Most samples will contain asbestos fibers with fiber diameters less than 1 µm. Look carefully for faint fiber images. The small diameter fibers will be very hard to see. However, they are an important contribution to the total count.
(5) Count only fibers equal to or longer than 5 µm. Measure the length of curved fibers along the curve.
(6) Count fibers which have a length to width ratio of 3:1 or greater.
(7) Count all the fibers in at least 20 fields. Continue counting until either 100 fibers are counted or 100 fields have been viewed; whichever occurs first. Count all the fibers in the final field.
(8) Fibers lying entirely within the boundary of the Walton-Beckett graticule field shall receive a count of 1. Fibers crossing the boundary once, having one end within the circle shall receive a count of 1⁄2 . Do not count any fiber that crosses the graticule boundary more than once. Reject and do not count any other fibers even though they may be visible outside the graticule area. If a fiber touches the circle, it is considered to cross the line.
(9) Count bundles of fibers as one fiber unless individual fibers can be clearly identified and each individual fiber is clearly not connected to another counted fiber. See figure 1 for counting conventions.
(10) Record the number of fibers in each field in a consistent way such that filter non-uniformity can be assessed.
(11) Regularly check phase ring alignment.
(12) When an agglomerate (mass of material) covers more than 25% of the field of view, reject the field and select another. Do not include it in the number of fields counted.
(13) Perform a “blind recount” of 1 in every 10 filter wedges (slides). Re-label the slides using a person other than the original counter.
6.7. Fiber Identification
As previously mentioned in Section 1.3., PCM does not provide positive confirmation of asbestos fibers. Alternate differential counting techniques should be used if discrimination is desirable. Differential counting may include primary discrimination based on morphology, polarized light analysis of fibers, or modification of PCM data by Scanning Electron or Transmission Electron Microscopy.
A great deal of experience is required to routinely and correctly perform differential counting. It is discouraged unless it is legally necessary. Then, only if a fiber is obviously not asbestos should it be excluded from the count. Further discussion of this technique can be found in reference 8.10.
If there is a question whether a fiber is asbestos or not, follow the rule:
“WHEN IN DOUBT, COUNT.”
6.8. Analytical Recommendations—Quality Control System
6.8.1. All individuals performing asbestos analysis must have taken the NIOSH course for sampling and evaluating airborne asbestos or an equivalent course.
6.8.2. Each laboratory engaged in asbestos counting shall set up a slide trading arrangement with at least two other laboratories in order to compare performance and eliminate inbreeding of error. The slide exchange occurs at least semiannually. The round robin results shall be posted where all analysts can view individual analyst's results.
6.8.3. Each laboratory engaged in asbestos counting shall participate in the Proficiency Analytical Testing Program, the Asbestos Analyst Registry or equivalent.
6.8.4. Each analyst shall select and count prepared slides from a “slide bank”. These are quality assurance counts. The slide bank shall be prepared using uniformly distributed samples taken from the workload. Fiber densities should cover the entire range routinely analyzed by the laboratory. These slides are counted blind by all counters to establish an original standard deviation. This historical distribution is compared with the quality assurance counts. A counter must have 95% of all quality control samples counted within three standard deviations of the historical mean. This count is then integrated into a new historical mean and standard deviation for the slide.
The analyses done by the counters to establish the slide bank may be used for an interim quality control program if the data are treated in a proper statistical fashion.
7. Calculations
7.1. Calculate the estimated airborne asbestos fiber concentration on the filter sample using the following formula:
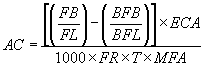
Where:
AC = Airborne fiber concentration
FB = Total number of fibers greater than 5 µm counted
FL = Total number of fields counted on the filter
BFB = Total number of fibers greater than 5 µm counted in the blank
BFL = Total number of fields counted on the blank
ECA = Effective collecting area of filter (385 mm2 nominal for a 25-mm filter.)
FR = Pump flow rate (L/min)
MFA = Microscope count field area (mm2). This is 0.00785 mm2 for a Walton-Beckett Graticule.
T = Sample collection time (min)
1,000 = Conversion of L to cc
Note: The collection area of a filter is seldom equal to 385 mm2. It is appropriate for laboratories to routinely monitor the exact diameter using an inside micrometer. The collection area is calculated according to the formula:
Area = π(d/2)2
7.2. Short-cut Calculation
Since a given analyst always has the same interpupillary distance, the number of fields per filter for a particular analyst will remain constant for a given size filter. The field size for that analyst is constant (i.e. the analyst is using an assigned microscope and is not changing the reticle).
For example, if the exposed area of the filter is always 385 mm2 and the size of the field is always 0.00785 mm2, the number of fields per filter will always be 49,000. In addition it is necessary to convert liters of air to cc. These three constants can then be combined such that ECA/(1,000 × MFA) = 49. The previous equation simplifies to:
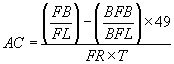
7.3. Recount Calculations
As mentioned in step 13 of Section 6.6.2., a “blind recount” of 10% of the slides is performed. In all cases, differences will be observed between the first and second counts of the same filter wedge. Most of these differences will be due to chance alone, that is, due to the random variability (precision) of the count method. Statistical recount criteria enables one to decide whether observed differences can be explained due to chance alone or are probably due to systematic differences between analysts, microscopes, or other biasing factors.
The following recount criterion is for a pair of counts that estimate AC in fibers/cc. The criterion is given at the type-I error level. That is, there is 5% maximum risk that we will reject a pair of counts for the reason that one might be biased, when the large observed difference is really due to chance.
Reject a pair of counts if:
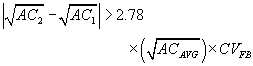
Where:
AC1 = lower estimated airborne fiber concentration
AC2 = higher estimated airborne fiber concentration
ACavg = average of the two concentration estimates
CVFB = CV for the average of the two concentration estimates
If a pair of counts are rejected by this criterion then, recount the rest of the filters in the submitted set. Apply the test and reject any other pairs failing the test. Rejection shall include a memo to the industrial hygienist stating that the sample failed a statistical test for homogeneity and the true air concentration may be significantly different than the reported value.
7.4. Reporting Results
Report results to the industrial hygienist as fibers/cc. Use two significant figures. If multiple analyses are performed on a sample, an average of the results is to be reported unless any of the results can be rejected for cause.
8. References
8.1. Dreesen, W.C., et al, U.S. Public Health Service: A Study of Asbestosis in the Asbestos Textile Industry, (Public Health Bulletin No. 241), US Treasury Dept., Washington, DC, 1938.
8.2. Asbestos Research Council: The Measurement of Airborne Asbestos Dust by the Membrane Filter Method (Technical Note), Asbestos Research Council, Rockdale, Lancashire, Great Britain, 1969.
8.3. Bayer, S.G., Zumwalde, R.D., Brown, T.A., Equipment and Procedure for Mounting Millipore Filters and Counting Asbestos Fibers by Phase Contrast Microscopy, Bureau of Occupational Health, U.S. Dept. of Health, Education and Welfare, Cincinnati,OH,1969.
8.4. NIOSH Manual of Analytical Methods, 2nd ed., Vol. 1 (DHEW/NIOSH Pub. No. 77-157-A). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Cincinnati, OH, 1977.pp.239-1-239-21.
8.5. Asbestos, Code of Federal Regulations 29 CFR 1910.1001. 1971.
8.6. Occupational Exposure to Asbestos, Tremolite, Anthophyllite, and Actinolite. Final Rule, Federal Register 51: 119 (20 June 1986). pp.22612-22790.
8.7. Asbestos, Tremolite, Anthophyllite, and Actinolite, Code of Federal Regulations 1910.1001. 1988. pp 711-752.
8.8. Criteria for a Recommended Standard—Occupational Exposure to Asbestos (DHEW/NIOSH Pub. No. HSM 72-10267), National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health NIOSH, Cincinnati, OH, 1972. pp. III-1-III-24.
8.9. Leidel, N.A., Bayer, S.G., Zumwalde, R.D., Busch, K.A., USPHS/NIOSH Membrane Filter Method for Evaluating Airborne Asbestos Fibers (DHEW/NIOSH Pub. No. 79-127). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Cincinnati, OH, 1979.
8.10. Dixon, W.C., Applications of Optical Microscopy in Analysis of Asbestos and Quartz, Analytical Techniques in Occupational Health Chemistry, edited by D.D. Dollberg and A.W. Verstuyft. Wash. D.C.: American Chemical Society, (ACS Symposium Series 120) 1980. pp. 13-41.
Quality Control
The OSHA asbestos regulations require each laboratory to establish a quality control program. The following is presented as an example of how the OSHA-SLTC constructed its internal CV curve as part of meeting this requirement. Data is from 395 samples collected during OSHA compliance inspections and analyzed from October 1980 through April 1986.
Each sample was counted by 2 to 5 different counters independently of one another. The standard deviation and the CV statistic was calculated for each sample. This data was then plotted on a graph of CV vs. fibers/mm2. A least squares regression was performed using the following equation:
CV = antilog10[A(log10(x))2 + B(log10(x)) + C]
Where:
x = the number of fibers/mm2
Application of least squares gave:
A = 0.182205
B = −0.973343
C = 0.327499
Using these values, the equation becomes:
CV = antilog10[0.182205(log10 (x))2−0.973343(log 10(x)) + 0.327499]
Sampling Pump Flow Rate Corrections
This correction is used if a difference greater than 5% in ambient temperature and/or pressure is noted between calibration and sampling sites and the pump does not compensate for the differences.
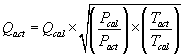
Where:
Qact = actual flow rate
Qcal = calibrated flow rate (if a rotameter was used, the rotameter value)
Pcal = uncorrected air pressure at calibration
Pact = uncorrected air pressure at sampling site
Tact = temperature at sampling site (K)
Tcal = temperature at calibration (K)
Walton-Beckett Graticule
When ordering the Graticule for asbestos counting, specify the exact disc diameter needed to fit the ocular of the microscope and the diameter (mm) of the circular counting area. Instructions for measuring the dimensions necessary are listed:
(1) Insert any available graticule into the focusing eyepiece and focus so that the graticule lines are sharp and clear.
(2) Align the microscope.
(3) Place a stage micrometer on the microscope object stage and focus the microscope on the graduated lines.
(4) Measure the magnified grid length, PL (µm), using the stage micrometer.
(5) Remove the graticule from the microscope and measure its actual grid length, AL (mm). This can be accomplished by using a mechanical stage fitted with verniers, or a jeweler's loupe with a direct reading scale.
(6) Let D = 100 µm. Calculate the circle diameter, dc (mm), for the Walton-Beckett graticule and specify the diameter when making a purchase:
![]()
Example: If PL = 108 µm, AL = 2.93 mm and D = 100 µm, then,
![]()
(7) Each eyepiece-objective-reticle combination on the microscope must be calibrated. Should any of the three be changed (by zoom adjustment, disassembly, replacement, etc.), the combination must be recalibrated. Calibration may change if interpupillary distance is changed.
Measure the field diameter, D (acceptable range: 100 ±2 µm) with a stage micrometer upon receipt of the graticule from the manufacturer. Determine the field area (mm2).
Field Area = π(D/2)2
If D = 100 µm = 0.1 mm, then
Field Area = π(0.1 mm/2)2 = 0.00785 mm2
The Graticule is available from: Graticules Ltd., Morley Road, Tonbridge TN9 IRN, Kent, England (Telephone 011-44-732-359061). Also available from PTR Optics Ltd., 145 Newton Street, Waltham, MA 02154 [telephone (617) 891-6000] or McCrone Accessories and Components, 2506 S. Michigan Ave., Chicago, IL 60616 [phone (312) 842-7100]. The graticule is custom made for each microscope.
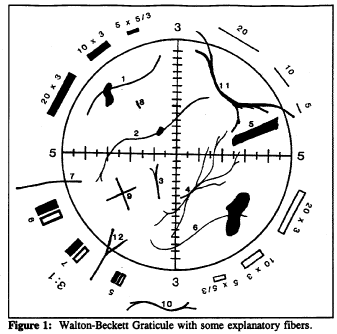
Counts for the Fibers in the Figure
Structure No. |
Count |
Explanation |
1 to 6 |
1 |
Single fibers all contained within the circle. |
7 |
1⁄2 |
Fiber crosses circle once. |
8 |
0 |
Fiber too short. |
9 |
2 |
Two crossing fibers. |
10 |
0 |
Fiber outside graticule. |
11 |
0 |
Fiber crosses graticule twice. |
12 |
1⁄2 |
Although split, fiber only crosses once. |
Appendix C to §1915.1001—Qualitative and Quantitative Fit Testing Procedures. Mandatory
Employers must perform fit testing in accordance with the fit-testing requirements of 29 CFR 1910.134(f) and the qualitative and quantitative fit-testing protocols and procedures specified in Appendix A of 29 CFR 1910.134.
Appendix D to §1915.1001—Medical Questionnaires. Mandatory
This mandatory appendix contains the medical questionnaires that must be administered to all employees who are exposed to asbestos, tremolite, anthophyllite, actinolite, or a combination of these minerals above the permissible exposure limit (0.1 f/cc), and who will therefore be included in their employer's medical surveillance program. Part 1 of the appendix contains the Initial Medical Questionnaire, which must be obtained for all new hires who will be covered by the medical surveillance requirements. Part 2 includes the abbreviated Periodical Medical Questionnaire, which must be administered to all employees who are provided periodic medical examinations under the medical surveillance provisions of the standard.
















Appendix E to §1915.1001—Classification of Chest X-Rays. Mandatory
(a) Chest X-rays shall be classified in accordance with the Guidelines for the use of the ILO International Classification of Radiographs of Pneumoconioses (revised edition 2011) (incorporated by reference, see §1915.5), and recorded on a classification form following the format of the CDC/NIOSH (M) 2.8 form. As a minimum, the content within the bold lines of this form (items 1 through 4) shall be included. This form is not to be submitted to NIOSH.
(b) All X-rays shall be classified only by a B-Reader, a board eligible/certified radiologist, or an experienced physician with known expertise in pneumoconioses.
(c) Whenever classifying chest X-ray film, the physician shall have immediately available for reference a complete set of the ILO standard format radiographs provided for use with the Guidelines for the use of the ILO International Classification of Radiographs of Pneumoconioses (revised edition 2011).
(d) Whenever classifying digitally-acquired chest X-rays, the physician shall have immediately available for reference a complete set of ILO standard digital chest radiographic images provided for use with the Guidelines for the Use of the ILO International Classification of Radiographs of Pneumoconioses (revised edition 2011). Classification of digitally-acquired chest X-rays shall be based on the viewing of images displayed as electronic copies and shall not be based on the viewing of hard copy printed transparencies of images.
Appendix F to §1915.1001—Work Practices and Engineering Controls for Class I Asbestos Operations Non-Mandatory
This is a non-mandatory appendix to the asbestos standards for construction and for shipyards. It describes criteria and procedures for erecting and using negative pressure enclosures for Class I Asbestos Work, when NPEs are used as an allowable control method to comply with paragraph (g)(5) (i) of this section. Many small and variable details are involved in the erection of a negative pressure enclosure. OSHA and most participants in the rulemaking agreed that only the major, more performance oriented criteria should be made mandatory. These criteria are set out in paragraph (g) of this section. In addition, this appendix includes these mandatory specifications and procedures in its guidelines in order to make this appendix coherent and helpful. The mandatory nature of the criteria which appear in the regulatory text is not changed because they are included in this “non-mandatory” appendix. Similarly, the additional criteria and procedures included as guidelines in the appendix, do not become mandatory because mandatory criteria are also included in these comprehensive guidelines.
In addition, none of the criteria, both mandatory and recommended, are meant to specify or imply the need for use of patented or licensed methods or equipment. Recommended specifications included in this attachment should not discourage the use of creative alternatives which can be shown to reliably achieve the objectives of negative-pressure enclosures.
Requirements included in this appendix, cover general provisions to be followed in all asbestos jobs, provisions which must be followed for all Class I asbestos jobs, and provisions governing the construction and testing of negative pressure enclosures. The first category includes the requirement for use of wet methods, HEPA vacuums, and immediate bagging of waste; Class I work must conform to the following provisions:
• oversight by competent person
• use of critical barriers over all openings to work area
• isolation of HVAC systems
• use of impermeable dropcloths and coverage of all objects within regulated areas
In addition, more specific requirements for NPEs include:
• maintenance of −0.02 inches water gauge within enclosure
• manometric measurements
• air movement away from employees performing removal work
• smoke testing or equivalent for detection of leaks and air direction
• deactivation of electrical circuits, if not provided with ground-fault circuit interrupters.
Planning the Project
The standard requires that an exposure assessment be conducted before the asbestos job is begun §1915.1001(f)(1). Information needed for that assessment, includes data relating to prior similar jobs, as applied to the specific variables of the current job. The information needed to conduct the assessment will be useful in planning the project, and in complying with any reporting requirements under this standard, when significant changes are being made to a control system listed in the standard, [see paragraph (k) of this section], as well as those of USEPA (40 CFR part 61, subpart M). Thus, although the standard does not explicitly require the preparation of a written asbestos removal plan, the usual constituents of such a plan, i.e., a description of the enclosure, the equipment, and the procedures to be used throughout the project, must be determined before the enclosure can be erected. The following information should be included in the planning of the system:
A physical description of the work area;
A description of the approximate amount of material to be removed;
A schedule for turning off and sealing existing ventilation systems;
Personnel hygiene procedures;
A description of personal protective equipment and clothing to worn by employees;
A description of the local exhaust ventilation systems to be used and how they are to be tested;
A description of work practices to be observed by employees;
An air monitoring plan;
A description of the method to be used to transport waste material; and
The location of the dump site.
Materials and Equipment Necessary for Asbestos Removal
Although individual asbestos removal projects vary in terms of the equipment required to accomplish the removal of the materials, some equipment and materials are common to most asbestos removal operations.
Plastic sheeting used to protect horizontal surfaces, seal HVAC openings or to seal vertical openings and ceilings should have a minimum thickness of 6 mils. Tape or other adhesive used to attach plastic sheeting should be of sufficient adhesive strength to support the weight of the material plus all stresses encountered during the entire duration of the project without becoming detached from the surface.
Other equipment and materials which should be available at the beginning of each project are:
—HEPA Filtered Vacuum is essential for cleaning the work area after the asbestos has been removed. It should have a long hose capable of reaching out-of-the-way places, such as areas above ceiling tiles, behind pipes, etc.
—Portable air ventilation systems installed to provide the negative air pressure and air removal from the enclosure must be equipped with a HEPA filter. The number and capacity of units required to ventilate an enclosure depend on the size of the area to be ventilated. The filters for these systems should be designed in such a manner that they can be replaced when the air flow volume is reduced by the build-up of dust in the filtration material. Pressure monitoring devices with alarms and strip chart recorders attached to each system to indicate the pressure differential and the loss due to dust buildup on the filter are recommended.
—Water sprayers should be used to keep the asbestos material as saturated as possible during removal; the sprayers will provide a fine mist that minimizes the impact of the spray on the material.
—Water used to saturate the asbestos containing material can be amended by adding at least 15 milliliters ( 1⁄4 ounce) of wetting agent in 1 liter (1 pint) of water. An example of a wetting agent is a 50/50 mixture of polyoxyethylene ether and polyoxyethylene polyglycol ester.
—Backup power supplies are recommended, especially for ventilation systems.
—Shower and bath water should be with mixed hot and cold water faucets. Water that has been used to clean personnel or equipment should either be filtered or be collected and discarded as asbestos waste. Soap and shampoo should be provided to aid in removing dust from the workers' skin and hair.
—See paragraphs (h) and (i) of this section for appropriate respiratory protection and protective clothing.
—See paragraph (k) of this section for required signs and labels.
Preparing the Work Area
Disabling HVAC Systems: The power to the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems that service the restricted area must be deactivated and locked off. All ducts, grills, access ports, windows and vents must be sealed off with two layers of plastic to prevent entrainment of contaminated air.
Operating HVAC Systems in the Restricted Area: If components of a HVAC system located in the restricted area are connected to a system that will service another zone during the project, the portion of the duct in the restricted area must be sealed and pressurized. Necessary precautions include caulking the duct joints, covering all cracks and openings with two layers of sheeting, and pressurizing the duct throughout the duration of the project by restricting the return air flow. The power to the fan supplying the positive pressure should be locked “on” to prevent pressure loss.
Sealing Elevators: If an elevator shaft is located in the restricted area, it should be either shut down or isolated by sealing with two layers of plastic sheeting. The sheeting should provide enough slack to accommodate the pressure changes in the shaft without breaking the air-tight seal.
Removing Mobile Objects: All movable objects should be cleaned and removed from the work area before an enclosure is constructed unless moving the objects creates a hazard. Mobile objects will be assumed to be contaminated and should be either cleaned with amended water and a HEPA vacuum and then removed from the area or wrapped and then disposed of as hazardous waste.
Cleaning and Sealing Surfaces: After cleaning with water and a HEPA vacuum, surfaces of stationary objects should be covered with two layers of plastic sheeting. The sheeting should be secured with duct tape or an equivalent method to provide a tight seal around the object.
Bagging Waste: In addition to the requirement for immediate bagging of waste for disposal, it is further recommended that the waste material be double-bagged and sealed in plastic bags designed for asbestos disposal. The bags should be stored in a waste storage area that can be controlled by the workers conducting the removal. Filters removed from air handling units and rubbish removed from the area are to be bagged and handled as hazardous waste.
Constructing the Enclosure
The enclosure should be constructed to provide an air-tight seal around ducts and openings into existing ventilation systems and around penetrations for electrical conduits, telephone wires, water lines, drain pipes, etc. Enclosures should be both airtight and watertight except for those openings designed to provide entry and/or air flow control.
Size: An enclosure should be the minimum volume to encompass all of the working surfaces yet allow unencumbered movement by the worker(s), provide unrestricted air flow past the worker(s), and ensure walking surfaces can be kept free of tripping hazards.
Shape: The enclosure may be any shape that optimizes the flow of ventilation air past the worker(s).
Structural Integrity: The walls, ceilings and floors must be supported in such a manner that portions of the enclosure will not fall down during normal use.
Openings: It is not necessary that the structure be airtight; openings may be designed to direct air flow. Such openings should be located at a distance from active removal operations. They should be designed to draw air into the enclosure under all anticipated circumstances. In the event that negative pressure is lost, they should be fitted with either HEPA filters to trap dust or automatic trap doors that prevent dust from escaping the enclosure. Openings for exits should be controlled by an airlock or a vestibule.
Barrier Supports: Frames should be constructed to support all unsupported spans of sheeting.
Sheeting: Walls, barriers, ceilings, and floors should be lined with two layers of plastic sheeting having a thickness of at least 6 mil.
Seams: Seams in the sheeting material should be minimized to reduce the possibilities of accidental rips and tears in the adhesive or connections. All seams in the sheeting should overlap, be staggered and not be located at corners or wall-to- floor joints. Areas Within an Enclosure: Each enclosure consists of a work area, a decontamination area, and waste storage area. The work area where the asbestos removal operations occur should be separated from both the waste storage area and the contamination control area by physical curtains, doors, and/or airflow patterns that force any airborne contamination back into the work area.
See paragraph (j) of §1915.1001 for requirements for hygiene facilities.
During egress from the work area, each worker should step into the equipment room, clean tools and equipment, and remove gross contamination from clothing by wet cleaning and HEPA vacuuming. Before entering the shower area, foot coverings, head coverings, hand coverings, and coveralls are removed and placed in impervious bags for disposal or cleaning. Airline connections from airline respirators with HEPA disconnects and power cables from powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs) will be disconnected just prior to entering the shower room.
Establishing Negative Pressure Within the Enclosure
Negative Pressure: Air is to be drawn into the enclosure under all anticipated conditions and exhausted through a HEPA filter for 24 hours a day during the entire duration of the project.
Air Flow Tests: Air flow patterns will be checked before removal operations begin, at least once per operating shift and any time there is a question regarding the integrity of the enclosure. The primary test for air flow is to trace air currents with smoke tubes or other visual methods. Flow checks are made at each opening and at each doorway to demonstrate that air is being drawn into the enclosure and at each worker's position to show that air is being drawn away from the breathing zone.
Monitoring Pressure Within the Enclosure: After the initial air flow patterns have been checked, the static pressure must be monitored within the enclosure. Monitoring may be made using manometers, pressure gauges, or combinations of these devices. It is recommended that they be attached to alarms and strip chart recorders at points identified by the design engineer.
Corrective Actions: If the manometers or pressure gauges demonstrate a reduction in pressure differential below the required level, work should cease and the reason for the change investigated and appropriate changes made. The air flow patterns should be retested before work begins again.
Pressure Differential: The design parameters for static pressure differentials between the inside and outside of enclosures typically range from 0.02 to 0.10 inches of water gauge, depending on conditions. All zones inside the enclosure must have less pressure than the ambient pressure outside of the enclosure (-0.02 inches water gauge differential). Design specifications for the differential vary according to the size, configuration, and shape of the enclosure as well as ambient and mechanical air pressure conditions around the enclosure.
Air Flow Patterns: The flow of air past each worker shall be enhanced by positioning the intakes and exhaust ports to remove contaminated air from the worker's breathing zone, by positioning HEPA vacuum cleaners to draw air from the worker's breathing zone, by forcing relatively uncontaminated air past the worker toward an exhaust port, or by using a combination of methods to reduce the worker's exposure.
Air Handling Unit Exhaust: The exhaust plume from air handling units should be located away from adjacent personnel and intakes for HVAC systems.
Air Flow Volume: The air flow volume (cubic meters per minute) exhausted (removed) from the workplace must exceed the amount of makeup air supplied to the enclosure. The rate of air exhausted from the enclosure should be designed to maintain a negative pressure in the enclosure and air movement past each worker. The volume of air flow removed from the enclosure should replace the volume of the container at every 5 to 15 minutes. Air flow volume will need to be relatively high for large enclosures, enclosures with awkward shapes, enclosures with multiple openings, and operations employing several workers in the enclosure.
Air Flow Velocity: At each opening, the air flow velocity must visibly “drag” air into the enclosure. The velocity of air flow within the enclosure must be adequate to remove airborne contamination from each worker's breathing zone without disturbing the asbestos-containing material on surfaces.
Airlocks: Airlocks are mechanisms on doors and curtains that control the air flow patterns in the doorways. If air flow occurs, the patterns through doorways must be such that the air flows toward the inside of the enclosure. Sometimes vestibules, double doors, or double curtains are used to prevent air movement through the doorways. To use a vestibule, a worker enters a chamber by opening the door or curtain and then closing the entry before opening the exit door or curtain.
Airlocks should be located between the equipment room and shower room, between the shower room and the clean room, and between the waste storage area and the outside of the enclosure. The air flow between adjacent rooms must be checked using smoke tubes or other visual tests to ensure the flow patterns draw air toward the work area without producing eddies.
Monitoring for Airborne Concentrations
In addition to the breathing zone samples taken as outlined in paragraph (f) of §1915.1001 , samples of air should be taken to demonstrate the integrity of the enclosure, the cleanliness of the clean room and shower area, and the effectiveness of the HEPA filter. If the clean room is shown to be contaminated, the room must be relocated to an uncontaminated area.
Samples taken near the exhaust of portable ventilation systems must be done with care.
General Work Practices
Preventing dust dispersion is the primary means of controlling the spread of asbestos within the enclosure. Whenever practical, the point of removal should be isolated, enclosed, covered, or shielded from the workers in the area. Waste asbestos containing materials must be bagged during or immediately after removal; the material must remain saturated until the waste container is sealed.
Waste material with sharp points or corners must be placed in hard air-tight containers rather than bags.
Whenever possible, large components should be sealed in plastic sheeting and removed intact.
Bags or containers of waste will be moved to the waste holding area, washed, and wrapped in a bag with the appropriate labels.
Cleaning the Work Area
Surfaces within the work area should be kept free of visible dust and debris to the extent feasible. Whenever visible dust appears on surfaces, the surfaces within the enclosure must be cleaned by wiping with a wet sponge, brush, or cloth and then vacuumed with a HEPA vacuum.
All surfaces within the enclosure should be cleaned before the exhaust ventilation system is deactivated and the enclosure is disassembled. An approved encapsulant may be sprayed onto areas after the visible dust has been removed.
Appendix G to §1915.1001 [Reserved]
Appendix H to §1915.1001—Substance Technical Information for Asbestos. Non-Mandatory
I. Substance Identification
A. Substance: “Asbestos” is the name of a class of magnesium-silicate minerals that occur in fibrous form. Minerals that are included in this group are chrysotile, crocidolite, amosite, anthophyllite asbestos, tremolite asbestos, and actinolite asbestos.
B. Asbestos is and was used in the manufacture of heat-resistant clothing, automotive brake and clutch linings, and a variety of building materials including floor tiles, roofing felts, ceiling tiles, asbestos-cement pipe and sheet, and fire-resistant drywall. Asbestos is also present in pipe and boiler insulation materials and in sprayed-on materials located on beams, in crawlspaces, and between walls.
C. The potential for an asbestos-containing product to release breathable fibers depends largely on its degree of friability. Friable means that the material can be crumbled with hand pressure and is therefore likely to emit fibers. The fibrous fluffy sprayed-on materials used for fireproofing, insulation, or sound proofing are considered to be friable, and they readily release airborne fibers if disturbed. Materials such as vinyl-asbestos floor tile or roofing felt are considered non-friable if intact and generally do not emit airborne fibers unless subjected to sanding, sawing and other aggressive operations. Asbestos—cement pipe or sheet can emit airborne fibers if the materials are cut or sawed, or if they are broken.
D. Permissible exposure: Exposure to airborne asbestos fibers may not exceed 0.1 fibers per cubic centimeter of air (0.1 f/cc) averaged over the 8-hour workday, and 1 fiber per cubic centimeter of air (1.0 f/cc) averaged over a 30 minute work period.
II. Health Hazard Data
A. Asbestos can cause disabling respiratory disease and various types of cancers if the fibers are inhaled. Inhaling or ingesting fibers from contaminated clothing or skin can also result in these diseases. The symptoms of these diseases generally do not appear for 20 or more years after initial exposure.
B. Exposure to asbestos has been shown to cause lung cancer, mesothelioma, and cancer of the stomach and colon. Mesothelioma is a rare cancer of the thin membrane lining of the chest and abdomen. Symptoms of mesothelioma include shortness of breath, pain in the walls of the chest, and/or abdominal pain.
III. Respirators and Protective Clothing
A. Respirators: You are required to wear a respirator when performing tasks that result in asbestos exposure that exceeds the permissible exposure limit (PEL) of 0.1 f/cc and when performing certain designated operations. Air-purifying respirators equipped with a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter can be used where airborne asbestos fiber concentrations do not exceed 1.0 f/cc; otherwise, more protective respirators such as air-supplied, positive-pressure, full facepiece respirators must be used. Disposable respirators or dust masks are not permitted to be used for asbestos work. For effective protection, respirators must fit your face and head snugly. Your employer is required to conduct a fit test when you are first assigned a respirator and every 6 months thereafter. Respirators should not be loosened or removed in work situations where their use is required.
B. Protective Clothing: You are required to wear protective clothing in work areas where asbestos fiber concentrations exceed the permissible exposure limit (PEL) of 0.1 f/cc.
IV. Disposal Procedures and Clean-up
A. Wastes that are generated by processes where asbestos is present include:
1. Empty asbestos shipping containers.
2. Process wastes such as cuttings, trimmings, or reject materials.
3. Housekeeping waste from wet-sweeping or HEPA-vacuuming.
4. Asbestos fireproofing or insulating material that is removed from buildings.
5. Asbestos-containing building products removed during building renovation or demolition.
6. Contaminated disposable protective clothing.
B. Empty shipping bags can be flattened under exhaust hoods and packed into airtight containers for disposal. Empty shipping drums are difficult to clean and should be sealed.
C. Vacuum bags or disposable paper filters should not be cleaned, but should be sprayed with a fine water mist and placed into a labeled waste container.
D. Process waste and housekeeping waste should be wetted with water or a mixture of water and surfactant prior to packaging in disposable containers.
E. Asbestos-containing material that is removed from buildings must be disposed of in leak-tight 6-mil plastic bags, plastic-lined cardboard containers, or plastic-lined metal containers. These wastes, which are removed while wet, should be sealed in containers before they dry out to minimize the release of asbestos fibers during handling.
V. Access to Information
A. Each year, your employer is required to inform you of the information contained in this standard and appendices for asbestos. In addition, your employer must instruct you in the proper work practices for handling asbestos-containing materials, and the correct use of protective equipment.
B. Your employer is required to determine whether you are being exposed to asbestos. Your employer must treat exposure to thermal system insulation and sprayed-on and troweled-on surfacing material as asbestos exposure, unless results of laboratory analysis show that the material does not contain asbestos. You or your representative has the right to observe employee measurements and to record the results obtained. Your employer is required to inform you of your exposure, and, if you are exposed above the permissible exposure limit, he or she is required to inform you of the actions that are being taken to reduce your exposure to within the permissible limit.
C. Your employer is required to keep records of your exposures and medical examinations. These exposure records must be kept for at least thirty (30) years. Medical records must be kept for the period of your employment plus thirty (30) years.
D. Your employer is required to release your exposure and medical records to your physician or designated representative upon your written request.
Appendix I to §1915.1001—Medical Surveillance Guidelines for Asbestos, Non-Mandatory
I. Route of Entry
Inhalation, ingestion.
II. Toxicology
Clinical evidence of the adverse effects associated with exposure to asbestos is present in the form of several well- conducted epidemiological studies of occupationally exposed workers, family contacts of workers, and persons living near asbestos mines. These studies have shown a definite association between exposure to asbestos and an increased incidence of lung cancer, pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma, gastrointestinal cancer, and asbestosis. The latter is a disabling fibrotic lung disease that is caused only by exposure to asbestos. Exposure to asbestos has also been associated with an increased incidence of esophageal, kidney, laryngeal, pharyngeal, and buccal cavity cancers. As with other known chronic occupational diseases, disease associated with asbestos generally appears about 20 years following the first occurrence of exposure: There are no known acute effects associated with exposure to asbestos.
Epidemiological studies indicate that the risk of lung cancer among exposed workers who smoke cigarettes is greatly increased over the risk of lung cancer among non-exposed smokers or exposed nonsmokers. These studies suggest that cessation of smoking will reduce the risk of lung cancer for a person exposed to asbestos but will not reduce it to the same level of risk as that existing for an exposed worker who has never smoked.
III. Signs and Symptoms of Exposure-Related Disease
The signs and symptoms of lung cancer or gastrointestinal cancer induced by exposure to asbestos are not unique, except that a chest X-ray of an exposed patient with lung cancer may show pleural plaques, pleural calcification, or pleural fibrosis, and may also show asbestosis (i.e., small irregular parenchymal opacities). Symptoms characteristic of mesothelioma include shortness of breath, pain in the chest or abdominal pain. Mesothelioma has a much longer average latency period compared with lung cancer (40 years versus 15-20 years), and mesothelioma is therefore more likely to be found among workers who were first exposed to asbestos at an early age. Mesothelioma is a fatal disease.
Asbestosis is pulmonary fibrosis caused by the accumulation of asbestos fibers in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath, coughing, fatigue, and vague feelings of sickness. When the fibrosis worsens, shortness of breath occurs even at rest. The diagnosis of asbestosis is most commonly based on a history of exposure to asbestos, the presence of characteristic radiologic abnormalities, end-inspiratory crackles (rales), and other clinical features of fibrosing lung disease. Pleural plaques and thickening may be observed on chest X-rays. Asbestosis is often a progressive disease even in the absence of continued exposure, although this appears to be a highly individualized characteristic. In severe cases, death may be caused by respiratory or cardiac failure.
IV. Surveillance and Preventive Considerations
As noted in section III of this appendix, exposure to asbestos have been linked to an increased risk of lung cancer, mesothelioma, gastrointestinal cancer, and asbestosis among occupationally exposed workers. Adequate screening tests to determine an employee's potential for developing serious chronic diseases, such as a cancer, from exposure to asbestos do not presently exist. However, some tests, particularly chest X-rays and pulmonary function tests, may indicate that an employee has been overexposed to asbestos increasing his or her risk of developing exposure related chronic diseases. It is important for the physician to become familiar with the operating conditions in which occupational exposure to asbestos is likely to occur. This is particularly important in evaluating medical and work histories and in conducting physical examinations. When an active employee has been identified as having been overexposed to asbestos measures taken by the employer to eliminate or mitigate further exposure should also lower the risk of serious long-term consequences.
The employer is required to institute a medical surveillance program for all employees who are or will be exposed to asbestos at or above the permissible exposure limits (0.1 fiber per cubic centimeter of air) for 30 or more days per year and for all employees who are assigned to wear a negative-pressure respirator. All examinations and procedures must be performed by or under the supervision of licensed physician at a reasonable time and place, and at no cost to the employee.
Although broad latitude is given to the physician in prescribing specific tests to be included in the medical surveillance program, OSHA requires inclusion of the following elements in the routine examination,
(i) Medical and work histories with special emphasis directed to symptoms of the respiratory system, cardiovascular system, and digestive tract.
(ii) Completion of the respiratory disease questionnaire contained in appendix D to this section.
(iii) A physical examination including a chest X-ray and pulmonary function test that includes measurement of the employee's forced vital capacity (FVC) and forced expiratory volume at one second (FEV1).
(iv) Any laboratory or other test that the examining physician deems by sound medical practice to be necessary.
The employer is required to make the prescribed tests available at least annually to those employees covered; more often than specified if recommended by the examining physician; and upon termination of employment.
The employer is required to provide the physician with the following information: A copy of the standard in this section (including all appendices to this section); a description of the employee's duties as they relate to asbestos exposure; the employee's representative level of exposure to asbestos; a description of any personal protective and respiratory equipment used; and information from previous medical examinations of the affected employee that is not otherwise available to the physician. Making this information available to the physician will aid in the evaluation of the employee's health in relation to assigned duties and fitness to wear personal protective equipment, if required.
The employer is required to obtain a written opinion from the examining physician containing the results of the medical examination; the physician's opinion as to whether the employee has any detected medical conditions that would place the employee at an increased risk of exposure-related disease; any recommended limitations on the employee or on the use of personal protective equipment; and a statement that the employee has been informed by the physician of the results of the medical examination and of any medical conditions related to asbestos exposure that require further explanation or treatment. This written opinion must not reveal specific findings or diagnoses unrelated to exposure to asbestos, and a copy of the opinion must be provided to the affected employee.
Appendix J to §1915.1001—Smoking Cessation Program Information for Asbestos—Non-Mandatory
The following organizations provide smoking cessation information.
1. The National Cancer Institute operates a toll-free Cancer Information Service (CIS) with trained personnel to help you. Call 1-800-4-CANCER* to reach the CIS office serving your area, or write: Office of Cancer Communications, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Building 31, Room 10A24, Bethesda, Maryland 20892.
2. American Cancer Society, 3340 Peachtree Road, N.E., Atlanta, Georgia 30026, (404) 320-3333.
The American Cancer Society (ACS) is a voluntary organization composed of 58 divisions and 3,100 local units. Through “The Great American Smokeout” in November, the annual Cancer Crusade in April, and numerous educational materials, ACS helps people learn about the health hazards of smoking and become successful ex-smokers.
3. American Heart Association, 7320 Greenville Avenue, Dallas, Texas 75231, (214) 750-5300.
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a voluntary organization with 130,000 members (physicians, scientists, and laypersons) in 55 state and regional groups. AHA produces a variety of publications and audiovisual materials about the effects of smoking on the heart. AHA also has developed a guidebook for incorporating a weight-control component into smoking cessation programs.
4. American Lung Association, 1740 Broadway, New York, New York 10019, (212) 245-8000.
A voluntary organization of 7,500 members (physicians, nurses, and laypersons), the American Lung Association (ALA) conducted numerous public information programs about the health effects of smoking. ALA has 59 state and 85 local units. The organization actively supports legislation and information campaigns for non-smokers' rights and provides help for smokers who want to quit, for example, through “Freedom From Smoking,” a self-help smoking cessation program.
5. Office on Smoking and Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services 5600 Fishers Lane, Park Building, Room 110, Rockville, Maryland 20857.
The Office on Smoking and Health (OSHA) is the Department of Health and Human Services' lead agency in smoking control. OSHA has sponsored distribution of publications on smoking-related topics, such as free flyers on relapse after initial quitting, helping a friend or family member quit smoking, the health hazards of smoking, and the effects of parental smoking on teenagers.
*In Hawaii, on Oahu call 524-1234 (call collect from neighboring islands),
Spanish-speaking staff members are available during daytime hours to callers from the following areas: California, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, New Jersey (area code 201), New York, and Texas. Consult your local telephone directory for listings of local chapters.
Appendix K to §1915.1001—Polarized Light Microscopy of Asbestos—Non-Mandatory
Method number: ID-191
Matrix: Bulk
Collection Procedure
Collect approximately 1 to 2 grams of each type of material and place into separate 20 mL scintillation vials.
Analytical Procedure
A portion of each separate phase is analyzed by gross examination, phase-polar examination, and central stop dispersion microscopy.
Commercial manufacturers and products mentioned in this method are for descriptive use only and do not constitute endorsements by USDOL-OSHA. Similar products from other sources may be substituted.
1. Introduction
This method describes the collection and analysis of asbestos bulk materials by light microscopy techniques including phase- polar illumination and central-stop dispersion microscopy. Some terms unique to asbestos analysis are defined below:
Amphibole: A family of minerals whose crystals are formed by long, thin units which have two thin ribbons of double chain silicate with a brucite ribbon in between. The shape of each unit is similar to an “I beam”. Minerals important in asbestos analysis include cummingtonite-grunerite, crocidolite, tremolite- actinolite and anthophyllite.
Asbestos: A term for naturally occurring fibrous minerals. Asbestos includes chrysotile, cummingtonite-grunerite asbestos (amosite), anthophyllite asbestos, tremolite asbestos, crocidolite, actinolite asbestos and any of these minerals which have been chemically treated or altered. The precise chemical formulation of each species varies with the location from which it was mined. Nominal compositions are listed:
Chrysotile |
Mg3 Si2 O5(OH)4 |
Crocidolite (Riebeckite asbestos) |
Na2Fe32 + Fe23 + Si8O22(OH)2 |
Cummingtonite-Grunerite asbestos (Amosite) |
(Mg,Fe)7 Si8O22(OH)2 |
Tremolite-Actinolite asbestos |
Ca2(Mg,Fe)5Si8O22(OH)2 |
Anthophyllite asbestos |
(Mg,Fe)7 Si8O22(OH)2 |
Asbestos Fiber: A fiber of asbestos meeting the criteria for a fiber. (See section 3.5.)
Aspect Ratio: The ratio of the length of a fiber to its diameter usually defined as “length : width”, e.g. 3:1.
Brucite: A sheet mineral with the composition Mg(OH)2.
Central Stop Dispersion Staining (microscope): This is a dark field microscope technique that images particles using only light refracted by the particle, excluding light that travels through the particle unrefracted. This is usually accomplished with a McCrone objective or other arrangement which places a circular stop with apparent aperture equal to the objective aperture in the back focal plane of the microscope.
Cleavage Fragments: Mineral particles formed by the comminution of minerals, especially those characterized by relatively parallel sides and moderate aspect ratio.
Differential Counting: The term applied to the practice of excluding certain kinds of fibers from a phase contrast asbestos count because they are not asbestos.
Fiber: A particle longer than or equal to 5 µm with a length to width ratio greater than or equal to 3:1. This may include cleavage fragments. (see section 3.5 of this appendix).
Phase Contrast: Contrast obtained in the microscope by causing light scattered by small particles to destructively interfere with unscattered light, thereby enhancing the visibility of very small particles and particles with very low intrinsic contrast.
Phase Contrast Microscope: A microscope configured with a phase mask pair to create phase contrast. The technique which uses this is called Phase Contrast Microscopy (PCM).
Phase-Polar Analysis: This is the use of polarized light in a phase contrast microscope. It is used to see the same size fibers that are visible in air filter analysis. Although fibers finer than 1 µm are visible, analysis of these is inferred from analysis of larger bundles that are usually present.
Phase-Polar Microscope: The phase-polar microscope is a phase contrast microscope which has an analyzer, a polarizer, a first order red plate and a rotating phase condenser all in place so that the polarized light image is enhanced by phase contrast.
Sealing Encapsulant: This is a product which can be applied, preferably by spraying, onto an asbestos surface which will seal the surface so that fibers cannot be released.
Serpentine: A mineral family consisting of minerals with the general composition Mg3(Si2O5(OH)4 having the magnesium in brucite layer over a silicate layer. Minerals important in asbestos analysis included in this family are chrysotile, lizardite, antigorite.
1.1. History
Light microscopy has been used for well over 100 years for the determination of mineral species. This analysis is carried out using specialized polarizing microscopes as well as bright field microscopes. The identification of minerals is an on-going process with many new minerals described each year. The first recorded use of asbestos was in Finland about 2500 B.C. where the material was used in the mud wattle for the wooden huts the people lived in as well as strengthening for pottery. Adverse health aspects of the mineral were noted nearly 2000 years ago when Pliny the Younger wrote about the poor health of slaves in the asbestos mines. Although known to be injurious for centuries, the first modern references to its toxicity were by the British Labor Inspectorate when it banned asbestos dust from the workplace in 1898. Asbestosis cases were described in the literature after the turn of the century. Cancer was first suspected in the mid 1930's and a causal link to mesothelioma was made in 1965. Because of the public concern for worker and public safety with the use of this material, several different types of analysis were applied to the determination of asbestos content. Light microscopy requires a great deal of experience and craft. Attempts were made to apply less subjective methods to the analysis. X-ray diffraction was partially successful in determining the mineral types but was unable to separate out the fibrous portions from the non-fibrous portions. Also, the minimum detection limit for asbestos analysis by X-ray diffraction (XRD) is about 1%. Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) was no more successful. These provide useful corroborating information when the presence of asbestos has been shown by microscopy; however, neither can determine the difference between fibrous and non-fibrous minerals when both habits are present. The same is true of Infrared Absorption (IR).
When electron microscopy was applied to asbestos analysis, hundreds of fibers were discovered present too small to be visible in any light microscope. There are two different types of electron microscope used for asbestos analysis: Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM). Scanning Electron Microscopy is useful in identifying minerals. The SEM can provide two of the three pieces of information required to identify fibers by electron microscopy: morphology and chemistry. The third is structure as determined by Selected Area Electron Diffraction—SAED which is performed in the TEM. Although the resolution of the SEM is sufficient for very fine fibers to be seen, accuracy of chemical analysis that can be performed on the fibers varies with fiber diameter in fibers of less than 0.2 µm diameter. The TEM is a powerful tool to identify fibers too small to be resolved by light microscopy and should be used in conjunction with this method when necessary. The TEM can provide all three pieces of information required for fiber identification. Most fibers thicker than 1 µm can adequately be defined in the light microscope. The light microscope remains as the best instrument for the determination of mineral type. This is because the minerals under investigation were first described analytically with the light microscope. It is inexpensive and gives positive identification for most samples analyzed. Further, when optical techniques are inadequate, there is ample indication that alternative techniques should be used for complete identification of the sample.
1.2. Principle
Minerals consist of atoms that may be arranged in random order or in a regular arrangement. Amorphous materials have atoms in random order while crystalline materials have long range order. Many materials are transparent to light, at least for small particles or for thin sections. The properties of these materials can be investigated by the effect that the material has on light passing through it. The six asbestos minerals are all crystalline with particular properties that have been identified and cataloged. These six minerals are anisotropic. They have a regular array of atoms, but the arrangement is not the same in all directions. Each major direction of the crystal presents a different regularity. Light photons travelling in each of these main directions will encounter different electrical neighborhoods, affecting the path and time of travel. The techniques outlined in this method use the fact that light traveling through fibers or crystals in different directions will behave differently, but predictably. The behavior of the light as it travels through a crystal can be measured and compared with known or determined values to identify the mineral species. Usually, Polarized Light Microscopy (PLM) is performed with strain-free objectives on a bright-field microscope platform. This would limit the resolution of the microscope to about 0.4 µm. Because OSHA requires the counting and identification of fibers visible in phase contrast, the phase contrast platform is used to visualize the fibers with the polarizing elements added into the light path. Polarized light methods cannot identify fibers finer than about 1µm in diameter even though they are visible. The finest fibers are usually identified by inference from the presence of larger, identifiable fiber bundles. When fibers are present, but not identifiable by light microscopy, use either SEM or TEM to determine the fiber identity.
1.3. Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of light microcopy are:
(a) Basic identification of the materials was first performed by light microscopy and gross analysis. This provides a large base of published information against which to check analysis and analytical technique.
(b) The analysis is specific to fibers. The minerals present can exist in asbestiform, fibrous, prismatic, or massive varieties all at the same time. Therefore, bulk methods of analysis such as X-ray diffraction, IR analysis, DTA, etc. are inappropriate where the material is not known to be fibrous.
(c) The analysis is quick, requires little preparation time, and can be performed on-site if a suitably equipped microscope is available.
The disadvantages are:
(a) Even using phase-polar illumination, not all the fibers present may be seen. This is a problem for very low asbestos concentrations where agglomerations or large bundles of fibers may not be present to allow identification by inference.
(b) The method requires a great degree of sophistication on the part of the microscopist. An analyst is only as useful as his mental catalog of images. Therefore, a microscopist's accuracy is enhanced by experience. The mineralogical training of the analyst is very important. It is the basis on which subjective decisions are made.
(c) The method uses only a tiny amount of material for analysis. This may lead to sampling bias and false results (high or low). This is especially true if the sample is severely inhomogeneous.
(d) Fibers may be bound in a matrix and not distinguishable as fibers so identification cannot be made.
1.4. Method Performance
1.4.1. This method can be used for determination of asbestos content from 0 to 100% asbestos. The detection limit has not been adequately determined, although for selected samples, the limit is very low, depending on the number of particles examined. For mostly homogeneous, finely divided samples, with no difficult fibrous interferences, the detection limit is below 1%. For inhomogeneous samples (most samples), the detection limit remains undefined. NIST has conducted proficiency testing of laboratories on a national scale. Although each round is reported statistically with an average, control limits, etc., the results indicate a difficulty in establishing precision especially in the low concentration range. It is suspected that there is significant bias in the low range especially near 1%. EPA tried to remedy this by requiring a mandatory point counting scheme for samples less than 10%. The point counting procedure is tedious, and may introduce significant biases of its own. It has not been incorporated into this method.
1.4.2. The precision and accuracy of the quantitation tests performed in this method are unknown. Concentrations are easier to determine in commercial products where asbestos was deliberately added because the amount is usually more than a few percent. An analyst's results can be “calibrated” against the known amounts added by the manufacturer. For geological samples, the degree of homogeneity affects the precision.
1.4.3. The performance of the method is analyst dependent. The analyst must choose carefully and not necessarily randomly the portions for analysis to assure that detection of asbestos occurs when it is present. For this reason, the analyst must have adequate training in sample preparation, and experience in the location and identification of asbestos in samples. This is usually accomplished through substantial on-the-job training as well as formal education in mineralogy and microscopy.
1.5. Interferences
Any material which is long, thin, and small enough to be viewed under the microscope can be considered an interference for asbestos. There are literally hundreds of interferences in workplaces. The techniques described in this method are normally sufficient to eliminate the interferences. An analyst's success in eliminating the interferences depends on proper training.
Asbestos minerals belong to two mineral families: the serpentines and the amphiboles. In the serpentine family, the only common fibrous mineral is chrysotile. Occasionally, the mineral antigorite occurs in a fibril habit with morphology similar to the amphiboles. The amphibole minerals consist of a score of different minerals of which only five are regulated by federal standard: amosite, crocidolite, anthophyllite asbestos, tremolite asbestos and actinolite asbestos. These are the only amphibole minerals that have been commercially exploited for their fibrous properties; however, the rest can and do occur occasionally in asbestiform habit.
In addition to the related mineral interferences, other minerals common in building material may present a problem for some microscopists: gypsum, anhydrite, brucite, quartz fibers, talc fibers or ribbons, wollastonite, perlite, attapulgite, etc. Other fibrous materials commonly present in workplaces are: fiberglass, mineral wool, ceramic wool, refractory ceramic fibers, kevlar, nomex, synthetic fibers, graphite or carbon fibers, cellulose (paper or wood) fibers, metal fibers, etc.
Matrix embedding material can sometimes be a negative interference. The analyst may not be able to easily extract the fibers from the matrix in order to use the method. Where possible, remove the matrix before the analysis, taking careful note of the loss of weight. Some common matrix materials are: vinyl, rubber, tar, paint, plant fiber, cement, and epoxy. A further negative interference is that the asbestos fibers themselves may be either too small to be seen in Phase contrast Microscopy (PCM) or of a very low fibrous quality, having the appearance of plant fibers. The analyst's ability to deal with these materials increases with experience.
1.6. Uses and Occupational Exposure
Asbestos is ubiquitous in the environment. More than 40% of the land area of the United States is composed of minerals which may contain asbestos. Fortunately, the actual formation of great amounts of asbestos is relatively rare. Nonetheless, there are locations in which environmental exposure can be severe such as in the Serpentine Hills of California.
There are thousands of uses for asbestos in industry and the home. Asbestos abatement workers are the most current segment of the population to have occupational exposure to great amounts of asbestos. If the material is undisturbed, there is no exposure. Exposure occurs when the asbestos-containing material is abraded or otherwise disturbed during maintenance operations or some other activity. Approximately 95% of the asbestos in place in the United States is chrysotile.
Amosite and crocidolite make up nearly all the difference. Tremolite and anthophyllite make up a very small percentage. Tremolite is found in extremely small amounts in certain chrysotile deposits. Actinolite exposure is probably greatest from environmental sources, but has been identified in vermiculite containing, sprayed-on insulating materials which may have been certified as asbestos-free.
1.7. Physical and Chemical Properties
The nominal chemical compositions for the asbestos minerals were given in Section 1. Compared to cleavage fragments of the same minerals, asbestiform fibers possess a high tensile strength along the fiber axis. They are chemically inert, non-combustible, and heat resistant. Except for chrysotile, they are insoluble in Hydrochloric acid (HCl). Chrysotile is slightly soluble in HCl. Asbestos has high electrical resistance and good sound absorbing characteristics. It can be woven into cables, fabrics or other textiles, or matted into papers, felts, and mats.
1.8. Toxicology (This Section is for Information Only and Should Not Be Taken as OSHA Policy)
Possible physiologic results of respiratory exposure to asbestos are mesothelioma of the pleura or peritoneum, interstitial fibrosis, asbestosis, pneumoconiosis, or respiratory cancer. The possible consequences of asbestos exposure are detailed in the NIOSH Criteria Document or in the OSHA Asbestos Standards 29 CFR 1910.1001 and 29 CFR 1926.1101 and 29 CFR 1915.1001.
2. Sampling Procedure
2.1. Equipment for Sampling
(a) Tube or cork borer sampling device
(b) Knife
(c) 20 mL scintillation vial or similar vial
(d) Sealing encapsulant
2.2. Safety Precautions
Asbestos is a known carcinogen. Take care when sampling. While in an asbestos-containing atmosphere, a properly selected and fit-tested respirator should be worn. Take samples in a manner to cause the least amount of dust. Follow these general guidelines:
(a) Do not make unnecessary dust.
(b) Take only a small amount (1 to 2 g).
(c) Tightly close the sample container.
(d) Use encapsulant to seal the spot where the sample was taken, if necessary.
2.3. Sampling procedure
Samples of any suspect material should be taken from an inconspicuous place. Where the material is to remain, seal the sampling wound with an encapsulant to eliminate the potential for exposure from the sample site. Microscopy requires only a few milligrams of material. The amount that will fill a 20 mL scintillation vial is more than adequate. Be sure to collect samples from all layers and phases of material. If possible, make separate samples of each different phase of the material. This will aid in determining the actual hazard. DO NOT USE ENVELOPES, PLASTIC OR PAPER BAGS OF ANY KIND TO COLLECT SAMPLES. The use of plastic bags presents a contamination hazard to laboratory personnel and to other samples. When these containers are opened, a bellows effect blows fibers out of the container onto everything, including the person opening the container.
If a cork-borer type sampler is available, push the tube through the material all the way, so that all layers of material are sampled. Some samplers are intended to be disposable. These should be capped and sent to the laboratory. If a non-disposable cork borer is used, empty the contents into a scintillation vial and send to the laboratory. Vigorously and completely clean the cork borer between samples.
2.4 Shipment
Samples packed in glass vials must not touch or they might break in shipment.
(a) Seal the samples with a sample seal over the end to guard against tampering and to identify the sample.
(b) Package the bulk samples in separate packages from the air samples. They may cross-contaminate each other and will invalidate the results of the air samples.
(c) Include identifying paperwork with the samples, but not in contact with the suspected asbestos.
(d) To maintain sample accountability, ship the samples by certified mail, overnight express, or hand carry them to the laboratory.
3. Analysis
The analysis of asbestos samples can be divided into two major parts: sample preparation and microscopy. Because of the different asbestos uses that may be encountered by the analyst, each sample may need different preparation steps. The choices are outlined below. There are several different tests that are performed to identify the asbestos species and determine the percentage. They will be explained below.
3.1. Safety
(a) Do not create unnecessary dust. Handle the samples in HEPA-filter equipped hoods. If samples are received in bags, envelopes or other inappropriate container, open them only in a hood having a face velocity at or greater than 100 fpm. Transfer a small amount to a scintillation vial and only handle the smaller amount.
(b) Open samples in a hood, never in the open lab area.
(c) Index of refraction oils can be toxic. Take care not to get this material on the skin. Wash immediately with soap and water if this happens.
(d) Samples that have been heated in the muffle furnace or the drying oven may be hot. Handle them with tongs until they are cool enough to handle.
(e) Some of the solvents used, such as THF (tetrahydrofuran), are toxic and should only be handled in an appropriate fume hood and according to instructions given in the safety data sheet (SDS).
3.2. Equipment
(a) Phase contrast microscope with 10x, 16x and 40x objectives, 10x wide-field eyepieces, G-22 Walton-Beckett graticule, Whipple disk, polarizer, analyzer and first order red or gypsum plate, 100 Watt illuminator, rotating position condenser with oversize phase rings, central stop dispersion objective, Kohler illumination and a rotating mechanicalstage. (See figure 1).
(b) Stereo microscope with reflected light illumination, transmitted light illumination, polarizer, analyzer and first order red or gypsum plate, and rotating stage.
(c) Negative pressure hood for the stereo microscope
(d) Muffle furnace capable of 600 °C
(e) Drying oven capable of 50-150 °C
(f) Aluminum specimen pans
(g) Tongs for handling samples in the furnace
(h) High dispersion index of refraction oils (Special for dispersion staining.)
n = 1.550
n = 1.585
n = 1.590
n = 1.605
n = 1.620
n = 1.670
n = 1.680
n = 1.690
(i) A set of index of refraction oils from about n = 1.350 to n = 2.000 in n = 0.005 increments. (Standard for Becke line analysis.)
(j) Glass slides with painted or frosted ends 1 × 3 inches 1mm thick, precleaned.
(k) Cover Slips 22 × 22 mm, #11⁄2
(l) Paper clips or dissection needles
(m) Hand grinder
(n) Scalpel with both #10 and #11 blades
(o) 0.1 molar HCl
(p) Decalcifying solution (Baxter Scientific Products) Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid,
Tetrasodium0.7 g/l
Sodium Potassium Tartrate8.0 mg/liter
Hydrochloric Acid99.2 g/liter
Sodium Tartrate0.14 g/liter
(q) Tetrahydrofuran (THF)
(r) Hotplate capable of 60 °C
(s) Balance
(t) Hacksaw blade
(u) Ruby mortar and pestle
3.3. Sample Pre-Preparation
Sample preparation begins with pre-preparation which may include chemical reduction of the matrix, heating the sample to dryness or heating in the muffle furnace. The end result is a sample which has been reduced to a powder that is sufficiently fine to fit under the cover slip. Analyze different phases of samples separately, e.g., tile and the tile mastic should be analyzed separately as the mastic may contain asbestos while the tile may not.
(a) Wet Samples
Samples with a high water content will not give the proper dispersion colors and must be dried prior to sample mounting. Remove the lid of the scintillation vial, place the bottle in the drying oven and heat at 100 °C to dryness (usually about 2 h). Samples which are not submitted to the lab in glass must be removed and placed in glass vials or aluminum weighing pans before placing them in the drying oven.
(b) Samples With Organic Interference—Muffle Furnace
These may include samples with tar as a matrix, vinyl asbestos tile, or any other organic that can be reduced by heating. Remove the sample from the vial and weigh in a balance to determine the weight of the submitted portion. Place the sample in a muffle furnace at 500 °C for 1 to 2 h or until all obvious organic material has been removed. Retrieve, cool and weigh again to determine the weight loss on ignition. This is necessary to determine the asbestos content of the submitted sample, because the analyst will be looking at a reduced sample.
Notes: Heating above 600 °C will cause the sample to undergo a structural change which, given sufficient time, will convert the chrysotile to forsterite. Heating even at lower temperatures for 1 to 2 h may have a measurable effect on the optical properties of the minerals. If the analyst is unsure of what to expect, a sample of standard asbestos should be heated to the same temperature for the same length of time so that it can be examined for the proper interpretation.
(c) Samples With Organic Interference—THF
Vinyl asbestos tile is the most common material treated with this solvent, although, substances containing tar will sometimes yield to this treatment. Select a portion of the material and then grind it up if possible. Weigh the sample and place it in a test tube. Add sufficient THF to dissolve the organic matrix. This is usually about 4 to 5 mL. Remember, THF is highly flammable. Filter the remaining material through a tared silver membrane, dry and weigh to determine how much is left after the solvent extraction. Further process the sample to remove carbonate or mount directly.
(d) Samples With Carbonate Interference
Carbonate material is often found on fibers and sometimes must be removed in order to perform dispersion microscopy. Weigh out a portion of the material and place it in a test tube. Add a sufficient amount of 0.1 M HCl or decalcifying solution in the tube to react all the carbonate as evidenced by gas formation; i.e., when the gas bubbles stop, add a little more solution. If no more gas forms, the reaction is complete. Filter the material out through a tared silver membrane, dry and weigh to determine the weight lost.
3.4. Sample Preparation
Samples must be prepared so that accurate determination can be made of the asbestos type and amount present. The following steps are carried out in the low-flow hood (a low-flow hood has less than 50 fpm flow):
(1) If the sample has large lumps, is hard, or cannot be made to lie under a cover slip, the grain size must be reduced. Place a small amount between two slides and grind the material between them or grind a small amount in a clean mortar and pestle. The choice of whether to use an alumina, ruby, or diamond mortar depends on the hardness of the material. Impact damage can alter the asbestos mineral if too much mechanical shock occurs. (Freezer mills can completely destroy the observable crystallinity of asbestos and should not be used). For some samples, a portion of material can be shaved off with a scalpel, ground off with a hand grinder or hack saw blade.
The preparation tools should either be disposable or cleaned thoroughly. Use vigorous scrubbing to loosen the fibers during the washing. Rinse the implements with copious amounts of water and air-dry in a dust-free environment.
(2) If the sample is powder or has been reduced as in 1) above, it is ready to mount. Place a glass slide on a piece of optical tissue and write the identification on the painted or frosted end. Place two drops of index of refraction medium n = 1.550 on the slide. (The medium n = 1.550 is chosen because it is the matching index for chrysotile. Dip the end of a clean paper-clip or dissecting needle into the droplet of refraction medium on the slide to moisten it. Then dip the probe into the powder sample. Transfer what sticks on the probe to the slide. The material on the end of the probe should have a diameter of about 3 mm for a good mount. If the material is very fine, less sample may be appropriate. For non-powder samples such as fiber mats, forceps should be used to transfer a small amount of material to the slide. Stir the material in the medium on the slide, spreading it out and making the preparation as uniform as possible. Place a cover-slip on the preparation by gently lowering onto the slide and allowing it to fall “trapdoor” fashion on the preparation to push out any bubbles. Press gently on the cover slip to even out the distribution of particulate on the slide. If there is insufficient mounting oil on the slide, one or two drops may be placed near the edge of the coverslip on the slide. Capillary action will draw the necessary amount of liquid into the preparation. Remove excess oil with the point of a laboratory wiper.
Treat at least two different areas of each phase in this fashion. Choose representative areas of the sample. It may be useful to select particular areas or fibers for analysis. This is useful to identify asbestos in severely inhomogeneous samples.
When it is determined that amphiboles may be present, repeat the above process using the appropriate high- dispersion oils until an identification is made or all six asbestos minerals have been ruled out. Note that percent determination must be done in the index medium 1.550 because amphiboles tend to disappear in their matching mediums.
3.5. Analytical procedure
Note: This method presumes some knowledge of mineralogy and optical petrography.
The analysis consists of three parts: The determination of whether there is asbestos present, what type is present and the determination of how much is present. The general flow of the analysis is:
(1) Gross examination.
(2) Examination under polarized light on the stereo microscope.
(3) Examination by phase-polar illumination on the compound phase microscope.
(4) Determination of species by dispersion stain. Examination by Becke line analysis may also be used; however, this is usually more cumbersome for asbestos determination.
(5) Difficult samples may need to be analyzed by SEM or TEM, or the results from those techniques combined with light microscopy for a definitive identification. Identification of a particle as asbestos requires that it be asbestiform. Description of particles should follow the suggestion of Campbell. (Figure 1)
For the purpose of regulation, the mineral must be one of the six minerals covered and must be in the asbestos growth habit. Large specimen samples of asbestos generally have the gross appearance of wood. Fibers are easily parted from it. Asbestos fibers are very long compared with their widths. The fibers have a very high tensile strength as demonstrated by bending without breaking. Asbestos fibers exist in bundles that are easily parted, show longitudinal fine structure and may be tufted at the ends showing “bundle of sticks” morphology. In the microscope some of these properties may not be observable. Amphiboles do not always show striations along their length even when they are asbestos. Neither will they always show tufting. They generally do not show a curved nature except for very long fibers. Asbestos and asbestiform minerals are usually characterized in groups by extremely high aspect ratios (greater than 100:1). While aspect ratio analysis is useful for characterizing populations of fibers, it cannot be used to identify individual fibers of intermediate to short aspect ratio. Observation of many fibers is often necessary to determine whether a sample consists of “cleavage fragments” or of asbestos fibers.
Most cleavage fragments of the asbestos minerals are easily distinguishable from true asbestos fibers. This is because true cleavage fragments usually have larger diameters than 1 µm. Internal structure of particles larger than this usually shows them to have no internal fibrillar structure. In addition, cleavage fragments of the monoclinic amphiboles show inclined extinction under crossed polars with no compensator. Asbestos fibers usually show extinction at zero degrees or ambiguous extinction if any at all. Morphologically, the larger cleavage fragments are obvious by their blunt or stepped ends showing prismatic habit. Also, they tend to be acicular rather than filiform.
Where the particles are less than 1 µm in diameter and have an aspect ratio greater than or equal to 3:1, it is recommended that the sample be analyzed by SEM or TEM if there is any question whether the fibers are cleavage fragments or asbestiform particles.
Care must be taken when analyzing by electron microscopy because the interferences are different from those in light microscopy and may structurally be very similar to asbestos. The classic interference is between anthophyllite and biopyribole or intermediate fiber. Use the same morphological clues for electron microscopy as are used for light microscopy, e.g. fibril splitting, internal longitudinal striation, fraying, curvature, etc.
(1) Gross examination:
Examine the sample, preferably in the glass vial. Determine the presence of any obvious fibrous component. Estimate a percentage based on previous experience and current observation. Determine whether any pre-preparation is necessary. Determine the number of phases present. This step may be carried out or augmented by observation at 6 to 40 × under a stereo microscope.
(2) After performing any necessary pre-preparation, prepare slides of each phase as described above. Two preparations of the same phase in the same index medium can be made side-by-side on the same glass for convenience. Examine with the polarizing stereo microscope. Estimate the percentage of asbestos based on the amount of birefringent fiber present.
(3) Examine the slides on the phase-polar microscopes at magnifications of 160 and 400 × . Note the morphology of the fibers. Long, thin, very straight fibers with little curvature are indicative of fibers from the amphibole family. Curved, wavy fibers are usually indicative of chrysotile. Estimate the percentage of asbestos on the phase-polar microscope under conditions of crossed polars and a gypsum plate. Fibers smaller than 1.0 µm in thickness must be identified by inference to the presence of larger, identifiable fibers and morphology. If no larger fibers are visible, electron microscopy should be performed. At this point, only a tentative identification can be made. Full identification must be made with dispersion microscopy. Details of the tests are included in the appendices.
(4) Once fibers have been determined to be present, they must be identified. Adjust the microscope for dispersion mode and observe the fibers. The microscope has a rotating stage, one polarizing element, and a system for generating dark-field dispersion microscopy (see Section 4.6. of this appendix). Align a fiber with its length parallel to the polarizer and note the color of the Becke lines. Rotate the stage to bring the fiber length perpendicular to the polarizer and note the color. Repeat this process for every fiber or fiber bundle examined. The colors must be consistent with the colors generated by standard asbestos reference materials for a positive identification. In n = 1.550, amphiboles will generally show a yellow to straw-yellow color indicating that the fiber indices of refraction are higher than the liquid. If long, thin fibers are noted and the colors are yellow, prepare further slides as above in the suggested matching liquids listed below:
Type of asbestos |
Index of refraction |
Chrysotile |
n = 1.550. |
Amosite |
n = 1.670 or 1.680. |
Crocidolite |
n = 1.690. |
Anthophyllite |
n = 1.605 and 1.620. |
Tremolite |
n = 1.605 and 1.620. |
Actinolite |
n = 1.620. |
Where more than one liquid is suggested, the first is preferred; however, in some cases this liquid will not give good dispersion color. Take care to avoid interferences in the other liquid; e.g., wollastonite in n = 1.620 will give the same colors as tremolite. In n = 1.605 wollastonite will appear yellow in all directions. Wollastonite may be determined under crossed polars as it will change from blue to yellow as it is rotated along its fiber axis by tapping on the cover slip. Asbestos minerals will not change in this way.
Determination of the angle of extinction may, when present, aid in the determination of anthophyllite from tremolite. True asbestos fibers usually have 0° extinction or ambiguous extinction, while cleavage fragments have more definite extinction.
Continue analysis until both preparations have been examined and all present species of asbestos are identified. If there are no fibers present, or there is less than 0.1% present, end the analysis with the minimum number of slides (2).
(5) Some fibers have a coating on them which makes dispersion microscopy very difficult or impossible. Becke line analysis or electron microscopy may be performed in those cases. Determine the percentage by light microscopy. TEM analysis tends to overestimate the actual percentage present.
(6) Percentage determination is an estimate of occluded area, tempered by gross observation. Gross observation information is used to make sure that the high magnification microscopy does not greatly over- or under-estimate the amount of fiber present. This part of the analysis requires a great deal of experience. Satisfactory models for asbestos content analysis have not yet been developed, although some models based on metallurgical grain-size determination have found some utility. Estimation is more easily handled in situations where the grain sizes visible at about 160 × are about the same and the sample is relatively homogeneous.
View all of the area under the cover slip to make the percentage determination. View the fields while moving the stage, paying attention to the clumps of material. These are not usually the best areas to perform dispersion microscopy because of the interference from other materials. But, they are the areas most likely to represent the accurate percentage in the sample. Small amounts of asbestos require slower scanning and more frequent analysis of individual fields.
Report the area occluded by asbestos as the concentration. This estimate does not generally take into consideration the difference in density of the different species present in the sample. For most samples this is adequate. Simulation studies with similar materials must be carried out to apply microvisual estimation for that purpose and is beyond the scope of this procedure.
(7) Where successive concentrations have been made by chemical or physical means, the amount reported is the percentage of the material in the “as submitted” or original state. The percentage determined by microscopy is multiplied by the fractions remaining after pre-preparation steps to give the percentage in the original sample. For example:
Step 1. 60% remains after heating at 550 °C for 1 h.
Step 2. 30% of the residue of step 1 remains after dissolution of carbonate in 0.1 m HCl.
Step 3. Microvisual estimation determines that 5% of the sample is chrysotile asbestos.
The reported result is:
R = (Microvisual result in percent) × (Fraction remaining after step 2) × (Fraction remaining of original sample after step 1)
R = (5) × (.30) × (.60) = 0.9%
(8) Report the percent and type of asbestos present. For samples where asbestos was identified, but is less than 1.0%, report “Asbestos present, less than 1.0%.” There must have been at least two observed fibers or fiber bundles in the two preparations to be reported as present. For samples where asbestos was not seen, report as “None Detected.”
4. Auxiliary Information
Because of the subjective nature of asbestos analysis, certain concepts and procedures need to be discussed in more depth. This information will help the analyst understand why some of the procedures are carried out the way they are.
4.1. Light
Light is electromagnetic energy. It travels from its source in packets called quanta. It is instructive to consider light as a plane wave. The light has a direction of travel. Perpendicular to this and mutually perpendicular to each other, are two vector components. One is the magnetic vector and the other is the electric vector. We shall only be concerned with the electric vector. In this description, the interaction of the vector and the mineral will describe all the observable phenomena. From a light source such a microscope illuminator, light travels in all different direction from the filament.
In any given direction away from the filament, the electric vector is perpendicular to the direction of travel of a light ray. While perpendicular, its orientation is random about the travel axis. If the electric vectors from all the light rays were lined up by passing the light through a filter that would only let light rays with electric vectors oriented in one direction pass, the light would then be POLARIZED.
Polarized light interacts with matter in the direction of the electric vector. This is the polarization direction. Using this property it is possible to use polarized light to probe different materials and identify them by how they interact with light. The speed of light in a vacuum is a constant at about 2.99 × 108 m/s. When light travels in different materials such as air, water, minerals or oil, it does not travel at this speed. It travels slower. This slowing is a function of both the material through which the light is traveling and the wavelength or frequency of the light. In general, the more dense the material, the slower the light travels. Also, generally, the higher the frequency, the slower the light will travel. The ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to that in a material is called the index of refraction (n). It is usually measured at 589 nm (the sodium D line). If white light (light containing all the visible wavelengths) travels through a material, rays of longer wavelengths will travel faster than those of shorter wavelengths, this separation is called dispersion. Dispersion is used as an identifier of materials as described in Section 4.6.
4.2. Material Properties
Materials are either amorphous or crystalline. The difference between these two descriptions depends on the positions of the atoms in them. The atoms in amorphous materials are randomly arranged with no long range order. An example of an amorphous material is glass. The atoms in crystalline materials, on the other hand, are in regular arrays and have long range order. Most of the atoms can be found in highly predictable locations. Examples of crystalline material are salt, gold, and the asbestos minerals.
It is beyond the scope of this method to describe the different types of crystalline materials that can be found, or the full description of the classes into which they can fall. However, some general crystallography is provided below to give a foundation to the procedures described.
With the exception of anthophyllite, all the asbestos minerals belong to the monoclinic crystal type. The unit cell is the basic repeating unit of the crystal and for monoclinic crystals can be described as having three unequal sides, two 90° angles and one angle not equal to 90°. The orthorhombic group, of which anthophyllite is a member has three unequal sides and three 90° angles. The unequal sides are a consequence of the complexity of fitting the different atoms into the unit cell. Although the atoms are in a regular array, that array is not symmetrical in all directions. There is long range order in the three major directions of the crystal. However, the order is different in each of the three directions. This has the effect that the index of refraction is different in each of the three directions. Using polarized light, we can investigate the index of refraction in each of the directions and identify the mineral or material under investigation. The indices α, β, and γ are used to identify the lowest, middle, and highest index of refraction respectively. The x direction, associated with α is called the fast axis. Conversely, the z direction is associated with γ and is the slow direction. Crocidolite has α along the fiber length making it “length-fast”. The remainder of the asbestos minerals have the γ axis along the fiber length. They are called “length-slow”. This orientation to fiber length is used to aid in the identification of asbestos.
4.3. Polarized Light Technique
Polarized light microscopy as described in this section uses the phase-polar microscope described in Section 3.2. A phase contrast microscope is fitted with two polarizing elements, one below and one above the sample. The polarizers have their polarization directions at right angles to each other. Depending on the tests performed, there may be a compensator between these two polarizing elements. Light emerging from a polarizing element has its electric vector pointing in the polarization direction of the element. The light will not be subsequently transmitted through a second element set at a right angle to the first element. Unless the light is altered as it passes from one element to the other, there is no transmission of light.
4.4. Angle of Extinction
Crystals which have different crystal regularity in two or three main directions are said to be anisotropic. They have a different index of refraction in each of the main directions. When such a crystal is inserted between the crossed polars, the field of view is no longer dark but shows the crystal in color. The color depends on the properties of the crystal. The light acts as if it travels through the crystal along the optical axes. If a crystal optical axis were lined up along one of the polarizing directions (either the polarizer or the analyzer) the light would appear to travel only in that direction, and it would blink out or go dark. The difference in degrees between the fiber direction and the angle at which it blinks out is called the angle of extinction. When this angle can be measured, it is useful in identifying the mineral. The procedure for measuring the angle of extinction is to first identify the polarization direction in the microscope. A commercial alignment slide can be used to establish the polarization directions or use anthophyllite or another suitable mineral. This mineral has a zero degree angle of extinction and will go dark to extinction as it aligns with the polarization directions. When a fiber of anthophyllite has gone to extinction, align the eyepiece reticle or graticule with the fiber so that there is a visual cue as to the direction of polarization in the field of view. Tape or otherwise secure the eyepiece in this position so it will not shift.
After the polarization direction has been identified in the field of view, move the particle of interest to the center of the field of view and align it with the polarization direction. For fibers, align the fiber along this direction. Note the angular reading of the rotating stage. Looking at the particle, rotate the stage until the fiber goes dark or “blinks out”. Again note the reading of the stage. The difference in the first reading and the second is an angle of extinction.
The angle measured may vary as the orientation of the fiber changes about its long axis. Tables of mineralogical data usually report the maximum angle of extinction. Asbestos forming minerals, when they exhibit an angle of extinction, usually do show an angle of extinction close to the reported maximum, or as appropriate depending on the substitution chemistry.
4.5. Crossed Polars With Compensator
When the optical axes of a crystal are not lined up along one of the polarizing directions (either the polarizer or the analyzer) part of the light travels along one axis and part travels along the other visible axis. This is characteristic of birefringent materials.
The color depends on the difference of the two visible indices of refraction and the thickness of the crystal. The maximum difference available is the difference between the α and the γ axes. This maximum difference is usually tabulated as the birefringence of the crystal.
For this test, align the fiber at 45° to the polarization directions in order to maximize the contribution to each of the optical axes. The colors seen are called retardation colors. They arise from the recombination of light which has traveled through the two separate directions of the crystal. One of the rays is retarded behind the other since the light in that direction travels slower. On recombination, some of the colors which make up white light are enhanced by constructive interference and some are suppressed by destructive interference. The result is a color dependent on the difference between the indices and the thickness of the crystal. The proper colors, thicknesses, and retardations are shown on a Michel-Levy chart. The three items, retardation, thickness and birefringence are related by the following relationship:
R = t(nγ—α)
R = retardation, t = crystal thickness in µm, and
α,γ = indices of refraction.
Examination of the equation for asbestos minerals reveals that the visible colors for almost all common asbestos minerals and fiber sizes are shades of gray and black. The eye is relatively poor at discriminating different shades of gray. It is very good at discriminating different colors. In order to compensate for the low retardation, a compensator is added to the light train between the polarization elements. The compensator used for this test is a gypsum plate of known thickness and birefringence. Such a compensator when oriented at 45° to the polarizer direction, provides a retardation of 530 nm of the 530 nm wavelength color. This enhances the red color and gives the background a characteristic red to red-magenta color. If this “full-wave” compensator is in place when the asbestos preparation is inserted into the light train, the colors seen on the fibers are quite different. Gypsum, like asbestos has a fast axis and a slow axis. When a fiber is aligned with its fast axis in the same direction as the fast axis of the gypsum plate, the ray vibrating in the slow direction is retarded by both the asbestos and the gypsum. This results in a higher retardation than would be present for either of the two minerals. The color seen is a second order blue. When the fiber is rotated 90° using the rotating stage, the slow direction of the fiber is now aligned with the fast direction of the gypsum and the fast direction of the fiber is aligned with the slow direction of the gypsum. Thus, one ray vibrates faster in the fast direction of the gypsum, and slower in the slow direction of the fiber; the other ray will vibrate slower in the slow direction of the gypsum and faster in the fast direction of the fiber. In this case, the effect is subtractive and the color seen is a first order yellow. As long as the fiber thickness does not add appreciably to the color, the same basic colors will be seen for all asbestos types except crocidolite. In crocidolite the colors will be weaker, may be in the opposite directions, and will be altered by the blue absorption color natural to crocidolite. Hundreds of other materials will give the same colors as asbestos, and therefore, this test is not definitive for asbestos. The test is useful in discriminating against fiberglass or other amorphous fibers such as some synthetic fibers. Certain synthetic fibers will show retardation colors different than asbestos; however, there are some forms of polyethylene and aramid which will show morphology and retardation colors similar to asbestos minerals. This test must be supplemented with a positive identification test when birefringent fibers are present which can not be excluded by morphology. This test is relatively ineffective for use on fibers less than 1 µm in diameter. For positive confirmation TEM or SEM should be used if no larger bundles or fibers are visible.
4.6. Dispersion Staining
Dispersion microscopy or dispersion staining is the method of choice for the identification of asbestos in bulk materials. Becke line analysis is used by some laboratories and yields the same results as does dispersion staining for asbestos and can be used in lieu of dispersion staining. Dispersion staining is performed on the same platform as the phase-polar analysis with the analyzer and compensator removed. One polarizing element remains to define the direction of the light so that the different indices of refraction of the fibers may be separately determined. Dispersion microscopy is a dark-field technique when used for asbestos. Particles are imaged with scattered light. Light which is unscattered is blocked from reaching the eye either by the back field image mask in a McCrone objective or a back field image mask in the phase condenser. The most convenient method is to use the rotating phase condenser to move an oversized phase ring into place. The ideal size for this ring is for the central disk to be just larger than the objective entry aperture as viewed in the back focal plane. The larger the disk, the less scattered light reaches the eye. This will have the effect of diminishing the intensity of dispersion color and will shift the actual color seen. The colors seen vary even on microscopes from the same manufacturer. This is due to the different bands of wavelength exclusion by different mask sizes. The mask may either reside in the condenser or in the objective back focal plane. It is imperative that the analyst determine by experimentation with asbestos standards what the appropriate colors should be for each asbestos type. The colors depend also on the temperature of the preparation and the exact chemistry of the asbestos. Therefore, some slight differences from the standards should be allowed. This is not a serious problem for commercial asbestos uses. This technique is used for identification of the indices of refraction for fibers by recognition of color. There is no direct numerical readout of the index of refraction. Correlation of color to actual index of refraction is possible by referral to published conversion tables. This is not necessary for the analysis of asbestos. Recognition of appropriate colors along with the proper morphology are deemed sufficient to identify the commercial asbestos minerals. Other techniques including SEM, TEM, and XRD may be required to provide additional information in order to identify other types of asbestos.
Make a preparation in the suspected matching high dispersion oil, e.g., n = 1.550 for chrysotile. Perform the preliminary tests to determine whether the fibers are birefringent or not. Take note of the morphological character. Wavy fibers are indicative of chrysotile while long, straight, thin, frayed fibers are indicative of amphibole asbestos. This can aid in the selection of the appropriate matching oil. The microscope is set up and the polarization direction is noted as in Section 4.4. Align a fiber with the polarization direction. Note the color. This is the color parallel to the polarizer. Then rotate the fiber rotating the stage 90° so that the polarization direction is across the fiber. This is the perpendicular position. Again note the color. Both colors must be consistent with standard asbestos minerals in the correct direction for a positive identification of asbestos. If only one of the colors is correct while the other is not, the identification is not positive. If the colors in both directions are bluish-white, the analyst has chosen a matching index oil which is higher than the correct matching oil, e.g. the analyst has used n = 1.620 where chrysotile is present. The next lower oil (Section 3.5.) should be used to prepare another specimen. If the color in both directions is yellow-white to straw-yellow-white, this indicates that the index of the oil is lower than the index of the fiber, e.g. the preparation is in n = 1.550 while anthophyllite is present. Select the next higher oil (Section 3.5.) and prepare another slide. Continue in this fashion until a positive identification of all asbestos species present has been made or all possible asbestos species have been ruled out by negative results in this test. Certain plant fibers can have similar dispersion colors as asbestos. Take care to note and evaluate the morphology of the fibers or remove the plant fibers in pre-preparation. Coating material on the fibers such as carbonate or vinyl may destroy the dispersion color. Usually, there will be some outcropping of fiber which will show the colors sufficient for identification. When this is not the case, treat the sample as described in Section 3.3. and then perform dispersion staining. Some samples will yield to Becke line analysis if they are coated or electron microscopy can be used for identification.
5. References
5.1. Crane, D.T., Asbestos in Air, OSHA method ID160, Revised November 1992.
5.2. Ford, W.E., Dana's Textbook of Mineralogy; Fourth Ed.; John Wiley and Son, New York, 1950, p. vii.
5.3. Selikoff,.I.J., Lee, D.H.K., Asbestos and Disease, Academic Press, New York, 1978, pp. 3, 20.
5.4. Women Inspectors of Factories. Annual Report for 1898, H.M. Statistical Office, London, p. 170 (1898).
5.5. Selikoff,.I.J., Lee, D.H.K., Asbestos and Disease, Academic Press, New York, 1978, pp. 26, 30.
5.6. Campbell, W.J., et al, Selected Silicate Minerals and Their Asbestiform Varieties, United States Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines, Information Circular 8751, 1977.
5.7. Asbestos, Code of Federal Regulations, 29 CFR 1910.1001 and 29 CFR 1926.58.
5.8. National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants; Asbestos NESHAP Revision, Federal Register, Vol. 55, No. 224, 20 November 1990, p. 48410.
5.9. Ross, M. The Asbestos Minerals: Definitions, Description, Modes of Formation, Physical and Chemical Properties and Health Risk to the Mining Community, Nation Bureau of Standards Special Publication, Washington, D.C., 1977.
5.10. Lilis, R., Fibrous Zeolites and Endemic Mesothelioma in Cappadocia, Turkey, J. Occ Medicine, 1981, 23, (8) ,548-550.
5.11. Occupational Exposure to Asbestos—1972, U.S. Department of Health Education and Welfare, Public Health Service, Center for Disease Control, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, HSM-72-10267.
5.12. Campbell,W.J., et al, Relationship of Mineral Habit to Size Characteristics for Tremolite Fragments and Fibers, United States Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines, Information Circular 8367, 1979.
5.13. Mefford, D., DCM Laboratory, Denver, private communication, July 1987.
5.14. Deer, W.A., Howie, R.A., Zussman, J., Rock Forming Minerals, Longman, Thetford, UK, 1974.
5.15. Kerr, P.F., Optical Mineralogy; Third Ed. McGraw-Hill, New York, 1959.
5.16. Veblen, D.R. (Ed.), Amphiboles and Other Hydrous Pyriboles—Mineralogy, Reviews in Mineralogy, Vol 9A, Michigan, 1982, pp 1-102.
5.17. Dixon, W.C., Applications of Optical Microscopy in the Analysis of Asbestos and Quartz, ACS Symposium Series, No. 120, Analytical Techniques in Occupational Health Chemistry, 1979.
5.18. Polarized Light Microscopy, McCrone Research Institute, Chicago, 1976.
5.19. Asbestos Identification, McCrone Research Institute, G & G printers, Chicago, 1987.
5.20. McCrone, W.C., Calculation of Refractive Indices from Dispersion Staining Data, The Microscope, No 37, Chicago, 1989.
5.21. Levadie, B. (Ed.), Asbestos and Other Health Related Silicates, ASTM Technical Publication 834, ASTM, Philadelphia 1982.
5.22. Steel, E. and Wylie, A., Riordan, P.H. (Ed.), Mineralogical Characteristics of Asbestos, Geology of Asbestos Deposits, pp. 93-101, SME-AIME, 1981.
5.23. Zussman, J., The Mineralogy of Asbestos, Asbestos: Properties, Applications and Hazards, pp. 45-67 Wiley, 1979.
Appendix L to §1915.1001—Work Practices and Engineering Controls for Automotive Brake and Clutch Inspection, Disassembly, Repair and Assembly—Mandatory
This mandatory appendix specifies engineering controls and work practices that must be implemented by the employer during automotive brake and clutch inspection, disassembly, repair, and assembly operations. Proper use of these engineering controls and work practices by trained employees will reduce employees' asbestos exposure below the permissible exposure level during clutch and brake inspection, disassembly, repair, and assembly operations. The employer shall institute engineering controls and work practices using either the method set forth in paragraph [A] or paragraph [B] of this appendix, or any other method which the employer can demonstrate to be equivalent in terms of reducing employee exposure to asbestos as defined and which meets the requirements described in paragraph [C] of this appendix, for those facilities in which no more than 5 pairs of brakes or 5 clutches are inspected, disassembled, reassembled and/or repaired per week, the method set forth in paragraph [D] of this appendix may be used:
[A] Negative Pressure Enclosure/HEPA Vacuum System Method
(1) The brake and clutch inspection, disassembly, repair, and assembly operations shall be enclosed to cover and contain the clutch or brake assembly and to prevent the release of asbestos fibers into the worker's breathing zone.
(2) The enclosure shall be sealed tightly and thoroughly inspected for leaks before work begins on brake and clutch inspection, disassembly, repair, and assembly.
(3) The enclosure shall be such that the worker can clearly see the operation and shall provide impermeable sleeves through which the worker can handle the brake and clutch inspection, disassembly, repair and assembly. The integrity of the sleeves and ports shall be examined before work begins.
(4) A HEPA-filtered vacuum shall be employed to maintain the enclosure under negative pressure throughout the operation. Compressed-air may be used to remove asbestos fibers or particles from the enclosure.
(5) The HEPA vacuum shall be used first to loosen the asbestos containing residue from the brake and clutch parts and then to evacuate the loosened asbestos containing material from the enclosure and capture the material in the vacuum filter.
(6) The vacuum's filter, when full, shall be first wetted with a fine mist of water, then removed and placed immediately in an impermeable container, labeled according to paragraph (k)(8) of this section and disposed of according to paragraph (l) of this section.
(7) Any spills or releases of asbestos containing waste material from inside of the enclosure or vacuum hose or vacuum filter shall be immediately cleaned up and disposed of according to paragraph (l) of the section.
[B] Low Pressure/Wet Cleaning Method
(1) A catch basin shall be placed under the brake assembly, positioned to avoid splashes and spills.
(2) The reservoir shall contain water containing an organic solvent or wetting agent. The flow of liquid shall be controlled such that the brake assembly is gently flooded to prevent the asbestos-containing brake dust from becoming airborne.
(3) The aqueous solution shall be allowed to flow between the brake drum and brake support before the drum is removed.
(4) After removing the brake drum, the wheel hub and back of the brake assembly shall be thoroughly wetted to suppress dust.
(5) The brake support plate, brake shoes and brake components used to attach the brake shoes shall be thoroughly washed before removing the old shoes.
(6) In systems using filters, the filters, when full, shall be first wetted with a fine mist of water, then removed and placed immediately in an impermeable container, labeled according to paragraph (k)(8) of this section and disposed of according to paragraph (l) of this section.
(7) Any spills of asbestos-containing aqueous solution or any asbestos-containing waste material shall be cleaned up immediately and disposed of according to paragraph (l) of this section.
(8) The use of dry brushing during low pressure/wet cleaning operations is prohibited.
[C] Equivalent Methods
An equivalent method is one which has sufficient written detail so that it can be reproduced and has been demonstrated that the exposures resulting from the equivalent method are equal to or less than the exposures which would result from the use of the method described in paragraph [A] of this appendix. For purposes of making this comparison, the employer shall assume that exposures resulting from the use of the method described in paragraph [A] of this appendix shall not exceed 0.016 f/cc, as measured by the OSHA reference method and as averaged over at least 18 personal samples.
[D] Wet Method
(1) A spray bottle, hose nozzle, or other implement capable of delivering a fine mist of water or amended water or other delivery system capable of delivering water at low pressure, shall be used to first thoroughly wet the brake and clutch parts. Brake and clutch components shall then be wiped clean with a cloth.
(2) The cloth shall be placed in an impermeable container, labelled according to paragraph (k)(8) of this section and then disposed of according to paragraph (l) of this section, or the cloth shall be laundered in a way to prevent the release of asbestos fibers in excess of 0.1 fiber per cubic centimeter of air.
(3) Any spills of solvent or any asbestos containing waste material shall be cleaned up immediately according to paragraph (l) of this section.
(4) The use of dry brushing during the wet method operations is prohibited.
[59 FR 41080, Aug. 10, 1994, as amended at 60 FR 33344, June 28, 1995; 60 FR 33987, June 29, 1995; 60 FR 36044, July 13, 1995; 60 FR 50412, Sept. 29, 1995; 61 FR 43457, Aug. 23, 1996; 63 FR 35137, June 29, 1998; 67 FR 44545, 44546, July 3, 2002; 70 FR 1143, Jan. 5, 2005; 71 FR 16674, Apr. 3, 2006; 71 FR 50191, Aug. 24, 2006; 73 FR 75587, Dec. 12, 2009; 76 FR 33610, June 8, 2011; 77 FR 17888, Mar. 26, 2012; 78 FR 9315, Feb. 8, 2013; 84 FR 21555, 12597, May 14, 2019]
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | Cannon, Belinda - OSHA |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2023-07-29 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy