Teacher Math Knowledge for Teaching Assessment
Efficacy Evaluation of the Mathematics Intervention Toolkit for the Elementary Grades
Teacher Math Knowledge for Teaching Assessment rev2
Efficacy Evaluation of the Mathematics Intervention Toolkit for the Elementary Grades
OMB: 1850-0987

Teacher Math Knowledge for Teaching Assessment
Instructions:
Please complete this brief assessment to help us better understand the role that teachers’ math knowledge can have on supporting student learning. Note that the information you provide here will falls under the confidentiality and data protection requirements of the Institute of Education Sciences (The Education Sciences Reform Act of 2002, Title I, Part E, Section 183), and the data collected will be securely protected. You may opt out of responding to a question or the entire instrument at any time without any consequences. None of your responses will be individually attributed to you or your school/district. Your responses will be used for statistical purposes only.
1.

2.

0.240
0.30
0.08
These incorrect answers should be about equally popular.
3.

Kiara has 11 dimes. She gave 4 dimes to Jackie. How many dimes does Kiara have now?
Penelope has 11 carrots. She gave some to Todd. How many did she give to Todd?
Dominic has 11 flowers. 7 of them are red and the rest of yellow. How many yellow flowers does Dominic have?
Aria’s pencil is 11 inches long. Maxwell’s pencil is 4 inches long. How much longer is Aria’s pencil than Maxwell’s?
4.
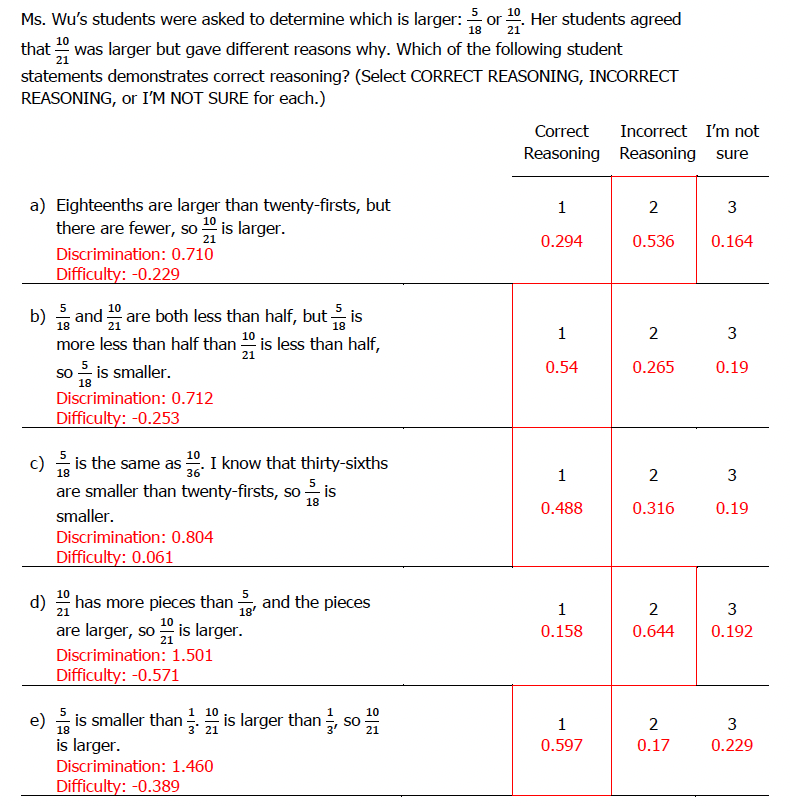
Eighteenths are larger than twenty-firsts, but there are fewer, so 10/21 is larger.
5/18 and 10/21 are both less than half, but 5/18 is more less than half than 10/21 is less than half, so 5/18 is smaller.
5/18 is the same as 10/36. I know that thirty-sixths are smaller than twenty-firsts, so 5/18 is smaller.
10/21 has more pieces than 5/18, and the pieces are larger, so 10/21 is larger.
5/18 is smaller than 1/3, 10/21 is larger than 1/3, so 10/21 is larger.
5.

Diego doesn’t understand the definition of fraction.
Diego is thinking that the grey shaded part is a fraction of the big rectangle and is using “one-half” as a generic name for a fractional part.
Diego has interpreted the whole or unit differently than intended.
Diego is thinking that the two shaded parts are equal.
6.

Lydia bought 100 pencils. She gave away 28 of those pencils. How many pencils does she have left?
Lydia bought 100 pencils. She gave away some of those pencils. She has 28 pencils left. How many pencils does she have left?
Lydia wants 100 pencils. So far, she has collected 28 pencils. How many will she need to collect before she reaches her goal?
Lydia has some pencils. She bought 28 more pencils. Now she has 100 pencils. How many pencils did she have to start?
7.

8.

Makayla thinks that because there were two digits to the right of the decimal point instead of one, 12.17 must be greater than 12.4.
Makayla is comparing the numbers as if they were 1217 and 124.
Makayla is comparing the digits after the decimal point and sees that 17 is greater than 4.
Makayla is comparing the final digits, the 7 and the 4.
9.

b) Example 2
c) Example 3
d) Example 4
10.
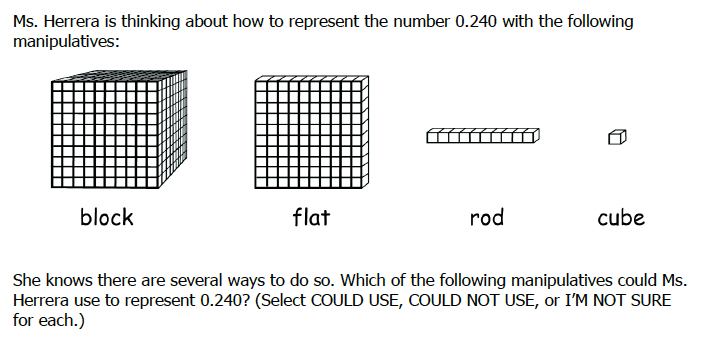
Two flats, four cubes
Two hundred cubes, four rods
Two cubes, four rods
Two blocks, four flats
Two flats, forty rods
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | Kirk Walters |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2023-08-23 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy