CMS-10305_Supporting Statement B_
CMS-10305_Supporting Statement B_.docx
Medicare Part C and Part D Data Validation (42 CFR 422.516(g) and 423.514(g)) (CMS-10305)
OMB: 0938-1115
Supporting Statement B
Medicare Part C and Part D Data Validation (42 CFR 422.516(g) and 423.514(j))
CMS-10305, OMB 0938-1115
Employing Statistical Methods for Information Collections
Describe (including a numerical estimate) the potential respondent universe and any sampling or other respondent selection method to be used. Data on the number of entities (e.g., establishments, State and local government units, households, or persons) in the universe covered by the collection and in the corresponding sample are to be provided in tabular form for the universe as a whole and for each of the strata in the proposed sample. Indicate expected response rates for the collection as a whole. If the collection had been conducted previously, include the actual response rate achieved during the last collection.
All Part C and Part D organizations that report Part C and/or Part D data to CMS per the Part C/Part D Reporting Requirements, regardless of enrollment size, are required to undergo an annual data validation review. The only organization types that the data validation requirement does not apply to are Program of All-Inclusive Care for the Elderly (PACE) organizations and 1833 Cost Plans. Because 100 percent of applicable sponsoring organizations will undergo the data validation process, sampling is not relevant for respondent selection.
Within the data validation process, DVCs are encouraged to collect the entire data set (the census) relied on by sponsoring organizations to meet Medicare Part C and D Reporting Requirements. If the census method proves impractical due to an unusual time burden placed on sponsoring organizations during data extraction, each sponsoring organization is required to perform a sampling task in collaboration with the DVC. In such cases, each sponsoring organization draws an initial sample of either 150 or 205 administrative records, at a minimum, depending on the Medicare Part C or Part D reporting section. Sample sizes may be larger and are determined by the DVC using standard statistical methodologies. All relevant records associated with these samples are then selected for review (for example, all claims for a random sample of 205 members). In cases where the population is smaller than the required sample size, records for the entire population are provided for evaluation.
Describe the procedures for the collection of information including:
− |
Statistical methodology for stratification and sample selection |
− |
Estimation procedure |
− |
Degree of accuracy needed for the purpose described in the justification |
− |
Unusual problems requiring specialized sampling procedures |
− |
Any use of periodic (less frequent than annual) data collection cycles to reduce |
burden
For data warehouse database files requiring sampling, simple random samples are used in the data validation review. The underlying standard is a quantifiable error rate in key fields which is assumed to have a binomial distribution0. The sample sizes are designed to detect error rates of 5% or more, assuming an underlying error rate of 15% or more, with a one-tailed Type I error rate (α)=.05, except for samples based on eligibility. In those cases, because more confidence is needed, α is set at .025. A standard normal approximation to the binomial distribution is used to establish critical values. A finite population correction factor has been included in sample size calculations. The variation formula below is solved for n to obtain the sample size:
pq N n−
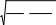
| ∆ =| Z , n−1 N
where │∆│is the desired precision (5%), N is the number in the population, p is the assumed proportion (.15), q is 1-p, and Z is the appropriate critical value from the normal curve (either 1.645 or 1.96, depending on the error rate, and n is the sample size.
Describe methods to maximize response rates and to deal with issues of non-response. The accuracy and reliability of information collected must be shown to be adequate for intended uses. For collections based on sampling, a special justification must be provided for any collection that will not yield “reliable” data that can be generalized to the universe studied.
Since extraction of the full census or use of the sampling process is required for all sponsoring organizations and their applicable reporting sections, survey-related issues such as non-response bias are not applicable.
Describe any tests of procedures or methods to be undertaken. Testing is encouraged as an effective means of refining collections of information to minimize burden and improve utility. Tests must be approved if they call for answers to identical questions from 10 or more respondents. A proposed test or set of tests may be submitted for approval separately or in combination with the main collection of information.
CMS conducted pilot tests of all methodologies, including the sampling of all supporting documents, with one Medicare Part C sponsoring organization and one Part D sponsoring organization prior to the first data validation cycle in 2010.
Provide the name and telephone number of individuals consulted on statistical aspects of the design and the name of the agency unit, contractor(s), grantee(s), or other person(s) who will actually collect and/or analyze the information for the agency.
Nelvis Njei, PharmD
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services
Medicare Drug Benefit and Part C and D Data Group
Division of Clinical and Operational Performance
410-786-9937
0 The binomial distribution measures the statistical behavior of percentages.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | Supporting Statement For Paperwork Reduction Act Submissions: Medicare Part D Reporting Requirements and |
| Author | CMS |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2023-08-18 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy