2609ss03
2609ss03.docx
Disposal of Coal Combustion Residuals From Electric Utilities (Renewal)
OMB: 2050-0223
SUPPORTING STATEMENT FOR
INFORMATION COLLECTION REQUEST OMB CONTROL NUMBER 2050-0223
“DISPOSAL OF COAL COMBUSTION RESIDUALS FROM ELECTRIC UTILITIES”
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 3
1(a) TITLE AND NUMBER OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 3
2. NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION 4
2(a) NEED AND AUTHORITY FOR THE COLLECTION 4
2(b) PRACTICAL UTILITY AND USERS OF THE DATA 4
3. NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA 5
3(b) PUBLIC NOTICE REQUIRED PRIOR TO ICR SUBMISSIONS TO OMB 6
3(d) EFFECTS OF LESS FREQUENT COLLECTION 6
4. THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED 7
4(a) RESPONDENTS AND NAICS CODES 7
5(b) COLLECTION METHODOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT 40
5(c) SMALL ENTITY FLEXIBILITY 41
6. ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF THE COLLECTION 41
6(a) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT BURDEN 41
6(b) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT COSTS 41
6(c) ESTIMATING AGENCY BURDEN AND COST 45
6(d) ESTIMATING
THE RESPONDENT UNIVERSE AND
TOTAL BURDEN AND COST 45
6(e) BOTTOM LINE BURDEN HOURS AND COSTS 45
1(a) TITLE AND NUMBER OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
This information collection request (ICR) is entitled “Disposal of Coal Combustion Residuals (CCR),” EPA ICR No. 2609.03, OMB Control No. 2050-0223.
1(b) SHORT CHARACTERIZATION
Coal combustion residuals (CCR) are generated from the combustion of coal, including solid fuels classified as anthracite, bituminous, subbituminous, and lignite, for the purpose of generating steam for the purpose of powering a generator to produce electricity or electricity and other thermal energy by electric utilities and independent power producers. CCR includes fly ash, bottom ash, boiler slag, and flue gas desulfurization materials.
CCR are solid wastes that are neither listed nor characteristic hazardous waste and thus, are subject to the requirements of Subtitle D of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act, as amended (RCRA). RCRA Subtitle D establishes a framework for federal, state, and local government cooperation in controlling the management of non-hazardous solid waste. The federal role in this management structure is to establish the overall regulatory direction, by providing minimum national standards that will protect human health and the environment, and to provide technical assistance to states for planning and developing their own environmentally sound waste management practices. The actual planning and any direct implementation of solid waste programs under RCRA Subtitle D, however, remains a state and local function, and RCRA envisions that states will devise programs to deal with state-specific conditions and needs. 40 CFR Part 257 contains provisions regarding the management of CCR under RCRA Subtitle D.
In 2015, EPA published a final rule to regulate the disposal of CCR from electric utilities as solid waste under RCRA Subtitle D (see 80 FR 21302; April 17, 2015). In the final rule, EPA established national minimum criteria for existing and new CCR landfills and CCR surface impoundments and all lateral expansions1 to include location restrictions, design and operating criteria, groundwater monitoring and corrective action, closure requirements and post-closure care, and recordkeeping, notification, and internet posting requirements.
The 2015 rule requires any existing unlined CCR surface impoundment that is contaminating groundwater above a regulated constituent’s groundwater protection standard to stop receiving CCR and either retrofit or close, except in limited circumstances. The rule also requires the closure of any CCR landfill or CCR surface impoundment that cannot meet the applicable performance criteria for location restrictions or structural integrity established in this rule. CCR surface impoundments that are no longer receiving CCR as of the effective date of the rule, but still contain water and CCR, will be subject to all applicable regulatory requirements, unless the owner or operator of the facility closes the inactive unit (e.g., the impoundment is closed with a final cover system) no later than three years from the effective date of the rule.
This rule applies to all CCRs generated by electric utilities and independent power producers that fall within the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) code 221112 and may affect the following entities: electric utility facilities and independent power producers that fall under the NAICS code 221112. Specifically, the final rule applies to owners and operators of new and existing landfills and new and existing surface impoundments, including all lateral expansions of landfills and surface impoundments that dispose or otherwise engage in solid waste management of CCRs generated from the combustion of coal at electric utilities and independent power producers. These requirements also apply to CCR units located off-site of the electric utilities’ or independent power producers’ facilities that receive CCR for disposal. In addition, the rule applies to certain inactive CCR surface impoundments (i.e., units not receiving CCR after the effective date of the rule) at active electric utilities’ or independent power producers’ facilities, regardless of the fuel currently used at the facility to produce electricity (e.g., coal, natural gas, oil), if the CCR unit still contains CCR and liquids.
Since the 2015 final rule, several Court decisions required accelerated closure timelines for many units and forced closures for many units previously categorized as lined.2 In addition, in December 2016, the President signed the Water Infrastructure Improvements for the Nation (WIIN) Act. The WIIN Act amended RCRA Subtitle D and established new statutory provisions applicable to CCR landfills and CCR surface impoundments. In particular, the WIIN Act provides that, states may, but are not required to, develop and submit a permit (or other system of prior approval) program for CCR disposal to EPA for approval. Such a program does not have to be identical to the requirements in the CCR rule (40 CFR Part 257, Subpart D), but must be at least as protective as the CCR rule.
In response to the Court decisions and the RCRA Subtitle D amendments, in 2018, EPA published a final rule (see 83 FR 36435; July 30, 2018) that modifies a number of the requirements applicable to CCR landfills and CCR surface impoundments and allows for units to receive variances for unlined surface impoundments. The final rule also incorporates anticipated state applications and programs consistent with the WIIN Act, but does not change the scope or focus of the program.
In Sections 1 through 5 of this ICR, EPA presents a comprehensive description of the 40 CFR Part 257 information collection requirements related to the disposal of CCR. In Section 6, EPA estimates the total annual burden and cost to respondents and the government associated with these paperwork requirements.
Finally, EPA merged the burden associated with the information collection requirements related to the disposal of CCR from existing ICR 2050-0053 to this ICR.
2(a) NEED AND AUTHORITY FOR THE COLLECTION
EPA regulates the disposal of CCR generated by electric utilities as solid waste under RCRA Subtitle D. In addition, EPA established national minimum criteria for existing and new CCR landfills and existing and new CCR surface impoundments and all lateral expansions. These regulations are established under the authority of Sections 1006(b), 1008(a), 2002(a), 3001, 4004, and 4005(a) of the Solid Waste Disposal Act of 1970, as amended by the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act of 1976 (RCRA), as amended by the Hazardous and Solid Waste Amendments of 1984 (HSWA), 42 U.S.C. Sections 6906(b), 6907(a), 6912(a), 6944, and 6945(a).
At the time the CCR regulations were issued on April 17, 2015, under RCRA Subtitle D, EPA had no formal role in rule implementation nor could the agency enforce the requirements in the rule. Therefore, the regulations were “self-implementing,” that is, a facility must comply with them without any action by a regulatory agency. As a result, the EPA also encouraged states to revise their Solid Waste Management Plans (SWMPs) and submit these revisions to the EPA for approval. EPA explained that revised SWMPs were the best mechanisms available to show alignment between state and federal requirements, provide the public the opportunity to review and comment on states’ plans for regulating CCR landfills and surface impoundments in their state, and to demonstrate consistency with the federal requirements.
To address concerns about the absence of adequate regulatory oversight under Subtitle D, EPA also sought to enhance the protectiveness of the regulatory requirements by providing for state and public notifications of the third-party certifications, as well as requiring a robust set of other information that documents the decisions made or actions taken to comply with the technical requirements of the rule.
The combined mechanisms of recordkeeping, notifications, and maintaining a publicly accessible internet site under the final rule are needed to provide interested parties with the information necessary to determine whether the owner or operator is operating in accordance with the requirements of the rule. These requirements reduce the danger of owners or operators abusing the self-implementing system established in this rule, through increased transparency that facilitates enforcement by states and private citizens. EPA has consolidated the recordkeeping, notification, and internet posting requirements into a single section of the regulations in an effort to make the regulations easier to follow. See 40 CFR 257.105, 257.106, and 257.107.
2(b) PRACTICAL UTILITY AND USERS OF THE DATA
The CCR rule requires owners or operators of CCR units to document how the various provisions of the rule have been met by placing information (e.g., demonstrations, plans, records, notifications, and reports) in the operating record and providing notification of these actions to the state and/or appropriate Tribal authority. The owner or operator also is required to establish and maintain a publicly accessible internet site that posts documentation that has, in many instances, also been entered into the operating record. The owner or operator must place files documenting compliance with the location restrictions; design criteria; operating criteria; groundwater monitoring and corrective action; closure and post-closure care, into the operating record, with the specific documentation requirements found in 40 CFR 257.105. Each file must be maintained in the operating record for a period of at least five years following submittal of the file into the operating record. In certain instances, however, files must be maintained until the CCR unit complete closure.
Owners or operators are required to notify State Directors and/or the appropriate Tribal authority when specific documentation has been placed in the operating record and on the owner or operator’s publicly accessible web site. In most instances these notifications must be certified by a qualified professional engineer and, in certain instances will be accompanied with additional information and or data supporting the notification. Notification requirements have been consolidated in 40 CFR 257.106, and are required for location criteria, design criteria, operating criteria, groundwater monitoring and corrective action and closure and post-closure care.
EPA believes that these requirements will enhance the protectiveness of the rule by providing for state and public notifications of the third-party certifications, as well as requiring a robust set of other information that documents the decisions made or actions taken to comply with the technical requirements of the rule. Further, EPA believes that the establishment and maintenance of this information in both the operating record and on a publicly accessible internet site is appropriate so as to allow states and citizens access to all of the information necessary to show that the rule has been implemented in accordance with the regulatory requirements. EPA has consolidated the recordkeeping and notification requirements into a comprehensive listing in a single section of the regulations. See 40 CFR 257.105 and 257.106, respectively. The Agency anticipates that this will facilitate compliance and will provide other interested parties with an easy-to-read guide to the reporting provisions of the rule.
With the passage of the WIIN Act in December 2016, RCRA Subtitle D was amended to provide new statutory authority pertaining to the management of CCR in landfills and surface impoundments. The WIIN Act allows states to seek CCR permit program approval from EPA. If a state elects to pursue program approval, the information provided by the state will allow EPA to assess and determine whether the state submission meets the statutory requirements.
NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA
3(a) NONDUPLICATION
None of the information required by the regulations covered in this ICR is available from any source but the respondents. None of the regulations are duplicative of any other EPA regulations.
3(b) PUBLIC NOTICE REQUIRED PRIOR TO ICR SUBMISSIONS TO OMB
In compliance with the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995, EPA opened a 60-day public comment period for the collection activities, which was published on May 1, 2023 in the Federal Register (88 FR 26537). EPA received no comments on this ICR in response to the Federal Register notice.
3(c) CONSULTATIONS
The regulations covered by this ICR were promulgated using proper rulemaking procedures. In updating this ICR, EPA spoke with Agency staff in Headquarters and the Regions, State representatives, and industry representatives. Their feedback is reflected in this ICR. The following members of EPA Regions, the States, and regulated community were contacted:
Michelle Peace, U. S. EPA Region 6
Kevin Snowden, U. S. EPA Region
Dave Bartus, U.S. EPA Region 10
Jim Ferritto, Michigan Department of Environmental Quality
Kenney Setliff, ExxonMobil Oil Corporation
Caleb Poenitzsch, Samsung
3(d) EFFECTS OF LESS FREQUENT COLLECTION
EPA has carefully considered the information collection burden imposed upon the regulated community by the requirements covered in this ICR. EPA is confident that those activities required of respondents are necessary to provide sufficient information to state and public users to make informed decisions about policies and actions related to the implementation of the 40 CFR Part 257 information collection requirements related to the disposal of CCR. To the extent possible, the Agency has attempted to minimize the burden imposed by refining existing information requirements and specifying electronic publication of the information on existing web sites. EPA believes strongly that, if the minimum requirements specified under the regulations are not met, EPA cannot ensure that CCR are properly managed and do not pose a serious threat to human health and the environment.
3(e) GENERAL GUIDELINES
This ICR adheres to the guidelines stated in the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995, the Office of Management and Budget’s (OMB’s) implementing regulations, OMB’s Information Collection Review Handbook, applicable OMB guidance, and EPA’s ICR Handbook.
3(f) CONFIDENTIALITY
None of the information collection requirements covered in this ICR require the disclosure of confidential business information. EPA believes that the recordkeeping, notification, and internet posting requirements under the final rule are necessary as a mechanism for States and citizens to monitor the situation of CCR units, such as when groundwater monitoring shows evidence of potential contamination, so that they can determine when intervention is appropriate. The “transparency” requirements under the final rule serve as a key component by ensuring that the entities primarily responsible for enforcing the requirements have access to the information necessary to determine whether enforcement is warranted.
3(g) SENSITIVE QUESTIONS
No questions of a sensitive nature are included in any of the information collection requirements covered in this ICR.
4. THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED
4(a) RESPONDENTS AND NAICS CODES
The information collection requirements covered in this ICR may affect electric utility facilities and independent power producers that fall under the NAICS code 221112 (Fossil Fuel Electric Power Generation).
4(b) INFORMATION REQUESTED
Beneficial Use of CCR
Under 40 CFR 257.53, beneficial use of CCR means the CCR meet all of the following conditions: (1) the CCR must provide a functional benefit; (2) the CCR must substitute for the use of a virgin material, conserving natural resources that would otherwise need to be obtained through practices, such as extraction; (3) the use of the CCR must meet relevant product specifications, regulatory standards or design standards when available, and when such standards are not available, CCR are not used in excess quantities; and (4) when unencapsulated use of CCR involving placement on the land of 12,400 tons or more in non-roadway applications, the user must demonstrate and keep records, and provide such documentation upon request, that environmental releases to ground water, surface water, soil and air are comparable to or lower than those from analogous products made without CCR, or that environmental releases to ground water, surface water, soil and air will be at or below relevant regulatory and health-based benchmarks for human and ecological receptors during use.
Data Item:
Demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.53.
Respondent Activities:
Beneficial users of CCR must perform the following activities:
Prepare and keep demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.53.
Location Restrictions
Placement above the Uppermost Aquifer
Under 40 CFR 257.60, new CCR landfills, existing and new CCR surface impoundments, and all lateral expansions of CCR landfills and CCR surface impoundments must be constructed with a base that is located no less than 1.52 meters (five feet) above the upper limit of the uppermost aquifer, or to demonstrate that there will not be an intermittent, recurring, or sustained hydraulic connection between any portion of the base of the CCR unit and the uppermost aquifer due to normal fluctuations in groundwater elevations (including the seasonal high water table). The owner or operator must demonstrate by the dates specified in 40 CFR 257.60(c) that the CCR unit meets the minimum requirements for placement above the uppermost aquifer.
In addition, the owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(e), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(e), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(e). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.60(a).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.60(b).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Prepare demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.60(a).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.60(b).
Wetlands
Under 40 CFR 257.61, new CCR landfills, existing and new CCR surface impoundments, and all lateral expansions of CCR landfills and CCR surface impoundments must not be located in wetlands, as defined in 40 CFR 232.2, unless the owner or operator demonstrates by the dates specified in 40 CFR 257.61(c) that the CCR unit meets the requirements of 40 CFR 257.61(a)(1) through (a)(5).
In addition, the owner or operator must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(e), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(e), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(e). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.61(a).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.61(b).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Prepare demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.61(a).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.61(b).
Fault Areas
Under 40 CFR 257.62, new CCR landfills, existing and new CCR surface impoundments, and all lateral expansions of CCR landfills and CCR surface impoundments must not be located within 60 meters (200 feet) of the outermost damage zone of a fault that has had displacement in Holocene time unless the owner or operator demonstrates by the dates specified in 40 CFR 257.62(c) that an alternative setback distance of less than 60 meters (200 feet) will prevent damage to the structural integrity of the CCR unit.
In addition, the owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(e), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(e), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(e). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.62(a).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.62(b).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Prepare demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.62(a).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.62(b).
Seismic Impact Zones
Under 40 CFR 257.63, new CCR landfills, existing and new CCR surface impoundments, and all lateral expansions of CCR landfills and CCR surface impoundments must not be located in seismic impact zones unless the owner or operator demonstrates by the dates specified in 40 CFR 257.63(c) that all structural components including liners, leachate collection and removal systems, and surface water control systems, are designed to resist the maximum horizontal acceleration in lithified earth material for the site.
In addition, the owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(e), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(e), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(e). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.63(a).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.63(b).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Prepare demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.63(a).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.63(b).
Unstable Areas
Under 40 CFR 257.64, an existing or new CCR landfill, existing or new CCR surface impoundment, or any lateral expansion of a CCR landfill or CCR surface impoundment must not be located in an unstable area unless the owner or operator demonstrates by the dates specified in 40 CFR 257.64(d) that recognized and generally accepted good engineering practices have been incorporated into the design of the CCR unit to ensure that the integrity of the structural components of the CCR unit will not be disrupted. The owner or operator must consider all of the factors at 40 CFR 257.64(b), at a minimum, when determining whether an area is unstable.
In addition, the owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(e), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(e), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(e). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.64(a).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.64(c).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Prepare demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.64(a).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.64(c).
Design Criteria
Liner Design Criteria for New CCR Landfills and Any Lateral Expansion of a CCR Landfill
Under 40 CFR 257.70, new CCR landfills and any lateral expansion of a CCR landfill must be designed, constructed, operated, and maintained with either a composite liner that meets the requirements of 40 CFR 257.70(b) or an alternative composite liner that meets the requirements in 40 CFR 257.70(c), and a leachate collection and removal system that meets the requirements of 40 CFR 257.70(d).
In addition, the owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(f), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(f), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(f). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.70(c)(2).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.70(e).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.70(f).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.70(c)(2).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.70(e).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.70(f).
Liner Design Criteria for Existing CCR Surface Impoundments
Under 40 CFR 257.71, the owner or operator of an existing CCR surface impoundment must document whether or not such unit was constructed with any one of the following: (i) a liner consisting of a minimum of two feet of compacted soil with a hydraulic conductivity of no more than 1x10-7 cm/sec; (ii) a composite liner that meets the requirements of 40 CFR 257.70(b); or (iii) an alternative liner that meets the requirements of 40 CFR 257.70(c)
In addition, the owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(f), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(f), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(f). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Documentation of liner type under 40 CFR 257.71(a).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.71(b).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Document liner type under 40 CFR 257.71(a).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.71(b).
Liner Design Criteria for New CCR Surface Impoundments and Any Lateral Expansion of a CCR Surface Impoundment
Under 40 CFR 257.72, new CCR surface impoundments and lateral expansions of existing and new CCR surface impoundments must be designed, constructed, operated, and maintained with either a composite liner or an alternative composite liner that meets the requirements of 40 CFR 257.70(b) or (c).
In addition, the owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(f), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(f), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(f). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.
Data Items:
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.72(c).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.72(d).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.72(c).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.72(d).
Alternate Liner Demonstrations
For each CCR unit, owners/operators must demonstrate that the surface impoundment’s clay liner meets the Section 4004(a) standard for sanitary landfill classification, and therefore that the unit should be classified as “lined.”
This provision is voluntary; owners/operators of CCR impoundments are not required to submit the application, or to submit the demonstration if their application is approved.
Data Item:
Alternate liner demonstration application.
Alternate liner demonstration.
(ii) Respondent Activities:
Owners/operators of a CCR surface impoundment are expected to perform the following activities:
For each unit, submit an application to EPA expressing their interest to pursue a liner demonstration.
If the demonstration for a given unit is approved by EPA, proceed to complete the demonstration.
Structural Integrity Criteria for Existing CCR Surface Impoundments
40 CFR 257.73 provides structural integrity criteria requirements for existing CCR surface impoundments. These requirements include: periodic hazard potential classification assessments, a written Emergency Action Plan (EAP), changes to the history of construction, periodic structural stability assessments, and periodic safety factor assessments
The requirements of 40 CFR 257.73(a) apply to all existing CCR surface impoundments, except for those existing CCR surface impoundments that are incised CCR units. If an incised CCR surface impoundment is subsequently modified (e.g., a dike is constructed) such that the CCR unit no longer meets the definition of an incised CCR unit, the CCR unit is subject to the requirements of 40 CFR 257.73(a)
Owners and operators of CCR units must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(f), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(f), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(f). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
A permanent identification marker showing the identification number of the CCR unit, as required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(1).
Documentation of the initial and periodic hazard potential classification assessments of the CCR unit, as required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(2).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(2)(ii).
A written EAP, as required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3).
Documentation on an annual face-to-face meeting or exercise between representatives of the owner/operator of the CCR unit and the local emergency responders, as required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(i)(E).
Amended EAP, as required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(ii).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(iv)).
Documentation required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(v).
History of construction required under 40 CFR 257.73(c).
Documentation of initial and periodic structural stability assessments, as required under 40 CFR 257.73(d).
Action plan required under 40 CFR 257.73(d)(2).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.73(d)(3).
Documentation of initial and periodic safety factor assessments for each CCR unit, as required under 40 CFR 257.73(e).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.73(e)(2).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Place on or immediately adjacent to the CCR unit a permanent identification marker showing the identification number of the CCR unit, as required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(1).
Document the initial and periodic hazard potential classification assessments of the CCR unit, as required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(2).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(2)(ii).
Prepare a written EAP, as required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3).
Prepare documentation on an annual face-to-face meeting or exercise between representatives of the owner/operator of the CCR unit and the local emergency responders, as required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(i)(E).
Amend the EAP, as required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(ii).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(iv)).
Prepare documentation required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(v).
Compile history of construction required under 40 CFR 257.73(c).
Conduct and document initial and periodic structural stability assessments, s required under 40 CFR 257.73(d).
Prepare action plan required under 40 CFR 257.73(d)(2).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.73(d)(3).
Conduct and document initial and periodic safety factor assessments for each CCR unit, as required under 40 CFR 257.73(e).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.73(e)(2).
Structural Integrity Criteria for New CCR Surface Impoundments and Any Lateral Expansion of a CCR Surface Impoundment
40 CFR 257.74 provides structural integrity criteria requirements for new CCR surface impoundments and any lateral expansion of a CCR surface impoundment. These requirements include: periodic hazard potential classification assessments, a written Emergency Action Plan (EAP), design and construction plans, periodic structural stability assessments, and periodic safety factor assessments
Owners and operators of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(f), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(f), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(f). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.
Data Items:
A permanent identification marker showing the identification number of the CCR unit, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(1).
Documentation of the initial and periodic hazard potential classification assessments of the CCR unit, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(2). .
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(2)(ii).
A written EAP, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(3).
Documentation on an annual face-to-face meeting or exercise between representatives of the owner/operator of the CCR unit and the local emergency responders, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(3)(i)(E)
Amended EAP, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(3)(ii)
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(3)(iv).
Documentation required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(3)(v).
Design and construction plans for the CCR unit, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(c).
Documentation of initial and periodic structural stability assessments, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(d).
Action plan required under 40 CFR 257.74(d)(2).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.74(d)(3).
Documentation of initial and periodic safety factor assessments for each CCR unit, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(e).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.74(e)(2).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Place on or immediately adjacent to the CCR unit a permanent identification marker showing the identification number of the CCR unit, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(1).
Document the initial and periodic hazard potential classification assessments of the CCR unit, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(2). .
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(2)(ii).
Prepare a written EAP, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(3).
Prepare documentation on an annual face-to-face meeting or exercise between representatives of the owner/operator of the CCR unit and the local emergency responders, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(3)(i)(E)
Amend the EAP, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(3)(ii)
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(3)(iv).
Prepare documentation required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(3)(v).
Compile the design and construction plans for the CCR unit, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(c).
Conduct and document initial and periodic structural stability assessments, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(d).
Prepare action plan required under 40 CFR 257.74(d)(2).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.74(d)(3).
Conduct and document initial and periodic safety factor assessments for each CCR unit, as required under 40 CFR 257.74(e).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.74(e)(2).
Operating Criteria
Air Criteria
Under 40 CFR 257.80, the owner or operator of a CCR landfill, CCR surface impoundment, or any lateral expansion of a CCR unit must adopt measures that will effectively minimize CCR from becoming airborne at the facility, including CCR fugitive dust originating from CCR units, roads, and other CCR management and material handling activities
The owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(g), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(g), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(g). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
CCR fugitive dust control plan required under 40 CFR 257.80(b).
Amended CCR fugitive dust control plan, as required under 40 CFR 257.80(b)(6).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.80(b)(7)
Aannual CCR fugitive dust control report required under 40 CFR 257.80(c).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Prepare CCR fugitive dust control plan required under 40 CFR 257.80(b).
Amend CCR fugitive dust control plan, as required under 40 CFR 257.80(b)(6).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.80(b)(7)
Prepare annual CCR fugitive dust control report required under 40 CFR 257.80(c).
Run-On and Run-Off Controls for CCR Landfills
Under 40 CFR 257.81, the owner or operator of an existing or new CCR landfill or any lateral expansion of a CCR landfill must design, construct, operate, and maintain: (1) a run-on control system to prevent flow onto the active portion of the CCR unit during the peak discharge from a 24-hour, 25-year storm; and (2) a run-off control system from the active portion of the CCR unit to collect and control at least the water volume resulting from a 24-hour, 25-year storm. Run-off from the active portion of the CCR unit must be handled in accordance with the surface water requirements under 40 CFR 257.3-3
The owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(g), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(g), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(g). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.
Data Items:
Initial and periodic run-on and run-off control system plans required under 40 CFR 257.81(c).
Amended run-on and run-off control system plans, as required under 40 CFR 257.81(c)(2).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.81(c)(5).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Prepare initial and periodic run-on and run-off control system plans required under 40 CFR 257.81(c).
Amend run-on and run-off control system plans, as required under 40 CFR 257.81(c)(2).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.81(c)(5).
Hydrologic and Hydraulic Capacity Requirements for CCR Surface Impoundments
Under 40 CFR 257.82, the owner or operator of an existing or new CCR surface impoundment or any expansion of a CCR surface impoundment must design, construct, operate, and maintain an inflow design flood control system as specified in 40 CFR 257.82(a)(1) and (a)(2).
The owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(g), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(g), and the internet requirements specified in CFR 257.107(g). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Initial and periodic inflow design flood control system plans required under 40 CFR 257.82(c).
Amended inflow design flood control system plan, as required under 40 CFR 257.82(c)(2).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.82(c)(5).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Prepare initial and periodic inflow design flood control system plans required under 40 CFR 257.82(c).
Amend the inflow design flood control system plan, as required under 40 CFR 257.82(c)(2).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.82(c)(5).
Inspection Requirements for CCR Surface Impoundments
Under 40 CFR 257.83, all CCR surface impoundments and any lateral expansion of a CCR surface impoundment must be inspected.
The owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(g), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(g), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(g). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Inspections required under 40 CFR 257.83(a).
Inspections required under 40 CFR 257.83(b)(1)).
Inspection report required under 40 CFR 257.83(b)(2).
Action plan to remedy structural weakness or disrupting condition, as required under 40 CFR 257.83(b)(5).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Conduct inspections required under 40 CFR 257.83(a).
Conduct inspections required under 40 CFR 257.83(b)(1)).
Develop inspection report required under 40 CFR 257.83(b)(2).
Develop and implement action plan to remedy structural weakness or disrupting condition, as required under 40 CFR 257.83(b)(5).
Inspection Requirements for CCR Landfills
Under 40 CFR 257.84, all CCR landfills must be inspected.
The owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(g), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(g), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(g). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Inspections required under 40 CFR 257.84(a).
Inspections required under 40 CFR 257.84(b)(1).
Inspection report required under 40 CFR 257.84(b)(2).
Action plan to remedy structural weakness or disrupting condition, as required under 40 CFR 257.84(b)(5).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Conduct inspections required under 40 CFR 257.84(a).
Conduct inspections required under 40 CFR 257.84(b)(1).
Develop inspection report required under 40 CFR 257.84(b)(2).
Develop and implement action plan to remedy structural weakness or disrupting condition, as required under 40 CFR 257.84(b)(5).
Groundwater Monitoring and Corrective Action
Applicability
Except as provided for in 40 CFR 257.100 for inactive CCR surface impoundments, all CCR landfills, CCR surface impoundments, and lateral expansions of CCR units are subject to the groundwater monitoring and corrective action requirements under 40 CFR 257.90 through 257.98.
The owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(h), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(h), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(h). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Item:
Annual groundwater monitoring and corrective action report required under 40 CFR 257.90(e).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Develop annual groundwater monitoring and corrective action report required under 40 CFR 257.90(e).
Groundwater Monitoring Systems
Owners and operators of CCR units must install a groundwater monitoring system.
The owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(h), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(h), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(h). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Documentation in the operating record of the design, installation, development, and decommissioning of any monitoring wells, piezometers and other measurement, sampling, and analytical devices, as required under 40 CFR 257.91(e)(1).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.91(f).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Document and include in the operating record the design, installation, development, and decommissioning of any monitoring wells, piezometers and other measurement, sampling, and analytical devices, as required under 40 CFR 257.91(e)(1).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.91(f).
Groundwater Sampling and Analysis Requirements
Under 40 CFR 257.93, the groundwater monitoring program must include consistent sampling and analysis procedures that are designed to ensure monitoring results that provide an accurate representation of groundwater quality at the background and downgradient wells required by 40 CFR 257.91.
The owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(h), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(h), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(h). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Sampling and analysis program.
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.93(f)(6).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Develop sampling and analysis program.
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.93(f)(6).
Detection Monitoring Program
Owners and operators of a CCR unit must conduct detection monitoring at all groundwater monitoring wells consistent with 40 CFR 257.94.
The owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(h), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(h), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(h). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.94(d)(1)-(2).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.94(d)(3).
Demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.94(e)(2).
Notification required under 40 CFR 257.94(e)(3).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Prepare demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.94(d)(1)-(2).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.94(d)(3).
Prepare demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.94(e)(2).
Prepare notification required under 40 CFR 257.94(e)(3).
Assessment Monitoring Program
Pursuant to 40 CFR 257.95, assessment monitoring is required whenever a statistically significant increase over background levels has been detected for one or more of the constituents listed in Appendix III to 40 CFR Part 257.
The owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(h), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(h), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(h). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.95(c)(1)-(2).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.95(c)(3).
Results of the Appendix III and Appendix IV constituent concentrations required under 40 CFR 257.95(d)(1).
Notification required under 40 CFR 257.95(e).
Notification required under 40 CFR 257.95(g).
Notification required under 40 CFR 257.95(g)(2).
Demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.95(g)(3)(ii).
Report that includes the factual or evidentiary basis for any conclusions in the demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.95(g)(3)(ii).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.95(g)(3)(ii).
Notification required under 40 CFR 257.95(g)(5).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Prepare demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.95(c)(1)-(2).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.95(c)(3).
Compile results of the Appendix III and Appendix IV constituent concentrations required under 40 CFR 257.95(d)(1).
Prepare notification required under 40 CFR 257.95(e).
Prepare notification required under 40 CFR 257.95(g).
Prepare notification required under 40 CFR 257.95(g)(2).
Prepare demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.95(g)(3)(ii).
Develop report that includes the factual or evidentiary basis for any conclusions in the demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.95(g)(3)(ii).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.95(g)(3)(ii).
Prepare notification required under 40 CFR 257.95(g)(5).
Assessment of Corrective Measures
40 CFR 257.96 identifies the requirements for the assessment of corrective measures.
The owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(h), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(h), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(h). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.96(a).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.96(a).
Assessment of corrective measures required under 40 CFR 257.96(d).
Results of the corrective measures assessment prior to the selection of remedy in a public meeting with interested and affected parties, as required under 40 CFR 257.96(e).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Prepare demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.96(a).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.96(a).
Complete assessment of corrective measures required under 40 CFR 257.96(d).
Discuss the results of the corrective measures assessment prior to the selection of remedy in a public meeting with interested and affected parties, as required under 40 CFR 257.96(e).
Selection of Remedy
Based on the results of the corrective measures assessment conducted under 40 CFR 257.96, the owner or operator of the CCR unit must select a remedy that, at a minimum, meets the standards listed in 40 CFR 257.97(b).
The owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(h), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(h), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(h). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Semi-annual report describing the progress in selecting and designing the remedy.
Report on selected remedy.
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.97(a).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Prepare semi-annual report describing the progress in selecting and designing the remedy.
Prepare report on selected remedy.
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.97(a).
Implementation of the Corrective Action Program
40 CFR 257.98 identifies the requirements for implementation of the Corrective Action Program.
The owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(h), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(h), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(h). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Notification required under 40 CFR 257.98(e).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.98(e).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Prepare notification required under 40 CFR 257.98(e).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.98(e).
Closure and Post-Closure Care
Closure or Retrofit of CCR Landfills and CCR Surface Impoundments
40 CFR 257.101 identifies the requirements for the closure or retrofit of CCR landfills and CCR surface impoundments for cause.
Data Items:
Statement in the notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(g) that the CCR surface impoundment is closing or retrofitting under the requirements of 40 CFR 257.101(a)(1), as required under 40 CFR 257.101(a)(2).
Statement in the notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(g) that the CCR surface impoundment is closing under the requirements of 40 CFR 257.101(b)(1) or (b)(2), as required under 40 CFR 257.101(b)(3).
Statement in the notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(g) that the CCR surface impoundment is closing under the requirements of 40 CFR 257.101(c)(1), as required under 40 CFR 257.101(c)(2).
Statement in the notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(g) that the CCR landfill is closing under the requirements of 40 CFR 257.101(d)(1), as required under 40 CFR 257.101(d)(2).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Include statement in the notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(g) that the CCR surface impoundment is closing or retrofitting under the requirements of 40 CFR 257.101(a)(1), as required under 40 CFR 257.101(a)(2).
Include statement in the notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(g) that the CCR surface impoundment is closing under the requirements of 40 CFR 257.101(b)(1) or (b)(2), as required under 40 CFR 257.101(b)(3).
Include statement in the notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(g) that the CCR surface impoundment is closing under the requirements of 40 CFR 257.101(c)(1), as required under 40 CFR 257.101(c)(2).
Include statement in the notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(g) that the CCR landfill is closing under the requirements of 40 CFR 257.101(d)(1), as required under 40 CFR 257.101(d)(2).
Criteria for Conducting Closure or Retrofit of CCR Landfills and CCR Surface Impoundments
40 CFR 257.102 identifies the requirements for conducting closure of CCR landfills and CCR surface impoundments.
The owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(i), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(i), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(i). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Written closure plan required under 40 CFR 257.102(b).
Amended written closure plan required under 40 CFR 257.102(b)(3).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.102(b)(4).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.102(d)(3)(iii).
Written documentation that the CCR unit will continue to accept wastes or will start removing CCR for the purpose of beneficial use, as required under 40 CFR 257.102(e)(2)(ii).
Demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.102(f)(2).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.102(f)(3).
Notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(g).
Notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(h).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.102(h).
Notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(i).
Written retrofit plan required under 40 CFR 257.102(k)(2).
Notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(k)(5).
Notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(k)(6).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Prepare written closure plan required under 40 CFR 257.102(b).
Amend written closure plan required under 40 CFR 257.102(b)(3).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.102(b)(4).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.102(d)(3)(iii).
Provide written documentation that the CCR unit will continue to accept wastes or will start removing CCR for the purpose of beneficial use, as required under 40 CFR 257.102(e)(2)(ii).
Prepare demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.102(f)(2).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.102(f)(3).
Prepare notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(g).
Prepare notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(h).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.102(h).
Prepare notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(i).
Prepare written retrofit plan required under 40 CFR 257.102(k)(2).
Prepare notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(k)(5).
Prepare notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(k)(6).
Alternative Closure Requirements
Per 40 CFR 257.103, the owner or operator of a CCR landfill, CCR surface impoundment, or any lateral expansion of a CCR landfill or CCR surface impoundment that is subject to closure or retrofit pursuant to 40 CFR 257.101(a), (b)(1), or (d) may continue to receive CCR in the unit provided the owner or operator meets the requirements of either 40 CFR 257.103(a) or (b).
The owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(i), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(i), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(i). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.103(a)(1).
Documentation that there is no alternative CCR disposal capacity.
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.103(b)(1).
Documentation of the permanent cessation of a coal-fired boiler(s) by a certain date.
Notification required under 40 CFR 257.103(c)(1).
Periodic progress reports required by 40 CFR 257.103(a)(1)(iii) or (b)(1)(iii),
Notification required under 40 CFR 257.103(c)(3).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.103(a)(1).
Document that there is no alternative CCR disposal capacity.
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.103(b)(1).
Document the permanent cessation of a coal-fired boiler(s) by a certain date.
Prepare notification required under 40 CFR 257.103(c)(1).
Prepare periodic progress reports required by 40 CFR 257.103(a)(1)(iii) or (b)(1)(iii),
Prepare notification required under 40 CFR 257.103(c)(3).
Post-Closure Care Requirements
Except as provided by either 40 CFR 257.104(a)(2) or (a)(3), 40 CFR 257.104 applies to the owners or operators of CCR landfills, CCR surface impoundments, and all lateral expansions of CCR landfills and CCR surface impoundments that are subject to the closure criteria under 40 CFR 257.102.
An owner or operator of a CCR unit that elects to close a CCR unit by removing CCR as provided by 40 CFR 257.102(c) is not subject to the post-closure care criteria under this section. An owner or operator of an inactive CCR surface impoundment that elects to close a CCR unit pursuant to the requirements under 40 CFR 257.100(b) is not subject to the post-closure care criteria under this section.
In addition, the owner or operator of the CCR unit must comply with the recordkeeping requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.105(i), the notification requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.106(i), and the internet requirements specified in 40 CFR 257.107(i). These requirements are covered under “Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet.”
Data Items:
Written post-closure plan required under 40 CFR 257.104(d).
Amended written post-closure plan, as required under 40 CFR 257.104(d)(3).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.104(d)(4).
Notification required under 40 CFR 257.104(e).
Certification required under 40 CFR 257.104(e).
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Prepare written post-closure plan required under 40 CFR 257.104(d).
Amend written post-closure plan, as required under 40 CFR 257.104(d)(3).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.104(d)(4).
Prepare notification required under 40 CFR 257.104(e).
Obtain certification required under 40 CFR 257.104(e).
Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet
Recordkeeping Requirements
40 CFR 257.105 identifies the recordkeeping requirements applicable to owners and operator of CCR units subject to 40 CFR Part 257, Subpart D. Owners and operators must maintain files of all information required by this section in a written operating record at their facility. Unless specified otherwise, each file must be retained for at least five years following the date of each occurrence, measurement, maintenance, corrective action, report, record, or study.
An owner or operator of more than one CCR unit subject to the provisions of 40 CFR Part 257, Subpart D may comply with the requirements of 40 CFR 257.105 in one recordkeeping system provided the system identifies each file by the name of each CCR unit. The files may be maintained on microfilm, on a computer, on computer disks, on a storage system accessible by a computer, on magnetic tape disks, or on microfiche.
The owner or operator of a CCR unit must submit to the State Director and/or appropriate Tribal authority any demonstration or documentation required by 40 CFR Part 257, Subpart D, if requested, when such information is not otherwise available on the owner or operator’s publicly accessible internet site.
Data Items:
Location restrictions
Demonstrations documenting whether or not the CCR unit is in compliance with the requirements under 40 CFR 257.60(a), 257.61(a), 257.62(a), 257.63(a), and 257.64(a). (40 CFR 257.105(e))
Design criteria
The design and construction certifications as required by 40 CFR 257.70(e) and (f). (40 CFR 257.105(f)(1))
The documentation of liner type as required by 40 CFR 257.71(a). (40 CFR 257.105(f)(2))
The design and construction certifications as required by 40 CFR 257.72(c) and (d). (40 CFR 257.105(f)(3))
Documentation prepared by the owner or operator stating that the permanent identification marker was installed as required by 40 CFR 257.73(a)(1) and 257.74(a)(1). (40 CFR 257.105(f)(4))
The initial and periodic hazard potential classification assessments as required by 40 CFR 257.73(a)(2) and 257.74(a)(2). (40 CFR 257.105(f)(5))
The emergency action plan (EAP), and any amendment of the EAP, as required by 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3) and 257.74(a)(3), except that the most recent EAP must be maintained in the facility’s operating record irrespective of the time requirement specified in 40 CFR 257.105(b). (40 CFR 257.105(f)(6))
Documentation prepared by the owner or operator recording the annual face-to-face meeting or exercise between representatives of the owner or operator of the CCR unit and the local emergency responders as required by 40 257.73(a)(3)(i)(E) and 257.74(a)(3)(i)(E). (40 CFR 257.105(f)(7))
Documentation prepared by the owner or operator recording all activations of the emergency action plan as required by 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(v) and 257.74(a)(3)(v). (40 CFR 257.105(f)(8))
The history of construction, and any revisions of it, as required by 40 CFR 257.73(c), except that these files must be maintained until the CCR unit completes closure of the unit in accordance with 40 CFR 257.102. (40 CFR 257.105(f)(9))
The initial and periodic structural stability assessments as required by 40 CFR 257.73(d) and 257.74(d). (40 CFR 257.105(f)(10))
The action plan to remedy structural stability deficiencies as required by 40 CFR 257.73(d)(2) and 257.74(d)(2). (40 CFR 257.105(f)(11))
The initial and periodic safety factor assessments as required by 40 CFR 257.73(e) and 257.74(e). (40 CFR 257.105(f)(12))
The design and construction plans, and any revisions of it, as required by 40 CFR 257.74(c), except that these files must be maintained until the CCR unit completes closure of the unit in accordance with 40 CFR 257.102. (40 CFR 257.105(f)(13))
Operating criteria
The CCR fugitive dust control plan, and any subsequent amendment of the plan, required by 40 CFR 257.80(b), except that the most recent control plan must be maintained in the facility’s operating record irrespective of the time requirement specified in 40 CFR 257.105(b). (40 CFR 257.105(g)(1))
The annual CCR fugitive dust control report required by 40 CFR 257.80(c). (40 CFR 257.105(g)(2))
The initial and periodic run-on and run-off control system plans as required by 40 CFR 257.81(c). (40 CFR 257.105(g)(3))
The initial and periodic inflow design flood control system plan as required by 40 CFR 257.82(c). (40 CFR 257.105(g)(4))
Documentation recording the results of each inspection and instrumentation monitoring by a qualified person as required by 40 CFR 257.83(a). (40 CFR 257.105(g)(5))
The periodic inspection report as required by 40 CFR 257.83(b)(2). (40 CFR 257.105(g)(6))
The action plan as required by 40 CFR 257.83(b)(5). (40 CFR 257.105(g)(7))
Documentation recording the results of the weekly inspection by a qualified person as required by 40 CFR 257.84(a). (40 CFR 257.105(g)(8))
The periodic inspection report as required by 40 CFR 257.84(b)(2). (40 CFR 257.105(g)(9))
Groundwater monitoring and corrective action
The annual groundwater monitoring and corrective action report as required by 40 CFR 257.90(e). (40 CFR 257.105(h)(1))
Documentation of the design, installation, development, and decommissioning of any monitoring wells, piezometers and other measurement, sampling, and analytical devices as required by 40 CFR 257.91(e)(1). (40 CFR 257.105(h)(2))
The groundwater monitoring system certification as required by 40 CFR 257.91(f). (40 CFR 257.105(h)(3))
The selection of a statistical method certification as required by 40 CFR 257.93(f)(6). (40 CFR 257.105(h)(4))
Within 30 days of establishing an assessment monitoring program, the notification as required by 40 CFR 257.94(e)(3). (40 CFR 257.105(h)(5))
The results of the Appendix III to this part and Appendix IV to this part constituent concentrations as required by 40 CFR 257.95(d)(1). (40 CFR 257.105(h)(6))
Within 30 days of returning to a detection monitoring program, the notification as required by 40 CFR 257.94(e). (40 CFR 257.105(h)(7))
Within 30 days of detecting one or more constituents in Appendix IV to this part at statistically significant levels above the groundwater protection standard, the notifications as required by 40 CFR 257.94(g) and (g)(2). (40 CFR 257.105(h)(8))
Within 30 days of initiating the assessment of corrective measures requirements, the notification as required by 40 CFR 257.95(g)(5). (40 CFR 257.105(h)(9))
The completed assessment of corrective measures as required by 40 CFR 257.96(d). (40 CFR 257.105(h)(10))
Documentation prepared by the owner or operator recording the public meeting for the corrective measures assessment as required by 40 CFR 257.96(e). (40 CFR 257.105(h)(11))
The semi-annual reports describing the progress in selecting and designing the remedy and the selection of remedy report as required by 40 CFR 257.97(a), except that the selection of remedy report must be maintained until the remedy has been completed. (40 CFR 257.105(h)(12))
Within 30 days of completing the remedy, the notification as required by 40 CFR 257.98(e). (40 CFR 257.105(h)(13))
Closure and post-closure care
The notification of intent to initiate closure of the CCR unit as required by 40 CFR 257.100(c)(1). (40 CFR 257.105(i)(1))
The annual progress reports of closure implementation as required by 40 CFR 257.100(c)(2)(i) and (c)(2)(ii). (40 CFR 257.105(i)(2))
The notification of closure completion as required by 40 CFR 257.100(c)(3). (40 CFR 257.105(i)(3))
The written closure plan, and any amendment of the plan, as required by 40 CFR 257.102(b). (40 CFR 257.105(i)(4))
The written demonstration(s), including the certification required by 40 CFR 257.102(e)(2)(iii), for a time extension for initiating closure as required by 40 CFR 257.102(e)(2)(ii). (40 CFR 257.105(i)(5))
The written demonstration(s), including the certification required by 40 CFR 257.102(f)(2)(iii), for a time extension for completing closure or retrofit as required by 40 CFR 257.102(f)(2)(i). (40 CFR 257.105(i)(6) and (j)(4))
The notification of intent to close a CCR unit as required by 40 CFR 257.102(g). (40 CFR 257.105(i)(7))
The notification of completion of closure of a CCR unit as required by 40 CFR 257.102(h). (40 CFR 257.105(i)(8))
The notification recording a notation on the deed as required by 40 CFR 257.102(i). (40 CFR 257.105(i)(9))
The notification of intent to comply with the alternative closure requirements as required by 40 CFR 257.103(c)(1). (40 CFR 257.105(i)(10))
The annual progress reports under the alternative closure requirements as required by 40 CFR 257.103(c)(2). (40 CFR 257.105(i)(11))
The written post-closure plan, and any amendment of the plan, as required by 40 CFR 257.104(d). (40 CFR 257.105(i)(12))
The notification of completion of post-closure care period as required by 40 CFR 257.104(e). (40 CFR 257.105(i)(13))
The written retrofit plan, and any amendment of the plan, as required by 40 CFR 257.102(k)(2). (40 CFR 257.105(j)(1))
The notification of intent to retrofit a CCR unit as required by 40 CFR 257.102(k)(5). (40 CFR 257.105(j)(5))
The notification of completion of retrofit of a CCR unit as required by 40 CFR 257.102(k)(6). (40 CFR 257.105(j)(6))
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Location restrictions
Place the demonstrations required under 40 CFR 257.60(a) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the demonstrations required under 40 CFR 257.61(a) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the demonstrations required under 40 CFR 257.62(a) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the demonstrations required under 40 CFR 257.63(a) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the demonstrations required under 40 CFR 257.64(a) in the facility’s operating record.
Design criteria
Place the certification required under 40 CFR 257.70(e) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the certification required under 40 CFR 257.70(f) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the documentation required under 40 CFR 257.71(a) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the certifications required under 40 CFR 257.72(c) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the certifications required under 40 CFR 257.72(d) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the documentation required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(1) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the documentation required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(1) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the initial and periodic hazard potential classification assessments required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(2) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the initial and periodic hazard potential classification assessments required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(2) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the EAP, and any amendment of the EAP, required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the EAP, and any amendment of the EAP, required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(3) in the facility’s operating record.
Place documentation required under 40 257.73(a)(3)(i)(E) in the facility’s operating record.
Place documentation required under 40 257.74(a)(3)(i)(E) in the facility’s operating record.
Place documentation required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(v) in the facility’s operating record.
Place documentation required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(3)(v) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the history of construction, and any revisions of it, required under 40 CFR257.73(c) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the initial and periodic structural stability assessments required under 40 CFR 257.73(d) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the initial and periodic structural stability assessments required under 40 CFR 257.74(d) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the action plan to remedy structural stability deficiencies required under 40 CFR 257.73(d)(2) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the action plan to remedy structural stability deficiencies required under 40 CFR 257.74(d)(2) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the initial and periodic safety factor assessments required under 40 CFR 257.73(e) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the initial and periodic safety factor assessments required under 40 CFR 257.74(e) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the design and construction plans, and any revisions of it, required under 40 CFR 257.74(c) in the facility’s operating record.
Operating criteria
Place the CCR fugitive dust control plan, and any subsequent amendment of the plan, required under 40 CFR 257.80(b) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the annual CCR fugitive dust control report required under 40 CFR 257.80(c) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the initial and periodic run-on and run-off control system plans required under 40 CFR 257.81(c) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the initial and periodic inflow design flood control system plan required under 40 CFR 257.82(c) in the facility’s operating record.
Place documentation required under 40 CFR 257.83(a) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the periodic inspection report required under 40 CFR 257.83(b)(2) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the action plan required under 40 CFR 257.83(b)(5) in the facility’s operating record.
Place documentation required under 40 CFR 257.84(a) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the periodic inspection report required under 40 CFR 257.84(b)(2) in the facility’s operating record.
Groundwater monitoring and corrective action
Place the annual groundwater monitoring and corrective action report required under 40 CFR 257.90(e) in the facility’s operating record.
Place documentation required under 40 CFR 257.91(e)(1) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the groundwater monitoring system certification required under 40 CFR 257.91(f) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the selection of a statistical method certification required under 40 CFR 257.93(f)(6) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.94(e)(3) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the documentation required under 40 CFR 257.95(d)(1) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.94(e) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the notifications required under 40 CFR 257.94(g) and (g)(2) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.95(g)(5) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the completed assessment of corrective measures required under 40 CFR 257.96(d) in the facility’s operating record.
Place documentation required under 40 CFR 257.96(e) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the semi-annual reports describing the progress in selecting and designing the remedy required under 40 CFR 257.97(a) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the selection of remedy report required under 40 CFR 257.97(a) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.98(e) in the facility’s operating record.
Closure and post-closure care
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.100(c)(1) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the annual progress reports of closure implementation required under 40 CFR 257.100(c)(2)(i) and (c)(2)(ii) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.100(c)(3) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the written closure plan, and any amendment of the plan, required under 40 CFR 257.102(b) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the written demonstration(s) required under 40 CFR 257.102(e)(2)(ii) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the certification required under 40 CFR 257.102(e)(2)(iii) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the written demonstration(s) required under 40 CFR 257.102(f)(2)(i) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the certification required under 40 CFR 257.102(f)(2)(iii) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(g) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(h) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(i) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.103(c)(1) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the annual progress reports required under 40 CFR 257.103(c)(2) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the written post-closure plan, and any amendment of the plan, required under 40 CFR 257.104(d) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.104(e) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the written retrofit plan, and any amendment of the plan, required under 40 CFR 257.102(k)(2) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(k)(5) in the facility’s operating record.
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.102(k)(6) in the facility’s operating record.
Notification Requirements
40 CFR 257.106 identifies the notification requirements applicable to owners and operator of CCR units subject to 40 CFR Part 257, Subpart D. Owners and operators must notify the State Director and/or appropriate Tribal authority when information has been placed in the operating record and on the owner or operator’s publicly accessible internet site.
The notifications required 40 CFR 257.106(e) through (i) must be sent to the relevant State Director and/or appropriate Tribal authority before the close of business on the day the notification is required to be completed. For purposes of 40 CFR 257.106, before the close of business means the notification must be postmarked or sent by electronic mail (e-mail). If a notification deadline falls on a weekend or federal holiday, the notification deadline is automatically extended to the next business day.
If any CCR unit is located in its entirety within Indian Country, the notifications of this section must be sent to the appropriate Tribal authority. If any CCR unit is located in part within Indian Country, the notifications of this section must be sent both to the appropriate State Director and Tribal authority.
Notifications may be combined as long as the deadline requirement for each notification is met. Unless otherwise required in 40 CFR 257.106, the notifications specified in this section must be sent to the State Director and/or appropriate Tribal authority within 30 days of placing in the operating record the information required by 40 CFR 257.105.
Data Items:
Location restrictions
Notification to the State Director and/or appropriate Tribal authority that each demonstration specified under 40 CFR 257.105(e) has been placed in the operating record and on the owner or operator’s publicly accessible internet site). (40 CFR 257.106(e))
Design criteria
Notification of the availability of the design certification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(1) or (f)(3) and copy of the alternative composite liner design, if applicable. (40 CFR 257.106(f)(1))
Notification of the availability of the construction certification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(1) or (f)(3). (40 CFR 257.106(f)(2))
Notification of the availability of the documentation of liner type specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(2). (40 CFR 257.106(f)(3))
Notification of the availability of the initial and periodic hazard potential classification assessments specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(5). (40 CFR 257.106(f)(4))
Notification of the availability of emergency action plan (EAP), and any revisions of the EAP, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(6). (40 CFR 257.106(f)(5))
Notification of the availability of documentation prepared by the owner or operator recording the annual face-to-face meeting or exercise between representatives of the owner or operator of the CCR unit and the local emergency responders specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(7). (40 CFR 257.106(f)(6))
Notification of documentation prepared by the owner or operator recording all activations of the emergency action plan specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(8). (40 CFR 257.106(f)(7))
Notification of the availability of the history of construction, and any revision of it, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(9). (40 CFR 257.106(f)(8))
Notification of the availability of the initial and periodic structural stability assessments specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(10). (40 CFR 257.106(f)(9))
Notification of the availability of the action plan to remedy structural stability deficiencies specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(11). (40 CFR 257.106(f)(10))
Notification of the availability of the initial and periodic safety factor assessments specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(12). (40 CFR 257.106(f)(11))
Notification of the availability of the design and construction plans, and any revision of them, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(13). (40 CFR 257.106(f)(12))
Operating criteria
Notification of the availability of the CCR fugitive dust control plan, or any subsequent amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(1). (40 CFR 257.106(g)(1))
Notification of the availability of the annual CCR fugitive dust control report specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(2). (40 CFR 257.106(g)(2))
Notification of the availability of the initial and periodic run-on and run-off control system plans specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(3). (40 CFR 257.106(g)(3))
Notification of the availability of the initial and periodic inflow design flood control system plans specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(4). (40 CFR 257.106(g)(4))
Notification of the availability of the periodic inspection reports specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(6). (40 CFR 257.106(g)(5))
Notification of the availability of the action plan specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(7). (40 CFR 257.106(g)(6))
Notification of the availability of the periodic inspection reports specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(9). (40 CFR 257.106(g)(7))
Groundwater monitoring and corrective action
Notification of the availability of the annual groundwater monitoring and corrective action report specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(1). (40 CFR 257.106(h)(1))
Notification of the availability of the groundwater monitoring system certification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(3). (40 CFR 257.106(h)(2))
Notification of the availability of the selection of a statistical method certification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(4). (40 CFR 257.106(h)(3))
Notification that an assessment monitoring programs has been established specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(5). (40 CFR 257.106(h)(4))
Notification that the CCR unit is returning to a detection monitoring program specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(7). (40 CFR 257.106(h)(5))
Notification that one or more constituents in Appendix IV to this part have been detected at statistically significant levels above the groundwater protection standard and the notifications to land owners specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(8). (40 CFR 257.106(h)(6))
Notification that an assessment of corrective measures has been initiated specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(9). (40 CFR 257.106(h)(7))
Notification of the availability of assessment of corrective measures specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(10). (40 CFR 257.106(h)(8))
Notification of the availability of the semi-annual report describing the progress in selecting and designing the remedy under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(12). (40 CFR 257.106(h)(9))
Notification of the availability of the selection of remedy report specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(12). (40 CFR 257.106(h)(9))
Notification of the completion of the remedy specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(13). (40 CFR 257.106(h)(10))
Closure and post-closure care
Notification of the intent to initiate closure of the CCR unit specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(1). (40 CFR 257.106(i)(1))
Notification of the availability of the annual progress reports of closure implementation specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(2). (40 CFR 257.106(i)(2))
Notification of closure completion specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(3). (40 CFR 257.106(i)(3))
Notification of the availability of the written closure plan, and any amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(4). (40 CFR 257.106(i)(4))
Notification of the availability of the demonstration(s) for a time extension for initiating closure specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(5). (40 CFR 257.106(i)(5))
Notification of the availability of the demonstration(s) for a time extension for completing closure specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(6). (40 CFR 257.106(i)(6)
Notification of intent to close a CCR unit specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(7). (40 CFR 257.106(i)(7))
Notification of completion of closure of a CCR unit specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(8). (40 CFR 257.106(i)(8))
Notification of the deed notation as required by 40 CFR 257.105(i)(9). (40 CFR 257.106(i)(9))
Notification of intent to comply with the alternative closure requirements specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(10). (40 CFR 257.106(i)(10))
The annual progress reports under the alternative closure requirements as required by 40 CFR 257.105(i)(11). (40 CFR 257.106(i)(11))
Notification of the availability of the written post-closure plan, and any amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(12). (40 CFR 257.106(i)(12))
Notification of completion of post-closure care specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(13). (40 CFR 257.106(i)(13))
Notification of the availability of the written retrofit plan, and any amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(j)(1). (40 CFR 257.106(j)(1))
Notification of intent to retrofit a CCR unit specified under 40 CFR 257.105(j)(5). (40 CFR 257.106(j)(5))
Notification of completion of retrofit of a CCR unit specified under 40 CFR 257.105(j)(6). (40 CFR 257.106(j)(6))
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Location restrictions
Provide notification that each demonstration specified under 40 CFR 257.105(e) has been placed in the operating record and on the owner or operator’s publicly accessible internet site.
Design criteria
Provide notification of the availability of the design certification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(1) or (f)(3) and copy of the alternative composite liner design, if applicable.
Provide notification of the availability of the construction certification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(1) or (f)(3).
Provide notification of the availability of the documentation of liner type specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(2).
Provide notification of the availability of the initial and periodic hazard potential classification assessments specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(5).
Provide notification of the availability of the EAP, and any revisions of the EAP, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(6).
Provide notification of the availability of documentation specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(7).
Provide notification of documentation specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(8).
Provide notification of the availability of the history of construction, and any revision of it, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(9).
Provide notification of the availability of the initial and periodic structural stability assessments specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(10).
Provide notification of the availability of the action plan to remedy structural stability deficiencies specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(11).
Provide notification of the availability of the initial and periodic safety factor assessments specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(12).
Provide notification of the availability of the design and construction plans, and any revision of them, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(13).
Operating criteria
Provide notification of the availability of the CCR fugitive dust control plan, or any subsequent amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(1).
Provide notification of the availability of the annual CCR fugitive dust control report specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(2).
Provide notification of the availability of the initial and periodic run-on and run-off control system plans specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(3).
Provide notification of the availability of the initial and periodic inflow design flood control system plans specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(4).
Provide notification of the availability of the periodic inspection reports specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(6).
Provide notification of the availability of the action plan specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(7).
Provide notification of the availability of the periodic inspection reports specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(9).
Groundwater monitoring and corrective action
Provide notification of the availability of the annual groundwater monitoring and corrective action report specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(1).
Provide notification of the availability of the certification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(3).
Provide notification of the availability of the certification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(4).
Provide notification that an assessment monitoring programs has been established specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(5).
Provide notification that the CCR unit is returning to a detection monitoring program specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(7)
Provide notification that one or more constituents in Appendix IV to 40 CFR Part 257 have been detected at statistically significant levels above the groundwater protection standard and the notifications to land owners specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(8).
Provide notification that an assessment of corrective measures has been initiated specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(9)
Provide notification of the availability of assessment of corrective measures specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(10).
Provide notification of the availability of the semi-annual report describing the progress in selecting and designing the remedy specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(12).
Provide notification of the availability of the selection of remedy report specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(12).
Provide notification of the completion of the remedy specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(13).
Closure and post-closure care
Provide notification of the intent to initiate closure of the CCR unit specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(1).
Provide notification of the availability of the annual progress reports of closure implementation specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(2).
Provide notification of closure completion specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(3).
Provide notification of the availability of the written closure plan, and any amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(4).
Provide notification of the availability of the demonstration(s) specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(5).
Provide notification of the availability of the demonstration(s) specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(6).
Provide notification of intent to close a CCR unit specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(7).
Provide notification of completion of closure of a CCR unit specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(8).
Provide notification of the deed notation as required by 40 CFR 257.105(i)(9).
Provide notification of intent to comply with the alternative closure requirements specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(10
Provide notification of the annual progress reports under the alternative closure requirements required under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(11).
Provide notification of the availability of the written post-closure plan, and any amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(12).
Provide notification of completion of post-closure care specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(13).
Provide notification of the availability of the written retrofit plan, and any amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(j)(1).
Provide notification of intent to retrofit a CCR unit specified under 40 CFR 257.105(j)(5).
Provide notification of completion of retrofit of a CCR unit specified under 40 CFR 257.105(j)(6).
Publicly Accessible Internet Site Requirements
40 CFR 257.107 identifies the publicly accessible internet site requirements applicable to owners and operator of CCR units subject to 40 CFR Part 257, Subpart D. Owners and operators must maintain a publicly accessible internet site (CCR website) containing the information specified in this section. The owner or operator’s website must be titled “CCR Rule Compliance Data and Information.”
An owner or operator of more than one CCR unit subject to the provisions of 40 CFR Part 257, Subpart D may comply with the requirements of 40 CFR 257.107 by using the same internet site for multiple CCR units provided the CCR website clearly delineates information by the name of each unit.
Unless otherwise required in 40 CFR 257.107, the information required to be posted to the CCR website must be made available to the public for at least five years following the date on which the information was first posted to the CCR website.
Unless otherwise required in 40 CFR 257.107, the information must be posted to the CCR website within 30 days of placing the pertinent information required by 40 CFR 257.105 in the operating record.
Data Items:
Location restrictions
Each demonstration specified under 40 CFR 257.105(e) on the owner or operator’s CCR website. (40 CFR 257.107(e))
Design criteria
Design certification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(1) or (f)(3). (40 CFR 257.107(f)(1))
The construction certification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(1) or (f)(3). (40 CFR 257.107(f)(2))
The documentation of liner type specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(2). (40 CFR 257.107(f)(3))
The initial and periodic hazard potential classification assessments specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(5). (40 CFR 257.107(f)(4))
The emergency action plan (EAP) specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(6), except that only the most recent EAP must be maintained on the CCR website. (40 CFR 257.107(f)(5))
Documentation prepared by the owner or operator recording the annual face-to-face meeting or exercise between representatives of the owner or operator of the CCR unit and the local emergency responders specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(7). (40 CFR 257.107(f)(6))
Documentation prepared by the owner or operator recording any activation of the emergency action plan specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(8). (40 CFR 257.107(f)(7))
The history of construction, and any revisions of it, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(9). (40 CFR 257.107(f)(8))
The initial and periodic structural stability assessments specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(10). (40 CFR 257.107(f)(9))
The action plan to remedy structural stability deficiencies specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(11). (40 CFR 257.107(f)(10))
The initial and periodic safety factor assessments specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(12). (40 CFR 257.107(f)(11))
The design and construction plans, and any revisions of them, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(13). (40 CFR 257.107(f)(12))
Operating criteria
The CCR fugitive dust control plan, or any subsequent amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(1). (40 CFR 257.107(g)(1))
The annual CCR fugitive dust control report specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(2). (40 CFR 257.107(g)(2))
The initial and periodic run-on and run-off control system plans specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(3). (40 CFR 257.107(g)(3))
The initial and periodic inflow design flood control system plans specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(4). (40 CFR 257.107(g)(4))
The periodic inspection reports specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(6). (40 CFR 257.107(g)(5))
The action plan specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(7). (40 CFR 257.107(g)(6))
The periodic inspection reports specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(9). (40 CFR 257.107(g)(7))
Groundwater monitoring and corrective action
The annual groundwater monitoring and corrective action report specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(1). (40 CFR 257.107(h)(1))
The groundwater monitoring system certification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(3). (40 CFR 257.107(h)(2))
The selection of a statistical method certification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(4). (40 CFR 257.107(h)(3))
The notification that an assessment monitoring programs has been established specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(5). (40 CFR 257.107(h)(4))
The notification that the CCR unit is returning to a detection monitoring program specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(7). (40 CFR 257.107(h)(5))
The notification that one or more constituents in Appendix IV to this part have been detected at statistically significant levels above the groundwater protection standard and the notifications to land owners specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(8). (40 CFR 257.107(h)(6))
The notification that an assessment of corrective measures has been initiated specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(9). (40 CFR 257.107(h)(7))
The assessment of corrective measures specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(10). (40 CFR 257.107(h)(8))
The semi-annual reports describing the progress in selecting and designing the remedy. (40 CFR 257.107(h)(9))
The selection of remedy report specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(12), except that the selection of remedy report must be maintained until the remedy has been completed. (40 CFR 257.107(h)(9))
The notification that the remedy has been completed specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(13). (40 CFR 257.107(h)(10))
Closure and post-closure care
The notification of intent to initiate closure of the CCR unit specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(1). (40 CFR 257.107(i)(1))
The annual progress reports of closure implementation specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(2). (40 CFR 257.107(i)(2))
The notification of closure completion specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(3). (40 CFR 257.107(i)(3))
The written closure plan, and any amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(4). (40 CFR 257.107(i)(4))
The demonstration(s) for a time extension for initiating closure specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(5). (40 CFR 257.107(i)(5))
The demonstration(s) for a time extension for completing closure specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(6). (40 CFR 257.107(i)(6))
The notification of intent to close a CCR unit specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(7). (40 CFR 257.107(i)(7))
The notification of completion of closure of a CCR unit specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(8). (40 CFR 257.107(i)(8))
The notification recording a notation on the deed as required by 40 CFR 257.105(i)(9). (40 CFR 257.107(i)(9))
The notification of intent to comply with the alternative closure requirements as required by 40 CFR 257.105(i)(10). (40 CFR 257.107(i)(10))
The annual progress reports under the alternative closure requirements as required by 40 CFR 257.105(i)(11). (40 CFR 257.107(i)(11))
The written post-closure plan, and any amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(12). (40 CFR 257.107(i)(12))
The notification of completion of post-closure care specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(13). (40 CFR 257.107(i)(13))
The written retrofit plan, and any amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(j)(1). (40 CFR 257.107(j)(2))
The notification of intent to retrofit a CCR unit specified under 40 CFR 257.105(j)(5). (40 CFR 257.107(j)(5))
The notification of completion of retrofit of a CCR unit specified under 40 CFR 257.105(j)(6). (40 CFR 257.107(j)(6))
Respondent Activities:
Owners and operators must perform the following activities:
Location restrictions
Place each demonstration specified under 40 CFR 257.105(e) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Design criteria
Place the certification required under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(1) or (f)(3) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the certification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(1) or (f)(3)on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place he documentation specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(2) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the initial and periodic hazard potential classification assessments specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(5) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the EAP specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(6) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place documentation specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(7) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place documentation specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(8) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the history of construction, and any revisions of it, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(9) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the initial and periodic structural stability assessments specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(10) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the action plan to remedy structural stability deficiencies specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(11) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the initial and periodic safety factor assessments specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(12) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the design and construction plans, and any revisions of them, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(f)(13) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Operating criteria
Place the CCR fugitive dust control plan, or any subsequent amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(1) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the annual CCR fugitive dust control report specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(2) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the initial and periodic run-on and run-off control system plans specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(3) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the initial and periodic inflow design flood control system plans specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(4) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the periodic inspection reports specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(6) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the action plan specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(7) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the periodic inspection reports specified under 40 CFR 257.105(g)(9) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Groundwater monitoring and corrective action
Place the annual groundwater monitoring and corrective action report specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(1) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the certification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(3) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the certification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(4) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the notification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(5) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the notification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(7) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the notification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(8) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the notification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(9) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the assessment of corrective measures specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(10) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the semi-annual reports describing the progress in selecting and designing the remedy required under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(12) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the selection of remedy report specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(12) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the notification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(h)(13) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Closure and post-closure care
Place the notification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(1) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the annual progress reports of closure implementation specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(2) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the notification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(3) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the written closure plan, and any amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(4) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the demonstration(s) specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(5) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the demonstration(s) specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(6) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the notification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(7) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the notification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(8) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(9) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(10) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the annual progress reports required under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(11) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the written post-closure plan, and any amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(12) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the notification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(i)(13) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the written retrofit plan, and any amendment of the plan, specified under 40 CFR 257.105(j)(1) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the notification specified under 40 CFR 257.105(j)(5) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Place the notification required under 40 CFR 257.105(j)(6) on the owner or operator’s CCR website.
Solid Waste Management Plans
States and territories where the CCR units will be regulated under the final rule may prepare a solid waste management plan to address the issuance of the revised federal requirements in the CCR rule. This would be a voluntary activity.
Data Item:
Solid waste management plan.
Respondent Activity:
State government agencies and Tribal authorities are expected to perform the following activity:
Prepare solid waste management plan.
State CCR Permit Program Applications
With the passage of the WIIN Act in December 2016, RCRA Subtitle D was amended to provide new statutory authority pertaining to the management of CCR in landfills and surface impoundments. The WIIN Act allows states to seek CCR permit program approval from EPA. Such a program does not have to be identical to the requirements in the CCR rule (40 CFR Part 257, Subpart D), but must be at least as protective as the CCR rule. EPA is developing a Guidance document to provide states with the information needed to apply for permit program approval. States and territories where the CCR units will be regulated under the final rule may prepare and submit program approval from EPA. This would be a voluntary activity.
Data Item:
Application for a state CCR permit program consistent with EPA’s guidance document.
Respondent Activity:
State government agencies and Tribal authorities are expected to perform the following activity:
Prepare application for a state CCR permit program consistent with EPA’s guidance document.
5. THE INFORMATION COLLECTED– AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
5(a) AGENCY ACTIVITIES
Most of the information collection requirements covered in this ICR are maintained in records in the facility’s operating record and therefore are not formally submitted to EPA. For the information that may be submitted – specifically, a revised Solid Waste Management Plan (SWMP) or application for a CCR permit program submitted by a State – the Agency will review and, as appropriate, approve the SWMP or permit program submittal. Early in the development of the waste management infrastructure, a process was created to encourage States to effectively plan for and manage their solid wastes through the development of SWMPs. Currently, many states have SWMPs that have been submitted to and approved by EPA. EPA recommends that States take advantage of this process, already in the regulations, by revising their SWMPs to address the issuance of the revised federal requirements and to submit revisions of these plans to EPA. Currently, no states have approved CCR permit programs as authorized under the WIIN Act of 2016.
5(b) COLLECTION METHODOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
Most information can be maintained in the facility operating record or on a publicly accessible internet website rather than in submittals to EPA. For the information that is submitted (e.g., liner demonstrations), EPA ensures the accuracy and completeness of the collected information by reviewing each submittal.
5(c) SMALL ENTITY FLEXIBILITY
All owner/operators regardless of company size will be treated in the same manner. The information collection requirements do not have a significant economic impact on a substantial number of small entities, EPA nonetheless has tried to reduce the impact of these requirements on small entities.
5(d) COLLECTION SCHEDULE
The information provided varies based on provision and on the timing of the cessation of coal-fired boilers. The requirements outlined in this ICR contain some one-time submissions and some regularly-recurring reporting activities, including annual progress reports. The requirements are (voluntary) one-time submissions.
6. ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF THE COLLECTION
6(a) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT BURDEN
This ICR is a comprehensive presentation of all information collection activities required for disposal of CCR under RCRA Subtitle D. EPA estimated respondent burden hours associated with all 40 CFR Part 257 requirements covered in this ICR in Exhibits 1 through 9. Exhibit 1 addresses the burden for owners and operators of CCR units to read the regulations, and adhere to the location restrictions regulations under 40 CFR 257.60. Exhibit 2 addresses the respondent burden to comply with design criteria under 40 CFR 257.70 through 40 CFR 257.74. Exhibit 3 addresses the respondent burden to comply with operating criteria under 40 CFR 257.80 through 40 CFR 257.84. Exhibit 4 addresses provisions related to groundwater monitoring and corrective action covered under 40 CFR 257.90 through 40 CFR 257.98. Exhibit 5 addresses the respondent burden related to closure and post-closure care, as required under 40 CFR 257.101 through 40 CFR 257.104. Exhibit 5 addresses the respondent burden related to recordkeeping, notification, and posting information to the internet, as required under 40 CFR 257.105 through 40 CFR 257.107. Exhibit 7 addresses the state government agency and tribal authority burden related to recordkeeping, notification, and posting information to the internet, as required under 40 CFR 257.106. Exhibit 8a addresses the state government agency and tribal authority burden associated with the preparation of solid waste management plans and CCR permit program applications. Exhibit 8b addresses the Agency burden associated with the review and approval of solid waste management plans and CCR permit program applications. Exhibit 9 provides a summary of the total burden hours and costs for all activities related to the disposal of CCR under Subtitle D of RCRA.
EPA relies on estimates of the universe of affected respondents and estimates of the hourly burden associated with the individual requirements from the prior approved ICR for the CCR program.3
6(b) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT COSTS
Exhibits 1 through 8 provide estimates of the annual respondent costs associated with the 40 CFR Part 257 information collection requirements covered in this ICR. These costs are based on the cost of labor, capital, and operation and maintenance (O&M).
(1) Labor Costs
Using the total burden hours discussed in Section 6(a) and the hourly labor costs outlined in this section, Exhibits 1 through 8 illustrate the labor costs associated with the information collection requirements covered in this ICR.
Owners and Operators of CCR Units
EPA estimates an average hourly respondent labor cost (including fringe and overhead) of $140.50 for legal staff, $112.56 for managerial staff, $54.45 for technical staff, and $35.29 for clerical staff. These hourly labor rates are based on the most current estimates of national cross-industry wages by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS)4 for occupational groups SOC 23-1011: Lawyers; SOC 11-0000: Management Occupations; SOC 17-3026: Industrial Engineering Technicians; and SOC 43-9061: Office Clerks, General, respectively, multiplied by a factor5 of 1.78 to account for fringe benefits6 and overhead.7 The labor rates are displayed in the table below.
Labor Category |
US Bureau of Labor Statistics Standard Occupational Code |
Non-loaded 2023 average (mean) wage rate ($ per hour) |
Fringe benefits as percent of total employee compensation |
Overhead percentage |
Loaded 2023 average wage rate ($ per hour) |
1. Legal |
23-1011 Lawyers |
$78.74 |
33.3% |
12% |
$ 140.50 |
2. Managerial |
11-0000 Management Occupations |
$63.08 |
33.3% |
12% |
$112.56 |
3. Technical |
17-3026 Industrial Engineering Technicians |
$30.52 |
33.3% |
12% |
$54.46 |
4. Clerical |
43-9061 Office Clerks, General |
$19.78 |
33.3% |
12% |
$35.29 |
State Government Agencies and Tribal Authorities
EPA estimates an average hourly labor cost of $97.87 for legal staff, $95.19 for managerial staff, $55.84 for technical staff, and $37.23 for clerical staff. These hourly labor rates are based on the most current estimates of State government wages by BLS8 for occupational groups SOC 23-1011: Lawyers; SOC 11-0000: Management Occupations; SOC 19-4091: Environmental Science and Protection Technicians; and SOC 43‑9061: Office Clerks, General, respectively, multiplied by a factor9 of 1.97 to account for fringe benefits10 and overhead.11 The labor rates are displayed in the table below.
Labor Category |
US Bureau of Labor Statistics Standard Occupational Code |
Non-loaded 20123average (mean) wage rate ($ per hour) |
Fringe benefits as percent of total employee compensation |
Overhead percentage |
Loaded 2023 average wage rate ($ per hour) |
1. Legal |
23-1011 Lawyers |
$49.71 |
37.6% |
12% |
$97.87 |
2. Managerial |
11-0000 Management Occupations |
$48.35 |
37.6% |
12% |
$95.19 |
3. Technical |
19-4091 Environmental Science and Protection Technicians |
$28.36 |
37.6% |
12% |
$55.84 |
4. Clerical |
43-9061 Office Clerks, General |
$18.91 |
37.6% |
12% |
$37.23 |
(2) Capital Costs
EPA estimates there will be no capital costs incurred under this ICR.
(3) Operation and Maintenance Costs
O&M costs are those costs associated with a paperwork requirement incurred continually over the life of the ICR. For this ICR, O&M costs include: mailing costs, certification fees, sampling costs, alternate liner demonstration application, and alternate liner demonstration. O&M costs were obtained from regulatory impact analyses and updated to 2023 levels using Consumer Price Indexes developed by BLS.12 O&M costs are shown in Exhibits 1 through 8 for all applicable respondent activities. For this collection, the annual O&M cost for private entities is expected to be ($12,420,892 + $785,323.63).
6(c) ESTIMATING AGENCY BURDEN AND COST
For Agency burden related to CCR, EPA estimates an average hourly labor cost of $102.11 for legal staff (GS-15, Step 5), $90.10 for managerial staff (GS-15, Step 1), $64.82 for technical staff (GS-13, Step 1), and $27.65 for clerical staff (GS-06, Step 1). To derive these hourly estimates, EPA referred to the General Schedule (GS) Salary Table 2023.13 This publication summarizes the unloaded (base) hourly rate for various labor categories in the Federal Government. EPA then applied the standard government overhead factor of 1.6 to the unloaded rate to derive loaded hourly rates. The labor rates are summarized in the table below.
Labor Category |
General Schedule (GS) Code |
January 2023 Base Rate |
Overhead Rate |
2023 Loaded Rate |
Legal |
GS-15, Step 5 |
$63.82 |
1.6 |
$102.11 |
Managerial |
GS-15, Step 1 |
$56.31 |
1.6 |
$90.10 |
Technical |
GS-13, Step 1 |
$40.51 |
1.6 |
$64.82 |
Clerical |
GS-06, Step 1 |
$17.28 |
1.6 |
$27.65 |
6(d) ESTIMATING THE RESPONDENT UNIVERSE AND TOTAL BURDEN AND COST
EPA estimates that 300 coal-fired electric utility plants are subject to the information collection requirements covered in this ICR. Table below presents the number of CCR units subject to the information collection requirements covered in this ICR.
(2) Annual Respondent Burden
(a) Beneficial Use of CCR (Exhibit 1)
EPA estimates that, each year, zero users of CCR will demonstrate and keep records of beneficial use, as required under 40 CFR 257.53. This ICR assumes that all beneficial use respondents completed the requirements under 40 CFR 257.53.
(b) Reading the Regulations (Exhibit 1)
EPA estimates that 300 coal-fired electric utility plants will be subject to the information collection requirements under CCR regulations. EPA assumes that these respondents will read the regulations once during the three-year life of the ICR. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of this one-time activity by dividing the number of respondents by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 100 respondents (i.e., 300 respondents / 3 years), on average, will read the regulations each year.
(c) Location Restrictions (Exhibit 1)
(c1) Placement above the Uppermost Aquifer
EPA assumes that owners and operators of existing surface impoundments and all new CCR units (i.e., 460 existing surface impoundments + 20 new landfills + 102 new impoundments = 582 units) will demonstrate that each of their CCR units meet the minimum requirements for placement above the uppermost aquifer. EPA further assumes that these demonstrations, which include a certification from a qualified professional engineer, will be prepared once during the three-year life of the ICR.14 In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of this one-time activity by dividing the number of CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 194 units (i.e., 582 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to this requirement each year.
(c2) Wetlands
EPA assumes that owners and operators of existing surface impoundments and all new CCR units (i.e., 460 existing surface impoundments + 20 new landfills + 102 new impoundments = 582 units) will prepare the wetland location restriction demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.61. EPA further assumes that these demonstrations, which include a certification from a qualified professional engineer, will be prepared once during the three-year life of the ICR. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of this one-time activity by dividing the number of CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 194 units (i.e., 582 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to this requirement each year.
(c3) Fault Areas
EPA assumes that owners and operators of existing surface impoundments and all new CCR units (i.e., 460 existing surface impoundments + 20 new landfills + 102 new impoundments = 582 units) will prepare the fault area location restriction demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.62. EPA further assumes that these demonstrations, which include a certification from a qualified professional engineer, will be prepared once during the three-year life of the ICR. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of this one-time activity by dividing the number of CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 194 units (i.e., 582 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to this requirement each year.
(c4) Seismic Impact Zones
EPA assumes that owners and operators of existing surface impoundments and all new CCR units (i.e., 460 existing surface impoundments + 20 new landfills + 102 new impoundments = 582 units) will prepare the seismic impact zone location restriction demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.63. EPA further assumes that these demonstrations, which include a certification from a qualified professional engineer, will be prepared once during the three-year life of the ICR. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of this one-time activity by dividing the number of CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 194 units (i.e., 582 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to this requirement each year.
(c5) Unstable Areas
EPA assumes that owners and operators of existing surface impoundments and all new CCR units (i.e., 460 existing surface impoundments + 20 new landfills + 102 new impoundments = 582 units) will prepare the unstable areas location restriction demonstration required under 40 CFR 257.64. EPA further assumes that these demonstrations, which include a certification from a qualified professional engineer, will be prepared once during the three-year life of the ICR. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of this one-time activity by dividing the number of CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 194 units (i.e., 582 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to this requirement each year.
(d) Design Criteria (Exhibit 2)
(d1) Liner Design Criteria for New CCR Landfills and Any Lateral Expansion of a CCR Landfill
EPA assumes that none of the new CCR landfills will have an alternative composite liner. As a result, none of the new CCR landfills will be subject to the certification requirement at 40 CFR 257.70(c)(2).
EPA assumes that owners and operators of all new CCR landfills will obtain a certification from a qualified professional engineer that the composite liner and the leachate collection and removal system meet the requirements of 40 CFR 257.70. One certification will be obtained prior to the construction of the CCR landfill pursuant to 40 CFR 257.70(e) and one certification will be obtained upon completion of the construction pursuant to 40 CFR 257.70(f). EPA further assumes that each of these certifications will be obtained once during the three-year life of the ICR. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of this one-time activity by dividing the number of new CCR landfills by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 7 units (i.e., 20 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to these certification requirements each year.
(d2) Liner Design Criteria for Existing CCR Surface Impoundments
EPA assumes that owners and operators of all existing CCR surface impoundments have already documented the liner type as required under 40 CFR 257.71(a) and obtained the certification required under 40 CFR 257.71(b) are unaffected during this ICR.
(d3) Liner Design Criteria for New CCR Surface Impoundments and Any Lateral Expansion of a CCR Surface Impoundment
EPA assumes that owners and operators of all new CCR surface impoundments will obtain a certification from a qualified professional engineer that the composite liner complies with the requirements of 40 CFR 257.72. One certification will be obtained prior to the construction of the CCR surface impoundment pursuant to 40 CFR 257.72(c) and one certification will be obtained upon completion of the construction pursuant to 40 CFR 257.72(d). EPA further assumes that each of these certifications will be obtained once during the three-year life of the ICR. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of this one-time activity by dividing the number of new CCR surface impoundments by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 34 units (i.e., 102 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to these certification requirements each year.
(d4) Alternate Liner Demonstrations
EPA estimates that owners and operators of CCR surface impoundments will submit applications and demonstrations for alternate liners.
(d5) Structural Integrity Criteria for Existing CCR Surface Impoundments
Requirements at 40 CFR 257.73(a)
EPA estimates that 80 percent of existing CCR surface impoundments are not incised CCR units (i.e., 460 units x 0.80 = 368 units).15 EPA assumes that owners and operators of these CCR surface impoundments will comply with the requirements at 40 CFR 257.73(a).
EPA assumes that several one-time activities under 40 CFR 257.73(a) were already completed. These activities include placing a permanent identification marker showing the identification number of the CCR unit (40 CFR 257.73(a)(1)) and preparing the Emergency Action Plan (EAP) under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3). EPA also assumes that several additional activities required under 40 CFR 257.73 were completed in 2016. Because these activities are required once every five years, the next required date of completion will be in 2021, which is outside of the scope of this ICR. These activities include documenting the initial hazard potential classification assessment of the CCR unit (40 CFR 257.73(a)(2))16 and obtaining the certification required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(2)(ii)
EPA assumes that two requirements under 40 CFR 257.73(a) will be completed annually. EPA assumes that the requirement to prepare documentation on an annual face-to-face meeting or exercise between representatives of the owner/operator of the CCR unit and the local emergency responders (40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(i)(E)) will be conducted by the percentage of all units that present a high or significant hazard. EPA assumes that 62 percent of all units present a high or significant hazard.17 Thus, EPA assumes that 229 units (i.e., 62% of 368 units) will need to complete the documentation under (40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(i)(E)) annually. EPA also assumes that preparing documentation required under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(v) will be completed by one percent of all non-incised units (i.e., 368 units × 0.01= 4 units).18
EPA also assumes that the remaining requirements under 40 CFR 257.73(a) will not be completed during this ICR: amend the EAP (40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(ii)) and obtain certification (40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(iv)). EPA assumes that it will not be necessary to amend the EAP during this ICR.
Requirements at 40 CFR 257.73(c) through (e)
EPA estimates that 66 percent of existing CCR surface impoundments have a height of five feet or more and a storage volume of 20 acre-feet or more, or have a height of 20 feet or more (i.e., 460 existing units x 0.65 = 304 units). 19 EPA assumes that owners and operators of these CCR surface impoundments will comply with the requirements at 40 CFR 257.73(c) through (e).
EPA assumes that no units will be subject to the requirements at 40 CFR 257.73(c) through (e) during this ICR. Several requirements have been completed, including: compiling history of construction (40 CFR 257.73(c)), conducting and documenting the initial structural stability assessment (40 CFR 257.73(d)), 20 obtaining the certification required under 40 CFR 257.73(d)(3), conducting and documenting the initial safety factor assessment (40 CFR 257.73(e)) 21, and obtaining the certification required under 40 CFR 257.73(e)(2). In addition, any action plans for structural stability that would have been required under 257.73(d)(2) would have been completed at the time of the initial assessment (which has already been completed).
(d5) Structural Integrity Criteria for New CCR Surface Impoundments and Any Lateral Expansion of a CCR Surface Impoundment
Requirements at 40 CFR 257.74(a)
EPA estimates that 80 percent of new CCR surface impoundments are not incised CCR units (i.e., 102 units x 0.80 = 82 units).22 EPA assumes that owners and operators of these CCR surface impoundments will comply with the requirements at 40 CFR 257.74(a).
EPA also assumes that certain activities under 40 CFR 257.74(a) will be conducted once during the three-year life of the ICR. These activities include: placing a permanent identification marker showing the identification number of the CCR unit (40 CFR 257.74(a)(1)), documenting the initial hazard potential classification assessment of the CCR unit (40 CFR 257.74(a)(2)),23 obtaining the certification required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(2)(ii), and preparing a written EAP (40 CFR 257.74(a)(3)). In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of these one-time activities by dividing the number of CCR surface impoundments by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 27 units (i.e., 82 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to these requirements each year.
EPA further assumes that owners and operators of CCR units subject to the requirements of 40 CFR 257.74(a) will conduct the following activity on an annual basis: prepare documentation on an annual face-to-face meeting or exercise between representatives of the owner/operator of the CCR unit and the local emergency responders (40 CFR 257.74(a)(3)(i)(E)). EPA assumes that only those units that have a high or significant hazard (assumed to be 62%) will be required to complete the documentation.24
EPA assumes that no units will amend the EAP (40 CFR 257.74(a)(3)(ii)) during the ICR period. EPA assumes that the average number of new units will obtain the certification required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(3)(iv) annually (27), and that one percent of units (i.e., 27 units × 0.01 = 0 units) will need to implement the EAP and prepare the documentation required under 40 CFR 257.74(a)(3)(v).25
Requirements at 40 CFR 257.74(c) through (e)
EPA estimates that 66 percent of new CCR surface impoundments have a height of five feet or more and a storage volume of 20 acre-feet or more, or have a height of 20 feet or more (i.e., 102 units x 0.66 = 67 units). 26 EPA assumes that owners and operators of these CCR surface impoundments will comply with the requirements at 40 CFR 257.74 (c) through (e).
EPA also assumes that certain activities under 40 CFR 257.74(c) through (e) will be conducted once during the three-year life of the ICR. These activities include: compiling the design and construction plans for the CCR unit (40 CFR 257.74(c)), conducting and documenting the initial structural stability assessment (40 CFR 257.74(d)), 27 obtaining the certification required under 40 CFR 257.74(d)(3), conducting and documenting the initial safety factor assessment (40 CFR 257.74(e)) 28, and obtaining the certification required under 40 CFR 257.74(e)(2). In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of these one-time activities by dividing the number of CCR surface impoundments by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 22 units (i.e., 67 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to these requirements each year.
In addition, EPA assumes that no units will be required to prepare the action plan required under 40 CFR 257.74(d)(2).
(e) Operating Criteria (Exhibit CCR-3)
(e1) Air Criteria
EPA assumes that all owners and operators of existing and new CCR units will comply with the air criteria requirements at 40 CFR 257.80. EPA also assumes that owners and operators of new units will prepare the CCR fugitive dust control plan once during the three-year life of the ICR. EPA assumes that existing units have already prepared the dust control plan. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of this one-time activity by dividing the number of new CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 41 units (i.e., 122 units / 3 years), on average, will prepare the CCR fugitive dust control plan each year.
EPA assumes that none of the owners and operators will amend their CCR fugitive dust control plan during the three-year period covered by this ICR.29
Based on the above, owners and operators of 41 CCR units will need to obtain a certification from a qualified professional engineer that the initial CCR fugitive dust control plan, or any subsequent amendment of it, meets the requirements of 40 CFR 257.80 (40 CFR 257.80(b)(7)).
EPA assumes that owners and operators of 684 CCR units will prepare the annual CCR fugitive dust control report required under 40 CFR 257.80(c).30
(e2) Run-On and Run-Off Controls for CCR Landfills
EPA assumes that all owners and operators of new CCR landfills will prepare the initial run-on and run-off control system plan required under 40 CFR 257.81(c) once during the three-year life of the ICR. EPA assumes that existing units have already prepared the initial run-on and run-off control system plans. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of this one-time activity by dividing the number of new CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 7 units (i.e., 20 units / 3 years), on average, will prepare the run-on and run-off control plan each year.
EPA assumes that none of the owners and operators will amend their run-on and run-off control system plan during the three-year period covered by this ICR
Based on the above, owners and operators of 7 CCR units will need to obtain a certification from a qualified professional engineer that the initial and periodic run-on and run-off control system plans meet the requirements of 40 CFR 257.81 (40 CFR 257.81(c)(5)).
(e3) Hydrologic and Hydraulic Capacity Requirements for CCR Surface Impoundments
EPA assumes that all owners and operators of new CCR surface impoundments will prepare the initial inflow design flood control system plans required under 40 CFR 257.82(c) once during the three-year life of the ICR. EPA assumes that existing units have already prepared the initial inflow design flood control system plans. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of this one-time activity by dividing the number of CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 34 units (i.e., 102 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to this requirement each year.
Based on the above, owners and operators of 34 CCR units will need to obtain a certification from a qualified professional engineer that the initial inflow design flood control system plans meet the requirements of 40 CFR 257.82 (40 CFR 257.82(c)(5)).
(e4) Inspection Requirements for CCR Surface Impoundments
EPA assumes that owners and operators of all 494 existing and new CCR surface impoundments will comply with the inspection requirements at 40 CFR 257.83(a) each year.
EPA estimates that 66 percent of existing and new CCR surface impoundments are subject to the periodic structural stability assessment requirements under 40 CFR 257.73(d) or 40 CFR 257.74(d) (i.e., 494 units x 0.66 = 326 units). 31 EPA assumes that all of these CCR units will be inspected annually by a qualified professional engineer to ensure that the design, construction, operation, and maintenance of the CCR unit are consistent with recognized and generally accepted good engineering standards, as required under 40 CFR 257.83(b)(1). EPA also assumes that the qualified professional engineer will develop an inspection report, as required under 40 CFR 257.83(b)(2).
Finally, EPA assumes that owners and operators of 1 percent of the existing and new CCR surface impoundments (i.e., 494 units x 0.01 = 5 units) will develop and implement an action plan to remedy structural weakness or disrupting condition each year.
(e5) Inspection Requirements for CCR Landfills
EPA assumes that owners and operators of all 229 existing and new CCR landfills will comply with the inspection requirements at 40 CFR 257.84(a) and (b) each year.
EPA also assumes that owners and operators of 1 percent of the existing and new CCR landfills (i.e., 229 units x 0.01 = 2 units) will develop and implement an action plan to remedy structural weakness or disrupting condition each year.
(f) Groundwater Monitoring and Corrective Action (Exhibit CCR-4)
(f1) Applicability
EPA assumes that owners and operators of all 684 existing and new CCR units will develop the annual groundwater monitoring and corrective action report required under 40 CFR 257.90(e).32
(f2) Groundwater Monitoring Systems
EPA assumes that owners and operators of all 122 new CCR units will document and include in the operating record the design, installation, development, and decommissioning of any monitoring wells, piezometers and other measurement, sampling, and analytical devices. EPA assumes that existing units have already completed this requirement. Owners and operators of these units also will obtain a certification from a qualified professional engineer stating that the groundwater monitoring system has been designed and constructed to meet the requirements of 40 CFR 257.91. EPA also assumes that these activities will be conducted once during the three-year life of the ICR. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of these one-time activities by dividing the number of CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 41 units (i.e., 122 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to these requirements each year.
(f3) Groundwater Sampling and Analysis Requirements
EPA assumes that owners and operators of all 122 new CCR units will develop a sampling and analysis program. EPA also assumes that owners and operators of these units will obtain a certification from a qualified professional engineer stating that the selected statistical method is appropriate for evaluating the groundwater monitoring data for the CCR management area. EPA further assumes that these activities will be conducted once during the three-year life of the ICR. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of this one-time activity by dividing the number of CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 41 units (i.e., 122 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to this requirement each year.
(f4) Detection Monitoring Program
EPA assumes that owners and operators of 5 percent of existing and new CCR units (i.e., 723 units x 0.05 = 36 units) will demonstrate the need for an alternative monitoring frequency for repeated sampling and analysis for constituents listed in Appendix III during the active life and the post-closure care period based on the availability of groundwater. EPA also assumes that these owners and operators will obtain a certification from a qualified professional engineer stating that the demonstration for an alternative groundwater sampling and analysis frequency meets the requirements of 40 CFR 257.94. EPA further assumes that these activities will be conducted once during the three-year life of the ICR. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of these one-time activities by dividing the number of CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 12 units (i.e., 36 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to these requirements each year.
EPA assumes that, each year, owners and operators of 0.79 percent of existing and new CCR units (i.e., 723 units x 0.0079 = 6 units) will determine that there is a statistically significant increase over background levels for one or more of the constituents listed in Appendix III at any monitoring well at the waste boundary specified under 40 CFR 257.91(a)(2) and will be required to prepared the demonstration and the certification required under 40 CFR 257.94(e)(2).33
Finally, EPA assumes that owners and operators of 51 percent of CCR units will detect a statistically significant increase over background levels for one or more of the constituents listed in Appendix III at any monitoring well at the waste boundary specified under 40 CFR 257.91(a)(2). EPA assumes that 369 units (i.e., 0.51 × 723 units = 369 units) will prepare a notification stating that an assessment monitoring program has been established in the first year, and that an additional 51 percent of the remaining units that have not yet established an assessment monitoring program will also establish a program in each of the remaining two years of the ICR. Specifically, EPA assumes that 667 units will establish an assessment monitoring program over the three years (i.e., 723 × 0.51 + 723 × (1 - 0.51) × 0.51 + 723 × (1 - 0.51)2 × 0.51 = 638 units). On an annual basis, this ICR assumes that 213 units (i.e., 638 units / 3 years) will be required to prepare the notification under 40 CFR 257.94(e)(3).
(f5) Assessment Monitoring Program
EPA assumes that owners and operators of 5 percent of the CCR units subject to the assessment monitoring requirements (i.e., 638 units x 0.05 = 32 units) will demonstrate the need for an alternative monitoring frequency for repeated sampling and analysis for constituents listed in Appendix IV during the active life and the post-closure care period based on the availability of groundwater (40 CFR 257.95(c)(1)-(2)). EPA also assumes that these owners and operators will obtain a certification from a qualified professional engineer stating that the demonstration for an alternative groundwater sampling and analysis frequency meets the requirements of 40 CFR 257.95 (40 CFR 257.95(c)(3)). EPA further assumes that these activities will be conducted once during the three-year life of the ICR. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of these one-time activities by dividing the number of CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 11 units (i.e., 32 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to these requirements each year.
EPA assumes that, during the three-year period covered by this ICR, the concentrations of all constituents listed in Appendix IV will be shown to be at or below background values for two consecutive sampling events for 5 percent of the CCR units (i.e., 638 units x 0.05 = 32 units). EPA further assumes that these owners and operators will prepare a notification stating that detection monitoring is resuming for the CCR unit (40 CFR 257.95(e)). In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of this one-time activity by dividing the number of CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 11 units (i.e., 32 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to this requirement each year. EPA assumes that, during the three-year period covered by this ICR, one or more constituents in Appendix IV will be detected at statistically significant levels above the groundwater protection standard established under 40 CFR 257.95(h) for 5 percent of the CCR units (i.e., 638 units x 0.05 = 32 units). These owners and operators will need to prepare a notification identifying the constituents in Appendix IV that have exceeded the groundwater protection standard (40 CFR 257.95(g)). In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of these one-time activities by dividing the number of CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 11 units (i.e., 32 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to this requirement each year.
This ICR assumes that zero units will be required to notify all persons who own the land or reside on the land that directly overlies any part of the plume of contamination if contaminants have migrated off-site if indicated by sampling of wells in accordance with 40 CFR 257.95(g)(2) or demonstrate that a source other than the CCR unit caused the contamination, or that the statistically significant increase resulted from error in sampling, analysis, statistical evaluation, or natural variation in groundwater quality (40 CFR 257.95(g)(3)(ii).
This ICR assumes that 5 percent of all units will initiate corrective action, and will prepare a notification stating that an assessment of corrective measures has been initiated under 40 CFR 257.95(g)(5). EPA estimates that 38 units will be required to prepare this notification (i.e., 723 × 0.05 = 36 units). In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of these one‑time activities by dividing the number of CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 12 units (i.e., 36 units / 3 years), on average, will be subject to this requirement each year.
(f6) Assessment of Corrective Measures
EPA assumes that 12 CCR units will be subject to the assessment of corrective measures requirements under 40 CFR 257.96 each year. This includes the requirements to prepare the demonstration under 40 CFR 257.96(a), obtain the certification under 40 CFR 257.96(a), complete the assessment of corrective measures required under 40 CFR 257.96(d), and discuss the results of the corrective measures assessment prior to the selection of remedy in a public meeting with interested and affected parties, under 40 CFR 257.96(e).
(f7) Selection of Remedy
EPA assumes that 12 of the existing and new CCR units will be affected by the requirements under 40 CFR 257.97 during the three-year period covered by this ICR. This includes the requirements to prepare a semi-annual report describing the progress in selecting and designing the remedy, prepare a report on the selected remedy, and obtain the certification required under 40 CFR 257.97(a).
(f8) Implementation of the Corrective Action Program
EPA assumes that none of the existing and new CCR units will be affected by the requirements under 40 CFR 257.98 during the three-year period covered by this ICR.
(g) Closure and Post-Closure Care (Exhibit CCR-5)
(g1) Closure of CCR Landfills and CCR Surface Impoundments
The burden associated with inclusion of the specified statements in the notifications required under 40 CFR 257.102(g) has been considered under the corresponding regulatory requirements.
(g2) Criteria for Conducting Closure or Retrofit of CCR Landfills and CCR Surface Impoundments
EPA assumes that all owners and operators of new CCR units will prepare a written closure plan or written retrofit plan that describes the steps necessary to close or retrofit the CCR unit at any point during the active life of the CCR unit consistent with recognized and generally accepted good engineering practices (40 CFR 257.102(b) and (k)). EPA assumes that existing units completed this requirement. EPA also assumes that owners and operators will obtain a written certification from a qualified professional engineer that the written closure or retrofit plan meets the requirements of 40 CFR 257.102 (40 CFR 257.102(b)(4) and (k)(2)(iv)). EPA assumes that these activities will be conducted once during the three-year life of the ICR. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of these one-time activities by dividing the number of CCR units by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 41 units (i.e., 7 landfills + 34 surface impoundments), on average, will be subject to these requirements each year.
EPA assumes that none of the owners and operators will amend their closure or retrofit plan during the three-year period covered by this ICR.
EPA estimates that 7 CCR landfills and 68 CCR surface impoundments units will undergo closure on average each year.34 EPA assumes that owners and operators of these CCR units will conduct the following activities: obtain a written certification from a qualified professional engineer that the design of the final cover system meets the requirements of 40 CFR 257.102, if the unit is closing (40 CFR 257.102(d)(3)(iii)); obtain a certification from a qualified professional engineer verifying that closure or retrofit has been completed in accordance with the closure or retrofit plan specified in 40 CFR 257.102(b) or (k)(2) and the requirements of 40 CFR 257.102(f)(3) and (k)(4); prepare a notification of intent to close or retrofit a CCR unit (40 CFR 257.102(g) and (k)(5)); prepare a notification of closure of a CCR unit, if the unit is closing (40 CFR 257.102(h)); and prepare a notification stating that the notation on the deed to the property (or some other instrument that is normally examined during title search) has been recorded (40 CFR 257.102(i)). This ICR assumes that 75 units complete the preceding activities annually, with the exception of the notification of intent to close or retrofit a CCR unit required under 40 CFR 257.102(g), which is assumed to be zero.35
(g3) Alternative Closure Requirement
EPA assumes that none of the CCR units will be affected by the alternative closure requirements (units undergoing retrofit are also eligible for these alternatives as specified under 40 CFR 257.102(k)(3)) under 40 CFR 257.103 during the three-year period covered by this ICR.
(g4) Post-Closure Care Requirements
EPA assumes that all owners and operators of new CCR units will prepare a written post-closure plan (40 CFR 257.104(d)). EPA also assumes that owners and operators will obtain a written certification from a qualified professional engineer that the written post-closure plan meets the requirements of 40 CFR 257.104 (40 CFR 257.104(d)(4)). EPA assumes that these activities will be conducted once during the three-year life of the ICR. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of these one-time activities by using the average number of new CCR units. Thus, EPA estimates that 41 units (i.e., 34 new surface impoundments + 7 CCR landfills), on average, will be subject to this requirement each year.
EPA assumes that none of the owners and operators will amend their post-closure plan during the three-year period covered by this ICR.
Finally, EPA assumes that none of the owners and operators of the CCR units will prepare a notification verifying that post-closure care has been completed (40 CFR 257.104(e)).
(h) Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet - Owners and Operators of CCR Units (Exhibit CCR-6)
EPA assumes that, each year, the 300 owners and operator of the 723 existing and new CCR units will comply with the recordkeeping, notification, and posting requirements of the final rule.
EPA also assumes that these none of these owners and operators will develop a publicly accessible internet site (CCR website) containing the information specified at 40 CFR 257.107 during the three-year life of the ICR.36 EPA assumes that there are no new owners or operators during the three-year life of the ICR, and that all existing owners and operators have already completed this requirement.
(i) Recordkeeping, Notification, and Posting of Information to the Internet – State Government Agencies and Tribal Authorities (Exhibit CCR-7)
Owners and operators of CCR units must send the notifications required under 40 CFR 257.106(e) through (i) to the relevant State Director and/or appropriate Tribal authority. EPA assumes that State government agencies and Tribal authorities will review these notifications once received.
(j) Solid Waste Management Plans (Exhibits CCR-8a and CCR-8b)
In the currently approved ICR, EPA assumed that 48 States (i.e., 47 States and Puerto Rico) would prepare a solid waste management plan (SWMP) during the three-year life of the ICR. Under the SWMP approval process, a State with an approved SWMP can grant an extension to the compliance dates in the CCR rule to an entity unable to comply. Interest in this authority did not materialize as EPA believed it would at the time the CCR rule was issued. In fact, only three States have approved SWMPs at this time and EPA is not aware of any other States that will seek such approval from EPA. As a result, with this ICR revision, EPA is revising the number of respondents for this voluntary activity from 48 to three. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of this one-time activity by dividing the number of respondents by three. Thus, EPA estimates that one respondent (i.e., 3 respondents / 3 years), on average, will prepare a solid waste management plan each year.
(k) State Applications for CCR Permit Programs (Exhibits CCR-8a and CCR‑8b)
EPA is aware of 44 States (43 States and Puerto Rico) that have one or more facilities with a CCR website (a requirement of the CCR rule). Of these 44 States, 8 States have only one facility with a CCR website; 2 States have two facilities; 4 States have three facilities; 3 States have four facilities and 27 States have five or more facilities with a CCR website. EPA believes that those States with few facilities subject to the CCR rule (i.e., States with fewer than four facilities with a CCR website) will not invest the resources necessary to prepare and submit an application for a CCR permit program. In addition, based on information EPA has learned through its interactions with the States, EPA believes approximately 75 percent of States with five or more facilities with a CCR website will submit a state program application to the Agency. Thus, EPA estimates that 21 States will seek permit program approval (e.g., 75 percent of 27 States) during the three-year life of the ICR. In estimating the annual respondent hour and cost burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA annualized the hour and cost burden of this one-time activity by dividing the number of respondents by three. Thus, EPA estimates that 7 respondents (i.e., 21 respondents / 3 years), on average, will prepare an application for State CCR permit program each year.
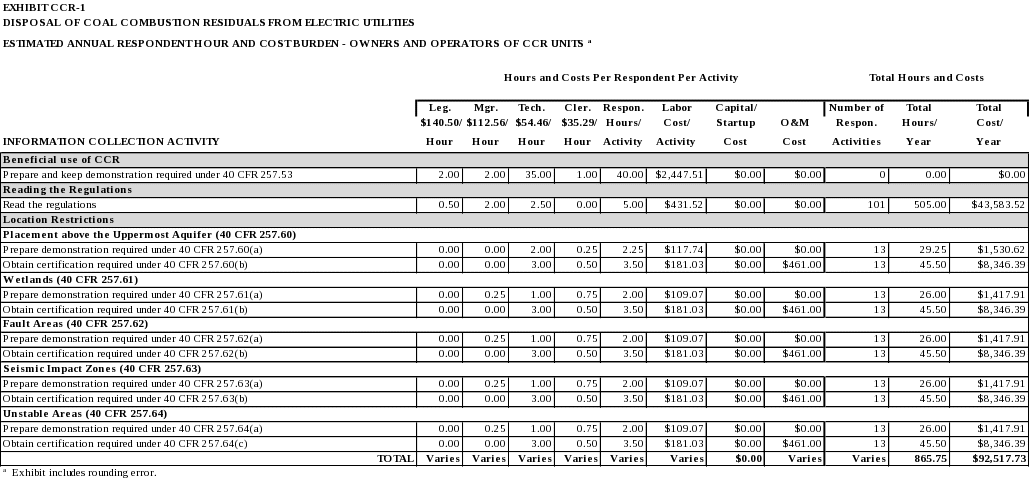
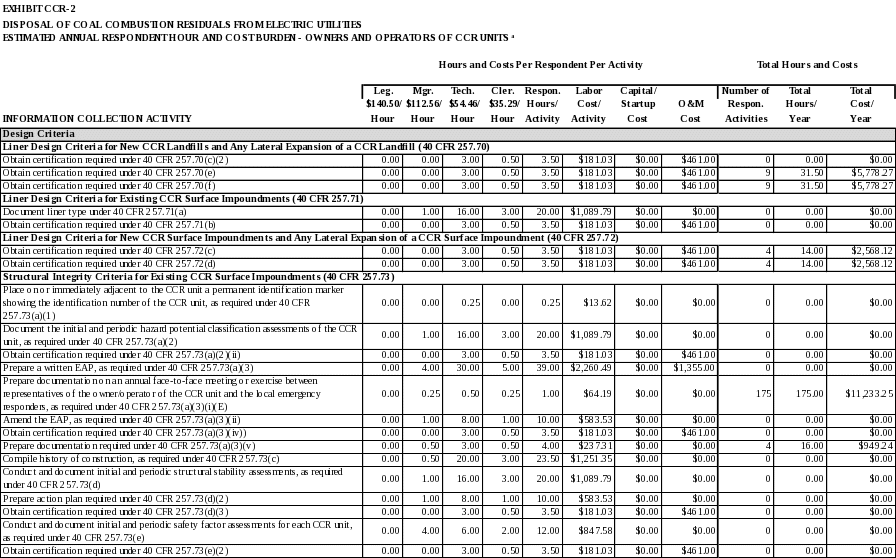
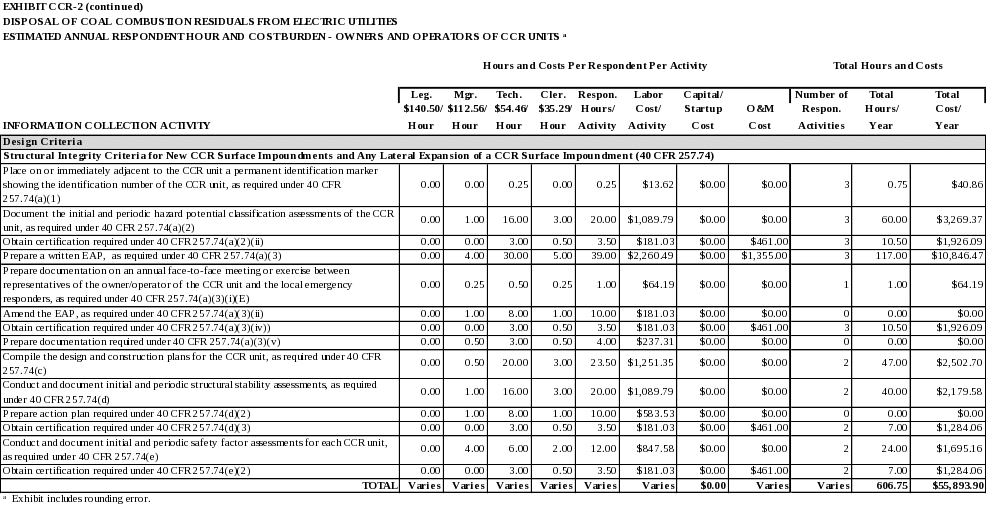
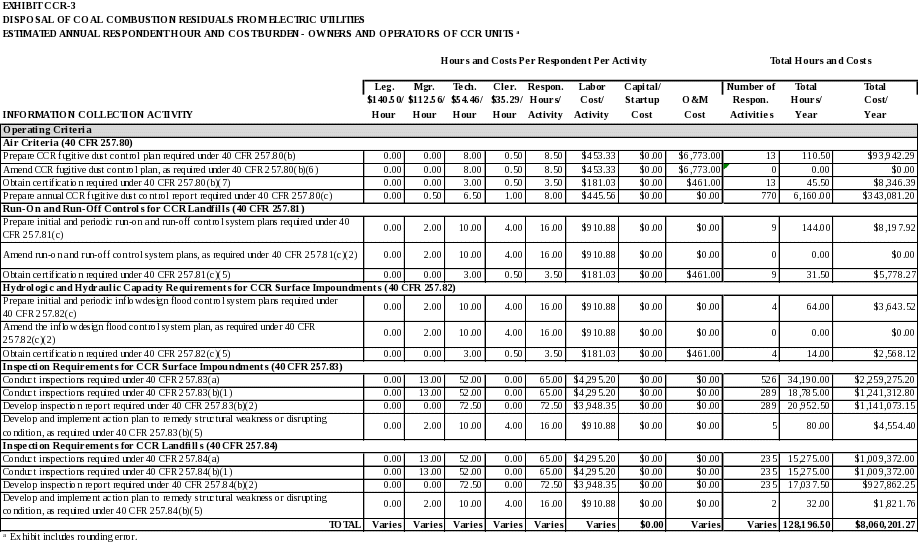
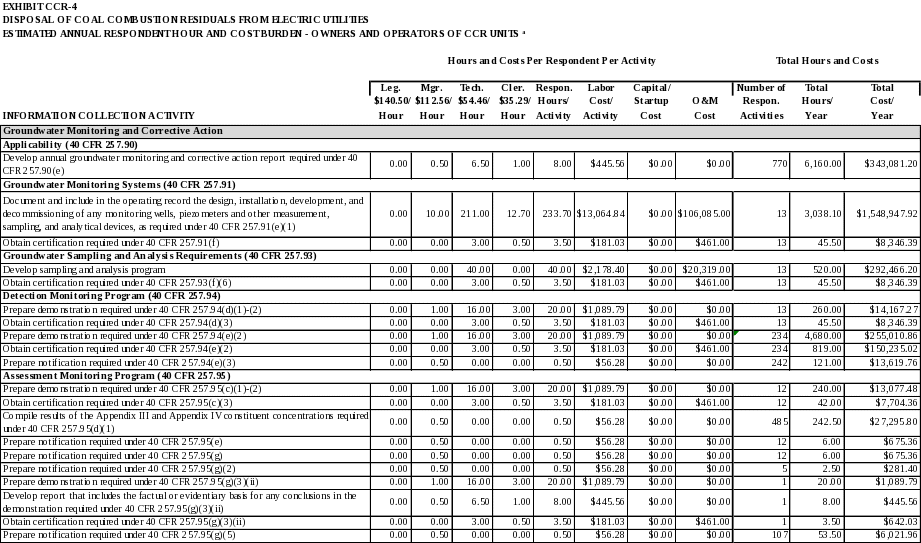
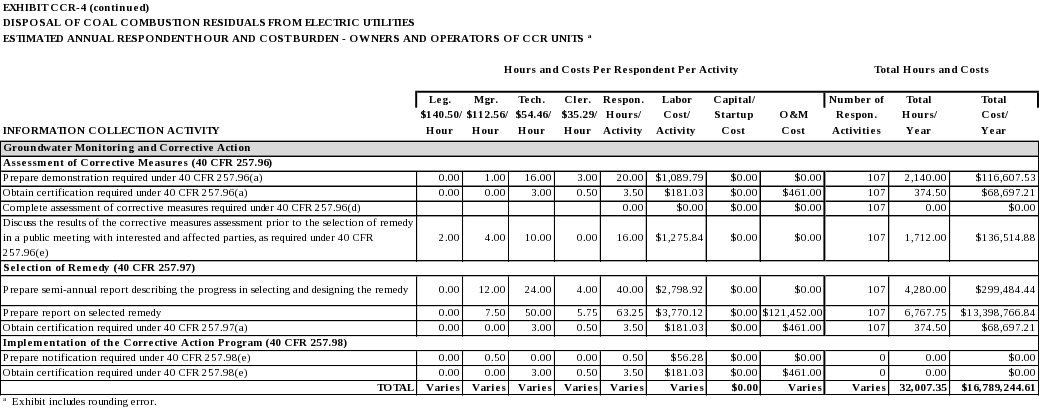

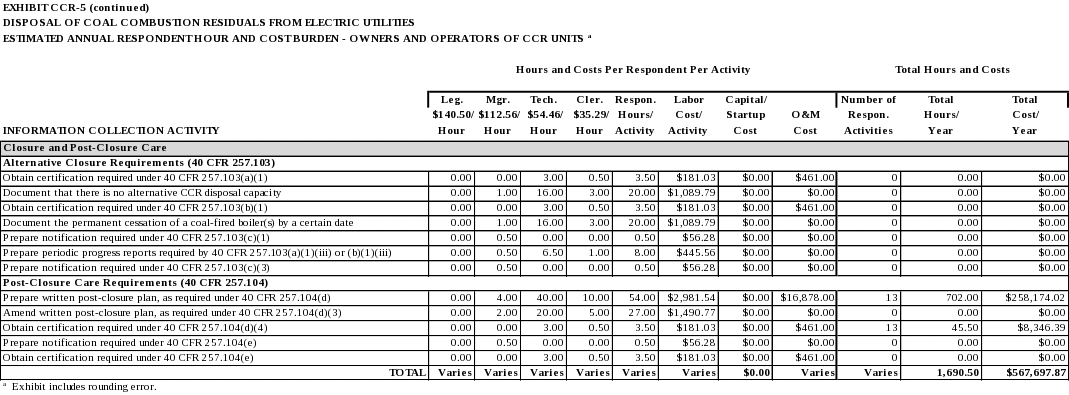

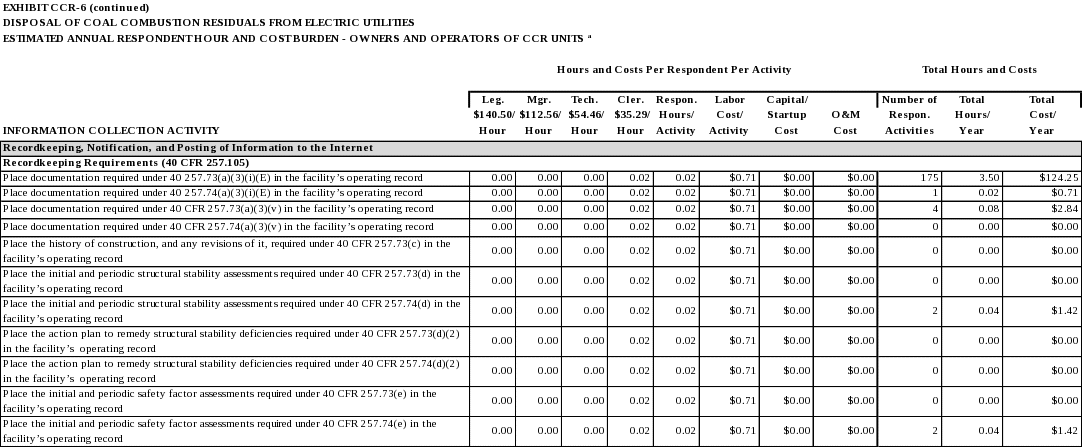
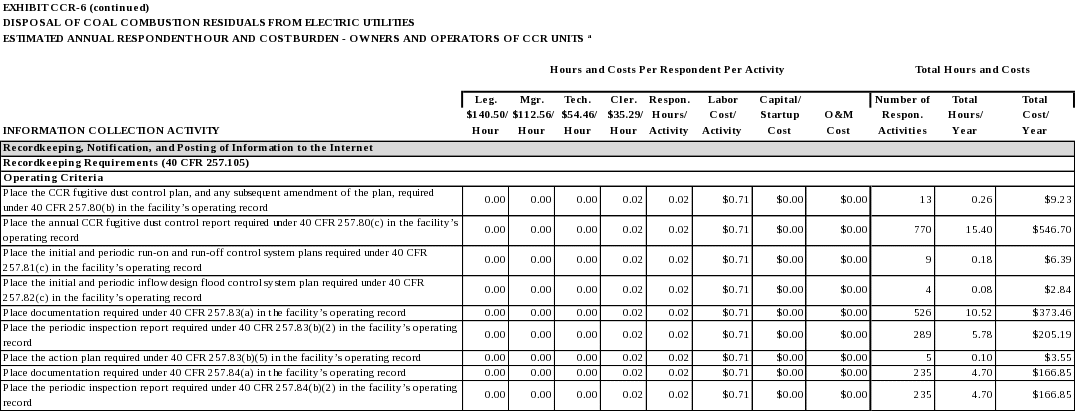
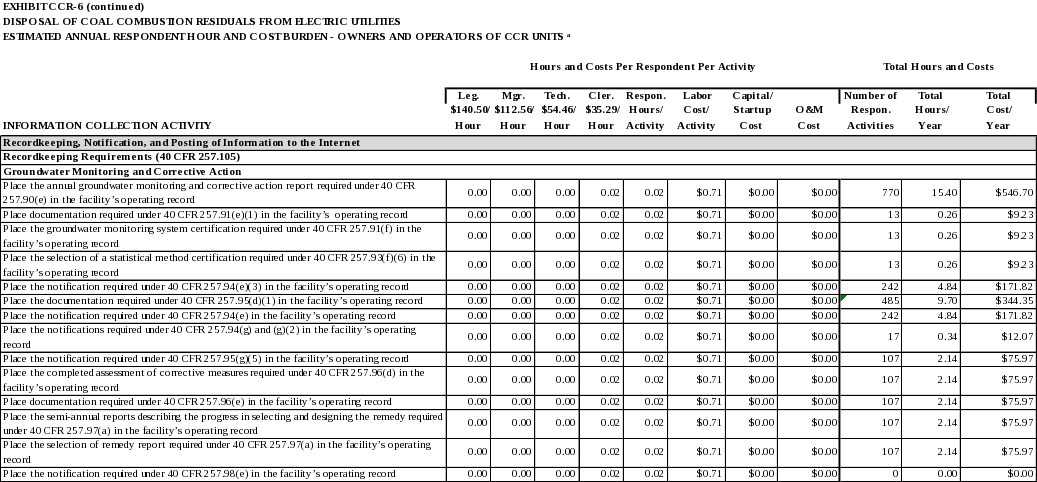
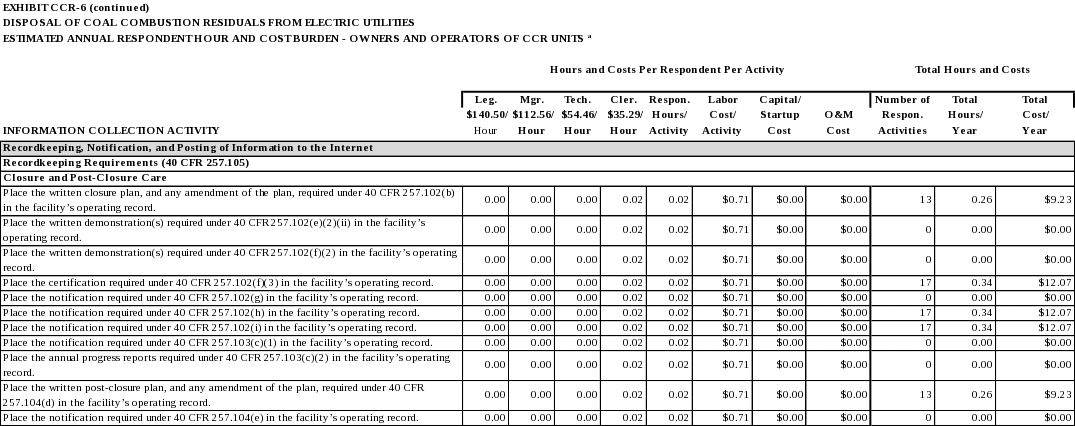

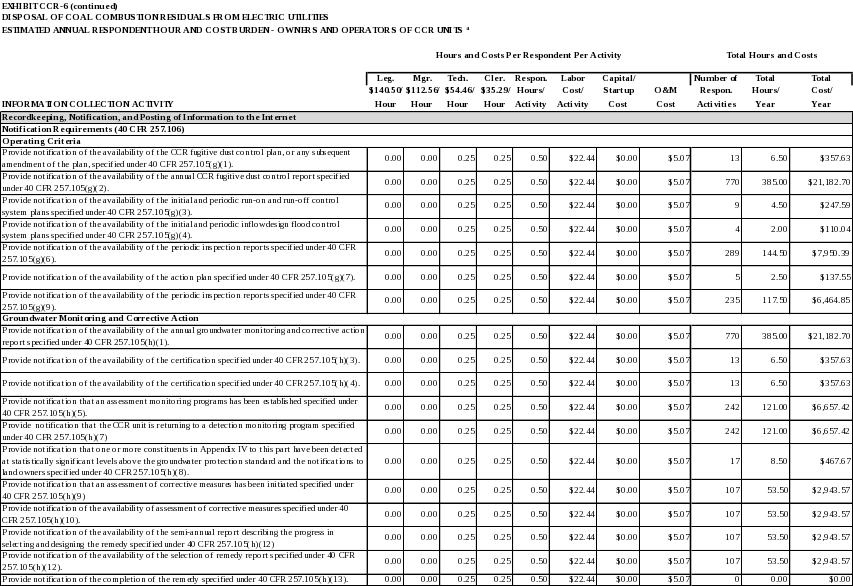
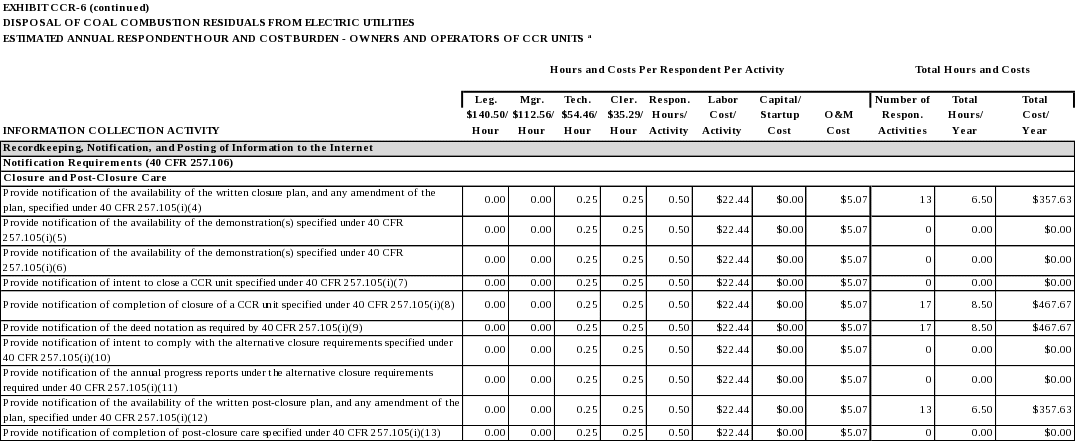
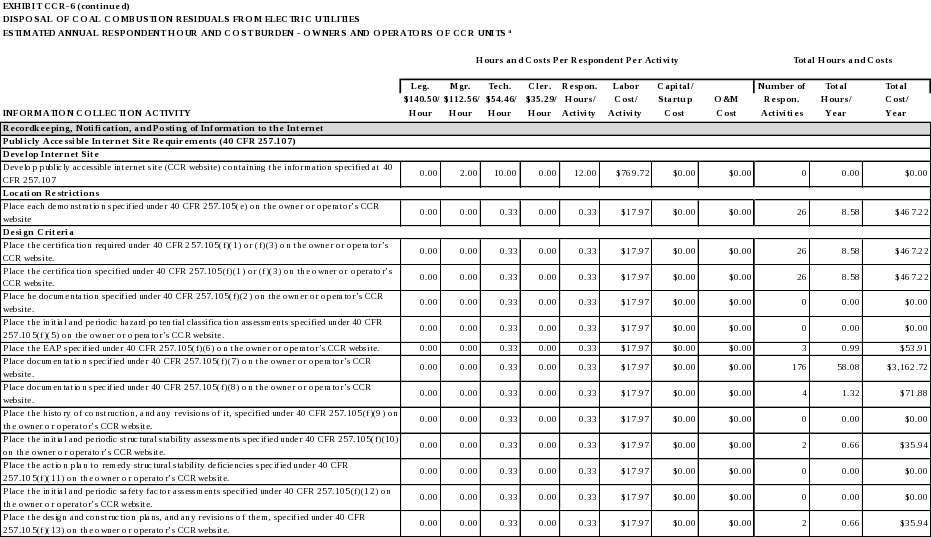
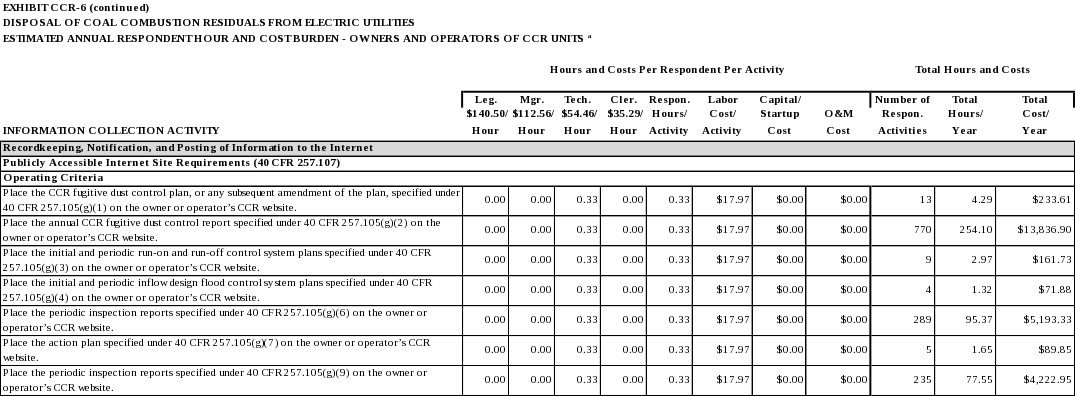

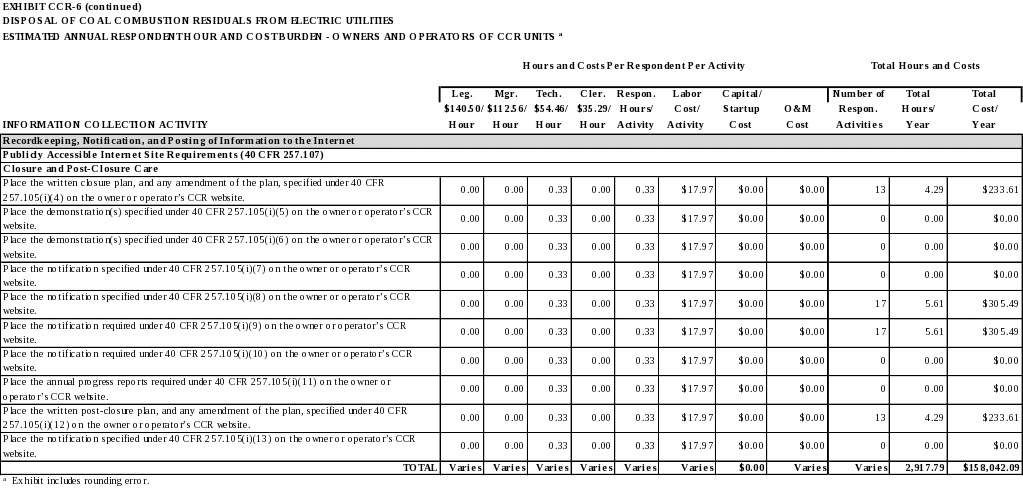
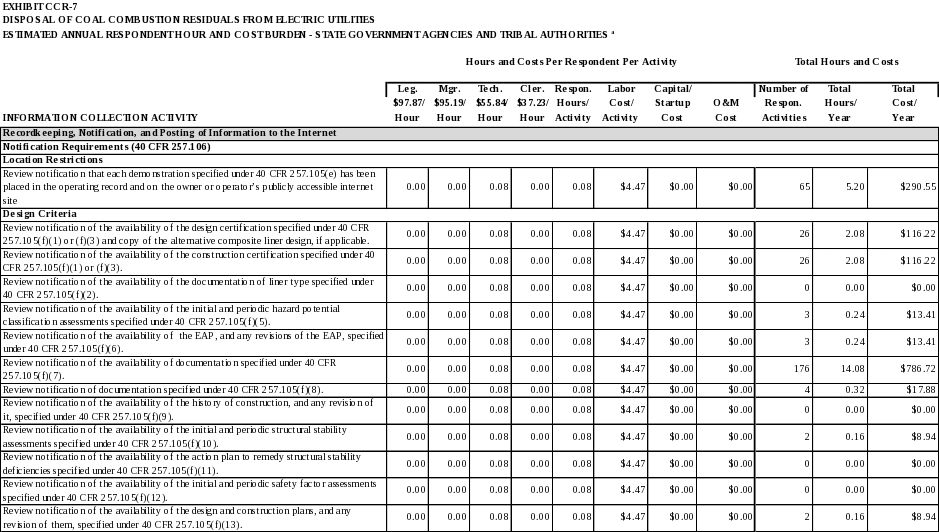

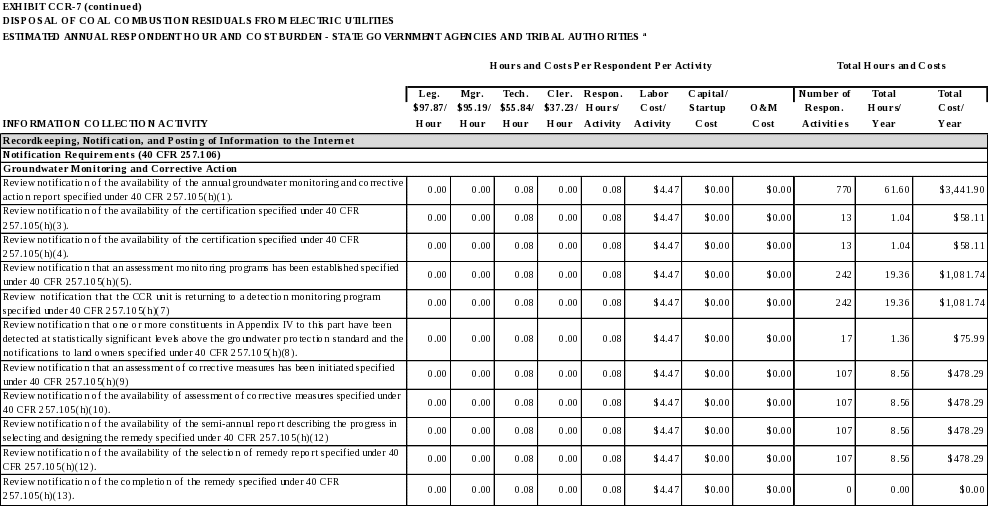
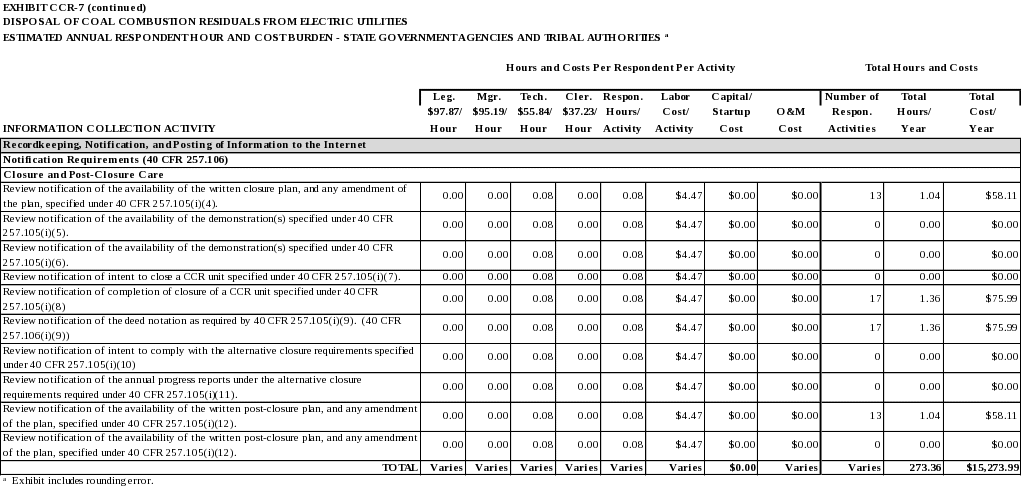
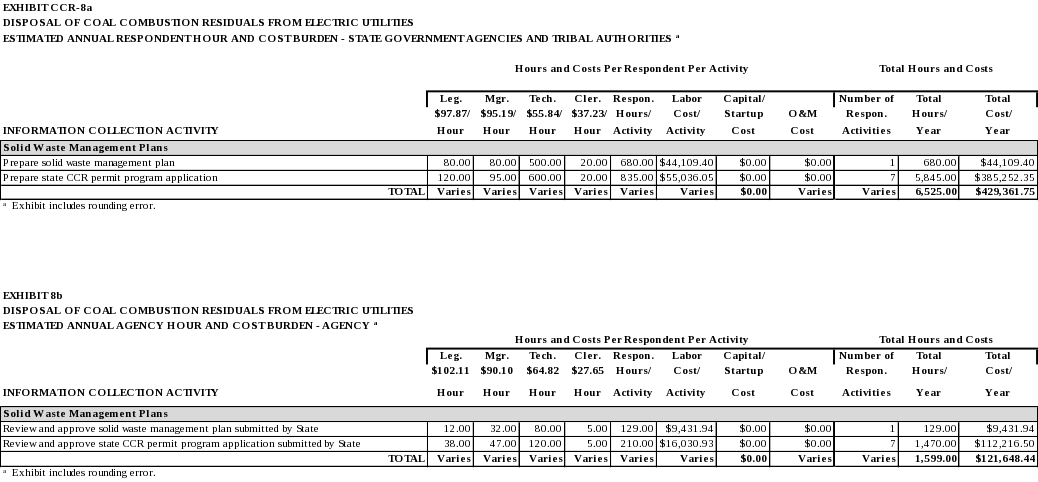

6(e) BOTTOM LINE BURDEN HOURS AND COSTS
Respondent Tally
As shown in Exhibit 9, EPA estimates the annual respondent burden to be 173,083 hours and $15,511426.
Agency Tally
Exhibit 8b summarizes the total annual Agency hour or cost burden associated with reviewing and approving State SWMPs and CCR permit program applications. As shown in the exhibit, EPA estimates the annual Agency burden to be 1,599 hours and $121,648.
6(f) REASONS FOR CHANGE IN BURDEN
The burden increased significantly from the previous ICR mainly due to the fact that EPA merged the burden associated with the information collection requirements related to the disposal of CCR from existing ICR 2050-0053 to this ICR. The annual respondent burden in this current ICR is estimated to be 173,083 hours, which is an increase of 170,904 hours from the previously finalized/approved ICR of 2,179 hours. The annual cost burden in this current ICR is estimated to be $15,511,426, which is an increase of $14,726,102 from the previously finalized/approved ICR of $785,324.
6(g) BURDEN STATEMENT
Burden means the total time, effort, or financial resources expended by persons to generate, maintain, retain, or disclose or provide information to or for a Federal agency. This includes the time needed to review instructions; develop, acquire, install, and utilize technology and systems for the purposes of collecting, validating, and verifying information, processing and maintaining information, and disclosing and providing information; adjust the existing ways to comply with any previously applicable instructions and requirements; train personnel to be able to respond to a collection of information; search data sources; complete and review the collection of information; and transmit or otherwise disclose the information. An agency may not conduct or sponsor, and a person is not required to respond to, a collection of information unless it displays a currently valid OMB control number. The OMB control numbers for EPA's regulations are listed in 40 CFR part 9 and 48 CFR chapter 15.
To comment on the Agency's need for this information, the accuracy of the provided burden estimates, and any suggested methods for minimizing respondent burden, including the use of automated collection techniques, EPA has established a public docket for this ICR under Docket ID number EPA-HQ-OLEM-2019-0173, which is available for online viewing at http://www.regulations.gov, or in person viewing in the EPA Docket Center (EPA/DC). The EPA/DC Public Reading Room is located in the WJC West Building, Room 3334, 1301 Constitution Ave., N.W., Washington, DC. The EPA/DC Public Reading Room is open from 8:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m., Monday through Friday, excluding legal holidays. The telephone number for the EPA/DC Public Reading Room is (202) 566-1744.
An electronic version of the public docket is available at http://www.regulations.gov. This site can be used to submit or view public comments, access the index listing of the contents of the public docket, and to access those documents in the public docket that are available electronically. When in the system, select “search,” then key in the Docket ID Number identified above. Also, you can send comments to the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs, Office of Management and Budget, 725 17th Street, NW, Washington, D.C. 20503, Attention: Desk Officer for EPA. Please include the EPA Docket ID No. EPA-HQ-OLEM-2019-0173 and OMB Control Number 2050-0053 in any correspondence.
1 A “lateral expansion” is defined in the CCR rule as a horizontal expansion of the waste unit boundaries of a CCR unit made after the rule’s effective date, October 19, 2015.
2 See Utility Solid Waste Activities Group, et al v EPA, No. 15-1219 (D.C. Circuit) and Waterkeeper Alliance Inc. et al. v. EPA No. 18-1289 (D.C. Circuit)
3 See EPA ICR Number1189.29.
4 U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS)’s May 2023 National Industry-Specific Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates cross all industry sectors, at: http://www.bls.gov/oes/current/oes_nat.htm.
5 = [1+ (Fringe Benefits %)] / [(100% - Fringe Benefits %) x (1+ Overhead %)].
6 Applied “All goods-producing” industry group fringe benefits percentage of 33.3% from “Table 6. Private industry, by major industry group” of the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) “Employer Costs for Employee Compensation” (ECEC), at https://www.bls.gov/news.release/ecec.t06.htm.
7 In absence of data specific to industry, applied 12% Federal civilian overhead cost factor from Figure C1 of the REVISED February 2008 OMB Circular A-76.
9 = [1+ (Fringe Benefits %)] / [(100% - Fringe Benefits %) x (1+ Overhead %)].
10 Applied 37.6% fringe benefits percentage from “Table 3. State and local government, by major occupational and industry group” of the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) “Employer Costs for Employee Compensation” (ECEC), at https://www.bls.gov/news.release/ecec.t03.htm.
11 In absence of data specific to state governments, applied 12% Federal civilian overhead cost factor from Figure C1 of the REVISED February 2008 OMB Circular A-76.
13 Office of Policy and Management (OPM) 2023 General Schedule (Base) Hourly Rate Pay Table.
14 Note that under the WIIN Act a participating State director (i.e., for a state which has an EPA-approved CCR permitting under the WIIN Act) may issue technical certification in lieu of the current requirements to have professional engineers issue the certifications. This does not affect total burden.
15 This assumption is based on information from information request responses from 240 electric utilities. EPA sent out this information request in March, April, and December of 2009. All responses, with the exception of information claimed as confidential business information, are available at EPA’s “Information Request Responses from Electric Utilities” web page at http://www.epa.gov/epawaste/nonhaz/industrial/special/fossil/surveys/index.htm, last accessed on December 17, 2014. Based on these responses, 127 of 678 CCR surface impoundments (i.e., 19 percent) are incised units.
16 40 CFR 257.73(f)(3) indicates that the frequency for conducting periodic assessments is every five years. The date of completing the initial assessment is the basis for establishing the deadline to complete the first subsequent assessment. As a result, no assessments will be conducted during the three-year period covered by this ICR.
17 According to the data collected by EPA ORCR from postings made to publicly-accessible internet sites required under 40 CFR 257.107, 183 out of 294 units with posted hazard classification assessments had hazard classifications of “high” or “significant.”
18 This assumption is retained from the 2017 ICR.
19 This assumption is based on information from information request responses from 240 electric utilities. EPA sent out this information request in March, April, and December of 2009. All responses, with the exception of information claimed as confidential business information, are available at EPA’s “Information Request Responses from Electric Utilities” web page at http://www.epa.gov/epawaste/nonhaz/industrial/special/fossil/surveys/index.htm, last accessed on December 17, 2014. Based on these responses, 448 of 678 CCR surface impoundments (i.e., 66 percent) have a height of five feet or more and a storage volume of 20 acre-feet or more, or have a height of 20 feet or more.
20 40 CFR 257.73(f)(3) indicates that the frequency for conducting periodic assessments is every five years. The date of completing the initial assessment is the basis for establishing the deadline to complete the first subsequent assessment. As a result, the initial assessment was conducted in 2016, and the next assessment will be conducted in 2021, which is outside of the scope of this ICR.
21 Ibid.
22 This assumption is based on information from information request responses from 240 electric utilities. EPA sent out this information request in March, April, and December of 2009. All responses, with the exception of information claimed as confidential business information, are available at EPA’s “Information Request Responses from Electric Utilities” web page at http://www.epa.gov/epawaste/nonhaz/industrial/special/fossil/surveys/index.htm, last accessed on December 17, 2014. Based on these responses, 127 of 678 CCR surface impoundments (i.e., 19 percent) are incised units.
23 40 CFR 257.74(f)(2) indicates that the frequency for conducting periodic assessments is every five years. The date of completing the initial assessment is the basis for establishing the deadline to complete the first subsequent assessment. As a result, only the initial assessment will be conducted during the three-year period covered by this ICR.
24 This assumption is consistent with the assumption applied to existing units as described under 40 CFR 257.73(a).
25 This assumption is consistent with the assumption applied to existing units as described under 40 CFR 257.73(a)(3)(v).
26 This assumption is based on information from information request responses from 240 electric utilities. EPA sent out this information request in March, April, and December of 2009. All responses, with the exception of information claimed as confidential business information, are available at EPA’s “Information Request Responses from Electric Utilities” web page at http://www.epa.gov/epawaste/nonhaz/industrial/special/fossil/surveys/index.htm, last accessed on December 17, 2014. Based on these responses, 448 of 678 CCR surface impoundments (i.e., 66 percent) have a height of five feet or more and a storage volume of 20 acre-feet or more, or have a height of 20 feet or more.
27 40 CFR 257.74(f)(2) indicates that the frequency for conducting periodic assessments is every five years. The date of completing the initial assessment is the basis for establishing the deadline to complete the first subsequent assessment. As a result, only the initial assessment will be conducted during the three-year period covered by this ICR.
28 Ibid.
29 The RIA for the final rule assumes that each dust control plan would be modified once over its lifespan. The RIA also assumes a 40-year CCR management unit lifespan. (p. 4-22)
30 EPA assumes that the annual dust control report will be prepared for existing units annually, and for new units the year after they come online..
31 This assumption is based on information from information request responses from 240 electric utilities. EPA sent out this information request in March, April, and December of 2009. All responses, with the exception of information claimed as confidential business information, are available at EPA’s “Information Request Responses from Electric Utilities” web page at http://www.epa.gov/epawaste/nonhaz/industrial/special/fossil/surveys/index.htm, last accessed on December 17, 2014. Based on these responses, 448 of 678 CCR surface impoundments (i.e., 66 percent) have a height of five feet or more and a storage volume of 20 acre-feet or more, or have a height of 20 feet or more.
32 EPA assumes that the annual groundwater monitoring and corrective action report will be prepared for existing units annually, and for new units the year after they come online.
33 This assumption reflects data collected by EPA ORCR from postings made to publicly-accessible internet sites required under 40 CFR 257.107. These data indicate that of 762 CCR management units, six have posted alternative source demonstrations following a determination of statistically significant increases (SSIs) resulting from detection monitoring activities.
34 This ICR assumes that the number of new CCR units is equal to one-half of the number of CCR unit closures in every year. According to the data collected on postings made to publicly-accessible internet sites required by the 2015 CCR final rule (“CCR compliance websites”) required under 40 CFR 257, the median number of impoundments per facility is 2. This ICR assumes that facilities consolidate impoundments after closures, rather than replacing all closing impoundments with the same number of new impoundments.
35 According to the data collected on postings made to publicly-accessible internet sites required by the 2015 CCR final rule (“CCR compliance websites”) required under 40 CFR 257, 126 CCR management units have already posted notices of intent (“NOIs”) to close. Because there have been more such notices of intent posted, posted than the number of anticipated annual closures (74), EPA assumes that no additional NOIs will be posted during this ICR.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | EPA |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2024-07-31 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy