Explanation for Program Changes or Adjustments
D. Explanation for Program Changes or Adjustments.docx
[NCEZID] The National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN)
Explanation for Program Changes or Adjustments
OMB: 0920-0666
National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN)
OMB Control No. 0920-0666
Revision Request October 2023
Explanation for Program Changes or Adjustments
This Revision includes proposed changes to 23 approved and 9 new NHSN data collection tools detailed below:
(57.103) Annual Survey Acute Care Hospitals (57.150) Long Term Acute Care Facilities (57.151) Acute Rehabilitation |
||
Type of Change |
Itemized Changes / Justification |
|
Addition |
1b. If Yes, do you also send out any antimicrobial susceptibility testing?
|
Increase |
Addition/Revision/Deletion |
2. For the following organisms, indicate which methods are used for: (1) Primary susceptibility testing and (2) Secondary, supplemental, or confirmatory testing (if performed).
If your laboratory does not perform susceptibility testing, indicate the methods used at the outside laboratory.
Use the testing codes listed below the table. Enterobacterales Pseudomonas aeruginosa Acinetobacter baumanni complex 1 = Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion 2.1 = Vitek 2 3.1 = BD Phoenix 4 = Sensititre 5.1 = MicroScan WalkAway 5.2 = MicroScan autoSCAN 6 = Other broth microdilution method 7 = Agar dilution method 10 = Gradient Dilution Strip (for example, Etest) 13 = Other (describe in Comments section)
|
0.5-minute increase |
Addition |
4. Has the laboratory implemented revised breakpoints recommended by CLSI for the following:
|
No change to burden. |
Addition |
5b. If Yes, which test is routinely performed to detect carbapenemase: (check all that apply) □ PCR □ MBL Screen □ Modified Hodge Test □ Carba NP □ mCIM/CIM □ Rapid CARB Blue □ E test □ Cepheid, BioFire array, Verigene, Genmark, etc. □ Other (specify): ______________
|
No change to burden. |
Addition |
6. Does your facility use commercial, or laboratory developed tests for rapid molecular detection of antimicrobial resistance markers in bacterial bloodstream infections? Examples of commercially available systems include BioFire FilmArray, Luminex Verigene, etc. 6a. If Yes, which test panel(s) does your facility use? (check all that apply)
|
1 minute increase |
Addition |
7. In a scenario where the mecA resistance marker and Staphylococcus aureus are detected by rapid molecular testing, select the procedure(s) your facility conducts. (check one) 7b. If both rapid molecular and culture based phenotypic antimicrobial susceptibility testing are performed to detect drug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus, and discordance is found between their results, how are results reported? (check one)
|
1 minute increase |
Addition |
8. In a scenario where the blaCTX-M (CTX-M) resistance marker and Escherichia coli are detected by rapid molecular testing, select the procedure(s) your facility conducts. (check one) 8a. If both rapid molecular and culture based phenotypic antimicrobial susceptibility testing are performed to detect drug resistance in Escherichia coli and discordance is found between their results, how are results reported? (check one)
|
1 minute increase |
Addition/Revision |
9. Does your facility perform extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) testing for E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca or Proteus mirabilis routinely or using a testing algorithm? □ Yes □ No
|
No change to burden. |
Deletion |
12. (number on 2022 survey since not on 2023) Are any culture-independent diagnostic tests (CIDTs) used to specifically identify Candida auris from clinical specimens?
|
0.5-minute decrease |
Revision |
12. Does the laboratory routinely use chromogenic agar for the identification or differentiation of Candida isolates?
|
No change to burden. |
Revision |
14. Does the laboratory employ any molecular tests to identify Candida from blood specimens? 14a. If yes, which molecular tests are used to identify Candida from blood specimens? (check all that apply) 14b. If yes and you get a positive result, does this lab culture the blood to obtain an isolate?
|
1 minute increase |
Deletion |
16. (Q16 on 2022 survey) If Vitek is used for AFST, which Candida species do you test with it? (check all that apply)
|
0.5-minute decrease |
Revised |
16. What method is used for antifungal susceptibility testing (AFST), excluding Amphotericin B? (check all that apply)
|
No change to burden. |
Revised |
17. What method is used for antifungal susceptibility testing (AFST) of Amphotericin B? (check all that apply)
|
No change to burden. |
Addition |
20. Is this laboratory developing antibiograms or other reports to track susceptibility trends for Candida spp. isolates tested in this laboratory?
|
1 minute increase |
Addition |
30a. If Yes, in which situations does the facility routinely perform screening testing for CRE? (check all that apply) 30b. If Yes, what method is routinely used by the lab conducting CRE testing of screening swabs from your facility? □ Culture-based methods □ PCR □ Other (specify):_____________
|
1 minute increase |
Addition |
31a. If Yes, in which situations does the facility routinely perform screening testing for Candida auris? (check all that apply)
|
No change in burden.
|
Addition |
32a. If yes, in which situations does the facility routinely perform screening testing for MRSA for non-NICU settings? (check all that apply)
|
No change in burden. |
Addition |
33a. If yes, in which situations does the facility routinely perform screening testing for MRSA for NICU settings? (check all that apply)
|
No change in burden. |
Addition |
35a. If yes, indicate which patients: (select all that apply)
|
No change in burden. |
Addition |
59. Our facility has a program or committee charged with monitoring and improving sepsis care and/or outcomes. (Check one) 59a. If yes was selected: the responsibilities of this program or committee include the following: (Check all that apply; check at least one response) 59b. If yes was selected: this program or committee includes the following healthcare personnel: (Check all that apply; check at least one response) 59c. If yes was selected: this program or committee includes representatives from the following locations or services: (Check all that apply; check at least one response)
|
1 minute increase |
Addition |
60. Our facility has one leader or two co-leaders responsible for sepsis program or committee management and outcomes. (Check one) 60a. If yes selected in 2: What is the professional background of the sepsis program or committee leader(s)? (Check all that apply; check at least one response) 60b. If yes selected in 2: Did the sepsis program leader(s) participate in responding to these questions? (Check one) 60c. If yes selected in 2a: What percentage of the APP leader’s effort is specified for sepsis activities? If there are two APP leaders, please indicate the sum of their combined effort if it were applied towards a single APP. (Check one) 60d. If nurse selected in 2a: What percentage of the nurse leader’s effort is specified for sepsis activities? If there are two nurse leaders, please indicate the sum of their combined effort if it were applied towards a single nurse. 60e. If physician selected in 2a: What percentage of the physician leader’s effort is specified for sepsis activities? If there are two physician leaders, please indicate the sum of their combined effort if it were applied towards a single physician.
|
1 minute increase |
Addition |
61. Facility leadership has demonstrated commitment to improving sepsis care by: (Check all that apply; check at least one response)
|
0.5-minute increase |
Addition |
62. Our facility uses the following approaches to assist in identification of sepsis upon presentation to the hospital: (Check all that apply; check at least one response)
|
0.5-minute increase |
Addition |
63. Our facility uses the following approaches to assist in the identification of sepsis throughout hospitalization: (Check all that apply; check at least one response)
|
0.5-minute increase |
Addition |
64. Our facility uses the following approaches to promote evidence-based management of patients with sepsis: (Check all that apply; check at least one response)
|
0.5-minute increase |
Addition |
65. Our facility uses the following approaches to promote rapid antimicrobial delivery to patients with sepsis: (Check all that apply; check at least one response)
|
0.5-minute increase |
Addition |
66. Our facility uses the following approaches to facilitate recovery after sepsis hospitalization: (Check all that apply; check at least one response)
|
0.5-minute increase |
Addition |
67. Our facility uses the following approaches to ensure that all patients hospitalized with sepsis (or their family or caregivers) are educated about sepsis. (Check all that apply; check at least one response)
|
0.5-minute increase |
Addition |
68. Our facility tracks the following hospital sepsis metrics: (Check all that apply; check at least one response)
|
0.5-minute increase |
Addition |
69. Describe your facility’s use of manual chart review for sepsis performance evaluation and improvement: (Check one)
|
0.5-minute increase |
Addition |
70. Sepsis treatment and/or outcome data are reported to unit-based or service-based leadership at following frequency. (Check one)
70a. If question 70a has answered either “continuously”, “at least monthly”, “at least quarterly”, or “at least annually”: Feedback data provided to clinician and/or unit-based leadership on sepsis treatment and outcomes includes the following elements at least annually. (Check all that apply; check at least one response)
|
0.5-minute increase |
Addition |
71. Clinicians receive feedback regarding their care of specific patients with sepsis: (Check all that apply; check at least one response)
|
0.5-minute increase |
Addition |
72. Our facility provides education on sepsis to the following groups as part of their hiring or onboarding process: (Check all that apply; check at least one response)
|
0.5-minute increase |
Addition |
73. Our facility provides sepsis education to the following groups at least annually, for example, through lectures, staff meetings, etc.: (Check all that apply; check at least one response)
|
0.5-minute increase |
Revision |
74a. If Yes, who is represented on your facility WMP team? (Check all that apply):
|
no change to burden |
Addition |
77. Does your facility regularly monitor the following parameters in the building water system(s)? (Check all that apply) Disinfectant (such as residual chlorine): If Yes, does your facility have a plan for corrective actions when disinfectant(s) are not within acceptable limits as determined by the water management program? If Yes, where and how frequently does your facility monitor disinfectant(s)? (Check all that apply) Water temperature: If Yes, does your facility have a plan for corrective actions when water temperatures are not within acceptable limits as determined by the water management program? If Yes, where and how frequently does your facility monitor water temperature? (Check all that apply) Water pH: If Yes, does your facility have a plan for corrective actions when water pH is not within acceptable limits as determined by the water management program? If Yes, where and how frequently does your facility monitor water pH? (Check all that apply) Heterotrophic plate count (HPC) testing: If Yes, does your facility have a plan for corrective actions when heterotrophic plate counts are not within acceptable limits as determined by the water management program? If Yes, where and how frequently does your facility perform HPC testing? (Check all that apply) Specific environmental Legionella testing: If Yes, does your facility have a plan for corrective actions when environmental tests for Legionella are not within acceptable limits as determined by the water management program If Yes, where and how frequently does your facility perform Legionella testing? (Check all that apply) Specific environmental Pseudomonas testing: If Yes, does your facility have a plan for corrective actions when environmental tests for Pseudomonas are not within acceptable limits as determined by the water management program? If Yes, where and how frequently does your facility perform Pseudomonas testing?
|
1 minute increase |
Addition |
78. Does your facility WMP address measures to prevent transmission of pathogens from wastewater premise plumbing to patients?
|
0.5 minutes increase |
57.120 Surgical Site Infection (SSI) |
||
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
Impact to Burden |
Revision |
Updated number of respondents, number of responses per respondent, and type of respondent. |
Decrease |
57.121 Denominator for Procedure |
||
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
Impact to Burden |
Revision |
Updated number of respondents, number of responses per respondent, and average burden per response. |
|
Revision |
Circle one: FUSN *Spinal Level (check one) □ Atlas-axis/Cervical □ Cervical □ Cervical/Dorsal/Dorsolumbar □ Dorsal/Dorsolumbar □ Lumbar/Lumbosacral
|
Decrease |
Addition |
*Approach/Technique (check one) □ Anterior □ Posterior □ Anterior and Posterior □ Lateral
Added lateral as an option. For NHSN operative procedure category, FUSN, Spinal approach ‘Lateral’ is a new option for selection based on advanced surgical technology. |
Decrease |
Revision |
Circle one: HPRO KPRO ICD-10-PCS Supplemental Procedure Code for HPRO/KPRO: *Check one: □ Total □ Hemi □ Resurfacing (HPRO only)
If Total: □ Total Primary □ Total Revision
If Hemi: □ Partial Primary □ Partial Revision
If Resurfacing (HPRO only): □ Partial Primary □ Partial Revision
*If total or partial revision, was the revision associated with prior infection at index joint? □ Yes □ No
|
Decrease |
57.123 (AUR)-Microbiology Data Electronic Upload Specification Tables |
||
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
Impact to Burden |
Increase in facilities completing the forms |
The number of facilities required to submit Antibiotic Use and Resistance data is increasing, due to the inclusion of the measure in the CMS Promoting Interoperability Program, leading to an overall increase in burden. |
Increase |
Addition |
Will capture three additional organisms for surveillance, which will allow for the capture of more complete data on Citrobacter freundii complex, specifically when laboratories cannot identify the organism to the species level. This will not increase the time needed to complete the form as this reporting is completely electronic and software vendors are responsible for ensuring the correct organisms are pulled. |
None |
Addition |
Adding the high-level tests for gentamicin and streptomycin to allow for more complete reporting of these specific tests when conducted on Enterococcus isolates. This will not increase the time needed to complete the form as this reporting is completely electronic and software vendors are responsible for ensuring the correct susceptibility tests are reported. |
None |
57.124: (AUR)-Pharmacy Data Electronic Upload Specification Tables |
||
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
Impact to Burden |
Increase in facilities completing the forms |
The number of facilities required to submit Antibiotic Use and Resistance data is increasing, due to the inclusion of the measure in the CMS Promoting Interoperability Program, leading to an overall increase in burden. |
Increase |
|
Adding one new drug that will likely be FDA approved prior to January 2024. This will not increase the time needed to complete the form as this reporting is completely electronic and software vendors are responsible for ensuring the correct drugs are reported. |
None |
Forms 57.138, 57.139, 57.141, 57.142, 57.143 |
||
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
Impact to Burden |
Burden Updates |
57.138-there is a decrease in the number of respondents, led to an overall decrease in total burden. 57.139-there is a decrease in the number of respondents, led to an overall decrease in total burden. 57.139-there is a decrease in the number of respondents, led to an overall decrease in total burden. 57.141- there is a decrease in the number of respondents and the Avg. Burden per Response, for an increase in the overall total burden. 57.142-Increase in the number of respondents, for an overall increase in total burden. 57.143- Increase in the number of respondents, for an overall increase in total burden. |
Decrease
Decrease Decrease
Increase Increase Increase |
Long Term Care Component: 57.138 Laboratory-Identified MDRO or CDI Event for LTCF 57.140 Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) for LTCF |
||
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
Impact to Burden |
Addition |
Sex at Birth and Gender Identity fields will be added as optional fields for CY 2024, with the intent to become required fields in CY 2025 to replace the current Gender field. Data collection on demographic characteristics such as gender identity is a critical component for understanding and addressing disparities and improving the health and well-being for gender diverse populations. Collecting these data will afford long-term care facilities the opportunity to include information on gender identity into their internal quality improvement and HAI prevention efforts. The current NHSN ‘Gender’ data field is available for reporting for all resident-level events and is intended to collect sex assigned at birth. However, the instructions do not specify the information being collected - sex assigned at birth vs. gender identity - and as such the data collected in the ‘Gender’ field may represent either of these concepts based on the respondent’s interpretation. This varied interpretation may lead to mismeasurement in the data among individuals for whom sex assigned at birth and gender identity differs. To improve accuracy in measurement of these data, NHSN is transitioning to a two-step approach to measuring gender by adding two new data collection fields – ‘Sex at Birth’ and ‘Gender Identity’ – that will replace the current ‘Gender’ field. The addition of these fields is intended to provide an opportunity to more clearly identify and better understand reported data that may be related to these concepts as well as more accurately address the unique needs in the LGBTQI+ population. In response to the increased and appropriate shift to focus on health equity and informed decisions for all populations, it is a Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion (DHQP) priority to improve collection of data that will move this priority forward. These data will be collected across all resident level modules of the LTCF Component as well as all age groups for all facility types that report data to the NHSN LTCF Component. |
None |
57.137 Long-Term Care Facility Component: Annual Facility Survey |
||
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
Impact to Burden |
Addition |
Question #2 added Candida Auris (C.Auris) as an option to the question as this organism is a pathogen that commonly occurs within the nursing home population. Added to include pathogen that affect every nursing home. |
No Change |
Revision |
S
|
Decrease |
Deletion |
Deleted question #7 to simplify response options. |
Decrease |
Deletion |
Deleted question #8 to simplify response options. |
Decrease |
Deletion |
Deleted question #9 to simplify response options. |
Decrease |
Addition |
Added question #7 to fully align with current CDC recommendation of enhanced barrier precautions for nursing homes. Is it a policy in your facility to use gowns/gloves for care of residents with certain characteristics that make them high-risk for transmission or acquisition of an MDRO (e.g., wounds, presence of an indwelling device) regardless of MDRO status?□Yes □ No |
Increase |
57.315 Hemovigilance Adverse Reaction - Transfusion Associated Dyspnea |
||
Burden Update |
Total burden was calculated incorrectly with last submission, total burden number updated. |
Decrease |
57.400 Outpatient Procedure Component—Annual Facility Survey 57.401 Outpatient Procedure Component - Monthly Reporting Plan 57.402 Outpatient Procedure Component Same Day Outcome Measures 57.403 Outpatient Procedure Component - Monthly Denominators for Same Day Outcome Measures |
||
Burden Update |
Decrease in the No. of Respondents, leading to an overall decrease in total burden. |
Decrease |
57.404 Outpatient Procedure Component - SSI Denominator 57.405 Outpatient Procedure Component - Surgical Site (SSI) Event |
||
Burden Update |
Decrease in the No. of Respondents, No. of Responses per Respondent for form 57.405, only, and Avg. Burden per Response, for a decrease in total burden. |
Decrease |
57.500 Outpatient Dialysis Center Practices Survey 57.501 Dialysis Monthly Reporting Plan |
||
Increase in the number of respondents |
Increase in the number of respondents, for an overall increase in burden. |
Decrease |
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
Impact to Burden |
Addition |
Sex at Birth and Gender Identity (Male, Female, Female-to-Male Transgender, Male-to-Female Transgender, identifies as non-conforming, Other, and Asked but Unknown) fields are being added. |
Increased |
Optional to required field |
Ethnicity and Race fields to become required, which will provide a more accurate capture of Identity data to further understand the true impact of each of these data elements (singly and in combination) on risk of HAIs and adverse events. Ethnicity and Race fields were optional in 2023 and will become required in 2024 on the form and in CDA. |
None |
Optional to required field |
The access used for dialysis at the time of the event question was optional in 2023 and will become required in 2024 on the form and in CDA. |
None |
Deletion |
The patient’s dialyzer is reused question will be removed as it is longer a relevant question. |
Decreased |
Burden change |
Increase in number of respondents, decrease in number of responses per respondent and decrease in Avg. Burden per Response, for an overall decrease in total burden. |
Decreased |
57.503 Denominator for Outpatient Dialysis |
||
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
Impact to Burden |
Deletion |
The question number of patients for whom dialyzers are reused is being eliminated on the denominator form. |
None |
Deletion |
The question does your center reuse dialyzers for any patients is being removed to remain in alignment with the dialysis event form and summary/denominator form. |
None |
Burden Change |
Increase in number of respondents and decrease in number of responses per respondent, for an overall decrease in total burden. |
Decreased |
57.507 Home Dialysis Center Practices Survey |
||
Burden Update |
Increase in number of respondents, and increase in the Avg. Burden per Response, for an overall increase in total burden. |
Increase |
New Form 57.130 Patient Safety Component FHIR Measure-Respiratory Pathogens Surveillance (RPS) |
||
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
Impact to Burden |
New See FHIR Measures Data Dictionary (RPS) and RPS Event Form-CSV |
In alignment with CDC’s Data Modernization Initiative, NHSN is developing a new approach to the collection of surveillance data for healthcare safety with the goal to minimize reporting burden of facilities and providers. To that end, NHSN is designing and developing new fully electronic definitions for healthcare-acquired events that adopt new healthcare data exchange standards (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources [FHIR]) that will be collected via new collection methods (NHSNLink). This new model is based on submission of FHIR bundles that contain up to 18 unique FHIR resources (such as Patient and Encounter) which contain specific FHIR data elements that can be used to calculate metrics and provide patient-level risk adjustment. For facilities that are not “FHIR ready,” data will be collected via 100% electronically automated data capture from the facility’s electronic health record (EHR) and exported to Comma Separated Values (CSV) files for submission to NHSN. CSV files will be submitted to the NHSN via NHSN DIRECT automation, or they can be manually imported into the NHSN. Manual data entry is not available for the NHSN Respiratory Pathogens Surveillance module. Because of the shift to new healthcare data exchange standards and fully electronic definitions for metrics, this new measure will require very little human time to input answers to a traditional form. The majority of the time burden estimated for this proposal is for the Information Technology/Clinical Informatics team at the facility. It will be their responsibility to read over the requirements documents and ensure that their systems meet the standardized terminology requirements, NHSN FHIR IG requirements, and that their facility’s data is mapped to the appropriate data elements. The data fields will not be filled by a person, but rather will be pulled from existing EHR data electronically. Thus, by shifting to fully electronic measures and expanding surveillance via FHIR, burden is being removed from clinicians and shifted to electronic reporting that is supported by Information Technologists. The time required per facility will vary based on their current FHIR readiness. This burden estimate is based on initial pilot studies. Once this data is collected, it can be used by NHSN to calculate patient-level risk adjusted metrics. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC’s) National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) is the most comprehensive surveillance system for healthcare-associated infections in the U.S., yet aside from device-associated ventilator-associated pneumonias (VAPs) and ventilator-associated events (VAEs), the system does not cover the more commonly occurring respiratory conditions among hospital inpatients, including non-device associated infections. Although the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network (FluSurv-NET) provides national estimates of influenza hospitalizations, the projections are based on data from 14 states, and comparable surveillance coverage is unavailable for other states. The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the public health threat of respiratory pathogens and highlighted the need for comprehensive, real-time data for prevention and response purposes. For these reasons, NHSN is expanding surveillance coverage to respiratory pathogens that are implicated in a large proportion of infections that frequently lead to hospitalizations, both seasonally and in public health emergency situations. To meet the national needs for more comprehensive and timely surveillance of hospitalizations due to respiratory pathogens, while avoiding increased reporting burden on hospitals to the fullest extent, NHSN plans to add a Respiratory Pathogens Surveillance (RPS) module to its surveillance system. |
Increase |
New Forms Patient Safety Component, Neonatal Component, and Medication Component FHIR Measures- (57.132) HOB (57.132) HT-CDI (57.133) VTE (57.600) Late Onset Sepsis Meningitis (LOSMEN) (57.700) Glycemic Control Module Hypoglycemia |
||
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
Impact to Burden |
New-See FHIR Measures Data Dictionary |
In alignment with CDC’s Data Modernization Initiative, NHSN is developing a new approach to the collection of surveillance data for healthcare safety with the goal to minimize reporting burden of facilities and providers. To that end, NHSN is designing and developing new fully electronic definitions for healthcare-acquired events that adopt new healthcare data exchange standards (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources i.e., FHIR) that will be collected via new collection methods (NHSNLink). This new model is based on submission of FHIR bundles that contain up to 18 unique FHIR resources (such as Patient and Encounter) which contain specific FHIR data elements that can be used to calculate metrics and provide patient-level risk adjustment. With this single stream of data, metrics for multiple healthcare associated events can be calculated, including but not limited to Hospital-Onset Bacteremia & Fungemia (HOB), Healthcare facility-onset, antibiotic-Treated Clostridiodes difficile Infection (HT-CDI), Venous Thromboembolism (VTE), Late Onset Sepsis Meningitis (LOSMEN), and Hypoglycemia (Hypo). Each of these new metrics are important to bring under national surveillance as the pose significant risk to patient safety. By providing standardized surveillance and national benchmarking for facilities to use for quality improvement to enhance patient safety. Because of the shift to new healthcare data exchange standards (FHIR) and fully electronic definitions for metrics, these new measures will require very little human time to input answers to a traditional form. An infection preventionist will be required to fill out the digital Measures Reporting plan once to enter the start date and year for each measure their facility wishes to participate in plus a single question about the testing type/algorithm used for CDI at their facility. If they choose, they can also enter an end month/year for each measure. The majority of the time burden estimated for this proposal is for the Information Technology/Clinical Informatics team at the facility. It will be their responsibility to read over the requirements documents and ensure that their systems meet the standardized terminology requirements, NHSN FHIR IG requirements, and that their facility’s data is mapped to the appropriate FHIR data elements. The data fields will not be filled by a person, but rather will be pulled from existing EHR data electronically. Thus by shifting to fully electronic measures and expanding surveillance via FHIR, burden is being removed from clinicians and shifted to electronic reporting that is supported by Information Technologists. The time required per facility will vary based on their current FHIR readiness. This burden estimate is based on initial pilot studies. Once this data is collected, it can be used by NHSN to calculate patient-level risk adjusted metrics. |
Increase |
New Forms Medication Safety Component, 57.600 Late Onset Sepsis Meningitis (LOSMEN) Module |
||
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
Impact to Burden |
CDA Data Collection |
For facilities that are not “FHIR ready,” data will be collected via 100% electronically automated data capture from the facility’s electronic health record (EHR) and exported to Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) files for submission to NHSN. CDA files will be submitted to the NHSN via manual CDA import and NHSN DIRECT automation. Manual data entry is not available for the NHSN Late-Onset Sepsis/Meningitis Events module. |
Increase |
New Form 57.701 Glycemic Control Module HYPO-Annual Hospital Survey |
||
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
|
New |
The Glycemic Control Module-Annual Hospital Survey is a new survey that is being implemented to support the launch of public health surveillance via a new NHSN component and module—NHSN Medication Safety Component, Glycemic Control, Hypoglycemia module. The initial launch will involve a small number of selected U.S. hospitals, with plans to expand in CY 2023 to all U.S. hospitals that are eligible report to the module. The NHSN Glycemic Control, Hypoglycemia module will use an open-source Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources® (FHIR) application (NHSNLink) and FHIR-based approach to using electronic health records (EHRs) as source systems for directly reporting EHR data via Health Level Seven® (HL7) industry-standard, vendor-neutral electronic messages. Aside from the annual and monthly forms described above, the process for reporting data is intended to be fully electronic with requirements for the information systems staff to enable authorization of the NHSN FHIR endpoint to connect to the facility’s or EHR’s endpoint. Data from the EHR are then pulled by or pushed to NHSN directly. To enable NHSNLink, each facility would be required to authenticate and configure their site to allow access to their EHR. The site would need to develop an internal process for generating a census of patient IDs to share with NHSNLink and set up the automated schedule for reporting. The initial release of NHSNLink requires manual provision of a list of patient IDs, a requirement intended to be eliminated in future releases as the process becomes fully automated. These processes represent technical communication between the facility and NHSN, but do not require the completion of any forms other than the forms represented above. The goal of the NHSN Glycemic Control, Hypoglycemia module is to enable collection of inpatient medication-related hypoglycemia metrics to improve patient safety, facilitate hospital quality improvement efforts, and inform national benchmarking. |
Increase |
New Form 57.144 Long-Term Care Facility Component: Respiratory Tract Infections (RTI) Module |
||
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
Impact to Burden |
New |
This will allow for tracking the occurrence and trends of three types of RTI events in LTCFs. |
Increase |
New |
This will allow for the evaluation of trends regarding vaccination status and positive tests. |
Increase |
New |
This will allow for the evaluation of trends regarding antiviral treatment administration and positive tests at the resident level. |
Increase
|
New |
This will capture trends in positive tests and hospitalizations- hospitalizations that have occurred within 10 days of a newly positive viral test result. |
Increase |
New |
This will capture trends in positive tests- deaths that have occurred within 30 days of a newly positive viral test result. |
Increase |
New Form 57.145 Long Term Care Facility Component Antimicrobial Use (LTC-AU) Module |
||
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
Impact to Burden |
New |
Analyze data based on demographic variables and understand trends in the LTC setting for AU. This will also allow for the vendors to submit CDA files on behalf of the facilities appropriately. |
None: upload via CDA from vendor |
New |
Allow for surveillance and analysis of event details, specifically antimicrobial use |
None: upload via CDA from vendor |
New Form Billing Code Data 837I Upload |
||
Type of Change |
Change / Justification |
Impact to Burden |
New |
In alignment with CDC’s Data Modernization Initiative, NHSN is developing a new approach to the collection of surveillance data for healthcare safety with the goal to minimize reporting burden of facilities and providers. To that end, NHSN is designing and developing new fully electronic definitions for healthcare-acquired events with patient-level risk adjustment. To obtain the most accurate data for risk adjustment, NHSN will be collecting billing code data based on the electronic 837I form which is the standard format used by institutional providers to transmit health care claims electronically. The data contained in this electronic form is equivalent to the UB-04 CMS-1450 form (OMB NO. 0938-0997). To allow for inter-facility comparison and national baseline of patient safety data, NHSN provides risk adjustment to the facility data. There has been a push in the field to improve risk adjustment and move from facility-level to patient-level risk adjustment. In order to best understand the patient mix within each facility, NHSN needs to collect the data found within the electronic 837I form which contains the condition and procedure codes associated with the admission, which can be used to identify comorbidities and other risk factors. The data contained in the 837I are produced by each facility for billing purposes and already exists within their billing system. These forms are required to be sent to CMS for reimbursement for Medicare patients, so the additional burden on facilities will be relatively low to also submit them to NHSN. The data will be sent to NHSN on a quarterly basis, so files will need to be uploaded or transmitted four times per year. |
|
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | Paula Farrell |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2024-08-04 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy
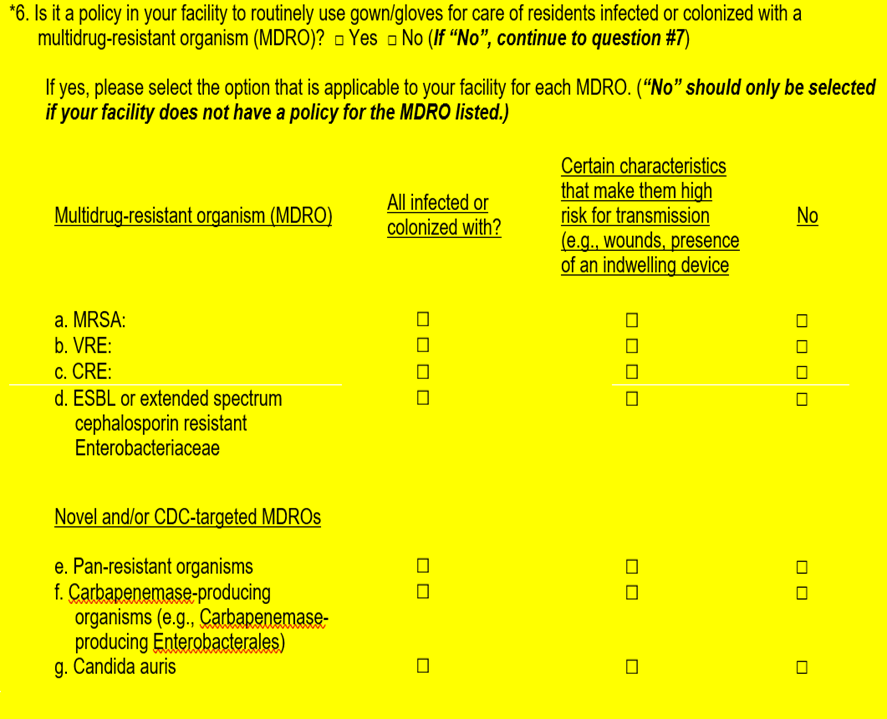 implified
question #6 options to ensure clarity for NHSN users to respond
accurately. Modified how options are displayed separating common
MDROs and novel and/or CDC targeted MDROs.
implified
question #6 options to ensure clarity for NHSN users to respond
accurately. Modified how options are displayed separating common
MDROs and novel and/or CDC targeted MDROs.