2024-QHP-EnrollSurvey-SS-B-508
2024-QHP-EnrollSurvey-SS-B-508.docx
Health Insurance Marketplace Consumer Experience Surveys: Enrollee Satisfaction Survey and Marketplace Survey Data Collection (CMS-10488)
OMB: 0938-1221
Health Insurance Exchange Consumer Experience Surveys: Qualified Health Plan Enrollee Experience Survey
Supporting
Statement—Part B
Collections of Information Employing
Statistical Methods
June 14, 2023
OMB Control Number: 0938-1221
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services
Table of Contents
1. Potential Respondent Universe and Sampling Methods 1
1.2 Sample Frame & Respondent Universe 2
2. Information Collection Procedures 3
3. Methods to Maximize Response Rates and Address Non-Response Bias 5
3.1 Maximizing Response Rates 5
3.2 Evaluating Non-Response Bias 5
4. Tests of Procedures 6
5. Statistical Consultants 6
Appendix A: Nonresponse Bias Analysis of the 2022 QHP Enrollee Survey 7
Appendix B: 2024 QHP Enrollee Survey Case-Mix Adjusters Variables 11
List of Exhibits
Exhibit B1. Data Collection Protocol for 2024 QHP Enrollee Survey 3
Exhibit B2. QHP Enrollee Survey Response Rates 5
Exhibit B3. 2022 Response Rates by Enrollee Characteristics 7
Exhibit B4. Multivariable Logistic Regression – Demographic Associations with Survey Completion 9
1. Potential Respondent Universe and Sampling Methods
This supporting statement includes information in support of the Qualified Health Plan (QHP) Enrollee Experience Survey (QHP Enrollee Survey or survey). The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) developed the QHP Enrollee Survey, which contributes a subset of survey measures to the Quality Rating System (QRS) as directed by Section 1311(c)(4) of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA). CMS designed the QRS to provide comparable and useful information to consumers about the quality of health care services and enrollee experience with QHPs offered through a Health Insurance Exchange (Exchange) (also known to consumers as to consumers as Health Insurance Marketplaces).1
1.1 Sampling Units
As outlined in 45 CFR § 156.1125(b), QHP issuers are required to conduct the QHP Enrollee Survey for each QHP with more than 500 enrollees in the previous year, and that have been offered in an Exchange for at least one year and following a survey sampling methodology provided by HHS.
In compliance with the legislation, CMS has specified several aspects of these requirements in a manner that meets the requirements while minimizing burden on the public. First, CMS established the reporting unit as the unique state-product type offered by a QHP issuer through the Exchange, including QHPs in both the Small Business Health Options Program (SHOP) and the individual market. The product type is defined as the discrete package of health insurance coverage benefits that a health plan insurance issuer offers using a particular product network type (i.e., health maintenance organization [HMO], preferred provider organization [PPO], exclusive provider organization [EPO], and point of service [POS]) within a service area. QHP issuers will create a sample frame for each reporting unit they offer through the Exchange. Child-only QHPs and standalone dental plans (SADPs) are excluded from the QHP Enrollee Survey at this time.
Second, CMS has established detailed criteria to help issuers determine which QHPs are required to collect QHP Enrollee Survey data. Eligible reporting units for the 2024 QHP Enrollee Survey are those that meet all of the following criteria:
The reporting unit was offered through an Exchange in 2023;
The reporting unit will be offered as the exact same product through an Exchange in 2024; and
The reporting unit had more than 500 enrollees on July 1, 2023 and January 1, 2024.
Issuers must collect and report survey data for all eligible reporting units to comply with the regulation. For the 2024 survey, CMS estimates that no more than 325 reporting units will be required to field the QHP Enrollee Survey. This estimate is primarily based on trends in the number of reporting units required to collect and report survey data along with review of several data sources used to update the list of eligible reporting units maintained by CMS. In 2021, 265 reporting units submitted survey data, in 2022 it was 297, and CMS anticipates that approximately 300 reporting units will participate in the 2023 survey data collection. Updates to the QHP Issuer List are based on a combination of reports provided to CMS by issuers, CMS review of enrollment data maintained by the Center for Consumer Information and Insurance Oversight (CCIIO), and other sources.
1.2 Sample Frame & Respondent Universe
QHP issuers generate the sample frame for each reporting unit, then provide the sample frames to their contracted HHS-approved survey vendor, which is responsible for drawing a simple random sample. The sample frame must include every enrollee within an eligible reporting unit who meets the following criteria:
Member is enrolled in an eligible QHP that is offered through the Exchange and provides family and/or adult medical coverage, and
Member is 18 years or older on December 31, 2023, and
Member has been enrolled in the eligible QHP from July 1, 2023 through December 31, 2023 with no more than one 45-day break in enrollment during those six months, and
Member is still enrolled in the eligible QHP on the specified anchor date, such as January 6, in January 2024.
Issuers are to exclude individuals who discontinue their coverage through the QHP for plan year 2024 and those who are deceased as of the January 2024 anchor date. Vendors must deduplicate the sample frame by the Subscriber of Family Identifier (SFID) before selecting the sample frame to ensure that only one person in each household is surveyed. The sample frame is audited by a National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA)-Licensed Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS®)2 Compliance Organization (NCQA-Certified HEDIS Compliance Auditor) to verify that the sample frame conforms to all established specifications. Survey vendors then draw a random sample from each audited eligible sample frame.
1.3 Sample Size
For the 2024 QHP Enrollee Survey, CMS continues to propose a sample size of 1,300 enrollees per reporting unit. In the 2022 administration of the QHP Enrollee Survey, reporting units that had sufficient enrollment to produce the full sample of 1,300 enrollees received an average of 154 responses.
Additionally, CMS will continue to allow QHP issuers the option to oversample in increments of 5 percent up to 30 percent (1,690 enrollees maximum) upon approval. QHP issuers may want to oversample in an effort to increase response rates, improve the likelihood that a reportable result for QRS is achieved, or increase the reliability and validity of survey results. There is precedent to allow for oversampling in the implementation of CMS Consumer Assessment of Health Providers Surveys (CAHPS®) surveys, such as Medicare Advantage and Prescription Drug Plans (MA & PDP) CAHPS, which permit oversampling at the contract level upon request to CMS. In the 2022 administration of the QHP Enrollee Survey, 121 out of the 297 eligible reporting units opted to oversample.
2. Information Collection Procedures
The QHP Enrollee Survey is conducted by HHS-approved survey vendors that meet minimum business requirements. A similar system is currently used for CMS surveys, including Medicare CAHPS, Hospital CAHPS (HCAHPS), Home Health CAHPS (HHCAHPS), the CAHPS Survey for Accountable Care Organizations, and the Health Outcomes Survey.
Under this model, all issuers that are required to conduct the QHP Enrollee Survey must contract with an HHS-approved survey vendor to collect the data and submit it to CMS on their behalf (45 CFR § 156.1125(a)). CMS is responsible for approving and training vendors, providing technical assistance to vendors, and overseeing vendors to verify that they are following the data collection protocols.
The data collection protocol for the 2024 QHP Enrollee Survey continues to utilize the same data collection protocol, using a mixed-mode methodology that combines internet, mail, and telephone surveys. All sampled enrollees receive a prenotification letter that informs them that they have been sampled for the survey and provides them with information about the survey and how the data collected will be used. The pre-notification letter also provides information on completing the survey online, including the website URL and the sample member’s login credentials, which are unique to each sample member. Vendors also have the option of using a quick-response (QR) code to link enrollees to the online survey.
On Day 7 of fielding, sampled enrollees who provided their issuer with an email address receive a notification email and survey vendors will mail the first mail survey. The mail survey does not include a link to the internet survey. The first mail survey is followed by a reminder email to nonrespondents on Day 13. This is followed by a second reminder email to nonrespondents on Day 19 and a reminder letter on Day 20.
A second mail survey are mailed to nonrespondents on Day 34. Finally, on Day 55, survey vendors will initiate telephone follow-up calls, making no more than six attempts on varying days of the week and at differing times of the day. Data collection ends on Day 73. Exhibit B1 includes the complete fielding schedule.
Exhibit B1. Data Collection Protocol for 2024 QHP Enrollee Survey
Task |
Timeframe (need to confirm days) |
Sample enrollees per sampling protocols. |
January–February 2024 |
|
Day 1 |
|
Day 7 |
|
Day 13 |
|
Day 19 |
|
Day 20 |
|
Day 34 |
|
Days 55–73 |
|
Day 73 |
a If a mailout/email day falls on a Sunday or federal holiday, mail/email on the following business day.
QHP Enrollee Survey Scoring
CMS calculates composite scores, individual item scores, reliability, and response rates for each reporting unit using the CAHPS macro program for all scoring questions.3 Survey scores are weighted to adjust for the reporting unit’s beneficiary mix and the unequal probability of being selected for the survey across reporting units. The weight variable is calculated according to the formula below to reflect the number of eligible enrollees represented by the sampled enrollee in each reporting unit:
![]()
m = Total number of records in the deduplicated file for the reporting unit
![]() =
Total number of sampled enrollees in the reporting unit
=
Total number of sampled enrollees in the reporting unit
k = Number of survey-eligible enrollees covered by the sampled enrollee’s Subscriber or Family ID (SFID) before deduplication
Additionally, CMS case-mix adjusts composite and individual question scores to control for predictable, consistent effects associated with enrollee characteristics that are not under the control of the issuer, but that may affect survey responses. Common case-mix adjusters in survey-based applications include overall health status, age, and education. These factors are necessary to account for biases due to survey respondent tendencies.
CMS will determine the case-mix adjusters annually once the prior year’s QHP Enrollee Survey data are analyzed. A list of the 2024 QHP Enrollee Survey case-mix adjusters is available in Appendix B: 2024 QHP Enrollee Survey Case-Mix Adjusters Variables.
CMS calculates the case-mix adjustment for each question or composite in the following steps:
Perform ordinary least squared regression on the entire person-level QHP data using the n case-mix adjusters as independent variables and the unadjusted score as the dependent variable. Coefficients obtained in this regression estimate the tendency of enrollees across RUs to respond more or less favorably to a given question or composite. To counter the estimated tendency, CMS multiplies the coefficients by negative one (-1) and denotes them as:
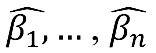
Calculate reporting unit i’s raw unadjusted score:
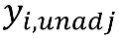
Calculate reporting unit i’s mean values for adjuster variables4:

Calculate national-level mean values for adjuster variables:
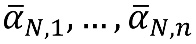
Calculate reporting unit i’s case-mix adjusted raw score,
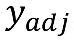 ,
using the following formula:
,
using the following formula:
![]()
3. Methods to Maximize Response Rates and Address Non-Response Bias
3.1 Maximizing Response Rates
CMS will make every effort to maximize the response rate, while retaining the voluntary nature of the survey. The mixed-mode methodology of the QHP Enrollee Survey provides sampled individuals with numerous methods for completing the survey across a 73-day time period. CMS developed this methodology using best practices within the survey research field, including the Tailored Design Method.5
CMS has also implemented an email outreach protocol, required survey vendors to optimize the internet survey for mobile devices, and added an alternative phone number field to the sample frame to maximize the survey response rate.
3.2 Evaluating Non-Response Bias
Exhibit B2 summarizes the QHP Enrollee Survey response rate since beginning nationwide fielding.
Exhibit B2. QHP Enrollee Survey Response Rates
QHP Enrollee Survey Year |
Response Rate |
2016 |
30.0% |
2017 |
26.7% |
2018 |
25.8% |
2019 |
23.2% |
2021 |
22.1% |
2022 |
18.3% |
Response rates for the QHP Enrollee Survey are calculated using the Response Rate 3 (RR3) formula established by the American Association for Public Opinion Research (AAPOR). A response is counted as a completed survey if the respondent completes 50 percent of the questions that are applicable to all respondents, excluding the questions in the “About You” section of the survey. Other CMS surveys have reported response rates between 23% and 39%6.
Given that the 2022 QHP Enrollee Survey response rate was below 80 percent, CMS conducted a non-response bias analysis to determine whether non-respondents systematically differ from respondents based on their experience with their health plan per Office of Management and Budget (OMB) guidelines. Similar to previous survey administration years, CMS found that older enrollees (those over the age of 55) continued to be more likely to respond compared to younger enrollees. CMS also found associations between enrollee characteristics like sex and written language preferences and the likelihood of completing the survey. This pattern was observed in the 2014 psychometric test, the 2015 beta test, and the 20162021 nationwide administration years. More detailed findings from the 2022 non-response bias evaluation are included in Appendix A: Nonresponse Bias Analysis of the 2022 QHP Enrollee Survey.
4. Tests of Procedures
The QHP Enrollee Survey uses core questions and supplemental items from the CAHPS Health Plan Adult Commercial 5.0, CAHPS Health Plan Adult Commercial 4.0, and CAHPS Clinician and Groups 2.0 surveys, as well as Section 4302 of the PPACA. These items have undergone extensive testing and practical use by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, OMB, NCQA, and other users since they were first developed.
In 2014, CMS conducted a psychometric test to evaluate the psychometric properties of the QHP Enrollee Survey in the Exchange population with 30 QRS reporting units (defined by state, issuer, and product type (i.e., HMO, PPO, POS, or EPO) and a Beta Test in 2015. As a result of the psychometric and beta tests, CMS identified changes in the questionnaire items, data collection procedures, and sampling specifications that obtained approval for the 2016 implementation of the survey.
For the 2017 implementation and beyond, CMS added six disability status items to address requirements of Section 4302 data collection standards of the PPACA. CMS removed several question items between 2017 and 2018 due to either low screen-in rates or question being removed from the QRS.
In consultation with the QHP Enrollee Survey Technical Expert Panel (TEP), CMS has continued to review the survey to evaluate the impact of the survey’s length and consider options to reduce the respondent burden. In 2023, CMS will conduct focus groups and cognitive testing to support identification of future refinements for the QHP Enrollee Survey. If any refinements are proposed that may impact the future administrations of the survey, CMS will submit a revision of this information.
5. Statistical Consultants
This sampling and statistical plan was prepared and reviewed by staff of CMS and American Institutes for Research (AIR). The primary statistical design was provided by Christian Evensen at [email protected], Chris Pugliese at [email protected], and Coretta Lankford at [email protected].
Appendix A: Nonresponse Bias Analysis of the 2022 QHP Enrollee Survey
Given the potential detrimental impact that nonresponse bias can have on survey estimates, OMB requires that all federal surveys that achieve a response rate below 80 percent perform a nonresponse bias analysis (Office of Management and Budget, 2006). This nonresponse bias analysis utilizes demographic information that QHP issuers included in the sample frame about all survey-eligible individuals.
First, the research team calculated the 2019 response rate by enrollees’ Census divisions, age, gender, and spoken and written language preferences and then compared these rates to the national response rate. The results of this analysis are shown in Exhibit B3.
Exhibit B3. 2022 Response Rates by Enrollee Characteristics
Enrollee characteristic |
AAPOR response rate 3 |
Number of completed surveys |
% of Total completed surveys |
% of QHP enrollee survey sample |
Census Region |
|
|
|
|
East
North Central |
21.2% |
9,045 |
17.8% |
14.3% |
East
South Central |
18.0% |
2,344 |
4.6% |
4.6% |
Mid-Atlantic |
18.5% |
6,073 |
12.0% |
11.3% |
Mountain |
19.2% |
7,171 |
14.1% |
13.8% |
New
England |
17.4% |
3,851 |
7.6% |
8.1% |
Pacific |
18.1% |
6,076 |
12.0% |
12.8% |
South
Atlantic |
15.7% |
7,174 |
14.1% |
16.9% |
West
North Central |
20.6% |
5,432 |
10.7% |
9.2% |
West
South Central |
15.4% |
3,609 |
7.1% |
8.9% |
Age |
|
|
|
|
18–24 |
9.1% |
1,013 |
2.0% |
5.8% |
25–34 |
10.7% |
4,429 |
8.7% |
20.4% |
35–44 |
12.8% |
5,273 |
10.4% |
17.8% |
45–54 |
16.5% |
8,463 |
16.7% |
19.0% |
55–64 |
26.7% |
30,110 |
59.3% |
35.2% |
65–74 |
31.2% |
1,284 |
2.5% |
1.5% |
75+ |
24.1% |
203 |
0.4% |
0.3% |
Gender |
|
|
|
|
Female |
19.9% |
31,720 |
62.5% |
54.8% |
Male |
16.3% |
19,055 |
37.5% |
45.2% |
Language Preferences |
|
|
|
|
Spoken Language |
|
|
|
|
English |
18.2% |
22,175 |
43.7% |
43.7% |
Spanish |
14.0% |
806 |
1.6% |
2.0% |
Chinese |
18.4% |
267 |
0.5% |
0.5% |
Other |
17.1% |
3,513 |
6.9% |
7.7% |
Missing |
18.7% |
24,014 |
47.3% |
45.9% |
Written Language |
|
|
|
|
English |
18.0% |
19,290 |
38.0% |
38.6% |
Spanish |
14.0% |
621 |
1.2% |
1.5% |
Chinese |
18.6% |
236 |
0.5% |
0.5% |
Other |
15.4% |
1,926 |
3.8% |
4.9% |
Missing |
18.8% |
28,702 |
56.5% |
54.5% |
Total |
18.3% |
50,775 |
100.00 |
Similar to previous survey administration years, response rates were lower among younger enrollees (ages 44 and below) and higher among older enrollees (ages 55 and more). In addition, the response rate was higher among female sampled enrollees.
The Project Team then used a unweighted multivariable logistic regression model to estimate the probability of completing a survey and assess whether the respondent characteristics reviewed examined in the previous section were significantly associated with survey response or nonresponse, controlling for the impact of other respondent characteristics.
The team did not adjust the regression with the survey weights because nonresponses were contained to only those in the sample (i.e., those who had an opportunity to respond/not respond). The logistic regression model included predictors for enrollee gender, age, written and spoken language preference, and Census division. The odds ratio and 95 percent confidence interval estimates from the logistic regression are presented in Exhibit B4.
Exhibit B4. Multivariable Logistic Regression – Demographic Associations with Survey Completion
Demographic |
N |
Odds ratio |
95% lower CI |
95% upper CI |
Gender (Ref: Male) |
|
|
|
|
Male (Reference Group) |
181,447 |
— |
— |
— |
Female |
219,607* |
1.35* |
1.32 |
1.37 |
Age (Ref: 18–24) |
|
|
|
|
18–24 (Reference Group) |
23,215 |
— |
— |
— |
25–34 |
81,666 |
1.25* |
1.16 |
1.34 |
35–44 |
71,490 |
1.74* |
1.63 |
1.87 |
45–54 |
76,313 |
2.73 |
2.56 |
2.92 |
55–64 |
141,097 |
5.76* |
5.40 |
6.15 |
65–74 |
6,145 |
5.89* |
5.39 |
6.44 |
75 or older |
1,133 |
4.93* |
4.18 |
5.82 |
Written Language Preference (Ref: English) |
|
|
|
|
English (Reference Group) |
154,861 |
— |
— |
— |
Spanish |
5,979 |
1.116 |
0.93 |
1.338 |
Chinese |
1,902 |
1.001 |
0.754 |
1.329 |
Other |
19,626 |
0.835* |
0.768 |
0.907 |
Missing |
218,691 |
1.033 |
0.99 |
1.078 |
Spoken Language Preference (Ref: English) |
|
|
|
|
English (Reference Group) |
175,445 |
— |
— |
— |
Spanish |
8,178 |
0.707* |
0.602 |
0.831 |
Chinese |
2,164 |
0.91 |
0.697 |
1.188 |
Other |
30,991 |
0.965* |
0.904 |
1.031 |
Missing |
184,281 |
0.927 |
0.889 |
0.968 |
Census Division (Ref: South Atlantic) |
|
|
|
|
South Atlantic (DE, DC, FL, GA, MD, NC, SC, VA, WV) (Reference Group) |
67,958 |
— |
— |
— |
East North Central (IL, IN, MI, OH, WI) |
57,457 |
1.38* |
1.33 |
1.43 |
East South Central (AL, KY, MS, TN) |
18,590 |
1.18 |
1.12 |
1.24 |
Mountain (AZ, CO, ID, MT, NV, NM, UT, WY) |
55,379 |
1.19* |
1.16 |
1.24 |
New England (CT, ME, MA, NH, RI, VT) |
32,288 |
1.07* |
1.02 |
1.11 |
Pacific (AK, CA, HI, OR, WA) |
51,282 |
1.07* |
1.03 |
1.1 |
Mid-Atlantic (PA, NY, NJ) |
45,351 |
1.13 |
1.08 |
1.2 |
West North Central (IA, KS, MN, MO, NE, ND, SD) |
37,043 |
1.41* |
1.35 |
1.47 |
West South Central (AR, LA, OK, TX) |
35,711 |
1.01* |
0.96 |
1.05 |
Metal Level (Ref: Bronze) |
|
|
|
|
Catastrophic |
4,173 |
1.16 |
1.035 |
1.3 |
Bronze (Reference Group) |
133,561 |
— |
— |
— |
Bronze Expanded |
4,090 |
1.013 |
0.919 |
1.116 |
Silver |
189,296 |
1.037* |
1.015 |
1.06 |
Gold |
54,939 |
1.13* |
1.096 |
1.164 |
Platinum |
8,120 |
1.141 |
1.062 |
1.227 |
Missing |
6,880 |
1.131 |
1.049 |
1.219 |
Product Type (Ref: PPO) |
|
|
|
|
PPO (Reference Group) |
63,654 |
— |
— |
— |
EPO |
109,440 |
0.908* |
0.88 |
0.937 |
HMO |
205,559 |
0.911* |
0.885 |
0.938 |
POS |
22,406 |
1.047* |
0.998 |
1.098 |
Multiple logistic regression results showed that enrollee characteristics were associated with differences in the likelihood of survey completion, controlling for the effects of other characteristics. Females were 35 percent more likely to complete the survey when compared to males. Across age categories, the estimates suggest a trend such that older plan enrollees were more likely to complete the survey when compared with younger enrollees. Compared to enrollees whose preferred written language was English, enrollees who preferred to write in a language other than Spanish or Chinese were less likely to complete the survey. There were also Census division differences in the estimated associations with survey completion across census divisions. For example, being located in the West North Central division was associated with 41 percent higher odds of completing the survey when compared with being located in the South Atlantic division.
Appendix B: 2024 QHP Enrollee Survey Case-Mix Adjusters Variables
Exhibit B5 provides a list of the 2024 QHP Enrollee Survey case-mix adjusters.
Exhibit B5. Coding of Case-mix Adjusters Variables
Case-mix Variable |
Survey Question |
Variable Coding |
Education |
What is the highest grade or level of school that you have completed? |
1) 8th grade or less 2) Some high school, but did not graduate 3) High school graduate or GED (REFERENCE) 4) Some college or 2-year degree 5) 4-year college graduate 6) More than 4-year college degree |
Overall Health Rating |
In general, how would you rate your overall health? |
1) Excellent (REFERENCE) 2) Very good 3) Good 4) Fair 5) Poor |
Mental Health Rating |
In general, how would you rate your overall mental or emotional health? |
1) Excellent (REFERENCE) 2) Very good 3) Good 4) Fair 5) Poor |
Age |
What is your age? |
1) 18 to 24 2) 25 to 34 (REFERENCE) 3) 35 to 44 4) 45 to 54 5) 55 to 64 6) 65 to 74 7) 75 or older |
Survey Language |
From data collection vendor |
English (REFERENCE) Spanish Chinese |
Survey Mode |
From data collection vendor |
Telephone (REFERENCE) Web |
Chronic Conditions and Medications |
Question 52: Did you get health care 3 or more times for the same condition or problem? Question 53: Is this a condition or problem that has lasted for at least 3 months? Question 54: Do you now need or take medicine prescribed by a doctor? Question 55: Is this medicine to treat a condition that has lasted for at least 3 months? |
1) No care and No medications; Q52 = no and Q54 = no 2) Acute care and/or Acute medications; Q52 = yes and/or Q54 = yes. 3) Chronic care or chronic medications; (Q52 = yes and Q53 = yes) OR (Q54 = yes and Q55 = yes) 4) Chronic care and chronic medications (all 4 questions = yes) |
Received Help Responding |
Did someone help you complete this survey? |
1) Yes 0) No (REFERENCE) |
1 Health Insurance ExchangeSM and ExchangeSM are service marks of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
2 Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS®) is a registered trademark of the National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA).
4 Missing values are imputed by substituting the mean adjuster value of reporting unit i.
5 Dillman, D., Smyth, J., & Christian, L. (2014). Internet, phone, mail, and mixed-mode surveys: The tailored design method (4th ed.). Wiley.
6 This is the range of each CMS surveys’ publicly-reported response rate. Different CMS surveys calculate and report their offical response rates using different AAPOR formulas based on each survey’s fielding methodology.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | Health Insurance Exchange Consumer Experience Surveys: Qualified Health Plan Enrollee Experience Survey |
| Subject | Supporting Statement—Part B: Collections of Information Employing Statistical Methods |
| Author | Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2024-08-02 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy