Survey for Staff Supporting Infants and Toddlers for the National Center for Early Childhood Development, Teaching, and Learning's (NCECDTL's) Training and Technical Assistance Offerings
Formative Data Collections for ACF Program Support
Survey-for-Staff-Supporting-Infants-and-Toddlers_Instrument_24-9-6
Survey for Staff Supporting Infants and Toddlers for the National Center for Early Childhood Development, Teaching, and Learning's (NCECDTL's) Training and Technical Assistance Offerings
OMB: 0970-0531
Notes on this instrument: Text in green is not displayed to respondents and indicates annotations for the reviewers. Branching/survey flow overview is provided in a visual at the end of this document and is also annotated where appropriate throughout the document.
Survey for Staff Supporting Infants and Toddlers
1 - Welcome Page
[Welcome
Page Introduction] Thank
you for your willingness to participate in this survey education
staff and managers! This data is being collected to inform future
work and support that will be offered by the National Center on Early
Childhood Development, Teaching, and Learning. Your honest feedback
is extremely important to us.
We expect this survey will
take about 20 minutes to complete. Your responses will be
kept anonymous. If you wish to participate, please click the "Next"
button or ">>" icon below to continue.
PAPERWORK REDUCTION ACT OF 1995 (Pub. L. 104-13) STATEMENT OF PUBLIC BURDEN: The purpose of this information collection is to populate a National Head Start Alumni Roadmap that will hold information about fellowship alumni and reflect their transformational experiences. Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 20 minutes per respondent, including the time for reviewing instructions, gathering and maintaining the data needed, and reviewing the collection of information. This is a voluntary collection of information. agency may not conduct or sponsor, and a person is not required to respond to, a collection of information subject to the requirements of the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995, unless it displays a currently valid OMB control number. The OMB # is 0970-0531 and the expiration date is 09/30/2025. If you have any comments on this collection of information, please contact [contact info to be added].
2 – Role/Environment Page
What is your current, primary role?
( ) I am a lead teacher or co-teacher for infants and toddlers.
( ) I am a home visitor for infants and toddlers.
( ) I am a family child care provider.
( ) I am a child development specialist for infants and toddlers served in family child care settings.
( ) I am an education manager/coordinator.
( ) I am a home-based manager.
( ) I am a service area manager (disability services coordinator, health manager, mental health manager, etc.).
( ) I am a program/site/center director or assistant director.
( ) I have another role not listed here.
Page exit logic: For the purpose of this survey, we are only interested in responses from (1) educators in infant/toddler spaces and (2) staff who support educators in infant/toddler spaces. If the answer above is “I have a role not listed here,” the respondent falls outside the target audience and will be disqualified.
Disqualification display message: "Thank you for your interest in completing this survey. We are engaging only professionals with particular roles for this survey. We hope to engage your opinion in future surveys and we thank you for your time!"
In which Head Start setting do you currently support infants and toddlers?
[ ] Center-Based
[ ] Home-Based (Home Visiting)
[ ] Family Child Care
[ ] Early Head Start - Child Care Partnerships
[ ] I do not work in a Head Start/Early Head Start environment.
Page exit logic: For the purpose of this survey, we are only interested in responses from educators and staff working in Head Start or Early Head Start. If the answer above is “I do not work in a Head Start/Early Head Start Environment,” the respondent falls outside the target audience and will be disqualified.
Disqualification display message: “Thank you for your interest in completing this survey. We are currently looking for feedback from Head Start/Early Head Start professionals only. We hope to engage your opinion in future surveys and we thank you for your time!"
3 – Educator Page – Respondent Information
Page entry logic: These questions are only applicable to educators. This page is only shown to respondents who identify themselves as one of the following roles on Page 2: Lead Teacher/Co-Teacher, Home Visitor, or Family Child Care Provider.
This is the second page of the survey seen by educators. Role groups not listed in the above list do not see this page.
How long have you worked with infants and toddlers?
( ) Less Than 1 Year
( ) 1 - 3 Years
( ) 4 - 6 Years
( ) 7 - 10 Years
( ) 11 - 15 Years
( ) 16 - 20 Years
( ) 21 Years or More
Do you teach/work only in infant/toddler spaces?
( ) Yes, my only teaching/work responsibilities are with infants and toddlers.
( ) No, I work in settings with other ages (i.e., preschool, birth to five).
For your most
recent professional development year,
roughly how many of your 15 clock hours were focused specifically on
infants and toddlers?
If
you don't know the exact number, please provide your best guess. It's
okay if this number is zero.
_________________________________________________
Do you serve in any other roles in addition to being an educator?
( ) No
( ) Yes (please specify):: _________________________________________________*
What language do you primarily speak in your work?
( ) English
( ) Spanish
( ) Another Language (please specify):: _________________________________________________*
( ) Two or More Languages Equally (please specify):: _________________________________________________*
Do you work in Region XI or Region XII?
( ) Region XI (American Indian & Alaska Native)
( ) Region XII (Migrant Seasonal Head Start)
( ) Neither of these
( ) I'm not sure
What professional development experience(s) have been most valuable to you as an infant/toddler educator?
____________________________________________
____________________________________________
____________________________________________
____________________________________________
Are you familiar with ZERO TO THREE's Critical Competencies for Infants and Toddlers?
( ) Yes
( ) No
( ) Not Sure
4 – Educator Page – Respondent Knowledge Appraisal
Page entry logic: These questions are only applicable to center-based or FCC educators. This page is only shown to respondents who identify themselves as one of the following roles on Page 2: Lead Teacher/Co-Teacher or Family Child Care Provider.
This is the third page of the survey seen by Teachers/Co-Teachers and Family Child Care Providers. Role groups not listed in the above list do not see this page.
[Introductory Text]: Below are some key knowledge, skills, and practices for educators who work with infants and toddlers. For each area, please use the dropdown menus to tell us about
(1) your confidence in your own skills in this area, and
(2) how much interest you would have in additional professional development support in this area.
Please select from the dropdowns below: [Dropdown options are listed vertically in table cells]
Key Area |
Confidence Level in My Skillset |
Interest in Additional Professional Development/Support |
Building
Warm, Positive, and Nurturing Relationships
|
|
|
Providing Consistent and
Responsive Caregiving
|
|
|
Promoting
Socialization
|
|
|
Guiding Behavior
|
|
|
Promoting Children’s
Sense of Identity and Belonging
|
|
|
5 – Educator Page – Respondent Knowledge Appraisal
Page entry logic: These questions are only applicable to center-based or FCC educators. This page is only shown to respondents who identify themselves as one of the following roles on Page 2: Lead Teacher/Co-Teacher or Family Child Care Provider.
This is the fourth page of the survey seen by Teachers/Co-Teachers and Family Child Care Providers. Role groups not listed in the above list do not see this page.
[Introductory Text]: Below are some key knowledge, skills, and practices for educators who work with infants and toddlers. For each area, please use the dropdown menus to tell us about
(1) your confidence in your own skills in this area, and
(2) how much interest you would have in additional professional development support in this area.
Please select from the dropdowns below: [Dropdown options are listed vertically in table cells]
Key Area |
Confidence Level in My Skillset |
Interest in Additional Professional Development/Support |
Facilitating
Exploration and Concept Development
|
|
|
Building Meaningful
Curriculum
|
|
|
Promoting Imitation,
Symbolic Representation, and Play
|
|
|
Supporting Reasoning and
Problem Solving
|
|
|
6 – Educator Page – Respondent Knowledge Appraisal
Page entry logic: These questions are only applicable to center-based or FCC educators. This page is only shown to respondents who identify themselves as one of the following roles on Page 2: Lead Teacher/Co-Teacher or Family Child Care Provider.
This is the fifth question page of the survey seen by Teachers/Co-Teachers and Family Child Care Providers. Role groups not listed in the above list do not see this page.
[Introductory Text]: Below are some key knowledge, skills, and practices for educators who work with infants and toddlers. For each area, please use the dropdown menus to tell us about
(1) your confidence in your own skills in this area, and
(2) how much interest you would have in additional professional development support in this area.
Please select from the dropdowns below: [Dropdown options are listed vertically in table cells]
Key Area |
Confidence Level in My Skillset |
Interest in Additional Professional Development/Support |
Promoting
Communication Exchange
|
|
|
Expanding Expressive and
Receptive Language and Vocabulary
|
|
|
Promoting Early
Literacy
|
|
|
7 – Home-Based Educator Page – Respondent Knowledge Appraisal
Page entry logic: These questions are only applicable to home-based educators. This page is only shown to respondents who identify themselves as Home Visitors on Page 2.
This is the third page of the survey seen by Home Visitors. Respondents who are NOT Home Visitors do not see this page.
[Introductory Text]: Below are some key knowledge, skills, and practices for home-based educators who work with infants and toddlers. For each area, please use the dropdown menus to tell us about
(1) your confidence in your own skills in this area, and
(2) how much interest you would have in additional professional development support in this area.
Please select from the dropdowns below: [Dropdown options are listed vertically in table cells]
Key Area |
Confidence Level in My Skillset |
Interest in Additional Professional Development/Support |
Home Visitor Responsiveness
to Family
|
|
|
Home Visitor-Family
Relationship
|
|
|
Home Visitor Facilitation of
Parent-Child Interaction
|
|
|
Parent-Child Interaction
during the Home Visit
|
|
|
Parent Engagement with the
Home Visitor
|
|
|
Child Engagement with the
Home Visitor
|
|
|
8 –Educator Page – Open-Ended Items
Page entry logic: These questions are only applicable to educators. This page is only shown to respondents who identify themselves as Teachers/Co-Teachers, Family Child Care Providers, or Home Visitors on Page 2.
This is the fourth and last page of the survey seen by Home Visitors.
This is the sixth and last page of the survey seen by Family Child Care Providers and Teachers/Co-Teachers. Respondents who are NOT in these groups do not see this page.
What other supports are important for you as an infant/toddler educator?
____________________________________________
____________________________________________
Question logic: The question below is only asked if the respondent answered on page 2 that they were a Home Visitor. This question is hidden for other role groups.
What unique challenges do you face as a home-based infant/toddler educator?
____________________________________________
____________________________________________
Question logic: The question below is only asked if the respondent answered on page 2 that they were a Family Child Care Provider. This question is hidden for other role groups.
What unique challenges do you face in the family child care setting?
____________________________________________
____________________________________________
Page EXIT logic: At the end of this page, Teachers/Co-Teachers, Family Child Care Providers, and Home Visitors are routed to the “Thank You” page; their survey is marked complete.
9 – Manager Page – Respondent Information
Page entry logic: These questions are only applicable to managers. This page is only shown to respondents who identify themselves as one of the following roles on Page 2: Child Development Specialists, Education Managers, Home-Based Managers, Service Area Managers, or Center Directors/Assistant Directors.
This is the second page of the survey seen by managers. Role groups not listed in the above list do not see this page.
How long have you worked in your current role?
( ) Less Than 1 Year
( ) 1 - 3 Years
( ) 4 - 6 Years
( ) 7 - 10 Years
( ) 11 - 15 Years
( ) 16 - 20 Years
( ) 21 Years or More
Do you support staff only in infant/toddler spaces?
( ) Yes, my only support responsibilities are with educators of infants and toddlers.
( ) No, I support staff in settings with other ages (i.e., preschool, birth to five).
Was your training as a manager/director specific to infant/toddler education?
( ) I received training specifically to support infants and toddlers.
( ) I received training focused on all children birth to five.
( ) I did not receive any formal training specifically on infant/toddler education
Do you serve in any other roles in addition to being a manager/director?
( ) No
( ) Yes (please specify):: _________________________________________________*
What language do you primarily speak in your work?
( ) English
( ) Spanish
( ) Another Language (please specify):: _________________________________________________*
( ) Two or More Languages Equally (please specify):: _________________________________________________*
Do you work in Region XI or Region XII?
( ) Region XI (American Indian & Alaska Native)
( ) Region XII (Migrant Seasonal Head Start)
( ) Neither of these
( ) I'm not sure
What professional development supports do you offer that are specific to infant/toddler education?
____________________________________________
____________________________________________
____________________________________________
____________________________________________
Are you familiar with ZERO TO THREE's Critical Competencies for Infants and Toddlers?
( ) Yes
( ) No
( ) Not Sure
10 – Manager Page – Respondent Support Appraisal
Page entry logic: These questions are only applicable to managers working outside the home setting (center or FCC). This page is only shown to respondents who identify themselves as one of the following roles on Page 2: Child Development Specialists, Education Managers, Service Area Managers, or Center Directors/Assistant Directors.
This is the third page of the survey seen by center/FCC managers. Role groups not listed in the above list do not see this page.
[Introductory Text]: Below are some key knowledge, skills, and practices for educators who work with infants and toddlers. For each area, please use the dropdown menu to tell us your comfort level in supporting your staff in each of the competencies below.
Please select from the dropdowns below: [Dropdown options are listed vertically in table cells]
Key Area |
Comfort Level in Supporting My Staff in this Area |
Building
Warm, Positive, and Nurturing Relationships
|
|
Providing Consistent and
Responsive Caregiving
|
|
Promoting
Socialization
|
|
Guiding Behavior
|
|
Promoting Children’s
Sense of Identity and Belonging
|
|
11 – Manager Page – Respondent Support Appraisal
Page entry logic: These questions are only applicable to managers working outside the home setting (center or FCC). This page is only shown to respondents who identify themselves as one of the following roles on Page 2: Child Development Specialists, Education Managers, Service Area Managers, or Center Directors/Assistant Directors.
This is the fourth page of the survey seen by center/FCC managers. Role groups not listed in the above list do not see this page.
[Introductory Text]: Below are some key knowledge, skills, and practices for educators who work with infants and toddlers. For each area, please use the dropdown menu to tell us your comfort level in supporting your staff in each of the competencies below.
Please select from the dropdowns below: [Dropdown options are listed vertically in table cells]
Key Area |
Comfort Level in Supporting My Staff in this Area |
Facilitating
Exploration and Concept Development
|
|
Building Meaningful
Curriculum
|
|
Promoting Imitation,
Symbolic Representation, and Play
|
|
Supporting Reasoning and
Problem Solving
|
|
12 – Manager Page – Respondent Support Appraisal
Page entry logic: These questions are only applicable to managers working outside the home setting (center or FCC). This page is only shown to respondents who identify themselves as one of the following roles on Page 2: Child Development Specialists, Education Managers, Service Area Managers, or Center Directors/Assistant Directors.
This is the fifth page of the survey seen by center/FCC managers. Role groups not listed in the above list do not see this page.
[Introductory Text]: Below are some key knowledge, skills, and practices for educators who work with infants and toddlers. For each area, please use the dropdown menu to tell us your comfort level in supporting your staff in each of the competencies below.
Please select from the dropdowns below: [Dropdown options are listed vertically in table cells]
Key Area |
Comfort Level in Supporting My Staff in this Area |
Promoting
Communication Exchange
|
|
Expanding Expressive and
Receptive Language and Vocabulary
|
|
Promoting Early
Literacy
|
|
13 – Home-Based Manager Page – Respondent Support Appraisal
Page entry logic: These questions are only applicable to home-based managers. This page is only shown to respondents who identify themselves as Home-Based Managers on Page 2.
This is the third page of the survey seen by Home-Based Managers. Respondents who are NOT Home-Based Managers do not see this page.
[Introductory Text]: Below are some key knowledge, skills, and practices for home-based educators who work with infants and toddlers. For each area, please use the dropdown menu to tell us your comfort level in supporting your staff in each of the competencies below.
Please select from the dropdowns below: [Dropdown options are listed vertically in table cells]
Key Area |
Comfort Level in Supporting My Staff in this Area |
Home Visitor Responsiveness
to Family
|
|
Home Visitor-Family
Relationship
|
|
Home Visitor Facilitation of
Parent-Child Interaction
|
|
Parent-Child Interaction
during the Home Visit
|
|
Parent Engagement with the
Home Visitor
|
|
Child Engagement with the
Home Visitor
|
|
14 – Manager Page – Content Interest Appraisal
Page entry logic: These questions are only applicable to managers. This page is only shown to respondents who identify themselves as Child Development Specialists, Education Managers, Home-Based Managers, Service Area Managers, or Center Directors/Assistant Directors.
This is the fourth and last page of the survey seen by Home-Based Managers.
This is the sixth and last page of the survey seen by Child Development Specialists, Education Managers, Service Area Managers, and Center Directors/Assistant Directors. Respondents who are NOT in these groups do not see this page.
We
plan to offer a professional development event focused on infants and
toddlers in 2025. Please indicate your interest
level on a scale of
1 (not at all interested)
to 10 (extremely interested) in
attending sessions related to each of the following topics.
|
Not
at all |
2 |
3 |
4 |
Somewhat |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
Extremely |
Responsive Caregiving |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
Child Development Basics |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
Curriculum (Scope & Sequence) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
Brain Development |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
Milestones Informing Practice |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
Continuity of Care |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
Creating Safe and Nurturing Environments |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
Family Partnership (Engagement, Well-being, etc.) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
Equity with Infants/Toddlers |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
Challenging Behaviors |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
Infants/Toddlers with Disabilities/Suspected Delays |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
Social-Emotional Supports for Infants/Toddlers |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
Change in Scope / Slot Conversion |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
Quality of Care for Infants and Toddlers Instrument (QCIT) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |
( ) |

15 – Thank You Page
Thank
you for completing this survey. Your response is very important
to us, and we look forward to creating content that will support you
in your work based on the responses you provided.
Questions?
Contact the NCECDTL Data Team at [email protected].

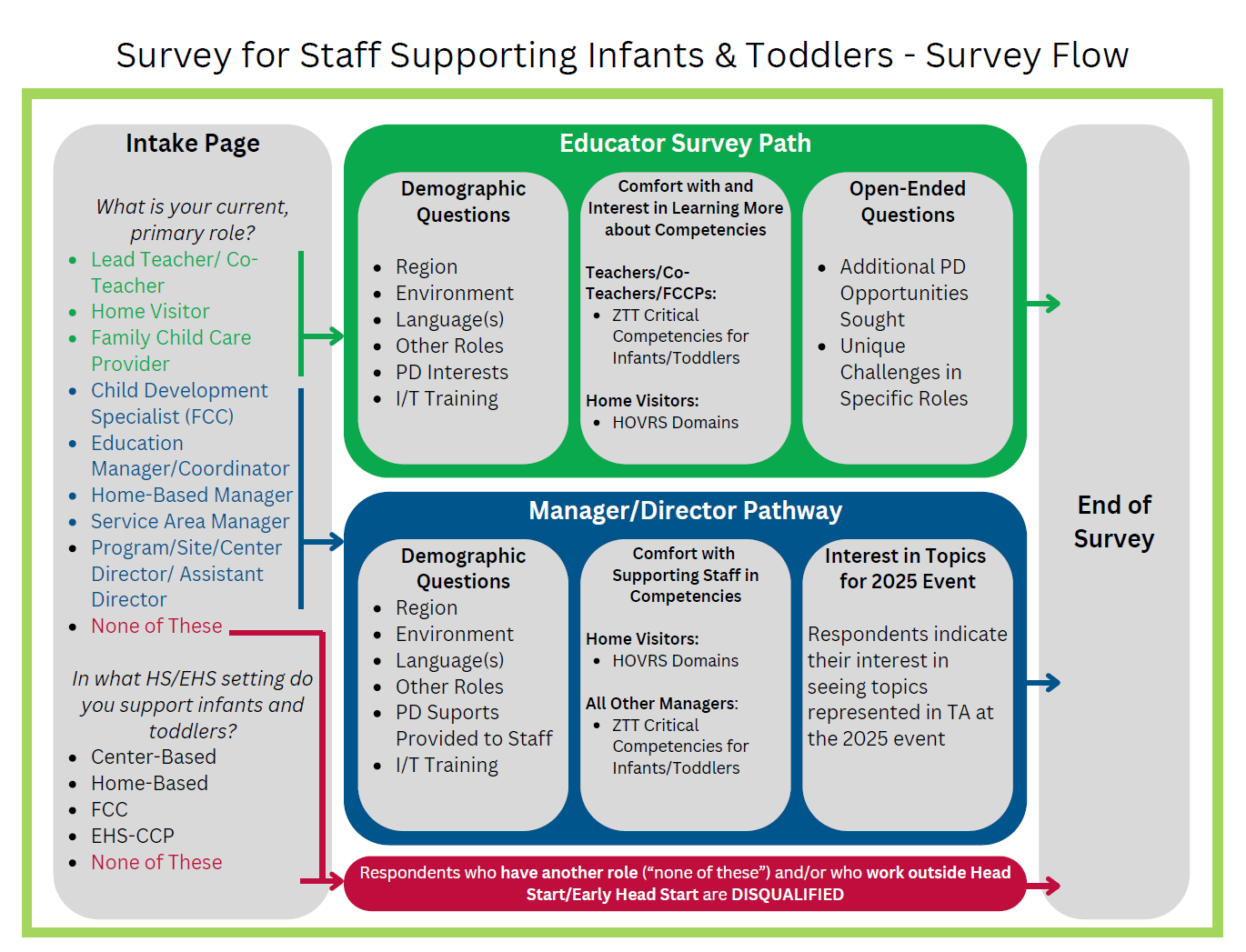
Addendum: Survey Flow Diagram – For Reviewer Purposes Only
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | Kaitlin Brunick |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2024-12-24 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy