SUPP STATE POS ICR (Final)_ 8-14-08
SUPP STATE POS ICR (Final)_ 8-14-08.doc
Jobs for Veterans Act Priority of Service Provisions
OMB: 1205-0468
SUPPORTING STATEMENT FOR REQUEST FOR OMB APPROVAL
UNDER THE PAPERWORK REDUCTION ACT OF 1995
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION |
PAGE |
A. JUSTIFICATION 2
A.1 Circumstances Necessitating Data Collection 2
A.2 How, by Whom, and For What Purpose the Information is to be Used 7
A.3 Use of Technology to Reduce Burden 8
A.4 Efforts to Identify Duplication 8
A.5 Methods to Minimize Burden on Small Businesses 8
A.6 Consequences of Less Frequent Data Collection 9
A.7 Special Circumstances for Data Collection 9
A.8 Summary of Public Comments 9
A.9 Payment of Gifts to Respondents 9
A.10 Confidentiality Assurances 9
A.11 Additional Justification for Sensitive Questions 10
A.12 Estimates of the Burden of Data Collection 10
A.13 Estimated Cost to Respondents 13
A.14 Estimates of Annualized Costs to Federal Government 13
A.15 Changes in Burden 14
A.16 Publication of Results 14
A.17 Approval Not to Display OMB Expiration Date 15
A.18 Exceptions to OMB Form 83-I 16
B. Collection of Information Employing Statistical Methods 16
SUPPORTING STATEMENT
APPLICATION FOR PRIORITY OF SERVICE DATA COLLECTION
A. Justification
A.1. Circumstances that make the collection of information necessary.
The information collection is requested to support the implementation of the priority of service provisions contained in the Jobs for Veterans Act (JVA). These provisions provide that veterans and certain spouses of veterans (together comprising the category of covered persons) are entitled to priority over non-covered persons for the receipt of employment, training, and placement services provided under new or existing qualified job training programs.
The Department of Labor’s (DOL) Veterans’ Employment and Training Service (VETS) is in the process of proposing a rule - 20 CFR Part 1010 - to implement priority of service requirements for qualified job training programs as prescribed in section 2(a)(1) of the JVA, Public Law (Pub. L.) No. 107-288 (Nov. 7, 2002). In conjunction with this effort, DOL is publishing a 60-day Federal Register Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) that contains proposed reporting requirements, which will assist DOL in assessing the extent to which employment and training programs are implementing priority of service.
Qualified job training programs are defined at 38 U.S.C. § 4215(a)(2) as any workforce preparation, development or delivery program or service that is directly funded, in whole or in part, by the Department of Labor. This Information Collection Request (ICR) specifically impacts the programs administered by DOL’s Employment and Training Administration (ETA). For purposes of this ICR, there are six affected programs that have served an average of 1,000 or more covered persons per year during their three most recent years of operation. These programs are: Workforce Investment Act (WIA) Adult, WIA Dislocated Worker, National Emergency Grants (NEGs), Wagner-Peyser (W-P) State Grants, Trade Adjustment Assistance (TAA), and the Senior Community Service Employment Program (SCSEP).
Under existing reporting requirements, the six affected ETA programs collect, for covered participants, data on demographic characteristics, services received and outcomes experienced. In conjunction with these reporting requirements, for all the programs except the Wagner-Peyser State Grants, data records are submitted annually for participants who “exit” from participation. With the proposed rule to implement priority of service in employment and training programs, additional data are needed to make a full account to Congress on the services delivered to covered persons. Therefore, the new reporting requirements proposed for these programs primarily involve: 1) identifying covered persons at the initial point of entry; and, 2) expanding the collection of participant data records to include those covered persons served by Wagner-Peyser State Grants.
Under the proposed information collection, a new customer classification would be created called covered entrants - a precursor to the participant customer classification, which already exists in ETA reporting. The new classification seeks to identify and capture data on covered persons at the initial point of entry, the earliest point that a covered person contacts the system in either a physical location (e.g., One-Stop Career Center or affiliate site) or remotely through electronic technologies. In this way, the proposed information collection offers a new dimension to DOL’s reporting procedures by making a distinction between covered entrants (those not yet receiving services) and covered participants (those receiving services). Under the provisions of the NPRM, the six programs affected by this ICR are required to collect and report data on covered entrants.
Those ETA programs serving less than 1,000 covered persons per year will not implement data collection and reporting on covered entrants. However, those programs must adopt the covered, non-covered, veteran and eligible spouse definitions as outlined in the JVA. Those programs will adopt these definitions in conjunction with the first approved ICR whose effective date falls on or after the effective date of this ICR, whether that ICR is for a renewal of an existing approved information collection or for approval of a new information collection.
The table below identifies: 1) the approved information collections impacted by this ICR; and, 2) the relationship between the impacted information collections and the six programs required to collect and report data on covered entrants.
Approved Information Collections Impacted by this ICR |
||
OMB Number |
Title of Information Collection |
Submission of Exiter Records |
1205-0420 |
WIA Management Information and Reporting System
|
Yes |
1205-0240 |
Labor Exchange Reporting System
|
No |
1205-0392 |
Trade Act Participant Report
|
Yes |
1205-0040 |
SCSEP Performance Measurement System
|
Yes |
This ICR proposes that the six affected programs will submit aggregate quarterly reports on: 1) the number of covered entrants; and, 2) the number of covered entrants who become participants. In addition, this ICR also proposes that data records will be submitted for all covered entrants. For all of the affected programs except the Wagner-Peyser State Grants, the submission of data records for covered entrants will be an adjunct of those programs’ current procedures for compiling and submitting participant data records. For those covered entrants who make their initial contact with the Wagner-Peyser State Grants, this ICR proposes that the data records will be compiled and submitted according to the procedures currently in effect under the WIA Management Information and Reporting System. This would serve two purposes: 1) assist DOL in receiving data records on all covered entrants who access workforce investment services; and, 2) support integration between WIA and the Wagner-Peyser State Grants.
The preceding paragraphs are based on the assumption that the reporting requirements proposed in this ICR will take effect prior to the effective date of the reporting procedures included in the Workforce Investment Streamlined Performance Reporting (WISPR) system, a new information collection proposed by ETA but not yet approved by OMB. Once approved by OMB, WISPR will replace three of the approved information collections impacted by this ICR:
The WIA Management Information and Reporting System (OMB No. 1205-0420);
The Labor Exchange Reporting System (OMB No. 1205-0240); and
The Trade Act Participant Report (OMB No. 1205-0392).
Therefore, if WISPR is approved to take effect on or before the effective date of this ICR, the reporting requirements proposed here will impact two information collections (WISPR and the SCSEP Performance Measurement System) rather than the four information collections currently anticipated to be impacted.
As indicated above, the relationship between the effective date of the reporting requirements proposed in this ICR and the effective date of the reporting requirements proposed under WISPR is significant. In addition to reducing the number of impacted information collections from four to two, there are two other advantages to implementing the reporting requirements proposed in this ICR on or after the effective date of WISPR. The first advantage relates to the twin facts that the Labor Exchange Reporting System is: 1) the only one of the four impacted information collections that does not compile and submit data records; and, 2) the system responsible for reporting on approximately 96% of the veterans served by the six affected programs. Since WISPR will include compilation and submission of data records for all participants in the Wagner-Peyser State Grants, compilation and submission of data records for the anticipated large number of covered entrants who first contact this program will be consistent with the procedures already in place under WISPR.
The second advantage of having the reporting requirements proposed in this ICR take effect on or after the effective date of WISPR is that a duplicate burden of effort would be avoided. Specifically, if: 1) the reporting requirements proposed in this ICR were to take effect prior to the effective date of WISPR, thus impacting the four currently approved information collections; and, 2) WISPR were to take effect subsequently; the effort required to revise the reporting requirements of both the currently approved information collections and of WISPR would represent a duplicate burden of effort.
Within the context of implementing the reporting requirements proposed in this ICR on or after the effective date of WISPR, it would be most advantageous if WISPR and the reporting requirements proposed here were to take effect on the same date. That is because simultaneous implementation of these two related reporting requirements would avoid a scenario under which WISPR would be implemented without including the reporting requirements proposed here and then would be revised subsequently to include these reporting requirements. This second type of potential duplication of effort would be avoided if both sets of requirements were approved to take effect on the same date.
ETA proposes that WISPR will take effect on July 1, 2009. In conjunction with that target date, ETA also assumes that the state agencies responsible for implementing WISPR will require a preparation period of approximately six months between the approval of WISPR and its effective date in order to make the preparations necessary to implement this new system. Therefore, if: 1) WISPR is approved for implementation on July 1, 2009; 2) the reporting requirements proposed in this ICR are approved to take effect on that same date; and, 3) the approval of the reporting requirements proposed in this ICR is received by December 21, 2008, the advantage of simultaneously implementing WISPR and the reporting requirements proposed here would be realized.
The new data elements associated with covered entrants and the expanded participant level data will enable DOL to more adequately assess the number of covered persons who entered the workforce investment system, how many received services, and how many did not (See: Individual Record Data Elements; and Proposed Reporting Format for Priority of Service Quarterly Aggregate Report). If priority of service is taking place, the number of covered entrants to the workforce investment system should be comparable to the number of served covered persons or participants (e.g., those who ultimately receive a service).
Once the priority of service rule is implemented, DOL anticipates that the six affected ETA programs will report on covered entrants as well as apply the new priority of service data elements for covered participants. Therefore, this supporting statement includes an estimate of the hourly burdens and costs for implementing these requirements across the six affected ETA programs.
PRIORITY OF SERVICE REPORTING FRAMEWORK
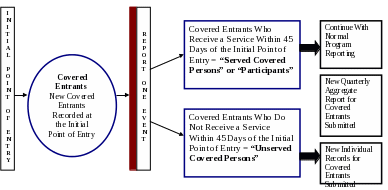
Glossary of Key Terms
Covered Entrant – A covered person at the initial point of entry. This classification occurs at the earliest point that a covered person contacts the system in either a physical location (e.g., One-Stop Career Center or affiliate site) or remotely through electronic technologies. Designation as a covered entrant occurs prior to receipt of a service, but receipt of a service will likely occur almost simultaneously for many covered entrants, at which point the covered person also would be counted as a participant.
Covered Person – A person entitled to priority of service under section 2(a) of the Jobs for Veterans Act, codified at 38 U.S.C. § 4215(a). Priority is extended to:
A veteran;
The spouse of any of the following individuals:
(1) Any veteran who died of a service-connected disability;
(2) Any member of the Armed Forces serving on active duty who, at the time of application for the priority, is listed in one or more of the following categories and has been so listed for a total of more than 90 days:
(i) Missing in action;
(ii) Captured in line of duty by a hostile force; or
(iii) Forcibly detained or interned in line of duty by a foreign government or power;
(3) Any veteran who has a total disability resulting from a service-connected disability;
(4) Any veteran who died while a disability so evaluated was in existence.
Covered Person Entry Date – The date that the covered person first made contact with the workforce investment system, as defined in initial point of entry, making them a covered entrant.
Initial Point of Entry – The earliest point that a covered person contacts the workforce investment system, either in-person (at a physical location - One-Stop Career Center or affiliate site) or remotely through electronic technologies. Data on covered entrants is captured at the initial point of entry.
Participant – A participant is an individual who is determined eligible to participate in the program (to the extent a program has eligibility requirements) and receives a service funded by the program in either a physical location (One-Stop Career Center or affiliate site) or remotely through electronic technologies.
Served Covered Person – A covered person who received a program service within 45 days of their covered person entry date (a served covered person is also a participant).
Unserved Covered Person – A covered person on who covered entrant data was collected, but who did not receive a service within 45 days of their covered person entry date.
Veteran - A person who served in the active military, naval, or air service, and who was discharged or released under conditions other than dishonorable. See 38 U.S.C. § 101(2).
A.2. How, by whom, and for what purpose the information is to be used.
In order to meet its statutory responsibilities under the JVA, the Department is requesting a new collection of information pertaining to covered entrants to the workforce investment system. The Department will use the information collected to begin to assess the extent to which priority of service is being implemented in the following programs: Workforce Investment Act (WIA) Adult, WIA Dislocated Worker, Wagner-Peyser (W-P) State Grants, National Emergency Grants (NEGs), Trade Adjustment Assistance (TAA), and the Senior Community Service Employment Program (SCSEP).
A.3. Extent to which collection is automated, reasons for automation, and considerations for reducing impact on burden.
It is anticipated that the collection of this information will be incorporated into web sites that provide workforce services, so the process will be automated for the electronic initial point of entry. However, when it comes to provision of services in a physical location, such as One-Stop Career Centers, affiliated One-Stop partner sites, or other specialized centers and sites designed to address special customer needs (such as company work sites for dislocated workers), intake forms and reporting processes that are not automated may be used, as DOL does not specify how data is collected. To assist grantees, DOL will provide grantees the approved data elements and accompanying forms for covered entrants. DOL also plans on providing technical assistance to grantees. For instance, DOL plans to provide program-specific information identifying available options for capturing data associated with this new customer classification.
In compliance with the Government Paperwork Elimination Act, the Department anticipates approval by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) for specified data elements that will amend existing electronic reporting systems (see the table above for impacted systems/records). All data reported back to DOL will be submitted electronically.
A.4. Efforts to identify duplication – why similar information already available cannot be used for purpose described in A.2.
The type of data being sought by this data collection (information on when covered persons first come into contact with the workforce investment system) is not currently available. The only data that currently exists on veterans is data collected on them after they have begun participation in a program(s). The newly proposed data elements are inclusive of all of the data needed for both these instances (i.e., covered participants and covered entrants) to assess priority of service, so many of the request elements are already captured in existing reporting systems. Reporting systems will only need to be amended for those data elements that are not currently captured (e.g., Covered Entrant Identifier, Covered Person Entry Date, etc.) (see the Information Collections: Individual Record Data Elements; and Proposed Reporting Format for Priority of Service Quarterly Aggregate Report).
A.5. Efforts to minimize burden on small businesses.
The recordkeeping and reporting requirements contained in this information collection request are addressed to state formula grant recipients and as such do not impact small businesses or other small entities.
A.6. Consequences to Federal program if collection not done or done less frequently and any technical or legal obstacles to reducing the burden.
Both the ETA and recipient states are mandated to implement priority of service requirements in qualified job training programs, as prescribed in section 2(a)(1) of the JVA, Public Law (Pub. L.) No. 107-288 (Nov. 7, 2002), and the proposed rule that would implement these provisions.
The inability to collect the information requested would negatively impact ETA’s responsibilities for oversight and monitoring of priority of service in these programs, because there is no other vehicle available for helping to assess the extent to which the priority of service provisions are being adhered to in workforce programs. Further, the Department would not have the data it would need to provide a complete report to Congress on priority of service to covered persons, as required by the JVA.
A.7. Special circumstances for conducting information collection.
There are no special circumstances that would require the information to be collected or kept in any manner other than those normally required under the Paperwork Reduction Act.
A.8. Summary of public comments.
The public is being given 60 days to comment on the proposed data collection requirements as part of the Notice of Proposed Rulemaking for Priority of Service. Any comments received will be addressed at the final rule stage.
A.9. Explanation of decision to provide any payment or gift to respondents.
There will be no special payments or gifts to respondents other than the formula funds and incentive funds provided for in the affected programs’ authorizing statutes.
A.10. Assurance of confidentiality provided to respondents.
ETA is responsible for protecting the confidentiality of any data and will maintain the data in accordance with all applicable Federal laws, with particular emphasis upon compliance with the provisions of the Privacy and Freedom of Information Acts. The proposed data collection does not contain any individually identifying information (e.g., names or Social Security Numbers). The quarterly report forms provide data in the aggregate. States also will submit individual data records to the Department each quarter, but these data records do not include any identifiers that permit retrieval of information on the identity of individuals. It should be noted that for all of its Privacy Act systems of records, DOL has established and published in the Federal Register a set of routine uses that apply to and are incorporated by reference into each system of records. (see Federal Register, V. 67, No. 67, dated April 8, 2002, pp. 16815-16948).
A.11. Justification for any sensitive questions.
There are no sensitive questions included in the proposed data collection. The only questions that would need to be asked of customers to comply with the new information collection requirements pertain to their veteran status and the opportunity to provide their basic demographic information.
A.12. Estimated hourly burden.
Several sections of the proposed rule involve Paper Work Reduction Act (PRA) information collections (See Section 1010.220; 1010.330(b) and 1010.330(c)). The majority of these PRA impacts will affect existing information collections. There are two information collections, however, that do not have a current OMB number and therefore are proposed in this Supporting Statement and ICR submission. These sections outline the responsibilities of grant recipients to collect and maintain data on covered and non-covered persons. A discussion of the estimated hourly burden ensues.
Based on previous program experience, the Department estimates that approximately 1,569,000 covered persons will access the public workforce system next year.
In estimating service provider staff time costs, the Department used the average hourly wage rate of employees in state Unemployment Insurance (UI) agencies for FY 2006, adjusted the figure for inflation for FY 2008 ($36.39) and increased it by a factor of 1.42 to account for employment benefits and compensation for a total of $51.67. Total estimated annual collection and reporting burden hours for all respondent data are 155,449 – see tables below. By way of explanation, the total estimated annual national burden for priority of service has two broad components: 1) an estimate of 92,564 burden hours for record keeping and reporting on covered entrants; and, 2) an estimate of 62,885 burden hours for record keeping and reporting on new covered persons (participants), which will capture characteristics, services, and outcomes. The following tables provide further details regarding the separate burden estimates for each component (e.g., covered entrant data and new covered person participant data).
TABLE 1.
The projected annual counts for covered entrants comes from actual data on covered persons served (participants) from the most recent full year of program reporting. Data was compiled from the following reporting systems: The WIA Management Information and Reporting System; The Labor Exchange Reporting System; The Trade Act Participant Report; and SPARQ. Though our current reporting culture does not recognize covered entrants, covered participants should be a good predictor of the number of new individual covered entrant records that will need to be produced by grantees.
The
projection of 92,564 burden hours is based on the completion of
individual covered entrant records. The burden will be the same
regardless of the mix of reporting systems that are ultimately
impacted; this is because the number of data elements for covered
entrants will be the same regardless of which reporting system they
are attached to.
TABLE 1. Covered Entrant Data Collection |
|||||
Program |
Projected Annual Counts* |
Hourly Rate** |
Minutes Per Record*** |
Annual National Burden Hours |
Annual National Burden Dollars |
Integrated W-P/,* WIA Adult, DW, NEG |
1,568,574 |
$51.67 |
3.5 |
91,500 |
$4,727,805 |
TAA |
6,410 |
$51.67 |
3.5 |
374 |
$19,325 |
SCSEP |
11,831 |
$51.67 |
3.5 |
690 |
$35,652 |
Total |
1,586,815 |
|
|
92,564 |
$4,782,782 |
*Note that covered entrants that enter physical offices or web sites funded by Wagner-Peyser State Grants will still need to be captured in the Workforce Investment Act Standardized Record Data (WIASRD) submissions.
**Hourly
rate is based on the FY 2006 salary of employees in state UI agencies
adjusted for inflation for FY 2008 and increased by a factor of 1.42
to account for employment benefits and compensation.
***Ten percent of this time represents information technology management including searching the multiple existing data sources needed to complete the quarterly report form, gathering and maintaining the data, completing and reviewing the collection of individual records, and submitting to DOL.
TABLE 2.
New covered person participant data to be collected under the WIA Management Information and Reporting System is also factored into the burden calculation. Some additional increases in the number of veterans participating in WIA services are likely to occur for the following reasons: 1) it is expected that priority of service will bring additional attention to serving veterans and thus create new opportunities for covered persons to access WIA services; 2) adoption of the JVA definition of covered person for WIA services will broaden the pool of those eligible for priority by including eligible spouses of veterans; and, 3) the reporting integration between W-P and WIA is expected to increase program integration and thus increase the number of veterans receiving WIA services. As a preliminary estimate, we believe these factors could lead to ten percent of those veterans who currently receive only W-P services also receiving WIA services. Currently, the W-P State Grants serve 1,151,530 veterans. The table below assumes that 10 percent of that number, or 151,530 covered persons, also will become WIA participants due to the factors identified above. Please see the annual burden hours and cost information table for these new WIA participants below.
TABLE 2. New Covered Person Participant Data Collection |
|||||
|
Projected Annual Counts* |
Hourly Rate** |
Minutes Per Record*** |
Annual National Burden Hours |
Annual National Burden Dollars |
Estimated Increase in Covered Persons Served |
151,530 |
$51.67 |
24.9 |
62,885 |
$3,249,268 |
*This represents the new covered participants served as a result of the ICR. The projection is based on counts from the most recent full year of W-P reporting. The estimate of 151,530 new covered person participants in WIA represents 10 percent of the number of veteran participants currently served by W-P State Grants.
**Hourly rate is based on the FY 2006 salary of employees in state UI agencies adjusted for inflation for FY 2008 and increased by a factor of 1.42 to account for employment benefits and compensation.
***Ten percent of this time represents information technology management including searching the multiple existing data sources needed to complete the quarterly report form, gathering and maintaining the data, completing and reviewing the collection of individual records, and submitting to DOL.
A.13. Estimated cost burden to respondents.
Since these data collection requirements apply to state formula grant recipients, administrative resources are provided as part of the grant to off-set staff costs associated with reporting and systems modifications. As such, there is no additional cost to respondents other than those reported in Section A.12. above.
A.14. Estimated cost burden to the Federal government
To implement the new data collection requirement, ETA must change its reporting infrastructure to accommodate the new elements (see the following Information Collection: Individual Record Data Elements). Additionally, programs will need to submit aggregate quarterly reports (see the following Information Collection: Proposed Reporting Format for Priority of Service Quarterly Aggregate Report). The estimated cost burden to the Federal Government will vary, depending on what systems ultimately end up being modified by the new data collection requirements.
If ETA’s proposed Workforce Investment Streamlined Performance Reporting (WISPR) system is implemented it would replace the current reporting systems for all of the impacted programs, with the exception of the SCSEP. If WISPR has been implemented when the priority of service reporting requirements go into affect, only two reporting systems (WISPR and the SCSEP Performance and Results Quarterly [SPARQ]) will need to be modified:
WISPR: $400,000
SPARQ:
$400,000
Total:
$800,000
The estimated cost to the federal government for both WISPR and SPARQ is largely based on the addition of four new data elements associated with individual records for covered person participants; modifications to IT systems to collect and store additional data associated with covered entrants and the new quarterly reports; changes to the data validation software; and technical assistance to the states.
If the priority of service reporting requirements are implemented before the implementation of WISPR, three program reporting systems would be impacted (WIA, TAA and SCSEP). DOL would need a mechanism to capture individual record information on all covered entrants to the public workforce investment system (see the following Information Collection: Individual Record Data Elements). Since the reporting for the W-P State Grants does not include individual data records that are submitted to DOL, covered entrants that access services funded only by the W-P State Grants (in One-Stop physical locations or via virtual service delivery) will need to be tracked by the Workforce Investment Standardized Record Data (WIASRD). This would serve two key purposes: 1) assist DOL in receiving individual records on all covered entrants who access workforce investment services; and, 2) support integration between the WIA and W-P activities.
WIA: $2,100,000
TAA: $375,000
SPARQ: $400,000
Total: $2,875,000
The estimated cost to the federal government for the aforementioned systems is largely based on the addition of four new data elements associated with individual records for covered person participants; modifications to IT systems to collect and store additional data associated with covered entrants and covered person participants and the new quarterly reports; changes to the data validation software; and technical assistance to the states.
Note: For WIA, the estimate is larger due to the capturing of covered entrants and a slightly larger universe of covered person participants in the WIASRD submissions.
A.15. Reasons for any program changes reported in Items 13 or 14 of the OMB Form 83-1.
As this is a new information collection request, there is no burden currently associated with this information collection. The increase in burden is a result of new data that needs to be collected as a result of the promulgation of new priority of service regulations and the associated data collection and reporting requirements.
A.16. Method for publishing results.
ETA publishes program performance information on its public access webpage at: http://www.doleta.gov/performance
Based on the new individual record submissions, DOL will report on an annual basis the number of covered entrants, the number who received services, and the number who went unserved.
States and territories will submit aggregate reports on a quarterly basis to DOL within 45 days after the end of each Program Year (PY) quarter. Reports are due on the following dates:
Report Quarter |
Due Date |
1st Quarter PY July to September |
November 14 |
2nd Quarter PY October to December |
February 14 |
3rd Quarter PY January to March |
May 15 |
4th Quarter PY April to June |
August 14 |
Covered entrant individual record submissions will also be received according to the same schedule as the aggregate reports.
Individual record submissions on covered entrants that become participants will be received after they complete program services, on an annual basis, unless WISPR has been fully implemented by the time this requirement goes into affect. If WISPR is the system that is modified by this ICR, individual records will be submitted quarterly according to the above schedule as well.
Data will be analyzed by ETA and VETS staff. Data analysis is used to identify strategies for continuous improvement and areas where additional federal guidance is needed. DOL may use these data to prepare Government Performance and Results Act (GPRA) reports, budget reports, OMB’s Program Assessment Rating Tool (PART), and other ad hoc reports.
Each year, the Department issues an annual report summarizing program performance against the Secretary’s goals. Some of the data included in the Department’s annual report would be generated from these individual record submissions. Additionally, the Department prepares an Annual Performance Accountability Report (APAR), which includes performance data on all programs covered under this ICR. To satisfy its requirements under Title 38, VETS also submits an annual report to Congress. That report addresses the statutory requirement at 38 U.S.C. § 4215(d) to report annually to the Congress on: a) the extent to which covered persons are fully served; and, b) the extent to which the rate of representation of covered persons in workforce programs reflects their rate of incidence in the population. All reports are available on the Internet and accessible to the general public and interested stakeholders.
A.17. If seeking approval not to display the expiration date for OMB approval, explain why display would be inappropriate.
The Department will display the expiration date for OMB approval until the priority of service data collection and reporting requirements are assimilated into the impacted reporting systems. After that time, a Request to Discontinue this collection will be submitted to OMB, as this collection’s requirements would become part of the approvals of the impacted reporting systems.
A.18. Explanation of each exception in the certification statement identified in Item 19 “Certification for Paperwork Reduction Act Submissions” on OMB Form 83-1.
The Department is not seeking any exception to the certification requirements.
Collection of Information Employing Statistical Methods
This information collection request employs no statistical methods.
| File Type | application/msword |
| File Title | SUPPORTING STATEMENT |
| Author | Michael Qualter |
| Last Modified By | naradzay.bonnie |
| File Modified | 2008-08-15 |
| File Created | 2008-08-14 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy