1736ss06
1736ss06.docx
EPA's Natural Gas STAR Program (Renewal)
OMB: 2060-0328
SUPPORTING STATEMENT FOR
EPA INFORMATION COLLECTION REQUEST NUMBER 1736.06
EPA’S NATURAL GAS STAR PROGRAM
April 29, 2011
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 1
1(a) TITLE AND NUMBER OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 1
1(b) CHARACTERIZATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 1
1(c) TERMS OF CLEARANCE OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 1
2. NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION 4
2(a) NEED AND AUTHORITY FOR THE COLLECTION 4
2(b) PRACTICAL UTILITY/USERS OF THE DATA 4
3. NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA 4
3(a) NONDUPLICATION 4
3(b) PUBLIC NOTICE 5
3(c) CONSULTATIONS 5
3(d) EFFECTS OF LESS FREQUENT COLLECTION 5
3(e) GENERAL GUIDELINES 5
3(f) CONFIDENTIALITY 5
3(g) SENSITIVE QUESTIONS 5
4. THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED 6
4(a) RESPONDENTS/NAICS CODES 6
4(b) INFORMATION REQUESTED 6
5. THE INFORMATION COLLECTED--AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT 9
5(a) AGENCY ACTIVITIES 9
5(b) COLLECTION METHODOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT 10
5(c) SMALL ENTITY FLEXIBILITY 10
5(d) COLLECTION SCHEDULE 11
6. ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF THE COLLECTION 11
6(a) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT BURDEN 11
6(b) ESTIMATING RESPONDENT COSTS 11
6(c) ESTIMATING AGENCY BURDEN AND COST 12
6(d) ESTIMATING THE RESPONDENT UNIVERSE AND TOTAL BURDEN 15
6(e) BOTTOM LINE BURDEN HOURS AND COSTS 16
6(f) REASONS FOR CHANGE IN BURDEN 16
6(g) BURDEN STATEMENT 16
1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
1(a) Title of the Information Collection
This ICR is entitled "EPA’s Natural Gas STAR Program (Renewal)," ICR number 1736.06, OMB Control No. 2060-0328.
1(b) Short Characterization/Abstract
Natural Gas STAR is a voluntary program sponsored by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) that encourages oil and natural gas companies to adopt cost effective technologies and practices that improve operational efficiency and reduce methane emissions. Methane is the primary component of natural gas and a potent greenhouse gas. The Program works with oil and natural gas companies in the production, processing, storage, transmission, and distribution sectors to remove barriers that inhibit the implementation of technologies and practices that reduce methane emissions. The Program effectively promotes the adoption of emission reduction technologies and practices by engaging Natural Gas Star partners to evaluate Best Management Practices (BMPs) and Partner Reported Opportunities (PROs) in the context of their current operating circumstances, and implement them where cost effective. Implementation of the Program’s BMPs and PROs saves participants money, improves operational efficiency, and enhances the protection of the environment.
Participation in the Program begins with the completion and submittal of a one-page Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) that outlines responsibilities of the Natural Gas STAR partner company and EPA. The MOU commits a Natural Gas STAR partner to reviewing its activities that result in methane emissions and consider implementing BMPs and PROs appropriate for their operating circumstances that reduce methane emissions, generate revenue, and improve operational efficiency.
Natural Gas STAR partners also agree to submit an Implementation Plan within six to twelve months (depending on partner sector) of signing the MOU and to submit an Annual Report. Annual reporting is a key requirement to the Program. After one full year of participation in the Program, EPA requires partners to submit an Annual Report documenting the previous year’s methane emission reduction activities. Partners must report methane emission reduction activities on an annual basis to remain in good standing. Partners are encouraged to communicate their Program success and the EPA helps partners with communication efforts by providing various templates. EPA also provides Program implementation assistance by analyzing emerging technologies and conducting workshops and webinars.
This voluntary agreement can be terminated by the Natural Gas STAR partner or EPA with no notice or penalties and further obligation.
1(c) Terms of Clearance of the Information Collection
For the last collection, ICR 1736.05, approved in 2008, OMB gave the following Terms of Clearance:
“This Collection of Information is approved for renewal. The data gathered under this collection represents estimates of emissions reductions associated with activities reported by participants in the Natural Gas STAR Program. EPA acknowledges that some of the activities and emissions reductions may have been achieved in the absence of the Natural Gas STAR program. For this reason, the data is not appropriate for use as an aggregate summary of emissions reductions resulting from the program, but is instead correctly characterized as activities and reductions associated with Program partners’ reported activities. The Agency should exercise care to ensure that the data not be characterized inappropriately in program effectiveness measures, on the Program website, or in other communications. When this ICR is resubmitted for renewal, EPA should address the extent to which the partners would have reduced their emissions in the absence of this program.”
When this collection was approved in 2008, OMB noted that EPA should be careful to not characterize data reported by Partner companies as an aggregate summary of emissions reductions resulting from the Program. EPA fully agrees with OMB and recognizes that some of the activities and emissions reductions reported by Partners may have been achieved in the absence of the Program. EPA also recognizes that there are emissions reductions occurring in the industry that have been a direct or indirect result of the influence of the Program, but are not being reported to EPA. As a result, EPA has been and will continue to be clear in any Program related communication that when providing a summary or an aggregation of emission reductions it is appropriately characterized as resulting from Partners’ reported activities.
Also noted in the Terms of Clearance in 2008 was that EPA should address the extent to which partners would have reduced their methane emissions in the absence of the Program. As discussed in the previous ICR Supporting Statement from January 2008, the extent to which partners would have reduced emission in the absence of the Program is a challenging question that EPA takes very seriously. Partners in the Natural Gas STAR Program are asked to submit Implementation Plans every three years describing the methane emissions reduction practices they plan to evaluate and implement. Partners are also asked to submit annual progress reports detailing emission reduction activities undertaken during the previous calendar year. The Natural Gas STAR Program focuses on partner implementation of BMPs and PROs that were undertaken voluntarily; not reductions attributable to compliance with existing regulations. Because of increased state and local regulations focused on greenhouse gas emissions, air quality issues and the like, the number of voluntary practices that would have counted in the tally of emission reductions achieved by Natural Gas STAR partners has been reduced in recent years. This trend is expected to continue in the future.
The methane emission reductions reported by partners include reductions associated with the implementation of BMPs and through the adoption of PROs. PROs are activities identified by Natural Gas STAR partners, beyond the core BMPs that, result in methane emissions reductions. It is worth noting that for 2009 nearly 91 percent of the domestic methane emissions reductions reported to Natural Gas STAR could be attributed to PROs. A significant portion of Natural Gas STAR’s efforts in recent years has been devoted to promoting these PROs by highlighting them in the Program newsletter, developing technical documents, and hosting specialized technology transfer workshops.
The methane emission reduction data submitted to EPA are used to determine Program emission reduction totals and measure the overall effectiveness of the Natural Gas STAR Program. EPA, however, does not attribute all of these methane emission reductions to the Program. For example, Transmission and Distribution BMP 2—Identify and Rehabilitate Leaky Distribution Pipes—is an activity that is required by DOT regulations and is not included in our characterization of Program accomplishments. Additionally, each Annual Report receives a quality assurance/quality control check to ensure that all data are accurate. Any inconsistencies are resolved through direct correspondence with the appropriate partner company (ies). As appropriate, these data are omitted or adjusted prior to their inclusion in the Natural Gas STAR Program totals.
In an effort to ensure that EPA accurately reflects the impact of the Program, we have performed a scenario analysis. As shown in Figure 1, a business as usual scenario was developed that displays projected methane emissions in the absence of the Natural Gas STAR Program. Alternative emissions scenarios are constructed by multiplying emission factors by projected levels of production, processing and transmission/distribution and subtracting emission reductions from “Gas STAR” and then “All Cost Effective Options” respectively. The emission factors are assumed to decline 5% over 25 years to reflect increased efficiencies in the natural gas system. Overall, Figure 1 shows increased emissions over time with a brief decline between 2005 and 2010 due to the contraction of the U.S. economy.
In the same figure, cost-effective mitigation options are defined as those options where the project generates a positive internal rate of return. While these options are cost effective, they are not implemented in the no-action scenario because of information, policy and other non-cost barriers. The difference between this emission scenario and the no-action scenario represents the total potential emission reduction that would reasonably be achieved by the Natural Gas STAR Program if all barriers to implementation were removed.
Using this analysis as a guide, EPA is able to estimate the extent to which regulatory, information, and other barriers that often inhibit the implementation of these activities can be overcome by the Natural Gas STAR Program. The Program overcomes these barriers through a variety of activities including:
- Developing technical fact sheets, reports, and articles;
- Hosting Technology Transfer Workshops and an Annual Implementation Workshop;
- Providing support to partner companies;
- Supporting research activities;
- Publicizing achievements of partner companies; and
- Making available to partners a mechanism for recording and storing information about methane emission reduction activities.
In addition to benefiting partner companies, the above activities benefit non-partner companies. For example, all the technical documents developed by the Program are made available to the public on the Natural Gas STAR website, and workshop attendance is not restricted to Program partners. Thus, it can be assumed that a substantial portion of the natural gas industry not participating in Natural Gas STAR is also implementing some of the methane emission reduction activities that are encouraged by the Program. As noted above, Natural Gas STAR does not attempt to estimate the accomplishments of these companies, even though their activities are at least partially due to the existence of the Natural Gas STAR Program.
*Figure 1: Natural Gas Industry Methane Emission Projections
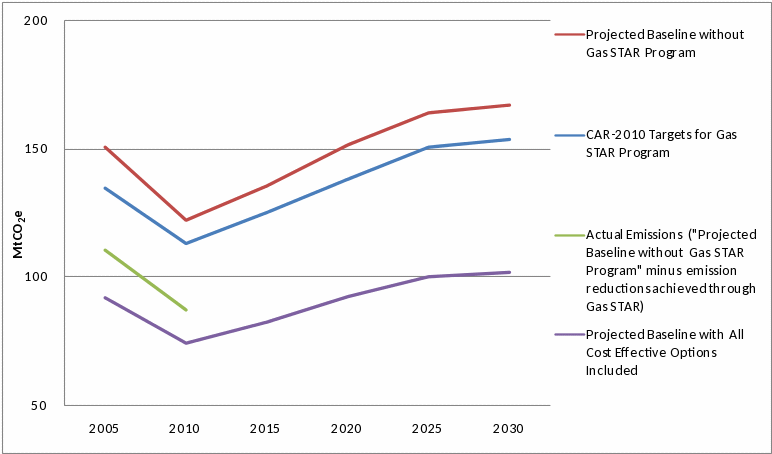
*Notes and Data Sources:
Projected emissions without Gas STAR are calculated from the Global Anthropogenic Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gas Emissions: 1990-2030, EPA Draft Report.
Projected emissions with cost effective options included are calculated using cost effective reduction estimates from the Global Mitigation of Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gases, EPA 430-R-06-005. The reduction estimates were updated to include mitigation cost estimates for ‘green completions’ and ‘liquid unloading’. More information on these mitigation technologies is available at: http://www.epa.gov/gasstar/tools/recommended.html
Program reductions are based on expert judgment and were used to measure the GHG intensity of the U.S. economy in the U.S. Climate Action Report - 2010, Department of State, Chapters 4-5 & Table 4-3.
The overall trend in the projected baseline is growth in emissions from natural gas; the emissions decline between 2005 and 2010 can be attributed to economic contraction.
2. NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION
2(a) Need/Authority for the Collection
EPA has developed this ICR to obtain authorization to collect information from Natural Gas STAR partners. EPA needs to collect initial information via the one-page MOU. The MOU provides general information on the Natural Gas STAR partner company to include relevant points of contact. EPA uses information obtained from the MOU to identify and initiate communication with the partners.
The Implementation Plan and annual reporting are necessary to evaluate a partner's progress in implementing the Program and to assess overall Program results. The information provided in the Plan and through annual reporting also allows EPA to track BMPs and PROs most commonly reported and to provide technical and other assistance to partners.
2(b) Practical Utility/Users of the Data
EPA uses information in the MOU to populate its contacts database/tracking system with information on Natural Gas STAR partners (current and past). This information is maintained in the contacts database/tracking system and serves as a source of general information as well as a mailing list.
EPA uses information submitted in the Implementation Plan and Annual Reports to document the progress of partner companies in implementing the Program and reducing methane emissions. EPA enters Annual Report information received from partners into iSTAR — a client management database. On an annual basis, EPA also aggregates these data and prepares the Program Accomplishments Flyer and partner summary reports.
With partner permission, EPA uses these data to develop technical documents on specific technologies and practices and prepare case studies showing successful implementation experiences. These documents are publicly available and serve to demonstrate the benefits that can be realized through the implementation of technologies and practices and to provide technical assistance.
3. NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA
3(a) Nonduplication
EPA recently finalized Subpart W of the Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program that requires companies to begin collecting methane emissions data as of January 1, 2011. The first year of mandatory greenhouse gas data collection for the oil and natural gas industry is 2011. While the data collected for the rule is methane emissions (and not methane emission reductions) it is anticipated that this information will complement and augment the emission reductions data EPA has received from companies over the years. This rule will increase the understanding of the location and magnitude of significant methane emissions sources in the petroleum and natural gas industry. This information will help companies improve the efficiency of their operations and deliver more natural gas to markets. This will result in cross-cutting benefits for public health, domestic energy supply, industrial efficiency and safety, and revenue generation. This information will inform the development of future greenhouse gas policy and regulation.
The information to be obtained under this ICR has not been collected by EPA or any other Federal agency.
3(b) Public Notice Required Prior to ICR Submission to OMB
In compliance with the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995, EPA solicited public comments on the ICR through an announcement in the Federal Register on February 4, 2011 (76 FR 6460). No comments were received in response to the notice.
3(c) Consultations
Since the last ICR Renewal, all of the information collection procedures for Natural Gas STAR have remained the same. EPA contacted the Mr. Zack Schaffer of the Chesapeake Energy Corporation and received no objections to this information request. His contact information is as follows:
Zack Schaffer
Asset Manager
Chesapeake Energy Corporation
6100 N. Western Avenue
Oklahoma City, OK 73118
(405) 935-1813
3(d) Effects of Less Frequent Collection
The completion and submittal of the MOU is a one-time activity for companies that voluntarily choose to become a partner in the Natural Gas STAR Program. Partners must also prepare and submit an Implementation Plan, and revise the plan every three years. Partners must also submit an Annual Report while participating in the Program. EPA believes that any reduction in the frequency of this information collection and submittal would impede efforts by EPA to evaluate results of the Program.
3(e) General Guidelines
None of these reporting or record keeping requirements violate any of the regulations established by OMB in 5 CFR 1320.5.
3(f) Confidentiality
Participation in the Natural Gas STAR Program is voluntary. Natural Gas STAR partners may designate information submitted under this ICR as confidential business information. EPA will treat such information as confidential business information and will not make the company or agency-specific information collected under this ICR available to the general public.
3(g) Sensitive Questions
No questions of a sensitive nature are asked in the MOU, Implementation Plan, or the Annual Report.
4. THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED
4(a) Respondents/NAICS Codes
The following is a list of North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) Codes and associated industries that may be affected by information collection requirements covered under this ICR:
211100 Oil and Gas Extraction
486200 Pipeline Transportation of Natural Gas
221200 Natural Gas Distribution
4(b) Information Requested
EPA's Natural Gas STAR Program specifies requirements for partners. All Natural Gas STAR partners must sign and submit a one-page MOU. This initiates the Partnership in the Program. The MOU identifies company points of contact.
Partners then develop an Implementation Plan within 6 to 12 months of joining. The Natural Gas STAR Program Implementation Plan facilitates development of a strategy for how partners will identify non-regulatory methane emission reduction activities they intend to undertake, plan for new activities, and develop mechanisms for tracking methane emission reduction data and activities. An Implementation Plan is a living document that changes over time as each partner's goals and commitment evolve.
After one full calendar year of participation in the Program, partners begin submitting Annual Reports documenting the previous year’s emission reduction activities and corresponding methane emissions reductions.
Memorandum of Understanding
Natural Gas STAR partners are required to sign and submit to EPA the one-page MOU that describes the terms of participation in the Program.
(i) Data items:
Partners must provide the following information in the MOU:
The name, title, address, telephone and facsimile number, and e-mail address of a Natural Gas STAR Program Implementation Manager and a Media Liaison and
The name and signature of the partners' Authorized Company Representative.
(ii) Respondent activities:
In signing the MOU, partners must perform the following activities:
Download (from the Natural Gas STAR website) and review the one-page MOU;
Gather requested information and complete the MOU; and
Sign the MOU and submit it to EPA.
Implementation Plan
Partners must complete and submit a Natural Gas STAR Implementation Plan within six to twelve months of signing the MOU.
(i) Data items:
The Implementation Plan form requests the following information:
General company information (e.g., company name and contact, position, mail and e-mail addresses, telephone and facsimile numbers, etc.);
Summary of activities that the partner intends to implement;
Information on applicable BMPs that the partner might implement. The BMPs are sector specific and include the following:
Directed inspection and maintenance at gate stations and surface facilities;
Identify and rehabilitate leaky distribution pipe;
Directed inspection and maintenance at compressor stations;
Use of turbines at compressor stations;
Identify and replace high bleed pneumatic devices;
Installation of flash tank separators on glycol dehydrators;
Convert gas pneumatics with instrument air systems; and
Directed inspection and maintenance at gas plants and booster stations.
Information on PROs that the company chooses to evaluate and implement; and
Plans to inventory past methane emission reductions as the Program encourages partners to report past emission reduction activities not previously reported to EPA.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Partners must conduct the following activities in preparing the Implementation Plan:
Review the instructions;
Gather the requested information and develop the Implementation Plan;
Complete the form(s);
Sign and submit the plan to EPA; and
Update the plan as priorities shift overtime. The Plan is revised or updated by submitting a new form to EPA.
Annual Report
Annual reporting is a key requirement to remain a partner in the Natural Gas STAR Program. After one full year of participation in the Program, EPA requires partners to submit an Annual Report documenting the previous year’s methane emission reduction activities. Essentially, the report documents voluntary (non-regulatory driven) methane emission reduction activities that partner companies have implemented in the previous year, including corresponding methane emissions reductions achieved, and to the extent available, the economics associated with each activity.
(i) Data items:
The Annual Report form requests the following information:
General company information (e.g., company name and contact, position, mail and e-mail addresses, telephone and facsimile numbers, period covered by report, etc.);
Annual Report Summary;
Information on Best Management Practices implemented. These are sector specific and reported as:
Directed inspection and maintenance at gate stations and surface facilities;
Identify and rehabilitate leaky distribution pipe;
Directed inspection and maintenance at compressor stations;
Use of turbines at compressor stations;
Identify and replace high bleed pneumatic devices;
Installation of flash tank separators on glycol dehydrators;
Convert gas pneumatics with instrument air systems; and
Directed inspection and maintenance at gas plants and booster stations.
Information on applicable PROs that the company implemented; and
Information on Additional Program Accomplishments that a partner wishes to share. This might include:
Efforts to strengthen program participation (e.g., training/education, innovative technologies or activities, pilot projects, employee incentive programs) and/or efforts to communicate participation (e.g., newsletters, press releases, external website).
(ii) Respondent activities:
Partners must conduct the following activities in preparing the Annual Report:
Review the instructions;
Gather the requested information for the initial report;
Complete the initial form(s);
Sign and date the initial report;
Submit the initial report to EPA; and
Prepare and submit a subsequent Annual Report.
Additional Activities
During participation in the Program, partners are required to notify EPA within two weeks of any change in Natural Gas STAR Program Implementation Manager and Media Liaison responsibility.
(i) Data items:
Partner must provide EPA with the name of the new Implementation Manager or Media Liaison.
(ii) Respondent activities:
Notify EPA within two weeks of any change in Natural Gas STAR Implementation Manager or Media Liaison responsibility.
5. THE INFORMATION COLLECTED-AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
5(a) Agency Activities
The Natural Gas STAR Program requires EPA to perform activities after a partner submits the MOU, Implementation Plan, and Annual Report.
Memorandum of Understanding
EPA must perform the following activities upon receipt of a MOU:
Review the MOU to ensure completeness and accuracy, and follow up, if necessary;
Countersign the MOU;
Develop a cover letter and welcome packet with useful program information;
Copy the cover letters and MOUs;
Send cover letter, original MOU with countersign and welcome packet to partner;
File copies of cover letters and MOUs; and
Enter MOU information into tracking database.
Implementation Plan
EPA must perform the following activities upon receipt of an Implementation Plan:
Review the plan to ensure completeness and accuracy, and follow-up, if necessary;
Make copies of the plan for the program files;
File copies of the plan; and
Enter information into a tracking database.
Annual Report
EPA must perform the following activities upon receipt of an Annual Report:
Review the report to ensure completeness and accuracy, and follow-up, if necessary;
Make copies of the report;
File copies of the report; and
Enter information into an emissions reduction data management database and review the entered data to assure correctness (quality assurance and/or quality control).
Additional Activities
EPA also may be required to perform the following additional activity:
Enter any changes in partner's information into a database (e.g., Implementation Manager’s responsibility, newsletter mailing list, etc.).
5(b) Collection Methodology and Management
In collecting and analyzing the information associated with this ICR, EPA used typical office equipment such as telephones, computers, and database and word processing software systems.
For the collection of Program information, Natural Gas STAR has developed various templates and tools to assist partners or partners are free to use their own reporting format. The standard Natural Gas STAR reporting forms are available in both PDF and MS Word. Partners using Natural Gas STAR templates and/or their own reporting format can submit data to EPA electronically via email. EPA has also created an online reporting system to allow partners to quickly and easily submit annual methane emissions reduction data.
EPA ensures the accuracy and completeness of collected information by reviewing each submittal. EPA enters the information obtained from the MOU, Implementation Plan, and Annual Reports into a database and aggregates data obtained from Annual Reports to track the progress of partners in reducing methane emissions.
5(c) Small Entity Flexibility
EPA reviewed available company websites for partner organizations that were believed to be small entities. Upon completion of the review, EPA estimated that several Natural Gas STAR partners and at least one new partner to be small entity. EPA has designed its Program forms and associated electronic reporting system to minimize respondent burden while obtaining sufficient and accurate information. It should be noted that the burden associated with the Natural Gas STAR Program is reduced over the course of a partner’s participation.
5(d) Collection Schedule
EPA collects initial information in the one-page MOU, which is completed and submitted by each partner upon their decision to participate in the Program. EPA collects information in the Implementation Plan that is submitted by partners within six to twelve months of signing the MOU. Each spring, EPA collects information in the Annual Report to monitor methane emissions reductions progress. EPA may also collect other Program information on a periodic basis or as the information is submitted. This could include notification of changes in Implementation Manager responsibility, and notification of changes in a partner's operating circumstance (change in ownership, assets, etc.)
6. ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF THE COLLECTION
6(a) Estimating Respondent Burden
Exhibit 1 presents the estimated annual respondent burden and costs for information collection activities associated with the Natural Gas STAR Program.
6(b) Estimating Respondent Costs
(i) Estimating Labor Costs
EPA used a national average hourly labor rate including an hourly rate plus 110% overhead of $149.73 for legal staff, $109.12 for managerial staff, $83.71 for technical staff, and $48.21 for clerical staff. Legal, managerial, technical, and clerical labor rates were obtained from the Bureau of Labor and Statistics average rates for Pipeline Transportation of Natural Gas (NAICS Code 486200), Natural Gas Distribution (NAICS Code 221200), and Oil and Gas Extraction (NAICS Code 211100). The labor rates used were calculated by averaging labor rates for the three NAICS Codes. Legal rates were based on lawyers, management wages were based on general and operations managers, technical wages were based on environmental engineers, and clerical rates were based on executive secretaries and administrative assistants for May 2009. A September 2010 labor rate for all rates was estimated by applying a 2.1% growth factor from the employment cost index to account for increases in wages from June 2009 to September 2010. The Employment Cost Index for wages and salaries, by ownership, occupational group, and industry is located at: http://www.bls.gov/news.release/eci.t02.htm .
(ii) Estimating Capital and Operations and Maintenance Costs
To develop respondent capital and O&M cost estimates, EPA consulted with members of the oil and gas industry. EPA believes that the capital or operations and maintenance costs of this Program are not significant. EPA has removed O&M costs for postage for respondents. Most Natural Gas STAR partners use the online reporting system to submit Annual Reports or submit reports via e-mail as Excel spreadsheets, Word documents, or scanned PDFs. Also, partners submit MOUs and Implementation Plans via e-mail as scanned PDFs or some other type of electronic format. Therefore, costs associated with postage are negligible to none.
(iii) Capital/Start-up vs. Operating and Maintenance (O&M) Costs
There are no capital/start-up costs or O&M costs associated with this information collection.
(iv) Annualizing Capital Costs
There are no capital costs associated with this information collection.
6(c) Estimating Agency Burden and Costs
Exhibit 2 presents the estimated Agency burden hours and costs for the information collection activities associated with this ICR. EPA estimates an average hourly labor cost (labor plus overhead) of $76.38 for legal staff, $71.42 for managerial staff, $52.37 for technical staff, and $21.02 for clerical staff. To derive these estimates, EPA used the “Hourly Salary Table 2011 - GS” from the Department of Personnel Management. For purposes of this ICR, EPA assigned staff the following government service levels:
Legal Staff GS-15, Step 1
Managerial Staff GS-14, Step 4
Technical Staff GS-12, Step 5
Clerical Staff GS-05, Step 1
To derive the loaded hourly estimates, EPA multiplied hourly rates by the standard government overhead factor of 1.6.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ESTIMATED ANNUAL RESPONDENT BURDEN AND COST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hours and Costs Per Respondent/Activity |
Total Hours and Costs |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of |
|
|
Leg. |
Mgr. |
Tech. |
Cler. |
Respon. |
Labor |
Capital/ |
|
Respon. |
Total |
Total |
|
$149.73 |
$109.12 |
$83.71 |
$48.21 |
Hours/ |
Cost/ |
Startup |
O & M |
or |
Hours/ |
Cost/ |
INFORMATION COLLECTION ACTIVITY1 |
Hour |
Hour |
Hour |
Hour |
Activity |
Activity |
Cost |
Cost1 |
Activities |
Year |
Year |
Memorandum of Understanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Receive and review the MOU |
1.00 |
8.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
9.00 |
$1,023 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
45 |
$5,113 |
Gather information and fill out MOU data sheet |
1.00 |
25.00 |
0.00 |
2.00 |
28.00 |
$2,974 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
140 |
$14,871 |
Sign and submit MOU to EPA |
0.00 |
0.50 |
0.00 |
0.50 |
1.00 |
$79 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
5 |
$393 |
SUBTOTAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
190 |
$20,378 |
Implementation Plan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Review instructions |
0.00 |
2.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
2.00 |
$218 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
10 |
$1,091 |
Gather information and develop the Implementation Plan |
0.00 |
10.00 |
10.00 |
0.00 |
20.00 |
$1,928 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
100 |
$9,642 |
Complete the form(s) |
0.00 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
1.00 |
2.00 |
$157 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
10 |
$787 |
Sign and submit plan to EPA |
0.00 |
0.50 |
0.00 |
0.50 |
1.00 |
$79 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
5 |
$393 |
Update Implementation Plan, as necessary and Submit to EPA |
0.00 |
6.50 |
4.00 |
1.50 |
12.00 |
$1,116 |
$0 |
$0 |
45 |
540 |
$50,240 |
SUBTOTAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
665 |
$62,152 |
Annual Report |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Review instructions |
0.00 |
7.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
7.00 |
$764 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
35 |
$3,819 |
Gather the requested information for the initial report |
0.00 |
10.00 |
37.00 |
0.00 |
47.00 |
$4,188 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
235 |
$20,942 |
Complete the initial form(s) |
0.00 |
4.00 |
0.00 |
1.00 |
5.00 |
$485 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
25 |
$2,423 |
Sign and submit the initial report to EPA |
0.00 |
0.50 |
0.00 |
0.50 |
1.00 |
$79 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
5 |
$393 |
Prepare and submit a subsequent Annual Report |
0.00 |
9.00 |
17 |
1 |
27.00 |
$2,453 |
$0 |
$0 |
149 |
4,023 |
$365,551 |
SUBTOTAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4,323 |
$393,129 |
Additional Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Notify EPA within two weeks of any change in Natural |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gas Star Implementation Manager responsibility |
0.00 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
0.50 |
1.50 |
$133 |
$0 |
$0 |
15 |
23 |
$1,998 |
SUBTOTAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
$1,998 |
TOTAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5,201 |
$477,657 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 Since the last ICR renewal, EPA has removed O&M costs for postage for respondents. The majority of Natural Gas STAR partners use the online reporting system to submit Annual Reports or submit reports via e-mail as Excel spreadsheets, Word documents, or scanned PDFs. Also, partners submit MOUs and Implementation Plans via e-mail as scanned PDFs or some other type of electronic format. Therefore, costs associated with postage are negligible. |
|||||||||||
EXHIBIT 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ESTIMATED ANNUAL AGENCY BURDEN AND COST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hours and Costs for Agency Per Activity |
Total Hours and Costs |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of |
|
|
Leg. |
Mgr. |
Tech. |
Cler. |
Agency |
Labor |
Capital/ |
|
Respon. |
Total |
Total |
|
76.38 |
$71.42 |
$52.37 |
$21.02 |
Hours/ |
Cost/ |
Startup |
O & M |
or |
Hours/ |
Cost/ |
INFORMATION COLLECTION ACTIVITY |
Hour |
Hour |
Hour |
Hour |
Activity |
Activity |
Cost |
Cost |
Activities |
Year |
Year |
Memorandum of Understanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Review MOU and follow up, if necessary |
0.00 |
0.00 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
1.00 |
$52 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
5 |
$262 |
Sign the MOU |
0.00 |
0.05 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.05 |
$4 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
.25 |
$18 |
Develop a cover letter |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.10 |
0.10 |
$2 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
.5 |
$11 |
Copy cover letters and MOUs |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
$2 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
.4 |
$8 |
Send cover letters and original MOU back |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
to partner |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.10 |
0.10 |
$2 |
$0 |
$5 |
5 |
.5 |
$36 |
File copies of cover letters and MOUs |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.10 |
0.10 |
$2 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
.5 |
$11 |
Enter MOU information into a data base |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.25 |
0.25 |
$5 |
$0 |
$0 |
5 |
1.25 |
$26 |
Subtotal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.4 |
$371 |
Implementation Plan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Review plan and follow up, if necessary |
0.00 |
0.00 |
2.00 |
0.00 |
2.00 |
$105 |
$0 |
$0 |
50 |
100 |
$5,237 |
Make copies of plan |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
$2 |
$0 |
$0 |
50 |
4 |
$84 |
File copies of plan |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.10 |
0.10 |
$2 |
$0 |
$0 |
50 |
5 |
$105 |
Enter information into data base |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.25 |
0.25 |
$5 |
$0 |
$0 |
50 |
12.5 |
$263 |
Subtotal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
121.5 |
$5,689 |
Annual Report |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Review report and follow up, if necessary |
0.00 |
0.00 |
4.00 |
0.00 |
4.00 |
$209 |
$0 |
$0 |
154 |
616 |
$32,260 |
Make copies of report |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
$2 |
$0 |
$0 |
154 |
12.32 |
$259 |
File copies of report |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.10 |
0.10 |
$2 |
$0 |
$0 |
154 |
15.4 |
$324 |
Enter information into data base |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.50 |
0.50 |
$11 |
$0 |
$0 |
154 |
77 |
$1,619 |
Subtotal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
721 |
$34,461 |
Additional Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enter updated information into data base |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.25 |
0.25 |
$5 |
$0 |
$0 |
15 |
4 |
$79 |
TOTAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
854 |
$40,600 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
6(d) Estimating the Respondent Universe and Total Burden and Costs
Currently, there are 144 Natural Gas STAR Program partners. The majority of Natural Gas STAR partners are large companies. EPA believes that many of the major domestic oil and natural companies have already joined the Program. Based on recent Program activity, EPA anticipates that an average of five new partners will join the Program annually. This number is expected to remain essentially constant as more international companies and smaller independent companies continue to join the Program.
The average annual cost and burden estimates during the next 3-year ICR period are based on the average number of partners as shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1
Estimated Number of Program Partners in Calendar Years 2011-2013
Type of Partner
|
2011 |
2012 |
2013 |
Average |
New Partners Enrolled
|
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
Total Program Partners
|
144 |
149 |
154 |
149 |
Memorandum of Understanding
Each partner must complete and submit a one-page MOU to join the Program. EPA expects that five new partners will complete and submit an MOU each year.
Implementation Plan
Each new partner must complete and submit the Implementation Plan within six to twelve months (depending on partner sector) of signing and submitting the MOU. EPA estimates that 30 percent of all existing partners (or 45 partner companies) will update the Implementation Plan and submit it to EPA each year.
Annual Report
All existing partners must complete and submit an Annual Report after one full (calendar) year of joining the Program and then annually in the subsequent years of participation. EPA estimates that completing the initial Annual Report will take approximately twice as long as subsequent reports. EPA expects that the five new Program partners joining each year will complete and submit an initial report and an average of 149 existing partners (as shown in Table 1) will complete and submit subsequent reports.
Additional Activities
EPA expects that additional information submittals may be required of some partners. EPA estimates that approximately 10 percent of all partners experience changes in their Implementation Manager and/or Media Liaison responsibilities each year. Thus, EPA estimates that an average of 15 partners (149 x 0.1) will notify EPA of changes in Implementation Manager and/or Media Liaison responsibilities.
6(e) Bottom Line Burden Hours and Costs
Exhibits 1 and 2 show the aggregate annual burden and cost to respondents and the government, respectively, for the information collection activities covered under this ICR.
(i) Respondent Tally
The bottom line burden for respondents is approximately 5,201 hours per year with an annual cost of approximately $477,657. Over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA estimates the burden of the Program to be 15,603 hours and $1,432,971 for respondents.
(ii) The Agency Tally
The annual bottom line burden to the Agency is approximately 854 hours, at a cost of approximately $40,600 per year. Over the three-year period covered by this ICR, EPA estimates the burden of the Program to be 2,562 hours and $121,800 for EPA.
(iii) Variations In The Annual Bottom Line
EPA anticipates minimal variation in the annual respondent reporting/recordkeeping burden over the three-year period covered by this ICR.
6(f) Reasons for Change in Burden
The overall annual reporting burden for respondents decreased from 5,610 hours in the previous ICR to 5,201 hours in the current ICR. This change is attributed to the Program’s maturity (as the partner reporting burden reduces over the course of their participation in the Program) and change in number of new Program partners. The average burden per partner decreased slightly; 36.2 hours per partner to 34.9 hours per partner. This can be attributed to a larger percentage of partners using the online Annual Report forms and/or internal data collection systems, Program information requested and the collection methodology did not change, the availability of materials on the Natural Gas STAR website, and maturity of the Program. Partner use of the online reporting system has been steadily increasing each year since its availability to partners. The hourly burden estimates for data collection remained the same per partner because the information requested and the collection methodology did not change.
Since the last ICR renewal, the overall annual cost decreased from $550,677 to $477,657. This change is largely the result of lower hourly labor rates due to inflation and fewer new partners joining the Program.
6(g) Burden Statement
The average per partner reporting burden for information collection requirements associated with completing this ICR is estimated to be 35 hours.
For new partners, the average reporting burden per partner for information collection requirements associated with completing the MOU is estimated to be 38 hours. This number has remained the same as compared to the previous ICR. The burden estimate includes time to receive and review the MOU; gather information and fill out the MOU data sheet; and sign and submit the MOU to EPA.
For new partners, the average reporting burden per partner for information collection requirements associated with completing the Implementation Plan is estimated to be 25 hours. This number has remained the same as compared to the previous ICR. The burden estimate includes time to review the plan form; gather the requested information; complete the form; sign and date the form; and submit the form to EPA.
For existing partners, the average per partner reporting burden for information collection requirements associated with updating the Implementation Plan is estimated to be 12 hours. This number has remained the same as compared to the previous ICR. The burden estimate includes time to review, update (if necessary), complete, sign and submit the form to EPA.
The average per partner reporting burden for information collection requirements associated with completing the initial Annual Report is estimated to be 60 hours. This number has remained the same as compared to the previous ICR. The average per partner reporting burden for information collection requirements associated with completing subsequent Annual Reports is estimated to be 27 hours. This number has remained the same as compared to the previous ICR. The burden estimate includes time to review the reporting package (forms and any Program updates); gather the requested information; complete the form; sign and date the form; and submit the form to EPA. This estimate includes a reduced estimate for those partners using the on-line reporting system, and a factor to account for the percentage of partners who are likely to use the on-line reporting system.
For Natural Gas STAR partners, the average per partner reporting burden for information collection requirements associated with additional activities is estimated to be 1.5 hours. This number has remained the same as compared to the previous ICR. The reporting burden includes time to notify EPA of changes in Natural Gas STAR Program Implementation Manager and/or Media Liaison responsibility.
Burden means the total time, effort, or financial resources expended by persons to generate, maintain, retain, or disclose or provide information to or for a Federal agency. This includes the time needed to review instructions; develop, acquire, install, and utilize technology and systems for the purposes of collecting, validating, and verifying information, processing and maintaining information, and disclosing and providing information; adjust the existing ways to comply with any previously applicable instructions and requirements; train personnel to be able to respond to a collection of information; search data sources; complete and review the collection of information; and transmit or otherwise disclose the information. An agency may not conduct or sponsor, and a person is not required to respond to, a collection of information unless it displays a currently valid OMB control number. The OMB control numbers for EPA's regulations are listed in 40 CFR part 9 and 48 CFR chapter 15.
To comment on the Agency's need for this information, the accuracy of the provided burden estimates, and any suggested methods for minimizing respondent burden, including the use of automated collection techniques, EPA has established a public docket for this ICR under Docket ID Number EPA-HQ-OAR-2004-0082, which is available for online viewing at www.regulations.gov, or in person viewing at the Air and Radiation Docket in the EPA Docket Center (EPA/DC), EPA West, Room 3334, 1301 Constitution Avenue, NW, Washington, D.C. The EPA Docket Center Public Reading Room is open from 8:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m., Monday through Friday, excluding legal holidays. The telephone number for the Reading Room is (202) 566-1744, and the telephone number for the Air and Radiation Docket is 202-566-1742. An electronic version of the public docket is available at www.regulations.gov. This site can be used to submit or view public comments, access the index listing of the contents of the public docket, and to access those documents in the public docket that are available electronically. When in the system, select “search,” then key in the Docket ID Number identified above. Also, you can send comments to the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs, Office of Management and Budget, 725 17th Street, NW, Washington, D.C. 20503, Attention: Desk Officer for EPA. Please include the EPA Docket ID Number EPA-HQ-OAR-2004-0082 and OMB Control Number 2060-0328 in any correspondence.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | SUPPORTING STATEMENT FOR |
| Author | Berkowitz/Honabarger |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-31 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy