2013 SIPP-EHC Section A
2013 SIPP-EHC Section A.docx
2013 Survey of Income and Program Participation Event History Calendar (SIPP-EHC) Field Test
OMB: 0607-0957
SUPPORTING STATEMENT
U.S. Department of Commerce
U.S. Census Bureau
2013 Survey of Income and Program Participation Event History Calendar Field Test
OMB NUMBER: 0607-0957
A. Justification
1. Necessity of Information Collection
The U.S. Census Bureau requests authorization from the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) to conduct the 2013 Survey of Income and Program Participation Event History Calendar (SIPP-EHC) Field Test.
The Census Bureau's SIPP-EHC computer-assisted personal interviewing (CAPI) will use an Event History Calendar (EHC) interviewing method and a 12-month, calendar-year reference period in place of the current SIPP questionnaire approach that uses a sliding 4-month reference period. The Census Bureau also plans to use Computer Assisted Recorded Interview (CARI) technology for a sample of the respondents during the 2013 SIPP-EHC. The Census Bureau is re-engineering the SIPP to accomplish several goals including re-engineering the collection instrument and processing system, development of the EHC in the instrument, use of the administrative records data where feasible, and increased stakeholder interaction. See Attachment A for the interview questions.
The main objective of the SIPP has been, and continues to be, to provide accurate and comprehensive information about the income and program participation of individuals and households in the United States. The survey’s mission is to provide a nationally representative sample for evaluating: 1) annual and sub-annual income dynamics,
2) movements into and out of government transfer programs, 3) family and social context of individuals and households, and 4) interactions among these items. A major use of the SIPP has been to evaluate the use of and eligibility for government programs and to analyze the impacts of modifications to those programs. The re-engineering of SIPP pursues these objectives in the context of several goals including cost reduction, improved accuracy, increased relevance and timeliness, reduced burden on respondents, and increased accessibility. The 2013 SIPP-EHC will collect detailed information on cash and non-cash income (including participation in government transfer programs) once per year.
A key component of the re-engineering process involves the proposed shift from the every-four-month data collection schedule of traditional SIPP to an annual data collection schedule for the re-engineered survey. To accomplish this shift with minimal impact on data quality, the Census Bureau proposes employing the use of an event history calendar to gather SIPP data. The 2013 SIPP-EHC will re-interview respondents interviewed in 2012, collecting data for the previous calendar year as the reference period. The content of the 2013 SIPP-EHC will closely match that of the 2012 SIPP-EHC. The SIPP-EHC design does not contain freestanding topical modules as in the current production SIPP instrument; however, a portion of traditional SIPP topical module content is integrated into the main body of the 2013 SIPP-EHC interview. The EHC allows recording dates of events and spells of coverage and should provide measures of monthly transitions of program receipt and coverage, labor force transitions, health insurance transitions, and others. The 2013 SIPP-EHC will be the second test using dependent data in conjunction with calendar methods to reduce burden and improve quality, and the first opportunity to re-engage respondents who either refused to participate or could not be located for the 2012 SIPP-EHC wave 2 interviews. Further, the 2013 SIPP-EHC will be the final dry-run prior to administration of the SIPP-EHC as the production SIPP instrument in early CY 2014.
During the field period for the 2012 SIPP-EHC, a separate sample was interviewed using the same instrument, but with Computer Assisted Recorded Interview (CARI) technology implemented. For a sample of the respondents during the 2013 SIPP-EHC audio recordings will again be used. The Census Bureau is using CARI during data collection to capture audio along with screen images and data values for responses during the computer-assisted personal interviews (CAPI). With the respondent’s consent, a portion of each interview is recorded unobtrusively and both the sound file and screen images are returned with the response data to a central location for coding. The CARI technology will again be used in conjunction with the 2013 SIPP-EHC. Portions of both the 2012 wave 2 SIPP-EHC and 2012 wave 1 SIPP-EHC (CARI) samples will be recorded as part of the 2013 SIPP-EHC administration. In 2012 the -CARI respondents were first interviewed and recorded as a separate sample utilizing a CARI enabled version of the 2012 SIPP-EHC instrument. In 2013, the CARI sample will be combined with the SIPP-EHC sample, which will test the capability of the SIPP-EHC instrument to perform multiple paths during the same interview period. In 2013, the SIPP-EHC CARI sample is a Wave 2 interview, while the 2012 SIPP-EHC sample will be in its third wave. The CARI recordings will not be limited to only the previously recorded cases; instead, the sample being recorded in 2013 will contain both previously recorded cases and some Wave 3 SIPP-EHC cases. This is a critical evaluation, as evidence from external surveys (Panel Study of Income Dynamics - PSID) suggests that simply asking the consent question could be associated with a significant increase in survey length. External researchers at the Institute for Social Research at the University of Michigan suspect that improved FR adherence to protocol is one of the sources for the longer interviews. Additionally, we need information on the association between CARI, interview length, and interview quality.
As a quality assurance tool, the recorded portions of the interview allow quality assurance analysts to evaluate the likelihood that the exchange between the field representative and respondent is authentic and follows critical survey protocol as defined by the sponsor and based on best practices. The 2013 SIPP-EHC field test instrument will utilize the CARI Interactive Data Access System (CARI System), an innovative, integrated, multifaceted monitoring system that features a configurable web-based interface for behavior coding, quality assurance, and coaching. This system assists in coding interviews for measuring question and interviewer performance and the interaction between interviewers and respondents.
The 2013 SIPP-EHC Field Test will be conducted in all 6 Census Regional Offices from January through March of 2013. Approximately 3,000 households are expected to be interviewed for the 2013 SIPP-EHC field test, which is comprised of approximately 2,000 cases returning for a third wave from the 2012 SIPP-EHC and approximately 1,000 cases returning for a second wave from the 2012 SIPP-EHC CARI. We estimate that each household contains 2.1 people aged 15 and above, yielding approximately 6,300 person-level interviews in the field test. Interviews take one hour on average. The 2013 SIPP-EHC will not be using the re-contact experiment previously used in the 2012 SIPP-EHC. The total annual burden for the 2013 SIPP-EHC interviews will be approximately 6,3001 hours in FY 2013.
The SIPP is authorized by Title 13, United States Code, Section 182.
2. Needs and Uses
Information quality, as described by the Census Bureau’s Information Quality Guidelines, is an integral part of the pre-dissemination review of information released by the Census Bureau. Information quality is essential to data collections conducted by the Census Bureau and is incorporated into the clearance process required by the Paperwork Reduction Act.
The 2013 SIPP-EHC Field Test will continue the EHC methodology implemented in the 2012 Field Test instrument. The EHC is intended to help respondents recall information in a more natural “autobiographical” manner by using life events as triggers to recall other economic events. For example, a residence change can in many cases occur contemporaneously with a change in employment. The entire process of compiling the calendar focuses, by its nature, on consistency and sequential order of events, and attempts to correct for otherwise missing data. For example, unemployed respondents may undertake a lengthy job search before becoming employed.
The 2013 SIPP-EHC Field Test instrument will be evaluated in several domains including field implementation issues and data comparability vis-à-vis the
2008 SIPP Panel and administrative records. Distributional characteristics such as the percent of persons receiving TANF, Food Stamps, Medicare, who are working, who are enrolled in school, or who have health insurance coverage reported in the EHC will be compared to the same distributions from the 2008 SIPP Panel. The primary focus will be to examine the quality of data that the new instrument yields for low-income programs relative to the current SIPP and other administrative sources. The field test sample is focused in low-income areas in order to increase the "hit rate" of households likely to participate in government programs. In general, there are two ways we will evaluate data quality:
(1) We will compare monthly estimates from the field test to estimates from parallel sample areas in the 2008 SIPP Panel for characteristics such as participation in Food Stamps, TANF, SSI, WIC, and Medicaid. We plan on conducting a rigorous statistical analysis using the model established for the 2010-2012 SIPP-EHC evaluations, where data from the 2008 Panel and 2012 SIPP-EHC for calendar year 2011 were mapped to a common analysis standard. The tests of significance conducted for the differences in monthly participation levels, identification of patterns of significance, and the likelihood of transition will again be applied to the 2012 calendar year comparison mapped data. Additional content will be included in the mapped data to expand the comparisons beyond the focus of the EHC section of the instrument. As with the 2010-2012 SIPP-EHC tests, we will also compare paradata related to interview performance (interview length and non-response) by region, interviewer and household characteristics, and training performance as measured by the certification test.
(2) For a small subset of characteristics, and for a subset of sample areas, we will have access to administrative record data. These data will permit a more objective data quality assessment. The acquisition of administrative data from national sources and especially from states is difficult and time consuming. We continue to work with Texas, Maryland, Illinois, and Wisconsin to acquire state level data (primarily focused on Food Stamps/SNAP and TANF). Additional state discussions are in progress. From national level administrative records, we are working to acquire additional data from the Internal Revenue Service, the detailed and summary earnings records, OASDI, SSI, Medicare, and Medicaid (from CMS). To the extent that data can be obtained in a timely way for calendar year 2012 we will include validation evaluations of the responses given both in the 2008 Panel and the 2013 SIPP-EHC data. These administrative data can tell us the rate of both false positive and false-negative reporting, as well as some indication of the accuracy of the timing of reports. The ability to make effective comparisons with administrative data is dependent on the match rate of administrative data to SIPP and re-engineered SIPP data, the timing of the receipt of the data, as well as the accuracy and quality of the administrative records. The importance of developing systems which can integrate administrative reports with survey data will continue to be demonstrated with this project.
Results from the 2010-2013 Field Tests and the 2008 SIPP Panel will be used to inform final decisions regarding the design, content, and implementation of the SIPP-EHC for its production beginning in 2014. This OMB clearance request is for the 2013 SIPP-EHC Field Test only.
3. Use of Information Technology
The survey is administered using CAPI and CARI methodologies. The Census Bureau field representatives (FRs) collect the data from respondents using laptop computers and the data are transmitted to the Census Bureau Headquarters via high-speed modems. Automation significantly enhances our efforts to collect high quality data with skip instructions programmed into the instrument and with information obtained in earlier interview segments fed back to the respondent. Response burden can be minimized by incorporating design features that make it easier to collect and record respondent information. Screening questions and lead-in questions are built into the automated instrument to skip respondents out of sections of the questionnaire that are not relevant or applicable.
Preliminary analysis from an Internet field test conducted by the SIPP Methods Panel in August and September 2000 indicated that using the Internet as a mode of collection for a complex demographic survey such as SIPP is not feasible. The SIPP automated instrument contains many complicated skip patterns and roster related components. The costs of converting a complex questionnaire such as SIPP to an online survey far outweigh the benefits even in a multimode environment. The final report is available upon request.
4. Efforts to Identify Duplication
The demographic data collected in the SIPP must be collected in conjunction with the labor force and program participation data in order for the information to be most useful; therefore, although we collect demographic data in conjunction with almost all surveys, we need to continue its present collection in the SIPP. There is no other current data source available that provides as comprehensive a set of statistics for analysis as described in question 2 above.
5. Minimizing Burden
The Census Bureau uses appropriate technology to keep respondent burden to a minimum. Examples of technology used to minimize respondent burden include: use of appropriate screening and lead in questions that serve to skip respondents out of sections of the CAPI instrument that are not relevant or applicable to them; use of flash cards to aid respondents with multiple response categories; and the arrangement of questions and sections of the CAPI instrument that facilitate the flow of administration from one topic area to another. The 2013 SIPP-EHC should likely lower respondent burden due to one interview per year rather than three in the previous SIPP instrument.
6. Less Frequent Collection
The 2013 SIPP-EHC will interview respondents annually, using the previous calendar year as the reference period. One possible consequence of the one year reference period in the 2013 SIPP-EHC, rather than the 4 month reference period in traditional SIPP, is the possibility of increased memory decay by respondents. However, use of the EHC methodology of interview should help to alleviate this decay by linking respondents’ memories to significant life events. See earlier explanation above.
7. Special Circumstances
There are no special circumstances associated with this clearance request.
8. Consultations Outside the Agency
The OMB established an Interagency Advisory Committee to provide guidance for the content and procedures for the SIPP. That committee along with the subcommittee on the topical modules has previously worked actively with the Census Bureau to assure that the SIPP content and procedures collect the appropriate data and that duplications between surveys are minimized to the extent possible. For the 2010 SIPP-EHC field test, the Census Bureau held five subject area meetings (health, general income and government programs, assets and wealth, labor force, and demographics and other items) as well as subsequent “virtual” meetings with SIPP stakeholders. These consultations were not held for individual consensus or group recommendation, and the opinions which were expressed were all given on an individual basis and not for purposes of producing a group consensus. Data users indicated a significant need for most of the existing SIPP core content. Select areas of content were added based on stakeholders input for lost topical module content. The 2013 SIPP-EHC will include revised content from the 2010-2012 SIPP-EHC instruments and will also include revisions developed subsequent to the 2012 SIPP-EHC test.
We published a notice in the Federal Register on June 11, 2012, Vol. 77, No. 112, page 34,338, inviting public comment on our plans to submit this request. We received one comment generally opposing collection.
9. Paying Respondents
Pursuant to the findings of the incentive experiment conducted as part of the 2008 SIPP panel, we will not be using incentives as part of the 2013 field data collection. However, we may plan to use incentives in the 2014 SIPP-EHC survey.
10. Assurance of Confidentiality
We are conducting this survey under the authority of Title 13, United States Code, Section 182. Section 9 of this law requires us to keep all information strictly confidential. The respondents will be informed of the confidentiality of their responses and that this is a voluntary survey by a letter from the Director of the Census Bureau that will be sent to all participants in the survey (Attachments B and C).
11. Justification for Sensitive Questions
The sources of income and assets are among the kinds of data collected and may be considered to be of a sensitive nature. The Census Bureau takes the position that the collection of these types of data is necessary for the analysis of important policy and program issues and has structured the questions to lessen their sensitivity.
12. Estimate of Respondent Burden
Based on our experience with the 1996, 2001, 2004, 2008 SIPP Panels, the
2010-2012 SIPP-EHC, and in-house testing, the burden estimates for the FY 2013 EHC test are as follows:
2012 SIPP-EHC TEST
FY 2012 BURDEN HOUR SUMMARY
-
Respondents
Waves
Responses
Hours Per Response
Total
HoursInterview
6,300
1
6,300
1.0
6,300
Totals
6,300
1
6,300
1.0
6,300
We will obtain interviews from approximately 3,000 households, yielding approximately 6,300 individual interviews (2.1 individuals 15 years old or over per household). The total number of burden hours requested for 2013 SIPP-EHC Field Test interviews is 6,300.
13. Estimate of Cost Burden
There are no direct costs to respondents participating in the survey other than the time involved in answering the survey questions.
14. Cost to Federal Government
The production costs of all parts of this field test are approximately $9,000,000 in
FY 2013. That amount is included in the estimate of total costs to the federal government of the Census Bureau's current programs supplied to the OMB.
15. Reason for Change in Burden
The 2013 SIPP-EHC Field Test will have an increase in burden hours from 5,460 in 2012 to 6,300 in 2013 due to the addition of the CARI sample.
16. Project Schedule
The 2013 SIPP-EHC Field Test advance letters will be mailed prior to interviewing. The 2013 field test interviews will be conducted from January 2013 to March 2013. No public use data product will be released, however, the research and evaluation of the data will occur from April 2013 to June 2014. A field activity status report will be available in April 2013.
The evaluation of the 2013 SIPP-EHC focuses on three components. The
2012 SIPP-EHC was administered from May through June 2012, and was the foundation for evaluating dependent interviewing (DI) with a wave-3 SIPP-EHC in 2013. Transitioning to an annual interview raised several concerns about sources of bias, including both measurement related sources of bias, such as respondent’s difficulty recalling events early in the previous year, as well as sample related sources, such as greater difficulties locating movers after one year.
The first component of the analysis rests in understanding the difficulties and impact associated with mover related loss-to-follow-up. The two components to the locating procedures considered in this project are as follows: (1) use of National Change of Address Database (NOCA) at headquarters; and (2) standardized and decentralized locating conducted by regions and interviewers. We are no longer using a mail-out and mail-back re-contact experiment to locate movers in the 2013 SIPP-EHC. However, as a component of our locating efforts, we utilize the National Change of Address (NCOA) database to evaluate the interviewed 2012 SIPP-EHC wave-2 sample information for reported changes to their mailing addresses. The first pass through the NCOA is scheduled for October, with a possible second run by December.
In addition, Field Division will propose procedures for the regions’ 2013 SIPP-EHC field activities. These procedures are evolving, but will include FastData, another data source. Each region will document the locating procedures they employ, and interviewers will record their case locating in the contact history. Following wave 3, we will evaluate forwarding addresses from the NCOA database, and these results will be compared to the actual interview responses in the 2013 SIPP-EHC as we continue to develop a reasonable mix of procedures for 2014 implementation.
The second major focus of this wave 3 SIPP-EHC evaluation is in the analysis of the data quality and especially the nature of the seam created by the joining of two annual SIPP-EHC interviews. Inherent to longitudinal panel surveys, seam bias, or the “seam effect” is a measurement error problem where the estimates of change measured across the “seam” between two successive interviews exceed the estimates of change measured within each interview. A longer recall period may exacerbate SIPP’s existing seam bias problem.
Dependent interviewing (DI), when previous interview responses are passed from a prior interview and used in the current interview, is one well-accepted approach to reduce seam bias and improve consistency. The Survey of Income and Program Participation (SIPP) has used DI in varying degrees since its inception. The current re-engineering of SIPP, using an annual survey centered on an Event History Calendar (EHC), focuses DI on reducing seam bias by providing proactive information for the interviewer.
The use of DI in SIPP-EHC is more conservative than the approach taken for the 2004 and 2008 SIPP panels; focusing on areas where DI should provide the most benefit in reducing erroneous or mistimed seam transitions. The first step towards incorporating dependent data was to extend the EHC reference period to include both the calendar reference year and interview-year months. In the 2011 SIPP-EHC this created the “overlap” of data to be passed into the 2012 SIPP-EHC. As noted above, fielding for the 2012 SIPP-EHC began in May of 2012 and was completed in June of 2012. These interview-year months are used as the data fed back to the 2013 instrument for dependent interviewing. Incorporating these dependent data in an EHC presents some design differences, as well as some unique opportunities, compared with their use in conventional questionnaires (CQ). First, the timeline data to be fed back is longer and variable. In the SIPP-CQ, dependent data includes details about only the last month of the reference period and the interview month. In SIPP-EHC, interviews can take place in any month from January to June of the interview year, and there is the possibility of up to six months of data fed back. The number of months of data fed back also varies across respondents, adding complexity.
In the short term, evaluation of the 2013 SIPP-EHC with respect to the effectiveness of DI includes field interview observations to evaluate the use of the dependent data in the course of the interview. In particular, we will focus on evaluating the utility of visual bounding in the EHC. We plan to hold interviewer focus groups to further evaluate DI in the SIPP-EHC. In the longer term, we will compare the 2011-2013 SIPP-EHC data with 2008 CQ SIPP seam and non-seam data for the three years of monthly transitions covered by both surveys.
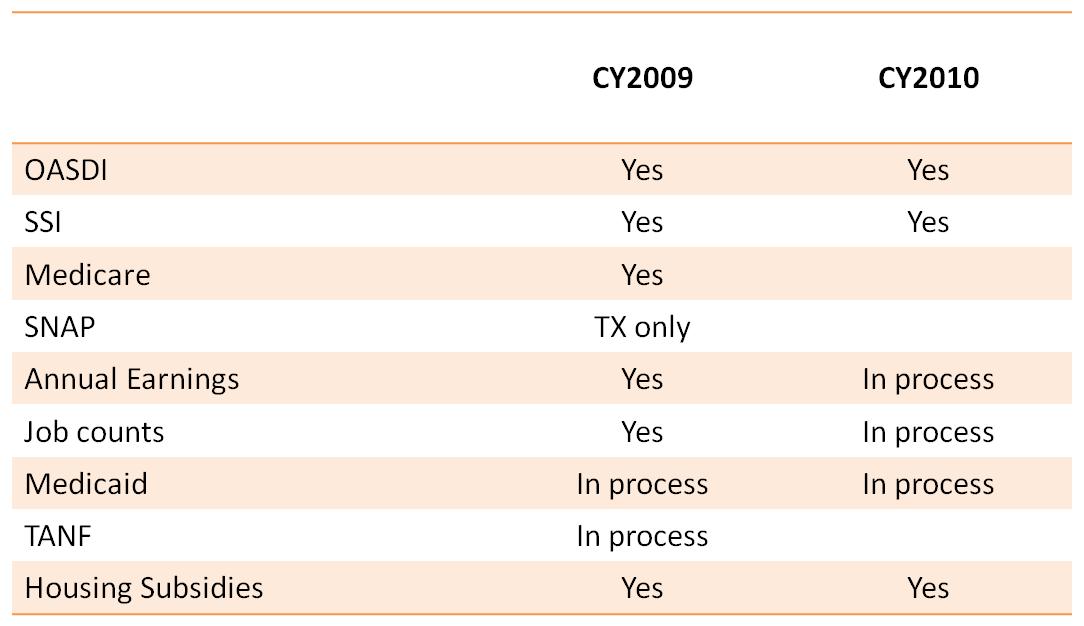
Finally, we will continue the comparisons of SIPP-EHC data to SIPP 2008 Panel data by topic, expanding the scope of topics included in the MSIPP comparison datafile, and the topics compared with administrative data. We will use available administrative records as a measure of a true monthly pattern to validate transitions and statuses against reported in the SIPP-EHC and SIPP surveys. Table 1 presents the topics for which administrative data are either available or in process of being acquired for the reference periods associated with the 2010 and 2011 SIPP-EHC data. We will continue to work to acquire these records for CY2011 as they become available.
Table 1
17. Request Not to Display Expiration Date
The expiration date for OMB number 0607-0957 is displayed in the advance letter that is sent to eligible households before the interview.
18. Exceptions to the Certification
There are no exceptions to the certification.
1See page 8 for a table on burden hours.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | Brian Harris-Kojetin |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-30 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy