Secondary studen watershed literacy items
Attachment 12 Secondary student watershed literacy items 2012-08-30.docx
NOAA Bay Watershed Education and Training (B-WET) Program National Evaluation System
Secondary studen watershed literacy items
OMB: 0648-0658
Attachment 12: Secondary
Student Watershed Literacy Items
Pre/Post Matching Code
Assign students a unique code for matching pre- and post-tests.
Demographics
What grade are you in?
Grade PreK, 1, 2, or 3
Grade 4
Grade 5
Grade 6
Grade 7
Grade 8
Grade 9, 10, 11, or 12
In science, do you usually get...
Mostly A's?
Mostly B's?
Mostly C's?
Mostly D's or below?
Our school does not give this type of grades
I prefer not to answer
Do you identify as (check all that apply):
Hispanic or Latino
American Indian or Alaska Native
Asian
Black or African American
Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander
White
Other
I prefer not to answer
Do you mostly speak English at home?
No
Yes
I prefer not to answer
Are you ....
Male
Female
I prefer not to answer
Objective 1: Define the term “watershed”
How sure are you that you know what a watershed is?
Not at all sure
A little sure
Very sure
I'm positive
Which of these is the best definition of a watershed?
A building at a water treatment plant
An area of land that drains into a specific body of water
A significant pollution event
Another name for a river or stream
Don't know
How sure are you that you know what groundwater is?
Not at all sure
A little sure
Very Sure
I'm positive
Watersheds contain groundwater.
No
Yes
Don't know

Look at the picture. Which of the following is in this river’s watershed?
|
No |
Yes |
Don't know |
The red school building |
|
|
|
The farm |
|
|
|
The city |
|
|
|
The small creek on the right |
|
|
|
Objective 2: Identify their local watershed(s)
Do you live in a watershed?
No
Yes
Don't know
Objective 3: Identify how watersheds are connected to the ocean via streams, rivers, and human-made structures
Where does most of the water from the land eventually end up?
Ocean
River
Sewer
Lake
Don't know
How sure are you that you know what a storm drain is?
Not at all sure
A little sure
Very sure
I'm positive
Ultimately, where does water end up after it enters a storm drain?
Wastewater treatment plant
A local body of water
In the ground
City sewer
Don't know
Objective 4: Identify the functions that occur in a watershed (transport, store, and cycle water)
What are some of the functions that occur within a watershed?
|
No |
Yes |
Don't know |
The transport of water |
|
|
|
The transport of materials, like soil through rivers |
|
|
|
The storage of water in lakes, rivers, groundwater, etc. |
|
|
|
The transformation of water from one state to another (liquid, ice, vapor, etc.) |
|
|
|
Objective 5: Recognize that both natural processes and human activities affect water flow and water quality in watersheds
Which of these statements is FALSE? Watershed boundaries …
Hardly ever change; they are nearly permanent
Can sometimes be changed by the actions of people
Can sometimes be changed by natural processes
Are constantly altered by both human activities and natural processes
Don't know
Which of the following can change how water drains in a watershed?
|
No |
Yes |
Don't know |
A flood |
|
|
|
A landslide |
|
|
|
A dam |
|
|
|
The construction of a storm drain |
|
|
|
How sure are you that you know what stormwater is?
Not at all sure
A little sure
Very sure
I'm positive
Stormwater pipes are similar to streams and creeks because they both:
Usually have greater water flow when it storms
Are natural habitats for plants and animals
Are constructed by people
Usually receive most of the water from drains and ditches
Don't know
When trees in a watershed are cut down and replaced with pavement and buildings, …
|
No |
Yes |
Don't know |
More water will drain into local rivers and lakes |
|
|
|
More water will drain into groundwater |
|
|
|
Water will drain into local rivers and lakes faster |
|
|
|
There will be a greater chance of flooding and erosion |
|
|
|
Vegetated buffers (that is, trees, shrubs, other plants along streams, rivers, and estuaries) …
Increase flooding along streams and rivers
Decrease erosion and filter water flowing to streams and rivers
Increase erosion and filter run-off along streams and rivers
Increase the nutrients that flow into water
Don't know
Which human activities might increase water pollution?
|
No |
Yes |
Don't know |
Water running off people’s yards and farm fields |
|
|
|
Water running off streets and parking lots |
|
|
|
Putting chemicals down storm drains |
|
|
|
Draining wetlands, such as marshes |
|
|
|
Removing trees and other plants |
|
|
|
Nutrients (such as nitrogen and phosphorus) in a stream, river, lake, or ocean can be a form of pollution.
No
Yes
Don't know
Objective 6: Identify connections between human welfare and water flow and quality
The quality of the water in rivers, lakes, and the ocean can affect the health of people living near them.
No
Yes
Don't know
The water from bodies of water, such as rivers and creeks, is used ...
|
No |
Yes |
Don't know |
for drinking after it's cleaned |
|
|
|
for farming |
|
|
|
by wildlife |
|
|
|
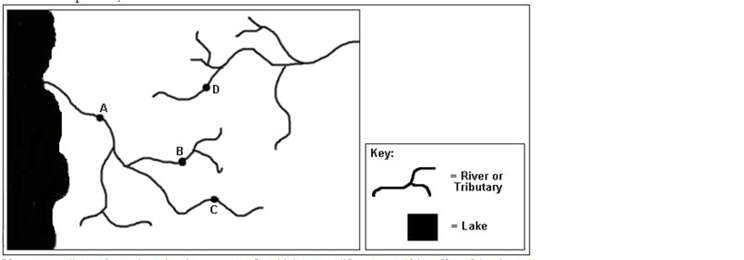
If a pollutant is put into the river at Town C, which town(s) (if any) would be directly affected by the pollution? Check all that apply.
A
B
C
D
Objective 7: Identify possible point and non-point sources of water pollution
How sure are you that you know what non-point source pollution is?
Not at all sure
A little sure
Very sure
I'm positive
Which of these is a type of non-point source pollution?
|
No |
Yes |
Don't know |
Oil in the water running off of streets and parking lots |
|
|
|
Soil in the water running off of farm fields |
|
|
|
Fertilizer in the water running off of lawns |
|
|
|
Chemicals in the water coming out of a factory pipe |
|
|
|
Rivers are the major ways through which non-point source pollution enters the ocean.
No
Yes
Don't know
How sure are you that you know what point source pollution is?
Not at all sure
A little sure
Very sure
I'm positive
Controlling point source pollution is typically easier than controlling non-point source pollution.
No
Yes
Don't know
Objective 8: Identify actions individuals can engage in to protect/restore water quality in watersheds
Which of the following would help keep water clean?
Disposing of household chemicals down the drain
Washing the car on the grass instead of on pavement
Leaving the water running while brushing teeth
Cutting down native trees in the woods
Don't know
People can help protect the water in their local watershed by:
|
No |
Yes |
Not sure |
Conserve water at home or school |
|
|
|
Help clean up or take care of a local stream, river, or beach |
|
|
|
Participate in a restoration activity such as planting trees or removing invasive plants |
|
|
|
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | UM MWEE Study Pilot Secondary Watershed Literacy |
| Author | Qualtrics |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-30 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy