2011 NRBS Technical Report
1625-0089 2011_NRBS_Technical_Report.docx
The National Recreational Boating Survey
2011 NRBS Technical Report
OMB: 1625-0089
a ppcccccc
ppcccccc
2011 NATIONAL RECREATIONAL BOATING SURVEY
TECHNICAL REPORT
February 2013
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SURVEY BACKGROUND 3
THE SURVEY DATA FILES 4
COMPUTING 2011 BOAT-RELATED STATISTICS 5
Recreational Boats in 2011 5
Exposure Hours in 2011 6
Detailed 2011 Boat Statistics 7
COMPUTING STATISTICS RELATED TO BOAT-OWNING
HOUSEHOLDS 8
COMPUTING STATISTICS RELATED TO INDIVIDUAL
PARTICIPATION IN RECREATIONAL BOATING 9
SOURCES OF DATA: THE MAIL AND TELEPHONE SAMPLES 13
6.1. The Telephone Sample 13
6.2. The Mail Sample 14
6.3. The Data Collection 17
6.4. Determining Eligibility of Survey Respondents 19
6.5. Collecting Participation and Exposure Information 20
Weighting Procedures, Response Rates,
and Accuracy of Estimates 23
7.1. Estimation Procedures 23
7.2. Survey Response Rates 32
7.3. Accuracy of Estimates 37
Definitions 43
Survey Background
The 2011 National Recreational Boating Survey (NRBS) was conducted from August 24, 2011 through December 31, 2011 by mail as well as by telephone. The mail survey targeted US households owning a recreational boat, which is registered in the state where it is most often used. The telephone survey’s target population was that of US households owning a recreational boat (whether it must be registered or not), or have a member who participated in recreational boating in 2011.
The mail survey sample was selected from States’ boat registries. A few states however, were unable to make their boat registries available for sampling to the Coast Guard. Those states were covered by the telephone survey only. The purpose of the mail survey was to collect detailed information about all boats (registered and unregistered) owned by each responding household. The boat information collected includes the type, length, model year, hull material, means of propulsion, and more). Additionally, expenditure data associated with each boat were collected as well as some information about the primary boat operator’s experience with the boat operation.
The household telephone survey was based on a Random Digit Dial (RDD) sample of landline and cell phone numbers. The sample of landline telephone numbers was selected from a stratified, list-assisted sampling frame. Within each State, we stratified zip codes as high-density or low-density boating areas. The boating density rating was based on the number of registered boats per capita. The cell phone sample on the other hand, consisted of an RDD sample of phone numbers from cellular dedicated 1000-blocks. Both the landline and cell phone samples were selected with the Virtual Genesys® system1 from the commercial vendor MSG, Inc.
The initial telephone sample was used in its entirety to target boat-owning households and to invite them to take the general boat survey. The general boat survey collects basic information about all boats owned by the household, such as the boat type, length, or the registration status. Its main objective is to cover all households, which own unregistered boats. A subsample of households from this general boat survey sample were allowed to take the detailed boat survey aimed at collecting specific information about all boats owned by households including the hull material, or the mean of propulsion. Data from the detailed boat survey is combined with that of the mail survey to obtain a comprehensive database for the analysis of registered and unregistered recreational boats used in 2011.
Note that another subsample of households from the initial telephone sample was used to find boating households (i.e. households with a member who used a recreational boat in 2011). When the computer generated a telephone number, the corresponding household was eligible to take the general boat survey if it owned a recreational boat. However, it was randomly determined whether that same household will also take the general participant survey (i.e. the questionnaire related to recreational boating participation) or not. Consequently, some boating households contacted for the general boat survey were not offered the opportunity to take the participant survey. They had to be included into the random telephone participant sample to take the participant survey. Because the number of boating households was expected to exceed that of boat-owning households, using only a portion of the initial telephone sample was sufficient to obtain the target number of households that participated in recreational boating in 2011.
When a household took the general participant survey, the survey respondent provided general information regarding each household member’s participation in recreational boating in 2011. That is, each household that took the general participant survey, indicated for each member whether he participated in recreational boating in 2011 or not, and the type of boat used by the boating participants. Furthermore, one adult and one child were randomly selected from each boating household to take the detailed participant survey that collected more information regarding the type of boating activities the boaters engaged in during the year 2011.
Sections 6 and 7 provide a detailed methodological background for the 2011 National Recreational Boating Survey. Section 6 entitled “Sources of Data: The Mail and Telephone Samples,” describes the approaches used to gather the key data elements needed to produce the statistics presented in this report. Key concepts are introduced in this section 6, and several data collection protocols are discussed. Section 7, entitled “Estimation Procedures, Response Rates, and Accuracy of Estimates,” discusses some statistical procedures that were implemented the possible bias associated with the differential selection probabilities of households, boats, and individuals. The survey nonresponse is discussed as well as the accuracy of estimates.
The Survey Data Files
The 2011 survey data are provided as CSV and SAS files, and are released in 4 datasets to facilitate their use. These 4 datasets are the following:
boat_file.sas7bdat, and boat_file.csv
boat_detailed_file.sas7bdat, and boat_detailed_file.csv
household_file.sas7bdat, and household_file.csv
file_of_individual_boaters.sas7bdat, and file_of_individual_boaters.csv
The SAS files can be imported into most statistical software and other database systems. The comma-separated values (CSV) files are released to increase the portability of the survey data.
The boat_file dataset contains information collected by telephone from the general boat survey, while the boat_detailed_file dataset contains data from both the mail survey and the detailed boat survey. The household_file dataset contains household-level data collected by telephone during the general boat survey and the participant survey. The file_of_individual_boaters dataset contains data about individual recreational boating participants. This file includes all individuals who took the general and the detailed participant survey. The variable PATCHSEL included in this file takes a value of 1 if an individual took the detailed survey and a value 0 if the individual only took the general participant survey.
The next few sections explain the use of these datasets to properly compute boating statistics.
Computing 2011 Boat-Related Statistics
Two files were created for the purpose of producing boat-level statistics. These files are named “boat_file,” and “boat_detailed_file.” The boat_file database contains all boat-related survey data collected during the telephone component of the 2011 general boat survey. This file is expected to be used primarily for producing general boat-level statistics involving registration status, usage, boat length, and exposure hours. However, a subsample of the general boat survey sample was selected for the administration of a more detailed boat survey aimed at collecting specific boat characteristics such as the hull material, the presence of engines, and associated horsepower. The data collected from the detailed boat survey were combined with the mail survey data to form the “boat_detailed_file” dataset.
Each record in the “boat_file,” and “boat_detailed_file” databases represents a recreational boat and is uniquely identified by the 2 variables MASTERID (the unique identifier of the boat-owning household) and BOATNUM (the boat number within the household). If a household owns 5 boats for example, they are numbered sequentially from 1 to 5, and the sequential number assigned to BOATNUM. One should note that for all boat-related statistics, the state used for defining US regions or for excluding some states from calculations, is always the state where the boat is registered for registered boats, and the state where the owner resides for unregistered boats and for boats with unknown registration status.
Recreational Boats in 2011
All boat statistics involving basic boat characteristics such as registration status, type of boat, length, usage in 2011 must be calculated using the boat_file dataset2. Since the survey data were obtained from a random sample of telephone numbers, the data must be weighted using the variable FINAL_WT_BOATX in order to remove any possible sample selection bias. Table 3.1 shows the weighted national distribution of boats by US regions, and boat registration status. Table 3.2 shows the national distribution of boats by boat type, registration status, and usage.
Table 3.1. Distribution of Recreational Boats by Region and Registration Status (Numbers in thousands) |
|||
Region |
Registered Boats1 |
Unregistered Boats2 |
Total |
United States, Total |
12,749 |
9,468 |
22,217 |
Northeast |
1,592 |
2,014 |
3,606 |
Midwest |
4,211 |
2,047 |
6,258 |
South |
5,059 |
3,544 |
8,603 |
West |
1,887 |
1,863 |
3,750 |
1 For registered boats, the region represents the region of registration. The State of residence was used when respondents did not know the state of registration or refused to reveal it.
2 For unregistered boats, the region represents the region of residence of the boat owner.
Table 3.2: Distribution of Recreational Boats by Type, Registration Status, and Usage in the US
Boat Type & Registration Status |
Used in 2011 |
Not Used in 2011 or Unknown |
Total |
All Boats |
14,537 |
7,680 |
22,217 |
Canoes |
1,254 |
1,251 |
2,505 |
Kayaks |
2,710 |
1,188 |
3,898 |
Pontoons |
713 |
141 |
854 |
Power Boats |
7,108 |
3,011 |
10,119 |
PWCs |
1,161 |
528 |
1,689 |
Row/Infl/Oth Boats |
1,224 |
1,194 |
2,418 |
Sail Boats |
367 |
367 |
733 |
Registered Boats |
9,510 |
3,239 |
12,749 |
Canoes |
151 |
124 |
275 |
Kayaks |
121 |
43 |
165 |
Pontoons |
692 |
110 |
801 |
Power Boats |
6,978 |
2,385 |
9,363 |
PWCs |
970 |
297 |
1,267 |
Row/Infl/Oth Boats |
379 |
183 |
561 |
Sail Boats |
219 |
98 |
317 |
Unregistered Boats |
5,027 |
4,441 |
9,468 |
Canoes |
1,103 |
1,127 |
2,230 |
Kayaks |
2,588 |
1,145 |
3,733 |
Pontoons |
21 |
31 |
53 |
Power Boats |
130 |
626 |
756 |
PWCs |
191 |
231 |
423 |
Row/Infl/Oth Boats |
845 |
1,011 |
1,856 |
Sail Boats |
147 |
269 |
417 |
Exposure Hours in 2011
Exposure hours are calculated using the boat_file dataset, the estimated number of days the boat was used in a year, the daily number of hours it was used, and the daily number of people aboard the boat on an average day. The estimated number of hours the boat was used in a year is provided by the variable DAYS_ANNUAL, the numbers of hours is given by the variable HOURS, while the number of people aboard the bard is in the variable PEOPLE. Assuming that the goal is to compute exposure hours at a certain aggregation level (e.g. boat type, region, or any combination of these), the procedure is as follows:
Compute the weighted mean number of DAYS, HOURS, and PEOPLE at the desired aggregation level using the weight variable FINAL_WT_BOATX.
Compute the weighted number of boats, and the weighted percent of boats used at the same aggregation level.
Total exposure person-hours is then calculated by as follows:
Exposure Hours = BOATS × Percent Usage × Number of Days × HOURS × PEOPLE.
This procedure was used to obtain exposure hours by region shown in Table 3.3.
Table 3.3: Exposure Hours for various US Regions
Region |
Total boats |
Boats used (%) |
Total Exposure (hrs) |
United States |
22,216,745 |
65.5 |
2,972,998,662 |
Power boats |
10,119,242 |
70.3 |
2,053,042,254 |
Sail boats |
733,457 |
50.4 |
70,905,689 |
PWCs |
1,689,344 |
69.3 |
130,685,741 |
Canoes |
2,505,300 |
50.1 |
90,349,786 |
Kayaks |
3,897,798 |
69.3 |
133,124,784 |
Pontoons |
853,940 |
83.4 |
301,208,760 |
Row/Inf/Oth boats |
2,417,663 |
50.7 |
193,681,648 |
Remark:
Note that boat-owning households that participated in the boat survey reported the number of days a particular boat was used from January 2011 until the reference month (i.e. the month prior to the survey month). The total number of days that boat was used in the entire year had to be estimated when the reference month was not the month of December. An adjustment factor was developed for different reference months, and different states to extrapolate the reported number of days to cover the entire year 2011. The method used to derive the adjustment factors is similar to the method used in section 5 for deriving similar adjustment factors for individual participation in recreational boating.
Detailed Statistics on Recreational Boat in 2011
As previously indicated, the “boat_detailed_file” database is a boat-level dataset, which is used to produce detailed boat-level statistics. These statistics will always be weighted using the weight variable named as FINAL_WT_BOATSEL. This dataset contains detailed boat characteristics such as the motor size, the hull material, or the engine type. Moreover, all data on the economic impact of boating is included in this dataset, which combines data from both the mail and the telephone surveys. The weight variable FINAL_WT_BOATSEL accounts for selection probability of each boat in the mail or telephone sampling frame it was selected from.
Computing Statistics Related to Boat-Owning and Boating Households in 2011
Household-level statistics are calculated using the household-level file named “household_file,” which contains data collected exclusively by telephone. All households were eligible to take the general boat survey provided they own a recreational boat. However only a randomly-selected subset of households were given the opportunity to take the participant survey aimed at collecting data on their participation in recreational boating. The 2011 household file has 36,959 records associated with households that participated in the boat survey as boat owners, or in the participant survey or in both.
Since the households were sampled with differential selection probabilities, the data must be weighted in order to obtain unbiased household statistics. This database contains 2 weight variables that should be used for this purpose. These weight variables are the following:
FINAL_WT_PHONE_HH
This variable represents the survey weight associated with all households in the database. The use of this weight variable is recommended when computing statistics that pertain to boat-owning households. For other statistics, it is recommended to use the second weight variable FINAL_WT_PHONE_HH_PATCH
FINAL_WT_PHONE_HH_PATCH
This variable represents the survey weight associated with all households in the database that completed the participant survey. For households that did not complete the participant survey, this variable contains a missing value.
Note that the 2 weight variables are identical for households that own no recreational boat. A total of 83,522 households, which were eligible to take the boat survey only, turned out not to own any boat. These households were not interviewed and did not provide any survey data. Therefore, they were excluded from the analysis. The 36,959 households contained in the household file are distributed by type of survey taken as shown in Table 4.1.
Table 4.1 Distribution of households by type of survey taken
Survey Completed |
Participant Survey Eligibility |
Total |
|
Eligible to Take Participant Survey |
Eligible to Take Boat Survey Only |
||
Boat Survey Only |
1,201 |
14,419 |
15,620 |
Boat & Participant Surveys |
3,928 |
0 |
3,928 |
Participant Survey Only |
17,411 |
0 |
17,411 |
Total |
22,540 |
14,419 |
36,959 |
SELECTION OF RECORDS FOR ANALYSIS
When computing percentages from the 2011 household database, it is essential to select the appropriate set of records in addition to selecting the correct analytical and weight variables. The estimation of household participation in recreational boating for example should be based solely on households that completed the participant survey. These households may be identified using the variable STATUS contained in the database. Using all households in the database will result in an underestimation of the participation rate.
A few questions in the participant survey were asked to a randomly selected sample of adults, and children. Although the corresponding variables do not represent household characteristics, they were included in the household database for possible use in special analyses.
Computing Statistics Related to Individual Participation in Recreational Boating
Statistics pertaining to participation in recreation boating by individuals are calculated using the file of individual boaters “file_of_individual_boaters.” In 2011, interviews were conducted continuously for the last 3 months of the year, and for the month of January of 2012. Therefore, there were 4 Survey Months, which are October 2011, November 2011, December 2011, and January 2013. In a given survey month however, respondents were asked questions about their boating participation from January until the Reference Month, which is the month prior to the survey month. Consequently, the 2011 survey gathered data about 4 reference months, which are September 2011, October 2011, November 2011, and December 2011. This notion of reference month is important here due to the fact that a survey respondent, who indicated not having participated in boating in September 2011, will no longer be interviewed for the rest of the year 2011 even though he may still participate in boating by the end of 2011. Therefore, boating participation data collected during each reference month must be adjusted in order to produce the 2011 annual boating participation statistics.
Adjusting Reference-Month Data
The file of individual boaters contains a variable named “Adjust,” which takes values from 1 to 1.113 with the exceptions of a few individuals who did not take the participant survey, and who were assigned an adjustment value of 0. This adjustment value represents the predicted number of 2011 boating participants for each individual who participated in boating any time from January 2011 to the reference month. For example suppose that the adjustment factor associated with an individual in the file is estimated at 1.09. If that individual boated anytime from January to the reference month, then he will count not as 1 boater for the whole year, but as 1.09 boater(s) for the entire year 2011. In other words, for each individual who boated from January to the reference month, there is 0.09 individual who did not boat during that period, but who eventually boated in 2011 at a later time. The magnitude of this adjustment factor varies by region, and by reference month.
In order to compute the number of recreational boating participants in a given geographic area, one needs to proceed as follows:
Creating the Analytical Variable
Create the appropriate analytical variable by multiplying the 2 variables PARTA3 and ADJUST. If the created analytical variable (i.e. the adjusted participation indicator) is named APARTA (adjustment factor), then both variables will be distributed for example as shown in the following 2 tables:
PARTA |
Frequency |
Percent |
(0) No |
43,213 |
74.3 |
(1) Yes |
14,917 |
25.7 |
APARTA |
Frequency |
Percent |
0 |
43,319 |
74.5 |
1 |
4,479 |
7.7 |
1.0173 |
1,643 |
2.8 |
1.0188 |
1,093 |
1.9 |
1.0411 |
1,756 |
3.0 |
1.0493 |
547 |
0.9 |
1.0505 |
39 |
0.1 |
1.0614 |
1,479 |
2.5 |
1.0744 |
1,072 |
1.8 |
1.0894 |
873 |
1.5 |
1.0902 |
1,401 |
2.4 |
1.1133 |
429 |
0.7 |
The analytical variable APARTA to be used for analysis, will general take value 1 for the boaters who participated in the survey in the month of December, and therefore represent only themselves.
Compute Proportion of Boaters Among “Participant Survey” Takers
Using the analytical variable APARTA created in the previous step; compute the proportion of boating participants by taking the weighted mean of that variable.
The average must be solely based on individuals who took the participant survey. The variable INPATCH contained in the file of individual boaters indicates who participated in the survey and who did not, and can be used to filter survey takers only.
The weighted average should be calculated using one of the 2 weight variables FINAL_WT_PATCH, or FINAL_WT_PATCHSEL. For the purpose of calculating general boating participation statistics, one should always use FINAL_WT_PATCH. However, if the goal is to compute participation in specific boating activities, or participation with specific boat types, then it is recommended to use the FINAL_WT_PATCHSEL weight variable developed for those who took the detailed participant survey.
Estimate the Total Number of Individuals in the Domain of Interest
The population total within the domain of interest is calculated by summing the appropriate weight variable for all individuals in the domain of interest, not just those who took the survey.
Estimate the Number of Boating Participants in the Domain of Interest
The number of boating participants is obtained by multiplying the population total within the domain of the last step (c) by the percent participation of step (b).
How Are Adjustment Factors Calculated?
For each reference month, all adults who for the first time in 2011 participated in recreational boating during that reference month are identified. These are 2011 first-time boaters.
For the purpose of calculating the adjustment factors, the South and West regions are further divided into northern and southern parts4. Moreover, for the reference month of November only, the northern parts associated with the South and West regions are collapsed, because the participant survey was administered in these 2 areas during the same month of November, and the resulting participation data will be adjusted the same way. Consequently, for the reference months 9, 10, and 12, a total of 6 new regions were defined, which are the Northeast, Midwest, South-South, South-North, West-South, and West-North. For reference month 11 however, 5 new regions were defined, which are the Northeast, Midwest, South-South, West-South, and the Southwest-North.
The percent of first-time boaters is calculated for each cell defined by the new region and the reference month. These estimates of percent first-time boaters are weighted using the weight variable FINAL_WT_PATCH contained in the individual database.
Let
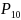 ,
,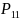 ,
and
,
and
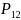 be the percent of first-time boaters in reference months 10, 11 and
12 respectively. The adjustment factors are calculated according to
the following table:
be the percent of first-time boaters in reference months 10, 11 and
12 respectively. The adjustment factors are calculated according to
the following table:
-
Region
Reference Month
Adjustment Factor
South-South, West-South, and PR
11
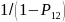
12
1
Northeast, Midwest, Southwest-North,
9
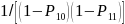
10
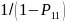
11
1
Sources of Data: The Mail and Telephone Samples
The target population for the USCG’s 2011 National Recreational Boating Survey was all US households that owned a recreational boat or had a member who participated in any recreational boating activity in 2011. The objectives of this survey were to measure the following:
Household boat ownership, and boating participation
Individual boating participation, boating safety awareness and behaviors
Exposure to hazards evaluated by the time boats and boaters are on the water, or the time when boats are in docked recreation.
Economic impact of recreational boating.
To produce individual-level statistics, we considered all members in the selected households to collect boating participation information, and randomly selected a maximum of 1 adult and 1 child to gather information on the participants’ boating activities. Children were interviewed only in the presence of an adult household member.
This survey used two data collection modes, which are the mail and the telephone. To ensure an adequate coverage of the target population, landline and cell phone samples were selected. The mail survey was used only for the collection of data on registered recreational boats in use in the United States, while the telephone was used to collect both boat-related information as well as household and individual data on participation in recreational boating.
The addresses used on the mail survey questionnaire were obtained from boat registries for the States that made that information available to the Coast Guard. The boat registries maintained by each State already contain a wealth of data about boats, which is readily available to the Coast Guard. However, that information is limited to recreational boats that owners are required to register. In order to collect information about unregistered boats and about registered boats in states for which boat registries were unavailable, we also conducted a telephone survey in all States. The use of boat registries was cost-effective since the owners were already identified, which made direct contact possible. The telephone survey on the other hand required a large number of random calls before a household that belongs in the target population can be reached.
The Telephone Sample
The initial telephone sample in its entirety was used to target boat-owning households. However, only a portion of the telephone sample was used to find boating households (i.e. a household with a member who used a recreational boat in 2011). When the computer generated a random telephone number, the corresponding household was eligible to take the boat survey (i.e. the boat-related questionnaire). However, it was also randomly determined whether that same household will also take the participant survey (i.e. the participation-related questionnaire). That is, some boating households called were not offered the opportunity to participate in the participant survey. They had to be included into the random telephone participant sample. Because the number of boating households is expected to exceed that of boat-owning households, using only a portion of the initial telephone sample was sufficient to obtain the target number of households that participated in recreational boating in 2011.
The sampling of landline telephone numbers was based on the Random Digit Dial (RDD) methodology, and was selected from a stratified, list-assisted sampling frame. Within each State, we stratified zip codes as high-density or low-density boating areas. The boating density rating was based on registered boats per capita, as provided by Info-Link. Within each density stratum, we selected an RDD sample from working banks (1+ blocks; see below for description). We sampled telephone numbers from exchanges in the high-density zip codes at a higher rate than from exchanges in the low-density zip codes.
All possible telephone numbers are divided into blocks (or banks) of 100 numbers. A 100-block is the series of 100 telephone numbers defined by the last two digits of a 10-digit phone number. For telephone numbers with the first eight digits in common, there are 100 possible combinations of the last two digits (ranging from 00–99) - this is one 100-block. To greatly enhance efficiency (and reduce costs), 100-blocks without directory-listed telephone numbers (called zero-blocks) are excluded (or truncated) from the sampling frame. The exclusion of zero-blocks reduces the frame coverage, but considerably increases productivity. The remaining 100-blocks, those with at least one listed residential number (or 1+ blocks), comprise the sampling frame - referred to as a truncated, list-assisted frame since listed telephone numbers help in improving sampling efficiency. All possible telephone numbers, both listed and unlisted, in 1+ blocks are eligible for RDD selection with equal probability.
The cell phone sample on the other hand, consisted of an RDD sample of phone numbers from cellular dedicated 1000-blocks. The blocks originated from the Telcordia® LERG. The cellular dedicated banks were then identified by coding provided on the LERG. Both the landline and cell phone samples were selected with the Virtual Genesys® system5 from the commercial vendor MSG, Inc.
The Mail Sample
The mail survey sample was used for gathering registered boat-related information only. We worked with a third-party vendor, Info-Link Technologies, Inc., to obtain the registered boat sample. Info-Link provided the count of registered boats by boat type. Based on these counts, we allocated the sample to boat types. In order to ensure an adequate coverage of registered boats, it was necessary to oversample large registered boats.
Table 6.1 describes the mail and telephone samples that were used to collect boat-related data, by boat type and size.
Table
6.1: Mail and
Telephone Survey Samples used to Collect Boat-Related
Information
Boat Type and Size |
Registered Boats |
Completed Interviews |
|||
Sampling Frame |
Selected |
Telephone |
Total |
||
Total, all boats |
12,505,656 |
36,126 |
13,020 |
19,548 |
32,568 |
Power Boat <16 ft. |
3,121,539 |
5,941 |
1,429 |
1,920 |
3,349 |
Power Boat 16–20 ft. |
4,562,441 |
8,708 |
3,184 |
4,474 |
7,658 |
Power Boat 21–28 ft. |
1,435,749 |
5,135 |
1,852 |
1,742 |
3,594 |
Power Boat >28 ft. |
270,313 |
2,021 |
929 |
466 |
1,395 |
Sail Boat <25 ft. |
205,132 |
2,099 |
930 |
677 |
1,607 |
Sail Boat >25 ft. |
112,301 |
2,318 |
1,252 |
349 |
1,601 |
Pontoon Boat |
801,466 |
2,811 |
1,410 |
904 |
2,314 |
Personal Water Craft (PWC) |
1,279,095 |
4,806 |
1,083 |
1,339 |
2,422 |
Canoe |
2,287 |
315 |
2,858 |
3,173 |
|
Kayak |
|
|
270 |
2,684 |
2,954 |
Other |
|
|
366 |
2,135 |
2,501 |
Table 6.2 shows the distribution of the allocated and complete samples by state and by data collection mode. The sample allocation represents the target number of households for which an interview should be completed. The “Completes” column contains the final number of interviews that were ultimately completed.
Table 6.2: Mail and Telephone Allocated and Complete Samples
|
Boat Sample |
Participation Telephone Sample |
||||||
Allocation |
Completes |
|||||||
State |
Phone |
Total |
Phone |
Total |
Allocation |
Completes |
||
Total U.S. |
12,705 |
17,295 |
30,000 |
13,020 |
19,548 |
32,568 |
22,540 |
21,339 |
Alabama |
360 |
376 |
736 |
341 |
391 |
732 |
349 |
324 |
Alaska |
123 |
200 |
323 |
143 |
349 |
492 |
356 |
320 |
Arizona |
213 |
200 |
413 |
152 |
213 |
365 |
334 |
322 |
Arkansas |
298 |
375 |
673 |
215 |
377 |
592 |
336 |
321 |
California |
0 |
654 |
654 |
0 |
668 |
668 |
1,993 |
1,915 |
Colorado |
156 |
200 |
356 |
110 |
256 |
366 |
388 |
375 |
Connecticut |
234 |
200 |
434 |
291 |
289 |
580 |
349 |
320 |
Delaware |
82 |
200 |
282 |
82 |
215 |
297 |
344 |
322 |
DC |
0 |
200 |
200 |
31 |
122 |
153 |
366 |
361 |
Florida |
695 |
677 |
1,373 |
703 |
704 |
1407 |
334 |
323 |
Georgia |
444 |
330 |
774 |
383 |
320 |
703 |
328 |
320 |
Hawaii |
0 |
200 |
200 |
47 |
233 |
280 |
342 |
325 |
Idaho |
0 |
342 |
342 |
0 |
392 |
392 |
356 |
328 |
Illinois |
482 |
323 |
804 |
505 |
324 |
829 |
410 |
384 |
Indiana |
0 |
523 |
523 |
0 |
472 |
472 |
924 |
875 |
Iowa |
311 |
419 |
729 |
295 |
415 |
710 |
421 |
396 |
Kansas |
210 |
200 |
410 |
219 |
241 |
460 |
336 |
322 |
Kentucky |
309 |
251 |
559 |
291 |
253 |
544 |
346 |
336 |
Louisiana |
366 |
441 |
807 |
2 |
650 |
652 |
1,274 |
1,201 |
Maine |
203 |
257 |
459 |
283 |
405 |
688 |
352 |
320 |
Maryland |
319 |
215 |
535 |
337 |
354 |
691 |
342 |
321 |
Massachusetts |
321 |
200 |
521 |
358 |
374 |
732 |
373 |
343 |
Michigan |
559 |
705 |
1,264 |
714 |
796 |
1,510 |
389 |
358 |
Minnesota |
0 |
1,346 |
1,346 |
0 |
1,378 |
1,378 |
400 |
361 |
Mississippi |
294 |
336 |
630 |
305 |
335 |
640 |
336 |
325 |
Missouri |
398 |
394 |
792 |
361 |
411 |
772 |
352 |
339 |
Montana |
0 |
434 |
434 |
7 |
459 |
466 |
391 |
361 |
Nebraska |
157 |
200 |
357 |
111 |
201 |
312 |
329 |
321 |
Nevada |
77 |
200 |
277 |
54 |
227 |
281 |
340 |
327 |
New Hampshire |
0 |
350 |
350 |
0 |
378 |
378 |
440 |
393 |
New Jersey |
297 |
200 |
497 |
248 |
246 |
494 |
392 |
375 |
New Mexico |
0 |
200 |
200 |
31 |
208 |
239 |
331 |
320 |
New York |
514 |
280 |
794 |
584 |
373 |
957 |
343 |
323 |
North Carolina |
448 |
355 |
802 |
471 |
378 |
849 |
340 |
323 |
North Dakota |
152 |
215 |
367 |
163 |
236 |
399 |
341 |
327 |
Ohio |
481 |
355 |
836 |
548 |
408 |
956 |
360 |
340 |
Oklahoma |
308 |
296 |
604 |
265 |
294 |
559 |
352 |
335 |
Oregon |
303 |
268 |
571 |
443 |
356 |
799 |
362 |
332 |
Pennsylvania |
458 |
291 |
749 |
566 |
306 |
872 |
334 |
321 |
Rhode Island |
53 |
200 |
253 |
90 |
278 |
368 |
360 |
332 |
South Carolina |
404 |
570 |
974 |
381 |
558 |
939 |
342 |
321 |
South Dakota |
153 |
200 |
353 |
162 |
259 |
421 |
358 |
343 |
Tennessee |
374 |
306 |
680 |
404 |
324 |
728 |
336 |
320 |
Texas |
590 |
333 |
923 |
482 |
370 |
852 |
346 |
331 |
Utah |
130 |
200 |
330 |
119 |
267 |
386 |
341 |
321 |
Vermont |
35 |
200 |
235 |
69 |
350 |
419 |
358 |
320 |
Virginia |
385 |
270 |
655 |
430 |
305 |
735 |
345 |
321 |
Washington |
384 |
313 |
697 |
518 |
356 |
874 |
352 |
333 |
West Virginia |
80 |
200 |
280 |
48 |
235 |
283 |
341 |
325 |
Wisconsin |
493 |
696 |
1,189 |
583 |
787 |
1,370 |
369 |
341 |
Wyoming |
26 |
200 |
226 |
54 |
229 |
283 |
362 |
343 |
Puerto Rico |
26 |
200 |
226 |
21 |
223 |
244 |
1,245 |
1,233 |
The Data Collection
The Telephone Collection Mode
The telephone sample contained a mix of cell and landline RDD records. Landline sample records were pre-screened to exclude businesses and non-working numbers. We released samples periodically throughout the fielding period. Sample management decisions were made by carefully monitoring completed interviews and sample resolution across each market. All phone numbers in the sample were dialed and assigned a final disposition. Table 6.3 shows that a total of 1,646,293 phone numbers were dialed, which resulted in 15,557 boat survey completes, and 20,137 participant survey completes. Note that these numbers represent phone calls that reached boat-owning and boating households respectively, and which resulted in an interview. However, the number of interviews may exceed the number of phone calls since occasionally two interviews were conducted during the same phone call.
The boat survey was administered to boat-owning households throughout the United States. Interviewers screened households to identify individuals who were16 years old or older. Next, interviewers identified if the household owned any boats. Finally, interviewers collected boat information from a household member who was knowledgeable about the boats that the household owned. When the selected household was eligible for the participation survey, the boating participation module of the questionnaire was administered, regardless of whether the household owned any boats or not.
The dispositions represent the final result of each telephone call for each record in the survey sample (some examples of dispositions include, Complete, Definite Refusal, Non-working number, etc.). The Computer-Assisted Telephone Interviewing (CATI) system automatically stored dispositions of each call attempt on all records in the sample. This provides a complete call history for each record. The call history was displayed on the interviewer’s screen during each attempt. As previously indicated, final dispositions for the telephone survey are provided in Table 6.3.
Table 6.3. Distribution of sample telephone numbers by disposition.
Disposition |
Number of Phone Calls |
Percent (%) |
Total Number of Phone Calls |
1,646,293 |
100 |
002 - Definite Refusal-Selected |
11,835 |
0.7 |
003 - Definite Refusal-Non-Selected |
160,905 |
9.8 |
004 - Language Barrier |
6,809 |
0.4 |
006 - Physical/Mental Impairment |
240 |
0.0 |
007 - Bad Audio Connection |
2 |
0.0 |
008 - Nonworking Number |
251,439 |
15.3 |
009 - Fax Machine/Modem |
38,195 |
2.3 |
010 - Not a Residence |
83,624 |
5.1 |
012 - Not a Cell Phone |
1 |
0.0 |
016 - Household Unavailable |
2,483 |
0.2 |
017 - No Adults Associated With This Line |
3,026 |
0.2 |
027 – Don’t Own Boat AND Not Selected for Patch |
83,521 |
5.1 |
028 - Boat Used to Make Money |
310 |
0.0 |
029 - Respondent Less Than 16 Years Old |
27 |
0.0 |
031 - Eligible Respondent Refused and No Other Adults in Household |
197 |
0.0 |
032 - Sampled Cell Phone Not Confirmed By Respondent |
4,593 |
0.3 |
036 - Boat Owner Whose Boat Was Not Eligible or Selected |
725 |
0.0 |
037 - Cell Phone Record, Respondent Not Knowledgeable About Boats Owned in Household |
810 |
0.0 |
061 - Boat Complete |
15,557 |
0.9 |
062 - Participant Complete |
20,137 |
1.2 |
075 - DIALER - Nonworking Number |
606,229 |
36.8 |
094 - Dialed Maximum Attempts |
355,628 |
21.6 |
The Mail Data Collection Mode
As previously indicated, we used a mail survey to collect boat survey data for registered boats in states where lists were made available, and for boats, which are documented with the United States Coast Guard. We worked Info-Link Technologies, Inc., to obtain state registration databases. Info-Link specializes in sample list procurement related to marine and outdoor recreation. To reinforce the legitimacy of our request, states were provided with a letter from the US Coast Guard describing the project and our request to use their registration lists. To facilitate the mailing, sample records obtained from the vendor were provided in standardized format, and contained the following variables: owner name, owner mailing address, and vessel type.
Almost all States authorized the use of their boat registries by the Coast Guard for the purpose of conducting the mail survey, with the exception of the following six: California, Idaho, Indiana, Louisiana, Minnesota, and New Hampshire. The mail survey protocol consisted of an initial contact, a mail survey packet, and two reminders (one postcard and a second survey packet). The mail survey was offered in English only. All sampled records were mailed an advance letter introducing the survey. This letter identified the U.S. Coast Guard as the survey sponsor, explained how the data will be used, and encouraged cooperation. The letter also communicated both the importance of the survey for improving boating safety, and the benefits of survey participation. Potential respondents were also informed that participation would be voluntary.
Determining Eligibility of Survey Respondents
As indicated in previous sections, the target population of the National Recreational Boating Surveys is all US households that own a recreational boat, or have a member who participated in a recreational boating activity in 2011. All mail survey respondents were generally eligible for the survey, since they all owned a registered boat. There were exceptions when the address was inaccurate, or the household no longer owned the selected boat. Eligibility to the telephone survey required the implementation of a specific identification protocol.
When a household responded to the telephone, its recreational boat ownership status had to be determined first. This task was accomplished by asking the responding household the following question: “Do you, or does anyone in your household own any boats? Please include canoes, kayaks, inflatable boats, and personal watercraft.” If the household owned a boat, the respondent was asked about the number of boats owned, and the interview continued with the household member knowledgeable about these boats. At this stage, we did not know whether the boats owned were used for recreational purposes only or not. Then, all boats owned were reviewed starting with the longest, and moving down to the shortest. Any boat that was used in 2011 for any purpose that makes money such as guiding tours or commercial fishing was not eligible for the survey, since it was not considered to be a recreational boat. For eligible boats, additional information such as the boat type, or it registration status was collected.
Only if the household was also selected for the participant survey, did we ask questions regarding household members’ participation in recreational boating. A selected household was considered as a boating household if any one of the following conditions was satisfied:
One of the recreational boats owned by the household was used by a household member anytime from January 2011 until the month before the interview date.
A household member has spent time in a recreational boat from January 2011 until the month before the interview day, whether the boat is owned by the household or not.
A household member has fished from a recreational boat from January 2011 until the month before the interview day.
The household owns boats but does not own a canoe, or a kayak, and has a member who used one these two boat types from January 2011 until the month before the interview day.
The household owns a canoe or a kayak but no one in the household used it. However, a household member used a canoe or a kayak that belongs to someone else from January 2011 until the month before the interview day.
The household does not own a boat, but a household member used a canoe or a kayak that belongs to someone else from January 2011 until the month before the interview day.
When the responding household was determined to be a boating household, the interview continued in order to determine the number of individual recreational boating participants who live in that same household. At this moment, the respondent was reminded that recreational boating includes boating in kayaks and canoes and fishing from boats, and that we were interested in days when he personally were on the boat. Afterwards, the respondent was asked the following two questions:
So far in 2011, was there any day when you went out on the water in a recreational boat? We are asking only about your participation in boating.
So far in 2011, was there any day when you spent more than an hour on a recreational boat while it was not on the open water?
If the respondent answered yes to either one of these two questions, he was considered to be a recreational boating participant. Afterwards, the same questions were asked about the other members of the household.
Collecting Participation and Exposure Information
Recreational Boating Participation
Boating participation by individuals represents the total number of people who participated in recreational boating during a given time period. Interviews for the NRBS took place between September 2011 and January 2012. In order to estimate participation for 2011, the sample was staggered across several months. The purpose of this was to obtain a respondent’s participation status for the month before the interview date, and at any time during the year 2011 before the previous month. That is, if the interview is conducted on any given day of month M, the respondent’s participation status is determined for month M-1 as well as for all previous months of 2011 from month 1 (i.e. January 2011) through M-2. The previous month estimates can then be combined with the cumulative month estimates to identify participants who participated for the first time in the previous month.
Northern states were administered the participant survey in September, October and November. In December of 2011, interviews were not conducted in the North. Southern states on the other hand, were administered the survey in December 2011, and in January 2012. Individual respondents to the participant survey were asked the following 3 questions:
So far in 2011, was there any day when you went out on the water in a recreational boat? We are asking only about your participation in boating.
Did you go out on the water in a recreational boat during the month of [last calendar month]?
Did you go out on the water in a recreational boat at any time in 2011 before the month of [last calendar month]?
Question (a) was asked for the sole purpose of deciding whether questions (b) and (c) should be asked too. However, only the last 2 questions (b) and (c) were used for the purpose of calculating the overall recreational boating participation. For Northern states where the data collection began in September, participation data was collected as follows:
Individuals interviewed in September provided the data needed to obtain total participation in Northern states from January through August (c.f. question (b)).
October interviews provided the data needed to calculate participation from January through August (c.f. question b), and for the month of September alone (c.f. question c). At this stage, we will have two estimates of participation in Northern States from January through August, with the first estimate obtained from September interviews, and the second from October interviews. A new January-August participation estimate will be calculated by averaging these two numbers, which will then be added to the September participation numbers obtained from October interviews to obtain the January-September recreational participation in Northern States.
The same process is continued until the month of November, which will ultimately yield participation numbers from January through the end of October. January-October numbers are then used as estimates for annual recreational boating participation in Northern States. The only recreational boating participants this estimation approach could have missed are those who boated in Northern States for the first time of the year, in November or in December. We assumed this number to be negligible given the cold temperatures observed in those States at that time of year.
The calculation of recreational boating participation in Southern States followed the same method, with the exception that interviews were conducted in those states until the month of January of 2012. This allowed us to compute boating participation until the month of December.
Calculation of Exposure Statistics
The evaluation of exposure is based on a procedure, which is similar to the one used for obtaining recreational boating participation. For a given boat type, the number of exposure hours is calculated using the following 5 numbers:
Number of boats of the type of interest
Percent of boats used in 2011
Average of days of use per boat
This average is calculated using all boats associated with the geographic area of interest. The number of days is collected by asking for each boat, the following question: “…how many days has the boat been used?”
Average number of boating hours per day
This average is calculated using all boats associated with the geographic area of interest. The number of boating hours is collected by asking for each boat, the following question: “…On an average day the boat was used . . . . how many hours was the boat on the water?”
Average number of passengers by trip.
This average is calculated using all boats associated with the geographic area of interest. The number of passengers per trip is collected by asking for each boat, the following question: “…On an average day the boat was used . . . . how many people were aboard the boat?”
All interviews conducted during the month of September in Northern States will provide sufficient data to compute total exposure from January through August in those states by summing the products (Number of boats) × (Percent boats used in 2011) × (Average number of boat days per boat) × (Average number of daily boating hours per boat) × (Average number of Passengers per boat). In the month of October, one can compute exposure hours as discussed in section 3.2.
Estimation Procedures, Response Rates, and Accuracy of Estimates
Section 6 describes how the mail and telephone samples were designed, as well as how key survey data elements were collected. In Section 7, we will describe the different response rates achieved in the mail and telephone surveys, as well as the general procedures used to extrapolate the survey data from observed samples to the different populations of interest.
Estimation Procedures
The 2011 National Recreational Boating Survey (NRBS) targeted all US households that owned recreational boats, or have members who participated in recreational boating in 2011. During the NRBS’ data collection phase, information was collected about boats, households, and individuals who were all selected with varying selection probabilities. For example all recreational boats owned by a household will have the same chance of being selected. However, randomly choosing one boat implies that the overall chance of selection of a boat depends on the number of boats owned by the household. Consequently, the sole boat owned by a household will have three times the chance of being selected than any one of the 3 boats owned by another household. Likewise, boating participants who live in one-person households will have twice the chance of selection of those who live in two-person households. Moreover, the number of cell and landline phone numbers owned by boating households will also affect the selection probability of their members. To avoid any possible selection bias in our estimates, these differential selection probabilities must be compensated for by weighting. The weighting process typically starts by assigning to each sample unit of analysis (e.g. a boat, a household, or an individual) a base weight that corresponds to the inverse of the probability with which the unit was included into the sample. This base weight may then go through several adjustment phases to account for additional random events that affected the selection of the sample units. These adjustments will ultimately produce what is known as the final weight.
Estimates of totals are obtained by calculating the weighted sum of all collected sample values, using the final weight. Likewise, means and ratios are calculated by dividing two weighted sums. The resulting estimates will be statistically unbiased in the case of estimates of totals, and approximately unbiased in the case of estimates of means or ratios.
The data collected at the household level was used to produce the following 7 types of statistics:
Household-level statistics, which are all based on information collected about households in the telephone survey. For example, statistics about household boat ownership are calculated based on all household interviews, whether the households were selected for the boating participation module or not. These statistics require the use of a “general household weight.”
Household-level statistics, which are based on information collected about the households that were randomly selected to take the boating participation series of questions. The “household participation weight” will be used for producing these statistics.
Boat-level statistics for registered boats only. These statistics are based on information collected about registered boats in the mail survey, and will be calculated using the “registered boat weight.”
Boat-level statistics for both registered and unregistered boats using data collected in the phone survey only. All statistics on exposure hours fall into this category. These calculations will be based on the “general boat weight.”
Boat-level statistics for both registered and unregistered boats using data collected in the mail survey of registered boats, as well as in the phone survey from a selected subsample of boats. Statistics related to the hull material fall into this category. The “selected boat weight” will be used for all statistics in this group.
Individual-level statistics, which are based on information collected about all members in households selected for the participation module. For example, the individual boating participation status of all members of a boating household was collected. The weight needed for these statistics is the “general individual weight.”
Individual-level statistics, which are based on information collected about randomly-selected adults or children who are members of a boating household. The data collected from these selected individuals was about their participation in specific recreational boating activities. We used the “selected individual weight” to analyze this data.
The next few sections discuss the general approaches used for deriving the 7 sets of weights we have just defined.
General Household Weights
A large number of steps were necessary to create the general household weights.
The Dual-Frame CATI Weighting
For each state and boating density stratum, the probability that a landline telephone number is selected from the RDD frame is the number of selected telephone numbers (nL) from the RDD frame divided by the number of possible numbers on the frame (NL). The base weight is the inverse of the selection probability, w1= NL/nL.
Similarly, for each state stratum, the probability that a cell phone number is selected from the RDD frame is the number of selected cell phone numbers (nc) divided by the total number of cell phone numbers on the frame (NC). The base weight is the inverse of the selection probability, w1= NC/nc.
The Adjustment for Survey Break-Offs
Boat owners have a longer survey than non-boat owners. This means that break-off rates will be higher for boat owners than non-boat owners. Some households were selected for the 2011 Participation survey, which required additional questions for boat owners and non-boat owners. To ensure accurate boat ownership rates, we adjusted for mid survey terminations after the boat ownership question, and whether the household was selected for the 2011 Participation survey. Within each state and sample type (landline or cell) we adjusted the households who completed the entire survey (c), and we accounted for the households who answered the boat ownership question but did not complete the entire survey (m). These adjustments were performed as follows:
Table 7.1. Survey Break-Off Adjustment Factors
Adjustment Cell |
Mid-Term Adjustment |
Adjusted Weight |
|
Boat-owning household |
Selected for 2011 Participation Survey |
|
|
Not Selected for the 2011 Participation Survey |
|||
Non boat-owning household |
Selected for 2011 Participation Survey |
||
Not Selected for the 2011 Participation Survey |
|||
Non-Boat Owning Household Subsample Weight
Within each state, a subsample of non-boat owning households were selected and surveyed about boating participation. For each state and sample type, the adjustment was,
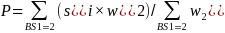 ,
,
where,
{BS1=2} represents non-boat owning households, si
= 1 if the ith
non-boat owning household was selected for the subsample, and si
= 0 if not selected. The adjusted weight was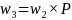 .
.
Combining Landline and Cell Phone Samples
To combine the landline and cell phone samples, we classified each respondent based on their phone status. The cell phone survey asked, “In addition to your cell phone, is there at least one telephone inside your home that is currently working and is not a cell phone? Do not include telephones only used for business or telephones only used for computers or fax machines.” Those who responded ‘yes’ were classified as cell and landline adults, while those who responded ‘no’ were classified as cell-only adults. The landline survey also asked, “In addition to your residential landline telephone, do you also use one or more cell phone numbers?” Those who answered ‘yes’ were classified as cell and landline, while those who responded ‘no’ were classified as landline-only.
Table 7.2. Categorization of Phone Users
-
Population
Dual Frame Samples
Landline (1)
Cell phone (2)
Landline only (A)
a1
Dual-user (B)
b1
b2
Cell-only (C)
c2
After determining the telephone groups, each is independently weighted to benchmarks for the population they are meant to represent. This is done for two reasons: 1) dual-users are overrepresented since they are eligible in both samples, and 2) there are differential response rates between dual-users and cell-only respondents in the cell phone sample. For the United States, the benchmark for the phone groups is regional estimates from the 2010 National Health Interview Survey (NHIS). The NHIS is an in-person household survey that collects information about cell phone and landline availability. It provides national estimates of the cell-only population, the landline-only population, and the dual-user population. For the dual-user ratio adjustment, we post-stratified into three categories: receive most calls on cell phone (b11), receive most calls on landline (b13), and receive calls on both regularly (b12).
Table 7.3. Adjustment Factors Dual-Phone Users
Region |
Landline only (A) |
Cell-only (C) |
Dual users (both samples reach this population) |
||
Receive most cell phone (B1) |
Receive calls on both (B2) |
Receive most landline (B3) |
|||
Northeast |
15.0% |
20.1% |
15.7% |
28.3% |
19.1% |
Midwest |
12.1% |
31.8% |
14.8% |
22.8% |
16.7% |
South |
12.0% |
33.6% |
16.0% |
21.7% |
14.4% |
West |
13.5% |
30.8% |
15.7% |
23.8% |
13.8% |
After ratio adjusting the samples to the benchmarks, we combined the overlapping groups by first multiplying the weights for one of the samples by a coefficient c and the weights for the other sample by 1-c, where 0 < c < 1. The coefficient was,
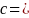 ,
,
where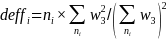 was a measure of variability of respondent level weights (w3),
and ni
was
the sample size for each sample type. Using c,
we adjusted the weights as
was a measure of variability of respondent level weights (w3),
and ni
was
the sample size for each sample type. Using c,
we adjusted the weights as
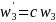 for the landline sample and
for the landline sample and
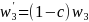 for the cell phone sample.
for the cell phone sample.
A summary of the calculations is presented in the table below.
Table 7.4. Ratio Adjustments to Benchmarks
Type of Phone |
Sample Size |
NHIS Benchmark |
Dual-frame Adjustment |
Landline only |
a1 |
A |
|
Landline dual users |
b1 |
B |
|
Cell-mostly |
b11 |
B1 |
|
Both |
b12 |
B2 |
|
Landline-mostly |
b13 |
B3 |
|
Cell phone dual users |
b2 |
B |
|
Cell-mostly |
b21 |
B1 |
|
Both |
b22 |
B2 |
|
Landline-mostly |
b23 |
B3 |
|
Cell phone only |
c2 |
C |
|
The General Household Weight
The cell phone sample and the landline sample were combined. Within each state, we adjusted the combined sample to match the total number of households (HH) from the 2010 Census as follows:
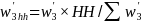 .
.
This was the final household weight, used for the questions asked about the household in the phone survey.
Household Participation Weights
The patch subsampling was already accounted for in a previous weighting step of non-boat owning households. For each state and sample type, the adjustment was given by,
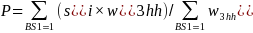 ,
,
where
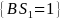 represents the group of boat-owning households, si
= 1 if the a boat-owning household was selected for the subsample,
and si
= 0 if not selected. The adjusted weight was:
represents the group of boat-owning households, si
= 1 if the a boat-owning household was selected for the subsample,
and si
= 0 if not selected. The adjusted weight was:
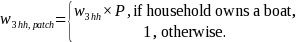
This is the household participation weight, used for the questions asked about the household in the participant survey.
Registered Boat Weights
For each state and boat type, the probability that a boat record is selected from the registry frame is the number of selected records (nR) divided by the number of registered boat records on the frame (NR). The base weight is the inverse of the selection probability, w1= NR/nR. Within each state, we adjust the returned boat surveys (r) to account for the unreturned boat surveys (k):
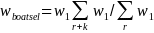 .
.
This is the mail mode selected boat weight used for registered boats only.
General Boat Weights
Each boat-owning household in the phone sample answered a set of questions about each boat they owned. From this set of questions, we determined the boat type and its registration status.
Treatment of Registered Boats
Using the count of registered boats by state and boat type (provided by Info-Link), we ratio adjusted the sample of boats to match the registration counts. The weighting adjustment was based on a raking algorithm with these dimensions: Census division × boat type, and registration state. Raking iteratively matched the sample to the population along each of the listed dimensions. After several iterations, each dimension matched the population totals within tolerance. The resulting weights are the boat weights for registered boats, w4boatx,r.
Note that there was a higher number of “other” registered boats in the sample than on the state registry counts. The “other” category indicated a boat that was not classifiable into any other boat type. Because the number of other boats did not align with the registry counts, we did not include them in the calibration adjustment to the registered boat counts. Instead, these boats were treated similarly to the unregistered boats in the weighting.
Treatment of Unregistered Boats
The
number of unregistered boats in each state is based on the ratio of
registered to unregistered boats as measured by the household
weights. For each state, the weight for unregistered boat u
was
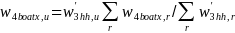 .
.
Combining registered and unregistered boats, we derived the following weight:
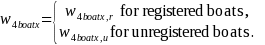
This is the final general boat weight, used for the question set asking about all boats in the household.
Selected Boat Weights
The selected boat sample included one boat selected from each boat-owning household combined with the completed surveys from the mail sample.
The Telephone Subsample Weight
We adjusted the selected boats from the phone sample to match the total number of boats from the phone sample. For each state and boat type, the adjustment was,
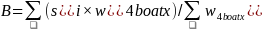 ,
,
where si = 1 if the ith boat was selected for the subsample and si = 0 if not selected. The weighting adjustment was based on a raking algorithm with these dimensions: Census division × boat type and registration state (state of residence for unregistered boats). Raking iteratively matched the sample to the population along each of the listed dimensions. After several iterations, each dimension matched the population totals within tolerance. The resulting weights are the phone selected boat weights, w4boatsel.
Combining the Mail and the Telephone Samples
We combined the mail and phone samples by first multiplying the weights for one of the samples by a coefficient c and the weights for the other sample by 1-c, where 0 < c < 1. The coefficient was,
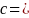 ,
,
where
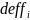 was a measure of variability of the selected boat weights
(w4boatsel)
defined by,
was a measure of variability of the selected boat weights
(w4boatsel)
defined by,
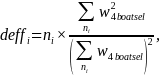
and
ni
was
the sample size for each sample type. Using c,
we adjusted the weights as
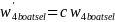 for the landline sample and
for the landline sample and
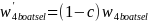 for the cell phone sample.
for the cell phone sample.
Due to small sample sizes within each state, we used the following boat type categories for combining the samples:
Table 7.5. Revised Boat Types for Weighting Purposes
Boat type |
Collapsed Boat type |
Power Boat <16 ft |
Power boat ≤20 ft and other boats |
Power Boat 16–20 ft |
Power boat ≤20 ft and other boats |
Power Boat 21–28 ft |
Power boat >20 ft and pontoons |
Power Boat >28 ft |
Power boat >20 ft and pontoons |
Sail <25 ft |
Sail all sizes |
Sail >25 ft |
Sail all sizes |
Pontoon Boat |
Power boat >20 ft and pontoons |
Personal Water Craft (PWC) |
Personal Water Craft (PWC) |
Canoe |
Self-propelled |
Kayak |
Self-propelled |
Other |
Power boat ≤20 ft and other boats |
We conducted additional collapsing when a state did not have at least 20 sample boats in these categories.
Finally we adjusted the phone (p) and mail (m) combined sample to match the total number of boats from the phone sample. For each state and boat type, the adjustment was done as follows:
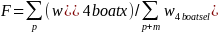 .
.
The weighting adjustment was based on a raking algorithm with these dimensions: Census division × boat type, and registration state (state or residence for unregistered boats) × collapsed boat type. Raking iteratively matched the sample to the population along each of the listed dimensions. After several iterations, each dimension matched the population totals within tolerance. The resulting weights are the phone selected boat weights, wboatsel. This is the final selected boat survey weight, used for all survey questions referring to the selected boat on the phone and mail survey.
General Person Weights
The respondent was asked participation and demographic questions about each person in the household. To calculate person weights, we post-stratified the participant sample, and calibrated the weighted data to reflect population distributions for state × age × sex based on the 2010 Census to obtain the following weight:
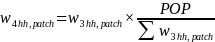 .
.
This weight was used to estimate 2011 participation rates.
Selected Person Weights
The calculation of the selected person-level weight was done in three steps, which involved adjusting for the within household subsampling, the individual participant random selection, and for the participant nonresponse.
Adjusting for the Within Household Subsampling
Within each household, up to one adult participant and one child participant were selected for the participation survey. We multiplied the selected participants by the inverse of the within household selection probability. This led to the following weight:
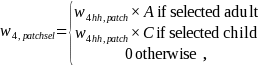 ,
,
where A is the number of eligible adult participants in the sample, and C is the number of eligible child participants in the household.
Participant Selection Adjustment
For the selected child and the selected adult, we adjusted the selected participants to reflect the child and adult gender distributions of all participants within the state. This produced the following weight:
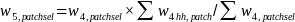 .
.
Participant Nonresponse Adjustment
Finally, we adjusted for participant non-response for child and adult participants within each census region. The non-response adjustment cells were based on gender, household boat ownership, and whether the selected participant was on the phone or whether someone else in the household was selected.
The nonresponse adjustment procedure produced the final selected person weight given by,
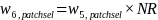 ,
,
where the nonresponse adjustment factor NR is defined as
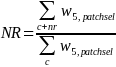
Survey Response Rates
The calculation of response rates for the 2011 National Recreational Boating Survey (NRBS) follows the standards and guidelines of by the American Association for Public Opinion Research (AAPOR)6. The response rates for the boat survey (mail and telephone) are based on AAPOR RR3 for the telephone and AAPOR RR1 for the mail survey.
RR1 = I/(N-X)
RR3 = I/(I+E+e(U)),
where,
I = Complete interview
E = Eligible
U = Unknown eligibility
X = Ineligible
N = Total records
e = (I+E)/(I+E+X), the proportion of eligible records.
Table 7.6: Mail Survey Response Rates by State
State |
Surveys sent (N) |
Surveys Returned |
|
|
Complete surveys (I) |
Ineligible (X) |
RR1 (%) |
||
US |
35670 |
13404 |
1427 |
39.0 |
AL |
1022 |
343 |
26 |
34.4 |
AK |
344 |
162 |
17 |
49.5 |
AZ |
646 |
147 |
143 |
29.2 |
AR |
860 |
232 |
49 |
28.6 |
CA |
|
|
|
|
CO |
437 |
133 |
30 |
32.7 |
CT |
654 |
304 |
17 |
47.7 |
DE |
225 |
97 |
20 |
47.3 |
DC |
147 |
60 |
6 |
42.6 |
FL |
1979 |
655 |
70 |
34.3 |
GA |
1261 |
422 |
30 |
34.3 |
HI |
147 |
53 |
11 |
39.0 |
ID |
|
|
|
|
IL |
1365 |
593 |
26 |
44.3 |
IN |
|
|
|
|
IA |
884 |
292 |
42 |
34.7 |
KS |
588 |
232 |
14 |
40.4 |
KY |
875 |
282 |
21 |
33.0 |
LA |
|
|
|
|
ME |
581 |
261 |
29 |
47.3 |
MD |
898 |
273 |
10 |
30.7 |
MA |
913 |
397 |
40 |
45.5 |
MI |
1595 |
697 |
49 |
45.1 |
MN |
|
|
|
|
MS |
836 |
309 |
25 |
38.1 |
MO |
1131 |
394 |
26 |
35.7 |
MT |
|
|
|
|
NE |
438 |
140 |
21 |
33.6 |
NV |
216 |
55 |
16 |
27.5 |
NH |
|
|
|
|
NJ |
840 |
260 |
125 |
36.4 |
NM |
138 |
36 |
38 |
36.0 |
NY |
1469 |
609 |
36 |
42.5 |
NC |
1275 |
481 |
33 |
38.7 |
ND |
430 |
167 |
8 |
39.6 |
OH |
1369 |
580 |
24 |
43.1 |
OK |
876 |
260 |
27 |
30.6 |
OR |
869 |
464 |
29 |
55.2 |
PA |
1290 |
576 |
29 |
45.7 |
RI |
143 |
71 |
4 |
51.1 |
SC |
1143 |
387 |
32 |
34.8 |
SD |
423 |
161 |
12 |
39.2 |
TN |
1060 |
412 |
20 |
39.6 |
TX |
1679 |
490 |
61 |
30.3 |
UT |
359 |
131 |
10 |
37.5 |
VT |
144 |
65 |
5 |
46.8 |
VA |
1095 |
493 |
32 |
46.4 |
WA |
1094 |
520 |
50 |
49.8 |
WV |
218 |
53 |
13 |
25.9 |
WI |
1402 |
582 |
33 |
42.5 |
WY |
146 |
53 |
6 |
37.9 |
PR |
166 |
20 |
62 |
19.2 |
Table 7.7: The Telephone Boat Survey’s Response Rates
State
|
Landline |
Cell Phone |
||||||||||
I |
E |
U |
X |
e1 (%) |
RR3 (%) |
I |
E |
U |
X |
e1 (%) |
RR3 (%) |
|
|
15,697 |
6,995 |
296,622 |
951,415 |
2.3 |
53 |
3,851 |
2,125 |
217,133 |
161,775 |
3.6 |
28.1 |
AL |
323 |
188 |
6,238 |
19,751 |
2.5 |
48.3 |
64 |
36 |
3,682 |
3,667 |
2.7 |
32.4 |
AK |
304 |
106 |
1,255 |
5,285 |
7.2 |
60.8 |
40 |
17 |
550 |
1,143 |
4.8 |
48.1 |
AZ |
182 |
77 |
6,285 |
18,056 |
1.4 |
52.3 |
37 |
30 |
3,583 |
2,450 |
2.7 |
22.8 |
AR |
305 |
164 |
4,285 |
15,945 |
2.9 |
51.6 |
78 |
53 |
3,154 |
3,664 |
3.5 |
32.5 |
CA |
542 |
217 |
17,179 |
34,262 |
2.2 |
47.9 |
114 |
72 |
10,564 |
6,503 |
2.8 |
23.8 |
CO |
219 |
79 |
5,044 |
16,558 |
1.8 |
56.6 |
44 |
20 |
2,454 |
1,832 |
3.4 |
30 |
CT |
257 |
70 |
3,401 |
8,372 |
3.8 |
56.5 |
43 |
20 |
2,649 |
1,488 |
4.1 |
25.2 |
DE |
185 |
84 |
3,882 |
8,299 |
3.1 |
47.3 |
47 |
23 |
2,262 |
1,268 |
5.2 |
25 |
DC |
151 |
51 |
12,412 |
43,331 |
0.5 |
58.2 |
37 |
22 |
4,610 |
2,731 |
2.1 |
23.6 |
FL |
536 |
254 |
11,555 |
32,155 |
2.4 |
50.2 |
138 |
75 |
6,647 |
4,940 |
4.1 |
28.3 |
GA |
262 |
161 |
7,477 |
23,350 |
1.8 |
47.1 |
66 |
44 |
5,774 |
4,716 |
2.3 |
27.3 |
HI |
188 |
87 |
3,890 |
14,585 |
1.9 |
54.2 |
60 |
44 |
2,841 |
1,705 |
5.8 |
22.4 |
ID |
306 |
109 |
3,292 |
13,743 |
2.9 |
59.8 |
88 |
34 |
1,775 |
1,303 |
8.6 |
32.1 |
IL |
281 |
127 |
7,091 |
25,151 |
1.6 |
53.9 |
55 |
43 |
5,150 |
4,045 |
2.4 |
25 |
IN |
394 |
178 |
7,675 |
24,653 |
2.3 |
52.8 |
112 |
63 |
5,511 |
3,964 |
4.2 |
27.5 |
IA |
342 |
168 |
6,002 |
26,338 |
1.9 |
54.8 |
80 |
33 |
3,144 |
2,343 |
4.6 |
31.1 |
KS |
199 |
107 |
4,667 |
18,827 |
1.6 |
52.3 |
56 |
23 |
3,041 |
3,380 |
2.3 |
37.7 |
KY |
208 |
107 |
4,980 |
16,305 |
1.9 |
50.8 |
47 |
33 |
3,162 |
2,308 |
3.4 |
25.3 |
LA |
524 |
282 |
9,830 |
31,464 |
2.5 |
49.8 |
131 |
80 |
6,832 |
6,124 |
3.3 |
29.9 |
ME |
299 |
83 |
1,469 |
5,449 |
6.6 |
62.5 |
87 |
31 |
1,414 |
818 |
12.6 |
29.4 |
MD |
227 |
83 |
3,340 |
8,900 |
3.4 |
53.7 |
72 |
29 |
5,374 |
2,425 |
4 |
22.8 |
MA |
330 |
114 |
4,726 |
8,980 |
4.7 |
49.5 |
52 |
24 |
3,003 |
1,671 |
4.4 |
25.2 |
MI |
616 |
258 |
6,122 |
22,304 |
3.8 |
55.8 |
140 |
77 |
6,535 |
5,348 |
3.9 |
29.7 |
MN |
1,078 |
486 |
9,376 |
33,206 |
4.5 |
54.3 |
290 |
167 |
7,515 |
5,528 |
7.6 |
28.1 |
MS |
273 |
193 |
7,156 |
24,628 |
1.9 |
45.6 |
63 |
35 |
2,833 |
3,019 |
3.1 |
33.7 |
MO |
319 |
216 |
6,571 |
22,194 |
2.4 |
46.3 |
82 |
53 |
4,229 |
3,136 |
4.1 |
26.5 |
MT |
370 |
121 |
2,693 |
12,816 |
3.7 |
62.7 |
87 |
26 |
1,749 |
2,888 |
3.8 |
48.6 |
NE |
169 |
65 |
3,621 |
15,095 |
1.5 |
58.4 |
35 |
21 |
2,304 |
1,740 |
3.1 |
27.4 |
NV |
193 |
73 |
5,209 |
12,975 |
2 |
52.1 |
50 |
35 |
4,087 |
2,437 |
3.4 |
22.5 |
NH |
296 |
105 |
3,135 |
8,714 |
4.4 |
54.9 |
68 |
25 |
1,686 |
1,021 |
8.4 |
29.1 |
NJ |
200 |
92 |
5,240 |
13,068 |
2.2 |
49.2 |
39 |
26 |
3,871 |
2,264 |
2.8 |
22.5 |
NM |
160 |
68 |
5,258 |
19,114 |
1.2 |
55.2 |
58 |
36 |
5,091 |
5,060 |
1.8 |
31 |
NY |
294 |
117 |
4,206 |
12,433 |
3.2 |
53.9 |
59 |
39 |
5,093 |
3,107 |
3.1 |
23.3 |
NC |
303 |
140 |
5,628 |
16,079 |
2.7 |
51 |
72 |
41 |
3,816 |
3,129 |
3.5 |
29.3 |
ND |
210 |
105 |
2,279 |
11,306 |
2.7 |
55.7 |
44 |
34 |
1,417 |
2,755 |
2.8 |
37.6 |
OH |
328 |
138 |
7,779 |
28,055 |
1.6 |
55.3 |
74 |
39 |
4,336 |
2,801 |
3.9 |
26.3 |
OK |
223 |
134 |
6,134 |
18,659 |
1.9 |
47.2 |
66 |
37 |
3,756 |
3,985 |
2.5 |
33.4 |
OR |
281 |
75 |
2,337 |
10,007 |
3.4 |
64.4 |
71 |
34 |
1,402 |
943 |
10 |
28.9 |
PA |
249 |
96 |
4,602 |
11,453 |
2.9 |
51.9 |
63 |
38 |
4,295 |
2,554 |
3.8 |
23.8 |
RI |
226 |
84 |
2,962 |
6,928 |
4.3 |
51.7 |
56 |
42 |
2,994 |
1,508 |
6.1 |
20 |
SC |
474 |
221 |
9,418 |
26,387 |
2.6 |
50.6 |
101 |
60 |
4,300 |
3,789 |
4.1 |
30 |
SD |
210 |
86 |
2,762 |
15,291 |
1.9 |
60.3 |
42 |
30 |
1,482 |
2,246 |
3.1 |
35.6 |
TN |
251 |
161 |
5,816 |
18,922 |
2.1 |
46.8 |
70 |
29 |
2,696 |
2,107 |
4.5 |
31.8 |
TX |
287 |
168 |
8,635 |
27,910 |
1.6 |
48.4 |
71 |
44 |
5,541 |
4,600 |
2.4 |
28.4 |
UT |
214 |
71 |
3,179 |
11,586 |
2.4 |
59.2 |
50 |
22 |
2,449 |
1,624 |
4.3 |
28.4 |
VT |
303 |
78 |
2,016 |
6,853 |
5.3 |
62.2 |
53 |
18 |
1,350 |
890 |
7.4 |
31 |
VA |
226 |
107 |
4,691 |
11,876 |
2.7 |
49 |
67 |
36 |
4,869 |
2,777 |
3.6 |
24.2 |
WA |
272 |
126 |
3,144 |
10,308 |
3.7 |
52.8 |
72 |
33 |
2,272 |
1,512 |
6.5 |
28.5 |
WV |
217 |
122 |
5,165 |
11,694 |
2.8 |
44.8 |
33 |
29 |
2,304 |
1,527 |
3.9 |
21.7 |
WI |
576 |
267 |
5,870 |
17,637 |
4.6 |
51.9 |
179 |
87 |
5,927 |
4,907 |
5.1 |
31.4 |
WY |
183 |
70 |
2,507 |
10,390 |
2.4 |
58.5 |
52 |
18 |
1,432 |
3,698 |
1.9 |
53.8 |
Table 7.8: The Telephone Participant Survey’s Response Rates
State |
Landline |
Cell Phone |
||||||||||
I |
E |
U |
X |
e1 |
RR3 |
I |
E |
U |
X |
e1 |
RR3 |
|
16,507 |
11,275 |
83,542 |
248,962 |
6.2 |
76.1 |
4,832 |
1,903 |
58,142 |
36,181 |
15.7 |
30.5 |
|
AL |
254 |
198 |
1,435 |
4,029 |
10.1 |
42.6 |
70 |
36 |
952 |
904 |
10.5 |
34 |
AK |
271 |
135 |
615 |
2,319 |
14.9 |
54.5 |
49 |
16 |
290 |
519 |
11.1 |
50.4 |
AZ |
260 |
146 |
1,622 |
4,188 |
8.8 |
47.3 |
62 |
24 |
556 |
398 |
17.8 |
33.6 |
AR |
255 |
197 |
1,204 |
4,221 |
9.7 |
44.9 |
66 |
25 |
540 |
669 |
12 |
42.4 |
CA |
1,436 |
939 |
9,469 |
16,676 |
12.5 |
40.4 |
479 |
179 |
6,135 |
2,895 |
18.5 |
26.7 |
CO |
310 |
195 |
1,796 |
5,263 |
8.8 |
46.8 |
65 |
21 |
778 |
430 |
16.7 |
30.1 |
CT |
245 |
180 |
1,517 |
2,626 |
13.9 |
38.5 |
75 |
43 |
970 |
430 |
21.5 |
22.9 |
DE |
246 |
181 |
1,387 |
2,479 |
14.7 |
39 |
76 |
35 |
746 |
328 |
25.3 |
25.4 |
DC |
235 |
138 |
1,808 |
6,157 |
5.7 |
49.3 |
126 |
52 |
1,332 |
582 |
23.4 |
25.7 |
FL |
258 |
205 |
1,614 |
4,071 |
10.2 |
41.1 |
65 |
28 |
856 |
518 |
15.2 |
29.1 |
GA |
262 |
179 |
1,617 |
4,874 |
8.3 |
45.6 |
58 |
24 |
655 |
437 |
15.8 |
31.3 |
HI |
243 |
143 |
907 |
3,225 |
10.7 |
50.3 |
82 |
45 |
483 |
227 |
35.9 |
27.3 |
ID |
268 |
178 |
1,154 |
4,329 |
9.3 |
48.4 |
60 |
42 |
606 |
355 |
22.3 |
25.3 |
IL |
289 |
229 |
1,756 |
5,672 |
8.4 |
43.5 |
95 |
30 |
1,224 |
753 |
14.2 |
31.8 |
IN |
807 |
466 |
1,106 |
12,165 |
9.5 |
58.6 |
68 |
21 |
623 |
369 |
19.4 |
32.4 |
IA |
310 |
248 |
1,295 |
5,105 |
9.9 |
45.2 |
86 |
40 |
843 |
550 |
18.6 |
30.4 |
KS |
241 |
195 |
1,365 |
4,109 |
9.6 |
42.5 |
81 |
23 |
628 |
634 |
14.1 |
42.1 |
KY |
258 |
178 |
1,204 |
3,357 |
11.5 |
44.9 |
78 |
20 |
800 |
474 |
17.1 |
33.2 |
LA |
934 |
639 |
5,605 |
16,569 |
8.7 |
45.4 |
267 |
126 |
3,696 |
2,926 |
11.8 |
32.1 |
ME |
244 |
141 |
646 |
2,143 |
15.2 |
50.5 |
76 |
26 |
622 |
292 |
25.9 |
28.9 |
MD |
230 |
154 |
1,303 |
2,919 |
11.6 |
43 |
91 |
33 |
1,041 |
358 |
25.7 |
23.2 |
MA |
274 |
196 |
1,576 |
2,477 |
16 |
38 |
69 |
30 |
948 |
394 |
20.1 |
23.8 |
MI |
255 |
176 |
1,145 |
3,774 |
10.3 |
46.5 |
103 |
30 |
1,270 |
878 |
13.2 |
34.3 |
MN |
270 |
218 |
1,201 |
3,987 |
10.9 |
43.6 |
91 |
43 |
1,048 |
652 |
17.1 |
29.1 |
MS |
259 |
204 |
1,306 |
4,747 |
8.9 |
44.7 |
66 |
35 |
704 |
681 |
12.9 |
34.4 |
MO |
256 |
201 |
1,222 |
3,656 |
11.1 |
43.2 |
83 |
30 |
868 |
499 |
18.5 |
30.4 |
MT |
280 |
172 |
937 |
3,934 |
10.3 |
51 |
81 |
20 |
534 |
817 |
11 |
50.7 |
NE |
253 |
196 |
1,152 |
4,139 |
9.8 |
45 |
68 |
17 |
673 |
380 |
18.3 |
32.7 |
NV |
256 |
163 |
1,510 |
3,614 |
10.4 |
44.5 |
71 |
35 |
667 |
410 |
20.5 |
29.2 |
NH |
329 |
275 |
1,725 |
4,304 |
12.3 |
40.3 |
64 |
25 |
655 |
343 |
20.6 |
28.6 |
NJ |
311 |
223 |
1,989 |
4,195 |
11.3 |
41 |
64 |
33 |
1,089 |
436 |
18.2 |
21.7 |
NM |
221 |
157 |
1,474 |
5,106 |
6.9 |
46.1 |
99 |
24 |
583 |
646 |
16 |
45.8 |
NY |
249 |
181 |
1,238 |
3,100 |
12.2 |
42.9 |
74 |
60 |
1,099 |
538 |
19.9 |
21 |
NC |
267 |
176 |
1,256 |
3,155 |
12.3 |
44.7 |
56 |
22 |
472 |
418 |
15.7 |
36.8 |
ND |
275 |
167 |
881 |
3,766 |
10.5 |
51.5 |
52 |
26 |
403 |
782 |
9.1 |
45.4 |
OH |
248 |
203 |
1,181 |
3,940 |
10.3 |
43.3 |
92 |
28 |
924 |
489 |
19.7 |
30.5 |
OK |
263 |
207 |
1,582 |
4,309 |
9.8 |
42 |
72 |
20 |
618 |
589 |
13.5 |
41 |
OR |
253 |
184 |
814 |
2,987 |
12.8 |
46.8 |
79 |
32 |
505 |
283 |
28.2 |
31.2 |
PA |
236 |
132 |
1,013 |
1,998 |
15.6 |
44.9 |
85 |
37 |
901 |
453 |
21.2 |
27.1 |
RI |
245 |
178 |
1,291 |
2,511 |
14.4 |
40.2 |
87 |
33 |
1,024 |
445 |
21.2 |
25.8 |
SC |
254 |
208 |
1,348 |
3,985 |
10.4 |
42.2 |
67 |
23 |
580 |
450 |
16.7 |
35.9 |
SD |
274 |
217 |
1,117 |
5,653 |
8 |
47.2 |
69 |
31 |
638 |
911 |
9.9 |
42.3 |
TN |
267 |
190 |
1,346 |
4,196 |
9.8 |
45.3 |
53 |
18 |
543 |
353 |
16.8 |
32.7 |
TX |
267 |
229 |
1,750 |
5,665 |
8.1 |
41.9 |
64 |
19 |
663 |
516 |
13.9 |
36.6 |
UT |
251 |
135 |
1,150 |
3,527 |
9.9 |
50.3 |
70 |
29 |
702 |
360 |
21.6 |
28 |
VT |
249 |
147 |
982 |
2,874 |
12.1 |
48.4 |
71 |
23 |
732 |
376 |
20 |
29.5 |
VA |
244 |
191 |
1,366 |
3,202 |
12 |
40.8 |
77 |
15 |
752 |
373 |
19.8 |
32 |
WA |
251 |
184 |
1,189 |
3,426 |
11.3 |
44.1 |
82 |
37 |
673 |
380 |
23.9 |
29.3 |
WV |
268 |
178 |
1,169 |
2,315 |
16.2 |
42.2 |
57 |
29 |
866 |
463 |
15.7 |
25.7 |
WI |
248 |
191 |
1,228 |
3,286 |
11.8 |
42.5 |
93 |
33 |
1,006 |
710 |
15.1 |
33.5 |
WY |
268 |
172 |
1,182 |
4,359 |
9.2 |
48.9 |
75 |
24 |
483 |
1,143 |
8 |
54.6 |
Accuracy of Estimates
The 2011 NRBS is based on a sample of households, and on the data provided over completed mail questionnaires, or telephone interviews. Consequently, the resulting survey estimates are expected to have two types of error: the sampling as well as the nonsampling errors. The precision of the estimates presented in this report depend on both types of error. While the nature of the sampling error is known given the survey design; the full extent of the nonsampling error is unknown.
Nonsampling Errors
There are several sources of nonsampling error that may occur during the development and the execution of the survey. A nonsampling error may be due to circumstances created by the interviewer, the respondent, the survey instrument, or the way the survey data are collected and processed. For example, errors could occur because the interviewer records the wrong answer, the respondent provides incorrect information, the respondent estimates the requested information, or an unclear survey question is misunderstood by the respondent (measurement error). Among other nonsampling errors, we could mention the following:
Some registered boats, which should have been included in the state boat registries, were missed, or others that were mistakenly included. These are coverage errors due to using an imperfect sampling frame.
Some recreational boating participants refused to participate in the survey. Therefore their boating participation or boat ownership information were not recorded, resulting in a nonresponse error.
Some completed mail survey questionnaires may have been lost in the mail, or information from a complete questionnaire may have been misreported.
To minimize the impact of these nonsampling errors, we have implemented many quality control procedures throughout the production process, including the overall design of surveys, the wording of questions, the review of the work of interviewers and coders, and the statistical review of reports. Table 7.8 summarizes some of the procedures that were put in place.
Table 7.8: Quality Control Procedures
Survey Step |
Quality Control Procedures |
Testing the CATI program |
Tested each response to
each question, and each path through the survey Reviewed
frequencies from randomly-generated data to ensure that the
program was organizing data properly and recording values
according to the survey specification |
CATI pre-test |
Pre-tested 100 interviews to ensure the CATI program was working properly and to verify questionnaire content, skip patterns, value verification, consistency of answers across questions, interviewer and supervisor training, and sample management procedures |
CATI quality assurance |
Monitored at least 10 percent of all interviews Monitored each interviewer at least once per week Assigned supervisors to manage a team of no more than 10 interviewers Participated in daily briefing call with call center management Reviewed call center shift reports and internal project tracking reports daily |
Preparation of data files |
Identified incomplete interviews and merged back into the main data file Cleaned and, when applicable, back-coded open-ended responses Assigned a final disposition to each record Produced frequency tabulations of every question and variable to detect missing data or errors in skip patterns |
Printing of Mail Surveys |
Printing utilized state-of-the-art software and hardware that printed large volumes very quickly, at low cost, and with outstanding image quality. Accuracy of insertion (i.e., matching of master IDs and address information on all mailed pieces) was checked by hand for a portion of the total outgoing pieces |
Receipt of Mail Returns |
Master IDs from returned documents were entered into the Data Collection Mail Tracking System within 48 hours of receipt. |
Input of Mail Data |
Data entered by data entry staff was verified at 100 percent through double data entry as well as custom range and logic checks incorporated into the data entry system. |
Sampling Errors
Sampling errors are often measured by standard errors. It is a mathematical measure that tells about how far we expect any given measurement to stray from the overall average value. The survey estimate and its standard error enable one to construct a confidence interval when needed. A confidence interval is a range of values that has a known probability of including the average result of all possible samples, and provides an indicator of the accuracy with which we know about the parameter of interest.
Given the large number of estimates presented in this report, and the even larger number of estimates that the data users will be able to produce from the microdata files, it would be impractical to produce a standard error or a confidence interval around each of them. However, we are recommending a general approach for evaluating the precision associated with survey estimates. It provides data users with a simple way to obtain approximate standard errors at various levels of aggregation.
Standard data analysis software, such as Excel, SAS, and SPSS, computes many statistics using the assumption that the sample used was generated following a simple random sampling (SRS) from an infinite population. Because the precision of statistics is influenced by the design of the survey used to collect the sample data (e.g., due to clustering and stratification), precision estimates for complex survey statistics will differ from those computed based on the assumption of simple random sampling. To allow the end-user with no access to advanced survey analysis software to compensate for this difference, average precision estimate multipliers (i.e., design effect or “DEFT” factors) have been calculated from a number of NRBS survey variables in a way that takes the complexity of the NRBS survey design into account7.
The provided DEFT tables list average design factors for the boat_file and boat_detailed_file datasets. For each dataset, DEFT factors are provided for both means and totals or proportions. Average DEFT factors are provided for both types of statistics at the national and regional levels and by boat type subclass. Users may also desire to approximate precision estimates for statistics not listed in the provided tables. In these cases, a rule of thumb is that the design effect will be smaller for groups that subdivide the classes listed in the tables. For example, estimates for the subclass “power boats in the Northeast” will generally have smaller design effects than estimates for “all power boats” or “all Northeast boats.” Consequently, the use of the class DEFT (e.g., for “all power boats” or “all Northeast boats”) will generally provide a conservative estimate for the precision of statistics calculated within a portion of that class.
(c) Approximate Standard Error for a Mean
To approximate the standard error for a mean that has been calculated from NRBS data on the assumption of simple random sampling, the SRS standard error should be multiplied by the DEFT factor corresponding to the dataset and subclass (if applicable) of the desired statistic. For example, to approximate the standard error for the mean number of hours per day spent on a boat (of any type) in 2011 within the Northeast, the standard error of the mean for the variable xptime from the boat_file dataset would first be computed as if the data were collected using simple random sampling. The weighted SRS standard error of a mean can be calculated using standard data analysis software as,
where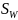 is the weighted standard deviation of the statistic and
is the weighted standard deviation of the statistic and
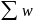 is
the sum of the weights in the total sample or subclass, as
appropriate. For example, SAS PROC SUMMARY will compute the STDERR
statistic for a mean using the preceding formula when a WEIGHT
variable is specified. For xptime in the Northeast region,
is
the sum of the weights in the total sample or subclass, as
appropriate. For example, SAS PROC SUMMARY will compute the STDERR
statistic for a mean using the preceding formula when a WEIGHT
variable is specified. For xptime in the Northeast region,
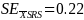 .
To compensate for the difference between the assumption of simple
random sampling and the complex design used in the NRBS Boat Survey,
this standard error would then be multiplied by the appropriate DEFT
factor from the provided tables. In this case, the factor would be
found using the boat_file tables for means within the Northeast
region, DEFT = 2.02. The approximate complex standard error of the
mean for xptime in the Northeast would then be,
.
To compensate for the difference between the assumption of simple
random sampling and the complex design used in the NRBS Boat Survey,
this standard error would then be multiplied by the appropriate DEFT
factor from the provided tables. In this case, the factor would be
found using the boat_file tables for means within the Northeast
region, DEFT = 2.02. The approximate complex standard error of the
mean for xptime in the Northeast would then be,
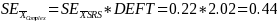
This approximate standard error could then be applied to the construction of confidence intervals. For example, the 95% confidence interval for the mean of xptime within the Northeast would be constructed around the weighted mean as follows:
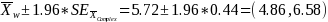
(d) Approximate Standard Error for a Proportion or Total
To approximate the standard error for a proportion that has been calculated from NRBS data on the assumption of simple random sampling, the SRS standard error should be multiplied by the DEFT factor corresponding to the dataset and subclass of the desired statistic. For example, to approximate the standard error for the proportion P (ranging between zero and one) of boats that have motors within the Northeast, the standard error of the proportion for the variable hasmot from the boat_detailed_file dataset would first be computed as if the data were collected using simple random sampling. The weighted SRS standard error of a proportion is,
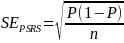
where
P is the weighted proportion and n is the number of elements in the
subclass for the sample. For hasmot = YES,
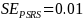 .
For example, SAS PROC FREQ will compute the weighted proportion when
a WEIGHT variable is specified, and the preceding formula can then be
used to calculate the SRS standard error for that appropriately
weighted proportion. To compensate for the difference between the
assumption of simple random sampling and the complex design used in
the NRBS Boat Survey, this standard error would then be multiplied by
the appropriate DEFT factor from the provided tables. In this case,
the factor would be found using the boat_detailed_file tables for
proportions within the Northeast region, DEFT = 1.75. The approximate
complex standard error of the proportion for hasmot = YES in the
Northeast would then be,
.
For example, SAS PROC FREQ will compute the weighted proportion when
a WEIGHT variable is specified, and the preceding formula can then be
used to calculate the SRS standard error for that appropriately
weighted proportion. To compensate for the difference between the
assumption of simple random sampling and the complex design used in
the NRBS Boat Survey, this standard error would then be multiplied by
the appropriate DEFT factor from the provided tables. In this case,
the factor would be found using the boat_detailed_file tables for
proportions within the Northeast region, DEFT = 1.75. The approximate
complex standard error of the proportion for hasmot = YES in the
Northeast would then be,
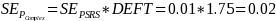
This approximate standard error could then be applied to the construction of confidence intervals. For example, the 95% confidence interval for the proportion of hasmot = YES within the Northeast would be constructed around the weighted proportion as follows:
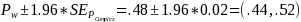
The approximate complex standard error for a total can be calculated directly from the complex standard error for a proportion by multiplying that standard error by T_w, the projected total population for the subclass of interest (calculated by weighting the sample total). For example, to approximate the standard error for the total number of boats that have motors (i.e., hasmot = YES) in the Northeast, multiply the complex standard error for the proportion calculated above by the projected population total for the subclass:
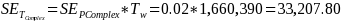
A 95% confidence interval could then be constructed around this projected total as follows:
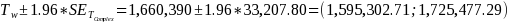
DEFT factors Data: boat_file
To use: multiply SE of statistic calculated assuming SRS by DEFT in table
Region |
Means |
Totals or Proportions |
US Overall |
1.90 |
1.68 |
Northeast |
2.02 |
1.57 |
Midwest |
1.45 |
1.38 |
South |
1.86 |
1.65 |
West |
2.16 |
1.46 |
Puerto Rico |
1.23 |
0.55 |
Boat Type |
Means |
Totals or Proportions |
Overall |
1.90 |
1.68 |
Power boats |
1.73 |
1.64 |
Sail boats |
1.52 |
1.30 |
PWCs |
1.58 |
1.73 |
Canoes |
1.76 |
1.47 |
Kayaks |
2.31 |
1.54 |
Pontoons |
1.62 |
1.48 |
Row/Inf/Oth boats |
2.06 |
1.50 |
DEFT factors Data: boat_detailed_file
To use: multiply SE of statistic calculated assuming SRS by DEFT in table
Region |
Means |
Totals or Proportions |
US Overall |
0.92 |
1.85 |
Northeast |
0.92 |
1.75 |
Midwest |
1.00 |
1.41 |
South |
0.88 |
1.79 |
West |
0.76 |
1.80 |
Puerto Rico |
0.55 |
0.59 |
Boat Type |
Means |
Totals or Proportions |
Overall |
0.92 |
1.85 |
Power boats |
0.83 |
1.45 |
Sail boats |
0.86 |
1.71 |
PWCs |
1.10 |
1.56 |
Canoes |
1.05 |
2.01 |
Kayaks |
1.54 |
2.35 |
Pontoons |
1.02 |
1.01 |
Row/Inf/Oth boats |
1.36 |
1.99 |
Definitions
Adult Individual
An individual is considered adult if aged 16 or more
CATI
This stands for “Computer-Assisted Telephone Interviewing.” In this telephone interviewing technique, the interviewer followed a script provided by CfMC’s Survent software package, which is designed specifically for programming and managing CATI studies. This questionnaire programming language offers the following benefits:
Call management;
Quota controls;
In-bound calling capabilities;
Data back-up;
Monitoring; and,
Incidence tracking.
Household
The National Recreational Boating Survey (NRBS) considers a household to be a person or group of persons who live in the same residence. No attempt was made to determine whether the household members had any family ties in a traditional sense.
Boating Household
The NRBS considers a (recreational) boating household to be a household that meets one of the following 2 conditions:
A household respondent indicated that the household owned a recreational boat that was used in 2011 by one of the household members
A household respondent indicated that a household had spent time on a recreational boat in 2011, or fished from a recreational boat 2011, or used a canoe or a kayak in 2011.
Boating Participant
A person was considered as boating participant if that person was member of a boating household, and indicated going out personally on the water in a recreational boat. During the interview, the respondent was read the following reminders:
We know that someone in the household has been on a boat in 2011. Now we are asking if the person on the phone has gone out on a boat
Remember that recreational boating includes boating in kayaks and canoes and fishing from boats.
We‘re interested in days when you personally were on the boat.
Child
An individual is considered to be a child if he/she has not turned 16 yet
PWC: Personal Watercraft
Recreational Boat
A recreational boat is a boat that is never used for purposes that make money. This could include boats that are rented, such as canoes or boats that are privately owned by you or someone else.
Recreational Boating
Recreational boating by individuals is defined as going out on water in a recreational boat and/or spending more than 1 hour on a recreational boat while it was docked.
US Census Regions
Census Regions are groupings of states and the District of Columbia used by Census Bureau to subdivide the United States for the presentation of census data. There are four census regions: Northeast, Midwest, South, and West. Puerto Rico and the Island Areas are not part of any census region.
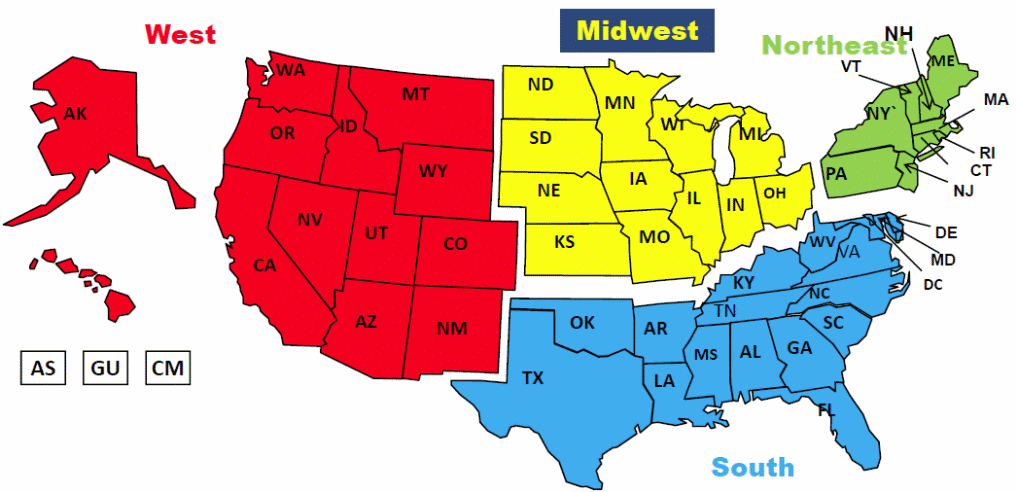
Northeast
Connecticut |
New Hampshire |
Pennsylvania |
Maine |
New Jersey |
Rhode Island |
Massachusetts |
New York |
Vermont |
Midwest
Illinois |
Michigan |
North Dakota |
Indiana |
Minnesota |
Ohio |
Iowa |
Missouri |
South Dakota |
Kansas |
Nebraska |
Wisconsin |
South
Alabama |
Kentucky |
South Carolina |
Arkansas |
Louisiana |
Tennessee |
Delaware |
Maryland |
Texas |
District of Columbia |
Mississippi |
Virginia |
Florida |
North Carolina |
West Virginia |
Georgia |
Oklahoma |
|
West
Alaska |
Idaho |
Utah |
Arizona |
Montana |
Washington |
California |
Nevada |
Wyoming |
Colorado |
New Mexico |
|
Hawaii |
Oregon |
|
1 The Genesys® frame is updated quarterly using the Bell Communications Research (BELLCORE) valid area code-exchange database and keyed residential and business listings from major providers. ICF has an unlimited license for using the Genesys system.
2 However, statistics related to specific boat characteristics such as the hull material, the motor size or the engine fuel type can be obtained using detailed boat file boat_detailed_file.
3 Initial variable, which takes value 1, if individual (child or adult) participated in recreational boating anytime from January to the reference month (contained in variable PREVMON)
4 The states, DE, DC, KY, MD, and WV constitute the northern part of the South region, while the remaining South states are included into the southern part. Likewise, the states AZ, CA, HI, NV, and NM constitute the southern part of the West region, and the remaining West states being part of the northern part. This new partition divides the US into Northern and Southern states. In Northern states, the participant survey was administered in September through November, while in Southern states it was administered in November and December of 2011 only.
5 The Genesys® frame is updated quarterly using the Bell Communications Research (BELLCORE) valid area code-exchange database and keyed residential and business listings from major providers. ICF has an unlimited license for using the Genesys system.
6 Documentation for these response rates are available at http://www.aapor.org/AM/Template.cfm?Section=Standard_Definitions2&Template=/CM/ContentDisplay.cfm&ContentID=3156
7 Average DEFT factors were computed from selected NRBS survey variables using SAS PROC SURVEYMEANS and PROC SURVEYFREQ with Taylor series expansion as the variance estimation procedure.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | Philippe Gwet |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-29 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy
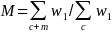
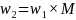
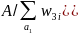 )
)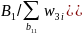 )
)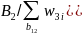 )
)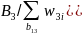 )
)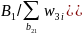 )
)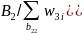 )
)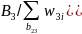 )
)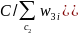 )
)