NAHMS 308 Dairy 2014 VS Visit
National Animal Health Monitoring System; Dairy 2014 Study
NAHMS-308
Dairy 2014 Study
OMB: 0579-0205
![]()

Animal
and Plant Health Inspection
Service Veterinary
Services
National
Animal Health Monitoring System 2150
Centre Ave, Bldg. B Fort
Collins, CO 80526 Form
Approved OMB
Number 0579-0205 Approval
expires: XX/XXXX


VS Visit
State FIPS: |
Operation #: |
Interviewer: |
Date: |
2 digits |
4 digits |
Initials |
(mm/dd/yy) |
Section A—Disease Preparedness
1. Which of the following categories best describes how familiar you are with the listed diseases?
Fairly Recognized the Haven’t
knowledge- Know some name, not heard of it
able basics much else before
a. Foot-and-mouth disease V005 1 2 3 4
b. Heartwater V006 1 2 3 4
c. Bovine spongiform encephalopathy
(BSE or mad cow disease) V007 1 2 3 4
d. Screwworm V008 1 2 3 4
e. Johne’s disease
(paratuberculosis) V009 1 2 3 4
f. Bluetongue V010 1 2 3 4
g. Vesicular stomatitis V011 1 2 3 4
h. Anthrax V012 1 2 3 4
i. Mycoplasma mastitis V013 1 2 3 4
j. Hemorrhagic bowel syndrome (HBS)
(Jejunal hemorrhage
syndrome, bloody gut) V014 1 2 3 4
k. Bovine viral diarrhea (BVD) V015 1 2 3 4
l. Leptospira hardjo bovis V016 1 2 3 4
According
to the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995, an
agency may not conduct or sponsor, and a person is not
required
to respond to a collection of information unless it displays a valid
OMB control number. The valid OMB control number for this
information collection is 0579-0205. The time required to complete
this information collection is estimated to average 1.25 hours per
response, including the time to review instructions, search existing
data resources, gather the data needed, and complete and review the
information collected.
NAHMS-308

JUL
2013
2. Did this operation participate in any of the following kinds of
Johne’s disease control or certification programs during 2013?
a. A unique program developed specifically for this operation V061 1 Yes 3 No
b. A State-sponsored program V062 1 Yes 3 No
c. Other (specify: ______________________________)V063OTH V063 1 Yes 3 No
3. Is colostrum from Johne’s test-positive cows fed to calves? V075 1 Yes 2 Don’t test 3 No
4. If an outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease (or other foreign animal disease)
occurred in the United States, how likely would you be to use the following
sources to get information about the disease?
Very Somewhat Not
likely likely likely
a. Other dairy producers V017 1 2 3
b. Private veterinarian V018 1 2 3
c. Extension agent V019 1 2 3
d. Dairy organization or cooperative V020 1 2 3
e. Magazines V021 1 2 3
f. Internet V022 1 2 3
g. State Veterinarian’s office V023 1 2 3
h. U.S. Department of Agriculture V024 1 2 3
i. Television/newspapers V025 1 2 3
j. Other (specify: ____________________)V026OTH V026 1 2 3
5. If you had an animal you suspected of having foot-and-mouth disease
(or other foreign animal disease) on your operation, would you
contact the following resources?
a. Extension agent/university V027 1 Yes 3 No
b. State Veterinarian’s office V028 1 Yes 3 No
c. U.S. Department of Agriculture V029 1 Yes 3 No
d. Private veterinarian V030 1 Yes 3 No
e. Feed company or milk cooperative representative V031 1 Yes 3 No
f. Other (specify: __________________________________)V032OTH V032 1 Yes 3 No
6. For each of the following signs associated with a potential herd disease
problem, what level of incidence (percentage or number) would need to
occur for you contact a veterinarian for assistance?
(Enter NA if you would never contact a veterinarian for assistance.)
% Number
a. Decline in total daily milk production (pounds) V033/600 _____ OR _____
b. Milk cows exhibiting fever within a short time period V034/601 _____ OR _____
c. Milk cows dying within a short time period V035/602 _____ OR _____
d. Milk cows aborting within a short time period V036/603 _____ OR _____
e. Milk cows showing lameness within a short time period V036/603 _____ OR _____
f. Milk cows with excessive drooling V036/603 _____ OR _____
7. Are you using any of the following biosecurity practices?
a. Guidelines to determine who is allowed in
animal areas V040 1 Yes 3 No
b. Guidelines regarding foreign travel by employees V041 1 Yes 2 No employees 3 No
c. Written standard operating procedures (SOPs)
(other than milking procedures)? V042 1 Yes 3 No
d. Training for employees in performing these practices? V043 1 Yes 2 No employees 3 No
8. During 2013, were records of visitors to this operation maintained? 1 Yes 3 No
9. During 2013, did any of the following make visits to your operation and if so, how many
visits were made, and did they have direct contact with animals on your operation?
Any visits? Visits/year Animal contact?
a. Veterinarians 1 Yes 3 No _____ 1 Yes 3 No
b. Milk truck 1 Yes 3 No _____ 1 Yes 3 No
c. Feed delivery 1 Yes 3 No _____ 1 Yes 3 No
d. Drug suppliers 1 Yes 3 No _____ 1 Yes 3 No
e. Nutritionist 1 Yes 3 No _____ 1 Yes 3 No
f. Contract hauler 1 Yes 3 No _____ 1 Yes 3 No
g. Neighbors 1 Yes 3 No _____ 1 Yes 3 No
h. University extension 1 Yes 3 No _____ 1 Yes 3 No
i. Visitors/tour groups 1 Yes 3 No _____ 1 Yes 3 No
j. Renderer 1 Yes 3 No _____ 1 Yes 3 No
k. Other (specify: ______________) 1 Yes 3 No _____ 1 Yes 3 No
10. Did you use any of the following practices during 2013?
a. Footbaths for visitors entering animal areas 1 Yes 2 No visitors entered animal areas 3 No
b. Disposable or clean boots for visitors
entering animal areas 1 Yes 2 No visitors entered animal areas 3 No
c. Insect control (such as sprays, foggers, treated ear tags, biological
control, products administered to animals [topical/oral], etc.) V048 1 Yes 3 No
d. Rodent control (such as cats, traps, chemical/bait, etc.) V049 1 Yes 3 No
e. Bird control (such as traps, noise, chemical/bait, etc.) V050 1 Yes 3 No
f. Limit cattle contact with other livestock, elk, and deer V051 1 Yes 3 No
g. Control access to cattle feed by other livestock
and wildlife, such as elk, deer, and raccoons V052 1 Yes 3 No
h. Closed herd (all replacements including bulls are from
this operation, no contact with cattle from other operations) V053 1 Yes 3 No
i. Restrictions on vehicles entering animal area V054 1 Yes 3 No
j. Restrictions on employee livestock ownership
outside this operation V055 1 Yes 2 No employees 3 No
11. During 2013, how often did this operation use the same
equipment to handle both manure and cattle feed? V056 1 Routinely 2 Rarely 3 Never
If Routinely or Rarely, which best describes cleaning procedures usually
used with equipment after handling manure and prior to handling feed?
(Check one only.)
1 Wash equipment with water or steam only
2 Chemically disinfect only
3 Wash equipment and chemically disinfect
4 Other (specify: _________________________)V057OTH
5 No procedures used
12. During 2013, did this operation share any heavy equipment
with other livestock operations (i.e., tractors, feeding equipment,
manure spreaders, trailers)? V058 1 Yes 3 No
[If Question 12 = No, SKIP to Section B.]
13. During 2013, how many times did this operation
share equipment with other operations? V059 _____ #
14. Which of the following best describes this operation’s cleaning
procedures of shared equipment prior to use on your operation?
(Check one only.)
1 Wash equipment with water or steam only
2 Chemically disinfect only
3 Wash equipment and chemically disinfect
4 Other (specify: _________________________)V060OTH
5 No procedures used
Section B—Employees
1. On average, how many paid and unpaid people, including owners and
family members, are assigned duties directly related to operation of the dairy?
(Exclude people that work exclusively with crop activities.)
Number
a. Full-time V038 _____
b. Part-time V039 _____
Training Personnel |
|
1 = Owner |
4 = Veterinarian |
2 = Manager/herdsperson |
5 = University/extension personnel |
3 = Other employees |
6 = Other (specify: ___________________) |
2. Were employees trained in the following procedures during 2013? If so, enter the
code from the table above for the person who was responsible for conducting the trainings.
-
Procedure
Employee training?
No employees
Training personnel
(Enter code from list above.)
a. Milking
1 Yes 3 No
b. Handling/movement of cattle
(e.g., flight zones etc.)1 Yes 3 No
c. Euthanasia
1 Yes 2 NA 3 No
d. Handling of nonambulatory animals
1 Yes 3 No
e. Dehorning
1 Yes 2 NA 3 No
d. Tail docking
1 Yes 2 NA 3 No
e. Castration
1 Yes 2 NA 3 No
[If Question 2a = No, SKIP to Section C.]
3. During 2013, how frequently were milkers trained? (Check one only.)
1 Trained as new employees only
2 1 to 2 times per year for all milkers
3 3 to 4 times per year for all milkers
4 More than 4 times per year for all milkers
5 Other (specify: __________________________)V253OTH
4. Which of the following training methods were used on this operation
during 2013 for training milkers?
a. Video training V254 1 Yes 3 No
b. Discussion/lecture V255 1 Yes 3 No
c. On-the-job training V256 1 Yes 3 No
d. Other training (specify: ___________________)V257OTH V257 1 Yes 3 No
Section C—Milk Quality and Milking Procedures
1. Which of the following best describes the average bulk tank
somatic cell count for milk shipped during 2013? (Check one only.)
1 Less than 100,000 cells/mL
2 100,000 to 199,000 cells/mL
3 200,000 to 299,000 cells/mL
4 300,000 to 399,000 cells/mL
5 400,000 to 499,000 cells/mL
6 500,000 to 599,000 cells/mL
7 600,000 cells/mL or greater
2. Who milked the majority of cows on this operation during 2013?
(Check one only.)
1 Owner/operator
2 Family member(s) of owner
3 Hired worker(s) (nonfamily member)
3. Which of the following best describes how frequently forestripping
occurred on this operation during 2013? (Check one only.)
1 Forestrip all cows
2 Forestrip some cows (i.e., with mastitis or fresh cows)
3 Do not forestrip any cows
[If Question 3 = 3, SKIP to Question 5.]
4. When was forestripping performed? (Check one only.)
1 Prior to teat disinfection
2 After teat disinfection but prior to drying teats
3 After disinfection and/or drying
5. Ask the Producer to briefly describe his/her premilking teat preparation routine from the
majority of cows and determine the general method used. After the general method has
been determined, pick the specific procedure(s) that are typically used. It is likely that only
one specific procedure will be checked.
If more than one procedure is checked, indicate the order in the overall routine.
“Single-use” and “multiple-use” refer to cows, not teats.
PREMILKING TEAT PREPARATION ROUTINE |
|||
General method |
Specific procedure |
Check all that apply |
Order in routine |
Wash pen |
Wash animals in pen prior to entering parlor |
V262 |
V283 |
Water hose |
With disinfectant |
V263 |
V284 |
Without disinfectant |
V264 |
V285 |
|
Dry
wipe |
Single-use cloth towel |
V265 |
V286 |
Multiple-use cloth towel |
V266 |
V287 |
|
Single-use paper towel |
V267 |
V288 |
|
Multiple use paper towel |
V268 |
V289 |
|
Wet wipe |
Commercial teat wipes, single use |
V269 |
V290 |
Commercial teat wipes, multiple use |
V270 |
V291 |
|
Towel using labeled disinfectant, single use |
V271 |
V292 |
|
Towel using labeled disinfectant, multiple use |
V272 |
V293 |
|
Towel using nonlabeled/homemade disinfectant, single use |
V273 |
V294 |
|
Towel using nonlabeled/homemade disinfectant, multiple use |
V274 |
V295 |
|
Multiple use sponge with disinfectant |
V275 |
V296 |
|
Predip |
Applied with sprayer using labeled disinfectant |
V276 |
V297 |
Applied with sprayer using nonlabeled/homemade disinfectant |
V277 |
V298 |
|
Applied with predip cup using labeled disinfectant |
V278 |
V299 |
|
Applied with predip cup using nonlabeled/homemade disinfectant |
V279 |
V300 |
|
Applied as foam using labeled disinfectant |
V280 |
V301 |
|
Applied as foam using nonlabeled/homemade disinfectant |
V281 |
V302 |
|
Other |
Other (specify: )V282OTH |
|
|
6. Which of the following best describes how teats are dried
prior to milking in both summer and winter seasons?
(Enter one code only for each season.)
1 = Not applicable—teats not wet prior to milking
2 = Air dry
3 = Single-use cloth towel
4 = Single-use paper towel
5 = Multiple-use cloth towel
6 = Multiple-use paper towel
7 = Other (specify: _________________________) V304/305 _____ code _____ code
Summer Winter
7. Which of the following best describes postmilking procedures
regarding teat disinfection in both summer and winter seasons?
(Enter one code only for each season.)
1 = Dip teats with labeled postdip product
2 = Dip teats with nonlabeled/homemade solution
3 = Spray teats with commercial postdip product
4 = Foam teats with commercial postdip product
5 = Teats covered in commercial powder product
6 = None
7 = Other (specify: __________________________)V306OTHV306/307 _____ code _____ code
Summer Winter
8. What premilking and postdip teat disinfectants does this operation
use primarily during both summer and winter seasons?
(Write in one code for each response for each season. See attached
VS Initial Visit Reference Card for brand names.)
1 = Iodophor (iodine containing)
2 = Chlorhexidine
3 = Fatty acid based
4 = Quaternary ammonium
5 = Phenols
6 = Chlorine product
7 = Other (specify: _________________)V308OTH
8 = None
Summer Winter
a. Premilking teat disinfectant V308/310 _____ code _____ code
b. Postdip teat disinfectant V309/311 _____ code _____ code
9. Which of the following best describes this operation’s use of a
barrier teat dip (Blockade™, Uddergold™ 5-star)?
(Check one only.)
1 Used on all cows on this operation all the time
2 Used on all cows during winter or adverse weather
3 No barrier teat dip used on this operation
4 Other (specify: _____________________)V312OTH
10. Did milkers wear latex or nitrile gloves when milking cows
during 2013? 1 Always 2 Sometimes 3 Never
11. Did this operation use a backflush system in milking units during 2013? V314 1 Yes 3 No
[If Question 11 = No, SKIP to Question 13.]
12. Was the backflush system currently used for every milking? V315 1 Yes 3 No
13. Did this operation use automatic takeoffs? 1 Yes 3 No
14. Were clinical mastitis cows generally milked:
a. Using a separate milking unit from healthy cows? V317 1 Yes 3 No
b. In a separate string from healthy cows? V318 1 Yes 3 No
15. During 2013, were cows vaccinated for:
any disease using autogenous vaccines? V324 1 All 2 Some 3 None
[If Question 15 = None, SKIP to Question 17.]
16. Were autogenous vaccines administered for the following mastitis pathogens?
a. Mycoplasma V325 1 Yes 3 No
b. Staph. aureus V326 1 Yes 3 No
c. E. coli V327 1 Yes 3 No
d. Strep. spp. V328 1 Yes 3 No
e. Other (specify: _________________________)V329OTH V329 1 Yes 3 No
17. During 2013, what was the average cost per cow of vaccinations used for mastitis prevention? $_______
18. Were any of the following milk cultures performed during 2013?
a. Individual cows V330 1 Yes 3 No
b. Bulk-tank milk V331 1 Yes 3 No
c. String samples V332 1 Yes 3 No
[If Questions 18a–18c are all No, SKIP to Question 21.]
19. During 2013, were any of the milk cultures performed by:
a. Farm personnel, done on farm? V333 1 Yes 3 No
b. A State or university diagnostic laboratory? V334 1 Yes 3 No
c. A commercial lab? V335 1 Yes 3 No
d. A private veterinary lab (veterinary clinic)? V336 1 Yes 3 No
[If Question 19a = No (no individual cow milk cultures performed), SKIP to Question 22.]
20. During 2013, which cows were typically selected for milk culturing?
a. Fresh cows V337 1 Yes 3 No
b. All clinical cases V338 1 Yes 3 No
c. Chronic clinical cases V339 1 Yes 3 No
d. Clinical cases that did not respond to treatment V340 1 Yes 3 No
e. High somatic cell count cows V341 1 Yes 3 No
f. Other (specify: ____________________________)V342OTH V342 1 Yes 3 No
21. Which of the following organisms were identified from milk
cultured during 2013?
a. Strep. agalactiae V343 1 Yes 3 No
b. Staph. aureus V344 1 Yes 3 No
c. Mycoplasma V345 1 Yes 3 No
d. E. coli/Klebsiella/other gram negative V346 1 Yes 3 No
e. Coagulase neg staph (Staph. spp.) non-aureus V347 1 Yes 3 No
f. Environmental strep (Strep. spp.) non-agalactiae V348 1 Yes 3 No
22. Which of the following were responsible for diagnosing mastitis?
a. Owner 1 Yes 3 No
b. Milkers 1 Yes 3 No
c. Manager/herdsperson 1 Yes 3 No
d. Other (specify_____________________________) 1 Yes 3 No
23. During 2013, did your mastitis treatment protocol involve the following:
Intramammary antibiotics? 1 Yes 3 No
Systemic antibiotics? 1 Yes 3 No
Quarter milking? 1 Yes 3 No
Early dry off? 1 Yes 3 No
Movement to a separate milking pen? 1 Yes 3 No
Other? (specify: _______________________) 1 Yes 3 No
[If Question 23a = No, SKIP to Question 26.]
24. During 2013, what was the maximum number of intramammary antibiotic
treatment regimens that were used to treat mastitis in an individual cow
before discontinuing antibiotic treatment? ______ #
[If Question 24 = 1, SKIP to Question 26.]
25. Were different antibiotics used for successive courses? 1 Yes 3 No
26. During 2013, what was the average cost of the following to treat a
single case of clinical mastitis (include the entire treatment regime
which may have been multiple days?
Intramammary antibiotics $______
Systemic antibiotics $______
Other drugs (e.g., Banamine, etc.) $______
Labor costs $______
Veterinary services $______
27. Did this operation perform on-farm antibiotic residue testing of milk during 2013? 1 Yes 3 No
[If Question 27 = No, SKIP to Question 30.]
28. Which test was most commonly used on this operation to screen
for antibiotic residues in milk? (Check one only.)
1 Snap® kit (beta lactam or tetracycline)
2 Delvotest®
3 CITE Probe®
4 Charm Farm
5 Penzyme® Milk Test
6 Other
(specify: ______________________)V350OTH V350
29. Were milk samples evaluated for antibiotic residues from:
a. Fresh cows? V351 1 Yes 3 No
b. Individual cows recently treated with anitbiotics? V352 1 Yes 3 No
c. Bulk tank prior to processor pickup? V353 1 Yes 3 No
d. Other? (specify: _______________________)V354OTH V354 1 Yes 3 No
30. Which of the following describes this operation’s typical dry-off procedures:
a. Stop milking based on set schedule (e.g., so many days prior to calving)
regardless of milk production 1 Yes 3 No
b. Stop milking based on minimum milk production level? 1 Yes 3 No
31. Which of the following dry off methods did this operation use during 2013?
a. Abruptly stop milking
b. Skip milkings prior to complete dry off (e.g., milk once a day for a number of days)
c. Other (specify: _______________________________________)
32. Which of the following management practices did this operation use at dry off in 2013?
a. Perform CMT test V351 1 Yes 3 No
b. Reduce the quality of feed V351 1 Yes 3 No
c. Restrict access to feed V352 1 Yes 3 No
If Yes, how long were cows generally without feed at dry off _____ hr
d. Restrict access to water V353 1 Yes 3 No
If Yes, how long were cows generally without water at dry off _____ hr
33. Please complete the following table based on procedures used at the time of drying off:
|
IMM antibiotics |
Internal teat sealant |
External teat sealant |
Dry cow treatments |
Not used on any cows on this operation |
Not used on any cows on this operation |
Not used on any cows on this operation |
Used on all cows |
1 Yes 3 No |
1 Yes 3 No |
1 Yes 3 No |
Use based on SCC |
1 Yes 3 No |
1 Yes 3 No |
1 Yes 3 No |
Use based on history of mastitis (clinical/chronic) |
1 Yes 3 No |
1 Yes 3 No |
1 Yes 3 No |
Use based on milk production |
1 Yes 3 No |
1 Yes 3 No |
1 Yes 3 No |
Used on all cows but only during adverse weather |
1 Yes 3 No |
1 Yes 3 No |
1 Yes 3 No |
All cows seasonally |
1 Yes 3 No |
1 Yes 3 No |
1 Yes 3 No |
34. During 2013, approximately what percentage of cows
were treated with dry cow intramammary antibiotics at drying off? V357 _____ %
[If Question 34 = 0, SKIP to Section D.]
35. Was it standard procedure to clean teats with alcohol pads
prior to administering antibiotics V351 1 Yes 3 No
36. Of those cows treated during 2013 with dry cow intramammary
antibiotics, what percentage were given the following antibiotics?
(See attached VS Initial Visit Reference Card.)
a. Spectramast DC (Ceftiofur hydrochloride) V358 _____ %
b. Cefa-Dri®/Tomorrow (Cephapirin benzathine) V359 _____ %
c. Boviclox; Dry-Clox®; Dry-Clox® Intramammary Infusion; Orbenin-DC®
(Cloxacillin benzathine) V360 _____ %
d. Gallimycin®-Dry (Erythromycin) V361 _____ %
e. Biodry® (Novobiocin) V362 _____ %
f. Hanford’s/US Vet Go Dry (Penicillin G procaine) V363 _____ %
g. Quartermaster® Dry Cow Treatment
(Penicillin G procaine/Dihydrostreptomycin) V364 _____ %
h. Albadry® Plus Suspension (Penicillin G procaine/ Novobiocin) V365 _____ %
i. Other (specify: __________________________________)V366OTH V366 _____ %
Total (should equal 100%) 100%
37. During 2013, what was the average cost per cow of intramammary antibiotics used at dryoff? $______
Section D—Reproduction
1. During 2013, were timed-AI programs used to manage
reproduction in any:
a. Heifers? S017 1 Yes 3 No
b. Cows? 1 Yes 3 No
[If Questions 1b and 1b = No, SKIP to Question 3.]
2. How many years have timed-AI programs (e.g., Ovsynch) been used? S019 _____
3. Did this operation use a controlled internal drug release (CIDR) insert
during 2013? S021 1 Yes 3 No
If Yes, were they used:
a. As part of a herd synchronization program? S022 1 Yes 3 No
b. Specifically for animals identified as anestrus (acyclic)? S023 1 Yes 3 No
c. Specifically for animals identified as cystic? S024 1 Yes 3 No
d. Postbreeding? S025 1 Yes 3 No
e. Other? (specify: _____________________)S026OTH S026 1 Yes 3 No
4. Which of the following categories best describes first service
breeding practices for the majority of heifers and during 2013?
(Choose one code for heifers and one code for cows.)
1 = Natural service (bull-bred)
2 = AI to natural estrus (no injections given to induce estrus)
3 = AI to induced estrus (prostaglandin injections only)
4 = AI to induced estrus after Ovsynch program (prostaglandin and GnRH injections)
5 = Timed AI after Ovsynch program (prostaglandin and GnRH injections)
6 = AI to estrus after Presynch/Ovsynch
7 = Timed AI after Presynch/Ovsynch
8 = Other (specify: _______________________)S013OTH S013/014 _____ _____
Heifers Cows
5. Which of the following categories best describes second or greater
service breeding practices for the majority of heifers and cows in the
last 12 months? (Choose one code for heifers and one code for cows.)
1 = Natural service (bull-bred)
2 = AI to natural estrus (no injections given to induce estrus)
3 = AI to induced estrus (prostaglandin injections only)
4 = AI to induced estrus after Ovsynch program (prostaglandin and GnRH injections)
5 = Timed AI after Ovsynch program (prostaglandin and GnRH injections)
6 = AI to induced estrus after Resynch (Ovsynch’s 1st GnRH started 1 week
prior to, or at, pregnancy diagnosis)
7 = Timed AI to Resynch (Ovsynch’s 1st GnRH started 1 week
prior to, or at, pregnancy diagnosis)
8 = Other (specify: _______________________)S015OTH S015/016 _____ _____
Heifers Cows
6. Did any heifers or cows have embryos transplanted into during 2013? S028 1 Yes 3 No
If Yes, how many heifers and how many cows received:
a. Fresh embryos? S029/030 _____ _____
Heifers Cows
b. Frozen embryos? S031/032 _____ _____
Heifers Cows
7. During 2013, what percentage of pregnancies was conceived through:
a. Natural service (bull bred)? S033 _____ %
b. AI after detected estrus (natural or induced)? S034 _____ %
c. Timed AI without detected estrus? S035 _____ %
d. Embryo Transfer (ET) using superovulated embryo? S036 _____ %
e. Embryo Transfer (ET) using in vitro produced embryo? S037 _____ %
Total (should equal 100%) 100%
[If Questions 7b and 7c = 0, SKIP to Question 11.]
8. Which of the following best describes who performed the majority of AI services during 2013?
(Check one only.)
1 Owner/operator
2 Herdsman
3 General employee
4 AI service/technician
5 Other (specify: _________________________)S038OTH
9. Has this person who is responsible for the majority of AI services
[Question 8] been formally trained (lecture and lab) in performing AI? S039 1 Yes 3 No
10. How many heifers and how many cows were inseminated with
sexed semen during 2013?
a. Heifers S040 _____ #
b. Cows S041 _____ #
11. Which of the following best describes how frequently pregnancy exams
(herd or preg checks) were performed during 2013?
(Check one only.)
1 Weekly
2 Every 2 weeks
3 Monthly
4 Every other month
5 No pregnancy exams performed
6 Other (specify: ____________________________)S043OTH
[If Question 11 = 5, SKIP to Section E.]
12. Which of the following best describes who performed the majority of
pregnancy exams on this operation during 2013? (Check one only.)
1 Private veterinarian
2 Veterinary technician
3 Employee—veterinarian
4 Employee—nonveterinarian
5 Owner/operator
6 Other (specify: ____________________________)S044OTH
13. How many days postbreeding was the pregnancy
diagnosis usually made during 2013? S045 _____ days
14. During 2013, was pregnancy status routinely determined
on this operation using:
a. Rectal palpation? S046 1 Yes 3 No
b. Ultrasound? S047 1 Yes 3 No
c. Blood test? S048 1 Yes 3 No
d. Milk progesterone? S049 1 Yes 3 No
e. Other? (specify: _____________________________)S050OTH S050 1 Yes 3 No
[If Question 14b = No, SKIP to Section E.]
15. In what year was routine ultrasound diagnosis of pregnancy first
performed on this operation? S051 _____ year
16. Who owned the ultrasound equipment used for the majority of
pregnancy diagnoses during 2013? (Check one only.)
1 Veterinarian
2 Dairy operation
3 Other (specify: ______________________________)S052OTH
17. In addition to pregnancy diagnosis, which of the following information
was collected/evaluated during ultrasound exams during 2013?
a. Twin pregnancies S053 1 Yes 3 No
b. Assessment of fetal viability S054 1 Yes 3 No
c. Noncycling (no heat) cows S055 1 Yes 3 No
d. Ovarian cysts S056 1 Yes 3 No
e. Fetal sexing S057 1 Yes 3 No
f. Other (specify: ______________________________)S058OTH S058 1 Yes 3 No
Section E— Surgical Procedures Questions
(dehorning, extra teat removal, tail docking, castration)
1. During 2013, were heifer calves routinely dehorned
while on this operation? S138 1 Yes 3 No
[If Question 1 = No, SKIP to Question 5.]
2. During 2013, what percentage of heifer calves were dehorned
by the following methods? What was the average age of calves (in weeks)
and were analgesics or anesthetics used?
Age % heifer average Analgesics/
calves (weeks) anesthetics
a. Hot iron (Buddex, electric, Portasol) S139/145/150 _____ _____ 1 Yes 3 No
b. Caustic paste S140/146/151 _____ _____ 1 Yes 3 No
c. Tube, spoon, or gouge S141/147/152 _____ _____ 1 Yes 3 No
d. Saws, wire, or Barnes S142/148/153 _____ _____ 1 Yes 3 No
e. Other (specify: _________________) S143/149/154 _____ _____ 1 Yes 3 No
Total (should be ≤100%) S144 _____
3. Was surgical dehorning equipment that causes bleeding
chemically disinfected between each animal? S155 1 Yes 2 NA 3 No
4. Who dehorned the majority of heifer calves on this operation during 2013?
(Check one only.)
1 Owner/operator
2 Employee
3 Veterinarian
4 Other (specify: ____________________________)S156OTH
5. Did this operation use polled bulls (either AI or natural service)
during 2013? S157 1 Yes 3 No
6. During 2013, were extra teats routinely removed from heifer calves? S157 1 Yes 3 No
[If Question 6 = No, SKIP to Question 9.]
7. In general, at what age (in weeks) were extra teats removed? S158 _____ weeks
8. When extra teats were removed, were analgesics or anesthesia
routinely used? S159 1 Yes 3 No
9. What percentage of dairy cows on this operation have docked tails? S160 _____ %
[If Question 9 = 0, SKIP to Question 13.]
10. What procedure was most commonly used to dock tails? (Check one only.)
1 Band
2 Surgical removal with blades or shears
4 Other (specify: ___________________________)S161OTH
5 Unknown procedure—purchased with tails already docked
11. How old were the majority of animals when tails were docked? (Check one only.)
1 Less than 2 months
2 2 months to less than 6 months
3 6 months to less than 2 years
4 2 years or older
5 Unknown
12. When tails were docked, were analgesics or
anesthesia routinely used? S163 1 Yes 2 Don’t Know 3 No
13. During 2013, were bull calves routinely castrated
while on this operation? S164 1 Yes 3 No
[If Question 13 = No, SKIP to Section F.]
14. What method was most commonly used to castrate bull calves? (Check one only.)
1 Burdizzo (crushes cord/bloodless)
2 Knife
3 Band
4 Other (specify: __________________________)S165OTH
15. At what age (in weeks) were bull calves routinely castrated? S166 _____ weeks
16. When calves were castrated, were analgesics or anesthesia
routinely used? S167 1 Yes 3 No
Section F—Hoof Health
1. During 2013, how many cases of lameness (gait abnormality)
occurred on this operation in:
a. Bred heifers? (Enter NA if bred heifers are not housed on this operation.) S168 _____ #
b. Cows? S169 _____ #
2. Of the cases of lameness in bred heifers and cows from the
previous question, what number of cases were due to digital
dermatitis (hairy-heel warts)?
a. Bred heifers (Enter NA if bred heifers are not housed on this operation.) S170 _____ #
b. Cows S171 _____ #
3. Which of the following best describes the use of a footbath for
cows during 2013? (Check one only.)
1 Footbath used throughout the year
2 Footbath used seasonally/occasionally
3 No footbath used
4 Other (specify: ________________________)S172OTH
[If Question 3 = 3, SKIP to Question 6.]
4. Which of the following footbath medications was most commonly used?
(Check one only.)
1 Copper sulfate
2 Formalin/formaldehyde
3 Oxytetracycline
4 Hydrogen peroxide
5 Other (list active ingredient: ____________________)S173OTH
5. How frequently were footbaths cleaned during 2013? How many times per month??
1 Daily or more frequently
2 Weekly
3 Monthly
4 Other (specify: ________________________________)S173OTH
6. What percentage of cows had their hooves trimmed at least once in 2013? S174 _____ %
[If Question 6 = 0, SKIP to Question 9.]
7. Which of the following describes who trimmed the majority
of the hooves during 2013? (Check one only.)
1 Professional hoof trimmer (not this operation’s personnel)
2 Veterinarian (not this operation’s personnel)
3 Owner or this operation’s personnel
4 Other (specify: _____________________________)S175OTH
8. During 2013, how many visits, for the purpose of trimming hooves
(as part of a routine trimming program) or for evaluation of lame cows,
were made by:
a. A professional hoof trimmer? S176 _____ #
b. A veterinarian? S177 _____ #
c. Other? (specify: ____________________________)S178OTH S178 _____ #
9. Which of the following were responsible for identifying lame cows during 2013?
a. All employees S159 1 Yes 3 No
a. Owner S159 1 Yes 3 No
b. Herdsperson S159 1 Yes 3 No
c. Milkers S159 1 Yes 3 No
d. Breeder S159 1 Yes 3 No
e. Other (specify: ________________________________) S159 1 Yes 3 No
10. How soon after being identified did lame cows generally receive treatment? (Check one only.)
1 The same day
2 Within a day
3 Within a week
4 Within a month
Section G—Treatment Practices
1. How many injections of any kind did a dairy cow typically receive
in the last 12 months? S190 _____ #
2. Of all injections administered on this operation, what percentage were:
a. Intramuscular (IM)? S192 _____ %
b. Subcutaneous (SQ)? S193 _____ %
c. Intravenous (IV)? S194 _____ %
Total (should equal 100%) 100%
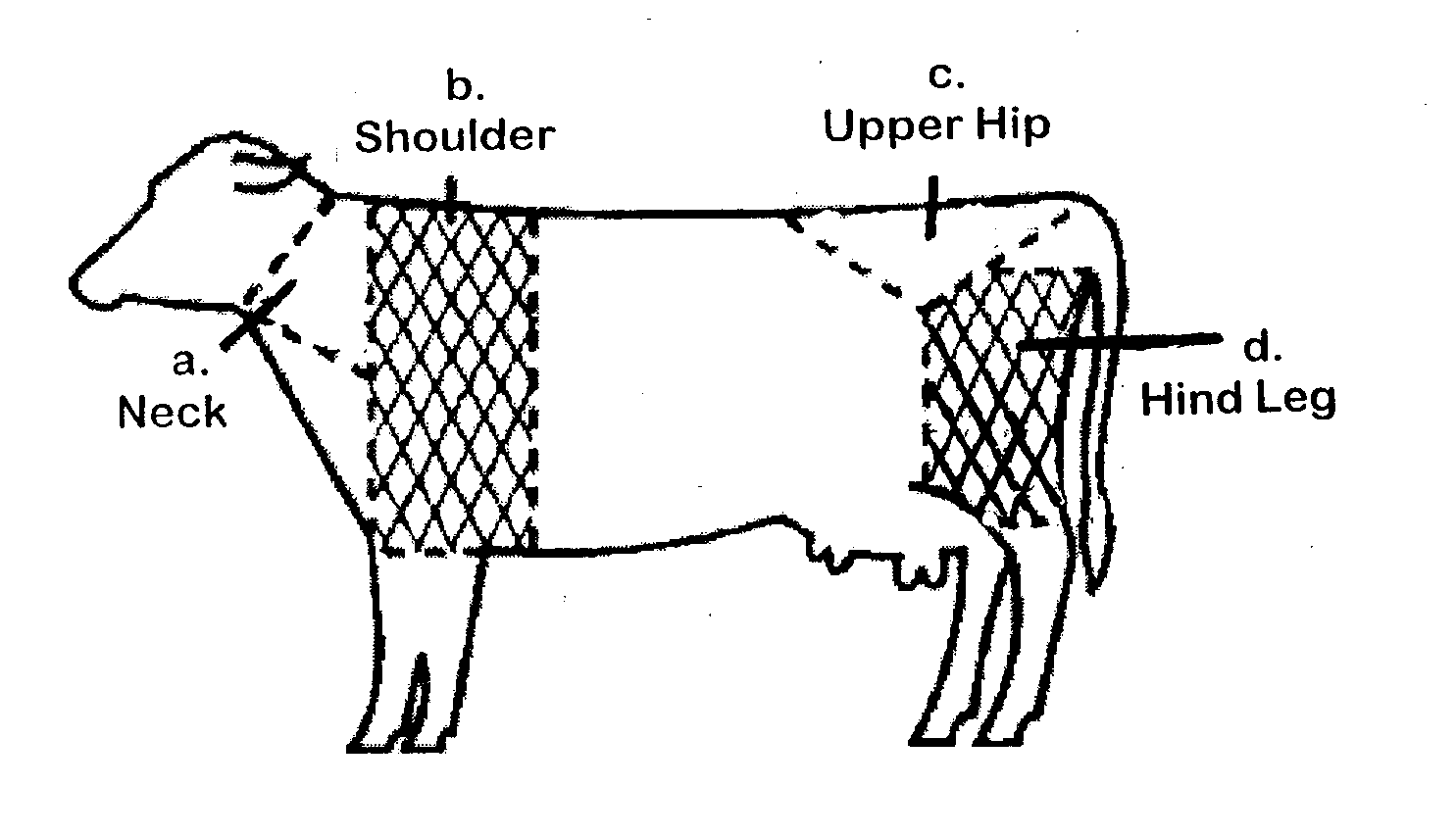
3. What percentage of the intramuscular (IM) injections were administered
for each of the following purposes and in what location were they administered? Primary
location
code
a. Antibiotic injection S195 _____ % ______
b. Production enhancement (e.g., oxytocin) S196 _____ % ______
c. Reproductive injection S197 _____ % ______
d. Vaccination S198 _____ % ______
e. Other S199 _____ % ______
Total (should equal 100%) 100%
4. Which of the following cattle-handling facilities were primarily used
for each type of injection for both heifers and cows?
1 = Stanchion/tie stall
2 = Lock-ups
3 = Chute/head gate
4 = Loose in freestalls
5 = Palpation rail
6 = Parlor
7 = NA
Heifers Cows
a. IM S225/228 _____ code _____ code
b. SQ S226/229 _____ code _____ code
c. IV S227/230 _____ code _____ code
5. When farm personnel administered injections during 2013,
how many injections were usually given before changing needles?
(Check one only.)
1 New needle for every injection
2 2 to 10 injections per needle
3 11 to 20 injections per needle
4 21 to 30 injections per needle
5 More than 30 injections per needle
Section H—Health, Deaths and Permanent Removals
1. During 2013, how many dairy cows were permanently removed, excluding
deaths, from the herd? _____ #
[If Question 1 = 0, SKIP to Question 5.]
2. Of the (Question 1) cows that were permanently removed, what percentage
were sent to the following and what was the average price received per head?
Price
Percent AND per head
a. Directly to another dairy _____ _____
b. To a market, auction, or stockyard _____ _____
c. Directly to a packer or slaughter plant _____ _____
d. Elsewhere (specify: ____________________________) _____ _____
Total 100%
3. Of the (Question 1) cows permanently removed during 2013, what percentage were:
a. Less than 50 days in milk (early lactation)? _____ %
b. 50 to 199 days in milk (mid lactation)? _____ %
c. 200 days or more in milk (late lactation)? _____ %
d. Dry cows? _____ %
Total 100%
4. Of the (Question 1) cows permanently removed during 2013, what percentage were:
a. First lactation? _____ %
b. 2 to 4 lactations? _____ %
c. 5 lactations or more? _____ %
Total 100%
5. During 2013, how many dairy cows were euthanized? _____ head
6. During 2013, how many dairy cows died (were not euthanized)? _____ head
7. Then the total number of dairy cow deaths during 2013 was? _____ head
8. During 2013, what percentage of dairy cows that died were necropsied
to determine the cause of death? _____ %
The following questions are used to determine the number of cases of diseases on
your operation in 2013, how many of those cases were removed from your herd (excluding
deaths), and how many died. If no animals were affected with the disease or disorder,
move to the next row. If any cows experienced the disease or disorder during 2013,
please record the number affected, the number removed, and the number that died.
9. During 2013, how many dairy cows were affected with, removed, and died from the following:
Health condition |
Affected? |
# head |
Removed? (# head) |
Died? (# head) |
a. Cancer eye? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
b. Clinical mastitis? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
c. Digestive: |
|
|||
i. Bloat? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
ii. Bloody gut (HBS)? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
iii. Diarrhead greater than 40 hr (Johne’s disease)? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
iv. DA (displaced abomasum)? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
v. Indigestion/diarrhea less than 48 hr? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
vi. Other digestive? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
d. Downers (nonambulatory)? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
e. Injuries (secondary to slip/fall)? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
f. Lameness? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
g. Lymphoma (bovine leucosis virus)? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
h. Metabolic: |
|
|||
i. Ketosis? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
ii. Milk fever (hypocalcemia)? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
iii. Other metabolic? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
i. Respiratory? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
j. Reproductive: |
|
|||
i. Dystocia (calving problems)? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
Of the dystocia cases, were any Cesarean section? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
ii. Infertility? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
iii. Metritis? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
iv. Retained placenta? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
v. Other reproductive? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
k. Other? |
1 Yes 3 No |
|||
l. Aggressive/kickers? |
|
|||
m. Poor production? |
|
|||
n. Sold as dairy replacements? |
|
|||
o. Other known reasons? |
|
|||
p. Unknown reasons? |
|
|||
Total (should match Question 1 [removals] and Question 7 [deaths]) |
|
Preweaned heifers Weaned heifers
10. During 2013, how many dairy heifers were euthanized? _____ _____
11. During 2013, how many dairy heifers died (were not
euthanized? _____ _____
12. Then the total number of dairy heifers deaths during 2013 was? _____ _____
[If Question 12 = 0 for both columns, SKIP to Section I.]
13. During 2013, what percentage of dairy heifers that died were
necropsied to determine the cause of death? _____ %
14. How many dairy heifers died or were euthanized due to the following:
Preweaned Weaned dairy heifers
dairy heifers that had not calved
a. Scours, diarrhea, or other digestive problems? _____ _____
b. Respiratory problems? _____ _____
c. Lameness? _____ _____
d. Injury? _____ _____
e. Calving problems? _____ _____
f. Joint or navel problems? _____ _____
g. Other known reasons? (specify: _____________) _____ _____
h. Unknown reasons? _____ _____
i. Total (should equal Question 12 for each type of heifer) _____ _____
15. During 2013, which one of the following was the primary method of
disposal for dead heifers and cows? (Enter one code for each cattle type.)
Method of disposal |
|
1 = Bury |
5 = Landfill |
2 = Burn/incinerate |
6 = Left for wildlife |
3 = Render |
7 = Other (specify: ) |
4 = Compost |
|
a. Preweaned heifers _____ code
b. Weaned heiferws _____ code
c. Cows _____ code
Section I—Antibiotic Use and Residue Avoidance
1. During 2013, did this operation use medications in feed or water
for any weaned or pregnant dairy heifers to prevent disease or
promote growth? 1Yes—Continue 3 No—Go to Question 3
2. During 2013, what percentage of weaned heifers and pregnant heifers received the following medications?
Medication |
Weaned heifers |
Pregnant heifers |
No weaned heifers on farm during 2013? 1 Yes 3 No |
No pregnant heifers on farm during 2013? 1 Yes 3 No |
|
1 No medications administered |
1 No medications administered |
|
a. Rumensin®, Bovatec®, Cattlyst® (ionophores) |
% |
% |
b. Corid®, Deccox® (coccidiostats) |
% |
% |
c. Aureomycin® (chlortetracycline compounds) |
% |
% |
d. Neo-Terramycin® 100/100 (neomycin- oxytetracycline) |
% |
% |
e. Neomycin sulfate |
% |
% |
f. OTC 4 Crumbles®, Terramycin® 200 (oxytetracycline compounds) |
% |
% |
g. Aureo S 700® 2G Crumbles (auremycin and sulfamethazine) |
% |
% |
h. Sulfamethazine |
% |
% |
i. Other (specify: Weaned ________________) Pregnant _______________) |
% |
% |
3. Complete the table below on antibiotics used during 2013 to treat diseases or disorders
in all cows. (This does NOT apply to dry cow treatments and to preventive treatments.)
(See attached VS Initial Visit Reference Card.)
If antibiotic is not listed, please write in name and active ingredient.
|
Disease or disorder |
Number of affected animals in the last 12 months |
Number of affected animals treated with ANTIBIOTICS |
Primary ANTIBIOTIC used (Enter one code from attached list.) |
Secondary ANTIBIOTIC used (Enter one code from attached list.) |
Tertiary ANTIBIOTIC used (Enter one code from attached list.) |
All cows |
Respiratory |
V386 |
V399 |
|
|
V412 |
Diarrhea or other digestive |
V387 |
V400 |
|
|
V413 |
|
Reproductive |
V388 |
V401 |
|
|
V414 |
|
Mastitis |
V389 |
V402 |
|
|
V415 |
|
Lameness |
V390 |
V403 |
|
|
V416 |
|
Other (specify) V391OTH |
V391 |
V404 |
|
|
V417 |
26. Of lactating cows treated for disease during 2013 with
antibiotics, were treatments based primarily on: (Enter one code for each cattle type.)
Antibiotic treatments based on…
1 = Veterinary recommendation
2 = Historical effectiveness
3 = Historical culture and antimicrobial sensitivity results
4 = Individual cow culture results prior to therapy
5 = Other (specify: _______________________________)
Disease or disorder |
Antibiotic treatments primarily based upon (code) |
Respiratory |
V386 |
Diarrhea or other digestive |
V387 |
Reproductive |
V388 |
Mastitis |
V389 |
Lameness |
V390 |
9. How did you determine which drug to select for treatment of cattle during 2013?
a. Consulting with your veterinarian S159 1 Yes 3 No
b. Utilizing a protocol provided by a veterinarian S159 1 Yes 3 No
c. Reviewing the drug label S159 1 Yes 3 No
d. Reviewing Promotional materials and Advertisements from drug companies S159 1 Yes 3 No
e. Breeder S159 1 Yes 3 No
f. Other (specify: ________________________________) S159 1 Yes 3 No
10. How do you determine which drug to select for treatment of cattle?
a. Consulting with your veterinarian 1 Yes 3 No
b. Utilizing a protocol provided by a veterinarian 1 Yes 3 No
c. Reviewing promotional materials and advertisements from drug companies 1 Yes 3 No
d. Searching the Internet (e.g., drug company Web sites, producer blogs, etc.) 1 Yes 3 No
e. Consulting drug company representatives 1 Yes 3 No
f. Friend/other producers 1 Yes 3 No
g. State/county services/extension agent 1 Yes 3 No
h. Other (specify: _____________________________________________) 1 Yes 3 No
11. How do you determine the withdrawal time of a drug?
a. Consulting with your veterinarian 1 Yes 3 No
b. Utilizing a protocol provided by a veterinarian 1 Yes 3 No
c. Reviewing the drug label 1 Yes 3 No
d. Reviewing the FARAD Web site (Food Animal Residue Avoidance
databank) 1 Yes 3 No
e. Reviewing promotional materials and advertisements from drug
companies 1 Yes 3 No
f. Searching the Internet (e.g., drug company Web sites, producer blogs, etc.) 1 Yes 3 No
g. Consulting drug company representatives 1 Yes 3 No
h. Friend/other producers 1 Yes 3 No
i. State/county services/extension agent 1 Yes 3 No
j. Other (specify: _______________________________________) 1 Yes 3 No
12. Does this operation keep a written or computerized record for each cow
that received a treatment that requires a withdrawal time before the
cow can be sent to market? S232 1 Yes 3 No
Office Use Only
State FIPS:__________ Operation #:_________ Interviewer:___________ Date: / /
2-digits 5-digits Initials (mm/dd/yy)
1. Total time for interview [include time to discuss the program
and complete the questionnaire] _____ min
2. Total travel time [round trip] _____ min
3. Data collector(s): [Enter the number for each category.]
____ Federal VMO ____ Federal AHT ____ State personnel ____ Other (specify)
4. Enter response code 99 if questionnaire is completed or enter
one code of 0 through 7 that best describes the reason why the owner
is not participating _____ code
99 - Survey completed
00 - Producer not contacted by VMO
01 - Poor time of year to contact or no time
02 - Does not want anyone on operation
03 - Bad experience with government veterinarians
04 - Does not want to do another survey or divulge information
05 - Told NASS they did not want to be contacted
06 - Ineligible (no dairy cows)
07 - Other reason (explain below)
5. Producer data quality 1 Good to excellent 2 OK 3 Poor
6. Field data quality 1 Good to excellent 2 OK 3 Poor
7. Which of the following best describes the respondent’s position
with this operation? _____ code VPOS
1 = Owner
2 = Manager
3 = Family member (other than owner or manager)
4 = Other hired employee
5 = Other (specify: _______________________________)VPOSOTH
Comments regarding this questionnaire or operation:
VMO or AHT Signature:___________________________________________________
TO BE COMPLETED BY THE COORDINATOR:
Field data quality 1 Good to Excellent 2 OK 3 Poor VFDQ
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | Lombard, Jason E - APHIS |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-29 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy