2442ss01
2442ss01.docx
NSPS for New Residential Hydronic Heaters and Forced-Air Furnaces (40 CFR part 60, subpart QQQQ) (Proposed Rule)
OMB: 2060-0693
1SUPPORTING STATEMENT
NSPS for New Residential Hydronic Heaters and Forced-Air Furnaces
(40 CFR Part 60, Subpart QQQQ)
PART A
1.0 Identification of the Information Collection
(a) Title and Number of the Information Collection.
The title of the Information Collection Request is NSPS for New Residential Hydronic Heaters and Forced-Air Furnaces (40 CFR Part 60, Subpart QQQQ)(Proposed Rule). This is a new information collection request (ICR), and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) tracking number is 2442.01, OMB Control Number 2060-NEW.
(b) Short Characterization.
This ICR covers information collection requirements in the proposed rule, New Source Performance Standards (NSPS) for new residential hydronic heaters and forced-air furnaces (40 CFR part 60, subpart QQQQ). The information collected will be used by the EPA and delegated state and local agencies to determine the compliance status of sources subject to the rule. A residential hydronic heater is defined as a fuel burning device designed to burn wood or biomass fuel for the purpose of heating building space and/or water through the distribution, typically through pipes, of a fluid heated in the device, typically water or a water and antifreeze mixture. Residential hydronic heaters typically have a maximum rated thermal output of 350,000 Btu/hr. A residential forced-air furnace is defined as a fuel burning device designed to be located outside of ordinary living areas and that warms spaces other than the space where the furnace is located, by the distribution through ducts of air heated by the furnace. Residential forced-air furnaces also typically have a maximum rated thermal output of 350,000 Btu/hr.
The residential hydronic heater and forced-air furnace NSPS is based on similar design principles as the NSPS for new residential wood heaters (40 CFR part 60, subpart AAA). These NSPS establish a certification program instead of the usual NSPS requirement that each affected facility demonstrate compliance through performance testing. Under this certification program, a single wood-heating appliance is tested to demonstrate compliance for an entire model line which could consist of thousands of stoves. The certification approach significantly reduces the compliance burden, including information collection, for the manufacturers of wood heating appliances. Because of the potential risks to the environment from the intentional or accidental misuse of the certification approach, there are several safeguards included, some of which entail reporting and recordkeeping. Under this proposed regulation, hydronic heater and forced-air furnace manufacturers and testing laboratories are required to submit reports to the EPA and/or to maintain records for demonstrating compliance with the NSPS. The manufacturers also must contract with third party certification bodies to develop and implement quality control plans.
The information supplied by the manufacturer to the agency is used: (1) to ensure that the best system of emission reduction is being applied to reduce emissions from hydronic heaters and forced-air furnaces; (2) to ensure that the appliance tested for certification purposes is in compliance with the applicable emission standards; (3) to provide assurance that non-tested production model appliances have emission performance characteristics similar to tested models; and (4) to provide an indicator of continued compliance. Information supplied to the agency by testing laboratories is used to grant or deny laboratory accreditation and to assist in enforcement and compliance activities.
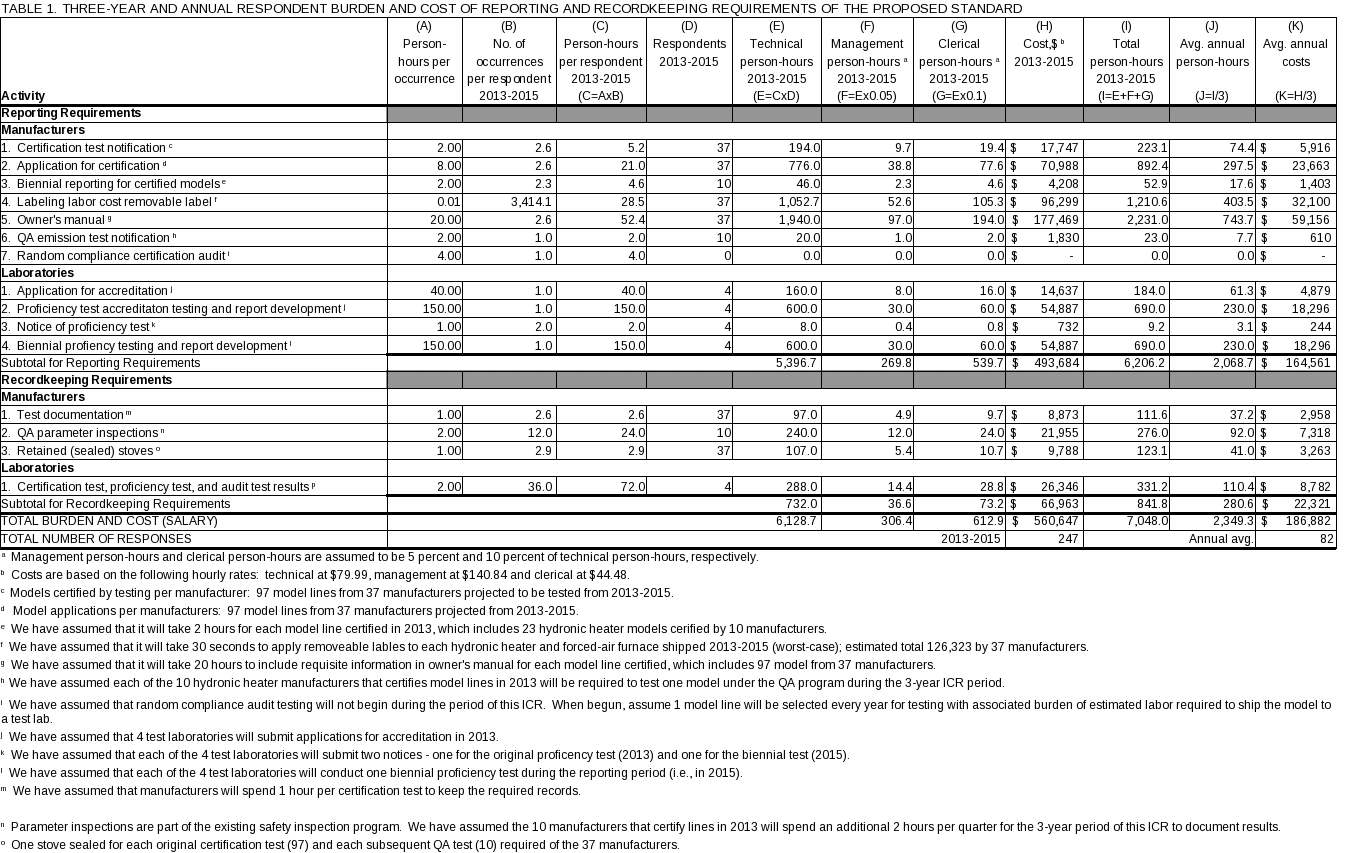
We believe that 30 hydronic heater manufacturers, 7 forced-air furnace manufacturers and 4 certification laboratories would be subject to the revised NSPS. The burden to the “Affected Public” is listed below in Table 1, Three-Year and Annual Respondent Burden and Cost of Reporting and Recordkeeping Requirements of the Proposed Standard. The federal government burden associated with the review of reports submitted by the respondent is shown below in Table 2, Three-Year and Annual Burden and Cost to the Federal Government of the Proposed Standard. (Tables 1 and 2 are located at the end of this supporting statement.) We do not anticipate any reporting or recordkeeping burden for state, local or tribal entities because we have only delegated ability to enforce the standards for residential hydronic heaters and forced-air furnaces sold or operated in their region. By retaining control over the certification and testing program, we ensure national consistency and provide the manufacturers with this resulting certainty.
We have not placed any reporting or recordkeeping requirements on the hydronic heater or forced-air furnace owner or operator, although we propose to establish stack height requirements for outdoor residential hydronic heaters. The proposed rule also provides a list of prohibited fuel types and prohibited operations in subpart QQQQ as well as good operating and good burning practices that are specified in the owner’s manual.
Subpart QQQQ includes a list of prohibitions that apply to the commercial owner (i.e., manufacturer, distributor, wholesaler or retailer) regarding labeling requirements for hydronic heaters and forced-air furnaces. Once again, failure to comply could result in enforcement actions, but there is no direct reporting or recordkeeping required under subpart QQQQ resulting from these actions.
Finally, as described above, the proposed subpart QQQQ would establish a responsibility for the hydronic heater or forced-air furnace manufacturer to develop a quality control plan for assuring that the units within a model line accurately reflect emission-critical components of the model line that has been reviewed and approved by a certifying entity for which the manufacturer has entered into a contract to provide certification services. We believe this approach will reduce costs associated with quality assurance/quality control (QA/QC) and reflect normal business operating expenses. In any case, subpart QQQQ does not impose any independent costs on the certifying entity.
The information collection requirements for new sources subject to the NSPS for Residential Hydronic Heaters and Forced-Air Furnaces are listed in Attachment 1.
2. Need For and Use of the Collection
(a) Need/Authority for the Collection.
The EPA is charged under section 111 of the Clean Air Act (CAA), as amended, to establish standards of performance for new stationary sources that reflect: “. . . application of the best system of emission reduction which (taking into consideration the cost of achieving such reduction and any non-air quality health and environmental impact and energy requirements) the Administrator determines has been adequately demonstrated. Section 111(a)(l). The agency refers to this charge as selecting the “best system of emission reduction.” Section 111 also requires that the Administrator review and, if appropriate, revise such standards every 8 years. Wood burning hydronic heaters and forced-air furnaces are part of the residential wood heating source category, pollutant emissions from which cause or contribute to air pollution that may reasonably be anticipated to endanger public health or welfare, in the Administrator's judgment. As part of the review process, the EPA has decided to expand the types of appliances regulated under the residential wood heating source category to include hydronic heaters and forced-air furnaces. Therefore, the NSPS is being proposed for these appliances at 40 CFR part 60, subpart QQQQ.
Certain records and reports are necessary for the Administrator to confirm the compliance status of new residential hydronic heaters and forced-air furnaces sold in the United States. These recordkeeping and reporting requirements are specifically authorized by section 114 of the CAA.
(b) Use/Users of the Data.
The control of pollution from new residential hydronic heaters and forced-air furnaces relies on the reduction of particulate matter emissions by proper appliance design. A representative unit for each model line is subjected to a certification test for particulate matter emissions and CO for a range of operating conditions. The manufacturer also contracts with a third party certifying entity, which reviews the test reports and design drawings, and conducts periodic quality assurance audits to ensure that hydronic heaters and forced-air furnaces manufactured subsequent to the initial certification test continue to comply with the NSPS. Manufacturers must recertify their model lines every 5 years or when they make changes to the model line that would exceed specified parameters.
The required notifications are used to inform the agency when a new model line is expected to be tested. The EPA may then observe the testing operation, if necessary. Emission test reports are needed as these are the agency’s record of a model line’s initial capability to comply with the emission standard, and serve as a record of the operating conditions under which compliance was achieved.
Adequate recordkeeping and reporting are necessary to ensure compliance with these standards as required by the Clean Air Act. The information collected from recordkeeping and reporting requirements is also used for targeting inspections and is of sufficient quality to be used as evidence in court.
3. Nonduplication, Consultations, and Other Collection Criteria
(a) Nonduplication.
A computer search of the EPA’s ongoing ICRs revealed no duplication of information-gathering efforts.
Similar requirements to this proposed NSPS are found in the requirements to 40 CFR part 60, subpart AAA, the NSPS for Residential Wood Heaters, and 40 CFR 60, subpart RRRR, the NSPS for Residential Masonry Heaters (proposed). Subpart AAA has a separate ICR undergoing OMB review, as does subpart RRRR. Although the requirements are similar, they are not duplicative because they apply to separate groups of appliances and the associated manufacturers. In the case of test laboratories, similar laboratory accreditation requirements are found each of the three NSPS, but each has different test methods. Therefore, these requirements are not duplicative because separate laboratory accreditation is required for each test method.
(b) Public Notice Required Prior to ICR Submission to OMB.
The preamble to the Proposed Rule will provide public notice.
(c) Consultations.
The proposed rule amendments were developed using extensive consultation with individual companies, trade associations and state agencies. Several of the key non-EPA persons consulted on the information collection activities are identified in Table 3. Additional meetings and contacts are documented in the project docket for this proposed rule, Docket No. EPA-HQ-OAR-2009-0734.
TABLE 3. PERSONS CONSULTED ON THE INFORMATION COLLECTION ACTIVITIES
Contact |
Organization |
Telephone Number |
Dennis Brazier |
Central Boiler |
|
John Crouch |
Hearth, Patio, Barbeque Association (HPBA) |
916.536.2390 |
Rick Curkeet |
Intertek Testing Services |
608.836.4400 |
Alice Edwards |
Alaska Dept. Of Environmental Conservation |
907.465.5105 |
Chuck Gagnor |
Northwest Manufacturing |
|
Stephen Hartsfield |
National Tribal Air Association |
505.242.2175 |
Frank Moore |
Hardy Manufacturing |
601.656.5866 |
Ben Myren |
Myren Consulting, Inc. |
509.684.1154 |
Scott Nichols |
Tarm Biomass |
|
Lisa Rector |
Northeast States for Coordinated Air Use Measurement (NESCAUM) |
617.259.2095
|
Rod Tinnemore |
Washington State Department of Ecology |
360.407.6978 |
(d) Effects of Less Frequent Collection.
Less frequent information collection would decrease the margin of assurance that manufacturers are producing residential hydronic heaters and forced-air furnaces that (1) pass the initial certification test, and (2) continue to be manufactured in a way that ensures continuous compliance with the emission standards. If the information required by these standards were collected less frequently, the likelihood of detecting violations would be reduced.
(e) General Guidelines.
None of the guidelines in 5 CFR 1320.6 are being exceeded.
(f) Confidentiality.
All information submitted to the agency for which a claim of confidentiality is made will be safeguarded according to the agency policies set forth in Title 40, Chapter 1, Part 2, Subpart B—Confidentiality of Business Information (see 40 CFR part 2; 41 FR 36902, September 1, 1976; amended by 43 FR 39999, September 28, 1978; 43 FR 42251, September 28, 1978; 44 FR 17674, March 23, 1979).
(g) Sensitive Questions.
This section is not applicable because this ICR does not involve matters of a sensitive nature.
4. The Respondents and the Information Requested
(a) Respondents/NAICS Codes.
Potential respondents under subpart QQQQ are manufacturers of new residential hydronic heaters and forced-air furnaces. The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) code for residential hydronic heating manufacturing facilities is 333414, Heating Equipment (Except for Warm Air Furnace Manufacturing). The NAICS code for forced-air furnaces is 333415, Air-Conditioning and Warm Air Heating Equipment and Commercial and Industrial Refrigeration Equipment Manufacturing. This subpart also applies to accredited testing laboratories that conduct wood heater certification tests for manufacturers. The NAICS code for testing laboratories is 541380.
(b) Information Requested.
(i) Data Items, Including Recordkeeping Requirements. In this ICR, all the data recorded or reported is required by the NSPS for New Residential Hydronic Heaters and Forced-air Furnaces (40 CFR Part 60, subpart QQQQ). The reporting requirements for NSPS subpart QQQQ were uniquely designed for the manufacturers and testing laboratories. A special table is attached that describes the reporting and recordkeeping requirements in detail. See Attachment 1.
Under the proposed NSPS, test results are to be submitted electronically to EPA’s Central Data Exchange (CDX) using the Electronic Reporting Tool (ERT) beginning as soon as the ERT is modified to be compatible with hydronic heater and forced-air furnace test methods. More generally, EPA may request a report in any form suitable for the specific case (e.g., by electronic media such as Excel spreadsheet, on CD, or hard copy). Currently, testing laboratories are working voluntarily with EPA to streamline performance and proficiency test reporting. While EPA retains the right to require reports to be submitted in paper format, we believe that the reports required under the NSPS will increasingly be submitted electronically.
In addition, the proposed rule would require the electronic submittal of applications for certification and recertification and other required reports.
(ii) Respondent Activities. The respondent activities that will be required by proposed subpart QQQQ are identified in Table 1 (located at the end of this supporting statement) and introduced in section 6(a).
5. The Information Collected–Agency Activities, Collection Methodology and Information Management
(a) Agency Activities.
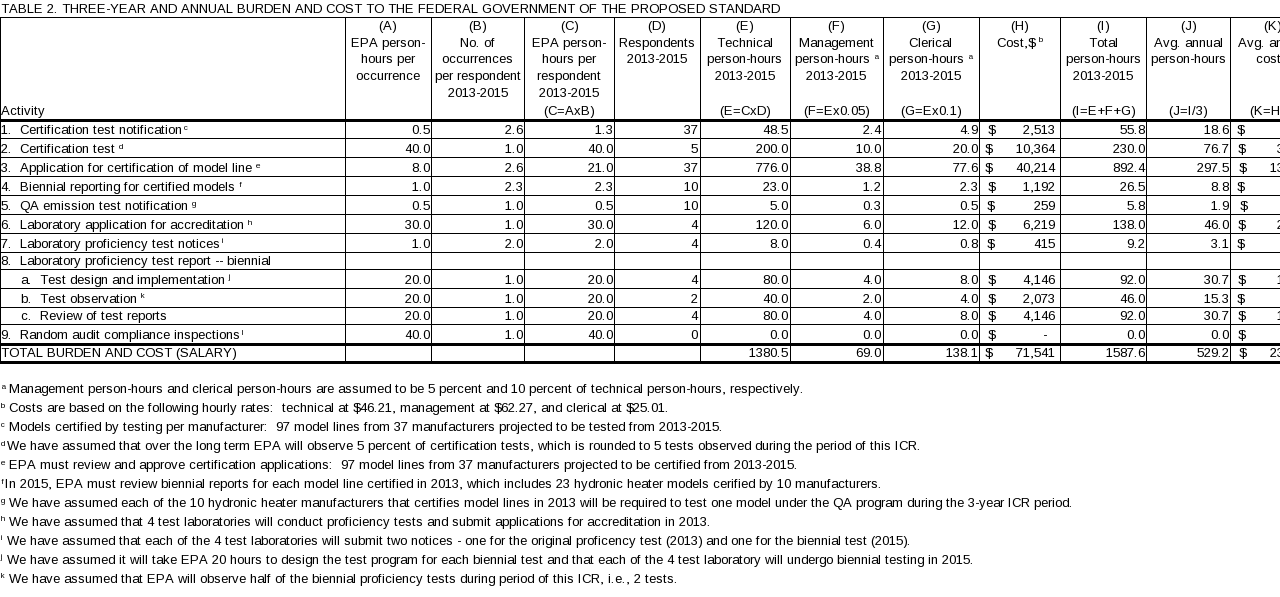
Attachment 2 is a summary of the reporting and recordkeeping requirements for the federal government. The agency activities associated with the proposed subpart QQQQ are provided in Table 2 (located at the end of this supporting statement) and are introduced in section 6(c).
(b) Collection Methodology and Management.
All reports are sent directly to the agency. Data obtained during periodic visits by agency personnel from records maintained by the respondents are tabulated and published for internal agency use in compliance and enforcement programs. Information contained in the reports is systematically filed at EPA headquarters. Portions of the data are entered into a special database program maintained exclusively by the agency for later retrieval, study and essential reports.
The EPA will provide public access to portions of the hydronic heater and forced-air furnace database on line. A list of certified appliances and their emissions ratings will be available on line by the time the proposed NSPS is promulgated.
The records required by this regulation must be retained by the manufacturer or test laboratory for 5 years.
(c) Small Entity Flexibility.
Most of the manufacturers, laboratories and commercial owners affected by this proposed regulation are considered small businesses based on the definition used by the Small Business Administration. Additional efforts were taken by the agency to reduce the burden imposed on the small businesses affected by this regulation. We believe that the proposed staggered compliance dates will allow additional time for sources to come into compliance and help reduce burden on small businesses by spreading out research and development (R&D) costs over several years. We also believe that the proposed approach to the quality assurance program will align with existing safety quality assurance procedures, thus avoiding potentially duplicative procedures.
(d) Collection Schedule.
The specific frequency for each information collection activity within this request is shown in Table 1 for the Residential Hydronic Heater and Forced-Air Furnace Source Category, which is located at the end of this supporting statement.
6. Estimating the Burden and Cost of the Collection
(a) Estimating Respondent Burden.
The annual burden estimates for the proposed subpart QQQQ are shown in Table 1, located at the end of this section. These numbers were derived from estimates based on EPA’s experience with implementing existing subpart AAA and other standards, and the EPA voluntary hydronic heater program.
(b) Estimating Respondent Costs.
(i) Estimating Labor Costs. Loaded labor rates have been calculated for 2010. We used May 2009 labor rates from the Bureau of Labor Statistics for the Ventilation, Heating, Air-Conditioning and Commercial Refrigeration Equipment Manufacturing (NAICS 333400),1 and escalated them to 2010 rates using the Employment Cost Index (ECI) provided by the BLS for the manufacturing industry.1 Loading factors (i.e., fringe benefits and overhead rates) were calculated using methodologies referenced in promulgated regulations and their accompanying ICRs, particularly those used in New Source Review regulations. Fringe benefits are calculated as 29 percent of hourly earnings, and overhead is calculated using a standard 110 percent above hourly earnings. Table 4 presents the labor rates used in the cost analysis.
Table 4. 2010 LOADED LABOR RATES
Labor Category |
Hourly earnings [$2009] |
Fringe |
Overhead |
Loaded |
ECI |
Loaded 2010 Hourly Earnings ($) |
Professional specialty and technical |
28.92 |
1.29 |
2.1 |
$78.34 |
2.1 |
$79.99 |
Executive, admin, managerial |
50.92 |
1.29 |
2.1 |
$137.94 |
2.1 |
$140.84 |
Admin support |
16.08 |
1.29 |
2.1 |
$43.56 |
2.1 |
$44.48 |
(ii) Estimating Capital and Operations and Maintenance (O&M) Costs. In this section we provide estimated capital costs and one-time start-up costs associated with complying with the NSPS over the 3-year ICR clearance period. These costs are summarized in Table 5 at the end of this section. See the manufacturer costs impacts memo2 and the unit cost memo3 for more information on assumptions used in this section.
As discussed in the manufacturer costs impacts memo, we estimate that there are currently 50 model lines of forced-air furnaces produced by 7 manufacturers and 120 model lines of hydronic heaters (about 10 percent of which are indoor hydronic heaters) produced by 30 manufacturers. For purposes of this ICR, we have assumed that of these 170 existing model lines, only the 23 existing outdoor hydronic heater model lines that are already qualified under the EPA voluntary program will meet the proposed NSPS without any design modifications. The manufacturers of these hydronic heater model lines would only be required by the NSPS to arrange for certification testing, which we believe they would do soon after promulgation of the final NSPS in 2013 because we believe that meeting the NSPS will be a selling point for these model lines. We assumed that these compliant model lines are produced by 10 manufacturers. Each certification test is a one-time start-up cost that is incurred when the test is performed, and we estimate certification testing to cost approximately $20,000 per model line.
For the remaining model lines, we assumed that all 37 manufacturers would undertake R&D efforts to modify or replace these model lines to meet the proposed NSPS. Although the R&D process may take several years to complete, we assumed that about half of the model lines (25 forced-air furnace models and 49 hydronic heater models) would be modified or replaced to comply with the NSPS during the 3 years covered by this ICR (2013-2015). These model lines also would undergo certification testing during the ICR clearance period.
The proposed NSPS would require a permanent label on each hydronic heater and forced-air furnace, just as required under subpart AAA. Also like subpart AAA, it would require a temporary label for each such appliance. To estimate the costs of the permanent and temporary labels, we used the same label cost estimates that are provided in ICR 1176.09 (2060-0161) for subpart AAA. We applied these costs to the number of shipments estimated for hydronic heaters and forced-air furnaces from 2013 to 2015. (See the unit cost memo for more information on estimated number of shipments.) We believe that manufacturers will act as quickly as possible to begin producing appliances that meet the proposed NSPS, even in advance of the applicable compliance date where possible, because certification will be a selling point for their units. Accordingly, we made the worst-case cost assumption that all hydronic heaters and forced-air furnaces shipped during between 2013 and 2015 would be compliant heaters with labels affixed, absent a reliable means of estimating the actual fraction that would be labeled.
We anticipate that the each manufacturer’s quality control assurance plan, as approved by the certifying entity, would include requirements to retest a certified model line under certain conditions to insure that such certified model lines continue to meet the NSPS emission limits. As for the certification tests, we estimate that the quality assurance tests would cost approximately $20,000 per test. We assumed that each of the 10 manufacturers that certifies existing outdoor hydronic heater model lines in 2013 would be subject to quality assurance testing requirements for one model line during the 3-year period covered by this ICR.
The last category of capital costs relates to the random audit testing requirement in the proposed NSPS. Under these requirements, EPA would select one certified hydronic heater or forced-air furnace model line at random each year for testing to verify that new units continue to meet the emission limits. The actual cost of conducting these audit tests is included in the cost of certification testing; that is, the test laboratories deposit a portion of the funds received for certification tests in escrow accounts to pay for subsequent audit testing. Thus, the test laboratories would be able to use the escrow accounts to defray the cost of testing. However, the manufacturers of the audited model lines would incur costs to supply from one to five units for testing, depending on test results. We have assumed that manufacturers would supply, on average, two units for each test, with the average cost of shipping estimated to be $1,000 per test. We assumed that over a 3-year period, one outdoor hydronic heater model line (at a cost of $11,571 per unit), one indoor hydronic heater model line ($11,543 per unit) and one forced-air furnace model line ($2,579 per unit) would be selected for audit testing (see the unit cost memo). However, no costs for random audit testing are included in this ICR because testing under this program is not expected to begin until after the period covered by this ICR, when escrow accounts have been built up by the testing laboratories.
TABLE 5. ESTIMATED CAPITAL/START-UP COSTS FOR 3-YEAR CLEARANCE PERIOD (2013-2015)
(A) |
(B) |
(C) |
(D) |
||
Data Collection Device |
Capital/Start-Up for One Respondent/Unit |
Number of New Respondents/Units |
Total Capital/Start-Up Cost |
||
|
|
|
(B X C) |
||
Certification Test a |
$52,432 per respondent |
37 respondents |
$1,940,000 |
||
Cost of Permanent Label b |
$2 per unit |
126,323 units |
$252,646 |
||
Removable Label Purchase/ Printing Cost c |
$0.75 per unit |
126,323 units |
$94,742 |
||
QA Emissions Test d |
$20,000 per respondent |
10 respondents |
$200,000 |
||
Random Audit Compliance Tests e |
$18,129 per respondent |
0 respondents |
$0 |
||
Total |
|
|
$2,487,388 |
||
Annual Average |
|
|
$829,129 |
||
|
a We have assumed that 23 outdoor hydronic heater models (10 of the 30 total hh manufacturers) to be tested in 2013. Additional 25 forced-air furnace models (7 manufacturers) and 6 indoor and 43 outdoor hydronic heater models (30 manufacturers) tested by 2015. $20,000 per test. |
|
|||
|
b Total costs of permanent labels are estimated to be $2.00 per label. Estimate 126,323 new masonry heaters produced by all manufacturers during the period covered by this ICR (2013-2015) and assume all will have permanent label affixed (worst-case assumption). |
|
|||
|
c Removable labels estimated to cost $0.75 per label. Estimate 126,323 new masonry heaters produced by all manufacturers during the period covered by this ICR (2013-2015) and assume all will have removable label affixed (worst-case assumption). |
|
|||
|
d We have assumed each of the 10 hydronic heater manufacturers that certifies model lines in 2013 will be required to test one model under the QA program during the period covered by this ICR (2013-2015) at $20,000 per test. |
|
|||
|
e When implemented (after the period covered by this ICR), 1 model line audited per year. Over 3 years, 1 outdoor ($11,571) and 1 indoor ($11,543) hydronic heater and 1 forced-air furnace ($2,579). Cost is average manufacturer cost of two appliances, plus $1,000 shipping. |
|
|||
(iii) Annualizing Capital Costs. The total annual capital/start-up costs average $829,129 over the period of this ICR (2013-2015).
(c) Estimating Agency Burden and Cost.
The major costs to the agency are those costs associated with reviewing applications for certification and laboratory accreditation and performing quality assurance functions. This is consistent with the overall EPA compliance and enforcement program, which includes activities such as the examination of records maintained by the respondents, periodic inspection of sources of emissions and the publication and distribution of collected information.
The average annual agency cost during the 3 years of the ICR is estimated to be $23,847. See Table 2, located at the end of this supporting statement.
The agency labor rates are from the Office of Personnel Management 2010 General Schedule which excludes locality rates of pay. These rates can be obtained from Salary Table 2010-GS available on the OPM website, http://www.opm.gov/oca/10tables/html/gs_h.asp. The government employee labor rates are $15.63/hour for clerical (GS-6, Step 3), $28.88 for technical (GS-12, Step 1) and $38.92/hr for management (GS-13, Step 5). These rates were increased by 60 percent to include fringe benefits and overhead. The fully-burdened wage rates used to represent agency labor costs are: clerical at $25.01; technical at $46.21 and management at $62.27.
(d) Estimating the Respondent Universe and Total Burden and Costs.
There are an estimated 37 existing manufacturers that will be subject to the Residential Hydronic Heater and Forced-Air Furnace NSPS. We recognize that this value may be high. We obtained information on the number of manufacturers by appliance type, which may double count manufacturers that make more than one type of appliance. Also, there seems to be a certain amount of consolidation in the industry. However, the number of new manufacturers, particularly outside of the United States, is unknown. Therefore, we consider the total of 37 manufacturers to be a reasonable surrogate for the number of new and existing manufacturers.
We have also assumed that there will be four laboratories in operation in 2013 that will seek accreditation for subpart QQQQ testing.
For the proposed subpart QQQQ, the components of the total annual responses attributable to this ICR are test notifications, applications for certification, biennial reporting for certified models, applications for accreditation and test report submittals for the 41 facilities (37 manufacturers and 4 testing laboratories that will be subject to the rule. The number of total annual responses for subpart QQQQ is estimated at 82.
(e) Bottom Line Burden Hours and Cost Tables.
(i) Respondent Tally. The bottom line respondent burden hours and costs for the 3 years (2013-2015) covered by this ICR are presented in Table 1 (located at the end of this supporting statement). The average annual burden for the recordkeeping and reporting requirements in subpart QQQQ for the estimated 41 existing facilities that will be subject to subpart QQQQ is 2,349 person-hours, with an annual labor average labor cost of $186,882 and annualized capital/start-up costs of $829,129.
(ii) The Agency Tally. The average annual Federal Government cost is $23,847 for 529 hours for subpart QQQQ. The bottom line agency burden hours and costs for the 3 years covered by this ICR are presented in Table 2 (located at the end of this supporting statement).
(iii) Variations in the Annual Bottom Line. This section does not apply since no significant variation is anticipated.
(f) Reasons for Change in Burden.
We are requesting a burden of 2,349 hours due to implementation of this new regulation.
(g) Burden Statement
The average annual respondent burden for the proposed Residential Wood Heating NSPS is estimated at 29 hours per response.
Burden means the total time, effort, or financial resources expended by persons to generate, maintain, retain, or disclose or provide information to or for a Federal agency. This includes the time needed to review instructions; develop, acquire, install, and utilize technology and systems for the purposes of collecting, validating, and verifying information, processing and maintaining information, and disclosing and providing information; adjust the existing ways to comply with any previously applicable instructions and requirements; train personnel to be able to respond to a collection of information; search data sources; complete and review the collection of information; and transmit or otherwise disclose the information.
An agency may not conduct or sponsor, and a person is not required to respond to a collection of information unless it displays a currently valid OMB control number. The OMB control numbers for EPA’s regulations in 40 CFR part 60 are listed in 40 CFR part 9.
To comment on the agency’s need for this information the accuracy of the provided burden estimates, and any suggestions for minimizing respondent burden, including through the use of automated collection techniques, EPA has established a public docket for this ICR under Docket ID No. EPA-HQ-OAR-2009-0734, which is available for online viewing at http://www.regulations.gov, or in person viewing at the Air and Radiation Docket and Information Center in the EPA Docket Center (EPA/DC), EPA West, Room 3334, 1301 Constitution Ave., NW, Washington, DC. The EPA Docket Center Public Reading Room is open from 8:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m., Monday through Friday, excluding legal holidays. The telephone number for the Reading Room is (202) 566-1744, and the telephone number for the Air Docket is (202) 566-1742. An electronic version of the public docket is available at http://www.regulations.gov. This site can be used to submit or view public comments, access the index listing of the contents of the public docket, and to access those documents in the public docket that are available electronically. When in the system, select “search,” then key in one of the Docket ID Numbers identified above. Also, you can send comments to the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs, Office of Management and Budget, 725 17th Street, NW, Washington, DC 20503, Attention Desk Officer for EPA. Please include the relevant Docket ID Number (EPA-HQ-OAR-2009-0734) and OMB Control Number (2060-NEW) in any correspondence.
PART B
This section is not applicable because statistical methods are not used in data collection associated with the proposed rule.
 Attachment
1
Attachment
1
Respondent Reporting and Recordkeeping Requirements
NSPS for New Residential Hydronic Heaters and Forced-Air Furnaces (40 CFR part 60, subpart QQQQ)
Regulatory Reference Title 40, Part 60 |
Regulated Entity |
Reporting/Recordkeeping Requirement |
Frequency/Other Comments |
60.5476(f) |
Manufacturer |
Report: notification of certification testing at least 30 days prior to test. |
Once per model. |
60.5475(a)(2) [60.533(f)] |
Manufacturer |
Report: Application for certification. Include results of performance test, identifying characterization results, quality control plan and various affirmations of compliance. |
Once for each model line. Must reapply every 5 years or whenever any change made in the design submitted that exceeds specified parameters. Can request waiver from need to retest. |
60.5479(d) |
Manufacturer |
Report: To EPA certifying that model line is unchanged. |
Every 2 years. |
60.5478(a) |
Manufacturer |
Produce and apply permanent label. |
One per unit produced. |
60.5478(e) |
Manufacturer |
Produce and apply removable label. |
One per unit produced. |
60.5478(g) |
Manufacturer |
Develop and publish owner’s manual. |
One per unit produced. |
60.5475(f) [60.533(o)(4)] |
Manufacturer |
Conduct periodic quality assurance audits. |
Periodically, as part of the regular safety audits that are now conducted. |
60.5479(a) |
Manufacturer |
Maintain records of all certification data, results of quality assurance program inspections, emission test data. |
Once per model for certification and test data. Periodically for all quality assurance inspections. |
60.5479(c) |
Manufacturer |
Retain sealed wood heater for the life of model. |
One for each certified model. |
60.5475(b) [60.533(g)(1)] |
Manufacturer |
Report: Request for waiver of testing requirement for certification testing. |
Up to once per model. |
60.5475(d) [60.533(k)(l)]* |
Manufacturer |
Report: Request for waiver of the requirement that a model line be recertified when changes exceed specified tolerances. |
Variable. |
60.5475(g) [60.533(p)(3)] |
Manufacturer |
Conduct random audit compliance testing on up to 5 appliances. Report results to Administrator. |
One time per year for the entire source category. Assume 2 appliances tested each time. |
60.5475(g) [60.533(p)(5)]** |
Manufacturer |
Development of documentation to rebut presumption of audit failure. |
Variable. |
60.5477 [60.535(a)] |
Laboratory |
Apply for accreditation. |
Once in the initial clearance period |
60.5477 [60.537(b)] |
Laboratory |
Report: Proficiency test and all test documentation |
At time of application and biennially. |
60.5477 [60.537(b)(3)] |
Laboratory |
Keep records of audit tests |
Once for each five certification tests. |
60.5479(b) |
Laboratory |
Maintain records of all certification test, proficiency test, and random compliance audit test data |
Once per tested model. |
* This is associated with an exemption or waiver (which would eliminate other reporting and recordkeeping burdens) and, therefore,,is not counted as a burden in the calculation.
** This is not a routine report. It is a provision for an extraordinary circumstance and, therefore, is not included in the calculations because it is very unlikely to occur during the next 3 years.
Attachment 2
Federal Reporting and Recordkeeping Requirements
NSPS for New Hydronic Heaters and Forced-Air Furnaces (40 CFR part 60, subpart QQQQ)
Regulatory Reference Title 40, Part 60 |
Agency |
Reporting/Recordkeeping |
Frequency/Other Comments |
60.5475(e)(2)* |
EPA |
Report: Notice of revocation of certification |
Once per model, if at all. |
60.5475(g) [60.533(p)(5)(i) or (ii)]* |
EPA |
Issue notification of audit test failure and certificate suspension or revocation |
Variable, if at all. |
60.5477 [60.535(a)] |
EPA |
Evaluate laboratory proficiency tests |
Biennially. |
60.5477 [60.535(b)(2)]* |
EPA |
Notice of intention to revoke laboratory accreditation with justification and basis |
Variable and infrequent. |
60.5481* |
Manufacturer EPA |
Various requests, submittals, motions, filings, etc., under hearing and appeal procedures |
Variable and infrequent. |
* This is not a routine occurrence. It is a provision for an extraordinary circumstance and, therefore, is not included in the calculations because it is very unlikely to occur during the next 3 years.
1 May 2009 National Industry-Specific Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates. Located http://www.bls.gov/oes/current/naics4_333400.htm.
1 Bureau of Labor Statistics. Table 5. Compensation (not seasonally adjusted): Employment Cost Index for total compensation, for private industry workers, by occupational group and industry Available: http://www.bls.gov/news.release/eci.t05.htm. Accessed February 22, 2011.
2 Memo to Gil Wood, USEPA, from Beth Friedman, EC/R, Inc. Draft Residential Heater Manufacturer Cost Impacts. February 11, 2011.
3 Memo to Gil Wood, USEPA, from Beth Friedman, EC/R, Inc. Unit Cost Estimates of Residential Wood Heating Appliances. February 11, 2010.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | SUPPORTING STATEMENT |
| Author | Marvin Branscome |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-28 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy