CMS-10569 ESRD QIP Supporting Statement A
CMS-10569 ESRD QIP Supporting Statement A.docx
(CMS-10569) Data Collection for Quality Measures Using the Consolidated Renal Operations in a Web-Enabled Network (CROWNWeb)
OMB: 0938-1289
Supporting Statement – Part A
Data Collection for Quality Measures Using the
Consolidated Renal Operations in a
Web-Enabled Network
(CROWNWeb)
Background
Pursuant to section 1881(h) of the Social Security Act (the Act) as amended by section 153(h) of the Medicare Improvements for Patients and Providers Act (MIPPA), the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) established the End-Stage Renal Disease Quality Incentive Program (ESRD QIP) starting in 2011. The ESRD QIP is the first value-based purchasing program established by CMS, and it is aimed at promoting patient health by providing a financial incentive for renal dialysis facilities to deliver high-quality care.
In implementing the End-Stage Renal Disease Quality Incentive Program (ESRD QIP), CMS believes that a successful quality incentive program will promote the delivery of high quality health care services in the renal dialysis facility setting. Under section 1881(h)(2) of the Act, the Secretary is required to specify quality measures for evaluating the quality of care ESRD patients receive at renal dialysis facilities. While the Act outlines few mandatory measure topics, the Secretary is authorized to adopt measures on specified areas or medical topics determined appropriate by the Secretary (§ 1881(h)(2)). The ESRD QIP began in calendar year (CY) 2011 with an initial set of three quality measures, and has dramatically increased its measure set over the intervening years through notice and comment rulemaking.
In order to score facility performance on quality measures, CMS must be able to collect data on these measures. CMS collects this data from multiple sources, including Medicare claims and other tools such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Healthcare Safety Network Dialysis Event Protocol. To further expand the measures used to evaluate the quality of care provided to ESRD patients in renal dialysis facilities, CMS also collects data using the Consolidated Renal Operations in a Web-Enabled Network (CROWNWeb) system. CROWNWeb went into production nationally on June 14, 2012, and brings together all of CMS’ information systems that collect, maintain, and report on data about ESRD patients and provides electronic reporting tools for use by renal dialysis facilities. Because of the complexity of the existing systems and because of the need to comply with the strong approved protections for private or confidential data, CROWNWeb was implemented in phases starting in February 2009.
Prior to this application for a new
OMB Control Number, the information collection requirements
associated with the ESRD QIP were (and, at present, continue to be)
approved under OMB Control Number 0938-0386. However, this package is
maintained by the Clinical Standards Group, not the Division for
Quality Measurement and Value-Based Incentives Group (QMVIG), which
maintains primary responsibility for CROWNWeb. In addition,
CROWNWeb reporting requirements for the ESRD QIP change
regularly, and has the requisite knowledge required to efficiently
manage changes to CROWNWeb uses and utilities. We therefore believe
it is most appropriate to develop a control number specific to
reporting and validating CROWNWeb data for the ESRD QIP in order to
ensure that the PRA package remains up-
to-date.
Data Collection for ESRD QIP Measures
In selecting measures for adoption into the ESRD QIP measure set, CMS strives to achieve several objectives. First, the measures should take into account national priorities such as those established by the Department of Health and Human Services’ National Quality Strategy (NQS) and the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services Quality Strategy. Second, the measures should be tailored to the needs of improved quality in the renal dialysis facility setting; thus, the measures selected are most relevant to renal dialysis facilities. Finally, the burden of measure compliance on renal dialysis facilities should be weighed against the potential for improvements in patient health and well-being resulting from the measure’s collection.
The majority of measures currently finalized for use in the ESRD QIP are extracted from Medicare claims and therefore require no additional effort on the part of dialysis facilities to report.1 However, some quality data relevant to the care received by ESRD patients cannot be derived from Medicare claims or other administrative forms. For these measures, dialysis facilities are required to submit data via a web-based tool such as CROWNWeb or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN). The burden associated with submitting measure data to the NHSN Healthcare Personnel Influenza Vaccination and Bloodstream Infection Modules2 and for the In-Center Hemodialysis Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems survey3 are already captured under previously approved packages; for this reason, this package is specific to the burdens associated with ESRD QIP measure data submitted via CROWNWeb.
The CY 2016 ESRD QIP
The CY 2015 End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) Prospective Payment System (PPS) final rule with comment period finalized quality measures, administrative processes, and data submission requirements for the CY 2016 (Payment Year 2018) ESRD QIP. During CY 2016, we will collect data for the following four measures using the CROWNWeb system:
Mineral Metabolism Reporting Measure (76 FR 70271):4 Number of months for which the facility reports serum phosphorus values for each Medicare patient.
Hypercalcemia Clinical Measure (76 FR 72203):5 Proportion of patient-months with 3-month rolling average of total uncorrected serum calcium greater than 10.2 mg/dL.
Pain Assessment and Follow-Up Reporting Measure (79 FR 66206):6 Facility reports in CROWNWeb one of the six conditions listed for each qualifying patient once before August 1 of the Performance Period and once before February 1 of the year following the Performance Period.
Clinical Depression Screening and Follow-Up Reporting Measure (79 FR 66203):7 Facility reports in CROWNWeb one of the six conditions listed for each qualifying patient once before February 1 of the year following the Performance Period.
We will continue to collect these measures in subsequent years unless the program deems their removal appropriate based on the measure removal criteria outlined in the CY 2013 ESRD Prospective Payment System final rule (77 FR 67475) and further clarified in the CY 2015 ESRD Prospective Payment System final rule (79 FR 66171 through 66173).
Table A. Measures Collected via CROWNWeb in CY 2016
NQS Goal |
NQF Endorsement Number |
Measure Title |
Data Collected |
Clinical Care |
1454 |
Hypercalcemia |
Uncorrected serum calcium |
Clinical Care |
N/A |
Mineral Metabolism |
Phosphorus measurement value Serum phosphorus or plasma phosphorus indicator |
Clinical Care |
N/A |
Pain Assessment and Follow-Up |
One of six pain assessment conditions |
Clinical Care |
N/A |
Clinical Depression Screening and Follow-Up |
One of six clinical depression screening conditions |
The CY 2017 ESRD QIP
As part of its effort to incentivize continued improvement in the quality of care provided to ESRD patients, in the CY 2016 ESRD PPS proposed rule, we are proposing to adopt two additional measures beginning in CY 2017 which would be collected via the CROWNWeb system:
Ultrafiltration Rate:8 Percentage of patients with a maximum ultrafiltration rate greater than 13 ml/kg/hr.
Full-Season Influenza Vaccination:9 Percentage of ESRD patients > 6 months of age on October 1 and on chronic dialysis > 30 days in a facility at any point between October 1 and March 31 of the Performance Period who either received an influenza vaccination, were offered and declined the vaccination, or were determined to have a medical contraindication.
If finalized, we will continue to collect these measures in subsequent years unless we deem their removal appropriate based on the measure removal criteria outlined in the CY 2013 ESRD Prospective Payment System final rule (77 FR 67475) and further clarified in the CY 2015 ESRD Prospective Payment System final rule (79 FR 66171 through 66173).
Table B. Measures Collected via CROWNWeb in CY 2017
NQS Goal |
NQF Endorsement Number |
Measure Title |
Data Collected |
Clinical Care |
1454 |
Hypercalcemia |
Uncorrected serum calcium |
Clinical Care |
N/A |
Mineral Metabolism |
Phosphorus measurement value Serum phosphorus or plasma phosphorus indicator |
Clinical Care |
N/A |
Pain Assessment and Follow-Up |
One of six pain assessment conditions |
Clinical Care |
N/A |
Clinical Depression Screening and Follow-Up |
One of six clinical depression screening conditions |
Safety |
N/A |
Ultrafiltration Rate |
Ultrafiltration rates (ml/kg/hr) |
Safety |
N/A |
Full-Season Influenza Vaccination |
Patient influenza immunization status |
CROWNWeb Data Validation for the ESRD QIP
One of the critical elements of the ESRD QIP’s success is ensuring that the data submitted to calculate measure scores and facility Total Performance Scores are accurate. We began a pilot validation study program for the ESRD QIP in CY 2013. In the CY 2014 ESRD PPS final rule with comment period, we finalized a requirement to sample approximately 10 records from 300 randomly selected facilities. In the CY 2015 ESRD PPS final rule with comment period, we continued this pilot for CY 2015. In the CY 2016 ESRD PPS proposed rule, we are proposing to continue this CROWNWeb data validation study during CY 2016.
Justification
Need and Legal Basis
Continued expansion of the End-Stage Renal Disease Quality Incentive Program (ESRD QIP) measure set is consistent with the letter and spirit of MIPPA. Section 1881(h)(2) of the Act requires that the Secretary specify measures for each year of the program and with each successive year of the ESRD QIP, CMS has increased the sophistication and scope of the program’s measure set. While Medicare claims can be an appropriate data source for some measures, claims do not represent the entirety of the ESRD population, and are also limited in the depth of information available. For these reasons, in furtherance of its obligations under section 1881(h)(2) of the Act, we have specified a number of measures utilizing data reported by renal dialysis facilities using the CROWNWeb system described below. These collections are authorized under section 494.180(h) of the Conditions for Coverage of End-Stage Renal Disease Facilities, which requires renal dialysis facilities to furnish data and information (both clinical and administrative) electronically to CMS at intervals specified by the Secretary. CMS proposes and finalizes data reporting requirements for the ESRD QIP through notice and comment rulemaking.
Information Users
Section 1881(h) of the Act requires the Secretary, generally, to adopt a set of quality measures and assess the quality of care provided by renal dialysis facilities using those measures. The measures adopted by the Secretary in satisfaction of these requirements utilize a number of different data sources including the CROWNWeb system, which collects data not otherwise available to CMS. As a result, collection of these data using CROWNWeb is necessary for assessing renal dialysis facility performance on quality measures finalized for the ESRD QIP; without it, the ESRD QIP would be unable to fulfill its statutory obligations as outlined in the Act. The data are used by CMS and others to monitor and assess the quality and type of care provided to ESRD patients, and will be made available to renal dialysis facilities for their use in internal quality improvement initiatives. The information is also used by CMS to direct its contractors to focus on particular areas of improvement and develop quality improvement initiatives. Most importantly, this information is available to beneficiaries, as well as to the public, to provide renal dialysis facility information to assist them in making decisions about their health care.
Use of Information Technology
As noted previously, CMS developed the Consolidated Renal Operations in a Web-Enabled Network (CROWNWeb) in order to reduce the burden to renal dialysis facilities of submitting data to CMS. This system brings together all of CMS’ information systems that collect, maintain, and report on data about ESRD patients and provides electronic reporting tools for use by renal dialysis facilities. Renal dialysis facility users are required to open an account under their CMS Certification Number and are then able to complete the necessary data submission. Copies of the data submission user interfaces are included with this package.
Duplication of Efforts/Similar Information
The information to be collected is not duplicative of similar information collected by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
Small Businesses
Information collection requirements were designed to impose minimal burdens on small renal dialysis facilities subject to the ESRD QIP. Specifically, the CROWNWeb system was created to allow small renal dialysis facilities to enter data via a web-based application rather than using paper-based data submission or employing a full electronic health record, which can be prohibitively expensive for these facilities. As a result, this effort facilitates small renal dialysis facilities’ collection and reporting of required data.
Less Frequent Collection
Measures developers employ clinical and statistical knowledge during the measure development process to determine the optimal schedule for collecting measure data. This data is then collected on the schedules provided in the CY 2015 ESRD PPS in order to best evaluate the care provided to ESRD patients. Without this frequency of information collection, CMS would be unable to assess the correlations between the endpoints collected and the health and well-being of ESRD patients treated by the renal dialysis facilities participating in the ESRD QIP.
Special Circumstances
Two of the measures previously adopted for use in the ESRD QIP, the Mineral Metabolism reporting measure and the Hypercalcemia clinical measure, require renal dialysis facilities to report data more often than quarterly. These measures evaluate a renal dialysis facility’s maintenance of ESRD patients’ serum calcium and serum or plasma phosphorus levels, both of which, when left unregulated, are associated with increased morbidity and mortality in ESRD patients. We therefore believe monthly collection is most appropriate in order to appropriately incentivize renal dialysis facilities to actively monitor their patients’ health and well-being.
We are also proposing to adopt one new measure, the Ultrafiltration Rate reporting measure, which will require renal dialysis facilities to submit data on their patients’ ultrafiltration rates more often than quarterly. The increased morbidity and mortality discussed previously are the cumulative effect of repeated or consistently elevated ultrafiltration rates; we therefore believe that less frequent collection would not accomplish the measure’s aim of ensuring that renal dialysis facilities remain vigilant in monitoring their patients’ ultrafiltration rates.
Federal Register Notice/Outside Consultation
The CY 2016 ESRD PPS proposed rule, serving as the 60-day Federal Register notice is scheduled to published on June 26, 2015. CMS will respond to any comments received on this notice.
Payment or Gift to Respondent
Dialysis facilities are required to submit measure data to CMS as part of the Conditions for Coverage of End-Stage Renal Disease Facilities (see 42 CFR 494.180(h)). No additional payments or gifts will be given to respondents for compliance with the reporting requirements of the ESRD QIP measures submitted via CROWNWeb.
Confidentiality
All information collected under the ESRD QIP will be maintained in strict accordance with statutes and regulations governing confidentiality requirements for CMS data, including the Privacy Act of 1974 (5 U.S.C. 552a), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the Quality Improvement Organizations confidentiality requirements, which can be found at 42 CFR Part 480. CMS maintains this information in the CMS data warehouse, which contains all information collected under this and other quality reporting and value-based purchasing programs. In addition, the tools used for transmission and storage of data are considered confidential forms of communication and are HIPAA compliant.
Sensitive Questions
There are no questions of a sensitive nature being collected as part of this quality assessment.
Burden Estimates
Section 1881(h) of the Act, as amended MIPPA, sets out requirements for the End-Stage Renal Disease Quality Incentive Program. Under section 1881(h)(2), CMS is required to specify measures for the ESRD QIP and, to the extent feasible and practicable, include measures set forth by one or more national consensus building entities. In the CY 2015 ESRD PPS final rule with comment period, CMS finalized quality measures, administrative processes, and data submission requirements for the CY 2016 (Payment Year 2018) ESRD QIP. In the CY 2016 ESRD PPS proposed rule, we are setting out the measures that CMS proposes to adopt for CY 2017. This burden estimate includes newly added measures, measures which CMS is continuing to collect as part of the ESRD QIP, and the ongoing CROWNWeb data validation study. As noted previously, this estimate excludes burden associated the NHSN Bloodstream Infection clinical measure, the NHSN Healthcare Personnel Influenza Vaccination reporting measure, and the In-Center Hemodialysis Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems measure because the burden associated with these measures is captured under OMB numbers 0920-066610 and 0938-0926, respectively. This burden estimate also excludes the burden associated with training facilities to use CROWNWeb, will continue to be accounted for in OMB Control Number 0938-0386.
The assumptions used to compute the estimated burdens associated with submitting ESRD QIP measure data via CROWNWeb and the ongoing CROWNWeb data validation study are described here.
a. Data Collection for ESRD QIP Measures Using CROWNWeb
We have used the following equation to estimate the burden associated with these data collection and submission efforts:
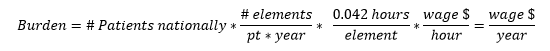
Table C. CROWNWeb Data Collection Burden Estimate Elements
Burden Estimate Elements |
CY 2016 |
CY 2017 |
Number of facilities11 |
6,264 |
6,264 |
Number of ESRD patients, nationally12 |
773,737 |
773,737 |
The time spent for data entry and submission per element13 |
0.042 hours (2.5 minutes) |
0.042 hours (2.5 minutes) |
Annual Hour Burden Nationally |
1,267,381 hours |
1,689,842 hours |
Hourly wage per hour engaged in data entry14 |
$18.68 |
$18.68 |
Hourly wage plus overhead and benefits |
$25.45 |
$25.45 |
The estimated number of patients per facility is estimated by calculating the mean number of patients per ESRD PPS-eligible facility nationwide, even though we recognize that the number of patients per renal dialysis facility is also highly variable, and may vary from month to month within a given facility. The estimated time per element entry for the CROWNWeb measures is based on historical estimates in the ESRD PPS proposed and final rules regarding the amount of time required to enter one data element for one patient (i.e., we assumed that it takes 2.5 minutes to report a data element, even though the time required is highly variable). Accordingly, we estimate the total annual hour burden for reporting measure data using the CROWNWeb system for CY 2016 to be 1,267,381 hours and the total hourly burden for CY 2017 to be 1,689,842 hours. The annual burden is 985,741.
We anticipate that the labor required to collect and submit this data will be completed by either Medical Records and Health Information Technicians or similar administrative staff. We have used the higher mean hourly wage of a Medical Record and Health Information Technician ($18.68/hour) in these calculations because the Bureau of Labor Standards identifies individuals holding this position as those responsible for organizing and managing health information data.15 Applying OMB Circular A-76, we assumed full fringe benefits of 36.25 percent, for a fully burdened labor rate of $25.45 that accounts for the full cost of labor. Accordingly, we estimate the total annual burden for reporting measure data using the CROWNWeb system for CY 2016 to be $32.2 million and the total annual burden for CY 2017 to be $43 million.
Table D1. CY 2016 CROWNWeb Data Collection Burden Per Measure
MEASURE REPORTING Renal Dialysis Facilities CY 2016 Measure Set |
Number of Facilities |
Number of Patients Nationally |
Number of Elements per Patient-Year |
Estimated Time for Data Entry per Element (hours) |
Estimated Wage plus Benefits per Hour for Data Entry |
Annual Hour Burden per Facility |
Annual Burden per Facility |
Hypercalcemia |
6,264 |
773,737 |
12 |
0.042 |
$25.45 |
62 |
$1,584.48 |
Mineral Metabolism |
6,264 |
773,737 |
24 |
0.042 |
$25.45 |
125 |
$3,168.95 |
Clinical Depression Screening and Follow-Up |
6,264 |
773,737 |
1 |
0.042 |
$25.45 |
5 |
$132.04 |
Pain Assessment and Follow-Up |
6,264 |
773,737 |
2 |
0.042 |
$25.45 |
10 |
$264.08 |
Table D2. CY 2016 CROWNWeb Total Data Collection Burden
Basis |
Number of Elements |
Annual Hour Burden |
Annual Burden |
Each Facility |
4,817 |
202 |
$5,149.55 |
National |
30,175,743 |
1,267,381 |
$32,256,752.76 |
Table E1. CY 2017 CROWNWeb Data Collection Burden Per Measure
MEASURE REPORTING Renal Dialysis Facilities CY 2017 Measure Set |
Number of Facilities |
Number of Patients Nationally |
Number of Elements per Patient-Year |
Estimated Time for Data Entry per Element (hours) |
Estimated Wage plus Benefits per Hour for Data Entry |
Annual Hour Burden per Facility |
Annual Burden per Facility |
Hypercalcemia |
6,264 |
773,737 |
12 |
0.042 |
$25.45 |
62 |
$1,584.48 |
Mineral Metabolism |
6,264 |
773,737 |
24 |
0.042 |
$25.45 |
125 |
$3,168.95 |
Clinical Depression Screening and Follow-Up |
6,264 |
773,737 |
1 |
0.042 |
$25.45 |
5 |
$132.04 |
Pain Assessment and Follow-Up |
6,264 |
773,737 |
2 |
0.042 |
$25.45 |
10 |
$264.08 |
Ultrafiltration Rate |
6,264 |
773,737 |
12 |
0.042 |
$25.45 |
62 |
$1,584.48 |
Influenza Immunization in the ESRD Population |
6,264 |
773,737 |
1 |
0.042 |
$25.45 |
5 |
$132.04 |
Table E2. CY 2017 CROWNWeb Total Data Collection Burden
Basis |
Number of Elements |
Annual Hour Burden |
Annual Burden |
Each Facility |
6,423 |
270 |
$5,149.55 |
National |
40,234,324 |
1,689,842 |
$43,009,003.69 |
b. CROWNWeb Data Validation
We have used the following equation to estimate the burden associated with the ongoing CROWNWeb data validation study:
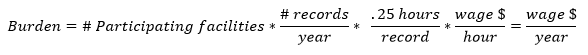
Table F. CROWNWeb Data Validation Burden Estimate Elements
Burden Estimate Element |
CY 2016 |
Number of facilities participating in the CROWNWeb data validation study, annually |
300 |
Number of medical records per facility per year |
10 |
Time spent for record collection and submission per facility16 |
2.5 hours (approx. 0.25 hours per record) |
Hourly wage per hour engaged in data collection and submission17 |
$18.68 |
Hourly wage plus overhead and benefits |
$25.45 |
Under the CROWNWeb data validation study proposed for CY 2016, we propose to randomly sample records from 300 facilities as part of its continuing pilot data validation program. Each sampled facility would be required to produce approximately 10 records. The burden associated with these validation requirements is the time and effort necessary to submit the requested records to a CMS contractor. We estimate that it will take each facility approximately 2.5 hours total, or .25 hours per medical record, to comply with this requirement. We therefore estimate the total annual hourly burden for the ongoing CROWNWeb data validation study for CY 2016 to be 750 hours.
We anticipate that the labor required to collect and submit this data will be completed by either Medical Records and Health Information Technicians or similar administrative staff. We have used the higher mean hourly wage of a Medical Record and Health Information Technician ($18.68/hour) in these calculations because the Bureau of Labor Standards identifies individuals holding this position as those responsible for organizing and managing health information data.18 Applying OMB Circular A-76, we assumed full fringe benefits of 36.25 percent, for a fully burdened labor rate of $25.45 that accounts for the full cost of labor. Accordingly, we estimate the total annual burden for the ongoing CROWNWeb data validation study for CY 2016 to be $19.1 thousand ($19,088.63).
Table G1. CY 2016 CROWNWeb Data Validation Burden
DATA VALIDATION Renal Dialysis Facilities CY 2016 |
Number of Facilities |
Number of Records per Year |
Estimated Time per Record |
Estimated Wage plus Benefits per Hour for Record Collection |
Annual Hour Burden per Facility |
Annual Burden per Facility |
CROWNWeb Data Validation |
300 |
10 |
0.25 |
$25.45 |
2.5 |
$63.63 |
Table G2. CY 2016 CROWNWeb Total Data Validation Burden
Basis |
Annual Hour Burden |
Annual Burden |
Each Facility |
2.5 |
$63.83 |
National |
750 |
$19,088.63 |
Capital Cost
There are no capital costs.
Cost to Federal Government
The cost to the Federal Government includes costs associated with the collection and validation of the data. The validation costs are an estimated $1,753,968 (FY) annually for the validation contract. The estimated cost to operate the collection of data through the CROWNWeb system includes five CMS staff at the GS-13 level (approximate annually salary is $92,000) and one at the GS-14 level (approximate annually salary is $106,000), for an additional cost of $566,000. This results in a total estimated cost of $2,319,968 annually.
Changes to Burden
As discussed above, the ESRD QIP has consistently expanded its measure set since the inception of the ESRD QIP in CY 2011, and is now proposing to add two new reporting measures beginning in CY 2017. These proposed additions to the ESRD QIP are expected to result in an increased burden to renal dialysis facilities. These added measures support the ESRD QIP’s mission of ensuring that ESRD patients receive high-quality care from their renal dialysis facilities by ensuring that the facilities are diligent in monitoring crucial aspects of ESRD patients’ care.
The CROWNWeb data validation study proposed for CY 2016 is a continuation of the study previously finalized for CY 2014 and CY 2015. As a result, this proposed continuation of the CROWNWeb is not expected to result in an increased burden to renal dialysis facilities.
Publication/Tabulation Date
The goal of the data collection is to evaluate facility performance on measures in the ESRD QIP measure set for the given year in order to assess the payment reductions required under section 1881(h)(1) of the Act. This data is also made publicly available pursuant to section 1881(h)(6) of the Act, and is used in other programs within the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, such as Dialysis Facility Compare.
Expiration Date
We request an exemption from displaying the expiration date because these tools will be used on a continuous basis by dialysis facilities reporting quality data.
Collection of Information Employing Statistical Methods
This information collection does not employ the use of statistical methods. The clinical data elements that will be collected under this package are necessary to calculate performance scores on quality measures for the ESRD QIP. At this point in time, all of the measures using clinical data collected under this package are specified for comprehensive datasets, not representative samples of comprehensive datasets. In addition, facility scores on the quality measures using this clinical data are the basis of subsequent improvement activities for dialysis facilities, and are intended to drive quality improvement in the dialysis facility setting. We therefore believe sampling and other statistical methods that may inappropriately impact the ESRD QIP’s calculation of performance scores for quality measures are inappropriate for this program.
1 For example, in the CY 2015 ESRD PPS final rule with comment period, CMS finalized 10 measures using Medicare claims as the primary data source.
2 Both the NHSN Bloodstream Infection and NHSN Healthcare Personnel Influenza Vaccination measure are accounted for under OMB Control Number 0920-0666.
3 OMB Control Number 0938-0926.
4 Abnormalities of bone mineral metabolism are exceedingly common and contribute significantly to morbidity and mortality in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease. Numerous studies have associated disorders of mineral metabolism with morbidity, including fractures, cardiovascular disease, and mortality. Overt symptoms of these abnormalities often manifest in only the most extreme states of calcium-phosphorus dysregulation, which is why CMS believes that routine blood testing of calcium and phosphorus is necessary to detect abnormalities.
5 Hypercalcemia has been shown to be significantly associated with increased all-cause mortality in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease, and both the KDIGO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, Prevention, and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease and the National Kidney Foundation’s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative support maintaining serum calcium levels within reference ranges. In addition, hypercalcemia is also a proxy for vascular and/or valvular calcification and subsequent risk for cardiovascular deaths.
6 Pain is one of the most common symptoms in patients with ESRD. Studies have shown that pain is a significant problem for more than 50 percent of patients with ESRD, and up to 82 percent of those patients report moderate to severe chronic pain. Furthermore, observational studies suggest that under-managed pain has the potential to induce or exacerbate comorbid conditions in ESRD, which may in turn adversely affect dialysis treatment.
7 Depression is the most common psychological disorder in patients with ESRD. Depression causes suffering, a decrease in quality of life, and impairment in social and occupational functions; it is also associated with increased health care costs. Current estimates put the depression prevalence rate as high as 20 percent to 25 percent of patients with ESRD, and studies have shown that depression and anxiety are the most common comorbid illnesses in patients with ESRD.
8 The ultrafiltration rate is the rate at which fluid is removed during the course of dialysis per unit (kilogram) body weight in the unit (hour) time. Observational studies have found that rapid ultrafiltration rates are associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular death. Based on its clinical relevance, CMS believes that proposing to adopt this measure is imperative as it supports our commitment to promoting sound clinical care to patients and supporting the NQF domains.
9 According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, seasonal influenza is associated with approximately 36,000 deaths and 226,000 hospitalizations annually. Infection is the second most common cause of death in patients with ESRD, and influenza accounts for significant morbidity and mortality in patients receiving dialysis. Vaccination is an effective preventive measure against influenza that can prevent many illnesses, deaths, and losses in productivity. Based on the clinical relevance, CMS believes that proposing to adopt this measure is imperative as it supports our commitment to promoting patient safety and community health and supporting the NQF domains.
10 Both the NHSN Bloodstream Infection and NHSN Healthcare Personnel Influenza Vaccination measure are accounted for under OMB Control Number 0920-0666.
11 Total number of ESRD PPS facilities in the United States treating ESRD QIP-eligible patients.
12 Total number of patients treated at ESRD PPS facilities in the United States
13 As stated in the PY 2019 ESRD PPS proposed rule, we estimate the amount of time required to submit measure data to CROWNWeb to be 2.5 minutes.
14 http://www.bls.gov/oes/current/oes_nat.htm#29-0000 (Estimates are based on national mean hourly wage).
15 http://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/medical-records-and-health-information-technicians.html
16 As stated in the PY 2019 ESRD PPS proposed rule, we estimate the amount of time required to submit measure data to CROWNWeb to be 2.5 minutes.
17 http://www.bls.gov/oes/current/oes_nat.htm#29-0000 (Estimates are based on national mean hourly wage).
18 http://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/medical-records-and-health-information-technicians.html
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | CMS-10569 ESRD QIP PRA Package Supporting Statement A |
| Author | CMS |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-24 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy