BAS Digital Tribal Respondent Guide
BASRespondentGuide_TribalDigital.docx
The Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS) & Boundary Validation Program (BVP)
BAS Digital Tribal Respondent Guide
OMB: 0607-0151
Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS) Tribal Respondent Guide: Digital
Instructions for Participating in the Boundary and Annexation Survey
Revised as of February 26, 2018
U.S.
Department of Commerce
Economic
and Statistics Administration
U.S.
CENSUS BUREAU
census.gov

This page intentionally left blank.
.
Table of Contents
A.1 The Boundary and Annexation Survey vii
A.2 What’s New for the BAS? vii
A.3 Key Dates for BAS Respondents vii
Part 1: DIGITAL BAS REQUIREMENTS 1
1.1 Digital BAS Participation Requirements 1
1.2 Tribal Areas that can be Submitted through BAS 1
1.3 BAS Informational and Tutorial Videos 2
Part 2: Topological Relationships and Spatial Accuracy 3
2.1 Topological Relationships in MAF/TIGER 3
2.2 GIS and Spatial Accuracy 4
2.3 Census Bureau Topology Training Video 6
Part 3: Census Bureau Provided Shapefiles 7
Part 4: Census Bureau Geocoding 8
4.1 MAF Structure Point Geocoding 8
Part 5: Updating the Census Bureau Shapefiles 11
5.1 General File Setup Guidelines 11
5.2 Changing the Map Projection 11
5.4 Additions and Deletions 12
5.6 New Tribal Subdivisions 13
5.9.1 Criteria for Defining Tribal Subdivisions 16
5.9.2 Updating Tribal Subdivisions 17
5.10 Linear Feature Updates 17
5.10.1 Adding, Deleting, Renaming, and Recoding Linear Features 17
5.10.2 Linear Feature Update Guidelines 18
5.10.3 Address Range Updates 18
5.11 Area Landmarks, Hydro Areas, and Point Landmarks 19
5.11.1 Area Landmark/Hydro Area Updates 19
5.11.2 Point Landmark Updates 21
5.12 Reviewing Changes to the Census Bureau Shapefiles 23
5.12.1 Boundary-to-Feature Relationships 23
5.12.2 Large Boundary Corrections 25
5.12.3 Including Required Attribute Information 26
5.12.4 Including Appropriate Metadata (Projection Information) 26
5.12.5 Linear Feature Updates 26
5.13 Additional Review Information 27
5.13.1 Submitting Acceptable Documentation 27
5.13.2 Submitting Digital Data 28
5.13.3 Change Polygon Naming Conventions 29
5.13.4 Whole Entity Polygon Naming Conventions 30
5.13.5 Linear Feature, Area Landmark/Hydro Area, and Point Landmark Updates (Not Required). 30
5.13.6 Compressing the Digital Files 30
5.13.7 Submitting Digital Files via SWIM 32
5.13.8 Additional Information 39
Appendix A. Data Dictionary A-1
Appendix B. Digital BAS – Example Process 1 B-1
B.1 Required Census Bureau Shapefiles B-1
B.2 Symbolizing Layers in ArcGIS B-1
B.3 Extracting AIA Data from Census Bureau Shapefiles B-2
B.4 Creating Change Polygons Using Symmetrical Difference B-4
B.5 Creating Change Polygons Using Union B-5
B.6 Reviewing and Attributing Change Polygons B-8
B.7 Renaming and Finalizing Change Polygons B-12
Appendix C. Digital BAS Example Process 2 C-1
C.1 Required Census Bureau Shapefiles C-1
C.2 Symbolizing Layers in ArcGIS C-1
C.3 Creating and Splitting Linear Features C-2
Appendix D. MTFCC Descriptions–Complete List D-1
Appendix E. Standard Street Type Abbreviations E-1
List of Tables
Table 1: BAS Shapefile Naming Conventions 6
Table 2: Additions and Deletions 10
Table 3: Boundary Corrections 10
Table 5: Geographic Corridors 12
Table 6: Geographic Offsets 13
Table 7: Linear Feature Updates 15
Table 8: Address Range Updates 16
Table 9: Area Landmark/Hydro Area Updates 17
Table 10: New Landmark/Hydro Area MTFCC Codes 17
Table 11: Point Landmark Updates 18
Table 12: Restricted Point Landmark MTFCC Codes 19
Table 13: Change Polygon Naming Conventions 26
Table 14: Whole Entity Polygon Naming Conventions. 26
Table 16: Alaska Native Regional Corporation (ANRC) Shapefile A-1
Table 17: American Indian Areas - Legal (AIAL) Shapefile A-2
Table 18: American Indian Tribal Subdivisions (AITS) Shapefile A-3
Table 20: Area Landmark Shapefile A-5
Table 21: Hydro Area Shapefile A-5
Table 22: Point Landmark Shapefile A-6
Table 23: Geographic Offset Shapefile A-6
Table 24: Suggested MTFCC Symbolization B-1
List of Figures
Figure 1. Road Representing 3 Types of Boundaries 3
Figure 2. Typological Integration of Four Classes 4
Figure 3. Overlay of Four Feature Classes 5
Figure 4. GIS Place Boundary Does Not Follow Road Feature 5
Figure 5. MSP Method of Geocoding 7
Figure 6. Address Range Method of Geocoding 8
Figure 7. Geographic Corridor Created 12
Figure 8. Geographic Corridor Not Created 12
Figure 10. Same Data Edited to Census Requirements 13
Figure 11. A Boundary Correction to Park A 16
Figure 12. Boundary Correction Not Snapped to Existing Linear Features 20
Figure 13. Annexation Created without Snapping to Centerlines 21
Figure 14. Small Spatial Correction Not Incorporated 21
Figure 15. Small Spatial Corretion Not Acepted 22
Figure 16. Large Boundary Corrections 22
Figure 17. New Road Features, Not Added to Existing Road 23
Figure 18. New Road Features, Correctly Added 23
Figure 19. Selecting and Zipping Return Files 27
Figure 20. Naming the Zip File 28
Figure 21. SWIM Account Registration 30
Figure 22. SWIM Login Window. 30
Figure 23. Welcome Screen with Upload History 31
Figure 24. Geographic Partnership Program Selection Window 31
Figure 25. Geographic Level Selection Window 32
Figure 26. Geographic Entity Selection Window 32
Figure 27. File Upload Screen 33
Figure 28. File Browser Dialog Box 33
Figure 29. Entering Comments into the File Upload Window 34
Figure 30. Thank You Screen 34
Figure 31. Suggested Map Symbolization B-2
Figure 33. Export Data Window B-3
Figure 34. Finalizing the Merge Process B-4
Figure 35. Finalizing the Symmetrical Difference Process B-5
Figure 36. Finalizing the Union Process B-6
Figure 37. Locating the Union Shapefile B-7
Figure 38. Small Slivers That Should Be Deleted B-8
Figure 39. Polygons That Should Be Snapped to Roads or Rivers B-8
Figure 40. Suggested Map Symbolization. C-2
Figure 41. Create Features Window. C-3
Figure 42. Linear Feature Selection Before Being Split C-5
Figure 43. Linear Feature Selection After Being Split C-5
Figure 44. Selecting the Linear Features of a Change Polygon C-6
Figure 45. Newly Created AIA Feature C-7
Introduction
The U.S. Census Bureau (Census Bureau) conducts an annual survey called the Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS) to collect information about selected legally defined geographic areas, such as counties (and equivalent areas), incorporated places, minor civil divisions (MCDs), federally recognized American Indian Areas (AIAs), including reservations, off-reservation trust lands and tribal subdivisions, Hawaiian Homelands, and Alaska Native Regional Corporations (ANRC). BAS also provides an opportunity for participants to review the names and geographic relationships for these areas. Title 13, U.S.C., Section 6, authorizes this survey.
The Census Bureau uses the boundary information collected during the BAS to tabulate data for the decennial and economic censuses, and to support the American Community Survey (ACS). Maintaining correct boundaries and boundary-to-feature relationships through the BAS helps ensure that the Census Bureau assigns the appropriate population to each governmental unit (GU).
In compliance with the Office of Management and Budget Circular A-16, the BAS supports the Census Bureau’s spatial data steward responsibilities for the Federal Geographic Data Committee (FGDC) and the Geospatial One-Stop by updating the inventory and boundaries of GUs.
In addition, the BAS is the source of up-to-date information on changes to the boundaries, codes and names of incorporated places, MCDs, counties (and equivalent areas), Hawaiian Homelands, ANRC, and federally recognized AIAs, which include reservations and off-reservation trust lands used by the U.S. Geological Survey’s (USGS), the National Map, and the Geographic Names Information System (GNIS).
Please visit the BAS program Web site at <https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/bas.html>. For more information on the BAS, please view the “Introduction to BAS” video series on the Census Bureau’s BAS Web site at <https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/bas/library/videos/bas-intro.html>.
The Geographic Partnership Support Desk (GPSD) is now fully functional and available to assist with any questions respondents may have regarding BAS.
Redistricting data contacts participating in the Voting District Project (VTD) may submit boundary updates for reconciliation with BAS contacts.
January 1 — All boundary changes must be legally in effect on or before this date to be reported in the current survey year.
March 1 — BAS submission date deadline for boundary updates to be reflected in the ACS and PEP published data. Boundary submissions received by this date are also reflected in next year’s BAS materials.
May 31 — BAS boundary updates submitted by this date will be reflected in next year’s BAS materials.
The Census Bureau has established a number of arrangements with states for reporting boundary changes. Please visit the BAS State Agreements webpage within the BAS program Web site at <https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/bas/information/state-agreements.html> or call (800) 972-5651 for information regarding state agreements.
Note: The Census Bureau can only establish BAS state agreements for states that require local governments to report boundary changes to a state agency.
If the Census Bureau discovers that an area of land is in dispute
between two or more jurisdictions, the Census Bureau will not make
any boundary corrections until the parties come to a written
agreement, or there is a documented final court decision regarding
the dispute.
If you have questions concerning this, please
contact the Census Bureau Legal Office at
301-763-9844.
For disputes involving tribal areas, the Census Bureau must defer to the Office of the Solicitor at the Department of the Interior for a legal opinion. Often complicated land issues require an extended period of time for resolution, and in those cases, the Census Bureau will retain the current boundary in the database until a legal opinion is issued by the Solicitor’s office.
All participants must have the ability to edit a Census Bureau shapefile. The Census Bureau requires that entities update Census Bureau shapefiles with boundary and feature changes, rather than submitting a shapefile from a local Geographic Information System (GIS);
All participants must provide current contact information for the tribal BAS point of contact, the person updating the shapefiles, and the tribal chair;
All participants must provide legal documentation (such as trust deeds and Federal Register Notice) and effective dates for all legal boundary changes (new reservation land and/or off-reservation trust lands);
Each non-legal boundary correction must contain proper update documentation; and
All participants must use the SWIM to submit their changes to the Census Bureau. Due to security requirements, we cannot accept submissions via FTP, email or any protocol other than the SWIM site (<https://respond.census.gov/swim/>). If you indicated on your Annual Response Form that you will download the Geographic Update Partnership Software (GUPS), download shapefiles, or requested the GUPS to be sent to you on DVD, you will automatically receive a SWIM registration token via email. The email should arrive 5 days after the BAS Annual Response Form is completed online (or 5 business days after the Census Bureau receives the paper form).To access the SWIM, enter the following URL in a new browser window: <https://respond.census.gov/swim/>.
The following can be updated through Tribal BAS:
Federal American Indian Reservations are areas that have been set aside by the United States for the use of tribes, the exterior boundaries of which are more particularly defined in the final tribal treaties, agreements, executive orders, federal statutes, secretarial orders, or judicial determinations.
Trust lands may be located on or off a reservation; however, the Census Bureau tabulates data only for off-reservation trust lands. Please do not submit on-reservation trust land because the Census Bureau can only show the exterior reservation boundary.
Federal Off-Reservation Trust Lands are areas for which the United States holds title in trust for the benefit of a tribe (tribal trust land) or for an individual American Indian (individual trust land).
The Census Bureau does not identify fee land (or land in fee simple status) or restricted fee lands as specific geographic areas.
Tribal Subdivisions are legal administrative subdivisions of federally recognized American Indian reservations and off-reservation trust lands and are described as additions, administrative areas, areas, chapters, county districts, communities, districts, or segments. These entities are internal units of self-government or administration that serve social, cultural, and/or economic purposes for the American Indians on the reservations and off-reservation trust lands.
Hawaiian Homelands are areas held in trust for Native Hawaiians by the state of Hawaii, pursuant to the Hawaiian Homes Commission Act of 1920, as amended.
Alaska Native Regional Corporation (ANRCs) were created pursuant to the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act (ANCSA) enacted in 1971 as a "Regional Corporation" and organized under the laws of the state of Alaska to conduct both the for-profit and non-profit affairs of Alaska Natives within a defined region of Alaska.
The Census Bureau created training videos to give BAS participants detailed instructions and information on how to report and submit BAS changes. These videos are available on the BAS Web site at: <https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/bas/library/videos/bas-intro.html>.
If there are any questions or concerns about the participation requirements, contact the Census Bureau at 1-800-972-5651 or [email protected]
The Geography Division of the Census Bureau is responsible for developing geographic applications and executing related activities needed to support the Census Bureau in collecting and disseminating census data. For more than twenty years, the Census Bureau’s Master Address File/Topologically Integrated Geographic Encoding and Referencing (MAF/TIGER) System has become critical resources for supporting the Census Bureau in its geographic activities.
The following section will describe how the Census Bureau uses a topologically integrated system and how this differs from traditional GIS systems, which use separate layers of data.
At the Census Bureau, we describe topology as the relationship between different levels of geography. MAF/TIGER is a geographic database in which the topological structures define the location, connection, and relationships of streets, rivers, railroads, and other features. These topological structures help define the geographic entities for which the Census Bureau tabulates data.
Instead of having a separate layer for each feature class (roads, boundaries, etc.) all MAF/TIGER information is stored in one layer or file. See Figure 1 and Figure 2 for samples of topologically integrated files in MAF/TIGER.
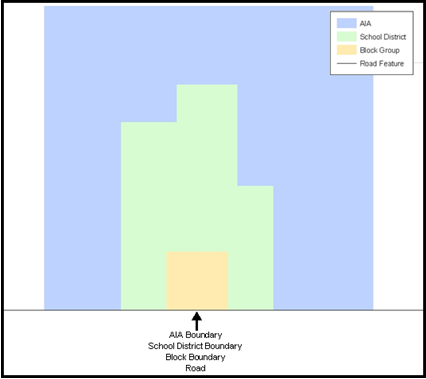
Figure 1. Road Representing 3 Types of Boundaries
This example shows how a road in MAF/TIGER can also represent a block boundary, American Indian Areas (AIAs) boundary and a school district boundary.
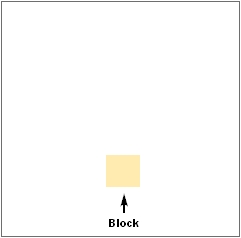
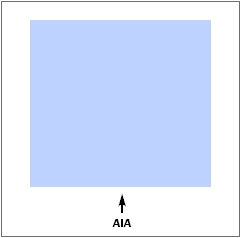
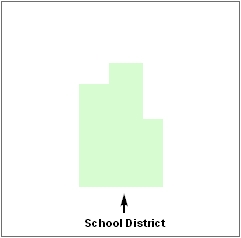
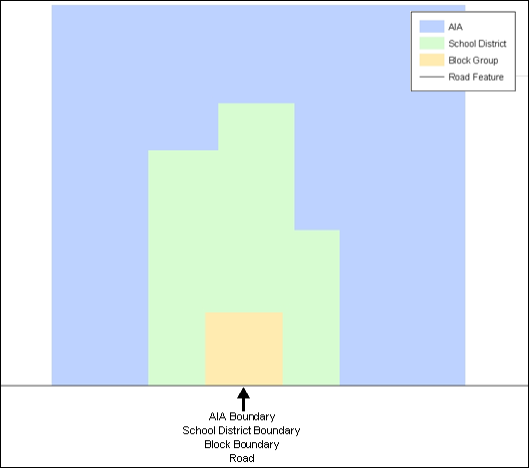
Figure 2. Typological Integration of Four Classes
This example shows how four different feature classes are topologically integrated into one layer. One road feature represents not only a road, but also a block boundary, AIA boundary, and a school district boundary.
In a GIS, feature classes are usually not topologically integrated: they are separated into layers. When you overlay these layers in a GIS, there may be boundary misalignments due to the nature of the data. These non-topologically integrated layers could cause issues in MAF/TIGER. Figure 3 and Figure 4 show how files that are not topologically integrated might appear in a GIS when overlaid.
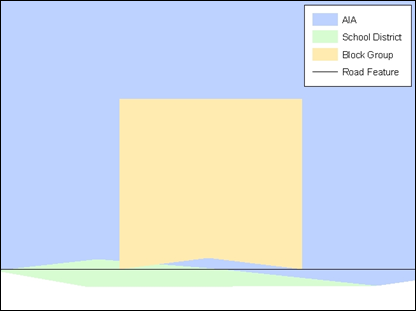
Figure 3. Overlay of Four Feature Classes
This example shows an overlay of four different feature classes. Notice how the topological relationship is compromised. The block, AIA, and school district boundaries, which are supposed to follow the road feature, no longer align with the road in several locations.
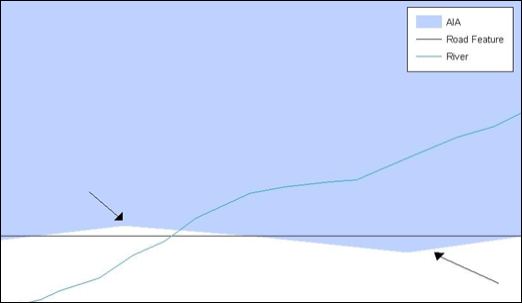
Figure 4. GIS Place Boundary Does Not Follow Road Feature
This example shows a situation where a local GIS AIA boundary does not follow a road feature. Assuming that the boundary follows the road feature, changing the AIA boundary to match the local file exactly, and become misaligned (see arrows) would dissolve the topological relationship in MAF/TIGER.
The spatial differences between local GIS data and the Census
Bureau’s topologically integrated file are often very small
(less than ten feet) and can create boundary-to-feature relationship
issues for the Census Bureau. Part 5:
Updating the Census Bureau Shapefiles,
Section 5.12 provides
instructions on how to review digital submissions for small spatial
boundary corrections. It also lists some of the potential
consequences of making spatial boundary corrections that dissolve the
topological relationships present in MAF/TIGER. You may find examples
of suggested methods for correctly making boundary changes in
Appendix B
and Appendix C.
The Census Bureau created a video on topology and why topology is important to the BAS. For more information, please go to <https://www.census.gov/library/video/intro_bas_topology.html> where you can watch the video.
Please download shapefiles from the Web site <https://www.census.gov/geographies/mapping-files/2019/geo/bas/2019-bas-shapefiles.html> in order to review your boundaries and submit changes. Please review and edit all applicable shapefiles. For example, if your tribe has new off-reservation trust land to report, you would use the “aial” shapefile. If your tribe also had tribal subdivision updates, you would use the “aial” shapefile and the “aitsl” shapefile. See Table 1 for the names of the shapefiles. The Census Bureau provides entity layers in ESRI shapefile format for download via the Web site.
Note: Shapefiles are ‘county’ based so you will need to download all the counties in which the tribe has reservation and/or ORLTs.
Table 1: BAS Shapefile Naming Conventions
Geographic Entity Type |
Shapefile Naming Convention |
Federal Reservations and Off-Reservation Trust Lands |
PVS_18_v2_aial_<ssccc>.shp |
Tribal Subdivision |
PVS_18_v2_aitsl_<ssccc>.shp |
ANRC |
PVS_18_v2_anrc_<ssccc>.shp |
Hawaiian Homeland |
PVS_18_v2_hhl_<ssccc>.shp |
Edges (Roads, Rail, Hydro, etc.) |
PVS_18_v2_edges_<ssccc>.shp |
Area Landmarks |
PVS_18_v2_arealm_<ssccc>.shp |
Point Landmarks |
PVS_18_v2_pointlm_<ssccc>.shp |
Hydro Area |
PVS_18_v2_water_<ssccc>.shp |
Geographic Offsets / Corridors |
PVS_18_v2_offset_<ssccc>.shp |
Note: <ssccc> represents the two-digit state code and three-digit county code.
All shapefiles provided by the Census Bureau are in the following unprojected geographic-based coordinate system:
Geographic Coordinate System – North American Datum 1983 (GCS NAD83)
Angular Unit: Degree (0.017453292519943299)
Prime Meridian: Greenwich (0.000000000000000000)
Datum: D_North_American_1983
Spheroid: GRS_1980
Semi-major Axis: 6378137.000000000000000
Semi-minor Axis: 6356752.314140356100000000
Inverse Flattening: 298.25722210100002000
Geocoding is how the Census Bureau codes population to geographic entities. There are two primary methods of geocoding used by the Census Bureau. Both of these involve coding an address to a spatial polygon, but one uses Global Positioning System (GPS) technology, while the other uses address ranges.
A field worker stands in front of a house or living quarters, and records the physical location with a GPS device (Figure 5). Usually, the GPS point should fall very close to the front door of the house. However, since this is a field operation, real-world obstacles like locked fences, poor satellite reception, or even aggressive dogs might sometimes prevent the worker from gaining access to the front door. In these circumstances, the worker may have to take the GPS coordinate from the sidewalk or side of the road.
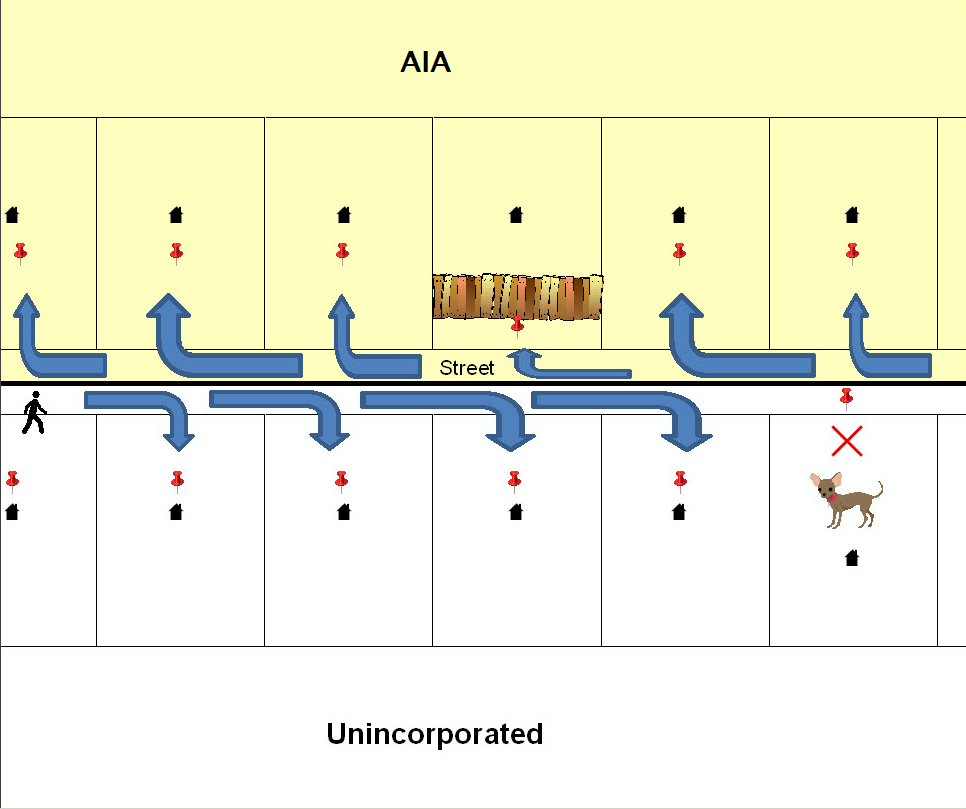
Figure 5. MSP Method of Geocoding
MAF Structure Point (MSP) method of geocoding. Notice that it is occasionally not possible for the field worker to go all the way to the front door, due to unforeseen circumstances, like the fence or the dog shown above. Thus, the MSP (represented here by the red pins) can sometimes fall within the road or the road right-of-way.
When no MSP Geocoding is available, the Census Bureau codes houses
and living
quarters according to a potential range of addresses
associated with the adjacent stretch
of road (Figure 6).
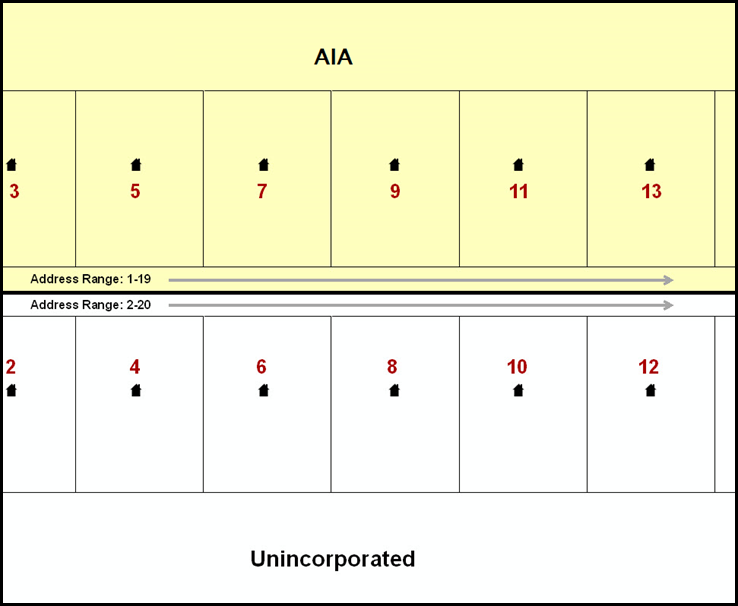
Figure 6. Address Range Method of Geocoding
When it is not possible to collect an MSP, houses are geocoded according to their placement along a range of potential addresses along that road. Since the address is being related to the road, boundaries placed on front lot lines will lead to mis-geocoding unless an offset flag is used.
While the two methods of geocoding differ greatly, both rely heavily on the integrated nature of MAF/TIGER. These geocoding methods are affected by the way streets and boundaries are represented in relation to one another. This interdependence between streets, boundaries, and geocoding means that Census Bureau representations of legal boundaries may sometimes differ from other representations (e.g., in local or state GIS). This is especially true regarding geographic corridors and offsets that follow road right of ways (or the front lot lines of parcels). In both of the examples above, delineating a boundary along the front lot line will tend to increase the risk of incorrect geocoding. As a result, using the road centerline as a boundary is the safer method.
When completing a BAS submission in which a road or road right-of-way is owned or maintained by a place or AIA but the adjacent housing is not, the respondent should use the centerline of the road (not the front lot-line) as the boundary whenever possible.
Census Bureau shapefiles can be updated to reflect boundary and/or linear feature changes that have occurred since the last Tribal BAS survey. Examples of these procedures can be found in Appendix B and Appendix C and in the Digital BAS demonstration video series at <https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/bas/library/videos/digital-bas.html>.
Note: If there are problems with the processing of returned files, the Census Bureau will email a feedback document requesting clarification of any issues. If the problem cannot be resolved before the project deadline, the changes in question will not be made during the current BAS.
After downloading the shapefiles from the PVS download page, follow these procedures before beginning actual updates:
Open the downloaded .ZIP file to verify its contents.
Copy the shapefiles into a directory on a server/hard drive.
Open the shapefiles with GIS software.
Census Bureau files are in GCS NAD83 format and can be projected into any local coordinate system/projection. Most GIS software packages will allow users to transform file coordinate systems and projections. For example, if using ArcView to update files, activate and utilize ArcView’s Projection Utility Wizard extension. If using ArcGIS, use its Project tool in ArcToolbox. MAF/TIGER shapefile extracts contain defined projection information in the *.prj file. ArcView and ArcGIS access the *.prj file for projection information so there is no need to define these parameters before changing the file coordinate systems.
When updates are complete, participants may submit the boundary shapefile using any local coordinate system/projection if the shapefile contains a .prj file or spatial reference materials such as metadata.
In order to update MAF/TIGER, participants must create a separate change polygon layer for each updated entity type (AIA, ANRC, tribal subdivision, or Hawaiian Homeland). Please create change polygons in relation to the current MAF/TIGER boundary.
Appendix B and Appendix C provide two examples for creating annexation, deannexation, boundary correction, new incorporation, geographic corridor, and geographic offset change polygons. Review any boundary change polygons before submitting them (Section 5.13).
If you need additional shapefiles, please contact the Census Bureau at 1-800-972-5651 or [email protected].
The Census Bureau will accept additions and deletions from AIAs, ANRCs, and Hawaiian Homelands, such as new reservation lands and off-reservation trust lands. Each addition or deletion change polygon must have the required attributes and corresponding change type populated, as seen in Table 2. The Census Bureau will snap any addition or deletion to a MAF/TIGER feature when it exists within thirty feet of that feature.
Note: Enter the name of the jurisdiction (AIA, ANRC or Hawaiian Homeland) adding or deleting the area in the NAME field.
Table 2: Additions and Deletions
|
NAME |
CHNG_TYPE |
EFF_DATE |
AUTHTYPE |
DOCU |
RELATE |
Addition |
X |
X(‘A’) |
X |
X |
X |
|
Deletion |
X |
X(‘D’) |
X |
X |
X |
|
(Note: ‘X’ = Required Field)
The Census Bureau will also accept specific boundary corrections from AIAs, ANRCs, and Hawaiian Homelands. As with new reservation lands and off-reservation trust lands, the participant must create individual change polygons for each boundary correction. Each boundary correction must also have the required attributes and corresponding change type populated, as seen in Table 3, or the Census Bureau will reject them.
Note: Enter the name of the jurisdiction that the boundary correction is for in the NAME field.
|
NAME |
CHNG_TYPE |
EFF_DATE |
AUTHTYPE |
DOCU |
RELATE |
Boundary Correction |
X |
X(‘B’) |
|
|
|
X(‘IN’) |
Boundary
Correction |
X |
X(‘B’) |
|
|
|
X(‘OUT’) |
(Note: ‘X’ = Required Field)
The Census Bureau uses a topologically integrated database. As a result, the Census Bureau cannot process all types of boundary corrections for inclusion into MAF/TIGER. The following are types of boundary corrections that the Census Bureau will accept, process, and update or reject during the current BAS.
The Census Bureau will accept and process properly documented boundary corrections during the current BAS that spatially interact with (abut) other BAS legal changes (annexation, deannexation, corridor, offset) and meet both of the following two conditions:
In situations where the existing boundary has been digitized incorrectly or appears in the incorrect location due to Census Bureau activities; and
Where the overall shape of the geographic entity is maintained and no feature-to-boundary relationships are dissolved.
The Census Bureau will reject boundary corrections:
That dissolve boundary-to-feature relationships (roads, rivers, railroads, etc.) if the difference is less than thirty feet;
Which are greater than one square mile, or not contiguous with the rest of the entity boundary. These boundary corrections may be part of additions which were never reported to the Census Bureau. If so, legal documentation should be provided; and
That have a width of less than thirty feet over the entire polygon.
Note: Remember that the Census Bureau will snap any entity boundary correction to a MAF/TIGER feature when it exists within thirty feet of that feature.
AIA participants may submit new entities (tribal subdivisions) through Tribal Digital BAS. As with other change types, an individual change polygon must be created for each new entity and possess the required attributes and the corresponding change type field must be populated (see Table 4). Please see Section 5.9 for more information about tribal subdivisions.
Note: Enter the name of the new jurisdiction in the NAME field.
|
NAME |
CHNG_TYPE |
EFF_DATE |
AUTHTYPE |
DOC |
RELATE |
New Entity |
X (subdivision name) |
X (‘E’) |
X (date of tribal resolution) |
X (‘R’) |
X (tribal resolution number) |
|
(Note: ‘X’ = Required Field)
The Census Bureau geocodes addresses based on the street centerline. If the geocoding of these addresses would result in the assignment of population to the incorrect geographic entity, participants should create a geographic corridor.
A geographic corridor is an area that includes only the road right-of-way and does not contain any structures addressed to either side of the street. Figure 7 shows a corridor created where the AIA owns the right-of-way but the housing units are not included within the AIA (shown in color). Without a corridor, the housing units along this road would be included in the AIA.
Figure 8 shows that the right-of-way belongs in the unincorporated area, while the housing units are included in the AIA (shown in color). This is important for some entities because they are portraying that the entity is not responsible for road maintenance. This is not relevant for Census Bureau tabulations and is not easy to depict in the Census Bureau’s nationwide database. This type of corridor should not be included in a BAS response.
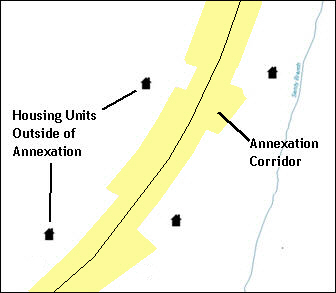
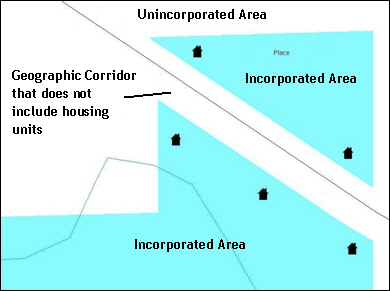
Figure 7. Geographic Corridor Created
Figure 8. Geographic Corridor Not Created
The image on the left (Figure 7) shows that a geographic corridor should be created to allow for proper geocoding of homes. The image on the right (Figure 8) shows that the geographic corridor should not be created and features should be snapped to the street centerline.
The Census Bureau will accept new geographic corridors. Please create individual change polygons for each new geographic corridor. Each change polygon must have the required attributes and corresponding change type populated, as seen in Table 5. In the NAME field, enter the name of the jurisdiction. In the RELATE field, indicate whether the change is adding IN or taking OUT (removing) the corridor.
|
NAME |
CHNG_TYPE |
EFF_DATE |
AUTHTYPE |
DOC |
AREA |
RELATE |
Geographic Corridor |
X |
X(‘C’) |
|
|
|
|
X(‘IN’, ‘OUT’) |
(Note: ‘X’ = Required Field)
A geographic offset is an area claimed by a geographic entity that is only on one side of a road and does not include structures addressed to that side of the road.
The Census Bureau is aware that many governments base their legal
boundaries on cadastral (parcel-based) right-of-way mapping. The
Census Bureau bases their maps on spatial data that is topologically
integrated. This makes the maintenance of geographic offsets
inefficient. Snapping an entity boundary to the centerline wherever
applicable will help to establish more accurate population counts. If
a boundary is the front lot line, Census Bureau strongly prefers
that the boundary be snapped to the road. If a boundary is at
the rear of a lot, then please depict it as such. Figure 9
depicts a cadastral (parcel-based) boundary map and Figure 10
shows how the boundary should be reported when sent to the Census
Bureau.
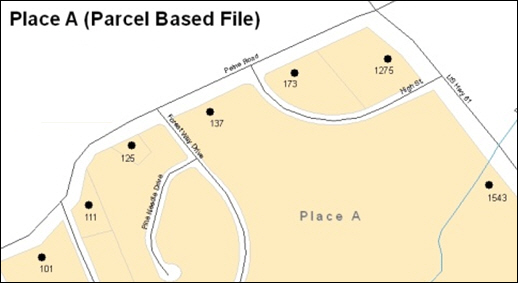
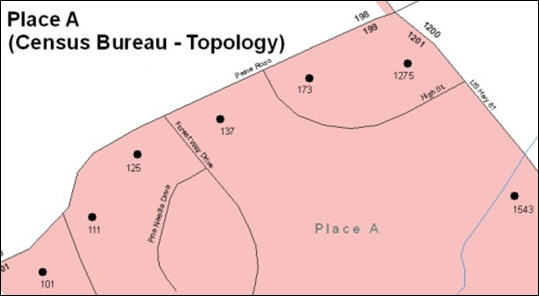
Figure 10. Same Data Edited to Census Requirements
On the left in Figure 9 is an example of cadastral data. Figure 10 on the right, is the same area shown edited to conform to census requirements.
The Census Bureau will accept new geographic offsets. Please create individual change polygons for each new geographic offset. Each change polygon must have the required attributes and corresponding change type populated, as seen in Table 6. In the NAME field, enter the name of the jurisdiction. In the RELATE field, indicate whether the change is adding IN or taking OUT (removing) the area represented as an offset.
|
NAME |
CHNG_TYPE |
EFF_DATE |
AUTHTYPE |
DOCU |
AREA |
RELATE |
Geographic Offset |
X |
X(‘F’) |
|
|
|
|
X(‘IN’, ‘OUT’) |
(Note: ‘X’ = Required Field)
Census Bureau has included an “offset” shapefile in the BAS materials (PVS_18_v2_offset_<ssccc>.shp), so that your jurisdiction can be checked for any existing corridors or offsets. While the Census Bureau prefers that you do not create new offsets, (see above), this information can be helpful in determining if current boundaries are correct.
Tribes may submit the boundaries for one type of administrative area within their reservation(s) and/or off-reservation trust lands (land base) for inclusion in MAF/TIGER. The Census Bureau will consider any type of unit of self-government or administration as a “tribal subdivision.” Tribal subdivisions should cover all, or most, of the tribe’s land base. If a tribe has more than one type of distinct administrative area that could qualify as a tribal subdivision (such as tribal election districts, tribal water districts, or health service areas with different boundaries), the tribe may submit only one type of subdivision. Tribal subdivisions can be considered either active (A) or inactive (I). Active subdivisions are defined as having a functioning government with elected officials that provide programs and services. Inactive subdivisions have no functioning government or elected officials and receive services solely from the tribe. Some examples of areas submitted as tribal subdivisions are:
Areas used by a tribe for the election of tribal government officials (such as districts or precincts used for the election of tribal council members).
Areas used by a tribal government for tax purposes.
Areas used by a tribal government for the provision of general services or specified services, such as:
Water districts;
Health service areas;
Emergency service delivery areas (such as 911, fire, and/or police); or
Grazing districts or range units.
Historical or traditional areas recognized by a tribal government.
Local tribal community governments.
The delineation of tribal subdivisions is restricted to the area contained within reservation(s) and/or associated off-reservation trust lands (land base).
There is no minimum population threshold for a tribal subdivision.
Tribal subdivisions should cover all, or most, of the tribe’s land base.
A tribal subdivision may be discontinuous.
A tribe may designate only ONE type of tribal subdivision. If a tribe has more than one level of tribal subdivisions within its land base, the Census Bureau recommends delineating subdivisions corresponding to the lowest geographic level (those geographic areas containing the smallest area) of the tribe’s administrative hierarchy.
Tribal subdivisions should not be based solely on land ownership or other cadastral areas, nor should they consist of divisions based on the U.S. Public Land Survey System (PLSS) of townships, ranges, and sections, if these areas have no governmental or administrative function for your tribe.
Some examples of descriptors for tribal subdivisions are:
District;
Community;
Area;
Chapter;
Segment;
Administrative Area;
Addition; and
County District.
Tribal Subdivisions are updated in a similar manner to boundary changes (such as additions or deletions). In order to submit tribal subdivision updates, please create a separate tribal subdivision change polygon layer. Updates that can be made to tribal subdivisions include additions, deletions, boundary corrections (adding and removing area), and creating new tribal subdivisions. Please note that all tribal subdivision updates (additions, deletions, name changes, and new entities), with the exception of boundary corrections, require a tribal resolution. Table 7, Table 8, and Table 9 displays the required attributes for each of the change types. Review the example processes in Appendix B and Appendix C for information on how to create change polygons. Change polygons for tribal subdivisions may be created in the same manner as for reservations and off-reservation trust lands.
The Census Bureau will accept linear feature modifications when needed. Please submit linear feature updates in a separate linear feature update layer. Each linear feature update must have the required attributes and corresponding change type populated, as seen in Table 7. In the TLID field, preserve the existing TLID for the feature.
Table 7: Linear Feature Updates
|
CHNG_TYPE |
TLID |
FULLNAME |
MTFCC |
Add Feature |
X(‘AL’) |
|
X |
X |
Delete Feature |
X(‘DL’) |
X |
|
|
Rename Feature |
X(‘CA’) |
X |
X |
|
Recode Feature |
X(‘CA’) |
X |
|
X |
(Note: ‘X’ = Required Field)
Note: A list of MTFCC codes can be found in Appendix D.
If a road, subdivision, etc. is missing from the Census Bureau’s feature network, add the feature(s) and provide the name and MTFCC.
If a feature does not exist and is in the Census Bureau’s feature network, delete the feature.
If a feature is in the incorrect location in the Census Bureau’s feature network, delete the feature and re-add it in the correct location. Only do this if the feature is very far off or in the wrong position relative to boundaries or other features.
The Census Bureau accepts address range data as part of the linear feature update layer. As with other linear feature updates, address ranges must have the required attributes and corresponding change type populated. As existing address ranges cannot be shown in our outgoing shapefiles, we recommend that participants generally only add address ranges to new features.
Table 8: Address Range Updates
|
CHNG_TYPE |
FULLNAME |
MTFCC |
LTOADD |
RTOADD |
LFROMADD |
RFROMADD |
Address Ranges |
X(‘CA’) |
|
|
X |
X |
X |
X |
(Note: ‘X’ = Required Field)
The Census Bureau accepts updates to area landmarks and hydrographic areas in a similar manner to legal boundary changes. However, area landmarks and hydro areas are not legal entities, so no documentation or effective dates are required.
In order to submit area landmark and hydro area updates, create a separate change polygon layer. Updates to area landmarks and hydro areas include:
Boundary corrections (adding and removing area);
Creating a new area landmark or hydro area;
Removing an area landmark or hydro area; and/or
Changing the name.
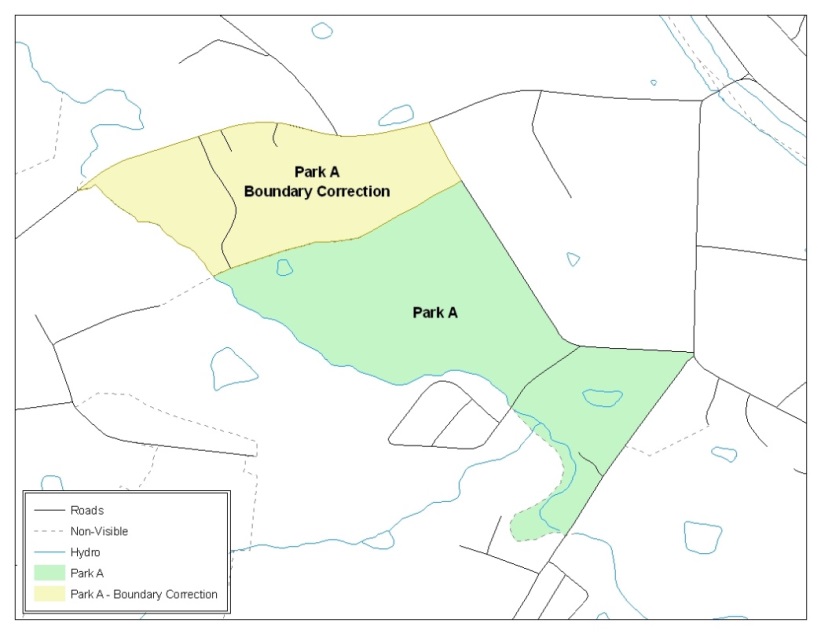
Figure 11. A Boundary Correction to Park A
This Example Shows a Boundary Correction to Park A. See Appendices B and C for more information on creating change polygons for area landmark and hydro areas.
Each area landmark or hydro area update must have the required attributes and corresponding change type populated. In the AREAID field, preserve the existing AREAID for the feature.
Table 9: Area Landmark/Hydro Area Updates
|
FULLNAME |
CHNG_TYPE |
RELATE |
MTFCC |
AREAID |
Boundary Correction (Add Area) |
X |
X(‘B’) |
X(‘IN’) |
|
X |
Boundary Correction (Remove Area) |
X |
X(‘B’) |
X(‘OUT’) |
|
X |
Delete Landmark |
|
X(‘D’) |
|
|
X |
Change Landmark Name |
X |
X(‘G’) |
|
|
X |
New Landmark |
X |
X(‘E’) |
|
X |
|
(Note: ‘X’ = Required Field).
The examples in Appendix B and Appendix C provide information on how to create change polygons. While the sample processes are written for legal boundary changes, the same methods apply for creating change polygons for area landmarks and hydro areas. When adding new area landmarks or hydro areas, only add the following types of areas:
Water bodies;
Glaciers;
Airports;
Cemeteries;
Golf courses; and
Parks.
The Census Bureau cannot add other types of areas at this time (although some may already exist in the database). The following are acceptable MTFCC codes for new area landmarks or hydro areas:
Table 10: New Landmark/Hydro Area MTFCC Codes
MTFCC |
Description |
H2030* |
Lake/Pond |
H2040* |
Reservoir |
H2041* |
Treatment Pond |
H2051* |
Bay/Estuary/Gulf/Sound |
H2081* |
Glacier |
C3023 |
Island |
K1231 |
Hospital/Hospice/Urgent Care Facility |
K1235 |
Juvenile Institution |
K1236 |
Local Jail or Detention Center |
K1237 |
Federal Penitentiary, State Prison, or Prison Farm |
K2110 |
Military Installation |
K2180* |
Park |
K2181 |
National Park Service Land |
K2182 |
National Forest or Other Federal Land |
K2183 |
Tribal Park, Forest, or Recreation Area |
K2184 |
State Park, Forest, or Recreation Area |
K2185 |
Regional Park, Forest, or Recreation Area |
K2186 |
County Park, Forest, or Recreation Area |
K2187 |
County Subdivision Park, Forest, or Recreation Area |
K2188 |
Incorporated Place Park, Forest, or Recreation Area |
K2189 |
Private Park, Forest, or Recreation Area |
K2190 |
Other Park, Forest, or Recreation Area (quasi-public, independent park, commission, etc.) |
K2424 |
Marina |
K2540 |
University or College |
K2457* |
Airport – Area Representation |
K2561 |
Golf Course |
K2582* |
Cemetery |
*May not be edited.
Due to heavy workloads for boundary changes to legal areas, changes to area landmarks and hydrographic areas may not be added to the database until after the next year’s BAS materials are created. It may take two BAS cycles in order to see these changes reflected in the materials.
The Census Bureau accepts updates to point landmarks. Please submit point landmark updates as a separate point landmark update layer. Updates to point landmarks include:
Adding a new point landmark;
Deleting an existing point landmark; and
Renaming a point landmark.
Each point landmark update must have the required attributes and corresponding change type populated. In the POINTID field, preserve the existing POINTID for the feature.
Table 11: Point Landmark Updates
|
FULLNAME |
CHNG_TYPE |
MTFCC |
POINTID |
New Point Landmark |
X |
X(‘E’) |
X |
|
Delete Point Landmark |
|
X(‘D’) |
|
X |
Change Name |
X |
X(‘G’) |
|
X |
The Census Bureau cannot make the following point landmark changes due to Title 13 privacy concerns. Do not include any of the following types of landmarks in the point landmark changes file.
Table 12: Restricted Point Landmark MTFCC Codes
MTFCC |
Description |
|
K1100 |
Housing Unit Location |
|
K1121 |
Apartment Building or Complex |
|
K1122 |
Rooming or Boarding House |
|
K1223 |
Trailer Court or Mobile Home Park |
|
K1226 |
Housing Facility/Dormitory for Workers |
|
K1227 |
Hotel, Motel, Resort, Spa, Hostel, YMCA, or YWCA |
|
K1228 |
Campground |
|
K1229 |
Shelter or Mission |
|
K1232 |
Halfway House/Group Home |
|
K1233 |
Nursing Home, Retirement Home, or Home for the Aged |
|
K1234 |
County Home or Poor Farm |
|
K1235 |
Juvenile Institution |
|
K1241 |
Sorority, Fraternity, or College Dormitory |
|
K1251 |
Military Group Quarters |
|
K1299 |
Other Group Quarters Location |
|
K2100 |
Governmental |
|
K2197 |
Mixed Use/Other Non-residential |
|
K2300 |
Commercial Workplace |
|
K2361 |
Shopping Center or Major Retail Center |
|
K2362 |
Industrial Building or Industrial Park |
|
K2363 |
Office Building or Office Park |
|
K2364 |
Farm/Vineyard/Winery/Orchard |
|
K2366 |
Other Employment Center |
|
K2464 |
Marina |
|
K2500 |
Other Workplace |
|
K2564 |
Amusement Center |
|
The Census Bureau also cannot delete or modify any point landmarks imported from the USGS GNIS database. Changes submitted for the following types of landmarks may be left unchanged:
K2451 (Airport);
K2582 (Cemetery);
C3022 (Summit or Pillar);
C3081 (Locale or Populated Place); and
C3061 (Cul-de-sacs).
Due to heavy workloads for boundary changes to legal areas, changes to point landmarks may not be added to the database until after the next year’s BAS materials are created. It may take two BAS cycles in order to see these changes reflected in local materials.
Please review all changes to ensure that they are intentional and correct. The Census Bureau has created videos with information on many of the topics below. The video series, “Introduction to the Digital BAS” can be found on the web at: <https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/bas/library/videos/bas-intro.html>.
Please review all changes to ensure that the correct boundary-to-feature relationships are being created or maintained. The Census Bureau is aware that many governments base their legal boundaries on cadastral (parcel-based) right-of-way mapping; however, the Census Bureau bases maps on spatial data that is topologically integrated. Therefore, snap boundaries to street centerlines (or rivers, railroads, etc.) wherever applicable. This will help establish a more accurate population count for tribal entities.
The following examples show situations where boundary changes should be snapped to existing linear features. The Census Bureau will snap boundary changes to any linear feature within thirty feet.
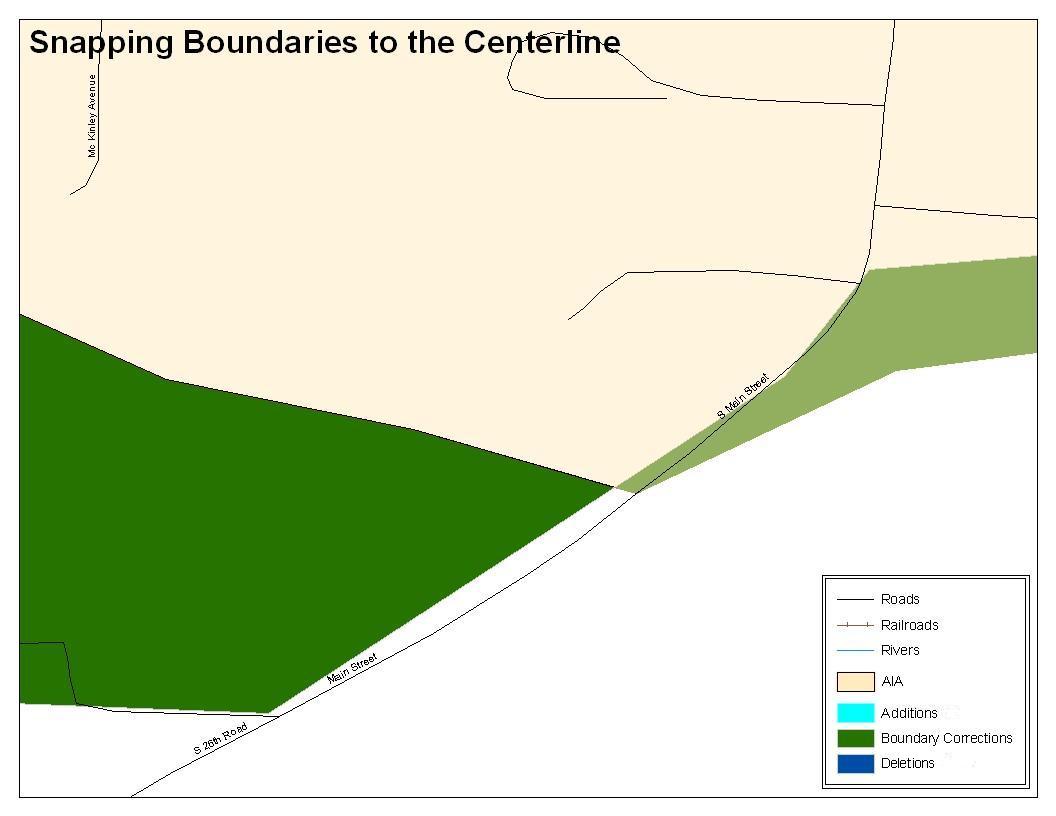
Figure 12. Boundary Correction Not Snapped to Existing Linear Features
These boundary corrections are not snapped to existing linear features in MAF/TIGER. Both boundary corrections should be snapped to centerlines or population may be assigned to incorrect entities.
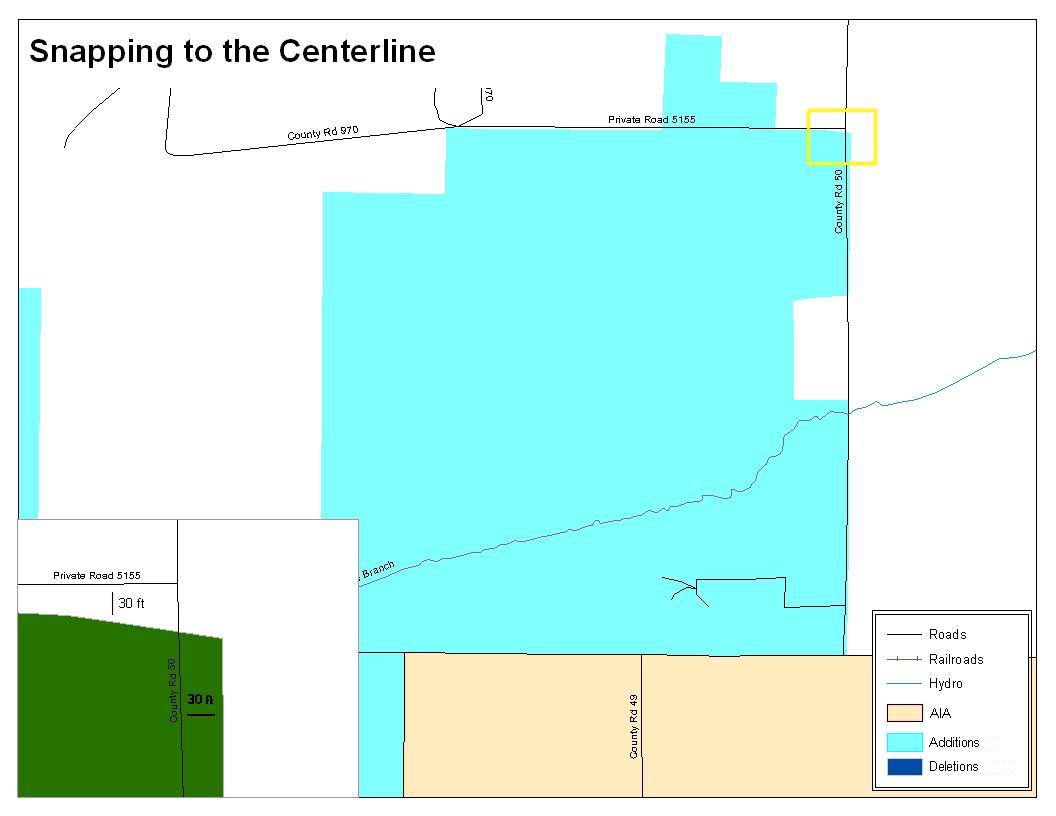
Figure 13. Annexation Created without Snapping to Centerlines
This is an example of an addition that has been created without snapping to existing centerlines in MAF/TIGER. Unless the boundary is snapped to centerlines, some of the population may be assigned to an incorrect entity.
The Census Bureau will not accept boundary corrections that dissolve the current relationship between an existing boundary and linear feature. Any boundary corrections that create thirty feet or less of gap or overlap between the existing linear feature and boundary will not be incorporated into MAF/TIGER. See below for examples of changes that will not be accepted.
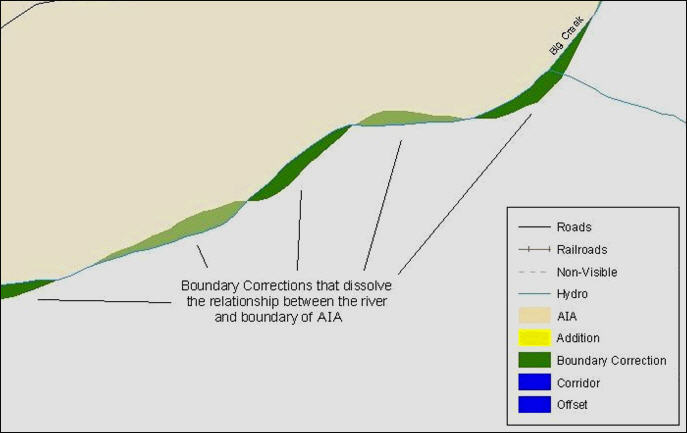
Figure 14. Small Spatial Correction Not Incorporated
Small spatial boundary corrections would dissolve the relationship with the river. These boundary corrections will not be incorporated into MAF/TIGER.
Figure 15
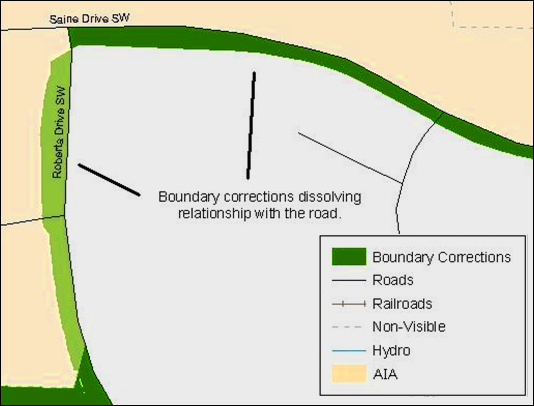 .
Small Spatial Corretion Not Acepted
.
Small Spatial Corretion Not Acepted
Small spatial boundary corrections that dissolve the boundary-to-feature relationship with multiple streets have been created. Incorporating these changes would affect the population counts for the area. Therefore, the Census Bureau will not accept these small boundary corrections.
The Census Bureau will not accept large boundary corrections to an AIA without the appropriate legal documentation (such as Trust Deed, Executive Order, new legal opinion, Act of Congress, or Federal Register Notice). These large boundary corrections may be legal boundary changes that occurred in the past and were never reported to the Census Bureau. Please submit the appropriate legal documentation and effective date so that changes may be incorporated into MAF/TIGER.
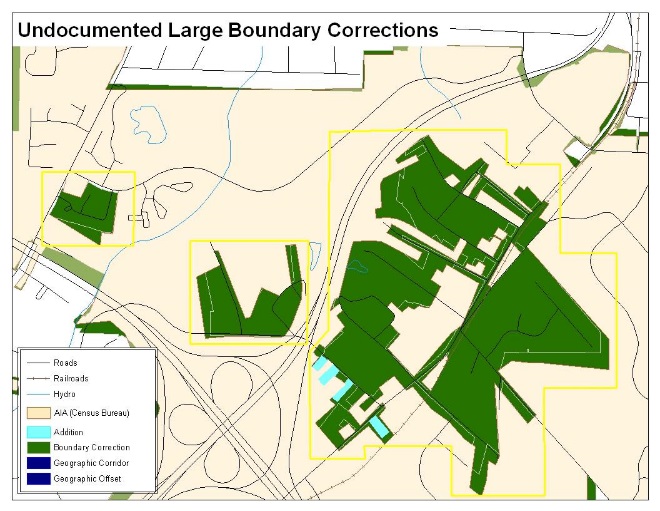
Figure 16. Large Boundary Corrections
Without the appropriate documentation, Census Bureau will not accept large boundary corrections.
Note: There may be a few instances when large boundary corrections need to be made because of incorrect digitizing or where the boundary appears in the incorrect location due to other Census Bureau activities.
It is important to review each change polygon and confirm that the correct attribute information is included. Without the correct attribute information, the Census Bureau will be unable to process and incorporate the changes into MAF/TIGER. See Section 5.3 for the required attribute information and corresponding change type codes.
It is important that the appropriate projection information is included. Each update layer submitted should contain a *.prj file so that the Census Bureau can convert the projection back to GCS_NAD83. If the GIS being used cannot create a *.prj file, include the projection information in metadata. This is critical for the Census Bureau to be able to process the file and incorporate the updates into MAF/TIGER.
Please review linear feature changes to ensure that they align with the features currently in MAF/TIGER.
If linear feature changes do not align with current MAF/TIGER linear features, the Census Bureau may not incorporate the submitted updates.
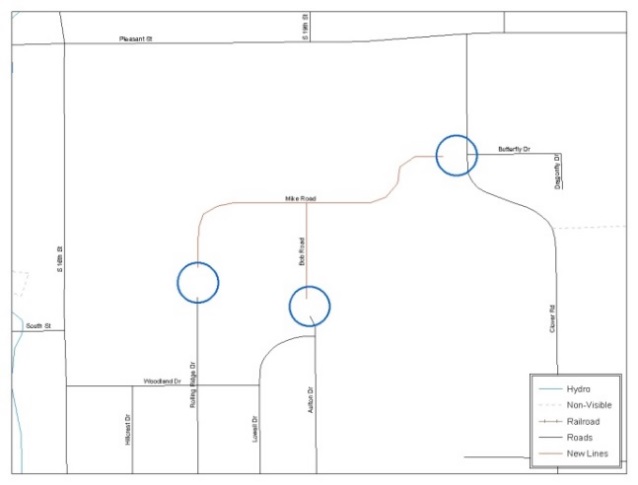
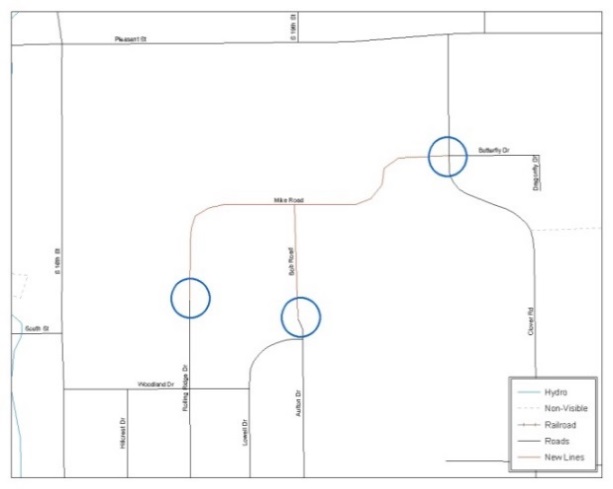
Figure 17. New Road Features, Not Added to Existing Road
Figure 18. New Road Features, Correctly Added
The image on the left (Figure 18) shows new road features added to the existing feature network, but do not connect to existing road features. The image on the right (Figure 19) shows the correction; connecting the new roads to the existing road features.
The Census Bureau will not make any boundary change that affects adjacent legal entities without the appropriate documentation. Review any change polygons that affect adjacent entities to determine if they are intentional, legal changes.
Note: The Census Bureau will snap any addition, deletion, or boundary correction to a MAF/TIGER feature when it exists within thirty feet of that feature. This helps maintain the boundary-to-feature relationships in MAF/TIGER and will ensure correct housing tabulation counts for entities.
The Census Bureau is responsible for depicting reservation and off-reservation trust land boundaries but because the Census Bureau is not the authority on the boundaries, we require documentation to update reservation and off-reservation trust land boundaries.
The following changes require documentation:
New off-reservation trust land;
New reservation land;
Changes from off-reservation trust land to reservation land and changes from reservation land to off-reservation trust land;
Large changes to existing off-reservation trust land;
Large changes to existing reservation land; and
Boundary corrections to off-reservation trust land or reservation land that do not follow the general shape of the boundary.
For off-reservation trust land, the most common documentation is a trust deed or a letter from the BIA. Documents should state that the land is “in trust” for your tribe.
For reservation land, documentation examples include (but are not limited to) federal register notice, Act of Congress, Executive Order, or a new legal opinion issued by the BIA. When submitting large boundary corrections to an existing reservation, please submit your reservation document.
If you cannot locate your documentation, you can contact your regional BIA office to obtain documentation. The Census Bureau will treat legal opinions issued in writing from the BIA as documentation since the BIA is the authority on reservation and off-reservation trust land boundaries. If the Census Bureau cannot interpret a document, such as a treaty, the Census Bureau will contact the BIA for assistance.
If you have questions about documentation, please call the Census
Bureau at
1-800-972-5651 or email [email protected].
If you need to contact the BIA, please see
<http://www.bia.gov/WhoWeAre/RegionalOffices/index.htm>
for contact information for your regional office.
If a participant is reporting changes to the BAS, the Census Bureau requires that each participant submit at least one shapefile (change polygons). The total number of layers submitted depends on what types of changes are reported. The following is a list of change layers that may need to be submitted:
Change Polygon Layers (ANRC, AIA, Tribal Subdivisions, Hawaiian Homelands)
These layers consist of the changes that the Census Bureau needs to make to entities; and
A layer of change polygons should be created for each level of geography (ANRC, AIA, Tribal Subdivisions, etc.) that changes are being submitted for.
Whole Modified Entity Layer (ANRC, AIA, Tribal Subdivisions, and Hawaiian Homelands)
These layers should only contain the complete and current boundary for the entity being updated; and
A whole entity layer should be created for each level of geography that change polygons are being created for.
Local Government Feature Network and Boundary Layers (optional)
These layers will help the Census Bureau resolve any questionable change polygons and establish the correct boundary-to-feature relationships.
Feature Update Layer (only if there are feature (road, river, railroad, etc.) additions, deletions, name changes, recodes, or address range updates)
Include a linear feature update layer with only feature segments that need to be corrected.
Area/Hydro Landmark Layer
Only if there are area and/or hydro landmark updates.
Point Landmark Layer
Only if there are point landmark updates.
BAS Contact Text File (if the BAS point of contact (the person that receives the BAS Annual Response Email) has changed);
This can be updated online at: http://www.census.gov/geo/partnerships/bas/bas_ar_form.html.
This BAS Contact update should include this information:
First Name;
Last Name;
Department;
Position;
Shipping Address;
City;
State;
ZIP Code;
Phone: xxx-xxx-xxxx;
FAX: xxx-xxx-xxxx;
Email;
Tribal Chair Term Expires: xx/xxxx; and
Tribal Chair Term Length: x years.
The following table provides change polygon naming conventions for ANRCs, AIAs and Hawaiian Homelands. The change polygon layer naming conventions: <basID> represents your BAS entity ID, found in the BAS Annual Response email or online from this link: <https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/bas/technical-documentation/code-lists.html>.
Table 13: Change Polygon Naming Conventions
Participant |
Changes Submitted For |
Shapefile Naming Conventions |
AIA |
AIA |
bas19_<basID>_changes_aiannh |
AIA |
Tribal Subdivisions |
bas19_<basID>_changes_tribalsub |
ANRC |
ANRC |
bas19_<basID>_changes_anrc |
Hawaiian Homelands |
Hawaiian Homelands |
bas19_<basID>_changes_hhl |
The following table provides the whole entity polygon naming conventions for ANRCs, AIAs and Hawaiian Homelands. The whole entity polygon layer naming conventions: <basID> represents your BAS entity ID, found on the BAS Annual Response email or online from this link: <https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/bas/technical-documentation/code-lists.html>.
Table 14: Whole Entity Polygon Naming Conventions.
Participant: |
Changes Submitted For |
Shapefile Naming Conventions |
AIA |
AIA |
bas19_<basID>_WholeEntity_aiannh |
AIA |
Tribal Subdivision |
bas19_<basID>_WholeEntity_trialsub |
ANRC |
ANRC |
bas19_<basID>_WholeEntity_anrc |
Hawaiian Homelands |
Hawaiian Homelands |
bas19_<basID>_WholeEntity_hhl |
The following table provides the update layer naming conventions for the edges, area landmark, and point landmark update layers. The naming conventions for the edges, area landmark, and point landmark update layers: <basID> represents your BAS entity ID, found on the BAS Annual Response email or online from this link: <https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/bas/technical-documentation/code-lists.html>.
Participant: |
Changes Submitted For |
Shapefile Naming Conventions |
All Participants |
Edges |
bas19_<basID>_LN_Changes |
All Participants |
Area / Hydro Landmarks |
bas19_<basID>_Alndk_Changes |
All Participants |
Point Landmarks |
bas19_<basID>_Plndk_Changes |
The SWIM requires all BAS returns to be zipped prior to submission. Please compress ALL update materials (including change polygon shapefiles, whole entity shapefiles, linear feature updates, landmark updates, local government feature network and boundary layers, any necessary supporting documentation (e.g., trust deeds), and the text or other file with your updated BAS contact information).
Navigate to the directory with the shapefiles.
Note: Centerline files or any additional information that may be helpful for the Census Bureau to process your file is optional. One example where this would be helpful is if a particular polygon was not snapped to a river or road because the boundary does not follow the river or road.
Select all files and right click on the selection.
Select WinZip, and then Add to Zip file.
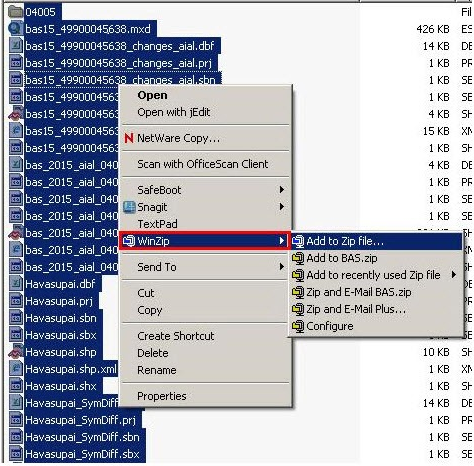
Figure 19. Selecting and Zipping Return Files
Note: Versions of WinZip may vary so the interface may be slightly different. Software other than WinZip may be used to zip the return files.
In the Add window, in the Add to archive field, type the filename in the proper naming convention: bas<yy>_<basID>_return and then click Add.
Note: Look for the basID number on the BAS Annual Response email or online from this link: <https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/bas/technical-documentation/code-lists.html>.
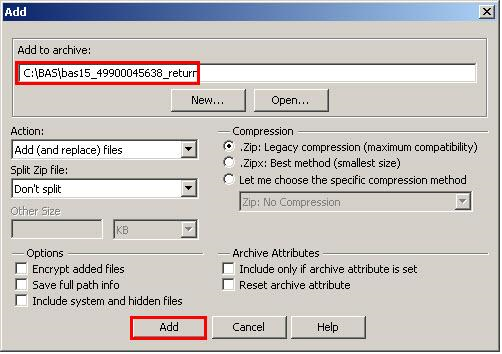
Figure 20. Naming the Zip File
Check the folder where the zip file was saved to verify that it was created properly. If so, the return file is ready for submission.
Note: If assistance is needed with preparing or zipping the BAS return files, contact the Census Bureau at 1-800-972-5651 or [email protected].
The Secure Web Incoming Module (SWIM) is a one-stop location for submitting your geographic program files to the Census Bureau. The Census Bureau now requires that all BAS participants use the Census Bureau’s SWIM for submitting update materials.
Do not send your submission as an email attachment, as we cannot accept them due to the security policy at the Census Bureau.
The Census Bureau will email the BAS contact a SWIM registration token and digital submission instructions five days after the BAS contact responds to the BAS Annual Response indicating that they have changes to report. To respond online, please fill out the online form at <http://www.census.gov/geo/partnerships/bas/bas_ar_form.html>. The five-day waiting period will give the Census Bureau staff time to update the BAS contact record if necessary so that the email reaches the right person.
This token is good for one personal account within the SWIM. Once you have registered for an account in SWIM, you will no longer need the token to login into the system. If you require additional individual SWIM accounts within your organization, please contact the Census Bureau at 1-800-972-5651 or email [email protected].
Current
SWIM Users If
you are a participant in another Census Bureau partnership program,
or participated in a previous BAS year, and already have a SWIM
account, you may use your current account to submit files for the
BAS. You do not need to set up a new account.
At this time, the SWIM only accepts ZIP files. Please zip all your update materials (e.g., spatial updates and other relevant update documents) into one ZIP file for your entity’s submission, and follow the instructions listed below:
In a web browser, go to <https://respond.census.gov/swim>.
Login:
New Users: You must have a registration token to create a new account. (Please see above). Once you have your token, please sign-up by clicking the ‘Register Account’ button. Registration is self-serve, but does require the new user to enter a registration token to validate their rights to the system.
Existing Users: If you already have a registered SWIM account, please login with your user credentials.
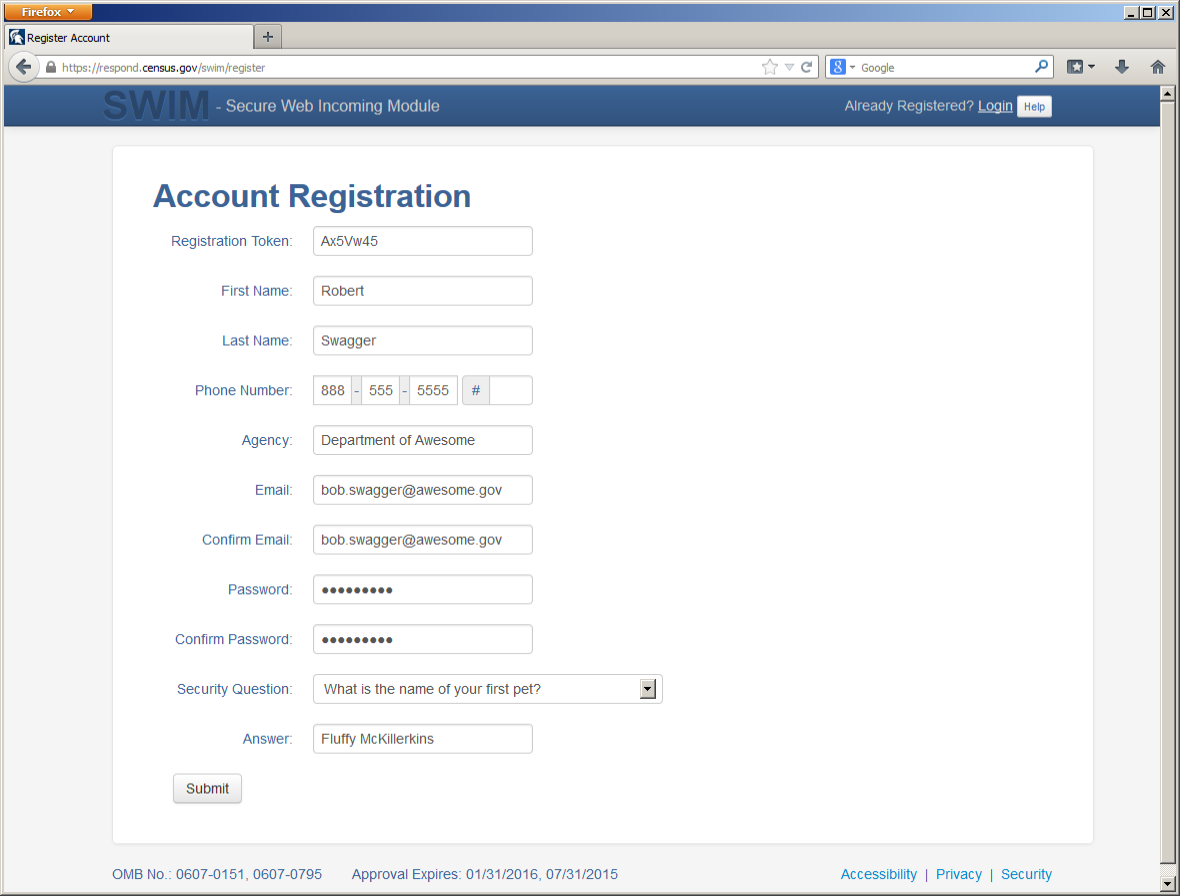
Figure 21. SWIM Account Registration
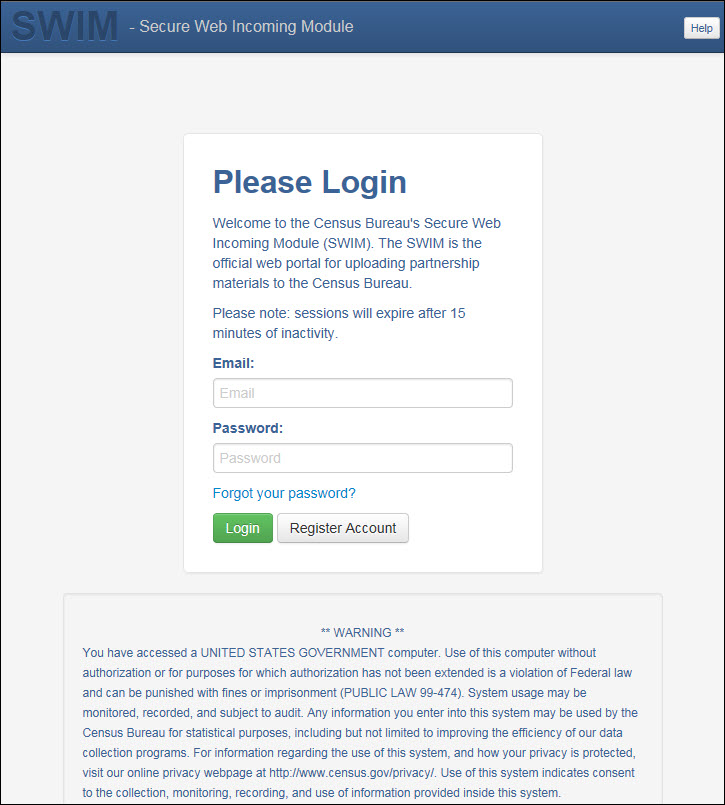
If you have submitted files before, the SWIM lists them on the startup screen upon login. Click 'Start New Upload' to continue.
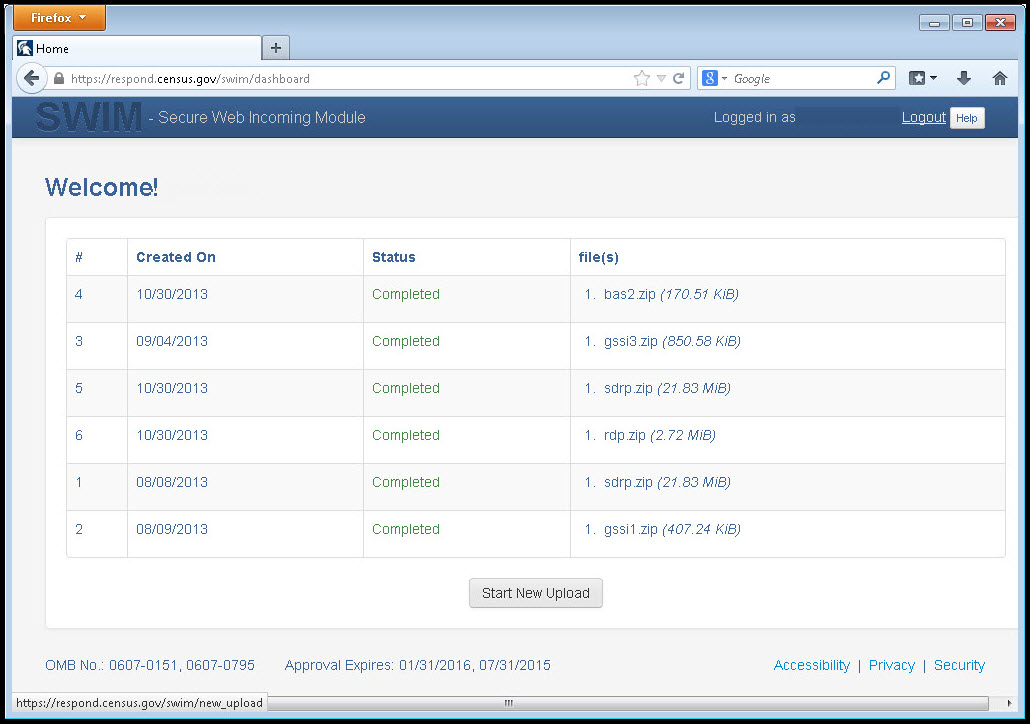
Figure 23. Welcome Screen with Upload History
On the next screen, select the Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS) option as the geographic partnership program, and click ‘Next’ to continue.
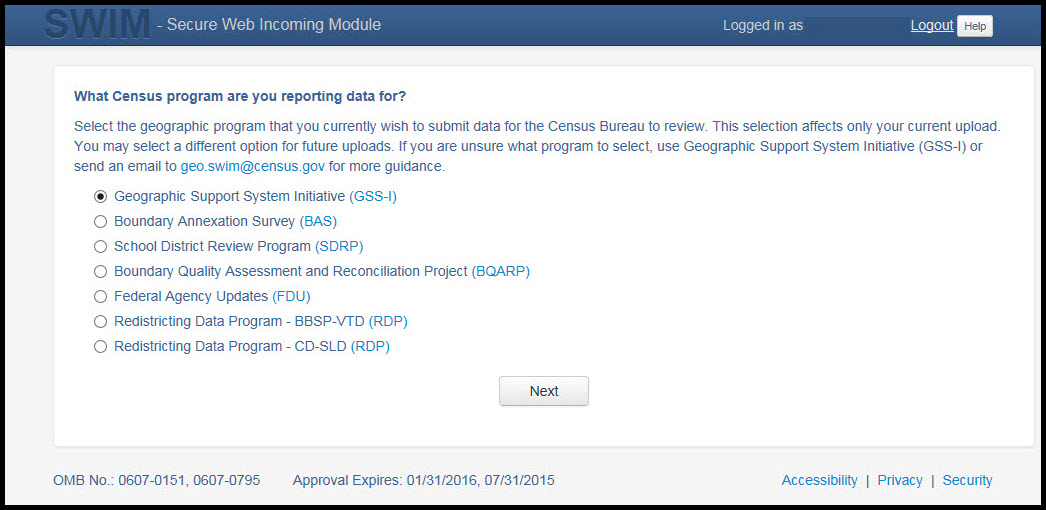
Figure 24. Geographic Partnership Program Selection Window
On this screen, you will select a geographic level. This is the geography type of your agency. Select ‘Tribal Area’. Click 'Next' to continue.
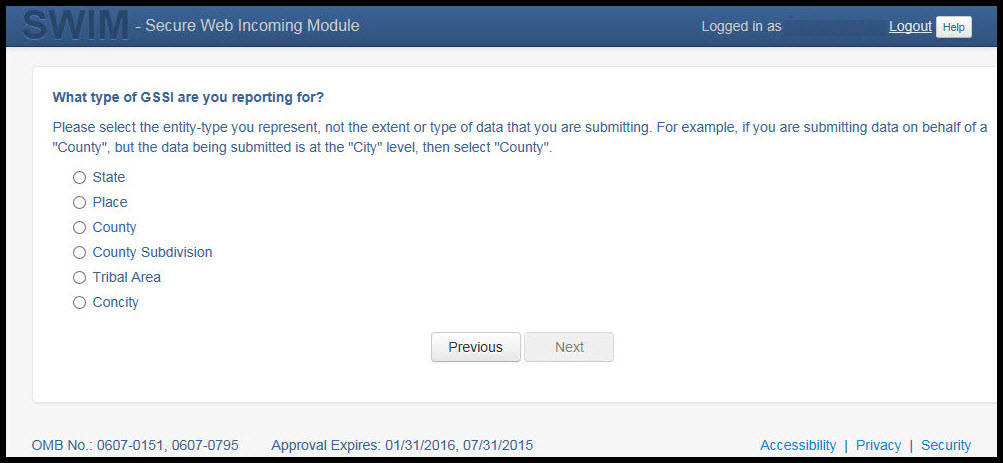
Figure 25. Geographic Level Selection Window
Use the drop-down selectors to find the name of your geographic entity. These options dynamically update based on the geography type selected from the previous screen. Click ‘Next’ to continue.
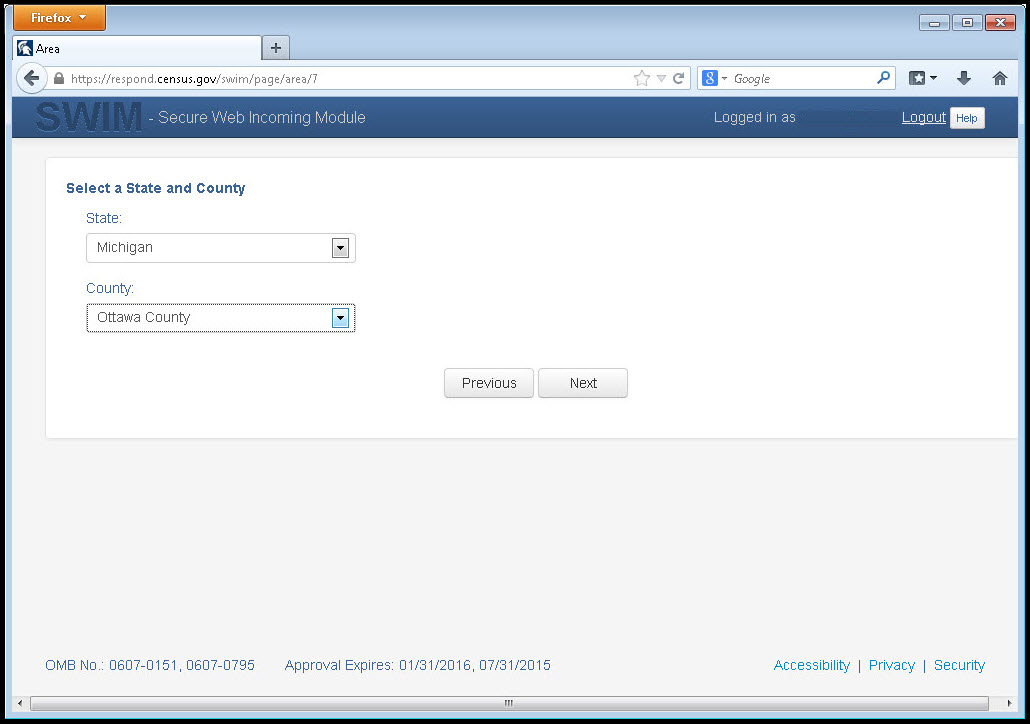
Figure 26. Geographic Entity Selection Window
On the file upload screen, please click on the ‘+ Add file', and a file browser dialog will appear.
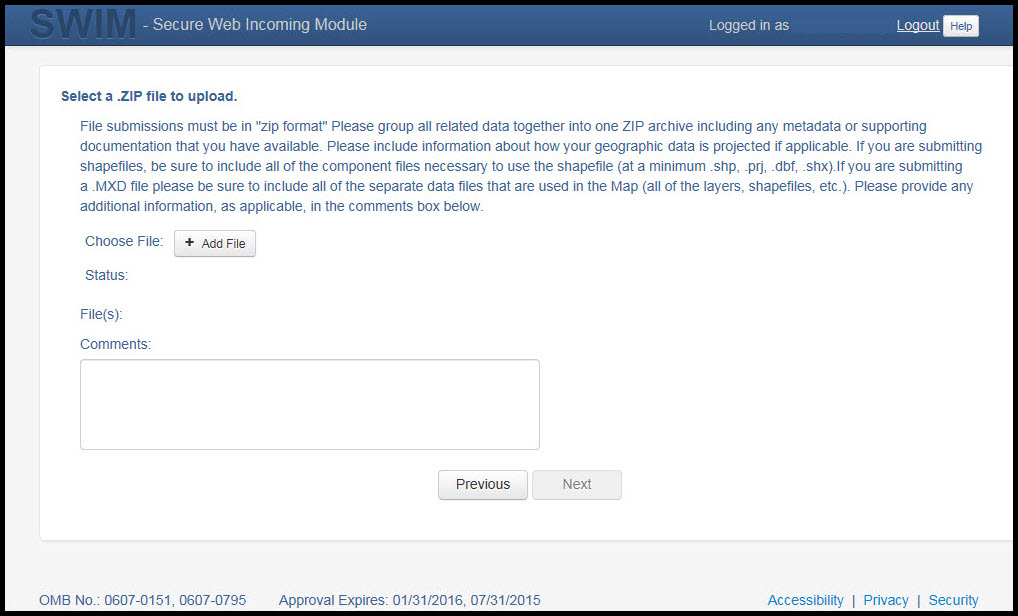
In the file browser dialog box, select the ZIP file you would like to upload. Please be aware that the SWIM Web site only accepts ZIP files. Click 'Open' to continue.
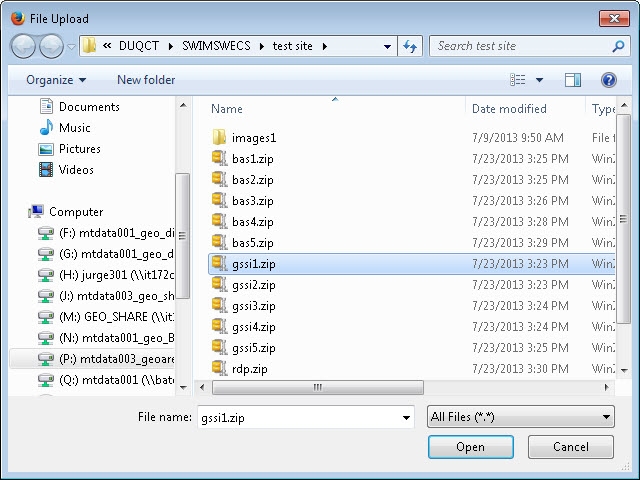
Figure 28. File Browser Dialog Box
At this time, you may enter any comments that you wish to include with your file. Click 'Next' to upload your submission.
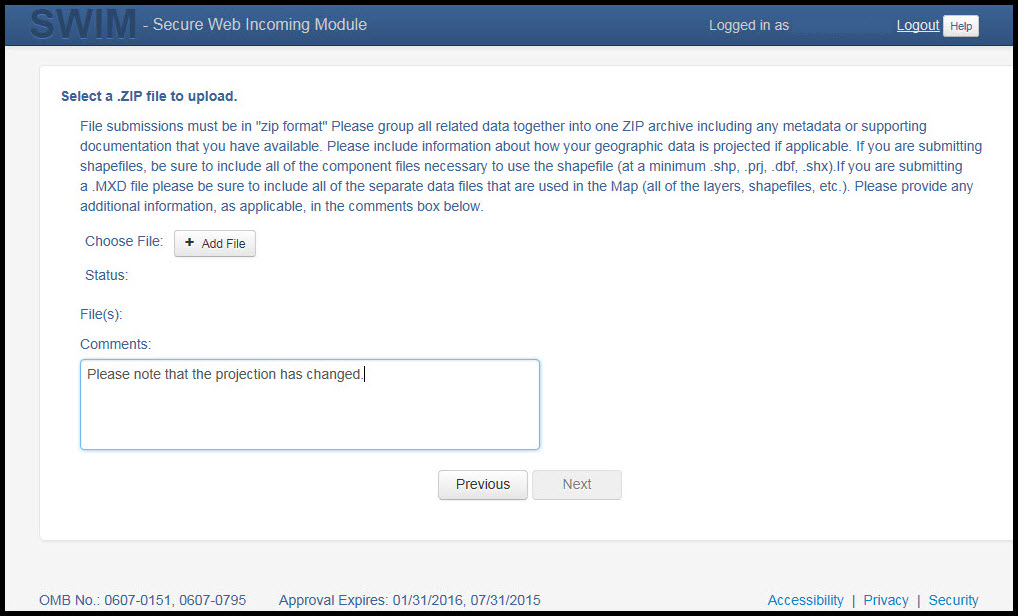
Figure 29. Entering Comments into the File Upload Window
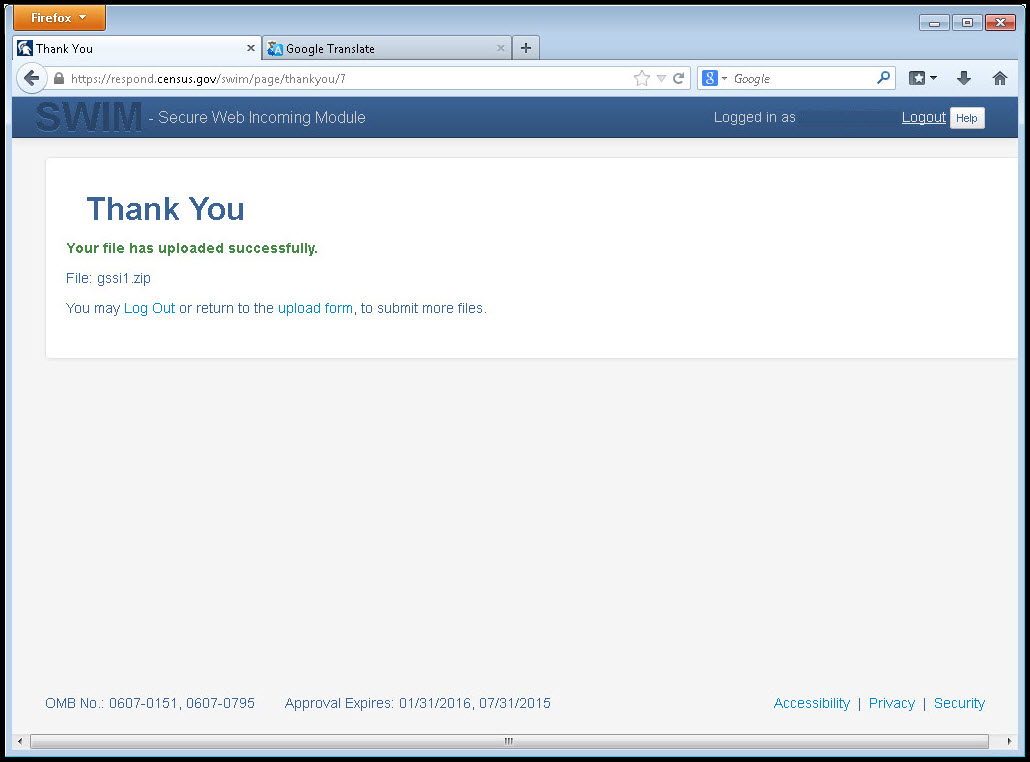
The final screen will be a ‘Thank You’ screen confirming receipt of your file submission. If you do not see this screen, or you encounter any issues during this upload process, please contact the Census Bureau.
The Census Bureau recommends using Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) codes to identify entities such as counties, AIAs, etc. Using a standard coding scheme facilitates the digital exchange of data.
The Census Bureau includes these codes in the BAS shapefiles. Online, you can find the codes at <http://geonames.usgs.gov/domestic/download_data.htm>. If there are any questions or problems, contact the Census Bureau at 1-800-972-5651 or [email protected].
Due to limited staff, the Census Bureau may not be able to make all updates this year. The Census Bureau will prioritize updates in the following order: legal changes, boundary corrections, linear feature changes, and landmark changes. The earlier the Census Bureau receives a submission, the greater the chance that the Census Bureau will be able to make all of the updates. Only submit changes that occurred on or before January 1 of the current survey year. The Census Bureau will not be able to make any updates effective after this date until next year’s BAS.
APPENDICES
Table 16: Alaska Native Regional Corporation (ANRC) Shapefile
ATTRIBUTE FIELD |
LENGTH |
TYPE |
DESCRIPTION |
STATEFP |
2 |
String |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
String |
FIPS County Code |
ANRCFP |
5 |
String |
FIPS ANRC Code |
ANRCCE |
2 |
String |
Current Census ANRC Code |
NAMELSAD |
100 |
String |
Name with Translated LSAD |
LSAD |
2 |
String |
Legal / Statistical Area Description |
AIANNHNS |
8 |
String |
ANSI Numeric Identifier for AIANNH Areas |
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
String |
Functional Status |
CLASSFP |
2 |
String |
FIPS 55 Class Code Describing an Entity |
PARTFLG |
1 |
String |
Part Flag Indicator |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
String |
Type of Area Update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective Date |
AUTHTYPE |
1 |
String |
Authorization Type (O – Ordinance, R – Resolution, L – Local Law, S – State Level Action, X – Other) |
DOCU |
120 |
String |
Supporting Documentation |
RECORD_ID |
4 |
String |
(GUPS Only) |
AREA |
10 |
Double |
Acreage of Area Update |
RELATE |
120 |
String |
Relationship Description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
String |
Justification of Change |
NAME |
100 |
String |
ANRC name |
VINTAGE |
2 |
String |
Vintage of the Data |
Table 17: American Indian Areas - Legal (AIAL) Shapefile
ATTRIBUTE FIELD |
LENGTH |
TYPE |
DESCRIPTION |
STATEFP |
2 |
String |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
String |
FIPS County Code |
AIANNHCE |
4 |
String |
Census AIANNH Code |
COMPTYP |
1 |
String |
Indicates if Reservation, Trust Land, or both are Present |
AIANNHFSR |
1 |
String |
Flag Indicating Level of Recognition of an AIA |
NAMELSAD |
100 |
String |
Name with Translated LSAD |
AIANNHNS |
8 |
String |
ANSI numeric identifier for AIA areas |
LSAD |
2 |
String |
Legal / Statistical Area Description |
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
String |
Functional Status |
CLASSFP |
2 |
String |
FIPS 55 Class Code Describing an Entity |
PARTFLG |
1 |
String |
Part Flag Indicator |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
String |
Type of Area Update |
AUTHTYPE |
1 |
String |
Authorization Type (O – Ordinance, R – Resolution, L – Local Law, S – State Level Action, X – Other) |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective Date |
DOCU |
120 |
String |
Supporting Documentation |
RECORD_ID |
4 |
String |
(GUPS Only) |
AREA |
10 |
Double |
Acreage of Area Update |
RELATE |
120 |
String |
Relationship Description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
String |
Justification of Change |
NAME |
100 |
String |
AIA name |
VINTAGE |
2 |
String |
Vintage of the Data |
Table 18: American Indian Tribal Subdivisions (AITS) Shapefile
ATTRIBUTE FIELD |
LENGTH |
TYPE |
DESCRIPTION |
STATEFP |
2 |
String |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
String |
FIPS County Code |
AIANNHCE |
4 |
String |
Census AIANNH Code |
TRIBALSUBCE |
3 |
String |
Census Tribal Subdivision Code |
NAMELSAD |
100 |
String |
Name with translated LSAD |
AIANNHNS |
8 |
String |
ANSI Numeric Identifier for AIANNH Areas |
LSAD |
2 |
String |
Legal / Statistical Area Description |
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
String |
Functional Status |
CLASSFP |
2 |
String |
FIPS 55 Class Code Describing an Entity |
PARTFLG |
1 |
String |
Part Flag Indicator |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
String |
Type of Area Update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective Date |
AUTHTYPE |
1 |
String |
Authorization Type (O – Ordinance, R – Resolution, L – Local Law, S – State Level Action, X – Other) |
DOCU |
120 |
String |
Supporting Documentation |
RECORD_ID |
4 |
String |
(GUPS Only) |
AREA |
10 |
Double |
Acreage of Area Update |
RELATE |
120 |
String |
Relationship Description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
String |
Justification of Change |
NAME |
100 |
String |
Tribal subdivision name |
VINTAGE |
2 |
String |
Vintage of the Data |
AIANNHFSR |
1 |
String |
Flag Indicating Level of Recognition of an AIA |
ATTRIBUTE FIELD |
LENGTH |
TYPE |
DESCRIPTION |
STATEFP |
2 |
String |
FIPS state code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
String |
FIPS county code |
TLID |
10 |
Double |
Permanent edge ID |
TFIDL |
10 |
Double |
Permanent face ID (left) |
TFIDR |
10 |
Double |
Permanent face ID (right) |
MTFCC |
5 |
String |
MAF/TIGER Feature Class Code |
FIDELITY |
1 |
String |
Indication to a respondent when their entity boundary has changed through spatial enhancement |
FULLNAME |
40 |
String |
Decoded feature name with abbreviated qualifier, direction, and feature type |
SMID |
22 |
String |
Spatial Theta ID |
SMIDTYPE |
1 |
String |
SMIDTYPE code |
BBSPFLG |
1 |
String |
Redistricting data project participant’s submitted request of an EDGE for selection as a block boundary |
CBBFLG |
1 |
String |
Indicates the status of an EDGE for a selection as a block boundary |
BBSP_2020 |
1 |
String |
New BBSP flag |
CHNG_TYPE |
4 |
String |
Type of linear feature update |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
String |
Justification of change |
LTOADD |
10 |
String |
Left To address |
RTOADD |
10 |
String |
Right To address |
LFROMADD |
10 |
String |
Left From address |
RFROMADD |
10 |
String |
Right From address |
ZIPL |
5 |
String |
Left zip code |
ZIPR |
5 |
String |
Right zip code |
EXTTYP |
1 |
Char |
Extension type |
MTUPDATE |
10 |
Date |
Date of last update to the edge |
Table 20: Area Landmark Shapefile
ATTRIBUTE FIELD |
LENGTH |
TYPE |
DESCRIPTION |
STATEFP |
2 |
String |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
String |
FIPS County Code |
MTFCC |
5 |
String |
MAF/TIGER Feature Class Code |
FULLNAME |
120 |
String |
Area landmark name |
PARTFLG |
1 |
String |
Indicates if only part of a feature is represented |
AREAID |
22 |
String |
Object ID |
ANSICODE |
8 |
String |
ANSI code for area landmarks |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
String |
Type of area landmark update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
RELATE |
120 |
String |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
String |
Justification of change |
BAG |
3 |
String |
Block area grouping |
Table 21: Hydro Area Shapefile
ATTRIBUTE FIELD |
LENGTH |
TYPE |
DESCRIPTION |
STATEFP |
2 |
String |
FIPS state code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
String |
FIPS county code |
ANSICODE |
8 |
String |
ANSI code for hydrography area |
MTFCC |
5 |
String |
MAF/TIGER Feature Class Code |
FULLNAME |
120 |
String |
Hydro landmark name |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
String |
Type of hydro area update |
HYDROID |
22 |
String |
Object ID |
RELATE |
120 |
String |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
String |
Justification of change |
Table 22: Point Landmark Shapefile
ATTRIBUTE FIELD |
LENGTH |
TYPE |
DESCRIPTION |
STATEFP |
2 |
String |
FIPS state code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
String |
FIPS county code |
POINTID |
22 |
String |
Object ID |
ANSICODE |
8 |
String |
ANSI code for point landmarks |
MTFCC |
5 |
String |
MAF/TIGER Feature Class Code |
FULLNAME |
120 |
String |
Point landmark name |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
String |
Type of point landmark update |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
String |
Table 23: Geographic Offset Shapefile
ATTRIBUTE FIELD |
LENGTH |
TYPE |
DESCRIPTION |
TFID |
20 |
Integer |
Permanent Face ID |
STATEFP |
2 |
String |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
String |
FIPS County Code |
OFFSET |
1 |
String |
Geographic Offset / Corridor Flag |
ADDEXCLUDE |
1 |
String |
Address Exclusion Indicator |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
String |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
RELATE |
120 |
String |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
String |
Justification of change |
The Census Bureau suggests that participants make an extra copy of the data as an emergency backup.
When downloading shapefiles for the BAS, shapefiles will begin with
the prefix PVS
(e.g., PVS_18_v2_edges_<ssccc>.shp).
Throughout this guide, Census Bureau uses the prefix of bas_2019,
but the PVS files are exactly the same.
Note: Contact the Census Bureau at 1-800-972-5651 or [email protected] with any questions.
Copy the data to a hard drive/server, and unzip the data to ensure that the correct data was downloaded. For an AIA, these layers are critical:
PVS_18_v2_aial_<ssccc>.shp
PVS_18_v2_edges_<ssccc>.shp
Note: <ssccc> represents the two-digit state code and three-digit county code.
The shapefiles should include the home county/counties for all reservations and off-reservation trust lands as well as all adjacent counties.
The following are suggestions for symbolizing Census Bureau data in ArcGIS. For the Edges layer, symbolize the linear features by grouping like MTFCC codes (codes sharing the same first character). See Table 24.
Table 24: Suggested MTFCC Symbolization
MTFCC 1st Character |
Linear Feature Type |
Symbol |
H |
Hydrology |
|
P |
Non-Visible Feature (boundary) |
|
R |
Railroad |
|
S |
Road |
|
Symbolizing Geographic Areas
Symbolize the AIAL layer by “COMPTYP” field to show reservation and off-reservation trust land.
Note: AIA participants working on changes for tribal subdivisions may want to use different colors to distinguish one from another.
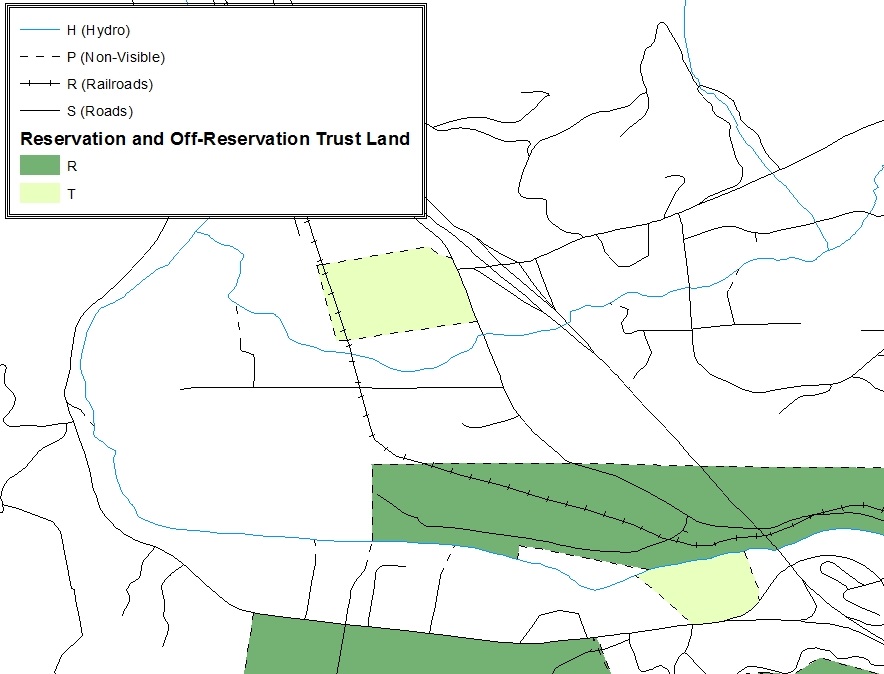
Figure 31. Suggested Map Symbolization
Note: If you do not have ArcGIS Advanced, skip ahead to Section B.4.
In ArcMap, click Selection and then click Select by Attributes.
In the Select By Attributes window:
From the Layer dropdown, select PVS_2019_v2_aial_<ssccc>.shp.
Double click “NAME”
Left click the = button,
Click the Get Unique Values button
In the list, locate and double click the name of the entity (it will appear in the formula).
Click OK
Exporting the Data to a New Shapefile
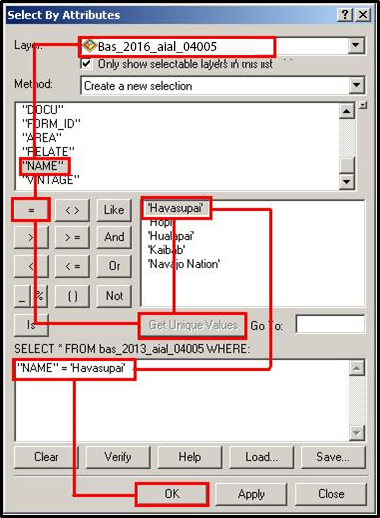
In the Table of Contents, right click the AIA layer, select Data, and then click Export Data.
In the Export Data window:
From the Export dropdown, choose Selected Features.
In the Output shapefile or feature class field, enter a location to save the shapefile.
Click OK.
Note: If the AIA spans more than one county, it will need to be exported from each county’s AIA shapefile and merged. Follow the instructions in Section B.4if the AIA needs to be merged, otherwise skip to Section B.5.
In ArcToolbox, double-click Data Management Tools, then double-click General, and then double-click Merge.
In the Merge window:
Next to the Input Datasets Input field, click the arrow and select each layer. (Or use the Browse button to the right of the field to find the layers.)
In the Output Dataset field, browse to and select a location to save the shapefile.
Name the shapefile Export_Output_Final or Merged, or anything easy to find/remember.
Click OK.
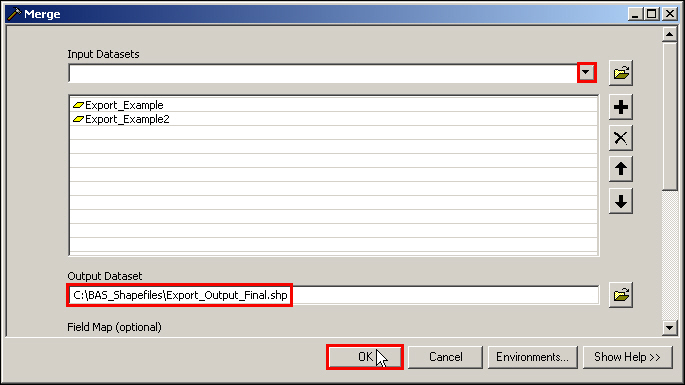
Figure 34. Finalizing the Merge Process
Note: If you do not have an ArcInfo license, you will have to use the Union operation rather than the Symmetrical Difference operation. See Section 0 if this is the case.
In ArcToolbox, double-click Analysis Tools, then double-click Overlay, and then double-click Symmetrical Difference.
In the Symmetrical Difference window:
In the Input Features field, click the arrow (or browse) and select the layer that was created in Section 3.
In the Update Features field, click the arrow (or browse) and select the tribal government boundary layer (your data).
In the Output Feature Class field, browse to and select a location to save the shapefile.
Name the shapefile Differences_between_BAS_tribal, Differences1, or anything easy to find/remember.
Click OK.
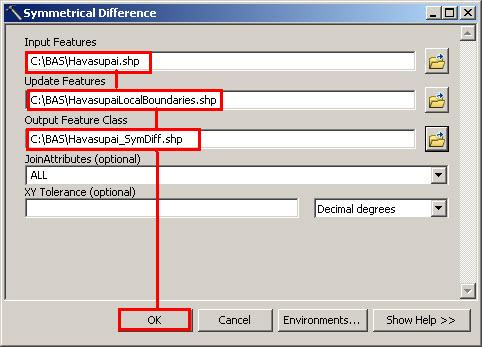
Figure 35. Finalizing the Symmetrical Difference Process
Note: This process creates a layer that contains all of the differences between Census Bureau and local boundaries. However, the Symmetrical Difference tool creates multipart polygons that need to be broken up and individually coded.
Turn on Editing (using the Editing dropdown in the Editor toolbar). Select all of the records in the layer that was created in the Symmetrical Difference step.
On the Advanced Editing toolbar, click the Explode tool
 .
The layer will now contain a separate record for each change.
.
The layer will now contain a separate record for each change.
The created layer shows individual change polygons representing the differences between the Census Bureau and tribal entity boundaries. These differences need to be reviewed and coded appropriately.
Skip to B.7 Renaming and Finalizing Change Polygons.
Note: Use this method if you do not have an ArcInfo license.
In ArcToolbox, double-click Analysis Tools, then double-click Overlay, and then double-click Union.
In the Union window:
In the Input Features field, click the arrow (or browse) and select PVS_18_v2_aial_<ssccc>, and the tribe’s own layer.
In the Output Feature Class, browse to and select a location to save the shapefile.
Name the shapefile Export_Output_union, or Union, or anything easy to find/remember.
Click OK.
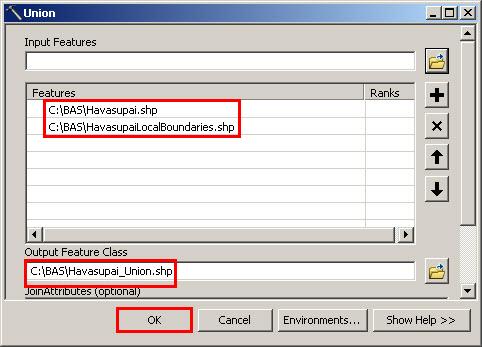
Figure 36. Finalizing the Union Process
The union operation will create records that contain differences as well as areas that are in common between the Census Bureau and local tribal boundary layers.
The next step is selecting and deleting the areas in common between the Census Bureau and local tribal boundary layers.
On the Editor toolbar, click Editor, and then click Start Editing.
If a Start Editing window opens, in the top pane, click to highlight the union shapefile, and then click OK.
Figure 37. Locating the Union Shapefile
In ArcMap, in the Tools toolbar, click the Select Features
 button.
button.
Locate features on the map that the Census Bureau and the local tribal layers have in common.
Select each feature individually, or click and hold the left mouse button and drag a box to highlight the common features.
Press Delete.
Repeat these steps until only the features that have changed are left in the map.
Once all of the areas in common have been removed from the union shapefile, on the Editor toolbar, click Editor, and then click Save Edits.
Select all of the remaining records in the layer that was created in the Union step.
On the Advanced Editing toolbar, click the Explode tool
 .
The layer will now contain a separate record for each change.
.
The layer will now contain a separate record for each change.
The new layer shows individual change polygons representing the differences between the Census Bureau and the tribal government’s representation of the boundaries. Please review these differences and make sure they are coded appropriately. Continue to the next section for instructions on reviewing and coding change polygons.
After the individual change polygons have been created, each must be reviewed and appropriately coded. When reviewing the polygons, please refer to Section 5.3 in the main part of this guide to look for polygons that should be deleted from your submission as well as those that should be snapped to nearby visible features to maintain boundary-to-feature relationships.
These examples show very small sliver polygons that should be deleted during review as they eliminate boundary-to-feature relationships with a river (left) and a road (right). Furthermore, these boundary corrections also are not located near legal changes or corridor/offset changes (type ‘A’, ‘D’, ‘C’, ‘F’), so they should be removed from consideration.
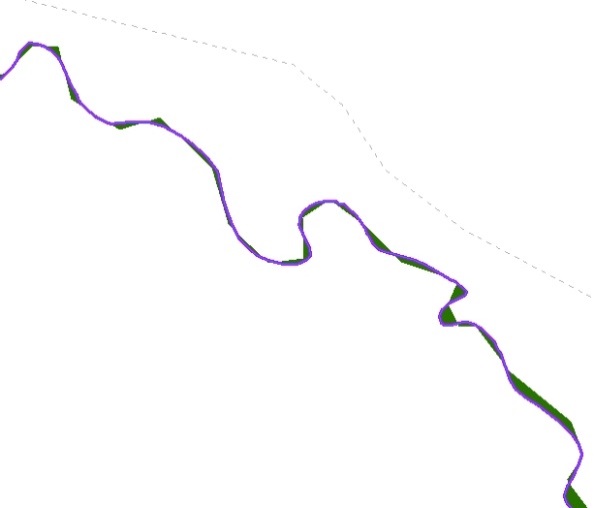
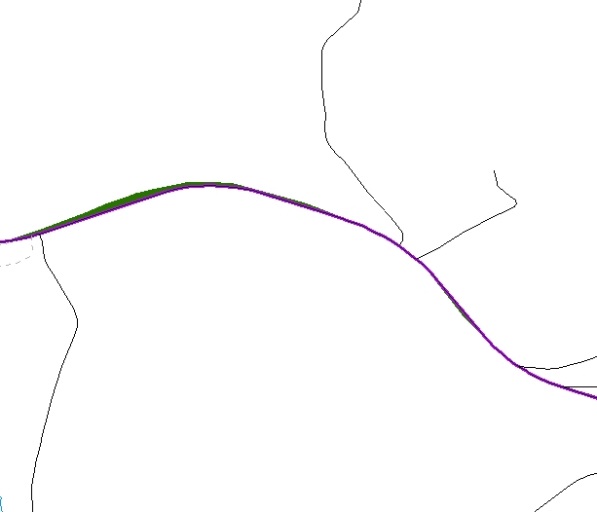
Figure 38. Small Slivers That Should Be Deleted
These examples show polygons that should be snapped to roads (left) or rivers (right).

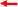
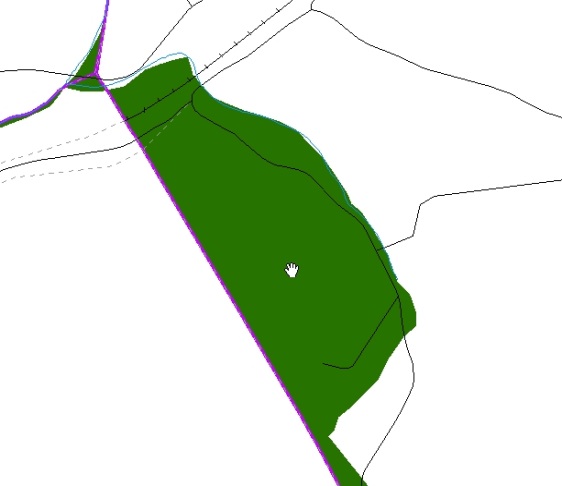
Figure 39. Polygons That Should Be Snapped to Roads or Rivers
Note: All updates MUST be attributed.
To begin updating attributes
On the Editor Toolbar, click Editor, and then click Start Editing.
Additions
On the Editor Toolbar, click the Edit Tool
 button and select the addition polygon.
button and select the addition polygon.On the Editor Toolbar, click the Attributes
 button.
button.In the Attributes window, fill out the mandatory fields required for an addition.
NAME, CHNG_TYPE, AUTHTYPE, DOCU and EFF_DATE.
The CHNG_TYPE for an addition is A.
Deletions
On the Editor Toolbar, click the Edit Tool
 button and select the deletion polygon.
button and select the deletion polygon.On the Editor Toolbar, click the Attributes
 button.
button.In the Attributes window, fill out the mandatory fields required for a deletion.
NAME, CHNG_TYPE, AUTHTYPE, DOCU and EFF_DATE.
The CHNG_TYPE for a deletion is D.
Corridors
On the Editor Toolbar, click the Edit Tool
 button and select the corridor polygon.
button and select the corridor polygon.On the Editor Toolbar, click the Attributes
 button.
button.In the Attributes window, fill out the mandatory fields required for a corridor.
NAME, CHNG_TYPE, RELATE.
The CHNG_TYPE for a corridor changes is C.
In the RELATE field, enter IN if the change is adding corridor area to the place or OUT if the change is removing corridor area.
Offsets
On the Editor Toolbar, click the Edit Tool
 button and select the offset polygon.
button and select the offset polygon.On the Editor Toolbar, click the Attributes
 button.
button.In the Attributes window, fill out the mandatory fields required for an offset.
NAME, CHNG_TYPE, RELATE.
The CHNG_TYPE for an offset change is F.
In the RELATE field, enter IN if the change is adding offset area to the place or OUT if the change is removing offset area.
Boundary Corrections
On the Editor Toolbar, click the Edit Tool
 button and select the boundary correction polygon.
button and select the boundary correction polygon.On the Editor Toolbar, click the Attributes
 button.
button.In the Attributes window, fill out the mandatory fields required for a boundary correction:
NAME, CHNG_TYPE, RELATE.
The CHNG_TYPE for a boundary correction is B.
In the RELATE field, enter IN if the boundary correction is adding area or OUT if the boundary correction is removing area.
Note: If a boundary correction to one tribal subdivision affects another, use RELATE = IN and NAME = <entity being added to>. This is due to the fact that RELATE = OUT leaves a question as to whether or not there should be a gap between the two entities.
To finish updating attributes
Once all of the attribute changes have been made, in the ArcMap menu, click Editor, and then click Stop Editing. (In the Save window, click Yes.)
Renaming the shapefile
After creating and coding all change polygons, please rename the change polygon layer prior to its submission to the Census Bureau. You must complete this process for each level of geography (AIA, tribal subdivision) that has changes.
In ArcMap, open the ArcCatalog
 tab.
tab.
In ArcCatalog, navigate to shapefile, right-click and select Rename.
Save the output shapefile in the proper naming convention: bas19_<basID>_changes_aiannh.
Note: You can find the basID numbers in the BAS Annual Response Email or online from this link: <https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/bas/technical-documentation/code-lists.html>.
Note: See Section5.13.6 for instructions on zipping updates.
Submitting the shapefile
The Census Bureau requires participants submit BAS return zip files
using the Census Bureau’s SWIM site. Please submit only
the zip file. The SWIM is located at
<https://respond.census.gov/swim>.
For instructions on how to use SWIM, refer to
Section
5.13.7 Submitting Digital Files via SWIM.
The Census Bureau suggests that participants make an extra copy of the data as an emergency backup.
When downloading shapefiles for the BAS, shapefiles will begin with the prefix PVS
(e.g., PVS_18_v2_edges_<ssccc>.shp).Throughout this guide, Census Bureau uses the prefix of bas_2019, but the PVS files are exactly the same.
Note: Contact the Census Bureau at 1-800-972-5651 or [email protected] with any questions.
Copy the data to a hard drive/server, and unzip the data to ensure that the correct data was downloaded. For an AIA, these layers are critical:
PVS_18_v2_aial_<ssccc>.shp
PVS_18_v2_edges_<ssccc>.shp
Note: <ssccc> represents the two-digit state code and three-digit county code.
The shapefiles should include the home county/counties for all of your reservation and off-reservation trust lands as well as all adjacent counties.
The following are suggestions for symbolizing Census Bureau data in ArcGIS. For the Edges layer, symbolize the linear features by grouping like MTFCC codes (codes sharing the same first character).
Table 25: Edges MTFCC Suggested Symbolization
MTFCC 1st Character |
Linear Feature Type |
Symbol |
H |
Hydrology |
|
P |
Non-Visible Feature (boundary) |
|
R |
Railroad |
|
S |
Road |
|
Symbolizing Geographic Areas
Symbolize the AIAL layer by “COMPTYP” field to show reservation and off-reservation trust land.
Note: AIA participants reporting tribal subdivisions may want to use different colors to distinguish one from another.
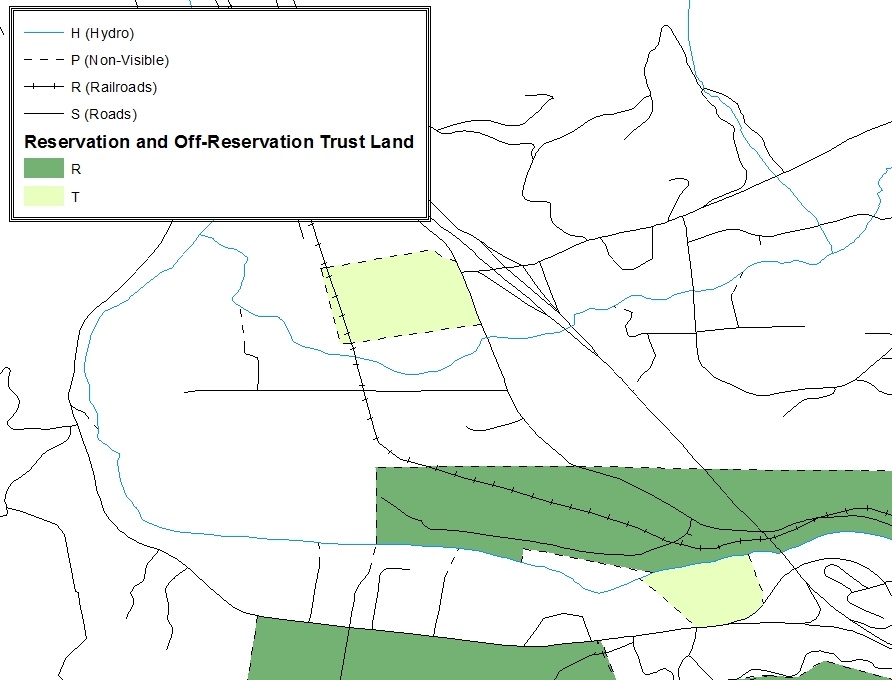
Figure 40. Suggested Map Symbolization.
Some of the linear features needed to create change polygons may not exist in MAF/TIGER. It may be necessary to create and split lines when forming changes. The existing and newly created linear features will then be selected to define the boundary changes.
In ArcMap, right click the edges layer in the Table of Contents, click Selection, and then click Make This The Only Selectable Layer, so that the edges layer is the only one which can be selected while editing.
In the Editor toolbar, click Editor and then click Start Editing.
In the Create Features window, highlight a non-visible boundary symbolization under the edges layer: PVS_18_v2_edges_<ssccc>.
Figure 41. Create Features Window.
In the Editor toolbar, click Editor and then click Snapping, then Snapping Toolbar.
On the snapping toolbar, ensure that Point, Vertex, Edge, and End Snapping are all enabled. Drop down the Snapping menu, and ensure that Use Snapping is checked. Snapping will ensure that newly created lines will follow existing MAF/TIGER linear features.
![]()
Figure 42. Snapping Toolbar.
For any new boundary lines that do not follow existing edges, ensure that Line is selected in the Construction Tools pane (see Figure 41), and in the Editor toolbar, click the Straight Segment Tool
 button and draw new features on the map by clicking to create a
line. Single clicking will add vertexes to the line, and
double-clicking will end the line and create the new feature. Any
new feature(s) will be highlighted.
button and draw new features on the map by clicking to create a
line. Single clicking will add vertexes to the line, and
double-clicking will end the line and create the new feature. Any
new feature(s) will be highlighted.
Figure 43. A Newly Created Linear Feature.
Adding Attribute Data to New Linear Features
After creating new linear features:
In the Editor toolbar, click the Attributes
 button.
button.
In the Attributes window, in the MTFCC field, add the appropriate MTFCC code (it should default to P0001, but can be changed if necessary).
Use P0001 if the feature is a non-visible political boundary.
If the feature is visible, see Appendix D for the appropriate codes.
Note: Each new feature must have an MTFCC code. If larger scale linear feature changes are going to be submitted, it is best to create those in a separate layer. It is not necessary to submit linear feature changes for non-visible boundaries.
Note: Click on Editor and then click Save Edits often so that work is not lost.
Once all lines are added, in the Editor toolbar, click Editor and then click Stop Editing (in the Save window, click Yes).
In the Editor toolbar, click Editor and then click Start Editing.
In the Editor toolbar, click the Edit Tool
 button and select a linear feature that needs to be split. The line
will be highlighted when it is selected.
button and select a linear feature that needs to be split. The line
will be highlighted when it is selected.In the Editor toolbar, click the Split Tool
 button. Click the line where it needs to be split. The following
examples display why it may be necessary to split lines when
creating change polygons.
button. Click the line where it needs to be split. The following
examples display why it may be necessary to split lines when
creating change polygons.
The desired boundary change is indicated below. When selecting the lines to form the boundary change, sections of the linear features that are not a part of the boundary update are included (highlighted in blue).
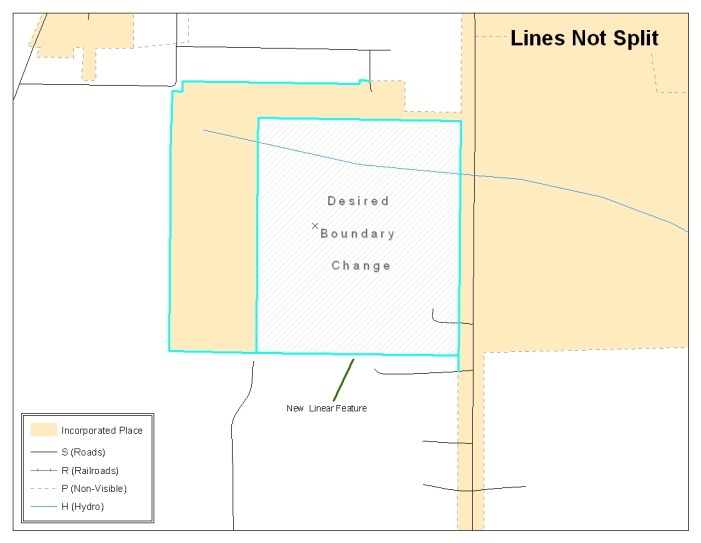
Figure 44. Linear Feature Selection Before Being Split
The existing linear features can be split to prevent unwanted line segments from being selected as part of the boundary update.
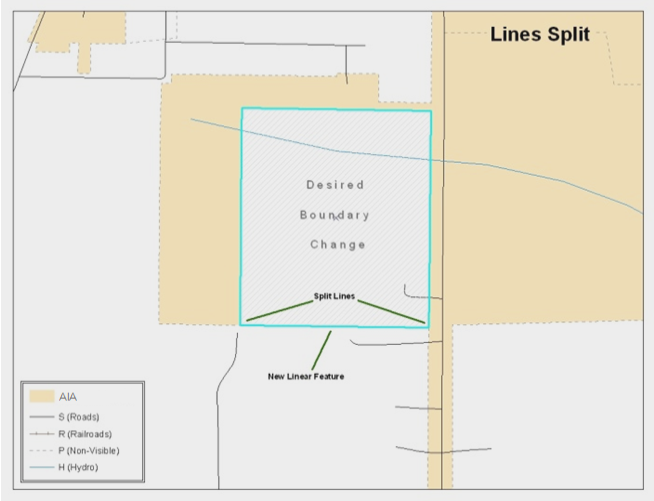
Figure 45. Linear Feature Selection After Being Split
Once all necessary splits are made, in the Editor toolbar, click Editor and then click Save Edits.
Selecting Lines and Creating Change Polygons
After creating and/ or splitting any necessary linear features, select those that will be used to form change polygons. Each change polygon must be created and coded separately.
Creating change polygons
If the Topology toolbar is not active, click the Customize menu, select Toolbars, and then select Topology to activate it.
In the Editor toolbar, click Editor and then click Start Editing.
In the Create Features window, switch the highlighted feature to the aia layer: PVS_18_v2_aial_<ssccc>.
In the Editor toolbar, click the Edit Tool
 button and select the linear features that comprise the boundary of
a change polygon (i.e. an addition, deletion, or incorrect area) by
holding the Shift key while clicking each linear feature segment.
button and select the linear features that comprise the boundary of
a change polygon (i.e. an addition, deletion, or incorrect area) by
holding the Shift key while clicking each linear feature segment.
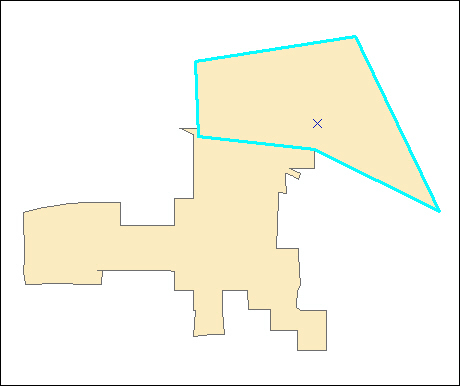
Figure 46. Selecting the Linear Features of a Change Polygon
On the Topology toolbar, click the Construct Features
 button.
button.
In the Construct Features dialog box, click OK (the default Cluster Tolerance is acceptable).
The polygon is now part of the AIA layer; however, it will not have any associated attribute values (see the next section).
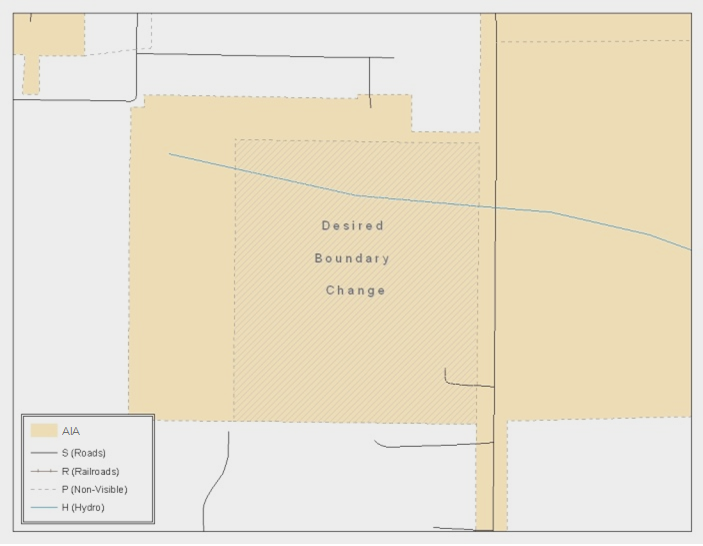
Figure 47. Newly Created AIA Feature
After creating the change polygons, each must be correctly attributed so that the boundaries can be appropriately updated in MAF/TIGER. Another option is to update the attributes for each change polygon after creating all boundary changes. The following steps will explain which attributes are mandated for each type of boundary change.
Note: All updates MUST be attributed.
To begin updating attributes
In ArcMap, right click the AIA layer in the Table of Contents, click Selection, and then click Make This The Only Selectable Layer, so that the AIA layer is the only one which can be selected while editing
On the Editor Toolbar, click Editor, and then click Start Editing.
Additions
On the Editor Toolbar, click the Edit Tool
 button and select the addition polygon.
button and select the addition polygon.On the Editor Toolbar, click the Attributes
 button.
button.In the Attributes window, fill out the mandatory fields required for an addition.
NAME, CHNG_TYPE, AUTHTYPE, DOCU and EFF_DATE.
The CHNG_TYPE for an addition is A.
Deletions
On the Editor Toolbar, click the Edit Tool
 button and select the deletion polygon.
button and select the deletion polygon.On the Editor Toolbar, click the Attributes
 button.
button.In the Attributes window, fill out the mandatory fields required for a deletion.
NAME, CHNG_TYPE, AUTHTYPE, DOCU and EFF_DATE.
The CHNG_TYPE for an addition is D.
Corridors
On the Editor Toolbar, click the Edit Tool
 button and select the corridor polygon.
button and select the corridor polygon.On the Editor Toolbar, click the Attributes
 button.
button.In the Attributes window, fill out the mandatory fields required for a corridor.
NAME, CHNG_TYPE, RELATE.
The CHNG_TYPE for a corridor changes is C.
In the RELATE field, enter IN if the change is adding corridor area to the place or OUT if the change is removing corridor area.
Offsets
On the Editor Toolbar, click the Edit Tool
 button and select the offset polygon.
button and select the offset polygon.On the Editor Toolbar, click the Attributes
 button.
button.In the Attributes window, fill out the mandatory fields required for an offset.
NAME, CHNG_TYPE, RELATE.
The CHNG_TYPE for an offset change is F.
In the RELATE field, enter IN if the change is adding offset area to the place or OUT if the change is removing offset area.
Boundary Corrections
On the Editor Toolbar, click the Edit Tool
 button and select the boundary correction polygon.
button and select the boundary correction polygon.On the Editor Toolbar, click the Attributes
 button.
button.In the Attributes window, fill out the mandatory fields required for a boundary correction:
NAME, CHNG_TYPE, RELATE.
The CHNG_TYPE for a boundary correction is B.
In the RELATE field, enter IN if the boundary correction is adding area or OUT if the boundary correction is removing area.
Note: If a boundary correction to one tribal subdivision affects another, use RELATE = IN and NAME = <entity being added to>. This is due to the fact that RELATE = OUT leaves a question as to whether or not there should be a gap between the two entities.
To finish updating attributes
Once all of the attribute changes have been made, on the Editor toolbar, click Editor, and then click Stop Editing (in the Save window, click Yes).
After creating and coding the change polygons, each level of geography (AIA, tribal subdivision) that has changes must be exported to a separate change polygon layer.
In ArcMap, click Selection and then click Select by Attributes.
In the Select By Attributes window:
Set the Layer dropdown to the AIA layer: bas_2019_aial_<ssccc>.
Set the Method dropdown to Create a new selection.
In the Select * FROM box, type one of the following formulas:
“CHNG_TYPE” < > ‘ ’ This equation would select all change polygons that have any change type which have been created and coded.
“CHNG_TYPE” = ‘A’ OR “CHNG_TYPE” = ‘B’ OR… (etc.) This equation can be written to select a specific change type for polygons that were created and coded.
Click OK.
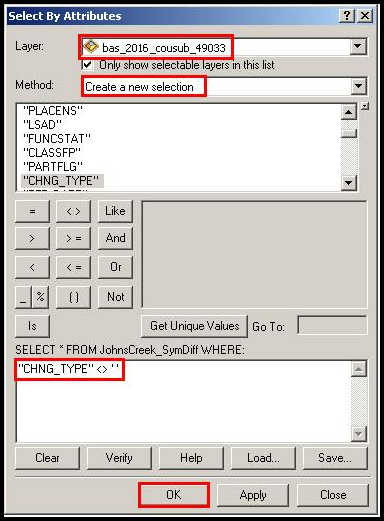
Figure 48. Select All Change Types Formula
After clicking OK, each change polygon that that has been created and coded should be highlighted on the map and in the attribute table.
Optional: Open the attribute table and sort to verify that all change polygons with a change type code were selected.
Exporting the selected change polygons
In the ArcMap Table of Contents, right-click on the AIA layer (PVS_18_v2_aial_<ssccc>), select Data, and then click Export Data.
In the Export Data window:
From the Export dropdown, choose Selected Features.
In the Output shapefile or feature class: field, browse to and select a location to save the shapefile.
Name the shapefile bas19_<basID>_changes_aiannh.shp.
Click OK.
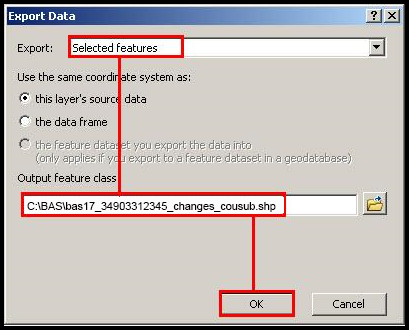
Note: The basID number can be found on the BAS Annual Response email or online from this link: <https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/bas/technical-documentation/code-lists.html>.
Note: See Section 5.13.6 for instructions on zipping updates.
The Census Bureau requires participants submit BAS return zip files using the Census Bureau’s SWIM site. Please submit only the zip file. The SWIM is located at <https://respond.census.gov/swim>. For instructions on how to use SWIM, you can find them in Section 5.12.2 and Section 5.12.4 Submitting Digital Files via the Secure Web Incoming Module (SWIM).
The MAF/TIGER Feature Classification Code (MTFCC) is a 5-digit code assigned by the Census Bureau to classify and describe geographic objects or features in Census Bureau MAF/TIGER products.
MTFCC |
Feature Class |
Feature Class Description |
C3022 |
Mountain Peak or Summit |
A prominent elevation rising above the surrounding level of the Earth’s surface. |
C3023 |
Island |
An area of dry or relatively dry land surrounded by water or low wetland [including archipelago, atoll, cay, hammock, hummock, isla, isle, key, moku and rock]. |
C3024 |
Levee |
An embankment flanking a stream or other flowing water feature to prevent overflow. |
C3026 |
Quarry (not water-filled), Open Pit Mine or Mine |
An area from which commercial minerals are or were removed from the Earth; not including an oilfield or gas field. |
C3027 |
Dam |
A barrier built across the course of a stream to impound water and/or control water flow. |
C3061 |
Cul-de-sac |
An expanded paved area at the end of a street used by vehicles for turning around. For mapping purposes, the Census Bureau maps it only as a point feature. |
C3062 |
Traffic Circle |
A circular intersection allowing for continuous movement of traffic at the meeting of roadways. |
C3066 |
Gate |
A movable barrier across a road. |
C3067 |
Toll Booth |
A structure or barrier where a fee is collected for using a road. |
C3071 |
Lookout Tower |
A manmade structure, higher than its diameter, used for observation. |
C3074 |
Lighthouse Beacon |
A manmade structure, higher than its diameter, used for transmission of light and possibly sound generally to aid in navigation. |
C3075 |
Tank/Tank Farm |
One or more manmade structures, each higher than its diameter, used for liquid (other than water) or gas storage or for distribution activities. |
C3076 |
Windmill Farm |
One or more manmade structures used to generate power from the wind. |
C3077 |
Solar Farm |
One or more manmade structures used to generate power from the sun. |
C3078 |
Monument or Memorial |
A manmade structure to educate, commemorate, or memorialize an event, person, or feature. |
C3079 |
Boundary Monument Point |
A material object placed on or near a boundary line to preserve and identify the location of the boundary line on the ground. |
C3080 |
Survey Control Point |
A point on the ground whose position (horizontal or vertical) is known and can be used as a base for additional survey work. |
C3081 |
Locality Point |
A point that identifies the location and name of an unbounded locality (e.g., crossroad, community, populated place or locale). |
C3085 |
Alaska Native Village Official Point |
A point that serves as the core of an Alaska Native village and is used in defining Alaska Native village statistical areas. |
G2100 |
American Indian Area |
A legally defined state- or federally recognized reservation and/or off-reservation trust land (excludes statistical American Indian areas). |
G2120 |
Hawaiian Home Land |
A legal area held in trust for the benefit of Native Hawaiians. |
G2130 |
Alaska Native Village Statistical Area |
A statistical geographic entity that represents the residences, permanent and/or seasonal, for Alaska Natives who are members of or receiving governmental services from the defining legal Alaska Native Village corporation. |
G2140 |
Oklahoma Tribal Statistical Area |
A statistical entity identified and delineated by the Census Bureau in consultation with federally recognized American Indian tribes that have no current reservation, but had a former reservation in Oklahoma. |
G2150 |
State-designated Tribal Statistical Area |
A statistical geographic entity identified and delineated for the Census Bureau by a state-appointed liaison for a state-recognized American Indian tribe that does not currently have a reservation and/or lands in trust. |
G2160 |
Tribal Designated Statistical Area |
A statistical geographic entity identified and delineated for the Census Bureau by a federally recognized American Indian tribe that does not currently have a reservation and/or off-reservation trust land. |
G2170 |
American Indian Joint Use Area |
An area administered jointly and/or claimed by two or more American Indian tribes. |
G2200 |
Alaska Native Regional Corporation |
Corporate entities established to conduct both business and nonprofit affairs of Alaska Natives pursuant to the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act of 1972 (Public Law 92-203). There are twelve geographically defined ANRCs and they are all within and cover most of the State of Alaska (the Annette Island Reserve-an American Indian reservation-is excluded from any ANRC). The boundaries of ANRCs have been legally established. |
G2300 |
Tribal Subdivision |
Administrative subdivisions of federally recognized American Indian reservations, off-reservation trust lands, or Oklahoma tribal statistical areas (OTSAs). These entities are internal units of self-government or administration that serve social, cultural, and/or economic purposes for the American Indians on the reservations, off-reservation trust lands, or OTSAs. |
G2400 |
Tribal Census Tract |
A relatively small and permanent statistical subdivision of a federally recognized American Indian reservation and/or off-reservation trust land, delineated by American Indian tribal participants or the Census Bureau for the purpose of presenting demographic data. |
G2410 |
Tribal Block Group |
A cluster of census blocks within a single tribal census tract delineated by American Indian tribal participants or the Census Bureau for the purpose of presenting demographic data. |
G3100 |
Combined Statistical Area |
A grouping of adjacent metropolitan and/or micropolitan statistical areas that have a degree of economic and social integration, as measured by commuting. |
G3110 |
Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Area |
An area containing a substantial population nucleus together with adjacent communities having a high degree of economic and social integration with that core, as measured by commuting. Defined using whole counties and equivalents. |
G3120 |
Metropolitan Division |
A county or grouping of counties that is a subdivision of a Metropolitan Statistical Area containing an urbanized area with a population of 2.5 million or more. |
G3200 |
Combined New England City and Town Area |
A grouping of adjacent New England city and town areas that have a degree of economic and social integration, as measured by commuting. |
G3210 |
New England City and Town Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Area |
An area containing a substantial population nucleus together with adjacent communities having a high degree of economic and social integration with that core, as measured by commuting. Defined using Minor Civil Divisions (MCDs) in New England. |
G3220 |
New England City and Town Division |
A grouping of cities and towns in New England that is a subdivision of a New England City and Town Area containing an urbanized area with a population of 2.5 million or more. |
G3500 |
Urban Area |
Densely settled territory that contains at least 2,500 people. The subtypes of this feature are Urbanized Area (UA), which consists of 50,000 + people and Urban Cluster, which ranges between 2,500 and 49,999 people. |
G4000 |
State or Equivalent Feature |
The primary governmental divisions of the United States. The District of Columbia is treated as a statistical equivalent of a state for census purposes, as is Puerto Rico. |
G4020 |
County or Equivalent Feature |
The primary division of a state or state equivalent area. The primary divisions of 48 states are termed County, but other terms are used such as Borough in Alaska, Parish in Louisiana, and Municipio in Puerto Rico. This feature includes independent cities, which are incorporated places that are not part of any county. |
G4040 |
County Subdivision |
The primary divisions of counties and equivalent features for the reporting of Census Bureau data. The subtypes of this feature are Minor Civil Division, Census County Division/Census Subarea, and Unorganized Territory. This feature includes independent places, which are incorporated places that are not part of any county subdivision. |
G4050 |
Estate |
Estates are subdivisions of the three major islands in the United States Virgin Islands (USVI). |
G4060 |
Subbarrio (Subminor Civil Division) |
Legally defined divisions (subbarrios) of minor civil divisions (barrios-pueblo and barrios) in Puerto Rico. |
G4110 |
Incorporated Place |
A legal entity incorporated under state law to provide general-purpose governmental services to a concentration of population. Incorporated places are generally designated as a city, borough, municipality, town, village, or, in a few instances, have no legal description. |
G4120 |
Consolidated City |
An incorporated place that has merged governmentally with a county or minor civil division, but one or more of the incorporated places continues to function within the consolidation. It is a place that contains additional separately incorporated places. |
G4210 |
Census Designated Place |
A statistical area defined for a named concentration of population and the statistical counterpart of an incorporated place. |
G4300 |
Economic Census Place |
The lowest level of geographic area for presentation of some types of Economic Census data. It includes incorporated places, consolidated cities, census designated places (CDPs), minor civil divisions (MCDs) in selected states, and balances of MCDs or counties. An incorporated place, CDP, MCD, or balance of MCD qualifies as an economic census place if it contains 5,000 or more residents, or 5,000 or more jobs, according to the most current data available. |
G5020 |
Census Tract |
Relatively permanent statistical subdivisions of a County or equivalent feature delineated by local participants as part of the Census Bureau’s Participant Statistical Areas Program. |
G5030 |
Block Group |
A cluster of census blocks having the same first digit of their four-digit identifying numbers within a Census Tract. For example, block group 3 (BG 3) within a Census Tract includes all blocks numbered from 3000 to 3999. |
G5035 |
Block Area Grouping |
A user-defined group of islands forming a single census tabulation block. A BAG must: (1) consist of two or more islands, (2) have a perimeter entirely over water, (3) not overlap, and (4) not cross the boundary of other tabulation geographies, such as county or incorporated place boundaries. |
G5040 |
Tabulation Block |
The lowest-order census defined statistical area. It is an area, such as a city block, bounded primarily by physical features but sometimes by invisible city or property boundaries. A tabulation block boundary does not cross the boundary of any other geographic area for which the Census Bureau tabulates data. The subtypes of this feature are Count Question Resolution (CQR), current, and census. |
G5200 |
Congressional District |
The 435 areas from which people are elected to the U.S. House of Representatives. Additional equivalent features exist for state equivalents with nonvoting delegates or no representative. The subtypes of this feature are 106th, 107th, 108th, 109th, and 111th Congressional Districts, plus subsequent Congresses. |
G5210 |
State Legislative District (Upper Chamber |
Areas established by a state or equivalent government from which members are elected to the upper or unicameral chamber of a state governing body. The upper chamber is the senate in a bicameral legislature, and the unicameral case is a single house legislature (Nebraska). |
G5220 |
State Legislative District (Lower Chamber) |
Areas established by a state or equivalent government from which members are elected to the lower chamber of a state governing body. The lower chamber is the House of Representatives in a bicameral legislature. |
G5240 |
Voting District |
The generic name for the geographic features, such as precincts, wards, and election districts, established by state, local, and tribal governments for the purpose of conducting elections. |
G5400 |
Elementary School District |
A geographic area within which officials provide public elementary grade-level educational services for residents. |
G5410 |
Secondary School District |
A geographic area within which officials provide public secondary grade-level educational services for residents. |
G5420 |
Unified School District |
A geographic area within which officials provide public educational services for all grade levels for residents. |
G6120 |
Public-Use Microdata Area
|
A decennial census area with a population of at least 100,000 or more persons for which the Census Bureau provides selected extracts of household-level data that are screened to protect confidentiality. |
G6300 |
Traffic Analysis District |
An area delineated by Metropolitan Planning Organizations (MPOs) and state Departments of Transportation (DOTs) for tabulating journey-to-work and place-of-work data. A Traffic Analysis District (TAD) consists of one or more Traffic Analysis Zones (TAZs). |
G6320 |
Traffic Analysis Zone |
An area delineated by Metropolitan Planning Organizations (MPOs) and state Departments of Transportation (DOTs) for tabulating journey-to-work and place-of-work data. |
G6330 |
Urban Growth Area |
An area defined under state authority to manage urbanization that the Census Bureau includes in the MAF/TIGER® System in agreement with the state. |
G6350 |
ZIP Code Tabulation Area (Five-Digit) |
An approximate statistical-area representation of a U.S. Postal Service (USPS) 5-digit ZIP Code service area. |
G6400 |
Commercial Region |
For the purpose of presenting economic statistical data, municipios in Puerto Rico are grouped into commercial regions. |
H1100 |
Connector |
A known, but nonspecific, hydrographic connection between two nonadjacent water features. |
H2025 |
Swamp/Marsh |
A poorly drained wetland, fresh or saltwater, wooded or grassy, possibly covered with open water [includes bog, cienega, marais and pocosin]. |
H2030 |
Lake/Pond |
A standing body of water that is surrounded by land. |
H2040 |
Reservoir |
An artificially impounded body of water. |
H2041 |
Treatment Pond |
An artificial body of water built to treat fouled water. |
H2051 |
Bay/Estuary/Gulf/ Sound |
A body of water partly surrounded by land [includes arm, bight, cove and inlet]. |
H2053 |
Ocean/Sea |
The great body of salt water that covers much of the earth. |
H2060 |
Gravel Pit/Quarry filled with water |
A body of water in a place or area from which commercial minerals were removed from the Earth. |
H2081 |
Glacier |
A body of ice moving outward and down slope from an area of accumulation; an area of relatively permanent snow or ice on the top or side of a mountain or mountainous area [includes ice field and ice patch]. |
H3010 |
Stream/River |
A natural flowing waterway [includes anabranch, awawa, branch, brook, creek, distributary, fork, kill, pup, rio, and run]. |
H3013 |
Braided Stream |
A natural flowing waterway with an intricate network of interlacing channels. |
H3020 |
Canal, Ditch or Aqueduct |
An artificial waterway constructed to transport water, to irrigate or drain land, to connect two or more bodies of water, or to serve as a waterway for watercraft [includes lateral]. |
K1225 |
Crew-of-Vessel Location |
A point or area in which the population of military or merchant marine vessels at sea are assigned, usually being at or near the home port pier. |
K1231 |
Hospital/Hospice/ Urgent Care Facility |
One or more structures where the sick or injured may receive medical or surgical attention [including infirmary]. |
K1235 |
Juvenile Institution |
A facility (correctional and non-correctional) where groups of juveniles reside; this includes training schools, detention centers, residential treatment centers and orphanages. |
K1236 |
Local Jail or Detention Center |
One or more structures that serve as a place for the confinement of adult persons in lawful detention, administered by a local (county, municipal, etc.) government. |
K1237 |
Federal Penitentiary, State Prison, or Prison Farm |
An institution that serves as a place for the confinement of adult persons in lawful detention, administered by the federal government or a state government. |
K1238 |
Other Correctional Institution |
One or more structures that serve as a place for the confinement of adult persons in lawful detention, not elsewhere classified or administered by a government of unknown jurisdiction. |
K1239 |
Convent, Monastery, Rectory, Other Religious Group Quarters |
One or more structures intended for use as a residence for those having a religious vocation. |
K1246 |
Community Center |
Community Center. |
K2110 |
Military Installation |
An area owned and/or occupied by the Department of Defense for use by a branch of the armed forces (such as the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marines, or Coast Guard), or a state owned area for the use of the National Guard. |
K2165 |
Government Center |
A place used by members of government (either federal, state, local, or tribal) for administration and public business. |
K2167 |
Convention Center |
An exhibition hall or conference center with enough open space to host public and private business and social events. |
K2180 |
Park |
Parkland defined and administered by federal, state, and local governments. |
K2181 |
National Park Service Land |
Area—National parks, National Monuments, and so forth—under the jurisdiction of the National Park Service. |
K2182 |
National Forest or Other Federal Land |
Land under the management and jurisdiction of the federal government, specifically including areas designated as National Forest, and excluding areas under the jurisdiction of the National Park Service. |
K2183 |
Tribal Park, Forest, or Recreation Area |
A place or area set aside for recreation or preservation of a cultural or natural resource and under the administration of an American Indian tribe. |
K2184 |
State Park, Forest, or Recreation Area |
A place or area set aside for recreation or preservation of a cultural or natural resource and under the administration of a state government. |
K2185 |
Regional Park, Forest, or Recreation Area |
A place or area set aside for recreation or preservation of a cultural or natural resource and under the administration of a regional government. |
K2186 |
County Park, Forest, or Recreation Area |
A place or area set aside for recreation or preservation of a cultural or natural resource and under the administration of a county government. |
K2187 |
County Subdivision Park, Forest, or Recreation Area |
A place or area set aside for recreation or preservation of a cultural or natural resource and under the administration of a minor civil division (town/township) government. |
K2188 |
Incorporated Place Park, Forest, or Recreation Area |
A place or area set aside for recreation or preservation of a cultural or natural resource and under the administration of a municipal government. |
K2189 |
Private Park, Forest, or Recreation Area |
A privately owned place or area set aside for recreation or preservation of a cultural or natural resource. |
K2190 |
Other Park, Forest, or Recreation Area (quasi-public, independent park, commission, etc.) |
A place or area set aside for recreation or preservation of a cultural or natural resource and under the administration of some other type of government or agency such as an independent park authority or commission. |
K2191 |
Post Office |
An official facility of the U.S. Postal Service used for processing and distributing mail and other postal material. |
K2193 |
Fire Department |
Fire Department. |
K2194 |
Police Station |
Police Station. |
K2195 |
Library |
Library. |
K2196 |
City/Town Hall |
City/Town Hall. |
K2400 |
Transportation Terminal |
A facility where one or more modes of transportation can be accessed by people or for the shipment of goods; examples of such a facility include marine terminal, bus station, train station, airport and truck warehouse. |
K2424 |
Marina |
A place where privately owned, light-craft are moored. |
K2432 |
Pier/Dock |
A platform built out from the shore into the water and supported by piles. This platform may provide access to ships and boats, or it may be used for recreational purposes. |
K2451 |
Airport or Airfield |
A manmade facility maintained for the use of aircraft [including airstrip, landing field and landing strip]. |
K2452 |
Train Station, Trolley or Mass Transit Rail Station |
A place where travelers can board and exit rail transit lines, including associated ticketing, freight, and other commercial offices. |
K2453 |
Bus Terminal |
A place where travelers can board and exit mass motor vehicle transit, including associated ticketing, freight, and other commercial offices. |
K2454 |
Marine Terminal |
A place where travelers can board and exit water transit or where cargo is handled, including associated ticketing, freight, and other commercial offices. |
K2455 |
Seaplane Anchorage |
A place where an airplane equipped with floats for landing on or taking off from a body of water can debark and load. |
K2456 |
Airport—Intermodal Transportation Hub/Terminal |
A major air transportation facility where travelers can board and exit airplanes and connect with other (i.e. non-air) modes of transportation. |
K2457 |
Airport—Statistical Representation |
The area of an airport adjusted to include whole 2000 census blocks used for the delineation of urban areas |
K2458 |
Park and Ride Facility/Parking Lot |
A place where motorists can park their cars and transfer to other modes of transportation. |
K2459 |
Runway/Taxiway |
A fairly level and usually paved expanse used by airplanes for taking off and landing at an airport. |
K2460 |
Helicopter Landing Pad |
A fairly level and usually paved expanse used by helicopters for taking off and landing. |
K2540 |
University or College |
A building or group of buildings used as an institution for post-secondary study, teaching, and learning [including seminary]. |
K2543 |
School or Academy |
A building or group of buildings used as an institution for preschool, elementary or secondary study, teaching, and learning [including elementary school and high school]. |
K2545 |
Museum, Visitor Center, Cultural Center, or Tourist Attraction |
An attraction of historical, cultural, educational or other interest that provides information or displays artifacts. |
K2561 |
Golf Course |
A place designed for playing golf. |
K2582 |
Cemetery |
A place or area for burying the dead [including burying ground and memorial garden]. |
K2586 |
Zoo |
A facility in which terrestrial and/or marine animals are confined within enclosures and displayed to the public for educational, preservation, and research purposes. |
K3544 |
Place of Worship |
A sanctified place or structure where people gather for religious worship; examples include church, synagogue, temple, and mosque. |
L4010 |
Pipeline |
A long tubular conduit or series of pipes, often underground, with pumps and valves for flow control, used to transport fluid (e.g., crude oil, natural gas), especially over great distances. |
L4020 |
Powerline |
One or more wires, often on elevated towers, used for conducting high-voltage electric power. |
L4031 |
Aerial Tramway/Ski Lift |
A conveyance that transports passengers or freight in carriers suspended from cables and supported by a series of towers. |
L4110 |
Fence Line |
A man-made barrier enclosing or bordering a field, yard, etc., usually made of posts and wire or wood, used to prevent entrance, to confine, or to mark a boundary. |
L4121 |
Ridge Line |
The line of highest elevation along a ridge. |
L4125 |
Cliff/Escarpment |
A very steep or vertical slope [including bluff, crag, head, headland, nose, palisades, precipice, promontory, rim and rimrock]. |
L4130 |
Point-to-Point Line |
A line defined as beginning at one location point and ending at another, both of which are in sight. |
L4140 |
Property/Parcel Line (Including PLSS) |
This feature class may denote a nonvisible boundary of either public or private lands (e.g., a park boundary) or it may denote a Public Land Survey System or equivalent survey line. |
L4150 |
Coastline |
The line that separates either land or Inland water from Coastal, Territorial or Great Lakes water. Where land directly borders Coastal, Territorial or Great Lakes water, the shoreline represents the Coastline. Where Inland water (such as a river) flows into Coastal, Territorial or Great Lakes water, the closure line separating the Inland water from the other class of water represents the Coastline. |
L4165 |
Ferry Crossing |
The route used to carry or convey people or cargo back and forth over a waterbody in a boat. |
P0001 |
Nonvisible Linear Legal/Statistical Boundary |
A legal/statistical boundary line that does not correspond to a shoreline or other visible feature on the ground. |
P0002 |
Perennial Shoreline |
The more-or-less permanent boundary between land and water for a water feature that exists year-round. |
P0003 |
Intermittent Shoreline |
The boundary between land and water (when water is present) for a water feature that does not exist year-round. |
P0004 |
Other non-visible bounding Edge (e.g., Census water boundary, boundary of an areal feature) |
A bounding Edge that does not represent a legal/statistical boundary, and does not correspond to a shoreline or other visible feature on the ground. Many such Edges bound area landmarks, while many others separate water features from each other (e.g., where a bay meets the ocean). |
R1011 |
Railroad Feature (Main, Spur, or Yard) |
A line of fixed rails or tracks that carries mainstream railroad traffic. Such a rail line can be a main line or spur line, or part of a rail yard. |
R1051 |
Carline, Streetcar Track, Monorail, Other Mass Transit |
Mass transit rail lines (including lines for rapid transit, monorails, streetcars, light rail, etc.) that are typically inaccessible to mainstream railroad traffic and whose tracks are not part of a road right-of-way. |
R1052 |
Cog Rail Line, Incline Rail Line, Tram |
A special purpose rail line for climbing steep grades that is typically inaccessible to mainstream railroad traffic. Note that aerial tramways and streetcars (which may also be called “trams”) are accounted for by other MTFCCs and do not belong in R1052. |
S1100 |
Primary Road |
Primary roads are generally divided, limited-access highways within the interstate highway system or under state management, and are distinguished by the presence of interchanges. These highways are accessible by ramps and may include some toll highways. |
S1200 |
Secondary Road |
Secondary roads are main arteries, usually in the U.S. Highway, State Highway or County Highway system. These roads have one or more lanes of traffic in each direction, may or may not be divided, and usually have at-grade intersections with many other roads and driveways. They often have both a local name and a route number. |
S1400 |
Local Neighborhood Road, Rural Road, City Street |
Generally a paved non-arterial street, road, or byway that usually has a single lane of traffic in each direction. Roads in this feature class may be privately or publicly maintained. Scenic park roads would be included in this feature class, as would (depending on the region of the country) some unpaved roads. |
S1500 |
Vehicular Trail (4WD) |
An unpaved dirt trail where a four-wheel drive vehicle is required. These vehicular trails are found almost exclusively in very rural areas. Minor, unpaved roads usable by ordinary cars and trucks belong in the S1400 category. |
S1630 |
Ramp |
A road that allows controlled access from adjacent roads onto a limited access highway, often in the form of a cloverleaf interchange. These roads are unaddressable and do not carry a name in the MAF/TIGER System. |
S1640 |
Service Drive usually along a limited access highway |
A road, usually paralleling a limited access highway, that provides access to structures along the highway. These roads can be named and may intersect with other roads. |
S1710 |
Walkway/Pedestrian Trail |
A path that is used for walking, being either too narrow for or legally restricted from vehicular traffic. |
S1720 |
Stairway |
A pedestrian passageway from one level to another by a series of steps. |
S1730 |
Alley |
A service road that does not generally have associated addressed structures and is usually unnamed. It is located at the rear of buildings and properties and is used for deliveries. |
S1740 |
Private Road for service vehicles (logging, oil fields, ranches, etc.) |
A road within private property that is privately maintained for service, extractive, or other purposes. These roads are often unnamed. |
S1750 |
Internal U.S. Census Bureau use |
Internal U.S. Census Bureau use. |
S1780 |
Parking Lot Road |
The main travel route for vehicles through a paved parking area. |
S1820 |
Bike Path or Trail |
A path that is used for manual or small, motorized bicycles, being either too narrow for or legally restricted from vehicular traffic. |
S1830 |
Bridle Path |
A path that is used for horses, being either too narrow for or legally restricted from vehicular traffic. |
S2000 |
Road Median |
The unpaved area or barrier between the carriageways of a divided road. |
Note: The information in this table was last updated in November 2017.
Street Name Type |
Standard Abbreviation |
ALLEY |
ALY |
ANEX |
ANX |
ARCADE |
ARC |
AVENUE |
AVE |
BAYOU |
BYU |
BEACH |
BCH |
BEND |
BND |
BLUFF |
BLF |
BLUFFS |
BLFS |
BOTTOM |
BTM |
BOULEVARD |
BLVD |
BRANCH |
BR |
BRIDGE |
BRG |
BROOK |
BRK |
BROOKS |
BRKS |
BURG |
BG |
BURGS |
BGS |
BYPASS |
BYP |
CAMP |
CP |
CANYON |
CYN |
CAPE |
CPE |
CAUSEWAY |
CSWY |
CENTER |
CTR |
CENTERS |
CTRS |
CIRCLE |
CIR |
CIRCLES |
CIRS |
CLIFF |
CLF |
CLIFFS |
CLFS |
CLUB |
CLB |
COMMON |
CMN |
COMMONS |
CMNS |
CORNER |
COR |
CORNERS |
CORS |
COURSE |
CRSE |
COURT |
CT |
COURTS |
CTS |
COVE |
CV |
COVES |
CVS |
CREEK |
CRK |
CRESCENT |
CRES |
CREST |
CRST |
CROSSING |
|
CROSSROAD |
XRD |
CROSSROADS |
XRDS |
CURVE |
CURV |
DALE |
DL |
DAM |
DM |
DIVIDE |
DV |
DRIVE |
DR |
DRIVES |
DRS |
ESTATE |
EST |
ESTATES |
ESTS |
EXPRESSWAY |
EXPY |
EXTENSION |
EXT |
EXTENSIONS |
EXTS |
FALL |
FALL |
FALLS |
FLS |
FERRY |
FRY |
FIELD |
FLD |
FIELDS |
FLDS |
FLAT |
FLT |
FLATS |
FLTS |
FORD |
FRD |
FORDS |
FRDS |
FOREST |
FRST |
FORGE |
FRG |
FORGES |
FRGS |
FORK |
FRK |
FORKS |
FRKS |
FORT |
FT |
FREEWAY |
FWY |
GARDEN |
GDN |
GARDENS |
GDNS |
GATEWAY |
GTWY |
GLEN |
GLN |
GLENS |
GLNS |
GREEN |
GRN |
GREENS |
GRNS |
GROVE |
GRV |
GROVES |
GRVS |
HARBOR |
HBR |
HARBORS |
HBRS |
HAVEN |
HVN |
HEIGHTS |
HTS |
HIGHWAY |
HWY |
HILL |
HL |
HILLS |
HLS |
HOLLOW |
HOLW |
INLET |
INLT |
ISLAND |
IS |
ISLANDS |
ISS |
ISLE |
ISLE |
JUNCTION |
JCT |
JUNCTIONS |
JCTS |
KEY |
KY |
KEYS |
KYS |
KNOLL |
KNL |
KNOLLS |
KNLS |
LAKE |
LK |
LAKES |
LKS |
LAND |
LAND |
LANDING |
LNDG |
LANE |
LN |
LIGHT |
LGT |
LIGHTS |
LGTS |
LOAF |
LF |
LOCK |
LCK |
LOCKS |
LCKS |
LODGE |
LDG |
LOOP |
LOOP |
MALL |
MALL |
MANOR |
MNR |
MANORS |
MNRS |
MEADOW |
MDW |
MEADOWS |
MDWS |
MEWS |
MEWS |
MILL |
ML |
MILLS |
MLS |
MISSION |
MSN |
MOTORWAY |
MTWY |
MOUNT |
MT |
MOUNTAIN |
MTN |
MOUNTAINS |
MTNS |
NECK |
NCK |
ORCHARD |
ORCH |
OVAL |
OVAL |
OVERPASS |
OPAS |
PARK |
PARK |
PARKS |
PARK |
PARKWAY |
PKWY |
PARKWAYS |
PKWY |
PASS |
PASS |
PASSAGE |
PSGE |
PATH |
PATH |
PIKE |
PIKE |
PINE |
PNE |
PINES |
PNES |
PLACE |
PL |
PLAIN |
PLN |
PLAINS |
PLNS |
PLAZA |
PLZ |
POINT |
PT |
POINTS |
PTS |
PORT |
PRT |
PORTS |
PRTS |
PRAIRIE |
PR |
RADIAL |
RADL |
RAMP |
RAMP |
RANCH |
RNCH |
RAPID |
RPD |
RAPIDS |
RPDS |
REST |
RST |
RIDGE |
RDG |
RIDGES |
RDGS |
RIVER |
RIV |
ROAD |
RD |
ROADS |
RDS |
ROUTE |
RTE |
ROW |
ROW |
RUE |
RUE |
RUN |
RUN |
SHOAL |
SHL |
SHOALS |
SHLS |
SHORE |
SHR |
SHORES |
SHRS |
SKYWAY |
SKWY |
SPRING |
SPG |
SPRINGS |
SPGS |
SPUR |
SPUR |
SPURS |
SPUR |
SQUARE |
SQ |
SQUARES |
SQS |
STATION |
STA |
STRAVENUE |
STRA |
STREAM |
STRM |
STREET |
ST |
STREETS |
STS |
SUMMIT |
SMT |
TERRACE |
TER |
THROUGHWAY |
TRWY |
TRACE |
TRCE |
TRACK |
TRAK |
TRAFFICWAY |
TRFY |
TRAIL |
TRL |
TRAILER |
TRLR |
TUNNEL |
TUNL |
TURNPIKE |
TPKE |
UNDERPASS |
UPAS |
UNION |
UN |
UNIONS |
UNS |
VALLEY |
VLY |
VALLEYS |
VLYS |
VIADUCT |
VIA |
VIEW |
VW |
VIEWS |
VWS |
VILLAGE |
VLG |
VILLAGES |
VLGS |
VILLE |
VL |
VISTA |
VIS |
WALK |
WALK |
WALKS |
WALK |
WALL |
WALL |
WAY |
WAY |
WAYS |
WAYS |
WELL |
WL |
WELLS |
WLS |
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-15 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy