0651-0040 Supporting Statement final
0651-0040 Supporting Statement final.docx
Trademark Trial and Appeal Board (TTAB) Actions
OMB: 0651-0040
SUPPORTING STATEMENT
United States Patent and Trademark Office
Trademark Trial and Appeal Board (TTAB) Actions
OMB CONTROL NO. 0651-0040
2020
A. JUSTIFICATION
Explain the circumstances that make the collection of information necessary. Identify any legal or administrative requirements that necessitate the information collection. Attach a copy of the appropriate section of each statute and regulation mandating or authorizing the collection of information.
This collection of information is required by the Trademark Act of 19461, Sections 13, 14, and 20, 15 U.S.C.1063, 1064, and 1070, respectively. Under the Trademark Act, any individual or entity that adopts a trademark or service mark to identify its goods or services may apply to federally register its mark. The mark will remain on the register for ten years and is renewable in ten-year increments. Section 14 of the Trademark Act allows individuals and entities to file a petition to cancel a registration of a mark, while Section 13 allows individuals and entities who believe that they would be damaged by the registration of a mark to file an opposition, or an extension of time to file an opposition, to the registration of a mark. Section 20 of the Trademark Act allows individuals and entities to file an appeal from any final decision of the Trademark Examining Attorney assigned to review an application for registration of a mark.
The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) administers, under the Trademark Act pursuant to 37 CFR Part 2, the various rules that govern the filing of petitions to cancel the registration of a mark, notices of opposition to the registration of a mark, extensions of time to file an opposition, appeals, and other submissions filed in connection with inter partes and ex parte proceedings. These petitions, notices, extensions, and additional submissions are filed with the Trademark Trial and Appeal Board (TTAB). The TTAB decides inter partes cases and ex parte appeals. The TTAB is an administrative tribunal empowered to determine the right to register as the issue may be presented in such cases. The Chief Administrative Trademark Judge, Deputy Chief Administrative Trademark Judge and administrative trademark judges decide proceedings filed with the TTAB. A panel of three judges decides each case when it is ready for final decision on the merits. The TTAB follows the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure when applicable, and the “Trademark Rules” in 37 CFR Part 2.
The USPTO is also part of the Madrid Protocol, an international agreement governing trademark protection, and accepts these international filings. Under the Madrid Protocol, parties can file oppositions to extensions of protection under the Madrid Protocol, as well as file requests for extensions of time to oppose these extensions of protection. Oppositions and extensions filed under the Madrid Protocol must be filed electronically through the Electronic System for Trademark Trials and Appeals (ESTTA).
Indicate how, by whom, and for what purpose the information is to be used. Except for a new information collection, indicate the actual use the agency has made of the information received from the current information collection.
The information in this information collection is a matter of public record, except confidential submissions pursuant to 37 C.F.R. § 2.126(c), and is used by the public for a variety of private business purposes related to establishing and enforcing trademark rights. This information is important to the public, as trademark owners and trademark registrants must actively protect their own rights.
The information collected, maintained, and used in this information collection is based on OMB and USPTO guidelines. This includes the basic information quality standards established in the Paperwork Reduction Act (44 U.S.C. Chapter 35), in OMB Circular A-130, and in the USPTO information quality guidelines.
Table 1 lists the specific statutes and regulations authorizing the USPTO to collect this information and outlines how this information is used by the public and the USPTO:
Table 1: Information Requirements and Needs and Uses of Information Collected
Item # |
Requirement |
Statute |
Regulation |
Form # |
Needs and Uses |
1 |
Petition to Cancel
|
15 U.S.C. § 1064 |
37 CFR 2.111 and 2.112 |
PTO 2188 |
|
2 |
Notice of Opposition
|
15 U.S.C. § 1063 |
37 CFR 2.101 and 2.104 |
PTO 2120 |
|
3 |
Extension of Time to File an Opposition
|
15 U.S.C. § 1063
|
37 CFR 2.102
|
PTO 2153 |
|
4 |
Submissions in Inter Partes Cases
|
15 U.S.C. § 1063 and 15 U.S.C. § 1071
|
37 CFR 2.106 -
37 CFR 2.299
|
PTO 2151
|
|
5 |
Notice of Appeal
|
15 U.S.C. § 1063 and 15 U.S.C. § 1071
|
37 CFR 2.102
|
PTO 2190
|
|
6 |
Miscellaneous Ex Parte submissions
|
Not Applicable
|
37 CFR 2.144
|
PTO 2189 |
|
Describe whether, and to what extent, the collection of information involves the use of automated, electronic, mechanical, or other technological collection techniques or other forms of information technology, e.g., permitting electronic submission of responses, and the basis for the decision for adopting this means of information collection. Also describe any consideration of using information technology to reduce burden.
The information in this information collection must be submitted electronically through Electronic System for Trademark Trials and Appeals (ESTTA) when a party files a petition to cancel a trademark registration, an opposition to the registration of a trademark, a request to extend the time to file an opposition, a notice of appeal, or additional submissions for inter partes and ex parte proceedings with the USPTO. Submissions filed in paper form via mail or hand delivery are permitted only when ESTTA is unavailable due to technical problems, or when extraordinary circumstances are present.
ESTTA can be accessed through the USPTO’s web site and allows filers to timely complete and submit forms to the TTAB electronically. ESTTA provides step-by-step instructions and help screens for completing the forms. The system prompts the filer to validate the required fields and sign the submission before it is electronically submitted to the TTAB.
Upon transmission, the form will be assigned an ESTTA tracking number. The forms that are filed through ESTTA are time-stamped with the official filing date when received on the USPTO server. In cases where a fee is required, the time-stamp, in Eastern Standard Time, is applied when the payment process is completed and the receipt screen is displayed. . The official filing date and time can be found on the confirmation web screen and in the e-mail confirmation. Once the form has been submitted electronically, the USPTO will immediately provide the sender with an acknowledgment of receipt via e-mail.
The information submitted through ESTTA moves directly into the Trademark Trial and Appeal Board Information System (TTABIS), the TTAB’s electronic workflow system. Electronically submitted forms need not be processed or scanned by hand, thereby eliminating the delays caused by the processing and scanning of paper filings. The TTAB’s electronic workflow system processes all incoming and outgoing documents electronically and permits staff to prepare correspondence, track cases, generate reports for management, and monitor proceedings in an effective, secure, and timely manner. Information regarding TTAB proceedings is available within the USPTO over the Intranet and by the public over the Internet via TTABVUE. TTABIS users will have the ability to add electronic notes and highlights directly to TTABIS electronic documents.
The TTAB disseminates the information collected through the notices of opposition, extensions of time to oppose, petitions to cancel, and miscellaneous submissions in inter partes and ex parte proceedings electronically through TTABVUE. This system can be accessed through the TTAB’s homepage on the USPTO’s website. TTABVUE provides online images of the TTAB filings indexed by prosecution history entry. It allows users to view proceedings with incoming filings from either Internet filings or scanned paper. Other features include the capability to print and enlarge the incoming document to a readable size.
TTABVUE allows the public and the TTAB staff to retrieve information concerning TTAB proceedings from the TTAB’s internal databases electronically using the Internet. Staff and customers can search, view, and print specific information using their browser. This provides a single point of access for querying information through a user-friendly interface. Information can be retrieved from TTABVUE using a proceeding number, a plaintiff or defendant name, the mark, any words within an index, the trademark serial number, or registration number.
The revised edition of the Trademark Trial and Appeal Board’s Manual of Procedure2 (TBMP) is only available online through the USPTO’s web site. The TBMP provides guidance to practitioners litigating cases before the TTAB and describes current TTAB practice, statutory changes and new rules that have been promulgated since 1995, video conferencing for final hearings, and telephone conferences. The TBMP addresses electronic filing, access to the TTAB’s electronic database via the Internet, and contains suggested formats for some of the TTAB’s filings. The TTAB also disseminates its decisions from 1996 to the present to the public through its home page on the USPTO website.
Describe efforts to identify duplication. Show specifically why any similar information already available cannot be used or modified for use for the purposes described in Item 2 above.
Every effort has been made to identify and eliminate duplication of information. This information collection provides the initial information required to give notice of opposition to the registration of a mark, to request additional time to file an opposition to the registration of a mark, to initiate the cancellation of a trademark registration, to request an appeal of the Trademark Examining Attorney’s final decision, and to submit the additional filings needed to prosecute an inter partes or ex parte appeal. This information is not collected elsewhere within the USPTO. Where possible, the ESTTA system retrieves already existing data and completes fields within the ESTTA forms to eliminate the need for the filer to provide data already in the TTAB database.
If the collection of information impacts small businesses or other small entities, describe any methods used to minimize burden.
Registrations, oppositions, cancellations, and appeals are voluntary activities on the part of the public. The USPTO expects that the submission of the information provided places no undue burden on small businesses or other small entities.
Describe the consequence to Federal program or policy activities if the information collection is not conducted or is conducted less frequently, as well as any technical or legal obstacles to reducing burden.
Less frequent collection of this information is not possible, since the information is collected only when voluntarily submitted by the public. Failure to collect this information would prevent parties from exercising their right to file an opposition to the registration of a mark, request an extension of time to file an opposition to a mark, to cancel a federally registered trademark, to appeal any final decision of the Trademark Examining Attorney in charge of the requested registration of a mark, and to file the submissions needed to further prosecute an inter partes or ex parte appeal. The information could not be collected less frequently. If the collection of information was not conducted, the USPTO could not comply with the requirements of 15 U.S.C. §§ 1063, 1064, and 1070, and 37 CFR Part 2, 2.101-102, 2.104, 2.111–2.112, and 2.141 to 2.142.
Explain any special circumstances that would cause an information collection to be conducted in a manner:
requiring respondents to report information to the agency more often than quarterly;
requiring respondents to prepare a written response to a collection of information in fewer than 30 days after receipt of it;
requiring respondents to submit more than an original and two copies of any document;
requiring respondents to retain records, other than health, medical, government contract, grant-in-aid, or tax records, for more than three years;
in connection with a statistical survey, that is not designed to produce valid and reliable results that can be generalized to the universe of study;
requiring the use of a statistical data classification that has not been reviewed and approved by OMB;
that includes a pledge of confidentiality that is not supported by authority established in statute or regulation, that is not supported by disclosure and data security policies that are consistent with the pledge, or which unnecessarily impedes sharing of data with other agencies for compatible confidential use; or
requiring respondents to submit proprietary trade secrets, or other confidential information unless the agency can demonstrate that it has instituted procedures to protect the information's confidentiality to the extent permitted by law.
There are no special circumstances associated with this collection of information.
If applicable, provide a copy and identify the date and page number of publication in the Federal Register of the agency's notice, required by 5 CFR 1320.8(d), soliciting comments on the information collection prior to submission to OMB. Summarize public comments received in response to that notice and describe actions taken by the agency in response to these comments. Specifically address comments received on cost and hour burden. Describe efforts to consult with persons outside the agency to obtain their views on the availability of data, frequency of activity, the clarity of instructions and recordkeeping, disclosure, or reporting format (if any), and on the data elements to be recorded, disclosed, or reported. Consultation with representatives of those from whom information is to be obtained or those who must compile records should occur at least once every 3 years - even if the collection of information activity is the same as in prior periods. There may be circumstances that may preclude consultation in a specific situation. These circumstances should be explained.
The 60-Day Federal Register Notice was published on May 26, 2020 (85 Fed. Reg. 31474). The public comment period ended on July 27, 2020. No comments were received from the public.
In addition, several large and well-organized bar associations and trade associations frequently communicate their views to the USPTO. Also, the Trademark Public Advisory Committee (TPAC) was created by the American Inventors Protection Act of 1999 to advise the Director of the USPTO on the Agency’s operations, including its goals, performance, budget, and user fees. The TPAC includes 9 voting members who are appointed by and serve at the pleasure of the Secretary of Commerce. Members include lawyers, corporate executives, entrepreneurs, and academicians with significant experience in management, finance, science, technology, labor relations, and intellectual property issues. The members of the TPAC reflect the broad array of USPTO’s stakeholders and embrace the USPTO’s e-government initiative. This diversity of interests is an effective tool in helping the USPTO nurture and protects the intellectual property that is the underpinning of America’s strong economy.
Explain any decision to provide any payment or gift to respondents, other than remuneration of contractors or grantees.
This information collection does not involve a payment or gift to any respondent.
Describe any assurance of confidentiality provided to respondents and the basis for the assurance in statute, regulation, or agency policy. If the information collection requires a systems of records notice (SORN) or privacy impact assessment (PIA), those should be cited and described here.
Trademark applications are open to public inspection. The case files for oppositions, extensions of time to oppose a registration, petitions to cancel a trademark registration, and appeals are open to the public for review and do not require confidentiality except for certain documents filed under a claim of confidentiality, which are not available for public review. Papers with confidential business information may be filed electronically, under separate cover, as specified in 37 CFR 2.126(c) and a copy of the submission for public viewing with the confidential portions redacted must be submitted concurrently. The TTAB has a standard order allowing for the submission of confidential material, but parties are free to agree to alternative arrangements.
This information collection contains information which is subject to the Privacy Act. This information is collected on petitions and applications filed for trademark products. Trademark Application information collection activities are covered under the Statement of Records Notice (SORN COMMERCE/USPTO-26; Trademark Application and Registration Records) at 85 FR 8847, published on February 18, 2020. This SORN identifies the categories of records in the system containing applicants for trademark registration, registrants, and legal and other authorized representatives for such applicants and registrants.
Provide additional justification for any questions of a sensitive nature, such as sexual behavior and attitudes, religious beliefs, and other matters that are commonly considered private. This justification should include the reasons why the agency considers the questions necessary, the specific uses to be made of the information, the explanation to be given to persons from whom the information is requested, and any steps to be taken to obtain their consent.
None of the required information is considered to be sensitive.
Provide estimates of the hour burden of the collection of information. The statement should:
Indicate the number of respondents, frequency of response, annual hour burden, and an explanation of how the burden was estimated. Unless directed to do so, agencies should not conduct special surveys to obtain information on which to base hour burden estimates. Consultation with a sample (fewer than 10) of potential respondents is desirable. If the hour burden on respondents is expected to vary widely because of differences in activity, size, or complexity, show the range of estimated hour burden, and explain the reasons for the variance. Generally, estimates should not include burden hours for customary and usual business practices.
If this request for approval covers more than one form, provide separate hour burden estimates for each form and aggregate the hour burdens.
Provide estimates of annualized cost to respondents for the hour burdens for collections of information, identifying and using appropriate wage rate categories. The cost of contracting out or paying outside parties for information collection activities should not be included here. Instead, this cost should be included under ‘Annual Cost to Federal Government’.
Provide an estimate for the total annual cost burden to respondents or record keepers resulting from the collection of information.
Table 2 calculates the burden hours and costs of this information collection to the public, based on the factors described below.
Respondent Calculation Factors
The USPTO estimates that this information collection will have 70,475 respondents; 67,005 (95%) from private sector entities and 3,470 (5%) from individuals and households. The USPTO further estimates that it will receive approximately 83,100 responses per year for this information collection.
These estimates are based on the Agency’s long-standing institutional knowledge of and experience with the type of information collected by these items.
Burden Hour Calculation Factors
The USPTO estimates that the responses in this information collection will take the public approximately 10 to 30 minutes (0.17 to 0.50 hours) to complete, depending on the request. This includes the time to gather the necessary information, prepare the petitions, notices, extensions, or additional filings, and submit the completed request to the USPTO. The USPTO calculates that, on balance, it takes the same amount of time to gather the necessary information, create the document, and submit it to the TTAB.
These estimates are based on the Agency’s long-standing institutional knowledge of and experience with the type of information collected and the length of time necessary to complete responses containing similar or like information. Across all respondent types USPTO estimates 21,133 burden hours.
Cost Burden Calculation Factors
The USPTO estimates that it will take a 50/50 level of effort by attorneys and paraprofessional/paralegals to complete the requirements in this information collection. The USPTO uses a professional rate of $400 per hour, which is the mean rate for attorneys in private firms. This rate is published in the 2019 Report of the Economic Survey3 from the Law Practice Management Committee of the American Intellectual Property Law Association (AIPLA). The hourly rate for paraprofessional/paralegals is $145, based on the average/typical rate for paraprofessionals/paralegals. This rate was published by the National Association of Legal Assistants4 (NALA) in 2018. Based on the Agency’s long-standing institutional knowledge of and experience with the type of information collected, the Agency expects a blended rate of $272.50 as an accurate estimate of the cost per hour to collect this information. Across all respondent types, USPTO estimates an hourly cost burden of $5,758,746.
Table 2: Burden Hour/Burden Cost to Respondents (Private Sector)
Item # |
Item |
Estimated Annual Respondents |
Estimated Annual Responses (yr)
(a) |
Estimated time for response (hours)
(b) |
Estimated annual burden (hrs/yr)
(a) x (b) =(c) |
Rate ($/hr)
(d) |
Estimated annual burden
(c) x (d) = (e) |
1 |
Petition to Cancel |
Same as line 4 |
2,660 |
0.50 |
1,330 |
$272.50 |
$362,425 |
2 |
Notice of Opposition |
Same as line 4 |
7,030 |
0.50 |
3,515 |
$272.50 |
$957,838 |
3 |
Request for Extension of Time to File an Opposition |
20,425 |
20,425 |
0.17 |
3,472 |
$272.50 |
$946,120 |
4 |
Submissions in Inter Partes Cases
|
39,900 |
39,900 |
0.25 |
9,975 |
$272.50 |
$2,718,188 |
5 |
Notice of Appeal |
Same as line 6 |
3,325 |
0.25 |
831 |
$272.50 |
$226,448 |
6 |
Miscellaneous Ex Parte Submissions |
5,605 |
5,605 |
0.17 |
953 |
$272.50 |
$259,693 |
|
Totals |
65,930 |
78,945 |
- - - |
20,076 |
- - - |
5,470,712 |
Table 3: Burden Hour/Burden Cost to Respondents (Individual and Households)
Item # |
Item |
Estimated Annual Respondents |
Estimated Annual Responses (yr)
(a) |
Estimated time for response (hours)
(b) |
Estimated annual burden (hrs/yr)
(a) x (b) =(c) |
Rate ($/hr)
(d) |
Estimated annual burden
(c) x (d) = (e) |
1 |
Petition to Cancel |
Same as line 4 |
140 |
0.50 |
70 |
$272.50 |
$19,075 |
2 |
Notice of Opposition |
Same as line 4 |
370 |
0.50 |
185 |
$272.50 |
$50,413 |
3 |
Request for Extension of Time to File an Opposition |
1,075 |
1,075 |
0.17 |
183 |
$272.50 |
$49,868 |
4 |
Submissions in Inter Partes Cases
|
2,100 |
2,100 |
0.25 |
525 |
$272.50 |
$143,063 |
5 |
Notice of Appeal |
Same as line 6 |
175 |
0.25 |
44 |
$272.50 |
$11,990 |
6 |
Miscellaneous Ex Parte Submissions |
295 |
295 |
0.17 |
50 |
$272.50 |
$13,625 |
|
Totals |
3,470 |
4,155 |
- - - |
1,057 |
_ _ _ |
288,034 |
Provide an estimate for the total annual cost burden to respondents or record keepers resulting from the collection of information. (Do not include the cost of any hour burden already reflected on the burden worksheet).
The cost estimate should be split into two components: (a) a total capital and start-up cost component (annualized over its expected useful life) and (b) a total operation and maintenance and purchase of services component. The estimates should take into account costs associated with generating, maintaining, and disclosing or providing the information. Include descriptions of methods used to estimate major cost factors including system and technology acquisition, expected useful life of capital equipment, the discount rate(s), and the time period over which costs will be incurred. Capital and start-up costs include, among other items, preparations for collecting information such as purchasing computers and software; monitoring, sampling, drilling and testing equipment; and record storage facilities.
If cost estimates are expected to vary widely, agencies should present ranges of cost burdens and explain the reasons for the variance. The cost of purchasing or contracting out information collections services should be a part of this cost burden estimate. In developing cost burden estimates, agencies may consult with a sample of respondents (fewer than 10), utilize the 60-day pre-OMB submission public comment process and use existing economic or regulatory impact analysis associated with the rulemaking containing the information collection, as appropriate.
The total annual (non-hour) respondent cost burden for this information collection is calculated in Table 3 below. This information collection has no capital start-up, maintenance, or recordkeeping costs but does have filing fees and postage costs.
Filing Fees
There are annual (non-hour) cost burdens in the way of filing fees associated with this information collection. These fees are set to recover the aggregate cost to the USPTO for processing the requests, petitions, oppositions, and appeals. These fees are per application for requests for extensions of time to file an opposition, and, per application, class of identified goods and/or services and/or parties (for inter partes proceedings only) for proceedings; therefore the total filing fees can vary depending on the number of classes involved in a proceeding.
Table 4 shows the annual filing fees for parties filing the petitions to cancel, the notices of opposition, and the notices of appeal.
Table 4: Annual Non-hour Cost Burden
# |
Item |
Estimated Annual Responses |
Filing fee ($)
|
Total Non-hour Cost Burden ($) |
1 |
Petition to Cancel (Paper Submission) |
6 |
$500.00 |
$3,000.00 |
1 |
Petition to Cancel |
2,794 |
$400.00 |
$1,117,600.00 |
2 |
Notice of Opposition (Paper Submission) |
15 |
$500.00 |
$7,500.00 |
2 |
Notice of Opposition |
7,385 |
$400.00 |
$2,954,000.00 |
3 |
Ex Parte Appeal to the Trademark Trial and Appeal Board Filed (Paper Submission) |
7 |
$300.00 |
$2,100.00 |
3 |
Ex Parte Appeal to the Trademark Trial and Appeal Board |
3,493 |
$200.00 |
$698,600.00 |
4 |
Request for Extension of Time to File an Opposition under §2.102(c)(3) (Paper Submission) |
5 |
$200.00 |
$1,000.00 |
4 |
Request for Extension of Time to File an Opposition under §2.102(c)(3) |
10,960 |
$100.00 |
$1,096,000.00 |
5 |
Request for Extension of Time to File an Opposition under §2.102(c)(1)(ii) or (c)(2) (Paper Submission) |
5 |
$300.00 |
$1,500.00 |
5 |
Request for Extension of Time to File an Opposition under §2.102(c)(1)(ii) or (c)(2) |
3,650 |
$200.00 |
$730,000.00 |
Total |
- - - |
28,320 |
- - - |
$6,611,300.00 |
Postage
Usually, there are no postage costs associated with this information collection. The petitions to cancel, the notices of opposition, the notices of appeal, the extensions of time to file an opposition, and the additional submissions filed in inter partes and ex parte cases must be submitted to the USPTO electronically or served on other parties by email. Express or first-class mail through the United States Postal Service or hand delivery to the TTAB is only available under extraordinary circumstances. The USPTO estimates that the average first-class postage cost for a mailed submission will be $8.05 (2 day legal flat rate envelope) and that approximately 38 submissions will be mailed to the USPTO per year.
Therefore, the total non-hour respondent cost burden for this information collection is estimated to be $6,611,606 which includes $6,611,300 in filing fees and $306 in postage.
Provide estimates of annualized costs to the Federal government. Also, provide a description of the method used to estimate cost, which should include quantification of hours, operational expenses (such as equipment, overhead, printing, and support staff), and any other expense that would not have been incurred without this collection of information. Agencies may also aggregate cost estimates from Items 12, 13, and 14 in a single table.
The majority of items in this information collection are processed automatically by electronic systems. Therefore TTAB staff do not process the majority of the extensions of time to file a notice of opposition, notices of opposition, notices of appeal, and miscellaneous submissions filed in both ex parte and inter partes proceedings submitted electronically through ESTTA. ESTTA enters the information into the file electronically and then passes the information to the TTABIS database. This database then processes the information electronically and updates the appropriate TTABIS application file. In addition, ESTTA automatically institutes 80% of the notices of opposition, 95% of the notices of appeal and 25% of petitions for cancellation. There is no human intervention at all during this process.
Although TTAB staff do not process the majority of the electronic submissions through ESTTA, they do perform additional processing for 20% of the notices of opposition, 5% of the notices of appeal, 75% of petitions for cancellation and 10% of the extensions of time to file an opposition. Out of approximately 7,400 notices of opposition and 3,500 notices of appeal filed electronically, the TTAB staff performs additional processing for approximately 1,480 notices of opposition and 175 notices of appeal. Out of approximately 21,500 electronic requests for extensions of time to file an opposition, TTAB staff perform additional processing for approximately 2,150. The TTAB staff perform additional processing for all 2,100 petitions to cancel filed electronically. The USPTO estimates that a GS-11, step 55 will process these papers and estimates that it takes approximately 10 minutes (0.17 hours) to complete the processing of extensions of time to file a notice of opposition, and 30 minutes (0.50 hours) to complete the processing of notices of opposition, petitions for cancellation, and notices of appeal. The hourly rate for a GS-11, step 5 is currently $39.12. When 30% is added to account for a fully loaded hourly rate (benefits and overhead), the cost per hour for a GS-11, step 5 is $50.86 ($39.12+ $11.74).
For the most part, personnel employed on a contractual basis process all of the submissions filed in Board proceedings in the paper format. The contract personnel scan each paper into the electronic record of the TTABIS system, file, and maintain the paper format of the document. Once the documents are in electronic format, the TTAB staff finish the processing of the electronic form of the document using TTABIS. The USPTO estimates that contract personnel with an hourly rate comparable to that of a GS-9, step 56 will process these papers, and estimates that it takes, on average, approximately 4 minutes (0.07 hours) to process each paper. The hourly rate for a GS-9, step 5, is currently $32.33. Generally, an additional 30% of the hourly rate is added to account for a fully-loaded rate that covers both overhead and benefits. Since this work is being performed by contract personnel, the USPTO will only pay for the overhead costs, not the benefits. Therefore, the USPTO estimates that approximately 15% will be added to the hourly rate. When 15% is added to account for an hourly rate including overhead, the cost per hour for the contract personnel is approximately $37.18 ($32.33 + $4.85).
In addition to the initial processing performed by the contract personnel, TTAB staff also process the extensions of time to file an opposition, the notices of opposition, the petitions for cancellation, and the notices of appeal filed in paper form. The USPTO estimates that a GS-11, step 57 will process these papers and estimates that it takes approximately 10 minutes (0.17 hours) to complete the processing of extensions of time to file a notice of opposition and 30 minutes (0.50 hours) to complete the processing of notices of opposition, petitions for cancellation, and notices of appeal. The hourly rate for a GS-11, step 5 is currently $39.12. When 30% is added to account for a fully loaded hourly rate (benefits and overhead), the cost per hour for a GS-11, step 5 is $50.86 ($39.12+ $11.74).
Table 4 calculates the processing hours and costs of this information collection to the Federal Government.
Table 4: Burden Hour/Burden Cost to the Federal Government
Item # |
Item |
Responses (yr) (a) |
Hours (b) |
Burden (hrs/yr) (c) (a) x (b) |
Rate ($/hr) (d) |
Total Cost ($/hr) (e) (c) x (d) |
1 |
Petition to Cancel GS-9, step 5 GS-11, step 5 |
2,100 |
0.50 |
1,050 |
$50.86 |
$53,403 |
2 |
Notice of Opposition GS-9, step 5 GS-11, step 5 |
1,480 |
0.50 |
740 |
$50.86 |
$37,636 |
3 |
Extension of Time to File an Opposition GS-9, step 5 GS-11, step 5 |
2,150 |
0.17 |
365.5 |
$50.86 |
$18,589 |
4 |
Submissions in Inter Partes Cases
|
84 |
0.25 |
21 |
$37.18 |
$781 |
5 |
Notice of Appeal GS-9, step 5 GS-11, step 5 |
175 |
0.07 0.50 |
12.25 87.5 |
$37.18 $50.86 |
$4,906 |
6 |
Miscellaneous Ex Parte Submissions |
12 |
0.07 |
.84 |
$37.18 |
$31 |
|
Total |
6,001 |
|
2,277.09 |
- - - |
$115,346 |
Explain the reasons for any program changes or adjustments reported on the burden worksheet.
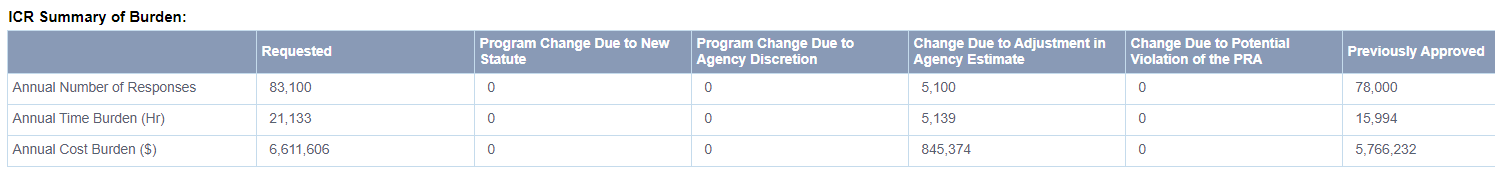
The proposed information collection, as outlined in the tables above, seeks to modify the existing information collection.
These changes are due to adjustments from updated annual response estimates.
Increase of 5,100 in estimated number of responses resulting in an increase of 5,139 estimated burden hours. These estimates are based on the Agency’s long-standing institutional knowledge of and experience with the type of information collected by these items and the internal submission statistics showing increasing responses.
Increase of $845,374 in non-hour cost burdens. These changes are due to an increase in agency estimates. For this renewal, the USPTO estimates that total fees will be $6,611,300 and $306 in postage costs.
For collections of information whose results will be published, outline plans for tabulation and publication. Address any complex analytical techniques that will be used. Provide the time schedule for the entire project, including beginning and ending dates of the collection of information, completion of report, publication dates, and other actions.
USPTO makes submissions under this information collection available to the public via ESTTA. The purpose of this public access is not for statistical use and the Agency does not perform statistical analysis on the details within submissions.
If seeking approval to not display the expiration date for OMB approval of the information collection, explain the reasons that display would be inappropriate.
The forms in this information collection will display the OMB Control Number and the OMB expiration date.
Explain each exception to the topics of the certification statement identified in “Certification for Paperwork Reduction Act Submissions.”
This collection of information does not include any exceptions to the certificate statement.
B. COLLECTIONS OF INFORMATION EMPLOYING STATISTICAL METHODS
This collection of information does not employ statistical methods.
5 https://www.opm.gov/policy-data-oversight/pay-leave/salaries-wages/salary-tables/pdf/2020/DCB_h.pdf
6 https://www.opm.gov/policy-data-oversight/pay-leave/salaries-wages/salary-tables/pdf/2020/DCB_h.pdf
7 https://www.opm.gov/policy-data-oversight/pay-leave/salaries-wages/salary-tables/pdf/2020/DCB_h.pdf
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | Trademark Trial and Appeal Board (TTAB) Actions |
| Author | USPTO |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-13 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy