HEC Income Verification PRA Feasibility Analysis - 2900-0867 - April 2021
VA HEC Income Verification Division- Paper Reduction Feasibility Analysis_update 2021.docx
Health Eligibility Center (HEC) Income Verification (IV) Forms
HEC Income Verification PRA Feasibility Analysis - 2900-0867 - April 2021
OMB: 2900-0867
VA Health Eligibility Center (HEC)
Income Verification Division – Paperwork Reduction Feasibility Study
Income Verification Division Background:
VHA Directive 1909 provides policy for the Income Verification (IV) Program. AUTHORITY: 38 United States Code (U.S.C.) 1722; 38 U.S.C. 5317.
Title 38 U.S.C. 1722 established eligibility assessment procedures, based on income levels, for determining whether nonservice-connected (NSC) Veterans and non-compensable zero percent service-connected (SC) Veterans, who have no other special eligibility are eligible to receive Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care at no cost. Title 26 U.S.C. 6103 (l)(7) of the Internal Revenue Code, and 38 U.S.C. 5317 establish authority for VA to verify Veterans’ gross household income information against records maintained by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and Social Security Administration (SSA) when that information indicates the Veteran is eligible for cost-free VA health care.
The social security numbers (SSNs) of all Veterans and their spouses identified in the financial assessment will be verified under the Social Security Number Verification Information Exchange Agreement (IEA), between the SSA and VHA HEC, prior to income matching activity with IRS. If IRS and SSA income matching identifies discrepancies in the Veteran’s self-reported gross household income information that potentially impacts eligibility for VA health care benefits, HEC must independently verify the IRS and SSA income data in accordance with Title 38 USC 5317(b). Title 38 USC 5317(b) states that “The Secretary may not, by reason of information obtained from the Commissioner of Social Security or the Secretary of the Treasury under section 6103(I)(7)(D)(viii) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, terminate, deny, suspend, or reduce any benefit or service until the Secretary takes appropriate steps to verify independently information related to the following:
The amount of the asset or income involved.
Whether such individual actually has (or had) access to such asset.
The period or periods when the individual actually had such asset or income.”
The IV Program must adhere to stringent confidentiality guidelines set forth by IRS and SSA to ensure appropriate security and safeguarding of Federal Tax Information (FTI). Information received from the income match activity cannot be shared with VA medical facilities. Any breach of security requirements may result in loss of VHA’s matching agreements with IRS and SSA.
HEC’s Income Verification Division (IVD) sends Veterans and spouses, individual letters to confirm income information reported by IRS and SSA. HEC does not change the Veteran’s copay status until information supplied by IRS and SSA has been independently verified either by the Veteran or through appropriate due process procedures.
Presently, data collection for HEC Form 200-1A, HEC Form 220-1, HEC Form 340-1 and the responses to the HEC IV Checklist cannot be accomplished via the web due to Federal Tax Information restrictions.
The personal information requested on these forms is necessary to better serve the Veteran and for the effective delivery of health care. The form shows federal tax information for the Veteran and Veteran’s spouse based on the computer matching agreement with IRS/SSA. The forms serve to validate that the information provided by IRS and SSA is accurate and reflect the gross household income for the Veteran and Veteran’s spouse. The Veteran is informed of why the information is needed and can refuse to respond to the request for information. This information is necessary to ensure that the Veteran is placed in the correct Priority Group (PG) for healthcare benefits. If this information is not collected as needed annually from designated Veterans, it could result in the inability to place Veterans in the correct priority group for proper medical care and treatment.
Paper Reduction Feasibility Analysis:
The Program Office has conducted the following analysis of the feasibility of reducing burden on respondents who would remain in the same priority group or move to a high priority group based on their IRS/SSA data.
No Change in Priority Group -
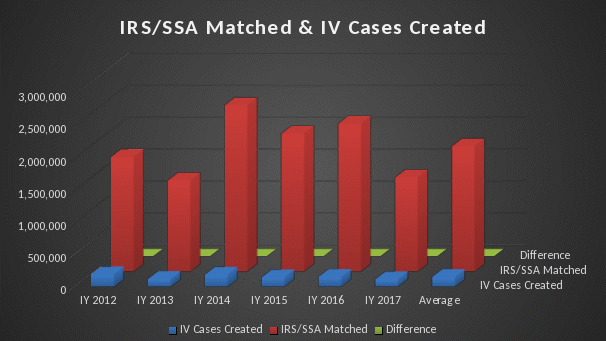
We conducted the below analysis of data between Income Year 2012 and Income Year 2017 which is depicted in Graph 1. On average the IRS/SSA matched 2 million Veterans self-reported income and only 156K cases were created as a result; which indicates that approximately 92% of Veterans remain in the same Priority Group and do not receive Income Verification letters. On average only 8% of IVD cases are created and approximately 156K Veterans and/or spouse receive letters.
Graph 1: IRS/SSA Matched compared to IV Cases Created (graph on page 3)
Outcome of IVD Cases Created:
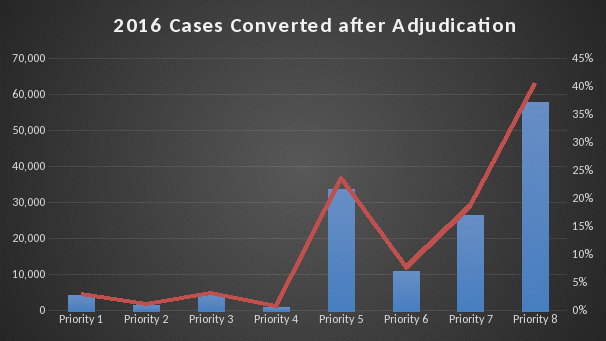
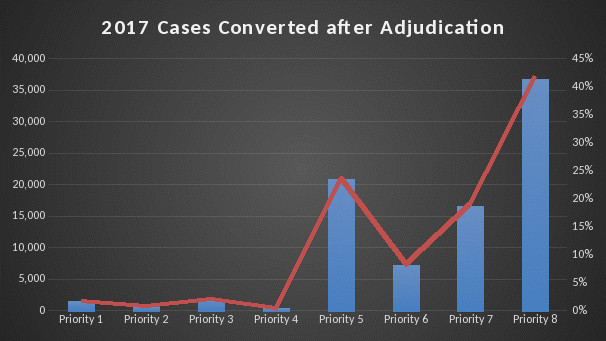
An analysis was performed for Income Year 2016 and Income Year 2017 which is depicted in Graph 2 & 3. On average less than approximately 10% are converted to PG 1-4, approximately 23% remain in PG 5 once paid out-of-pocket non-reimbursed deductible expense has been submitted by Veteran and approximately 67% are converted to PG 6-8.
Graph 2: 2016 Conversion Data
Graph 3: 2017 Conversion Data
Conclusion:
In summary, the Income Verification Division is committed to minimizing the burden on our Veterans by exploring system enhancements that will improve timeliness of service, optimize processes for Veterans, and modernize our information technology systems.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | Rogers, Serita |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2022-03-19 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy