0570-0065 Ss - 9003 7-2022
0570-0065 SS - 9003 7-2022.docx
Biorefinery, Renewable Chemical, and Biobased Product Manufacturing Assistance Program
OMB: 0570-0065
July 2022
SUPPORTING STATEMENT
Biorefinery, Renewable Chemical, and Biobased Product Manufacturing Assistance Program
OMB Control No. 0570-0065
A. Justification
1. Explain the circumstances that make the collection of information necessary.
This is a request for revision of a currently approved information collection package. The Rural Business-Cooperative Service (RBCS or the Agency) is a Rural Development agency of the U.S. Department of Agriculture and administers The Biorefinery, Renewable Chemical, and Biobased Product Manufacturing Assistance Program (Program).
The Program was established under Section 9003 of the 2008 Farm Bill and assists in the development, construction, and retrofitting of new and emerging technologies for the development of advanced biofuels by providing loan guarantees of up to $250 million. The Program’s authority was continued in the Agricultural Acts of 2014 and 2018.
This collection of information is necessary for Rural Development to identify projects eligible for loan guarantees under the Program. In accordance with the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995 (P.L. 104-13, 44 U.S.C. Chapter 35), Rural Development is submitting this information collection package to the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) for review and clearance.
2. Explain how, by whom, and for what purpose the information is to be used.
Each loan guarantee request must conform to the regulations governing the program, 7 CFR parts 4279 subpart C and 4287 subpart D. The Agency has developed an application guide that explains the application procedures and details the process for submission of an application in accordance with the regulations. The Agency will use the RD 4279-1 form and written evidence to collect information to determine lender, borrower, and project eligibility. The specific information requirements related to loan applications include reporting of:
Appeals
Sale or assignment of guarantee
Repurchase from holder
Replacement of document
Interest rate change
Hazard Insurance
Life Insurance
Flood or other insurance
Appraisal report
Request for Environmental Information
Transfer of Lenders
Changes in borrowers
Conditions precedent to issuance of guarantee (including issuance of guarantee)
Construction planning and performing development
Monthly construction reports
Quarterly progress reports
Post-construction permits, completion notice, and final accounting
Application Narrative
Lender analysis (formerly referred to as “lender credit analysis”)
Personal credit reports
Commercial credit reports
Project financial framework (replaces “financial studies”)
Financial statements
Feasibility studies
Proposed loan agreement
Statement for loan guarantees (formerly referred to as “Certification for contracts”)
Periodic Annual reports (formerly referred to as “periodic” reports)
Lender Inspections
Also included are the required forms for reporting and servicing, which help ensure that the lender protects the government’s financial interests.
As part of the process of monitoring construction, lenders have a continuing responsibility to provide the Agency with construction progress reports, on a quarterly basis, demonstrating that engineering and financial criteria used in the review and approval of the application continue to be met during the construction phase of the project. This is necessary to ensure that all terms of the loan guarantee agreement are being complied with.
Post-construction, information will be collected demonstrating that the facilities are operating and meeting all financial criteria projected during the application phase. This information is necessary in order for the Agency to adequately monitor the lender’s servicing activities.
The information sought by this collection will be stored in Agency files or computers. The Agency requires original borrower signatures on loan application forms and lender signatures on the loan documents. The Program requires the submission of substantial information essential to protect the Government’s interest.
The Agency, through its Program Processing Division in Washington, D.C., will be the primary user of the information collected. Under the Freedom of Information Act, the general public can request some of the data provided by the borrower and lender to the Agency, except data that are proprietary or confidential.
If the information is not collected, the Agency would neither be able to make prudent credit decisions nor would the Agency be able to effectively monitor the lenders’ servicing activities and thus minimize losses under the Program.
The estimates do not include burden hours for customary and usual business practices of entities other than the Agency. Therefore, this package only considers the information the Agency requires in excess of what a lender would typically require of a business, as well as the information the Agency regulation requires from the lender in excess of what it would typically do for a non-guaranteed loan. The burden to be cleared with this document is described below and detailed in the supporting worksheet.
REPORTING REQUIREMENTS - NO FORMS
System for Award Management (SAM) Registration, General Certifications and Representations. At the time of application, each applicant must have an active registration in SAM before submitting its application in accordance with 2 CFR 25. This registration must remain current, accurate, and complete at all times during which the applicant has an active Federal award or an application under consideration.
7 CFR Part 4279-C, Loan Processing
Appeals. The applicant or borrower and lender and/or holder may appeal or request a review of any adverse Agency decision. Appeals are handled in accordance with Departmental appeal regulations.
Lender eligibility. A lender seeking to participate in the Program must demonstrate that it meets the FDIC definition of “well capitalized” at the time of application and at the time of issuance of the loan note guarantee. In addition, the lender must notify the Agency, in writing, if it is under a cease-or-desist order (or similar constraint) from a Federal agency.
Sale or assignment of guarantee. The lender may sell the guaranteed portion of the loan in the secondary market. This is a typical business practice. The only burden imposed by the Agency is requiring the lender to advise the Agency that it wants to sell the loan and requesting the Agency to execute the appropriate documents. The balance of the burden is imposed by requirements of the secondary market and is not reported here.
Repurchase from holder. When a loan defaults, the holder makes demand for repurchase. A lender has the option to repurchase the unpaid guaranteed portion of the loan from a holder. If the lender does not repurchase the loan, the Agency will. The holder’s demand will include documentation and the amount due. If the lender does not repurchase the loan, the lender will provide the Agency with information necessary for the Agency to determine the amount due.
Replacement of document. When a Loan Note Guarantee or Assignment Guarantee Agreement is lost, stolen, destroyed, mutilated, or defaced, the lender must notify the Agency to request a replacement.
Interest rate change. Lender must seek and obtain Agency approval for any change in the interest rate between the date of issuance of the Conditional Commitment and before the issuance of the Loan Note Guarantee. Lender must also obtain Agency concurrence if there is an increase in interest rate from a variable interest rate to a higher interest rate that is a fixed rate.
Hazard insurance. Hazard insurance is required on every loan to protect the collateral from fire or other insurable losses. The Agency requires the lender to be named as mortgagee or loss payee. The lender would typically require hazard insurance on non-guaranteed loans. The borrower obtains the insurance, and the lender reviews it for sufficiency.
Life insurance. Life insurance may be required on key management officials of the business to ensure the success of the business if key management is lost. This is done by insuring the lives of key management, thus providing capital to hire new key management. This is a common practice of lenders, but the Agency may require life insurance when the lender would not. The borrower obtains the insurance, and the lender reviews it for sufficiency.
Flood and other insurance. National flood insurance is required on projects when available. Public liability, business interruption, malpractice, and other insurance appropriate to the borrower’s particular business and circumstances may be required. Lenders typically require flood and other insurance on non-guaranteed loans, but there may be situations where it is not recommended by the lender but required by the Agency. The borrower obtains the insurance, and the lender reviews it for sufficiency.
Construction planning and performing development. The lender must ensure the project design utilizes accepted architectural and engineering practices, conforms to applicable Federal, State, and local codes and will be completed with available funds. The lender must also monitor construction to ensure the project is completed in accordance with the plans and specifications and to keep the Agency informed.
Construction reports. During construction, the lender is required to submit monthly construction reports to the Agency. These reports cover a variety of areas such as certification of each draw request and that the work referred to in each draw has been successfully completed; certification to compliance with the Davis-Bacon Act; list of invoices; status of construction and inspection reports; and concerns, potential problems, and cost overruns.
Progress reports. During construction, the lender is required to submit quarterly progress reports to the Agency at the end of each calendar quarter. These reports will contain, at a minimum, construction milestone attainment and personnel hiring, training, and retention.
Post-construction permits, completion notice, and final accounting. Once construction is completed, the lender must provide the Agency with a copy of all required building permits with sign-offs; notice of completion or Agency-approved equivalent; and a final accounting of sources and uses of all project funds.
Non-binding letter of intent. The lender or the borrower must submit to the Agency a non-binding letter of intent to apply for loan guarantee prior to submitting the Phase 1 application. The letter must identify the borrower, the lender and project sponsors; describe the project and project location; describe the proposed feedstock, primary technologies of the facility and primary products produced; estimate the total project cost and amount of loan requested; and any additional information specified in the annual Federal Register notice, if any. If the lender or borrower do not submit a letter of intent, the Agency is not obligated to accept the Phase 1 application.
Application withdrawal notification. If, during the period between the submission of an application and the execution of documents, if the project is no longer viable or the borrower is no longer requesting financial assistance for the project, the lender must submit a written notification to the Agency. The Agency will then either rescind the project’s selection or withdraw the application, as applicable.
Application revisions and updates. If, during the period between the submission of an application and the execution of loan documents, there are changes to the project, the lender must notify the Agency, in writing, of those changes. Examples of changes include revisions to technology utilized in the project, feedstock, off-take, ownership structure, and project financing. Upon receipt of such notification, the Agency may require submittal of an updated application and supporting materials.
Phase 1 Application Requirements. (applicable to advanced biofuel, renewable chemical, and biobased product manufacturing projects). Applicants must submit, with the application form, a package that contains the following elements:
Borrower eligibility. A description of how the borrower meets the eligibility criteria for borrower.
Project eligibility. A description of how the project meets the eligibility criteria for projects.
Project funds. Identification of sources, amounts, and status of funds.
Project timeline. Identify the schedule of milestones and timeline for the project.
Application form. (See below)
Financial statements. The most recent audited financial statements of the borrower, unless alternative financial statements are authorized by the Agency and a current (not more than 90 days old) balance sheet and a pro forma balance sheet at startup.
Project financial framework. Submit electronically the project financial framework, which must address, but is not limited to, projected Project budget and projected balance sheets, income and expense statements, and cash flow statements, and Working Capital and capital expense projections for not less than the term of the loan. Provide list of assumptions used in the projections. Depending on the complexity of the project and the financial condition of the borrower, the Agency may require additional financial statements and related information.
Feasibility study. The study must address the economic, market, technical, financial, and management feasibility of the project, as well as the qualifications of the study’s authors and contributors. These studies are used by the lender and Agency to help determine the creditworthiness of the proposal.
Business plan. A business plan is prepared, typically by the applicant, which describes at a minimum, the business and project, management experience, products and services, proposed use of loan funds, availability of labor, raw materials and supplies, and the names of any corporate parent, affiliates, and subsidiaries with a description of the relationship.
Scoring information. Include information that allows the Agency to score the application in accordance with §4279.266 of the rule.
Intergovernmental consultation. The applicant is required to comply with RD Instruction 1940-J and 7 CFR part 3015, subpart V. This is to ensure the project is in compliance with State and local development strategies.
UEI number. For borrowers other than individuals, provide the Unique Entity Identifier (UEI) number.
Other information. Submit any other information as requested by the Agency to allow the Agency to evaluate the application.
Phase 2 Application Requirements. (applicable to advanced biofuel, renewable chemical, and biobased product manufacturing projects). The Agency will invite high-scoring Phase 1 applicants to submit a Phase 2 application, which contains the following elements:
Updates (as appropriate) and certification of lower loan guarantee amount. As appropriate, applicants must update the contents of the Phase 1 application.
If the remaining funds are insufficient to meet the requested loan guarantee amount for the next highest scoring application, the Agency will give the borrower with the next highest scoring application the opportunity to reduce the amount of its request to the amount of budgetary authority available. If the borrower agrees to lower its request, the borrower must submit a certification to the Agency that the purposes of the project can still be met at the lower request amount.
Appraisal reports. The applicant pays for certified appraisers to complete appraisals in accordance with industry standards. Lenders typically require appraisals completed in accordance with industry standard on non-guaranteed loans, and they typically require the applicant to pay for them. There may be situations where the Agency requires an appraisal when the lender would not. Appraisals are used to determine the value of borrower assets being offered as collateral to ensure the loan is adequately secured.
If the appraisal has not been completed at the time the Phase 2 application is filed, the applicant must submit an estimated appraisal. In all cases, a completed appraisal must be submitted prior to the loan being closed. Appraisals are used to determine the value of borrower assets being offered as collateral to ensure the loan is adequately secured.
Proposed Loan Agreement. An agreement between the lender and the borrower establishing conditions for the loan such as collateral, repayment schedule, loan purpose, and other conditions. They are a general lender practice for all commercial loans. The Agency reviews the proposed document to aid in its loan analysis.
Environmental assessment. An environmental assessment, prepared in accordance with the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), is to be submitted with the Phase II application. Such environmental assessments are likely to require consideration of siting, construction, operation, and decommissioning of the energy project. The primary purpose of environmental assessments is to determine whether the proposed project will require the preparation of an environmental impact statement or a finding of no significant impact.
Credit rating or credit assessment. For projects with total eligible project costs of $25 million or more, either a credit rating or a credit assessment of the total Project’s indebtedness, without consideration for a government guarantee, from a nationally-recognized rating agency as specified by the Agency.
Lender’s analysis and credit evaluation. The lender completes a comprehensive credit analysis that is the lender’s justification for making the loan. Included with this analysis are personal and commercial credit reports, as applicable, for the borrower, its principals, and any parent, affiliate, or subsidiary and a financial and sensitivity review.
Request for guarantee prior to construction. The application must indicate whether the loan guarantee is being requested prior to construction or after completion of the project’s construction.
Technical assessment. A technical assessment completed by a qualified independent engineer must be submitted. The technical assessment must address the following areas: qualifications of the project team; agreements and permits; resource assessment; design and engineering; project development schedule; equipment procurement and installation; operations and maintenance; and decommissioning. The technical assessment must be based upon verifiable data and contain sufficient information and analysis so that a determination can be made on the technical feasibility of achieving the levels of income or production that are projected in the financial statements.
Reduced request certification. There may be instances where the remaining funds are insufficient to meet the requested loan guarantee amount for the next highest scoring application. In such instances, the borrower with the next highest scoring application will be given the opportunity to reduce the amount of its request to the amount of budgetary authority available. If the borrower agrees to lower its request, the borrower must submit a certification to the Agency that the purposes of the project can still be met at the lower request amount.
Conditional Commitment changes. The lender and borrower may request changes to the Conditional Commitment by submitting the requested changes to the Agency. In such instances, the Agency may negotiate with the lender and the borrower regarding any proposed changes and any accepted changes will be documented via a written amendment to the Conditional Commitment. All changes must be for Good Cause.
Transfer of lender. When the applicant or lender desires to change lenders prior to issuance of the guarantee, the Agency needs information to determine if the new proposed lender is eligible and capable of making and servicing the proposed loan.
Changes in borrower. Because the guarantee has not yet been issued, the Agency must still ensure the borrower meets the requirements of the applicable program. Therefore, if there is a change in borrower, the Agency must have information to verify that the new borrower is still eligible.
Conditions precedent to issuance of Loan Note Guarantee. This is the final check prior to issuance of the guarantee. It is a comprehensive certification from the lender that the borrower meets all requirements of the Conditional Commitment and other program requirements. If requested by the Agency, the lender is to provide copies of loan documents for the Agency’s file.
Statement for loan guarantees. Submission of this statement is a prerequisite (prior to submitting SF-LLL) for making or entering into any transaction imposed by section 1352, title 31, U.S. Code.
Requirements after construction, annual reports. The borrower is required to prepare annual reports for completed projects and provide them to lender, who submits them to the Agency for the life of the guaranteed loan. Information to be contained in these reports include: (1) the actual amount of advanced biofuels, biobased products, renewable chemicals, and by-products, as applicable, produced to assess whether project goals are being met; (2) if applicable, documentation that identified health and/or sanitation problem has been solved; (3) a summary of the cost of operating and maintaining the facility; (4) description of any maintenance or operational problems associated with the facility; (5) certification that the project is and has been in compliance with all applicable State and Federal environmental laws and regulations; (6) the number of jobs created; (7) a description on the status of the project’s feedstock including, but not limited to, the feedstock being used, outstanding feedstock contracts, feedstock changes and interruptions, and quality of the feedstock; and (8) result of the required annual inspections.
Annual lender inspections. For the life of the guaranteed loan, the lender is required to conduct annual inspections of the facility and include the results in the annual report discussed immediately above.
7 CFR Part 4287-D, Servicing
Appeals. The applicant or borrower and lender and/or holder may appeal or request a review of any adverse Agency decision. Appeals are handled in accordance with Departmental appeal regulations.
Borrower Visits. The Agency will meet with each borrower as often as needed after the Loan Note Guarantee is issued, and more often if the account is delinquent or a problem. The lender is encouraged to participate in the visit. During the visit, a review of the collateral and the borrower’s operation is made.
Loan classification. At the time the Loan Note Guarantee is issued, the lender must notify the Agency of the loan’s classification or rating under its regulatory standards. Should the classification be changed at a future time, the lender must notify the Agency immediately.
Annual renewal fee transmittal. The lender transmits this fee once per year to the Agency.
Agency and lender conference. The lender will consult with the Agency at the Agency’s request to ascertain how the guaranteed loan is being serviced and ensure that conditions and covenants of the Loan Agreement and Conditional Commitment are being enforced. The Agency will consult with each lender at least annually, and these conferences can be done either face-to-face or via the telephone.
Borrower financial reports. Lenders must obtain, analyze, and submit to the Agency each quarter financial statements of the borrower and any guarantors within 45 days of the end of each quarter and audited financial statements with 180 days of the end of the borrower’s fiscal year. The lender must analyze the financial statements and provide the Agency with a written summary of the lender’s analysis, ratio analysis, and conclusions, including trends, strengths, weaknesses, extraordinary transactions, violations of loan covenants and covenant waivers proposed by the Lender, any routine servicing actions performed, and other indications of the financial condition of the borrower. After its review, the Agency will provide the lender with a written report of any concerns. The lender must address each Agency concern. This requirement is needed in order to evaluate the borrower’s financial performance as it would pertain to both its business plan and feasibility study, if applicable, as well as to whether the business is generating sufficient cash flow to satisfy its obligations, including the guaranteed loan.
Audits. Any public body, nonprofit corporation, or Indian Tribe that receives a guaranteed loan that meets the thresholds established by 2 CFR part 200, subpart F must provide an audit for the fiscal year of the borrower in which the Loan Note Guarantee was issued. If the loan is for development or purchases made in a previous fiscal year through interim financing, an audit will also be provided for the fiscal year in which the development or purchases occurred. Any audit meeting the requirements of this provision in the rule will be adequate to meet any audit requirements of the Program for that year.
Additional loans. The lender must notify the Agency whenever the lender makes any additional expenditures or new loans to the borrower.
Interest rate change. The lender is responsible for the legal documentation of interest rate changes by an endorsement or any other legally effective amendment to the promissory note. The Agency must be notified in writing of all interest rate change prior to the enactment of the negotiated interest rate change. The borrower, lender and holder (if any) may collectively initiate a permanent or temporary reduction in the interest rate of the guaranteed loan at any time during the life of the loan upon written agreement among these parties.
Release of collateral. All releases of collateral greater than $250,000 must be supported by a complete appraisal. Prior to the release being made, the lender must submit written justification to the Agency (1) for each release of collateral that results, individually or collectively, in more than 20 percent of the loan amount being released or when the proceeds will not be used to reduce the guaranteed loan and (2) for any release of collateral if the proceeds are not used to reduce the guaranteed loan or to buy replacement collateral.
Subordination of lien position. A subordination of the lender’s lien position must be requested in writing by the lender and concurred with by the Agency in writing in advance of the subordination. The subordination must be in the best financial interest of the Agency, the lien to which the guaranteed loan is subordinated is for a fixed dollar limit, lien priorities remain for the portion of the loan that was not subordinated and must be for Good Cause.
Alterations of loan instruments. Alterations or modifications to any loan instrument must be approved in writing by the Agency prior to the alterations or modifications. A request by the lender for approval to loan instrument changes must be supported by and explanation of the reason for the proposed changes, completed by the lender.
Transfer and assumption. All transfers and assumptions must be approved in writing by the Agency and must be made to eligible applicants. In all cases, the lender must make a complete credit analysis, subject to Agency review and approval. In addition, the lender will provide to the Agency a written certification that the transfer and assumption is valid, enforceable, and complies with all Agency regulations. A request by the lender for approval of new loan terms must be supported by an explanation of the reasons for the proposed change in loan terms.
Transfer and assumption - Credit Reports. An individual credit report must be provided for transferee proprietors, partners, officers, directors, and stockholders with 20 percent or more interest in the business. This information gives the loan officer a history of past credit payments on the transferee and aids the loan officer in making a determination as to the credit worthiness of the transferee. Credit reports are also typically requested for debt settlement transactions.
Transfer and assumption - Appraisals. If the transfer and assumption is for less than the full amount of the guaranteed loan, the lender must obtain an appraisal on all of the collateral being transferred. (Note: An appraisal is not required if the transfer and assumption is for the full amount of the guaranteed loan.)
Transfer and assumption – Legal opinion. Prior to Agency approval, the lender must provide the Agency a written legal opinion that the transaction can be properly and legally transferred and assurance that the conveyance instruments will be appropriately filed, registered, and recorded.
Substitution of lender. After the issuance of the Loan Note Guarantee, the lender can neither sell nor transfer the entire loan to a new lender without the prior written approval of the Agency. The substitution of lender is requested in writing by the borrower and the proposed substitute lender if the original lender is still in existence. The new lender must agree in writing to acquire title to the non-guaranteed portion of the loan held by the original lender and assume all original loan requirements.
Default by borrower - Meeting. If a monetary default exceeds 60 days, the lender will arrange a meeting with the Agency and the borrower to resolve the problem.
Curative actions. The primary curative actions include: payment deferment, re-amortization, rescheduling, reorganization, and moratoriums.
Protective advances. Protective advances are advances made by the lender to preserve and protect the collateral. They must constitute an indebtedness of the borrower to the lender and must be secured by the security instruments. The lender needs the Agency’s written authorization when the cumulative total of protective advances exceed $200,000 or 10 percent of the aggregate outstanding balance of principal, whichever is less, unless otherwise specified by the Agency at a lesser amount.
Liquidation plan - general. If the lender concludes that liquidation is necessary, it must request the Agency’s concurrence. Within 30 days after a decision to liquidate, the lender must submit to the Agency its proposed written detailed method of liquidation. While the Agency is reviewing the liquidation plan, the lender may proceed with the liquidation process after the lender has accelerated the loan. If the Agency has any concerns with the plan, the lender and Agency will attempt to resolve such concerns. Upon approval by the Agency of the liquidation plan, the lender will conduct the liquidation (as it would for any non-guaranteed loan). If significant changes to the plan become necessary, the lender must request Agency concurrence to alter the plan.
The lender must take action to maximize recovery from all personal and corporate guarantees, including seeking deficiency judgments when there is a reasonable chance of future collection. Compromise settlements must be approved by the Lender and the Agency, with complete current financial information on all parties obligated for the loan provided. If, during litigation proceedings, the Agency takes any legal action to protect the rights of the lender, the lender must cooperate with the Agency.
Liquidation - acceleration. The lender must proceed to accelerate the indebtedness as expeditiously as possible when acceleration is necessary, including giving any notices and taking any other legal actions required. If the acceleration of the loan is solely due a nonmonetary default, the lender must obtain Agency concurrence prior to the acceleration. In the case of a monetary default, prior Agency approval is not required, although Agency concurrence is required no later than when the liquidation plan is approved. The lender must provide the Agency with a copy of the acceleration notice and any other acceleration documents. The guaranteed loan will be considered in liquidation once the loan has been accelerated and a demand for payment has been made upon the borrower.
Liquidation - accounting and reports. When conducting the liquidation, the lender must account for all funds during the period of liquidation and must provide the Agency with monthly reports on the progress of liquidation including disposition of collateral, resulting costs, and additional procedures necessary for successful completion of the liquidation.
Final loss. If the lender received a final loss payment, the Lender must submit to the Agency an annual report on its collection activities for each unsatisfied account for 3 years following payment of the final loss claim.
Termination of Guarantee. A guarantee will be terminated automatically upon the written notice from the lender to the Agency that the guarantee will terminate in 30 days after the date of notice, provided that the lender holds the entire guaranteed portion of the loan.
REPORTING REQUIREMENTS –FORMS APPROVED UNDER THIS DOCKET
Form RD 4279-1, “Application for Loan Guarantee.” The information collected on the form is used by the Agency to determine applicant eligibility for program assistance and to provide financial and other data about the applicant and lender. The form contains two parts. The borrower completes part A, and the lender completes Part B.
Form RD 4279-3, “Conditional Commitment.” The form is used by the Agency to provide notice to the lender, subject to lender acceptance, that the guarantee request is approved subject to the conditions established by the Agency and listed on the form.
Form RD 4279-4, “Lender’s Agreement.”- This form is the signed agreement between USDA and the lender setting forth the lender’s loan responsibilities. Each lender will execute the form once. It will then apply to all Program loans the lender makes thereafter.
Form RD 4279-5, “Loan Note Guarantee.” This form is the signed agreement among the Agency and lender outlining the conditions and requirements of the loan.
Form RD 4279-6, “Assignment Guarantee Agreement.” The form is the signed agreement among the Agency, lender, and holder, setting forth the terms and conditions of an assignment of all or a portion of the guaranteed portion of a loan.
Form RD 4279-14, “Unconditional Guarantee.” This form is used to obtain either a partial or a full, unconditional personal or corporate guarantee for the full term of the loan when the Agency has determined that such guarantees are necessary based on the Agency’s assessment of the potential financial risk of the project. This form is in addition to any guarantee forms used by lenders.
Form RD 1980-19, “Guaranteed Loan Closing Report.” The information is used by the Agency to establish the account in its accounting system. The Agency prepares the form, and the lender verifies it for accuracy.
Form RD 449-30, “Loan Note Guaranteed Report of Loss.” The Agency requires the lender to use of this form to process estimated and final reports of loss on guaranteed loans.
Form RD 1980-41, “Guaranteed Loan Status Report.” The Agency requires the lender to complete this form four times per year, unless the Agency requests more frequent ones in order to protect the financial interests of the United States. Form RD 1980-41 is now accessible to the lender through the Lenders Interactive Network Connection (LINC). The lender must designate a Security Administrator. Lenders with access to LINC must complete the status report on-line at the LINC Web site. Lenders without LINC access must send a completed Form RD 1980-41 to the applicable State/Field Office.
Form RD 1980-43, “Lender’s Guaranteed Loan Payment to USDA.” The Agency requires the lender to use of this form to send guaranteed loan payments to the Agency Finance Office on loans repurchased from the secondary market.
Form RD 1980-44, “Guaranteed Loan Borrower Default Status.” The Agency requires the lender to complete this form on all delinquent loans every month. The Agency uses this information to determine the lender’s compliance with the Lender’s Agreement in properly servicing delinquent accounts. The lender submits Form RD 1980-44 when the loans are 30 days past due and cannot become current within 30 days. This form has been automated for the lender to access it electronically and update it bi-monthly through LINC.
REPORTING REQUIREMENTS – FORMS APPROVED UNDER OTHER OMB NUMBERS – BURDEN INCLUDED IN THIS COLLECTION
Environmental Report (OMB No. 0575-0197). As part of the Phase 2 application, the applicant is required to submit this report (along with environmental assessment, as discussed above). This report identifies environmental information regarding the application.
REPORTING REQUIREMENTS – FORMS APPROVED UNDER OTHER OMB NUMBERS
Form RD 400-1, "Equal Opportunity Agreement" (OMB No. 0575-0201). All applicants and recipients are required to complete this form to comply with Equal Opportunity requirements.
Form RD 400-4, "Assurance Agreement" (OMB No. 0575-0201). All applicants and recipients are required to complete this form to comply with Civil Rights Acts and laws.
Standard Form LLL, "Disclosure of Lobbying Activities" (OMB No. 4040-0013).
All applicants are required to complete this form, regardless of their involvement in lobbying activities.
3. Describe any consideration of the use of improved information technology to reduce burden any technical or legal obstacles to reducing burden.
4279-C, Loan Processing. The Agency has automated various forms used to apply for loan guarantees, and fillable forms are available on the USDA Service Center and Rural Development websites. Lenders may complete the automated forms and submit hard copies of the forms with original or electronic signatures to the Agency. Some application materials are accepted electronically, such as the lender’s analysis, financial statement spreads, credit reports, proposed loan agreements, and business plans. The Agency is currently working on the e-Gov initiative that will eventually be capable of receiving applications and other forms electronically. The Agency does not have an electronic application intake system for this program but applicants can submit their full applications electronically through a third-party data storage system.
4287-D, Servicing. The Agency has developed the capability to receive the default status reports electronically. Lenders can complete these forms through Guaranteed Loan System (GLS). They receive a certified, secure ID through the State office. However, only lenders with a high volume of guaranteed loans have elected to utilize them. The lender submits some information electronically through the LINC. The lender must designate a Security Administrator who can then add other users to the LINC system.
4. Describe efforts to identify duplication.
The Agency is utilizing existing forms used in the current Rural Development guaranteed loan programs, which includes the Biorefinery Assistance Program. If similar information is found to be available from another Federal agency, every effort is made to utilize that information as is or in an appropriately modified form for this program. There will be no similar or existing information that could be submitted; therefore, there will be no duplication.
5. If the collection of information involves small businesses or other small entities, describe the methods used to minimize the burden.
The majority of eligible projects, if not all, are likely to be larger than those that small businesses usually undertake. Therefore, it is possible that none of the projects will be undertaken by borrowers that are small businesses, based on their revenue, their employees, and the size and scale of their initial operations. Furthermore, Rural Development is using industry-standardized data elements and documents, supplementing them with Government-wide forms that are familiar to many applicants.
6. Describe the consequences to Federal program or policy activities if the collection is not conducted or is conducted less frequently, as well as any technical or legal obstacles to reducing burden.
Application information is only collected once (over a two-phase process), while various status reports and notifications are submitted at different times throughout the year. If this information was collected less frequently than required, the Agency would be unable to address delinquent loans, evaluate whether the borrower has sufficient cash flow to meet its obligations, and determine if the borrower is in compliance with all conditions contained in the Conditional Commitment. Thus, the Agency would increase its risk of loss and its oversight capabilities to help manage its outstanding loan portfolio would be hindered.
7. Explain any special circumstances that require the collection of information to be conducted in a manner:
a. Requiring respondents to report information more than quarterly. For 7 CFR part 4287, subpart D, lenders must submit Form RD 1980-44 (loan default status report) every month for borrowers who are delinquent. These reports give the Agency the ability to quickly address delinquent loans thereby decreasing the risk of loans defaulting and Agency loss. Certain unanticipated ad-hoc events (i.e., loan agreement violations, reductions in interest rates, changes in loan classification) may occur. If this happens, a lender is required to notify the Agency within 15 days of its occurrence thus triggering reports more frequently than quarterly.
b. Requiring respondents to prepare a written response to a collection of information in fewer than 30 days after receipt of it. There are no information requirements that require specific reporting in less than 30 days.
c. Requiring respondents to submit more than an original and two copies of any document. There are no information requirements that require more than an original and two copies.
d. Requiring respondents to retain records for more than 3 years. There are no such requirements.
e. Not using statistical sampling. There are no such requirements.
f. Requiring use of statistical data classification that has not been reviewed and approved by Office of Management and Budget (OMB). There are no such requirements.
g. Requiring a pledge of confidentiality that is not supported by authority in statute or regulation, that is not supported by disclosure and data security policies that are consistent with the pledge, or which unnecessarily impedes sharing of data with other agencies for compatible confidential use. There are no such requirements.
h. Requiring respondents to submit proprietary trade secrets or other confidential information unless the agency can demonstrate that it has instituted procedures to protect the information’s confidentiality to the extent permissible by law. There are no such requirements.
8. Comments on Agency’s notice in the Federal Register and efforts to consult with persons outside the Agency to obtain their views on the availability of data, frequency of collection, the clarity of the instructions and recordkeeping, disclosure, or reporting format (if any), and on the data elements to be recorded, disclosed, or reported.
As required by 5 CFR 1320.8(d), a Notice to request comments was published on May 16, 2022, at 87 FR 29732 (94). The agency did not receive any comments that pertained to this collection during the 60-day comment period.
Through administration of the Program, the Agency engages in routine communication with stakeholders on issues; including the paperwork burden associated with guaranteed loan making. These stakeholders include; national, regional, and community lenders; nontraditional lenders; business developers, national lending and banking associations; economic and/or community development organizations; and other Federal agencies associated with credit making activities.
In addition to this on-going engagement, interviews were conducted with lenders and business developer who had familiarity with the program, direct experience with the revised application process and servicing requirements. Respondents were asked to provide feedback on the amount of information that is collected, the required forms as well and supporting documentation. All responses were affirmative, and respondents unanimously expressed that the amount of information collected and required forms and documentation were reasonable. Respondents also commented on the usefulness of the application guide and responded favorably on the two-phase application process. The interviewees and their affiliations are listed below.
Founder and CEO
Westar Trade Resources/ Global Biofuture Solutions
Team Lead, Bioenergy Lending
Live Oak Bank
Executive Vice President
Greater Nevada Credit Union/ Greater Commercial Lending
9. Explain any decision to provide any payment or gift to respondents, other than remuneration of contractors or grantees.
No payments or gifts will be provided to respondents, including no remuneration of contractors or grantees.
10. Describe any assurances of confidentiality provided to respondents and the basis for the assurances in statute, regulation, or Agency policy.
No assurance of confidentiality is provided to respondents for the information required. When necessary, the Agency will process all requests for release of records and information in accordance with the Privacy Act of 1974. However, in some instances, the information collected under the provisions of this program is not considered to be of a confidential nature. For example, organizations, such as not-for-profit entities and public bodies from which information is collected, are ordinarily required to make their activities available for public scrutiny.
The Agency does support maintenance of confidentiality when appropriate. The Agency published a Privacy Act of 1974; System of Records in the Federal Register on May 14, 2019 (84 FR 21315). A copy of that document can be found at >https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2019-05-14/pdf/2019-09874.pdf<
11. Provide additional justification for any question of a sensitive nature, such as sexual behavior or attitudes, religious beliefs, and other matters that are commonly considered private.
The information collected does not contain any questions of a sensitive nature such as sexual behavior, religious beliefs, or other matters commonly considered private.
12. Provide estimates of the hour burden of the collection of information.
See separate spreadsheet for breakdown of burden.
The average yearly burden (based on three-year estimates) for this package is 8,0052 hours of burden and 312 responses. This is based on a yearly average of 9 applicants and 2 awardees.
The number of applicants was based on the average annual applications received for the previous three fiscal years.
The annual cost to the respondents is $396,683. There are three primary occupation classes needed to complete application and supporting documentation. The majority of the application and servicing tasks will be completed by representatives of either the Borrower or the Lender (such as packaging the application, producing financial statements, financial/credit analysis, appraisals, producing reports, etc.). For this reason, the Business and Financial Operations (Major Group – 13-0000) was used. This broad grouping includes a variety of applicable occupations and includes the following: Financial Specialists, Appraisers and Assessors of Real Estate, Market Research Analysts, Budget Analysts, Accountants and Auditors, Credit Analysts, Financial Analysts and Advisors, Financial Analysts, Financial Examiners, and Credit Counselors and Loan Officers. Specialty tasks will normally be completed by Lawyers-23-1011 (appeals and legal opinion) and Engineers-17-2000 (technical assessment). For each occupation, the median wage rate was used as the base wage. Each wage was accessed an additional 29.6 percent for benefits. The total wage amounts are listed below.
Table 1. Wages by Occupation
Occupation Class |
Median Wage (HR) – Base |
Benefits (29.6%) |
Total |
Business/ Financial (13-0000) |
$ 36.81 |
$ 10.90 |
$ 47.71 |
Engineer (17-2000) |
$ 47.62 |
$ 14.10 |
$ 61.72 |
Lawyer (23-1011) |
$ 61.54 |
$ 18.22 |
$ 79.76 |
All salary data used was obtained from the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ report “Occupational Employment and Wages, May 2021 Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates United States” (http://www.bls.gov/oes/current/oes_nat.htm) and https://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/ecec.pdf
13. Provide estimates of annualized cost to the respondents.
There are no capital and start-up costs, or operations and maintenance costs associated with this collection.
14. Provide estimates of annualized cost to the Federal Government.
The annual cost to the Federal Government to collect and evaluate this information is estimated at 1,665 hours at a cost of $110,864 per fiscal year (see attached spreadsheet). Most of the review work is completed by GS Grade 12, step 5 staff located in Washington, D.C. Accordingly, the average rate was determined to be $66.58 per hour.
The hours were computed by estimating the average time it takes to review an application package, including the lender analysis and conducting negotiations and conferences with lender, a site visit, and environmental assessment; assigning a loan priority score; approving and obligating the loan, including preparing the Conditional Commitment; and issuing the Loan Note Guarantee, including reviewing the lender’s certification and comparing it against conditions of the loan and program regulations. The summary breakdown of cost to the Government is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Summary of Government Costs
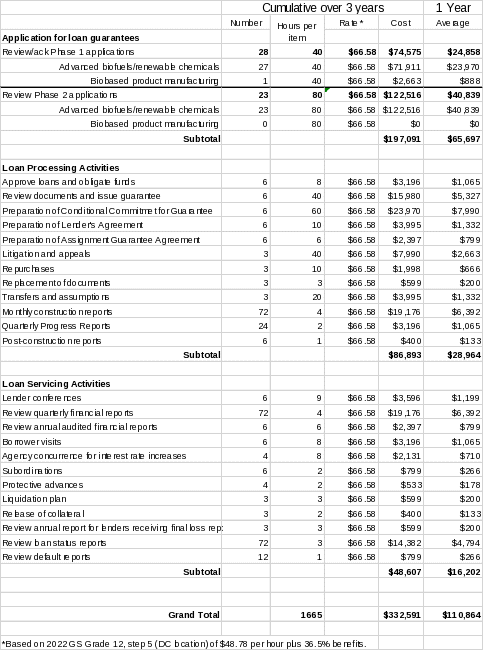
15. Explain reasons for changes in burden, including the need for any increase.
The decrease in burden responses, as shown in the Table 3 below, is attributed to the removal of the Application Guide in the burden calculation. This item was removed because the Application Guide does not collect information from the applicant. Rather, it provides information on how to build a successful application for the program. Three forms (RD 400-1, RD 400-4 and SF-LLL) were also removed from the calculation and will be submitted as common forms. The increase in burden hours is due to inserting placeholders in the burden worksheet for phase 2 BPM Applications (lines A39, A41 thru 43 on burden worksheet) to acknowledge this part of the application even though the program does not anticipate these items being submitted for this update.
Table 3. Change in Burden
|
Responses |
Hours |
Current |
312 |
8,005 |
Previous |
361 |
7,803 |
Change |
(49) |
202 |
16. For collection of information whose results are planned to be published for statistical use, outline plans for tabulation, statistical analysis, and publication.
The information collected will not be published for statistical use.
17. Approval not to display the expiration date for OMB approval.
These forms are used in other Rural Development information collections; therefore, it is not practical to include an OMB expiration date because of the different expiration dates for each collection. The public would have no way of knowing which burden package/expiration date applied to their particular program. RD is seeking approval to not display the OMB expiration date on these forms.
18. Exceptions to certification statement.
There are no exceptions to the certification.
19. How is this information collection related of the Service Center Initiative (SCI)? Will the information collection be part of the one stop-shopping concept?
The SCI calls for changes to improve services to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) customers. One aspect is providing one stop service for greater customer convenience in accessing USDA programs, including access to required forms.
Recipients of Section 9003 loan assistance are typically not agricultural businesses. Consequently, very little of the information collected for this program would be useful in the Service Center Initiative. The information is used only for administering the 9003 Program.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | OMB #0570-0065 60-day Notice |
| Author | USDA |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2023-08-03 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy