Sheep Study 2024 SS Part B
Sheep Study 2024 SS Part B.docx
NAHMS Sheep 2024 Study
OMB: 0579-0488
July 2023
Supporting Statement
Center for Epidemiology and Animal Health (CEAH)
National Animal Health Monitoring System (NAHMS) Sheep 2024 Study
OMB Control Number 0579-XXXX
Part B
B. Collections of Information Employing Statistical Methods
1. Describe (including a numerical estimate) the potential respondent universe and any sampling or other respondent selection method to be used. Data on the number of entities (e.g., establishments, state and local government units, households, or persons) in the universe covered by the collection and in the corresponding sample are to be provided in tabular form for the universe as a whole and for each of the strata in the proposed sample. Indicate expected response rates for the collection as a whole. If the collection had been conducted previously, include the actual response rate achieved during the last collection.
The potential respondent universe of the Sheep 2024 study is all operations on the National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS) frame with 1 or more adult ewes in 30 states1, with the reference population being all sheep operations with 1 or more adult ewes in those 30 states. See Table A.1 in Appendix A for the historical size of the reference population. Even with generally increasing counts of operations with any sheep and lamb inventory since 1997, the national counts of operations with any adult ewes have been between approximately 65,000 and 70,000 since 1997.
Previous Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS)–National Animal Health Monitoring System (NAHMS) Sheep studies, such as the NAHMS Sheep 2001 study, included all operations with 1 or more sheep or lambs, which provided inclusion of sheep feedlot operations. Including both operations with breeding sheep and feedlots in one study is difficult, as the two segments of the sheep industry have different uses of sheep, management and biosecurity practices, and health concerns. This approach of focusing on operations with 1 or more ewes was taken here in response to the results from a needs assessment performed in preparation for the study and because the same approach was used in the Sheep 2011 study, and so estimation of trends since 2011 will be appropriate.
One goal of APHIS–NAHMS national study design is to include states that account for at least 70 percent of the animals and operators/producers in the United States. The 30 specific states were chosen because they account for over 70 percent of the operations with 1 or more adult ewes and at least 70 percent of the adult ewes on operations in the United States (source: Census of Agriculture, NASS Sheep and Goats Survey, and unpublished NASS data). States were chosen based on their percentage of sheep inventory and sheep operations, the change in their percentage of sheep inventory or operations over time, for their geographic representativeness, and response burden. See Table A.2 and Figures A.1–A.5 in Appendix A for percentages of sheep and sheep operations in addition to other metrics used in state selection.
Phase 0 of the study will be the 2024 NASS Sheep and Goat Survey sample, wholly planned, designed, and administered by NASS. Phase 1 of the study will consist of a questionnaire being administered by mail, web, phone, and in person to sheep operations in the 30 study states by NASS-appointed enumerators. During Phase 1 of the study, respondents will have the opportunity to consent to participate in Phase 2 of the study, which will include APHIS data collectors administering a second questionnaire by mail and/or phone or in-person interview and the opportunity to participate in one or more biological sampling components. Expected response rates, estimated using response rates from the NAHMS Goat 2019, Sheep 2011, and Sheep 2001 studies, are given in Tables C.1 and C.2. Briefly, 56 percent of sampled producers are expected to complete Phase 1 and 55 percent of those are expected to consent to the opportunity to participate in Phase 2. Of those, 61 percent are expected to complete the Phase 2 questionnaire and 75, 28, and 76 percent of those are expected to complete the blood and swab, fecal pathogen, and parasites fecal egg count biologics components, respectively. Of those that complete the fecal egg count biologics component, 33 percent are expected to complete the parasite resistance biologics component.
Describe the procedures for the collection of information including:
For Phase 1 of the study, a total sample of up to 4,970 operations will be sampled. The sample will consist of two portions. The first portion will consist of an expected 3,940 sheep operations from all of the study states except for California that responded to the NASS January 2024 Sheep and Goats Survey – for which all sheep operations, regardless of size, have a chance of being chosen – and that had completed that survey and reported having any adult ewes. This design has been used in both the NAHMS Sheep 2001 and Sheep 2011 studies and has shown to provide low rates of ineligible operations (those with no sheep or are out of business or out of scope). The random sub-sampling of operations from the NASS January 2024 Sheep and Goats Survey will be performed by randomly selecting operations with 1 or more ewes from the 30 study states, stratifying by state and herd size (1–19 ewes, 20–99 ewes, 100–499 ewes, and 500 or more ewes), or a census of respondents will be taken. In addition, to ensure state-level estimates can be generated for the State of California, a stratified random sample of approximately 1,000 operations will be taken from the NASS list frame out of operations in California, stratifying by herd size (1–19 sheep, 20–99 sheep, 100–499 sheep, and 500 or more sheep) and NASS January 2024 Sheep and Goats Survey completion status (not selected for the study, selected and reported having any adult ewes, or selected and didn’t report having any adult ewes or didn’t respond).
Selection weights from the NASS January 2024 Sheep and Goats Survey will be adjusted for the sub-sampling procedure and for nonresponse, using state and herd size as primary weight adjustment strata. Reporting will be at the National, regional, and herd size levels, with region and herd size being defined as below.
Region (states)
West (CA, OR, WA)
Central (AZ, CO, ID, KS, MT, NE, NM, ND, SD, Central TX, UT, WY)
Northeast (IN, IA, MI, MN, NY, OH, PA, WI)
Southeast (FL, GA, KY, MO, NC, TN, Southeast TX, VA)
Herd size (number of ewes)
Very small (1–19)
Small (20–99)
Medium (100–499)
Large (500 or more)
Phase 1 of the Study will be implemented by NASS during and after the January 2024 Sheep and Goats Survey via mail, web, phone, and in-person interviews. Amenable operations will complete the Phase 1 questionnaire, following completion of the January 2024 Sheep and Goats Survey. At the same time, producers who complete the Phase 1 questionnaire will be asked to participate in Phase 2 of the survey. Producers who express an interest in Phase 2 will be asked to provide consent to allow NASS to turn over the producer’s name and contact information to APHIS, Veterinary Services (VS) staff so that they may be contacted to participate in Phase 2 of the study, which includes a second questionnaire and the opportunity to collect biological samples from sheep on the producer’s operation and have them tested for diseases or pathogens of interest.
Veterinary Services animal health officials will contact the consenting operations by mail, telephone, and in person visit to assess an appropriate time to administer the Phase 2 questionnaire and, if the producer consents, collect biological samples for testing.
The sampling design is a multi-stage stratified random sample with unequal probabilities of selection. The statistical estimation will be undertaken using either SAS survey procedures or SUDAAN. Both software packages use a Taylor series expansion to estimate appropriate variances for the stratified, weighted data.
APHIS–NAHMS’ goal is to produce descriptive statistics (proportions or means) with a coefficient of variation (CV) of 20 percent or less. If possible, given adequate response rates, estimates will be produced nationally, by region (West, Central, Northeast, Southeast), and by size category (1–19, 20–99, 100–499, and 500 or more adult ewes).
In order to meet the precision criteria within each of the given stratification cells, we require an overall sample size of approximately 807 assuming that a simple random sample with a perfect response rate is taken. However, due to practical considerations, we must account for the expected completion rate of approximately 56 percent for Phase 1, 55 percent turnover to participate in Phase 2, an expected Phase 2 completion rate of 61 percent, and an expected design effect of approximately 1.15 (derived from a sample of questions from NAHMS Sheep 2011) to obtain estimates meeting the precision criterion of aiming for a CV of 20 percent or less. An overall sample size of 4,970 is required after adjusting for these factors.
Tables B.1 and B.2 in Appendix B show estimates of precision based on the total sample of 4,970, Nationally, by region, and by herd size, for Phases 1 and 2. All of the estimated CVs for Phase 1 and most of the estimated CVs for Phase 2 are expected to be within the desired range.
In order to produce estimates at the state level for California, we require a sample size of approximately 1,000 to meet a 20 percent CV estimate at the state level. See Table B.3 in Appendix B for estimates of precision for estimates generated for California.
Reporting strata may be adjusted depending on the number of respondents. In general, if sample sizes are too small or CVs too large, those estimates are not published.
There are no unusual problems requiring specialized sampling procedures and data collection cycles.
Any use of periodic (less frequent than annual) data collection cycles to reduce burden:
The data collection described is not planned to be carried out on an annual or less than annual frequency basis.
3. Describe methods to maximize response rates and to deal with issues of non-response. The accuracy and reliability of information collected must be shown to be adequate for intended uses. For collections based on sampling, a special justification must be provided for any collection that will not yield "reliable" data that can be generalized to the universe studied.
The study minimizes collection of data to that which is absolutely necessary to meet the stated objectives. Questionnaires are extensively reviewed by APHIS staff, NASS staff, and industry experts.
The Sheep 2024 study lead has made numerous contacts and collaborative efforts to identify the information needs of the sheep industry and the best way to ask for that information via questionnaire.
Skip logic is used in both Phase 1 and 2 questionnaires to guide respondents to sections relevant to their operation and practices and avoid sections that would not be applicable or valuable for their operation.
Data collectors and data handlers will have been trained on data and information security guidelines.
For Phase 1 data collection, APHIS–NAHMS staff will develop training materials, including an interviewer’s manual, for NASS enumerators that explain the purpose of the study, benefits of participation to producers and to the industry, and address anticipated difficulties with questions. APHIS–NAHMS and NASS will co-lead training meetings with NASS staff and enumerators. APHIS–NAHMS field coordinators will be invited to participate in the NASS enumerator training.
For Phase 2 data collection, APHIS–NAHMS coordinators will receive specialized training via APHIS–NAHMS staff and will use that information to train the other APHIS–VS data collectors in their state.
Contacts will take place during and after the administration of the NASS January 2024 Sheep and Goats Survey. Producers of large operations will be contacted only once for the completion of the NASS January 2024 Sheep and Goats Survey and then the NAHMS Sheep 2024 Phase 1 questionnaire, rather than two separate contacts if the study administration windows did not overlap. Minimal overlap between the NASS and NAHMS sheep study samples is expected for the very small and small operations and moderate overlap is expected for the medium-sized operations.
The study has been announced by and is supported by the American Sheep Industry.
Promotional materials will be published to announce the upcoming study to potential study participants and stakeholders via stakeholder releases, social media releases, and other communications with industry and related groups.
Presurvey letters will be sent to selected producers prior to the study to notify them of the benefits of participation to them and to the industry and the upcoming study activities and timelines.
Reminder cards will be sent to producers to encourage participation in the study.
Thank you cards will be sent to producers who complete Phase 1 of the study.
Data collectors will contact producers to set up a convenient time for the producer to complete the questionnaire (and biological sampling in the case of the Phase 2 contacts).
NASS enumerators have gone through specific training to help them answer questions of reluctant producers to maximize response rates. Training for the VS data collectors will include specific suggestions from the NASS trainers based upon their experience in avoiding refusals.
Nonresponse adjustment:
Baseline response rates are taken from the NAHMS Goat 2019, Sheep 2011, and Sheep 2001 studies and are shown in Tables B.1 and B.2 in Appendix B.
APHIS will adjust selection weights, which will be provided by NASS, for non-response using NASS-supplied stratification variables. Weights of eligible non-respondents will be transferred to responding sheep operations that are most similar based on available data, including the state and size category stratification variables. The non-response adjustment will use the method of propensity scores, in which a logistic regression model is constructed to predict the probability of responding. The inverse of this probability is the nonresponse adjustment.
If the respondents differ substantially from the non-respondents, then there is potential for bias. NASS’ List Frame data may be available for both respondents and non-respondents to allow for examination of potential differences in type of responding and non-responding sheep operations. If needed, APHIS will perform a non-response bias analysis to investigate unexpected response patterns to guide future sampling efforts. If significant nonresponse bias is found, the factors contributing to the bias will be incorporated into the nonresponse weight adjustment using post-stratification raking procedures.
Sampling and design strategies:
The study sample will be a sub-sample of respondents to the NASS January 2024 Sheep and Goats Survey. Both the Sheep 2011 and Sheep 2001 studies used this same approach and have some of the lowest ineligible rates of all APHIS–NAHMS studies.
Multiple mode options for response were chosen to meet the varied response mode preferences of producers. Preferred response modes vary across the population, and so making available a selection of response opportunities to fit producer’s schedules and preferences has been important to maximizing response in a COVID-19-influenced environment and will continue to be important going forward.
In-person interview options are planned to be included in both phases of the study. Previous APHIS–NAHMS studies that included in-person interview options, including the Goat 2019 and Sheep 2011 studies, tend to have greater completion rates compared to studies for which that option is not available.
4. Describe any tests of procedures or methods to be undertaken. Testing is encouraged as an effective means of refining collections of information to minimize burden and improve utility. Tests must be approved if they call for answers to identical questions from 10 or more respondents. A proposed test or set of tests may be submitted for approval separately or in combination with the main collection of information.
APHIS and NASS will pretest the survey prior to field enumeration, involving fewer than 10 respondents. APHIS will use the results of these pretests to refine the surveys in order to reduce respondent burden and improve the accuracy and usefulness of the information. The pretested and revised questions from the NAHMS Sheep 2011, 2001, and 1996 Studies will be used as a baseline, where possible, in order to borrow from the work performed during those studies and to ensure that trends on particular topics can be drawn across the studies. The final questionnaires will have been reviewed by a variety of experts, including academic researchers, industry representatives, extension agents, veterinarians, health specialists, and epidemiologists.
5. Provide the name and telephone number of individuals consulted on statistical aspects of the design and the name of the agency unit, contractor(s), grantee(s), or other person(s) who will actually collect and/or analyze the information for the agency.
The statistical aspects of the design were coordinated by:
- Mr. Matthew Branan, Mathematical Statistician, National Animal Health Monitoring System, USDA, APHIS, VS, CEAH, Fort Collins, CO (970-494-7349).
- Mr. Matthew Vuolo, Mathematical Statistician, National Animal Health Monitoring System, USDA, APHIS, VS, CEAH, Fort Collins, CO (970-494-4179).
For survey design and methodology and for a NASS review of the OMB package submission, NAHMS will coordinate with survey methodologists reporting to:
- Mr. Daniel Beckler, Chief, Standards and Survey Development Methodology Branch, USDA, NASS, Washington, DC (202-720-8858).
The actual data collection will be conducted by NASS enumerators (Phase 1) and APHIS-designated data collectors (Phase 2). Contact persons for data collection are:
- Mr. Gerald Tillman, Chief, Survey Administration Branch, USDA, NASS, Washington, DC (202-720-3895).
- Dr. Rosemary Sifford, Deputy Administrator, Veterinary Services, USDA, APHIS, Washington, DC (202-799-7147).
- Dr. Amy Delgado, Director, Center for Epidemiology and Animal Health, USDA APHIS, VS, CEAH, Fort Collins, CO (970-494-7302).
Analysis of the data will be accomplished by APHIS–NAHMS veterinarians, epidemiologists, and statisticians under the direction of:
- Dr. Katherine Marshall, Assistant Director, National Animal Health Monitoring System, USDA APHIS, VS, CEAH, Fort Collins, CO (970-494-7259).
Appendix A: State selection
State selection was performed based on the percentage of sheep inventory and operations by state. State-level percentage data by operation type were taken from the Census of Agriculture and NASS January 2022 Sheep and Goats report data. The overall inventory and operation counts, by year, are given in Table A.1, while state-level inventory and operation counts are presented in Table A.2. Historical sheep inventory and numbers of sheep operations were taken from the same two reports and are depicted in Figures A.1–A.3.
Table A.1: Numbers of operations with any sheep or lambs, operations with any adult ewes, inventory of sheep and lambs, and inventory of adult ewes from the NASS Census of Agriculture, by year, Nationally, in the 30 study states, and as a ratio of the 30 study states to National counts.
|
|
|
Year |
||||
Metric |
Type |
Scope |
1997 |
2002 |
2007 |
2012 |
2017 |
Inventory |
Ewes |
30 states |
4,309,849 |
3,378,694 |
3,270,574 |
2,726,286 |
NA |
National |
4,579,121 |
3,632,196 |
3,516,409 |
2,967,908 |
NA |
||
Ratio |
94.1% |
93.0% |
93.0% |
91.9% |
NA |
||
Sheep and lambs |
30 states |
7,634,096 |
5,929,176 |
5,413,728 |
4,940,284 |
4,932,395 |
|
National |
8,083,457 |
6,341,799 |
5,819,162 |
5,364,844 |
5,391,252 |
||
Ratio |
94.4% |
93.5% |
93.0% |
92.1% |
91.5% |
||
Operations |
Ewes |
30 states |
55,784 |
56,384 |
57,334 |
55,194 |
NA |
National |
65,505 |
66,769 |
68,222 |
65,690 |
NA |
||
Ratio |
85.2% |
84.4% |
84.0% |
84.0% |
NA |
||
Sheep and lambs |
30 states |
65,379 |
62,109 |
69,889 |
74,556 |
85,495 |
|
National |
77,112 |
73,814 |
83,134 |
88,338 |
101,387 |
||
Ratio |
84.8% |
84.1% |
84.1% |
84.4% |
84.3% |
||
Table A.2: Sheep and lamb inventory and number of operations with sheep and lambs from the 2017 Census of Agriculture and sheep and lamb inventory and inventory of adult ewes from the NASS January 2022 Sheep and Goats Survey, by state. The 30 selected study states are highlighted in grey. |
||||||||
|
2017 Census of Agriculture |
NASS January 2022 Sheep and Goats |
||||||
|
All sheep and lamb inventory |
Operations with sheep and lambs |
All sheep and lamb inventory |
Ewe inventory |
||||
State |
No. |
Pct. |
No. |
Pct. |
No. |
Pct. |
No. |
Pct. |
TX |
729,438 |
13.5 |
14,672 |
14.5 |
700,000 |
13.8 |
430,000 |
14.8 |
CA |
475,291 |
8.8 |
3,807 |
3.8 |
575,000 |
11.4 |
270,000 |
9.3 |
CO |
414,672 |
7.7 |
1,731 |
1.7 |
430,000 |
8.5 |
155,000 |
5.3 |
WY |
367,702 |
6.8 |
859 |
0.8 |
330,000 |
6.5 |
215,000 |
7.4 |
UT |
300,749 |
5.6 |
1,898 |
1.9 |
270,000 |
5.3 |
194,000 |
6.7 |
ID |
248,289 |
4.6 |
1,447 |
1.4 |
230,000 |
4.5 |
113,000 |
3.9 |
SD |
233,006 |
4.3 |
1,337 |
1.3 |
235,000 |
4.6 |
146,000 |
5.0 |
MT |
218,544 |
4.1 |
1,383 |
1.4 |
190,000 |
3.8 |
122,000 |
4.2 |
OR |
177,646 |
3.3 |
3,263 |
3.2 |
145,000 |
2.9 |
82,000 |
2.8 |
AZ |
177,392 |
3.3 |
7,509 |
7.4 |
100,000 |
2.0 |
56,000 |
1.9 |
IA |
167,208 |
3.1 |
2,801 |
2.8 |
160,000 |
3.2 |
87,000 |
3.0 |
OH |
127,501 |
2.4 |
4,123 |
4.1 |
127,000 |
2.5 |
76,000 |
2.6 |
MN |
116,311 |
2.2 |
2,248 |
2.2 |
112,000 |
2.2 |
63,000 |
2.2 |
MO |
111,621 |
2.1 |
3,103 |
3.1 |
97,000 |
1.9 |
62,000 |
2.1 |
NM |
105,896 |
2.0 |
4,047 |
4.0 |
90,000 |
1.8 |
54,000 |
1.9 |
PA |
94,370 |
1.8 |
3,749 |
3.7 |
96,000 |
1.9 |
60,000 |
2.1 |
MI |
89,270 |
1.7 |
2,483 |
2.4 |
87,000 |
1.7 |
46,000 |
1.6 |
VA |
82,661 |
1.5 |
2,646 |
2.6 |
72,000 |
1.4 |
46,000 |
1.6 |
WI |
80,688 |
1.5 |
2,845 |
2.8 |
82,000 |
1.6 |
50,000 |
1.7 |
NY |
80,195 |
1.5 |
2,113 |
2.1 |
80,000 |
1.6 |
49,000 |
1.7 |
NV |
76,074 |
1.4 |
328 |
0.3 |
60,000 |
1.2 |
44,000 |
1.5 |
KS |
73,526 |
1.4 |
1,234 |
1.2 |
65,000 |
1.3 |
35,000 |
1.2 |
ND |
70,182 |
1.3 |
573 |
0.6 |
62,000 |
1.2 |
43,000 |
1.5 |
KY |
69,933 |
1.3 |
2,818 |
2.8 |
59,000 |
1.2 |
36,000 |
1.2 |
OK |
69,094 |
1.3 |
2,216 |
2.2 |
52,000 |
1.0 |
31,000 |
1.1 |
NE |
63,043 |
1.2 |
1,153 |
1.1 |
73,000 |
1.4 |
49,000 |
1.7 |
IN |
62,085 |
1.2 |
2,316 |
2.3 |
60,000 |
1.2 |
39,000 |
1.3 |
TN |
60,809 |
1.1 |
2,503 |
2.5 |
49,000 |
1.0 |
30,000 |
1.0 |
IL |
57,956 |
1.1 |
1,870 |
1.8 |
53,000 |
1.0 |
35,000 |
1.2 |
WA |
52,329 |
1.0 |
2,281 |
2.2 |
50,000 |
1.0 |
28,000 |
1.0 |
WV |
34,865 |
0.6 |
1,226 |
1.2 |
32,000 |
0.6 |
22,000 |
0.8 |
NC |
32,729 |
0.6 |
1,679 |
1.7 |
29,000 |
0.6 |
17,000 |
0.6 |
HI |
27,181 |
0.5 |
548 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
GA |
24,805 |
0.5 |
1,208 |
1.2 |
|
|
|
|
AL |
24,650 |
0.5 |
1,062 |
1.0 |
|
|
|
|
FL |
24,504 |
0.5 |
1,666 |
1.6 |
|
|
|
|
MD |
23,399 |
0.4 |
925 |
0.9 |
|
|
|
|
AR |
22,620 |
0.4 |
1,053 |
1.0 |
|
|
|
|
NJ |
17,791 |
0.3 |
1,047 |
1.0 |
|
|
|
|
VT |
17,367 |
0.3 |
704 |
0.7 |
|
|
|
|
MS |
16,640 |
0.3 |
748 |
0.7 |
|
|
|
|
ME |
13,488 |
0.3 |
738 |
0.7 |
|
|
|
|
MA |
13,310 |
0.2 |
728 |
0.7 |
|
|
|
|
LA |
13,161 |
0.2 |
785 |
0.8 |
|
|
|
|
SC |
12,627 |
0.2 |
738 |
0.7 |
|
|
|
|
NH |
8,213 |
0.2 |
502 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
CT |
6,049 |
0.1 |
428 |
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
RI |
1,781 |
0.0 |
108 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
DE |
1,758 |
0.0 |
89 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
AK |
833 |
0.0 |
49 |
0.0 |
|
|
|
|
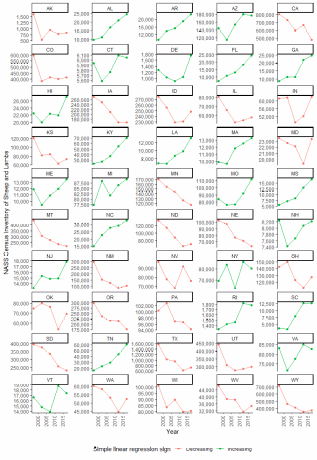
Figure A.1: NASS Census of Agriculture sheep and lamb inventory, by year 1997 to 2017 and by state
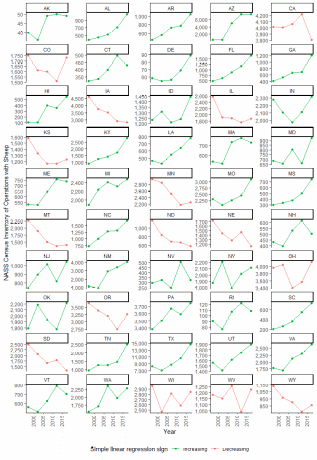
Figure A.2: NASS Census of Agriculture counts of operations with sheep, by year from 1997 to 2017 and by state
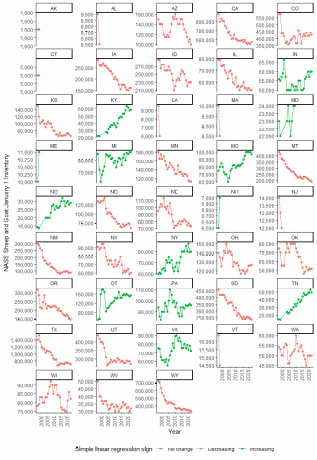
Figure A.3: NASS Sheep and Goats Survey of January 1 sheep and lamb inventory, by year from 1996 to 2022 and by state
As a comparison, the states included in previous NAHMS Sheep studies are depicted in Figure A.4, including by region for Sheep 2001 and 2011.
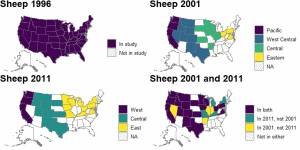
Figure A4: States included in previous NAHMS Sheep studies.
Finally, the 30 selected study states, by region, are presented in Figure A.5. Note that Texas is split into two portions roughly along I-352.
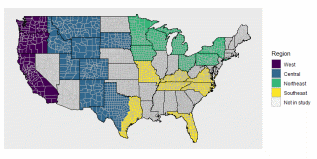
Figure A.5: Proposed regions for Sheep 2024.
Appendix B: Expected estimates of precision
Estimates of percentages of operations and percentages of animals will be reported at the national level, by region, and by size category (number of ewes).
Estimates of precision are shown for proportions of 0.5, 0.25, and 0.1. As an example, for the West category and an expected proportion of 0.5, the CV is 4.6 percent. Only estimates in Phase 2 down to estimates of proportions of 0.10 or less have CV estimates that exceed 20.0 percent, with the largest being for large operations (with 500 or more ewes), at a CV of 32.7, which is limited by the population size in that herd size category.
Table B.1. Precision of estimates by region and by expected proportion, at 95 percent confidence for Phases 1 and 2.
Region (states) |
Approximate overall sample size |
Proportion estimate |
Phase 1 CV estimate (%) |
Phase 2 CV estimate (%) |
West (CA, OR, WA) |
1,300 |
0.50 |
4.1 |
7.3 |
|
0.25 |
7.1 |
12.7 |
|
|
0.15 |
9.8 |
17.4 |
|
|
0.10 |
12.3 |
21.9 |
|
Central (CO, ID, MT, NM, SD, Central TX, UT, WY) |
1,640 |
0.50 |
3.4 |
6.0 |
|
0.25 |
5.9 |
10.5 |
|
|
|
8.2 |
14.4 |
|
|
0.10 |
10.2 |
18.1 |
|
Northeast (IA, MI, MN, NY, OH, PA, WI) |
1,100 |
0.50 |
4.2 |
7.3 |
|
0.25 |
7.3 |
12.7 |
|
|
0.15 |
10.0 |
17.4 |
|
|
0.10 |
12.6 |
21.9 |
|
Southeast (FL, KY, MO, NC, TN, Southeast TX, VA) |
900 |
0.50 |
4.8 |
8.3 |
|
0.25 |
8.2 |
14.4 |
|
|
0.15 |
11.3 |
19.7 |
|
|
0.10 |
14.2 |
24.9 |
|
Total
|
4,940 |
0.50 |
2.0 |
3.5 |
|
0.25 |
3.4 |
6.0 |
|
|
0.15 |
4.7 |
8.3 |
|
|
0.10 |
6.0 |
10.5 |
Table B.2. Precision of estimates by herd size and by expected proportion, at 95 percent confidence for Phases 1 and 2.
Herd size (number of ewes) |
Approximate overall sample size |
Proportion estimate |
Phase 1 CV estimate (%) |
Phase 2 CV estimate (%) |
Very small (1–19)
|
1,340 |
0.50 |
4.0 |
7.0 |
|
0.25 |
6.9 |
12.1 |
|
|
0.15 |
9.5 |
16.6 |
|
|
0.10 |
12.0 |
20.9 |
|
Small (20–99)
|
1,930 |
0.50 |
3.2 |
5.6 |
|
0.25 |
5.5 |
9.7 |
|
|
0.15 |
7.6 |
13.3 |
|
|
0.10 |
9.6 |
16.8 |
|
Medium (100–499)
|
1,200 |
0.50 |
4.0 |
7.1 |
|
0.25 |
6.9 |
12.3 |
|
|
0.15 |
9.4 |
17.0 |
|
|
0.10 |
11.9 |
21.4 |
|
Large (500 or more)
|
470 |
0.50 |
5.9 |
11.1 |
|
0.25 |
10.3 |
19.4 |
|
|
0.15 |
14.1 |
26.6 |
|
|
0.10 |
17.8 |
33.5 |
|
Total
|
4,940 |
0.50 |
2.0 |
3.5 |
|
0.25 |
3.4 |
6.0 |
|
|
0.15 |
4.7 |
8.3 |
|
|
0.10 |
6.0 |
10.5 |
Table B.3. Precision of estimates for proportions at the state level in California, by expected proportion, at 95 percent confidence for Phases 1 and 2.
Approximate overall sample size |
Proportion estimate |
Phase 1 CV estimate (%) |
Phase 2 CV estimate (%) |
1,000 |
0.50 |
4.5 |
8.3 |
|
0.25 |
7.8 |
14.4 |
|
0.15 |
10.7 |
19.8 |
|
0.10 |
13.5 |
24.9 |
Appendix C: Response rates
Table C.1. Completion counts and rates from the NAHMS Goat 2019, Sheep 2011, and Sheep 2001 studies, by phase.
Study |
Phase |
Sample |
Complete |
% Complete |
Goat 2019 |
1 |
4,770 |
1,840 |
38.6 |
Turnover |
1,840 |
1,320 |
71.2 |
|
2 |
1,320 |
779 |
59.0 |
|
Biologics – Blood and swab |
779 |
581 |
74.6 |
|
Biologics – Fecal pathogen |
779 |
188 |
24.1 |
|
Biologics – Parasites fecal egg count |
779 |
627 |
80.5 |
|
Biologics – Parasites resistance |
627 |
206 |
32.9 |
|
Sheep 2011 |
1 |
4,920 |
3,256 |
66.2 |
Turnover |
3,256 |
1,241 |
38.1 |
|
2 |
1,241 |
761 |
61.3 |
|
Biologics – Blood and swab |
761 |
571 |
75.0 |
|
Biologics – Fecal pathogen |
761 |
247 |
32.5 |
|
Biologics – Parasites fecal egg count |
761 |
538 |
70.7 |
|
Sheep 2001 |
1 |
5,080 |
3,210 |
63.2 |
Turnover |
3,210 |
1,785 |
55.6 |
|
2 |
1,775 |
1,101 |
62.0 |
The average response rates, by phase, are shown in Table C.2.
Table C.2. Average completion rates from the NAHMS Goat 2019, Sheep 2011, and Sheep 2001 studies, by phase.
Phase |
% Complete |
1 |
56 |
Turnover |
55 |
2 |
61 |
Biologics – Blood and swab |
75 |
Biologics – Fecal pathogen |
28 |
Biologics – Parasites fecal egg count |
76 |
Biologics – Parasites resistance |
33 |
Appendix D: Burden estimates
Table D.1. Response burden estimates from the NAHMS Goat 2019 and Sheep 2011 Studies (in minutes).
Study |
Phase |
Approximate Burden (min) |
Sheep 2011 |
1 |
64 |
2 |
90 |
|
Goat 2019 |
2 |
87 |
Biologics – Parasites fecal egg count |
168 |
|
Biologics – Blood and swab |
204 |
|
Biologics – Fecal pathogen |
162 |
1 Arizona, California, Colorado, Florida, Georgia, Idaho, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Virginia, Washington, Wisconsin, Wyoming
2 Counties in Texas that are classified into the Southeast region are: Anderson, Angelina, Aransas, Atascosa, Austin, Bastrop, Bee, Bowie, Brazoria, Brazos, Brooks, Burleson, Caldwell, Calhoun, Cameron, Camp, Cass, Chambers, Cherokee, Collin, Colorado, Dallas, Delta, De Witt, Duval, Ellis, Fannin, Fayette, Fort Bend, Franklin, Freestone, Galveston, Goliad, Gonzales, Grayson, Gregg, Grimes, Guadalupe, Hardin, Harris, Harrison, Henderson, Hidalgo, Hopkins, Houston, Hunt, Jackson, Jasper, Jefferson, Jim Hogg, Jim Wells, Karnes, Kaufman, Kenedy, Kleberg, Lamar, Lavaca, Lee, Leon, Liberty, Limestone, Live Oak, Madison, Marion, Matagorda, McMullen, Milam, Montgomery, Morris, Nacogdoches, Navarro, Newton, Nueces, Orange, Panola, Polk, Rains, Red River, Refugio,
Robertson, Rockwall, Rusk, Sabine, San Augustine, San Jacinto, San Patricio, Shelby, Smith, Starr, Titus, Trinity, Tyler, Upshur, Van Zandt, Victoria, Walker, Waller, Washington, Wharton, Willacy, Wilson, Wood, Zapata.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 0000-00-00 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy