IC 0694-0088 SUPPORTING STATEMENT 10 Oct 2023
IC 0694-0088 SUPPORTING STATEMENT 10 Oct 2023.docx
Simple Network Application Process and Multipurpose Application Form
OMB: 0694-0088
SUPPORTING STATEMENT
U.S. Department of Commerce Bureau of Industry and Security
Simple Network Application Process and Multipurpose Application
Form OMB No. 0694-0088
Justification:
This is a request for an emergency approval to add to this information collection the “Notified Integrated Circuits (NIC)” rule under EAR 740.8. In § 740.8, which prior to the effective date of this rule was reserved, today’s AC/S IFR adds new license exception NAC. This license exception is for less powerful ICs under ECCN 3A090.b (i.e., ICs designed or marketed for use in datacenters) and 3A090.a (i.e., ICs not designed or marketed for use in datacenters and that do have a ‘total processing performance’ of 4800 or more). NAC is available for exports, reexports, and transfers in or within Country Groups D:1, D:4, or D:5 with different requirements applicable to China and Macau. The purpose of the notification process, which is only required for exports and reexports to China and Macau, is to provide BIS and its interagency export controls partners the opportunity to evaluate the national security risk posed by ICs that fall within this parameter.
This license exception as specified under the paragraph (a) (Eligibility requirements) will authorize export, reexport, and transfer (in-country) of any item classified in ECCNs 3A090, 4A090, 3A001.z, 4A003.z, 4A004.z, 4A005.z, 5A002.z, 5A004.z, 5A992.z, 5D002.z, or 5D992.z, except for items designed or marketed for use in a datacenter and meeting the parameters of 3A090.a. License Exception NAC authorizes exports, reexports, or transfers (in-country) to any destination specified in Country Groups D:1, D:4, or D:5, provided the criteria specified under paragraphs (a) and (b) are met. For exports and reexports to China or Macau, in addition to meeting the criteria under paragraphs (a) and (b), the notification requirements under paragraph (c) of License Exception NAC must all be met. The notification requirement does not apply to transfers (in-country) within China and Macau.
Paragraph (a)(1) (Written purchase order) requires that any export or reexport authorized under License Exception NAC must be made pursuant to a written purchase order, except for commercial samples which are not subject to this purchase order requirement. Exports, reexports, or transfers (in-country) to or within any other destination identified under Country Groups D:1, D:4, or D:5 are authorized under License Exception NAC, provided the criteria under paragraphs (a) and (b) are met.
Paragraph (a)(2) (Notification to BIS) specifies that for exports or reexports to China or Macau, you must notify BIS prior to exporting or reexporting, according to the procedures set forth in paragraph (c) of License Exception NAC. Paragraph (a)(2) specifies that if you intend to engage in multiple exports or reexports after the signing of the purchase order, you need only notify BIS prior to the first export or reexport. A notification under paragraph (a)(2) is not required for transfers (in-country) within China or Macau.
Paragraph (b) (Restrictions) apply to all exports, reexports, or transfers (in-country) authorized under License Exception NAC. Paragraph (b)(1) (Prohibited end uses and end users) specifies that License Exception NAC is not able to overcome any part 744 or 746 license requirements. The restriction under paragraph (b)(2) (‘Military end use’ or ‘military end user’) specifies that no exports, reexports, or transfers (in-country) may be made under License Exception NAC to or for a ‘military end use’ as defined in § 744.21(f) or ‘military end user’ as defined in defined in § 744.21(g). This ‘military end use’ or ‘military end use’ restriction applies to a broader country scope than prohibited under §§ 744.17 and 744.21.
Paragraph (c) (Prior notification procedures) specifies the notification requirements that must be followed prior to making any export or reexport to China or Macau under License Exception NAC. Paragraph (c)(1) (Procedures) specifies the requirement to make this notification prior to using License Exception NAC as well as what Blocks need to be completed in SNAP-R for submitting a notification request. You do not need to submit a commodity classification determination from BIS with your notification, but doing so will be helpful in limiting any concerns associated with the technical nature of the item because BIS will already be familiar with the item’s performance characteristics if it has conducted a classification review.
Paragraph (c)(2) (Action by BIS) specifies that within two business days of the NAC notification being accepted in SNAP-R, BIS will return the notification without action if the information provided is incomplete. BIS intends during the 21-day review period, to review the notification together with the other export control agencies. Paragraph (c)(3) (Status of pending NAC notification requests) describes the process for entities to follow in BIS’s System for Tracking Export License Applications (STELA) (https://snapr.bis.doc.gov/stela) to obtain the status of a pending NAC notification or verify the status in BIS’s Simplified Network Applications Processing Redesign (SNAP-R) System. Paragraph (c)(3) also specifies that if no objection to a NAC notification is raised, STELA will, on the twenty-first business day following the date of registration, provide a confirmation of that fact and a NAC confirmation number to be submitted in the Automated Export System (AES). Paragraph (c)(3) also indicates that if the NAC notification it not approved because a majority of the agencies raised an objection, STELA and SNAP-R will indicate that a license is required.
Explain the circumstances that make the collection of information necessary.
Section 1761(h) under the Export Control Reform Act (ECRA) of 2018, authorizes the President and the Secretary of Commerce to issue regulations to implement the ECRA including those provisions authorizing the control of exports of U.S. goods and technology to all foreign destinations, as necessary for the purpose of national security, foreign policy and short supply, and the provision prohibiting U.S. persons from participating in certain foreign boycotts. Export control authority has been assigned directly to the Secretary of Commerce by the ECRA and delegated by the President to the Secretary of Commerce. This authority is administered by the Bureau of Industry and Security through the Export Administration Regulations (EAR).
BIS administers a system of export, re-export, and in-country transfer controls in accordance with the EAR. In doing so, BIS requires that parties wishing to engage in certain transactions apply for licenses, submit Encryption Review Requests, or submit notifications to BIS. BIS also reviews, upon request, specifications of various items and determines their proper classification under the EAR. Currently, members of the public submit these applications, requests, and notifications to BIS in one of four ways, via:
1. BIS’ Simplified Network Application Process - Redesign (SNAP-R);
2. BIS’ System for Tracking Export License Applications (STELA);
3. Multipurpose Application, Form BIS 748P, and its two appendices the BIS 748P-A (item appendix) and the BIS 748P-B (end-user appendix); or
4. Advisory opinion requests, pursuant to the instructions in § 748.3(c) of the EAR.
Specific
to the submission of applications, requests and notifications, BIS
will, under one or more of the circumstances specified in
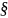 748.1(d)(1) of the EAR, accept paper submissions of license
applications, notifications, and requests. However, BIS has not
recently received any paper submissions of license applications,
notifications, or requests.
748.1(d)(1) of the EAR, accept paper submissions of license
applications, notifications, and requests. However, BIS has not
recently received any paper submissions of license applications,
notifications, or requests.
In many instances, BIS needs additional documents to act on the submission. For submissions made electronically via SNAP-R, the applicant must scan and attach the additional documents in SNAP-R.
For documents that relate to paper submissions, the documents can be mailed or delivered to BIS with the BIS 748P form, as appropriate.
2. Explain how, by whom, how frequently, and for what purpose the information will be used. If the information collected will be disseminated to the public or used to support information that will be disseminated to the public, then explain how the collection complies with all applicable Information Quality Guidelines.
Export information collected either electronically or from the Multipurpose Application (Forms BIS-748P, 748P-A and 748P-B) is used by BIS as the basis for decisions to grant licenses for export and re-export, for national security reviews of encryption items, and for classifications of items that are controlled for reasons of national security, short supply, or foreign policy. These decisions are typically made on a case-by-case basis and are dependent upon the information provided and the policies in effect at the time of the transaction. In many cases, this information is shared with other Federal agencies such as the Department of Defense, State Department, and Department of Energy, to obtain their recommendations on these decisions.
Both the paper and electronic versions of the Multipurpose Application provide detailed instructions and explanations of what data is required in each field. In addition, the SNAP-R system includes a large number of software validations to ensure high quality data.
BIS is revising and renewing this information collection and requesting an increase in burden hours due to an expected increase of license application submissions resulting from the publication of the following rules:
Information Security Controls: Cyber Security Items: This rule established a new control on certain cybersecurity items for National Security (NS) and Anti-terrorism (AT) reasons, as well as adding a new License Exception Authorized Cybersecurity Exports (ACE) that authorizes exports of these items to most destinations except in certain circumstances. These items warrant controls because these tools could be used for surveillance, espionage, or other actions that disrupt, deny, or degrade the network or devices on it. This rule also corrects Export Control Classification Number (ECCN) 5D001 in the Commerce Control List.
Implementation of Certain 2021 Wassenaar Arrangement Decisions on Four Section 1758 Technologies: The Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) maintains, as part of its Export Administration Regulations (EAR), the Commerce Control List (CCL), which identifies certain items subject to Department of Commerce (Commerce) jurisdiction. Commerce is revising the CCL, as well as corresponding parts of the EAR, to implement controls on four technologies. These changes reflect certain controls decided by governments participating in the Wassenaar Arrangement on Export Controls for Conventional Arms and Dual-Use Goods and Technologies (WA) at the December 2021 WA Plenary meeting. These four technologies meet the criteria of Section 1758 of the Export Control Reform Act (ECRA) pertaining to emerging and foundational technologies. Accordingly, BIS is accelerating their publication in this interim final rule and will publish the remaining WA-agreed controls in a later rule. These technologies are two substrates of ultra-wide bandgap semiconductors (Gallium Oxide (Ga2 O3) and diamond), Electronic Computer Aided Design (ECAD) software specially designed for the development of integrated circuits with any Gate-All-Around Field-Effect Transistor (GAAFET) structure, and pressure gain combustion (PGC) technology for the production and development of gas turbine engine components or systems.
Expansion of Nuclear Nonproliferation Controls on the People’s Republic of China and Macau: In response to China’s increased military modernization efforts, military-civil fusion, and involvement in unsafeguarded nuclear activities, the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) is amending the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) by adding additional nuclear nonproliferation controls on China and Macau. This change specifically applies Nuclear Nonproliferation (NP) column 2 reasons for control. These controls further allow the U.S. Government to monitor the exports of these items. This ensures that they are only being used in peaceful activities such as commercial nuclear power generation, medicine, and non-military related industries.
Implementation of Additional Export Controls: Certain Advanced Computing and Semiconductor Manufacturing Items; Supercomputer and Semiconductor End Use; Entity List Modification: This rule amends the EAR to implement necessary controls on advanced computing integrated circuits (ICs), computer commodities that contain such ICs, and certain semiconductor manufacturing items. In addition, BIS is expanding controls on transactions involving items for supercomputer and semiconductor manufacturing end uses. Advanced computing commodities and supercomputers can be used for purposes detrimental to U.S. national security and foreign policy interests, including for weapons of mass destruction, military modernization, and human rights abuses. Certain semiconductor manufacturing equipment is needed to develop, produce, or use ICs. To minimize short term impact on the semiconductor supply chain from this rule, BIS is establishing a 6-month Temporary General License to permit specific, limited manufacturing activities in China related to items destined for use outside China and is identifying a model certificate that may be used in compliance programs to assist, along with other measures, in conducting due diligence.
Implementation of Additional Export Controls: Certain Advanced Computing Items; Supercomputer and Semiconductor End Use; Updates and Corrections: On October 7, BIS released the interim final rule (IFR), “Implementation of Additional Export Controls: Certain Advanced Computing and Semiconductor Manufacturing Items; Supercomputer and Semiconductor End Use; Entity List Modification” (October 7 IFR) (87 FR 62186), which amended the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) to implement controls on advanced computing integrated circuits (ICs), computer commodities that contain such ICs, and certain semiconductor manufacturing items, and to make other EAR changes to implement appropriate related controls, including on certain “U.S. person” activities. Today’s Advanced Computing/Supercomputing IFR (AC/S IFR) addresses comments received in response to only the part of the October 7 IFR that controls advanced computing ICs and computer commodities that contain such ICs. This rule also makes other changes to be more effective and less burdensome, including by correcting and clarifying the controls to more effectively achieve the policy objectives identified in the October 7 IFR. Today’s AC/S IFR is published concurrently with a second BIS IFR, Expansion of Export Controls on Semiconductor Manufacturing Items, which addresses public comments received in response to other portions of the October 7 IFR. Together, these IFRs revise the October 7 IFR controls to more effectively achieve BIS’s targeted national security policy objectives. These revisions further restrict China’s ability to obtain critical technologies to modernize its military capabilities in ways that threaten the national security interests of the United States and its allies and to abuse human rights.
3. Describe whether, and to what extent, the collection of information involves the use of automated, electronic, mechanical, or other technological techniques or other forms of information technology.
BIS redesigned the SNAP system to enhance security, support electronic submission of supporting documents and provide increased functionality. BIS currently receives approximately 100% of all submissions of license applications, notifications and commodity classification and encryption registration requests electronically through the SNAP-R system. SNAP-R is located at: https://snapr.bis.doc.gov/.
Advisory opinion requests are delivered to BIS by mail, delivery service or via e-mail.
4. Describe efforts to identify duplication.
The information received when applying for an export license, classifications and advisory opinions, Encryption Review Request, or license exception AGR is unique to each application. The information is not duplicated anywhere else in Government nor is it available from any other source.
5. If the collection of information involves small businesses or other small entities, describe the methods used to minimize burden.
The information required when applying for an export license, classification request, advisory opinion, Encryption Review Request, License Exception AGR notification, and License Exception NAC notification must be submitted by exporters or their designated agents, regardless of size. This procedure, as part of the EAR, is governed by national security, foreign policy, and proliferation of weapons of mass destruction requirements. BIS maintains an active seminar and counseling program to help all businesses understand and comply with BIS requirements. BIS also maintains an informative web site that provides detailed instructions on how to comply with our paperwork requirements. This web site is located at: https://www.bis.doc.gov.
6. Describe the consequences to the Federal program or policy activities if the collection is not conducted or is conducted less frequently.
If this information were submitted less frequently, it could result in decreases and delays in trade as well as a higher number of exports to unapproved consignees with the possibility that illegal shipments would be made to countries of concern.
7. Explain any special circumstances that require the collection to be conducted in a manner inconsistent with OMB guidelines.
There are no special circumstances that require the collection to be conducted in a manner inconsistent with the guidelines in 5 CFR 1320.6.
8. Provide a copy of the PRA Federal Register notice that solicited public comments on the information collection prior to this submission. Summarize the public comments received in response to that notice and describe the actions taken by the agency in response to those comments. Describe the efforts to consult with persons outside the agency to obtain their views on the availability of data, frequency of collection, the clarity of instructions and record keeping, disclosure, or reporting format (if any), and on the data elements to be recorded, disclosed, or reported.
N/A. This is a request for an emergency approval. No FR notice for public comment was published.
9. Explain any decisions to provide payments or gifts to respondents, other than remuneration of contractors or grantees.
No payment or gift will be provided to respondents.
10. Describe any assurance of confidentiality provided to respondents and the basis for assurance in statute, regulation, or agency policy.
Section 1761(h) of the ECRA provides for the confidentiality of export licensing information submitted to the Department of Commerce.
11. Provide additional justification for any questions of a sensitive nature, such as sexual behavior and attitudes, religious beliefs, and other matters that are commonly considered private.
There are no questions of a sensitive nature.
12. Provide an estimate in hours of the burden of the collection of information.
The total estimated burden for this collection has increased by 950 hours due to the addition of the notification for exports and reexports to China and Macau in order to use new License Exception NAC. The total burden hours are now 36,689 hours. This estimate includes the increase of burden hours from the interim final rule. The burden hour estimate is detailed in the following table:
Burden Activity |
Annual Responses |
Average Minutes per Response |
Annual Burden Hours |
Commodity Classifications Without Supporting Documentation |
1,607 |
17 |
455 |
Other SNAP-R Applications Without Supporting Documentation |
17,373 |
17 |
4,922 |
Commodity Classifications With Supporting Documentation |
4,990 |
109 |
9,065 |
Other SNAP-R Applications With Significant Supporting Documentation |
10,575 |
49 |
8,636 |
Other Applications With Minimal Supporting Documentation |
38,112 |
19 |
12,069 |
EAR Amendments |
3,076 |
30 |
1,538 |
Reporting under Temporary General License |
11 |
20 |
4 |
Total |
75,744 |
29.4 |
36,689 |
The cost associated with this burden is estimated to be $ 1,284,115. This is obtained by multiplying 36,689 hours times $35 per hour.
13. Provide an estimate of the total annual cost burden to the respondents or record- keepers resulting from the collection (excluding the value of the burden hours in #12 above).
There is no additional cost to the respondent.
14. Provide estimates of annualized cost to the Federal government.
The annual cost to the Federal Government is approximately $2,556,360. This is based on licensing officers spending 45 minutes to review each of the 75,744 applications at an hourly salary of $45 per hour.
15. Explain the reasons for any program changes or adjustments reported in Items 13 or 14 of the OMB 83-I.
The burdens hours and government cost have increase due to the addition of the AI rule mentioned above.
16. For collections whose results will be published, outline the plans for tabulation and publication.
BIS publishes information based on aggregate data from export license applications.
It does not publish information that would identify the details of specific applications or requests. Section 1761(h) of the ECRA restricts release of such detailed data to Congress, the GAO, or to situations in which the Secretary (authority delegated to the Under Secretary for Industry and Security) determines that release is in the national interest.
17. If seeking approval to not display the expiration date for OMB approval of the information collection, explain the reasons why display would be inappropriate.
Not applicable.
18. Explain each exception to the certification statement identified in Item 19 of the
OMB 83-I.
Not applicable.
B. COLLECTIONS OF INFORMATION EMPLOYING STATISTICAL METHODS
Not applicable.

| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | Karen NiesVogel |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2023-10-16 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy