IdMAX Supt Stmt. 2017 Extension..
IdMAX Supt Stmt. 2017 Extension...docx
Personal Identity Validation for Routine and Intermittent Access to NASA Facilities, Sites, and Information Systems
OMB: 2700-0158
Supporting Statement
OMB Control Number 2700-0153
Personal Identity Verification for Routine and Intermittent Access to NASA Facilities, Sites, and Information Systems
Type of Information Collection: Extension without Change of a Currently Approved Information Collection
A. JUSTIFICATION
Explain the circumstances that make the collection of information necessary. Identify any legal or administrative requirements that necessitate the collection.
Homeland Security Presidential Directive (HSPD)-12 establishes the requirement for a mandatory Government-wide standard for secure and reliable forms of identification for Federal employees and contractors. As directed by HSPD-12, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 201: Personal Identity Verification of Federal Employees and Contractors and associated NIST publications establish standards and requirements for the identity verification of federal employees and contractors and for Personal Identity Verification (PIV) identity credentials to be issued. OMB policy memorandum M-05-24: Implementation of Homeland Security Presidential Directive 12 requires federal agencies to deploy products and operational systems to issue identity credentials meeting the FIPS 201.
In response to this Directive, as well as NIST and OMB guidance, NASA developed the Identity Management and Account Exchange System (IdMAX). This system manages identities, credentials, and access in an integrated, enterprise environment, to ensure that people have the access they need to further the mission of NASA, without putting NASA assets at risk.
Identity Management deals with three major facets of a person:
basic details about the person’s identity, such as name and date of birth
the affiliation that the person has with NASA, such as civil servant or contractor
the knowledge we have about the person based on investigations and records checks
Credential Management deals with the management of items that allow physical access, like doorkeys and badges, as well as items that allow access to IT systems, like userIDs/passwords and tokens.
Credential Management seeks to ensure that credentials are:
issued to the proper person
not tampered with or used by someone they do not belong to
properly revoked and disposed of when no longer valid
Access Management seeks to ensure that:
People are properly authorized to access particular NASA assets
Changes to a person’s affiliation, or the knowledge we have about that person, result in a re-assessment of appropriate access
Access is removed when a person leaves NASA
NOTE: NASA is one of the 24 federal agencies that us not using General Services Administration’s HSDP-12 compliant system. NASA determined it was more cost effective to meet HSPD-12 requirements through an independent approach (see response #4.)
2. Indicate how, by whom, and for what purpose the information is to be used.
NASA Office of Chief Information Officer and the NASA Office of Protective Services manages the collection of information from members of the public requiring access to NASA facilities and/or IT resources to include NASA contractors and grantees requiring access for 30 or more days. Information is also collected from foreign nationals seeking access to NASA facilities and/or IT resources regardless of their affiliation time.
The information collected is used for background investigation processes, establishing levels of confidence and user risk, and controlling access to NASA/federally owned/leased facilities and IT resources.
Information is collected either in person or remotely utilizing a secure information collection website. The data is utilized to create an “identity” in the IdMAX system and is affiliated with a NASA agreement (contract, grant, MOU, etc.). The identity is then approved by a NASA Affiliation Sponsor and forwarded to the applicable NASA Center Security Office for processing.
Security Office Enrollment Officials at NASA Centers collect information and documents to include demographic data, biometrics during enrollment, a photograph/digital image, and valid identity documents per NIST/FIPS requirements.
When required, NASA summarizes/submits the results of credentials issued, as reflected in the following link: http://www.whitehouse.gov/sites/default/files/omb/assets/egov_docs/hspd-12_reporting_workbook_q2fy2013_status_report.pdf
3. Describe whether, and to what extent, the collection of information involves the use of automated, electronic, mechanical, or other technological collection techniques or other forms of information technology, e.g., permitting electronic submission of responses, and the basis for the decision for adopting this means of collection. Also describe any consideration of using information technology to reduce burden.
Impacted members of the public can submit information via NASA’s secure information collection website (all information collected except the documents that must be presented face-to-face in accordance with FIP 201, NIST, etc.)
Information collected is stored, secured, and maintained electronically. Hard copies of select information, required for identity vetting, presented by the member of the public is scanned by the NASA enrollment official to include birth certificate, current driver's license or other state photo identity cards issued by Department of Motor Vehicles (or equivalent), U.S. passport, a foreign government-issued passport, Native American Tribal Photo ID.
4. Describe efforts to identify duplication.
The Identity Management and Account Exchange (IdMAX) System is the only NASA system used for managing Identity, Credential, and Access information for NASA civil servants, contractors, and affiliates. IdMAX provides access management (the authorization piece) to over 2,300 NASA applications, provides central authentication (mechanism for the person to log into the app) to over 300 NASA applications, and is the authoritative source of information for nearly all applications that utilize identity data (emergency notification, training, active directory, electronic health records, human resources, etc.). By centralizing all information collected and managing that information within IdMAX, NASA has substantially reduced the number of locations and NASA systems in which personal information for members of the public is stored.
The IdMAX credential management and universal registration client also performs all of the FIPS 201 required functions for a PIV Credential Issuance Facility. This saves NASA approximately $234 per PIV credential issued over a 5-year period, compared to the GSA shared services cost for PIV issuance. NASA realized a cost savings of approximately $16,000,000 per five year lifecycle when NASA began issuing PIV credentials (68,000 issued) compared to the cost of using the GSA shared services.
NASA utilizes OPMs Personnel Investigations Processing Systems and Central Verification System (e- QIP) to prevent duplication of investigation and vetting by providing reciprocity to members of the public who have a current investigation already completed by another agency or affiliate.
5. If the collection of information impacts small businesses or other small entities (Item 5 of OMB Form 83-I), describe any methods used to minimize burden.
Federal Information Processing Standards 201 has no exemptions or reduction of impact for small entities, therefore Small businesses and other small entities must adhere to HSPD-12 requirements to access federally owned/leased space and IT resources. However, NASA encourages small business to use the Remote Identity Invitation. Doing so reduces the burden associated with small businesses hiring an individual to gather all the information and submit. Small business representatives have expressed their satisfaction with the remote identity process.
6. Describe the consequence to Federal program or policy activities if the collection is not conducted or is conducted less frequently, as well as any technical or legal obstacles
to reducing burden.
NASA is required to adhere to HSPD 12, as well as NIST, FIPS and OMB requirements. The inability to collect and process this information would prevent members of the public from accessing federally owned/leased space used by NASA.
7. Explain any special circumstances.
NASA does not have any special circumstances associated with this information collection.
8. If applicable, provide a copy and identify the date and page number of publication in the Federal Register of the agency's notice, required by 5 CFR 1320.8(d), soliciting comments on the information collection prior to submission to OMB.
60-Day
FRN: Vol. 82, No. 73, April 18, 2017. No comments received from the
public.
30-Day
FRN: Vol. 82, No. 144, July 28, 2017. No comments received from the
public.
9. Explain any decision to provide any payment or gift to respondents, other than remuneration of contractors or grantees.
NASA does not provide any payment or gift to respondents for information collected to comply with Homeland Security Presidential Directive (HSPD)-12 requirements.
10. Describe any assurance of confidentiality provided to respondents and the basis for the assurance in statute, regulation, or agency policy.
NASA’s IdMAX system meets the privacy requirements listed in Federal Information Processing Standards Publication 201-1. This includes the assignment of a senior agency official for privacy in accordance with NASA NPD 1382.17H, the completion of a comprehensive Privacy Impact Assessment, and a published document containing a listing of all information types collected. The Privacy Impact Assessment is reviewed periodically as a part of the risk management framework process for IdMAX.
NASA incorporates a privacy policy statement link on every page where members of the public are required to enter information in IdMAX. A copy of the privacy statement is also provided to members of the public when enrolling in-person for a credential.
With regards to user privacy information, NASA protects confidentiality to the extent required by law.
The applicable NASA System of Records Notice (SORN) can be viewed at: http://www.nasa.gov/privacy/nasa_sorn_10SECR.html
11. Provide additional justification for any questions of a sensitive nature, such as sexual behavior and attitudes, religious beliefs, and other matters that are commonly considered private.
NASA does not collect information or ask questions of a sensitive nature associated with IdMAX to meet HSPD-12 requirements. NASA does not collect race and ethnicity information for identity vetting.
12. Provide estimates of the hour burden of the collection of information.
The collection of information takes an average of 10 minutes per respondent depending on the user’s requirements (i.e., new enrollment vs. update, etc.).
Annually, we have approximately 25,000 routine users and about 27,000 intermittent users that access, and input identity data into the Identity Management System:
25,000 routine users @ around 10 minutes each = 250,000 minutes
250,000/60 = 4,166 hours annually
27,000 intermittent users @ about 10 minutes each = 270,000 minutes
270,000/60 = 4,500 hours annually
Annual routine user cost: 4,167 hours x approximately $50/hr. = $208,350 annual cost
Annual intermittent user cost: 4,500 hours x approximately $50/hr. = $225,000 annual cost
Respondent |
Number of Responses |
Participation Time (minutes) |
Burden Hour |
Individual/US Citizens (routine) |
25,000 |
10 |
4,166 |
Individual/Foreign National (intermittent) |
27,000 |
10 |
4,500 |
|
52,000 |
|
8,666 |
13. Provide an estimate for the total annual cost burden to respondents or record keepers resulting from the collection of information.
Annual cost to NASA (as the record keeper) is provided as follows:
The equipment (servers, software, infrastructure) cost for NASA IdMAX was approximately $2 million, with a life expectancy of 8 years.
$2 million/8 years = $250,000 per year.
Support costs for NASA IdMAX system require approximately 5 people (5 FTEs) at an estimated cost of $100,000 each = $500,000 annually
14. Provide estimates of annualized costs to the Federal government.
Table 1: Compilation of Costs (Questions 12, 13, and 14)
-
Cost Category
Hour Burden
Annual Costs
Respondent (routine)
4,166
$ 208,350
Respondent (intermittent)
4,500
$ 225,000
Equipment
$ 250,000
Support (salary)
$ 500,000
Support (equipment)
$ 6,000
Total Annual Costs
$1,189,350
Expenses include the cost of computer support equipment and supplies estimated at approximately $1,200 annually per FTE -- $1,200 x 5 FTEs = $6,000 annually.
15. Explain the reasons for any program changes or adjustments reported in Items 13 or 14 of the OMB Form 83-I.
No program changes or adjustments are reported.
16. For collections of information whose results will be published, outline plans for tabulation and publication.
NASA does not tabulate and publish personal information collected from members of the public associated covered by the PRA.
When required, NASA summarizes information such as the information identified in the link below:
17. If seeking approval to not display the expiration date for OMB approval of the information collection, explain the reasons that display would be inappropriate.
NASA will display the expiration date for OMB approval of the information collection within the PRA Statement. A sample screen shot is provided below:
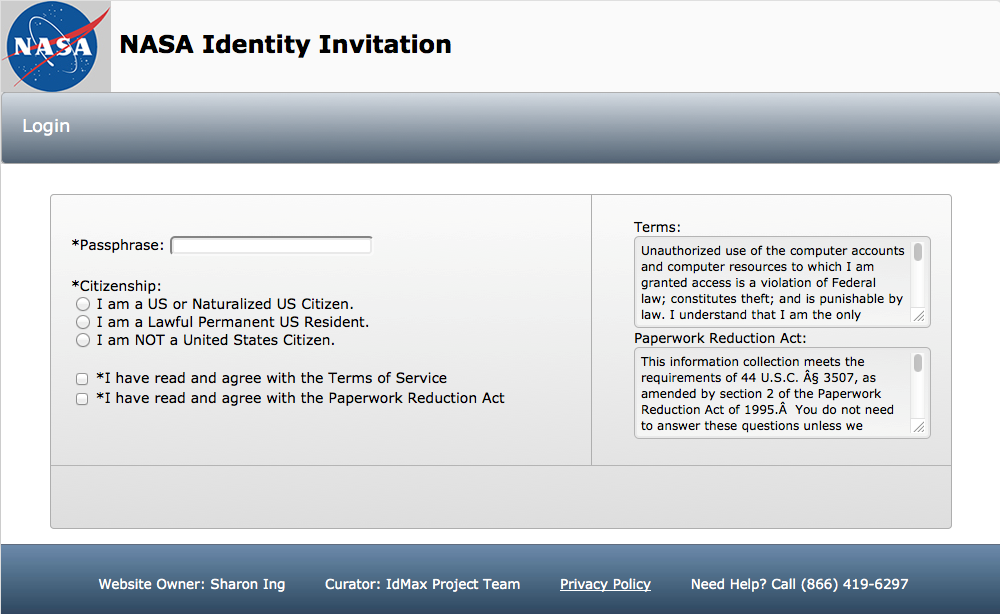
18. Explain each exception to the certification statement identified in Item 19, "Certification for Paperwork Reduction Act Submissions," of OMB Form 83-I.
NASA does not take exception to the certification statements in 5 CFR 1320.9
NASA Office of Protective Services/James Nicholas.
B. COLLECTIONS OF INFORMATION EMPLOYING STATISTICAL METHODS
Not applicable.
Page
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | During FY07, FY08, and FY09 the NASA-sponsored Classroom of the Future (COTF) will study how much people learn (assessment of le |
| Author | Debbie Denise Reese, Ph.D. |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-22 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy