NASS List Sampling Frames and Sampling Methodologies - Documentation
General Sampling and Frame Development Overview - 2016 (1).docx
Fruit, Nuts, and Specialty Crops
NASS List Sampling Frames and Sampling Methodologies - Documentation
OMB: 0535-0039
NASS List Sampling Frames and Sampling Methodologies
NASS LIST SAMPLING FRAMES
NASS’s list frame is a roster of known farmers and ranchers and includes a profile of each operation indicating the size of the operation and the commodities they produce. NASS continually works to keep the list frame as complete as possible by obtaining records for new or omitted operations from other USDA lists, producer association lists, and many other sources. A special effort is made to ensure that larger producers are included on the list. Nevertheless, a list frame can never provide complete coverage of all farms, since farming arrangements are constantly changing. Moreover, there will always be some farms on the list that are out of business. Despite these limitations, the list frame is an efficient method to select samples and data can be collected using less expensive methods such as mail, telephone, or internet.
SAMPLING METHODOLOGIES
NASS evaluates survey goals and available information (List Frame Data, Survey Data, Pilot Study, Administrative Data, etc.) when selecting a sample design for a particular survey. Two of many sample designs used by NASS are stratified simple random and Multivariate Probability Proportional to Size (MPPS).
The sample size formula for a stratified simple random sampling design is:
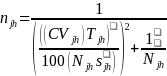
Where:
njh is the sample size for target commodity h in strata j,
Njh is the population for target commodity h in strata j,
Sjh is the standard deviation for target commodity h in strata j,
CVjh is the coefficient of variation for target commodity h in strata j, and
Tjh is the total for target commodity h in strata j.
The MPPS uses multiple auxiliary variables in the sample allocation to achieve the sampling efficiency of a Probability Proportional to Size (PPS) design in the estimation of multiple variables. The target sample size for each commodity was derived using a simple random sample size formula.
The probability of selection for an MPPS design is:
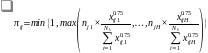
Where:
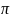 ij
is the maximum probability of selection for farm operator i in state
j.
ij
is the maximum probability of selection for farm operator i in state
j.
i is the farm operator.
h is the target commodity (h=1,…,H).
j is the state.
Nh is the number of farm operators in the sampling frame for target commodity h, and
xijh is the value of target commodity h for the ith farm operator in state j.
A
sample is chosen by sorting the sampling frame on a measure of size
variable, generating a uniform random number (RN), calculating the
cumulative probability for unit i as Cumulativei
= Cumulativei+1
+
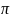 i,
and selecting unit i if Cumulativei+1<RN+k<
= Cumulativei
for
any k= 0,1,2,…n where n is the total number of units selected
for the sample1.
i,
and selecting unit i if Cumulativei+1<RN+k<
= Cumulativei
for
any k= 0,1,2,…n where n is the total number of units selected
for the sample1.
1 Hicks, Susan, Amrhein, John and Kott, Phil (1996), Methods to Meet Target Sample Sizes Under a Multivariate PPS Sampling Strategy, Proceedings of the Section on Survey Research Methods, American Statistical Association, pp. 234-238.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | Quan, Peter - NASS |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-15 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy